Surveillance Study of Klebsiella pneumoniae in the Giant Panda Revealed High Genetic Diversity and Antibiotic Therapy Challenge
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
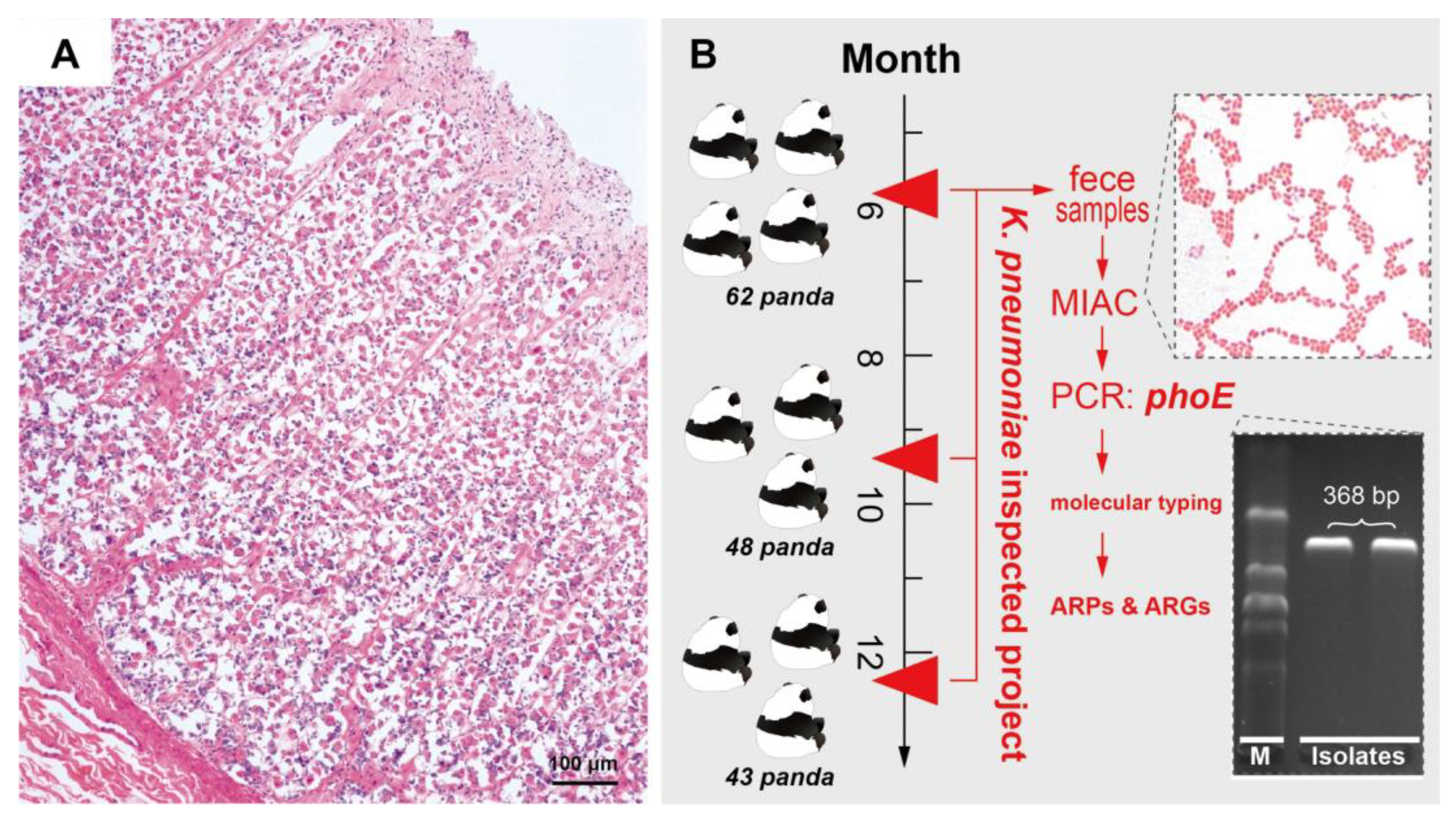
2.1. Isolation of K. pneumoniae
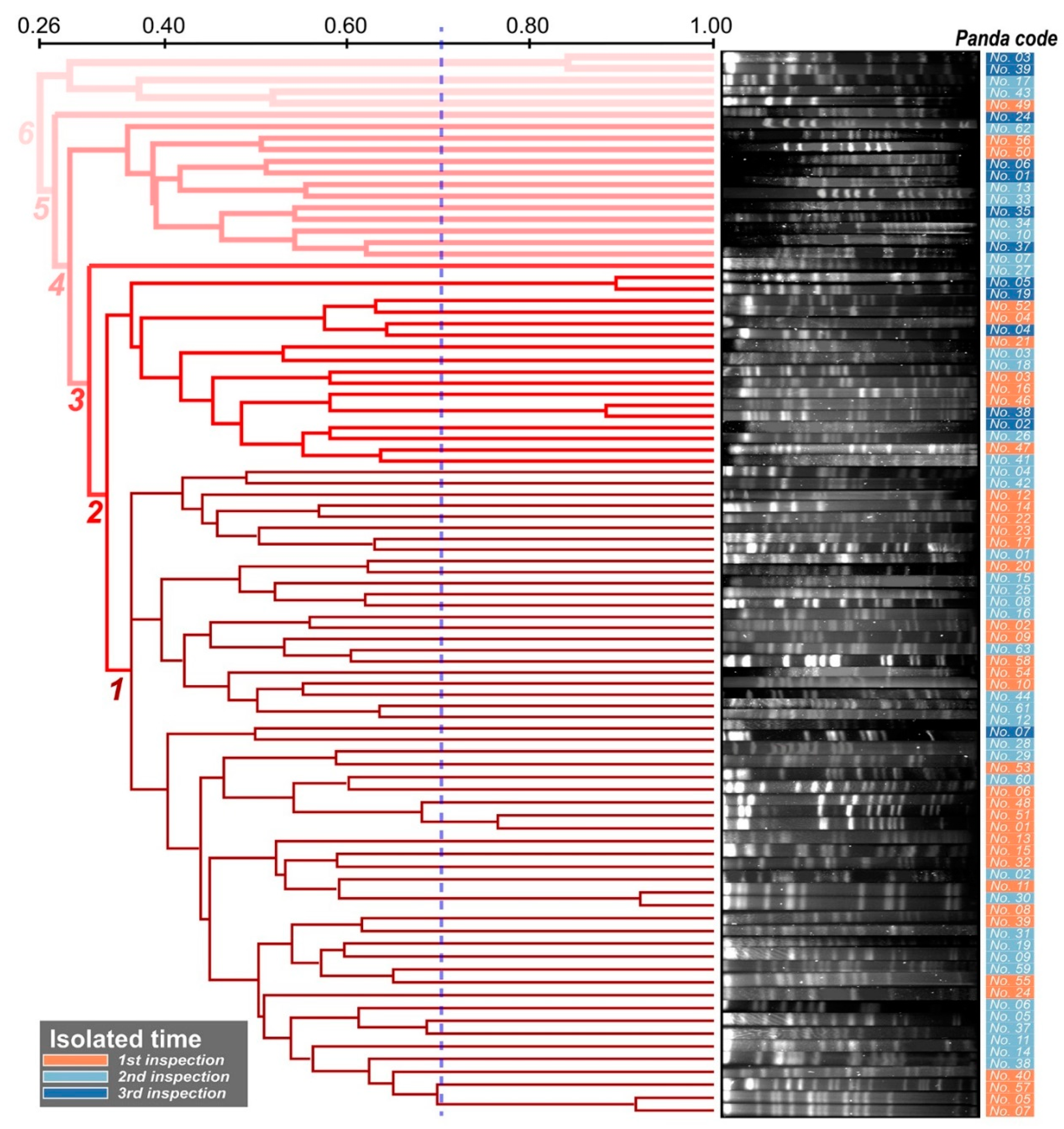
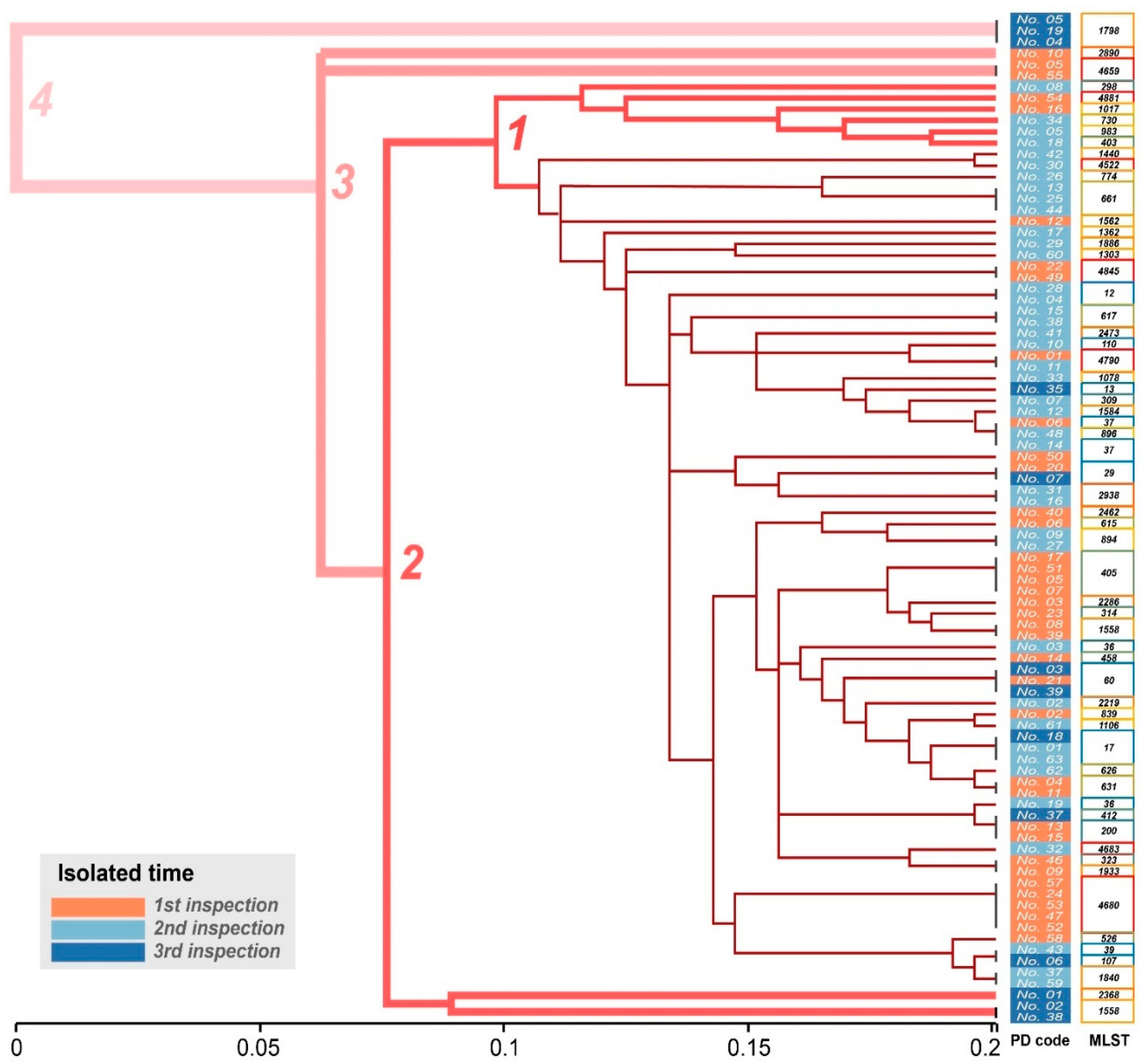
2.2. Genotype Characteristics of K. pneumoniae by PFGE and MLST
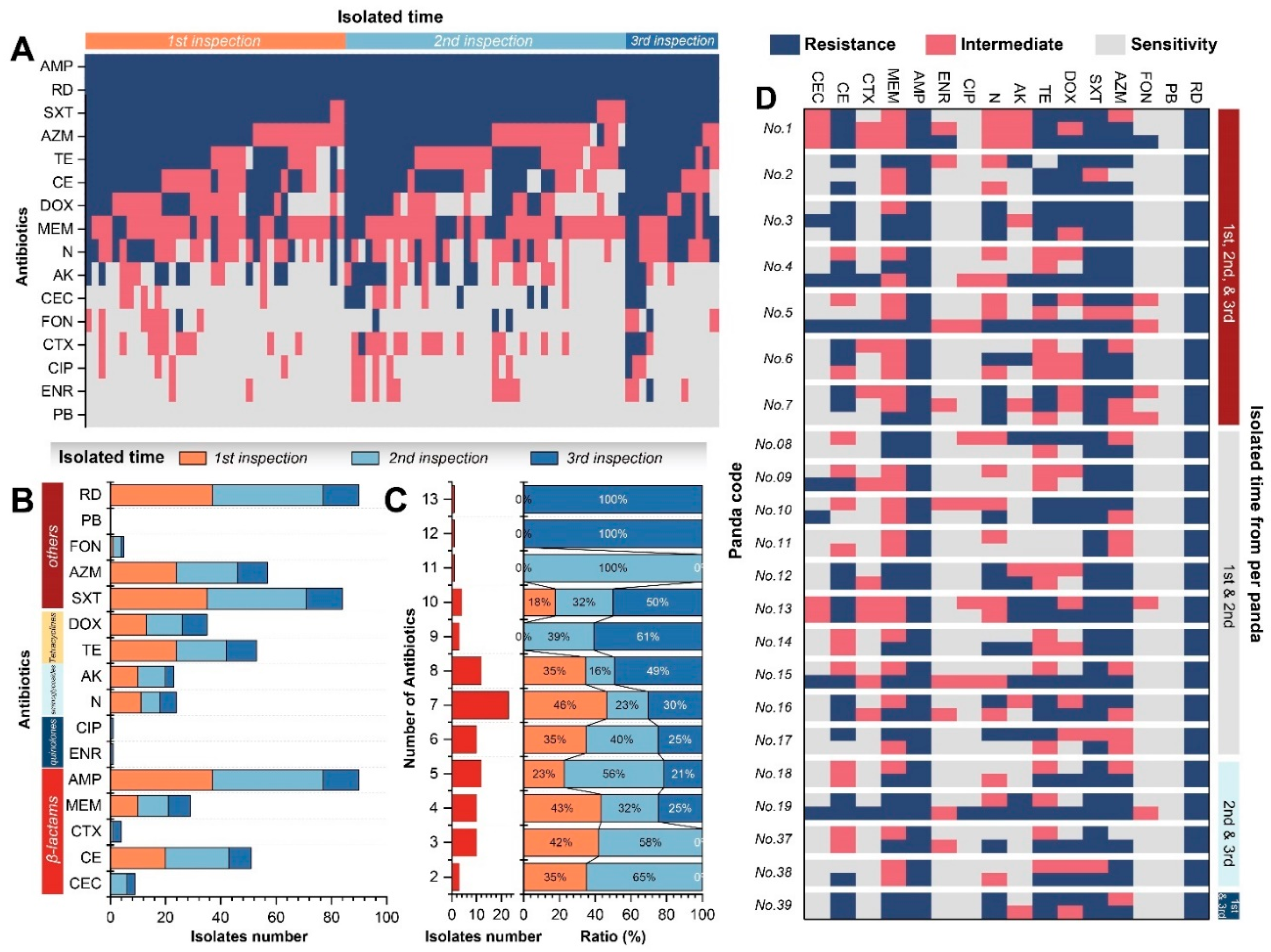
2.3. The Antibiotic Resistance Profiles of K. pneumoniae
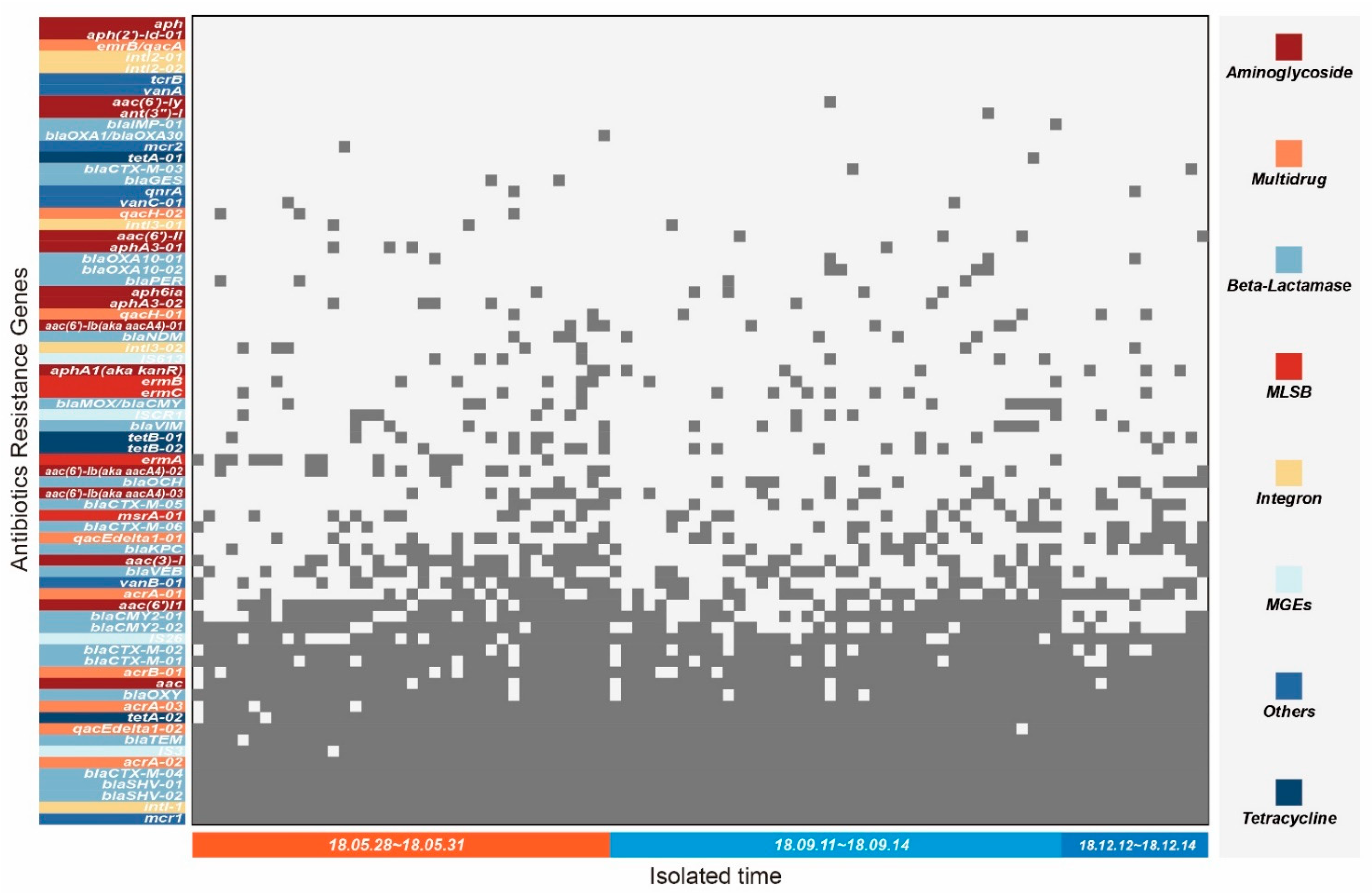
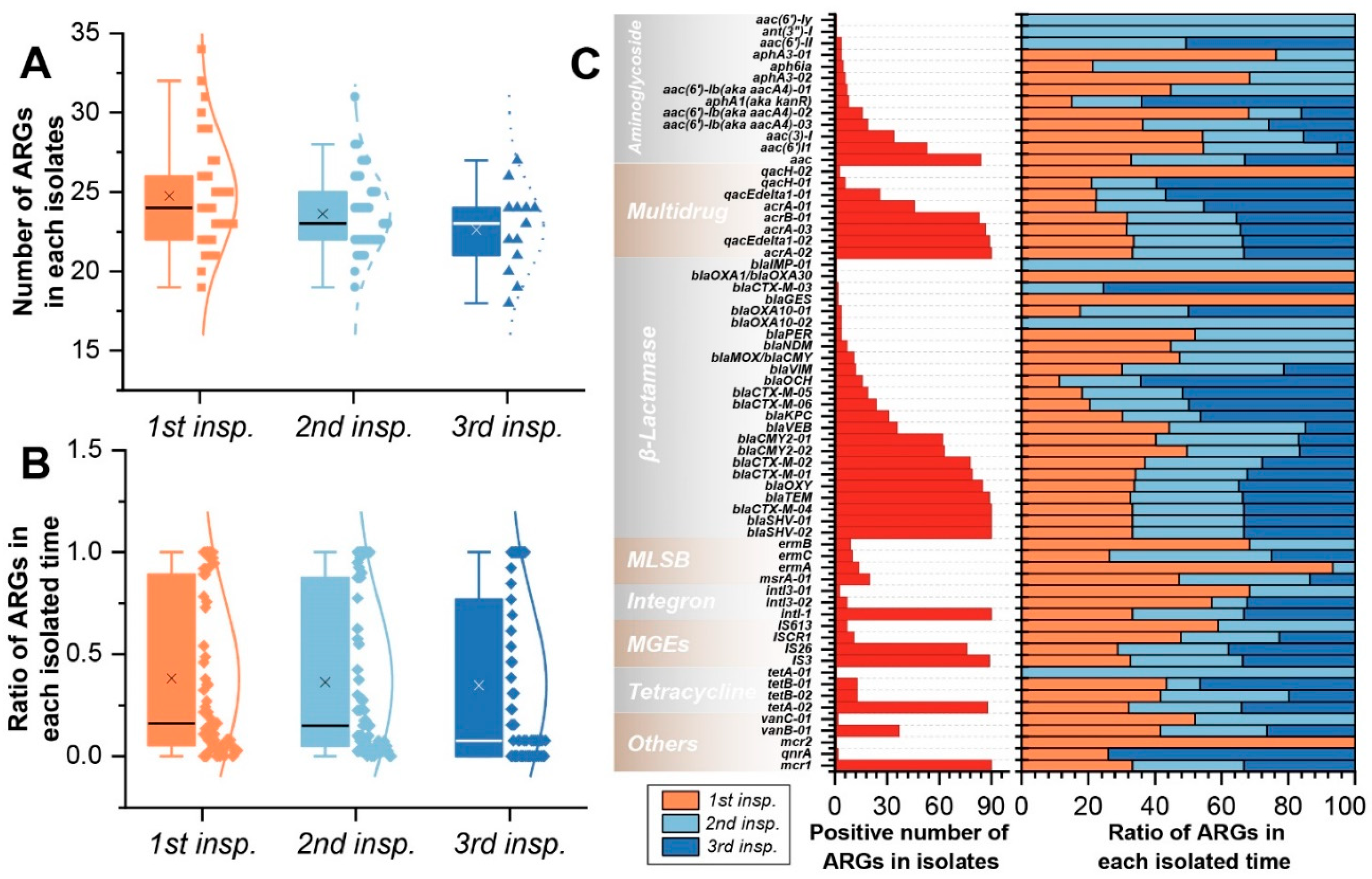
2.4. The Antibiotic Resistance Genes of K. pneumoniae
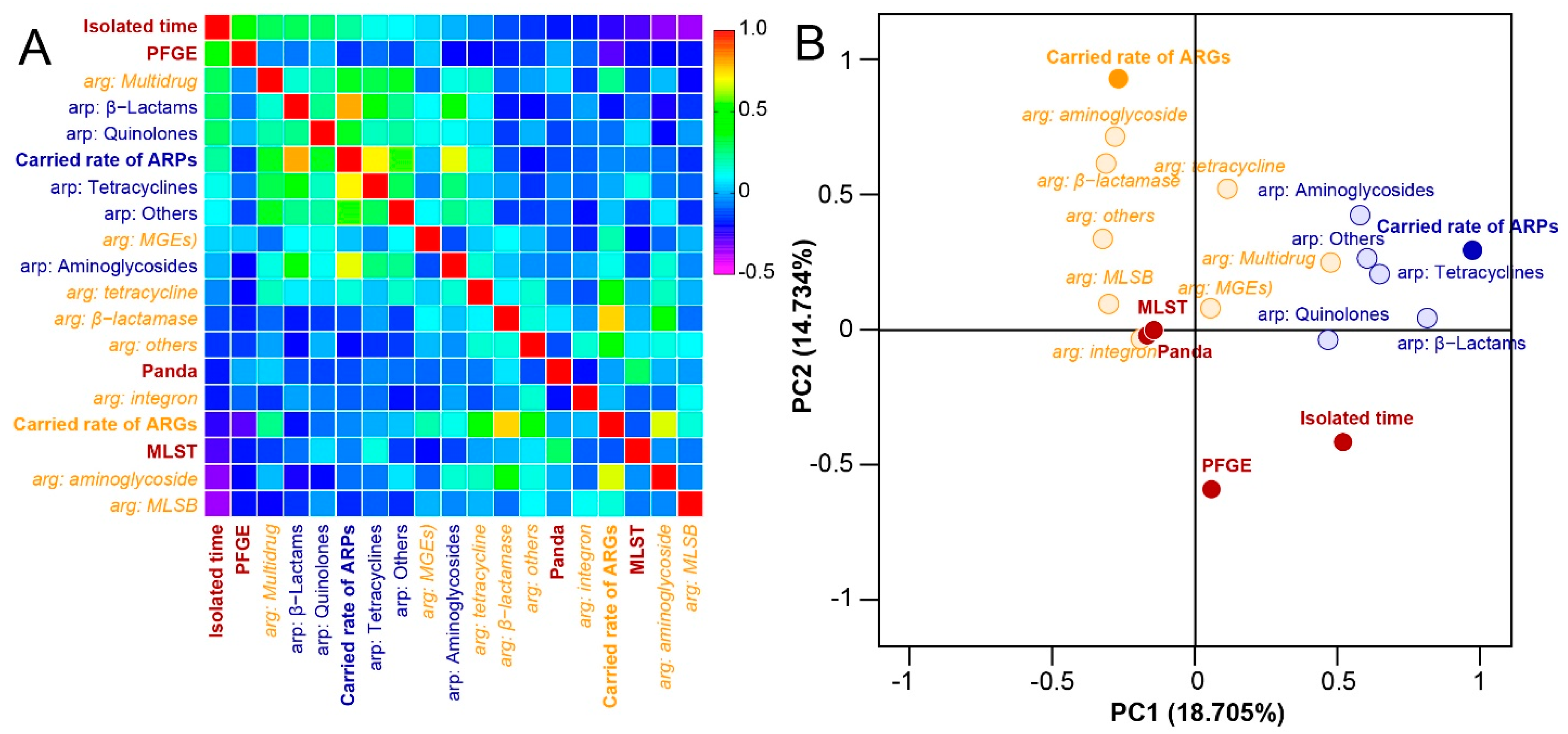
2.5. Correlation Analysis Based on Detected Parameters of Strains
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Isolation and Identification
4.2. Pulsed Field Gel Electrophoresis Analysis
4.3. Multilocus Sequence Typing Analysis
4.4. Antibiotic Resistance Profiles Assay
4.5. Antibiotic Resistance Gene Detection
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edmunds, D.R.; Kauffman, M.J.; Schumaker, B.A.; Lindzey, F.G.; Cook, W.E.; Kreeger, T.J.; Grogan, R.G.; Cornish, T.E. Chronic wasting disease drives population decline of white-tailed deer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, D.; Koehler, A.V.; Gasser, R.B. Parasites of the Giant Panda: A risk factor in the conservation of a species. Adv. Parasitol. 2018, 99, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yan, Q.; Xia, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, C.; Chen, S.; Hou, R. Serotypes, Virulence factors, and antimicrobial susceptibilities of vaginal and fecal isolates of Escherichia coli from Giant Pandas. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5146–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.D.; Lan, J.C.; Li, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Z.R. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Pathogen of urogenital hematuria of Giant Panda. Sichuan J. Zoo. 2006, 25, 83–85. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiu, Y.F.; Shao, L.P.; Chen, Y.C.; Wang, D.C.; Xu, S.-H. A case of Giant Panda suffered with Pneumonia by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and secogndary infection of enteritis by Candida albicans. J. Econ. Anim. 2006, 10, 103–105. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, M.G.-X.; Jiang, J.; Liu, L.; Ma, A.P.-Y.; Leung, F.C.-C. Complete Genome Sequence of Klebsiella variicola Strain HKUOPLA, a Cellulose-Degrading Bacterium Isolated from Giant Panda Feces. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e01200-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Li, M.; Luo, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Lyu, W.; Chen, L.; Su, W.; Ding, H.; et al. Impacts of canine distemper virus infection on the Giant Panda population from the perspective of gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, L.; Li, M. Isolation and identification of rotavirus from Giant Panda cubs. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2008, 28, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, M.G.-X.; Jiang, J.; Liu, L.; Ma, A.P.-Y.; Leung, F.C.-C. Complete Genome Sequence of Klebsiella pneumoniae Strain HKUOPLC, a Cellulose-Degrading Bacterium Isolated from Giant Panda Feces. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e01318-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puspanadan, S.; Af Sah-Hejri, L.; Loo, Y.Y.; Nillian, E.; Kuan, C.H.; Goh, S.G.; Chang, W.S.; Lye, Y.L.; John, Y.; Rukayadi, Y. Detection of Klebsiella pneumoniae in raw vegetables using most probable number-polymerase chain reaction (MPN-PCR). Int. Food Res. J. 2012, 19, 1757–1762. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, G.N.; Xiong, Y. The Studying status on the Panda Klebsiella pneumoniae. Sichuan Anim. Vet. Sci. 2000, 27, 86–87. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Su, X.; Geng, Y.; Huang, W.; Chen, X.; Bai, M.; Cheng, Z. A case of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Proteus mirabilis infection in Giant Panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca). Chin. J. Wildl. 2020, 41, 1013–1019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rahube, T.O.; Marti, R.; Scott, A.; Tien, Y.-C.; Murray, R.; Sabourin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Duenk, P.; Lapen, D.R.; Topp, E. Impact of fertilizing with raw or anaerobically digested sewage sludge on the abundance of antibiotic-resistant coliforms, antibiotic resistance genes, and pathogenic bacteria in soil and on vegetables at harvest. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 6898–6907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti, E.; Huerta, B.; Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Barcelo, D.; Marce, R.; Luis Balcazar, J. Abundance of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial community composition in wild freshwater fish species. Chemosphere 2018, 196, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; An, X.; Li, H.; Su, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, Y.G. Long-term field application of sewage sludge increases the abundance of antibiotic resistance genes in soil. Environ. Int. 2016, 92–93, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthopoulou, K.; Carattoli, A.; Wille, J.; Biehl, L.M.; Higgins, P.G. Antibiotic resistance and mobile genetic elements in extensively drug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 147 recovered from Germany. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasakthi, N.; Vadivelu, J.; Ariffin, H.; Iyer, L.; Palasubramaniam, S.; Arasu, A. Epidemiology and molecular characterization of nosocomially transmitted multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int. J. Infec. Dis. 2000, 4, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roberts, D.E.; McClain, H.M.; Hansen, D.S.; Currin, P.; Howerth, E.W. An outbreak of Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in dogs with severe enteritis and septicemia. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2000, 12, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, M.G.; Iovine, R.O.; Torres, L.N.; Catao-Dias, J.L.; Pissinatti, A.; Kierulff, M.C.M.; Carvalho, V.M. Pneumonia and bacteremia in a golden-headed lion tamarin (Leontopithecus chrysomelas) caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae subsp pneumoniae during a translocation program of free-ranging animals in Brazil. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2015, 27, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fair, R.J.; Tor, Y. Antibiotics and bacterial resistance in the 21st Century. Perspect. Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 25–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Deng, L.H.; Zhang, R.P.; Wang, C.D.; Li, D.S.; Xi, L.X.; Chen, Z.R.; Yang, R.; Huang, J.; Zeng, Y.R. Relationship between drug resistance and the clustered, regularly interspaced, short, palindromic repeat-associated protein genes cas1 and cas2 in Shigella from giant panda dung. Medicine 2017, 96, e5922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrër, A.; Nordmann, P. CTX-M-15-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: A change in the epidemiology of ESBL. Pathol. Biol. 2011, 59, 133–135. [Google Scholar]
- Mugnaioli, C.; Bassano, M.; Iaroli, F.B.C.; Frontini, P.; Rossolini, G.M. Evoluzione delle esbl in italia: Diffusione di un ceppo di klebsiella pneumoniae CTX-M-15 e multi-resistente. Microbiol. Med. 2007, 22, 170. [Google Scholar]
- Paterson, D.L.; Hujer, K.M.; Hujer, A.M.; Yeiser, B.; Bonomo, M.; Rice, L.B.; Bonomo, R.A. Extended-spectrum β-lactamases in Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream isolates from seven countries: Dominance and widespread prevalence of SHV- AND CTX-M-type β-lactamases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.Q.; Du, X.X.; Yu, Y.S.; Shen, P.; Chen, Y.G.; Li, L.J. Plasmid-mediated KPC-2 in a Klebsiella pneumoniae isolate from China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 763–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoska, D.; Klamiska-CeBula, H.; Dobrut, A.; Bulanda, M.; Brzychczy-Woch, M. Clonal dissemination of KPC-2, VIM-1, OXA-48-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST147 in Katowice, Poland. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2021, 70, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, R.A.; Abbas, A.M.; El-Shehawi, A.M.; Mabrouk, M.I.; Aboshanab, K.M. Serotyping and antimicrobial resistance profile of enteric nontyphoidal salmonella recovered from febrile neutropenic patients and poultry in Egypt. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyres, K.L.; Holt, K.E. Klebsiella pneumoniae as a key trafficker of drug resistance genes from environmental to clinically important bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 45, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, A.A.; Daszak, P.; Wood, J. One Health, emerging infectious diseases and wildlife: Two decades of progress? Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. 2017, 372, 20160167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Yang, S.; Chen, X.; Gao, G.; Yang, D. Detection of Klebsiella pneumoniae in Ailuropoda melanoleuca by PCR. J. Econ. Anim. 2003, 7, 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- Ribot, E.M.; Fair, M.A.; Gautom, R.; Cameron, D.N.; Hunter, S.B. Standardization of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis protocols for the subtyping of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella, and Shigella for PulseNet. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2006, 3, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenover, F.C.; Arbeit, R.D.; Goering, R.V.; Mickelsen, P.A.; Murray, B.E.; Persing, D.H.; Swaminathan, B. Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: Criteria for bacterial strain typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 2233–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Yang, X.; Wu, Y.; Yang, H.; Han, Y.; Yang, R.; Hu, L.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, D. MLST-based inference of genetic diversity and population structure of clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae, China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fothergill, A.W. Antifungal Susceptibility Testing: Clinical Laboratory and Standards Institute (CLSI) Methods; Interactions of Yeasts, Moulds, and Antifungal Agents; Humana Press: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
| Panda Code | 1st Time | 2nd Time | 3rd Time | Pos./Total | Panda Code | 1st Time | 2nd Time | 3rd Time | Pos./Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. 1 | + | + | + | 3/3 | No. 37 | ND | + | + | 2/2 |
| No. 2 | + | + | + | No. 38 | ND | + | + | ||
| No. 3 | + | + | + | No. 39 | + | ND | + | ||
| No. 4 | + | + | + | No. 40 | + | ND | − | 1/2 | |
| No. 5 | + | + | + | No. 41 | − | + | ND | ||
| No. 6 | + | + | + | No. 42 | − | + | ND | ||
| No. 7 | + | + | + | No. 43 | − | + | ND | ||
| No. 8 | + | + | − | 2/3 | No. 44 | − | + | ND | |
| No. 9 | + | + | − | No. 45 | − | ND | − | 0/2 | |
| No. 10 | + | + | − | No. 46 | + | ND | ND | 1/1 | |
| No. 11 | + | + | − | No. 47 | + | ND | ND | ||
| No. 12 | + | + | − | No. 48 | + | ND | ND | ||
| No. 13 | + | + | − | No. 49 | + | ND | ND | ||
| No. 14 | + | + | − | No. 50 | + | ND | ND | ||
| No. 15 | + | + | − | No. 51 | + | ND | ND | ||
| No. 16 | + | + | − | No. 52 | + | ND | ND | ||
| No. 17 | + | + | − | No. 53 | + | ND | ND | ||
| No. 18 | − | + | + | No. 54 | + | ND | ND | ||
| No. 19 | − | + | + | No. 55 | + | ND | ND | ||
| No. 20 | + | − | − | 1/3 | No. 56 | + | ND | ND | |
| No. 21 | + | − | − | No. 57 | + | ND | ND | ||
| No. 22 | + | − | − | No. 58 | + | ND | ND | ||
| No. 23 | + | − | − | No. 59 | ND | + | ND | ||
| No. 24 | + | − | − | No. 60 | ND | + | ND | ||
| No. 25 | − | + | − | No. 61 | ND | + | ND | ||
| No. 26 | − | + | − | No. 62 | ND | + | ND | ||
| No. 27 | − | + | − | No. 63 | ND | + | ND | ||
| No. 28 | − | + | − | No. 64 | − | ND | ND | 0/1 | |
| No. 29 | − | + | − | No. 65 | − | ND | ND | ||
| No. 30 | − | + | − | No. 66 | − | ND | ND | ||
| No. 31 | − | + | − | No. 67 | − | ND | ND | ||
| No. 32 | − | + | − | No. 68 | − | ND | ND | ||
| No. 33 | − | + | − | No. 69 | − | ND | ND | ||
| No. 34 | − | + | − | No. 70 | ND | − | ND | ||
| No. 35 | − | − | + | No. 71 | ND | ND | − | ||
| No. 36 | − | − | − | 0/3 | No. 72 | ND | ND | − | |
| right continued | pos./total | 37/62 | 40/48 | 13/43 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Hou, R.; Yan, X.; Geng, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Guo, H.; Ouyang, P.; Zhang, D.; et al. Surveillance Study of Klebsiella pneumoniae in the Giant Panda Revealed High Genetic Diversity and Antibiotic Therapy Challenge. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11040473
Feng Y, Chen Y, Liu S, Hou R, Yan X, Geng Y, Zhong Z, Guo H, Ouyang P, Zhang D, et al. Surveillance Study of Klebsiella pneumoniae in the Giant Panda Revealed High Genetic Diversity and Antibiotic Therapy Challenge. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(4):473. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11040473
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Yang, Yaoyan Chen, Songrui Liu, Rong Hou, Xia Yan, Yi Geng, Zhijun Zhong, Hongrui Guo, Ping Ouyang, Dongsheng Zhang, and et al. 2022. "Surveillance Study of Klebsiella pneumoniae in the Giant Panda Revealed High Genetic Diversity and Antibiotic Therapy Challenge" Antibiotics 11, no. 4: 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11040473
APA StyleFeng, Y., Chen, Y., Liu, S., Hou, R., Yan, X., Geng, Y., Zhong, Z., Guo, H., Ouyang, P., Zhang, D., & Su, X. (2022). Surveillance Study of Klebsiella pneumoniae in the Giant Panda Revealed High Genetic Diversity and Antibiotic Therapy Challenge. Antibiotics, 11(4), 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11040473







