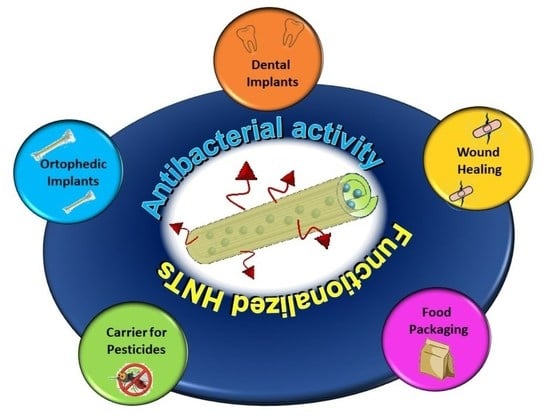
Antimicrobial Nanomaterials Based on Halloysite Clay Mineral: Research Advances and Outlook
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Halloysite Nanotubes Based Antimicrobial Materials
2.1. Orthopedic Implants
2.2. Dental Implants
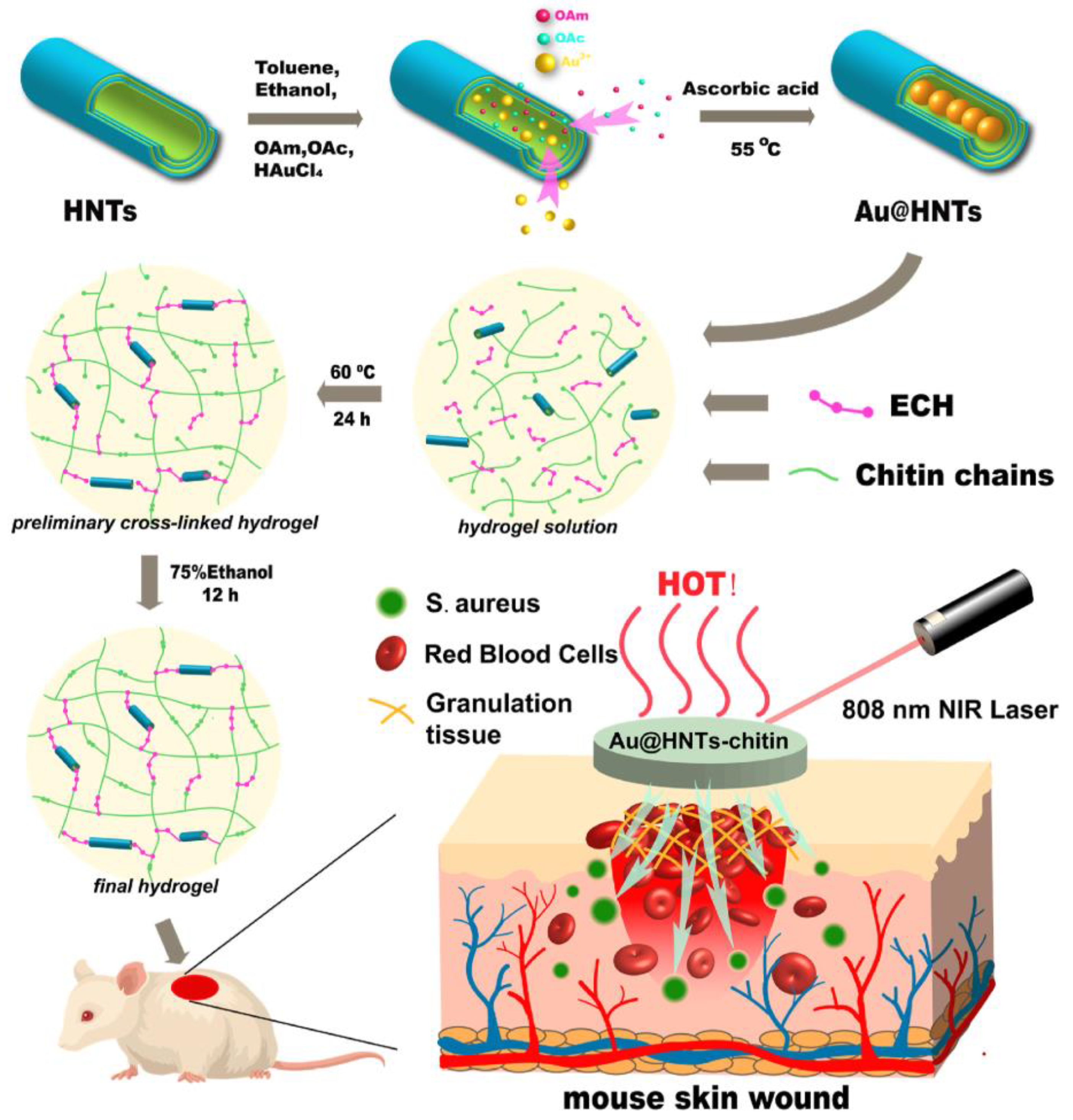
2.3. Halloysite Based Nanomaterials for Wound Healing
2.4. Food Packaging
2.5. Carrier for Pesticides
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taubes, G. The Bacteria Fight Back. Science 2008, 321, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, B.; Wang, W.; Arshad, M.I.; Khurshid, M.; Muzammil, S.; Rasool, M.H.; Nisar, M.A.; Alvi, R.F.; Aslam, M.A.; Qamar, M.U.; et al. Antibiotic resistance: A rundown of a global crisis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1645–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleraky, N.E.; Allam, A.; Hassan, S.B.; Omar, M.M. Nanomedicine Fight against Antibacterial Resistance: An Overview of the Recent Pharmaceutical Innovations. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Hong, M.; Xie, W.; Chen, Z.; Chen, D.; Xie, S. Progress and prospects of nanomaterials against resistant bacteria. J. Control. Release 2022, 351, 301–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notarbartolo, M.; Massaro, M.; de Melo Barbosa, R.; Emili, C.; Liotta, L.F.; Poma, P.; Raymo, F.M.; Sànchez-Espejo, R.; Vago, R.; Viseras-Iborra, C.; et al. Exploring the cellular uptake of hectorite clay mineral and its drug carrier capabilities. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 220, 112931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sposito, G.; Skipper, N.T.; Sutton, R.; Park, S.-H.; Soper, A.K.; Greathouse, J.A. Surface geochemistry of the clay minerals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3358–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neeraj, K.; Chandra, M. Basics of Clay Minerals and Their Characteristic Properties. In Clay and Clay Minerals; Gustavo Morari Do, N., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2021; Chapter 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rocha, M.C.; Galdino, T.; Trigueiro, P.; Honorio, L.M.C.; de Melo Barbosa, R.; Carrasco, S.M.; Silva-Filho, E.C.; Osajima, J.A.; Viseras, C. Clays as Vehicles for Drug Photostability. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fesharaki, O.; García-Romero, E.; Cuevas-González, J.; López-Martínez, N. Clay mineral genesis and chemical evolution in the Miocene sediments of Somosaguas, Madrid Basin, Spain. Clay Miner. 2007, 42, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christidis, G.E. Industrial Clays. In Advances in the Characterization of Industrial Minerals; Christidis, G.E., Ed.; European Mineralogical Union Mineralogical Society of Great Britain & Ireland: London, UK, 2010; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Glimcher, M.J. Bone: Nature of the Calcium Phosphate Crystals and Cellular, Structural, and Physical Chemical Mechanisms in Their Formation. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2006, 64, 223–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T.; Sovago, I.; Martin, R.B. Aluminum(3+) binding by adenosine 5′-phosphates: AMP, ADP, and ATP. Inorg. Chem. 1991, 30, 2130–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
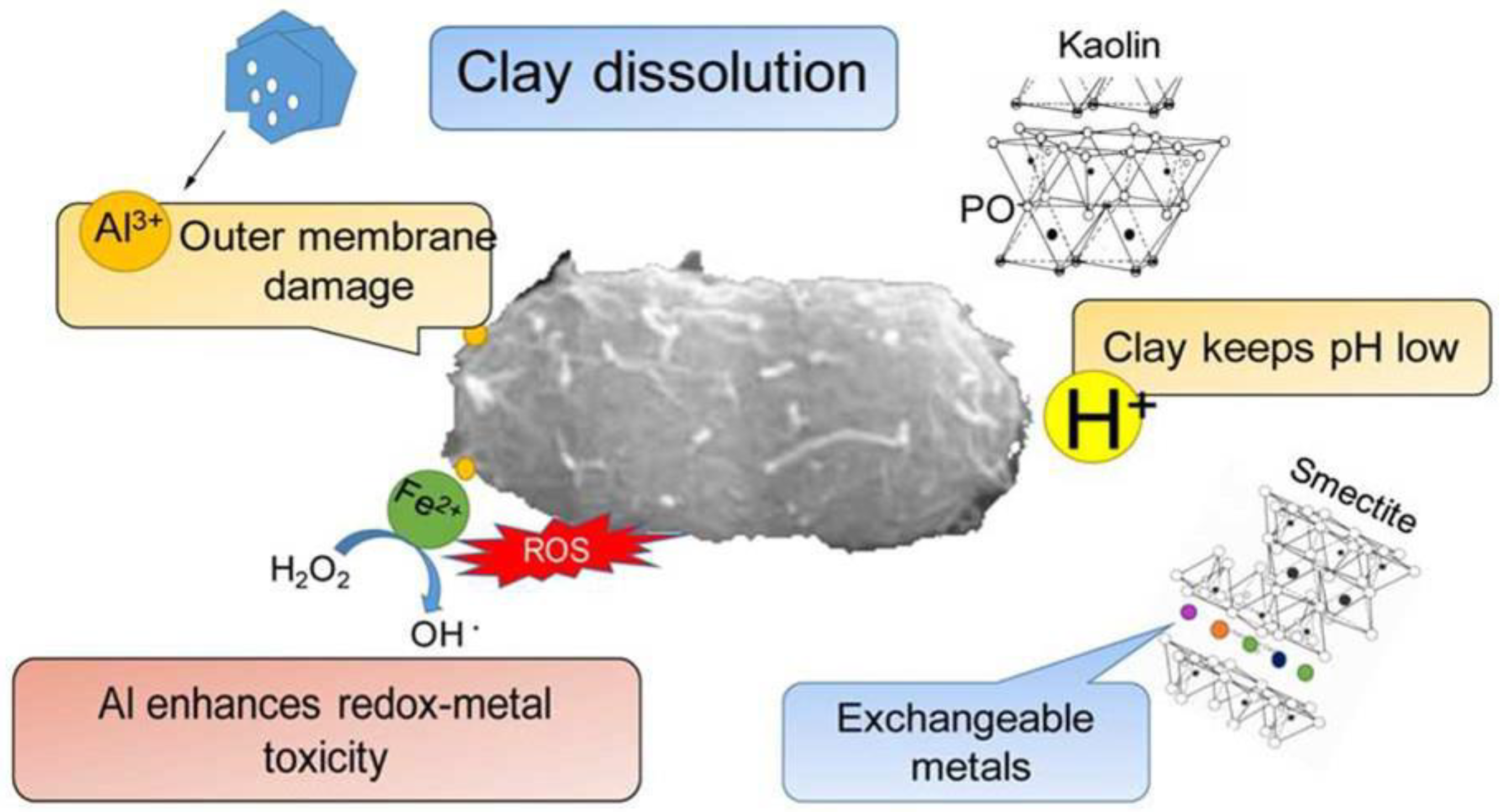
- Londono, S.C.; Hartnett, H.E.; Williams, L.B. Antibacterial Activity of Aluminum in Clay from the Colombian Amazon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2401–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, L.B.; Haydel, S.E. Evaluation of the medicinal use of clay minerals as antibacterial agents. Int. Geol. Rev. 2010, 52, 745–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, F.; Ōya, A. Antimicrobial and antifungal agents derived from clay minerals (II): Properties of montmorillonite supported by silver chelates of 1,10-phenanthroline and 2,2′-dipyridyl. Appl. Clay Sci. 1992, 6, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, F.; Oya, A.; Duclaux, L.; Beguin, F. Structural model calculation of antimicrobial and antifungal agents derived from clay minerals. Appl. Clay Sci. 1998, 12, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.J.; Li, L.F.; Hao, R.N.; Gong, M.; Wang, T.; Song, J.; Meng, Q.H.; Zhao, N.N.; Xu, F.J.; Lvov, Y.; et al. Phase-change composite filled natural nanotubes in hydrogel promote wound healing under photothermally triggered drug release. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 21, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.; Niu, Y.; Gong, M.; Ye, J.; Tian, W.; Zhang, L. Antimicrobial gelatin-based elastomer nanocomposite membrane loaded with ciprofloxacin and polymyxin B sulfate in halloysite nanotubes for wound dressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 87, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Wang, M.; Tang, M.; Hong, G.; Gao, J.; Chen, Y. Preparation of Robust Superhydrophobic Halloysite Clay Nanotubes via Mussel-Inspired Surface Modification. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Buscemi, G.; Arista, L.; Biddeci, G.; Cavallaro, G.; D’Anna, F.; Di Blasi, F.; Ferrante, A.; Lazzara, G.; Rizzo, C.; et al. Multifunctional Carrier Based on Halloysite/Laponite Hybrid Hydrogel for Kartogenin Delivery. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Licandro, E.; Cauteruccio, S.; Lazzara, G.; Liotta, L.F.; Notarbartolo, M.; Raymo, F.M.; Sánchez-Espejo, R.; Viseras-Iborra, C.; Riela, S. Nanocarrier based on halloysite and fluorescent probe for intracellular delivery of peptide nucleic acids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 620, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavitskaya, A.V.; Kozlova, E.A.; Kurenkova, A.Y.; Glotov, A.P.; Selischev, D.S.; Ivanov, E.V.; Kozlov, D.V.; Vinokurov, V.A.; Fakhrullin, R.F.; Lvov, Y.M. Ru/CdS Quantum Dots Templated on Clay Nanotubes as Visible-Light-Active Photocatalysts: Optimization of S/Cd Ratio and Ru Content. Chem.—A Eur. J. 2020, 26, 13085–13092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavitskaya, A.; Mazurova, K.; Kotelev, M.; Eliseev, O.; Gushchin, P.; Glotov, A.; Kazantsev, R.; Vinokurov, V.; Lvov, Y. Ruthenium-Loaded Halloysite Nanotubes as Mesocatalysts for Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis. Molecules 2020, 25, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavitskaya, A.; Glotov, A.; Pouresmaeil, F.; Potapenko, K.; Sitmukhanova, E.; Mazurova, K.; Ivanov, E.; Kozlova, E.; Vinokurov, V.; Lvov, Y. CdS Quantum Dots in Hierarchical Mesoporous Silica Templated on Clay Nanotubes: Implications for Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Colletti, C.G.; Fiore, B.; La Parola, V.; Lazzara, G.; Guernelli, S.; Zaccheroni, N.; Riela, S. Gold nanoparticles stabilized by modified halloysite nanotubes for catalytic applications. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33, e4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavitskaya, A.; Rubtsova, M.; Glotov, A.; Vinokurov, V.; Vutolkina, A.; Fakhrullin, R.; Lvov, Y. Architectural design of core–shell nanotube systems based on aluminosilicate clay. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 2823–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaro, M.; Colletti, C.G.; Guernelli, S.; Lazzara, G.; Liu, M.; Nicotra, G.; Noto, R.; Parisi, F.; Pibiri, I.; Spinella, C.; et al. Photoluminescent hybrid nanomaterials from modified halloysite nanotubes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 7377–7384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micó-Vicent, B.; Martínez-Verdú, F.M.; Novikov, A.; Stavitskaya, A.; Vinokurov, V.; Rozhina, E.; Fakhrullin, R.; Yendluri, R.; Lvov, Y. Stabilized Dye–Pigment Formulations with Platy and Tubular Nanoclays. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1703553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalieva, R.F.; Ishmukhametov, I.R.; Batasheva, S.N.; Rozhina, E.V.; Fakhrullin, R.F. Uptake of halloysite clay nanotubes by human cells: Colourimetric viability tests and microscopy study. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2018, 15, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhrullina, G.I.; Akhatova, F.S.; Lvov, Y.M.; Fakhrullin, R.F. Toxicity of halloysite clay nanotubes in vivo: A Caenorhabditis elegans study. Environ. Sci. Nano 2015, 2, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryuchkova, M.; Danilushkina, A.; Lvov, Y.; Fakhrullin, R. Evaluation of toxicity of nanoclays and graphene oxide in vivo: A Paramecium caudatum study. Environ. Sci. Nano 2016, 3, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konnova, S.A.; Sharipova, I.R.; Demina, T.A.; Osin, Y.N.; Yarullina, D.R.; Ilinskaya, O.N.; Lvov, Y.M.; Fakhrullin, R.F. Biomimetic cell-mediated three-dimensional assembly of halloysite nanotubes. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 4208–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, R.; Liu, M.; Shi, B.; Shan, A.; Cheng, B. Use of modified halloysite nanotubes in the feed reduces the toxic effects of zearalenone on sow reproduction and piglet development. Theriogenology 2015, 83, 932–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadziakiewicz, M.; Lis, M.W.; Micek, P. The Effect of Dietary Halloysite Supplementation on the Performance of Broiler Chickens and Broiler House Environmental Parameters. Animals 2021, 11, 2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gong, J.; Rong, R.; Gui, Z.; Hu, T.; Xu, X. Halloysite Nanotubes-Induced Al Accumulation and Fibrotic Response in Lung of Mice after 30-Day Repeated Oral Administration. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 2925–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinz Setter, O.; Segal, E. Halloysite nanotubes—The nano-bio interface. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 23444–23460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavitskaya, A.; Batasheva, S.; Vinokurov, V.; Fakhrullina, G.; Sangarov, V.; Lvov, Y.; Fakhrullin, R. Antimicrobial Applications of Clay Nanotube-Based Composites. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadat, S.; Pandey, G.; Tharmavaram, M.; Braganza, V.; Rawtani, D. Nano-interfacial decoration of Halloysite Nanotubes for the development of antimicrobial nanocomposites. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 275, 102063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapacz-Kmita, A.; Foster, K.; Mikołajczyk, M.; Gajek, M.; Stodolak-Zych, E.; Dudek, M. Functionalized halloysite nanotubes as a novel efficient carrier for gentamicin. Mater. Lett. 2019, 243, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oun, A.A.; Bae, A.Y.; Shin, G.H.; Park, M.-K.; Kim, J.T. Comparative study of oregano essential oil encapsulated in halloysite nanotubes and diatomaceous earth as antimicrobial and antioxidant composites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 224, 106522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendessi, S.; Sevinis, E.B.; Unal, S.; Cebeci, F.C.; Menceloglu, Y.Z.; Unal, H. Antibacterial sustained-release coatings from halloysite nanotubes/waterborne polyurethanes. Prog. Org. Coat. 2016, 101, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krepker, M.; Prinz-Setter, O.; Shemesh, R.; Vaxman, A.; Alperstein, D.; Segal, E. Antimicrobial Carvacrol-Containing Polypropylene Films: Composition, Structure and Function. Polymers 2018, 10, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavitskaya, A.; Sitmukhanova, E.; Sayfutdinova, A.; Khusnetdenova, E.; Mazurova, K.; Cherednichenko, K.; Naumenko, E.; Fakhrullin, R. Photoinduced Antibacterial Activity and Cytotoxicity of CdS Stabilized on Mesoporous Aluminosilicates and Silicates. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makaremi, M.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Aw, Y.K.; Lee, S.M.; Milioto, S. Effect of Morphology and Size of Halloysite Nanotubes on Functional Pectin Bionanocomposites for Food Packaging Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 17476–17488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurczewska, J.; Ratajczak, M.; Gajecka, M. Alginate and pectin films covering halloysite with encapsulated salicylic acid as food packaging components. Appl. Clay Sci. 2021, 214, 106270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krepker, M.; Shemesh, R.; Danin Poleg, Y.; Kashi, Y.; Vaxman, A.; Segal, E. Active food packaging films with synergistic antimicrobial activity. Food Control 2017, 76, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan Tas, B.; Sehit, E.; Erdinc Tas, C.; Unal, S.; Cebeci, F.C.; Menceloglu, Y.Z.; Unal, H. Carvacrol loaded halloysite coatings for antimicrobial food packaging applications. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 20, 100300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y. Preparation and antibacterial activity of copper nanoparticle/halloysite nanotube nanocomposites via reverse atom transfer radical polymerization. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 41993–41996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Du, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, K. Preparation and Characterization of Novel Polyethersulfone Hybrid Ultrafiltration Membranes Bending with Modified Halloysite Nanotubes Loaded with Silver Nanoparticles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 3081–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, M.; Mahmood, S.; Augustine, R.; Hasan, A.; Thomas, S.; Ghosal, K. Natural halloysite nanotubes/chitosan based bio-nanocomposite for delivering norfloxacin, an anti-microbial agent in sustained release manner. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1849–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, M.; Jabeen, S.; Gull, N.; Ghaffar, A.; Islam, A.; Rizwan, M.; Abdullah, H.; Rasool, A.; Khan, S.; Khan, R. Novel Silane Crosslinked Chitosan Based Electrospun Nanofiber for Controlled Release of Benzocaine. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 826251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatahi, Y.; Sanjabi, M.; Rakhshani, A.; Motasadizadeh, H.; Darbasizadeh, B.; Bahadorikhalili, S.; Farhadnejad, H. Levofloxacin-halloysite nanohybrid-loaded fibers based on poly (ethylene oxide) and sodium alginate: Fabrication, characterization, and antibacterial property. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 64, 102598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Rhim, J.-W. Effect of chitosan modified halloysite on the physical and functional properties of pullulan/chitosan biofilm integrated with rutin. Appl. Clay Sci. 2021, 211, 106205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, R.T.; Dissanayake, R.K.; Mantilaka, M.M.M.G.P.G.; Wijesinghe, W.P.S.L.; Kaleel, S.S.; Premachandra, T.N.; Weerasinghe, L.; Amaratunga, G.A.J.; de Silva, K.M.N. Drug-Loaded Halloysite Nanotube-Reinforced Electrospun Alginate-Based Nanofibrous Scaffolds with Sustained Antimicrobial Protection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 33913–33922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, J.; Sadeghi, K.; Seo, J. Controlled self-release of ClO2 as an encapsulated antimicrobial agent for smart packaging. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 74, 102802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boro, U.; Priyadarsini, A.; Moholkar, V.S. Synthesis and characterization of poly(lactic acid)/clove essential oil/alkali-treated halloysite nanotubes composite films for food packaging applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 216, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadat, S.; Rawtani, D.; Rao, P.K. Antibacterial activity of chitosan film containing Syzygium aromaticum (clove) oil encapsulated halloysite nanotubes against foodborne pathogenic bacterial strains. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 32, 104132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Su, Y.; Xu, J.; Ning, H.; Cheng, X.; Lu, L. Development of gas phase controlled-release antimicrobial and antioxidant packaging film containing carvacrol loaded with HNT-4M (halloysite nanotubes etched by 4 mol/L hydrochloric acid). Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 31, 100783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Liu, W.; Yao, J.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Silk microfibrous mats with long-lasting antimicrobial function. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhinayaa, R.; Jeevitha, G.; Mangalaraj, D.; Ponpandian, N.; Meena, P. Toxic influence of pristine and surfactant modified halloysite nanotubes on phytopathogenic bacteria. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 174, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saedi, S.; Shokri, M.; Rhim, J.-W. Preparation of carrageenan-based nanocomposite films incorporated with functionalized halloysite using AgNP and sodium dodecyl sulfate. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 106, 105934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikov, A.A.; Sayfutdinova, A.R.; Gorbachevskii, M.V.; Filatova, S.V.; Filimonova, A.V.; Rodrigues-Filho, U.P.; Fu, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Vinokurov, V.A.; et al. Natural Nanoclay-Based Silver–Phosphomolybdic Acid Composite with a Dual Antimicrobial Effect. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 6728–6736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Long, Y.; He, Y.; Cai, J.; Liu, M. HNTs@HKUST-1 strengthened PAAm hydrogel for strain sensing and antibacterial application. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 344, 112207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz Setter, O.; Movsowitz, A.; Goldberg, S.; Segal, E. Antibody-Functionalized Halloysite Nanotubes for Targeting Bacterial Cells. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 4094–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cyphert, E.L.; Zhang, N.; Learn, G.D.; Hernandez, C.J.; von Recum, H.A. Recent Advances in the Evaluation of Antimicrobial Materials for Resolution of Orthopedic Implant-Associated Infections In Vivo. ACS Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 3125–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Abdullayev, E.; Hollister, A.; Mills, D.; Lvov, Y.M. Clay Nanotube/Poly(methyl methacrylate) Bone Cement Composites with Sustained Antibiotic Release. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2012, 297, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarch-Pérez, C.; Shaqour, B.; Riool, M.; Verleije, B.; Beyers, K.; Vervaet, C.; Cos, P.; Zaat, S.A.J. 3D-Printed Gentamicin-Releasing Poly-ε-Caprolactone Composite Prevents Fracture-Related Staphylococcus aureus Infection in Mice. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1363. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bernabe, E.; Marcenes, W.; Hernandez, C.R.; Bailey, J.; Abreu, L.G.; Alipour, V.; Amini, S.; Arabloo, J.; Arefi, Z.; Arora, A.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Levels and Trends in Burden of Oral Conditions from 1990 to 2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease 2017 Study. J. Dent. Res. 2020, 99, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.S.; Bordini, E.A.F.; Ferreira, J.A.; Mei, L.; Dubey, N.; Fenno, J.C.; Piva, E.; Lund, R.G.; Schwendeman, A.; Bottino, M.C. Injectable MMP-Responsive Nanotube-Modified Gelatin Hydrogel for Dental Infection Ablation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 16006–16017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barot, T.; Rawtani, D.; Kulkarni, P. Development of Chlorhexidine Loaded Halloysite Nanotube Based Experimental Resin Composite with Enhanced Physico-Mechanical and Biological Properties for Dental Applications. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinelli, L.; Cacciatore, I.; Eusepi, P.; Dimmito, M.P.; Di Rienzo, A.; Reale, M.; Costantini, E.; Borrego-Sánchez, A.; García-Villén, F.; Viseras, C.; et al. In Vitro Wound-Healing Properties of Water-Soluble Terpenoids Loaded on Halloysite Clay. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Tan, C.; Liu, M. Gold@Halloysite nanotubes-chitin composite hydrogel with antibacterial and hemostatic activity for wound healing. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 20, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, R.; Sivakumar, S.; Kaur, H. Antimicrobial edible films in food packaging: Current scenario and recent nanotechnological advancements—A review. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.-H.; Jang, S.-R.; Lee, G.-M.; Ryu, J.-H.; Park, S.-I.; Park, N.-H. Halloysite Nanocapsules Containing Thyme Essential Oil: Preparation, Characterization, and Application in Packaging Materials. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2113–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorrasi, G. Dispersion of halloysite loaded with natural antimicrobials into pectins: Characterization and controlled release analysis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 127, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biddeci, G.; Cavallaro, G.; Di Blasi, F.; Lazzara, G.; Massaro, M.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Riela, S.; Spinelli, G. Halloysite nanotubes loaded with peppermint essential oil as filler for functional biopolymer film. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 152, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscusi, G.; Lamberti, E.; D’Amico, F.; Tammaro, L.; Gorrasi, G. Fabrication and Characterization of Bio-Nanocomposites Based on Halloysite-Encapsulating Grapefruit Seed Oil in a Pectin Matrix as a Novel Bio-Coating for Strawberry Protection. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, R.T.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Lee, S.M.; Kit, A.Y. ZnO deposited/encapsulated halloysite–poly (lactic acid) (PLA) nanocomposites for high performance packaging films with improved mechanical and antimicrobial properties. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 111, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakas, A.E.; Salmas, C.E.; Moschovas, D.; Baikousi, M.; Kollia, E.; Tsigkou, V.; Karakassides, A.; Leontiou, A.; Kehayias, G.; Avgeropoulos, A.; et al. Nanocomposite Film Development Based on Chitosan/Polyvinyl Alcohol Using ZnO@Montmorillonite and ZnO@Halloysite Hybrid Nanostructures for Active Food Packaging Applications. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Zhu, B.; Yan, J.; Qin, Y.; Yuan, M.; Cheng, G.; Yuan, M. Development of a Sodium Alginate-Based Active Package with Controlled Release of Cinnamaldehyde Loaded on Halloysite Nanotubes. Foods 2021, 10, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ren, T.; Perkins, P. The development and application of nanocomposites with pH-sensitive “gates” to control the release of active agents: Extending the shelf-life of fresh wheat noodles. Food Control 2022, 132, 108563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, M. Hydrophobic Halloysite Nanotubes via Ball Milling for Stable Pickering Emulsions: Implications for Food Preservation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 11289–11301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellani, L.; Giorgetti, L.; Riela, S.; Lazzara, G.; Scialabba, A.; Massaro, M. Ecotoxicity of halloysite nanotube–supported palladium nanoparticles in Raphanus sativus L. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 2503–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, M.; Li, J.; Chen, D. Cellular response of freshwater algae to halloysite nanotubes: Alteration of oxidative stress and membrane function. Environ. Sci. Nano 2021, 8, 3262–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Guo, Z.; Lao, B.; Li, C.; Zhu, J.; Yu, R.; Liu, M. Phytotoxicity of halloysite nanotubes using wheat as a model: Seed germination and growth. Environ. Sci. Nano 2021, 8, 3015–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, G.; Chen, C.; Jing, N.; Chen, C.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J. Halloysite nanotubes-based composite material with acid/alkali dual pH response and foliar adhesion for smart delivery of hydrophobic pesticide. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 139052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; An, T.; Cheng, H.; Su, W.; Meng, G.; Wu, J.; Guo, X.; Liu, Z. Functionalized halloysite nanotubes as chlorpyrifos carriers with high adhesion and temperature response for controlling of beet armyworm. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 222, 106488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Shi, Q.; Chen, T.; Qi, G.; Liu, M. Halloysite Nanotube-Based Pesticide Formulations with Enhanced Rain Erosion Resistance, Foliar Adhesion, and Insecticidal Effect. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 41605–41617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Pieraccini, S.; Guernelli, S.; Dindo, M.L.; Francati, S.; Liotta, L.F.; Colletti, G.C.; Masiero, S.; Riela, S. Photostability assessment of natural pyrethrins using halloysite nanotube carrier system. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 230, 106719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Viseras Iborra, C.; Cavallaro, G.; Colletti, C.G.; García-Villén, F.; Lazzara, G.; Riela, S. Synthesis and Characterization of Nanomaterial Based on Halloysite and Hectorite Clay Minerals Covalently Bridged. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Nanomaterial | Biocide | Pathogen | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HNTs-NH2 | Gentamicin | E. coli, S. aureus and S. epidermidis | Antibacterial | [39] |
| HNTs | Oregano essential oil | E. coli, S. aureus | Food packaging | [40] |
| HNTs | Carvacrol | A. hydrophila, P. putida, L. monocytogenes and S. aureus, A. alternata | Antibacterial | [41,42] |
| HNTs | CdS | E. coli, S. aureus | Antibacterial | [43] |
| HNTs/pectin | Salicylic acid | Salmonella, P. aeruginosa, E. coli and S. aureus | Food packaging | [44] |
| HNTs/pectin HNTs/alginate | Salicylic acid | E. coli, S. typhimurium, P. aeruginosa and S. aureus | Food packaging | [45] |
| HNTs/low-density polyethylene | Carvacrol and thymol | E. coli | Food packaging | [46] |
| HNTs/polyethylene | Carvacrol | A. hydrophila | Food packaging | [47] |
| HNTs-poly(4-vinylpyridine) | CuNPs | E. coli | Antibacterial | [48] |
| HNTs- poly(4-vinylpyridine)/polyethersulfone | AgNPs | E. coli, S. aureus | Antifouling and antibacterial | [49] |
| HNTs/chitosan | Norfloxacin | E. coli, S. aureus | Antibacterial | [50] |
| HNTs/chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol nanofibers | Benzocaine | E. coli, S. aureus | Antibacterial | [51] |
| HNTs/sodium alginate-poly (ethylene oxide) fibrous mats | Levofloxacin | E. coli, S. aureus | Wound dressing | [52] |
| HNTs/chitosan/pullulan | Rutin | E. coli, L. monocytogenes | Food packaging | [53] |
| HNTs/alginate | Cephalexin | E. coli, P. aeruginosa and S. aureus | Antibacterial protection | [54] |
| HNTs/polyethylene glycol | ClO2 | / | Food packaging | [55] |
| HNTs/poly(lactic) acid | Clove essential oil | / | Food packaging | [56] |
| HNTs/chitosan | Clove essential oil | B. mojavensis, E. coli | Food packaging | [57] |
| HNTs/LDPE | Carvacrol | E. coli, S. aureus | Food packaging | [58] |
| HNTs/silk fibroin microfibers | Tetracycline hydrochloride | E. coli, S. aureus | Wound dressing | [59] |
| HNTs/poly(lactic) acid | Clove essential oil | / | Food packaging | [56] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Massaro, M.; Ciani, R.; Cinà, G.; Colletti, C.G.; Leone, F.; Riela, S. Antimicrobial Nanomaterials Based on Halloysite Clay Mineral: Research Advances and Outlook. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1761. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11121761
Massaro M, Ciani R, Cinà G, Colletti CG, Leone F, Riela S. Antimicrobial Nanomaterials Based on Halloysite Clay Mineral: Research Advances and Outlook. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(12):1761. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11121761
Chicago/Turabian StyleMassaro, Marina, Rebecca Ciani, Giuseppe Cinà, Carmelo Giuseppe Colletti, Federica Leone, and Serena Riela. 2022. "Antimicrobial Nanomaterials Based on Halloysite Clay Mineral: Research Advances and Outlook" Antibiotics 11, no. 12: 1761. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11121761
APA StyleMassaro, M., Ciani, R., Cinà, G., Colletti, C. G., Leone, F., & Riela, S. (2022). Antimicrobial Nanomaterials Based on Halloysite Clay Mineral: Research Advances and Outlook. Antibiotics, 11(12), 1761. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11121761