Antibacterial and Anti-Biofilm Activity of Pyrones from a Pseudomonas mosselii Strain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Structure Identification of Compounds 1–6
2.2. Activities of Pseudopyronines A, B and C against Pathogens
2.3. Inhibition of Pseudopyronines on Biofilm Formation of S. aureus
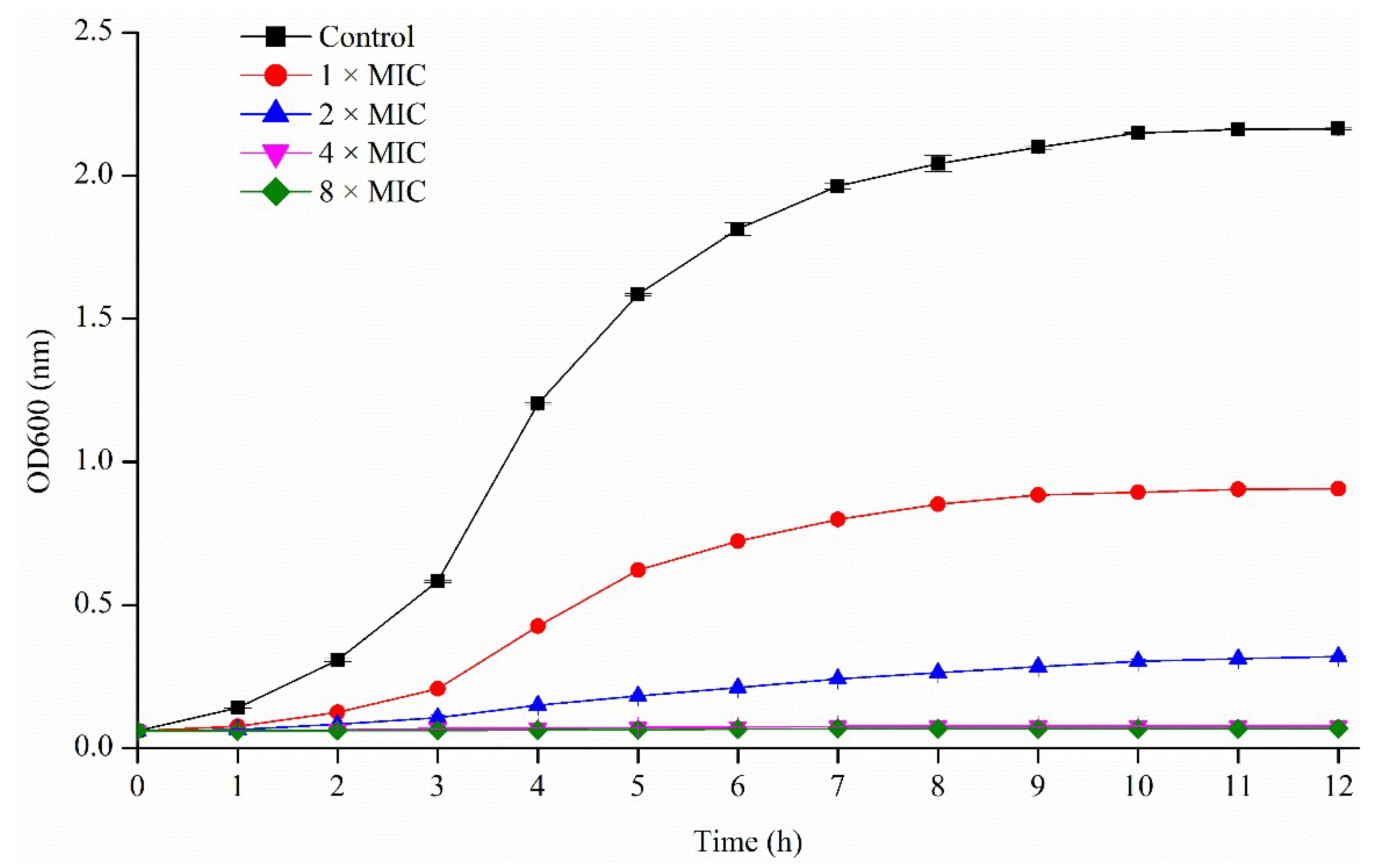
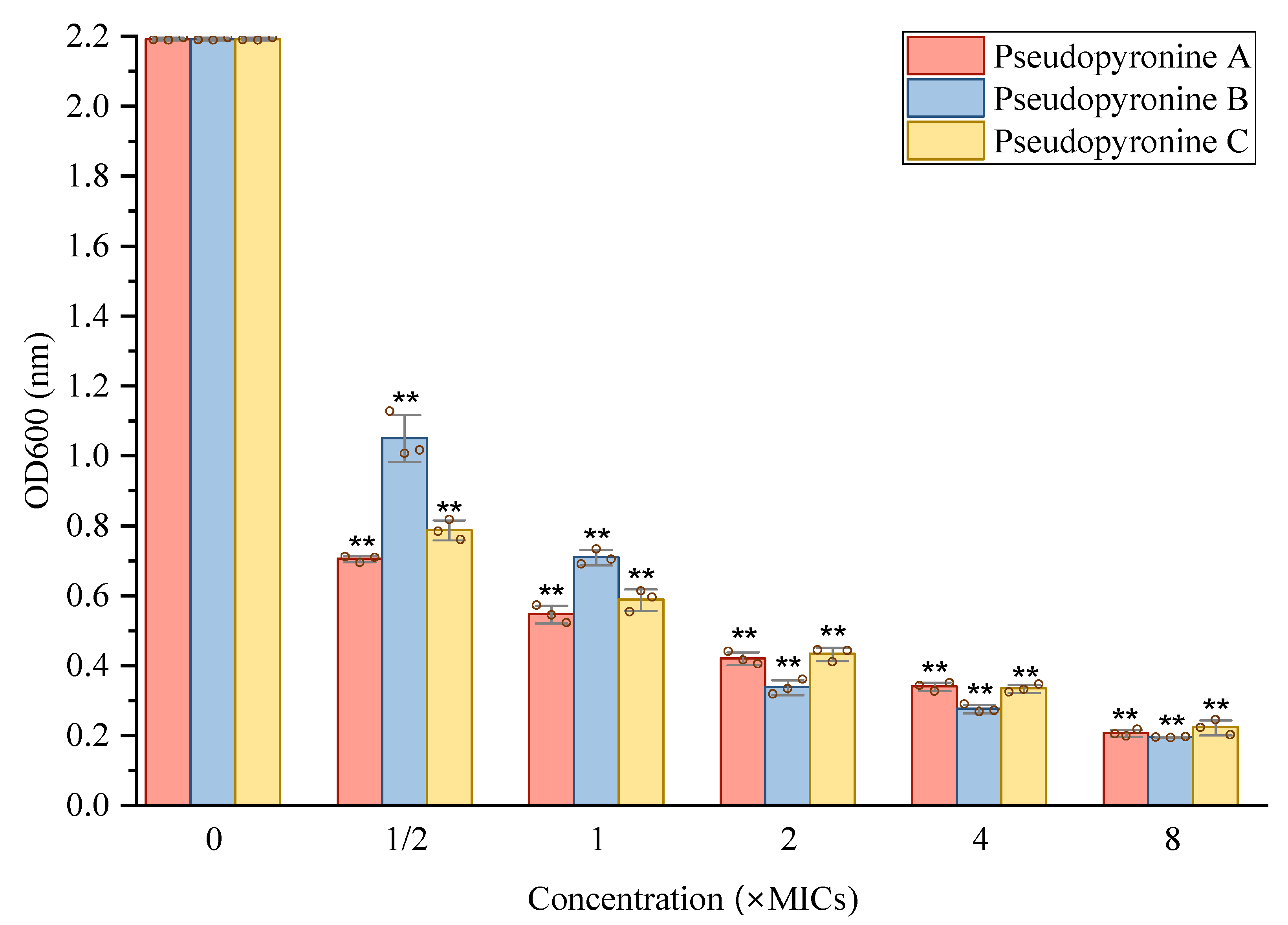
2.3.1. Activity of Pseudopyronines against Planktonic S. aureus
2.3.2. Inhibition of Pseudopyronines on S. aureus Biofilm Formation
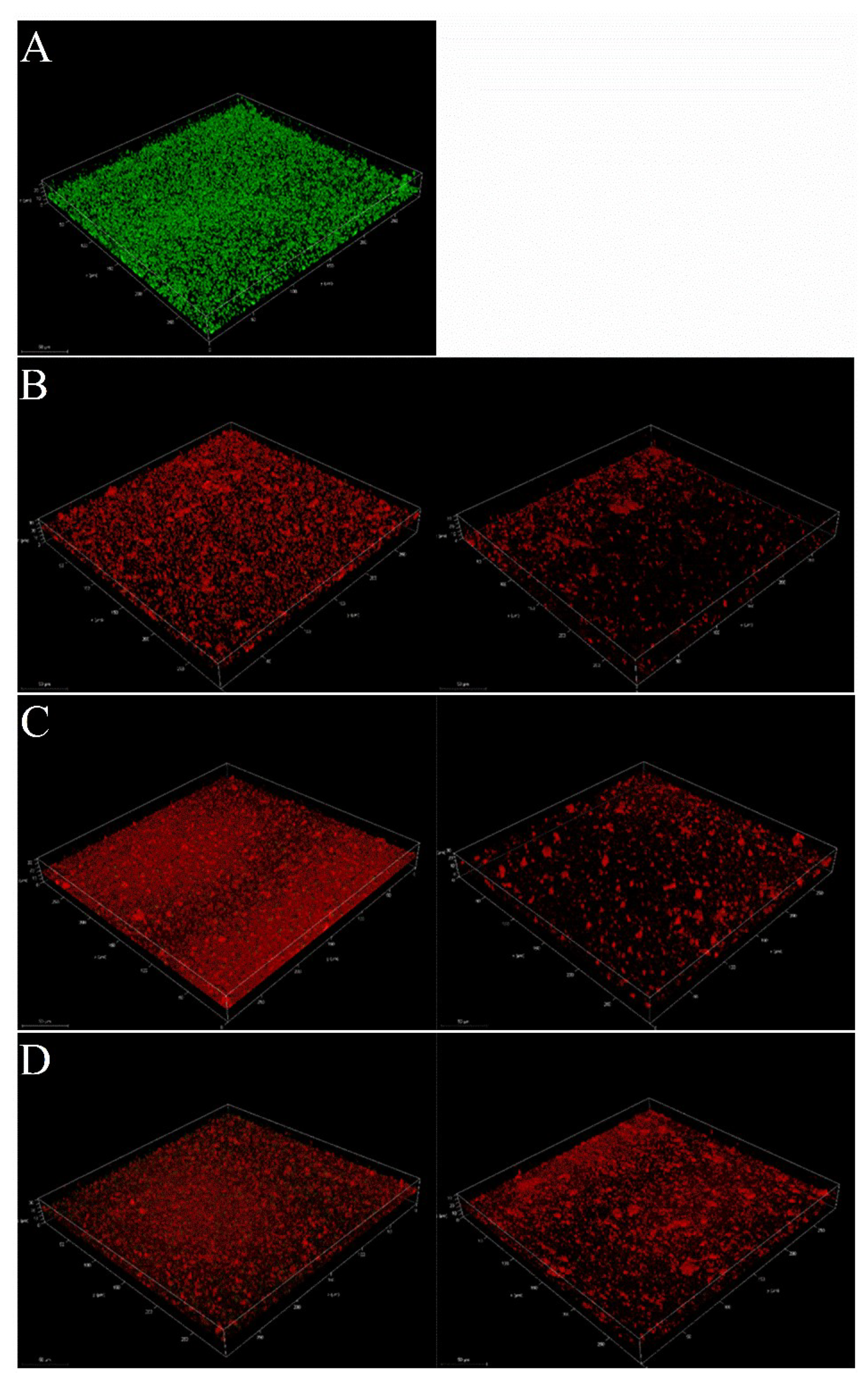
2.3.3. Reduction of Mature Biofilms of S. aureus by Pseudopyronines A-C
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General
4.2. Bacterial Strains and Materials
4.3. Large-Scale Extraction and Isolation
4.4. Biofilm Inhibition against Staphylococcus aureus
4.4.1. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
4.4.2. Growth Curve for S. aureus
4.4.3. Inhibition of Cell Attachment
4.4.4. Reduction of Biofilm Growth
4.4.5. Metabolic Activities of Pre-Formed Biofilm
4.4.6. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM) Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mann, J. Antibiotics: Actions, Origins, Resistance. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2005, 22, 304–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y. Biofilm Formation and Antimicrobial Resistance in Enterococcus. Infect. Chemother. 2017, 49, 236–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knox, J.; Uhlemann, A.C.; Lowy, F.D. Staphylococcus aureus Infections: Transmission within Households and the Community. Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagcigil, F.A.; Moodley, A.; Baptiste, K.E.; Jensen, V.F.; Guardabassi, L. Occurrence, Species Distribution, Antimicrobial Resistance and Clonality of Methicillin- and Erythromycin-Resistant Staphylococci in the Nasal Cavity of Domestic Animals. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 121, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gan, M.; Xu, H.; Chen, F.; Ming, X.; Xu, H.; Wei, H.; Xu, F.; Liu, C. Development of a Rapid and Sensitive Quantum Dot-Based Immunochromatographic Strip by Double Labeling PCR Products for Detection of Staphylococcus aureus in Food. Food Control 2014, 46, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, M.; Kalra, R.; Ponnan, P.; Jayaweera, J.A.A.S.; Kumbukgolla, W.W. Inhibition of Penicillin-Binding Protein 2a (PBP2a) in Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) by Combination of Oxacillin and a Bioactive Compound from Ramalinaroesleri. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 150, 104676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Chang, J.; Rimal, B.; Yang, H.; Schaefer, J. Surface Proteins and the Formation of Biofilms by Staphylococcus aureus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2018, 1860, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raafat, D.; Otto, M.; Reppschläger, K.; Iqbal, J.; Holtfreter, S. Fighting Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms with Monoclonal Antibodies. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 303–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Ge, C.; Yuan, P. Metabolomics Study Reveals Inhibition and Metabolic Dysregulation in Staphylococcus aureus Planktonic Cells and Biofilms Induced by Carnosol. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 538572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinski, T.F.; Dalisay, D.S.; Lievens, S.L.; Saludes, J.P. Drug Development from Marine Natural Products. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine Natural Products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2021, 38, 362–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peláez, F. The Historical Delivery of Antibiotics from Microbial Natural Products-Can History Repeat? Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 71, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Nearly Four Decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilson, Z.E.; Brimble, M.A. Molecules Derived from the Extremes of Life. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 44–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demain, A.L. From Natural Products Discovery to Commercialization: A Success Story. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 33, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wencewicz, T.A. Crossroads of Antibiotic Resistance and Biosynthesis. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 3370–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneyama, H.; Katsumata, R. Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria and Its Future for Novel Antibiotic Development. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 1060–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Song, J.; Kong, L.; Yuan, T.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Hou, B.; Lu, Y.; Du, G. The Strategies and Techniques of Drug Discovery from Natural Products. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 216, 107686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouthillette, L.M.; Darcey, C.A.; Handy, T.E.; Seaton, S.C.; Wolfe, A.L. Isolation of the Antibiotic Pseudopyronine B and SAR Evaluation of C3/C6 Alkyl Analogs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 2762–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giddens, A.C.; Nielsen, L.; Boshoff, H.I.; Tasdemir, D.; Perozzo, R.; Kaiser, M.; Wang, F.; Sacchettini, J.C.; Copp, B.R. Natural Product Inhibitors of Fatty Acid Biosynthesis: Synthesis of the Marine Microbial Metabolites Pseudopyronines A and B and Evaluation of Their Anti-Infective Activities. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 1242–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.S.; Ghequire, M.G.K.; Nett, M.; Josten, M.; Sahl, H.G.; De Mot, R.; Gross, H. Biosynthetic Origin of the Antibiotic Pseudopyronines A and B in Pseudomonas putida BW11M1. ChemBioChem 2015, 16, 2491–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.P.; Kong, F.; Janso, J.E.; Arias, D.A.; Suarez, P.A.; Bernan, V.S.; Petersen, P.J.; Weiss, W.J.; Carter, G.; Greenstein, M. Novel α-Pyrones Produced by a Marine Pseudomonas Sp. F92S91: Taxonomy and Biological Activities. J. Antibiot. 2003, 56, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kresovic, D.; Schempp, F.; Cheikh-Ali, Z.; Bode, H.B. A Novel and Widespread Class of Ketosynthase Is Responsible for the Head-to-Head Condensation of Two Acyl Moieties in Bacterial Pyrone Biosynthesis. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 1412–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Sun, W.; Saalim, M.; Wei, G.; Zaleta-Pinet, D.A.; Clark, B.R. Isolation of 2-Alkyl-4-Quinolones with Unusual Side Chains from a Chinese Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolate. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 2294–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Zaleta-Pinet, D.A.; Clark, B.R. Isolation, Identification, and Decomposition of Antibacterial Dialkylresorcinols from a Chinese Pseudomonas aurantiaca Strain. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.; Mierzwa, R.; Xu, L.; He, L.; Terracciano, J.; Patel, M.; Zhao, W.; Black, T.A.; Chan, T.M. Structure of Sch 419560, a Novel α-Pyrone Antibiotic Produced by Pseudomonas fluorescens. J. Antibiot. 2002, 55, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, F.; Singh, M.P.; Carter, G.T. Pseudopyronines A and B, α-Pyrones Produced by a Marine Pseudomonas Sp. F92S91, and Evidence for the Conversion of 4-Hydroxy-α-Pyrone to 3-Furanone. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 920–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, G.R.; Knight, J.C.; Herald, D.L.; Davenport, R.; Pettit, R.K.; Tucker, B.E.; Schmidt, J.M. Isolation of Labradorins 1 and 2 from Pseudomonas syringae Pv. coronafaciens. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1793–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundmann, F.; Dill, V.; Dowling, A.; Thanwisai, A.; Bode, E.; Chantratita, N.; Ffrench-Constant, R.; Bode, H.B. Identification and Isolation of Insecticidal Oxazoles from Pseudomonas Spp. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Z.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, W. Antimicrobial Activity of Cinnamaldehyde on Streptococcus mutans Biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.N.; Gobbato, N.; Rachid, M.; González, L.; Yantorno, O.; Valdez, J.C. Effect of Lactobacillus Plantarum and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Culture Supernatants on Polymorphonuclear Damage and Inflammatory Response. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2010, 10, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, E.; Hooyberghs, G.; Robijns, S.; Waldrant, K.; De Weerdt, A.; Delattin, N.; Liebens, V.; Kucharíková, S.; Tournu, H.; Verstraeten, N.; et al. Modulation of the Substitution Pattern of 5-Aryl-2-Aminoimidazoles Allows Fine-Tuning of Their Antibiofilm Activity Spectrum and Toxicity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 6483–6497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- M100-S23; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Twenty-Third Informational Supplement. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2013; ISBN 1-56238-865-7/1-56238-866-5.
- Cramton, S.E.; Gerke, C.; Götz, F. In Vitro Methods to Study Staphylococcal Biofilm Formation. Methods Enzymol. 2001, 336, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yestrepsky, B.D.; Sorenson, R.J.; Chen, M.; Larsen, S.D.; Sun, H. Novel Inhibitors of Staphylococcus aureus Virulence Gene Expression and Biofilm Formation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alejo-Armijo, A.; Glibota, N.; Frías, M.P.; Altarejos, J.; Gálvez, A.; Salido, S.; Ortega-Morente, E. Synthesis and Evaluation of Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Properties of A-Type Procyanidin Analogues against Resistant Bacteria in Food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 2151–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchese, A.; Bozzolasco, M.; Gualco, L.; Debbia, E.A.; Schito, G.C.; Schito, A.M. Effect of Fosfomycin Alone and in Combination with N-Acetylcysteine on E. coli Biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2003, 22, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Dong, J.; Xia, Y.; Shu, R. Antibacterial Activities of Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) and Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) against Planktonic and Biofilm Growing Streptococcus mutans. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 107, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Sharma, C.; Gulhane, R.D.; Rokana, N.; Singh, B.P.; Puniya, A.K.; Attri, S.; Goel, G.; Panwar, H. Inhibitory Effects of Lactobacilli of Goat’s Milk Origin against Growth and Biofilm Formation by Pathogens: An in Vitro Study. Food Biosci. 2018, 22, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Compound | MIC (µg/mL) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | S. epidermidis | P. aeruginosa | S. mutans | M. catarrhalis | E. hirae | B. subtilis | |
| Pseudopyronine A | 6.25 | 12.5 | 12.5 | -- | -- | 12.5 | 25 |
| Pseudopyronine B | 0.156 | 1.0 | 1.56 | 1.56 | 1.56 | 3.125 | 12.5 |
| Pseudopyronine C | 0.39 | 1.56 | 0.78 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Positive control | 0.01 a | 0.02 a | 0.0975 b | 2.5 c | 6.25 d | 0.78 c | 2.5 e |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zaleta-Pinet, D.A.; Borris, R.P.; Clark, B.R. Antibacterial and Anti-Biofilm Activity of Pyrones from a Pseudomonas mosselii Strain. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111655
Liu X, Wang Y, Zaleta-Pinet DA, Borris RP, Clark BR. Antibacterial and Anti-Biofilm Activity of Pyrones from a Pseudomonas mosselii Strain. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(11):1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111655
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xueling, Yali Wang, Diana A. Zaleta-Pinet, Robert P. Borris, and Benjamin R. Clark. 2022. "Antibacterial and Anti-Biofilm Activity of Pyrones from a Pseudomonas mosselii Strain" Antibiotics 11, no. 11: 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111655
APA StyleLiu, X., Wang, Y., Zaleta-Pinet, D. A., Borris, R. P., & Clark, B. R. (2022). Antibacterial and Anti-Biofilm Activity of Pyrones from a Pseudomonas mosselii Strain. Antibiotics, 11(11), 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111655








