A Broad-Host-Range Plasmid Outbreak: Dynamics of IncL/M Plasmids Transferring Carbapenemase Genes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli SAP1756 Harbours an IncM2 Plasmid Encoding blaNDM-1
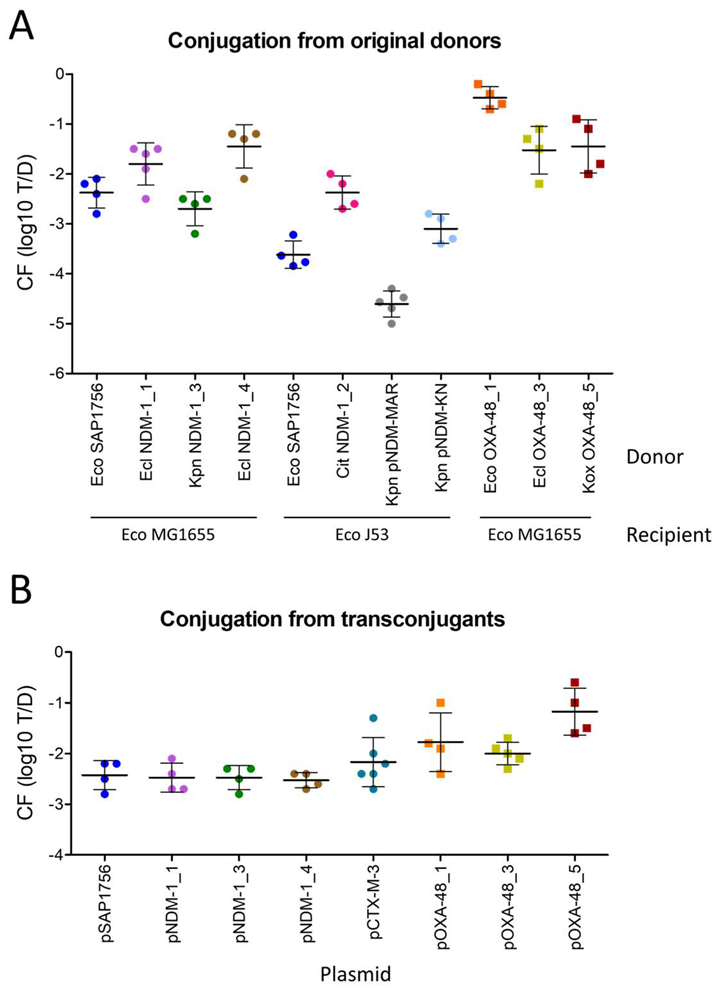
2.2. IncL OXA-48-Carrying Plasmids Transfer at Higher Rates than IncM2 Harbouring NDM-1
2.3. Most E. coli Isolates Tested as Recipients Were Not Permissive to pSAP1756 Entry
2.4. pSAP1756 Is Capable of Conjugating to (and From) Different Species of Enterobacterales
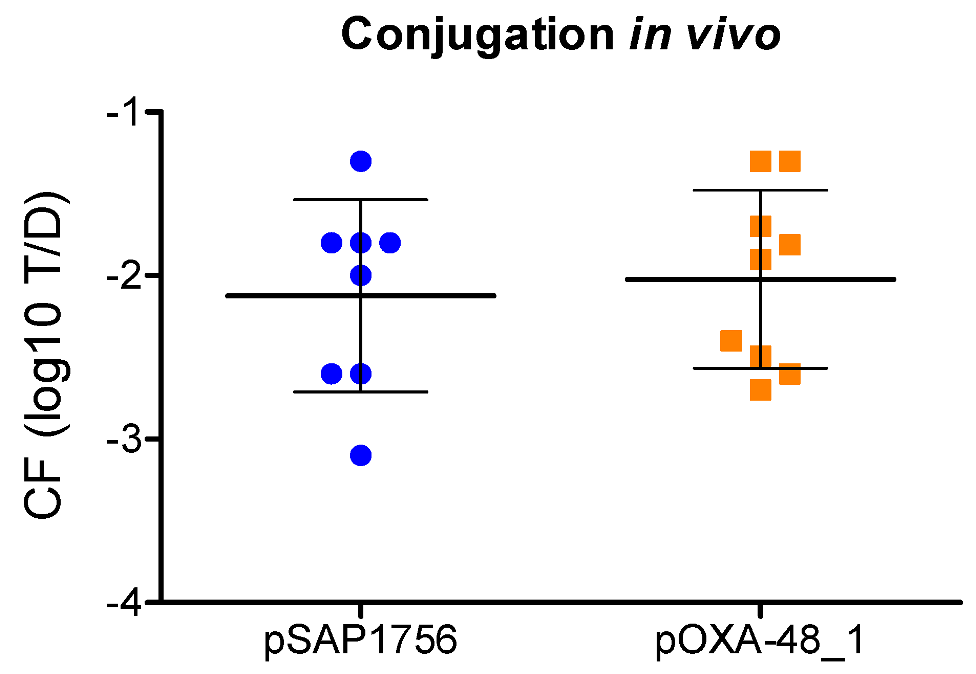
2.5. pSAP1756 and pOXA-48_1 Transfer at Similar Rates in a Galleria Mellonella Model
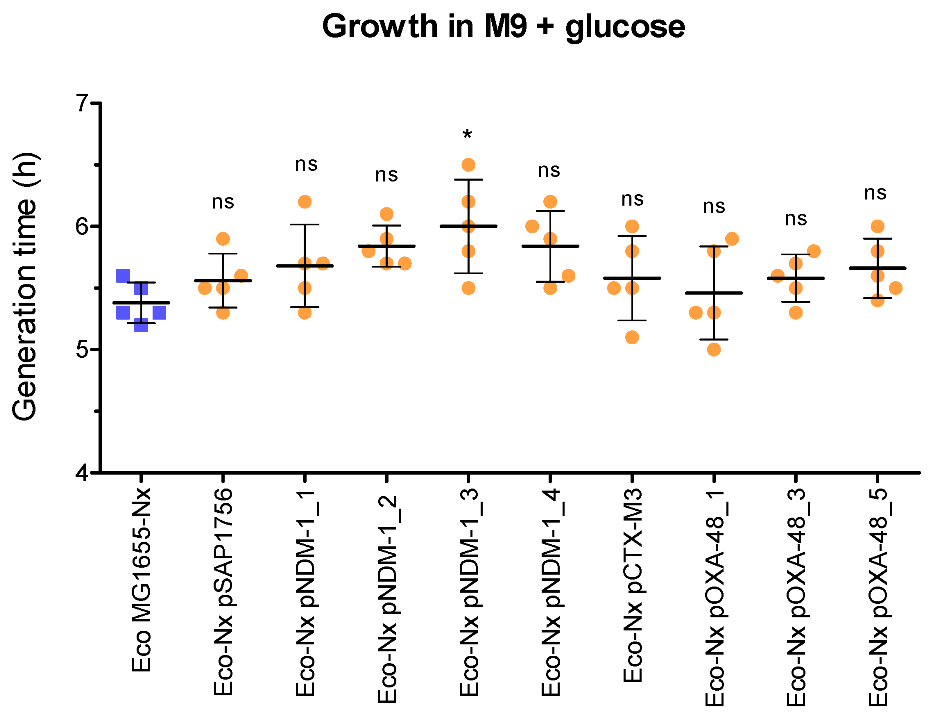
2.6. NDM-1-Harbouring Plasmids Impose a Higher Fitness Cost for the Growth of Their Host Than Those Carrying OXA-48
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Bacterial Cultures, DNA Extraction and Genome Sequencing
3.2. Genomic Analysis
3.3. In Vitro Conjugation Assays
3.4. In Vivo Conjugation Assays
3.5. Fitness Cost Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. WHO publishes List of Bacteria for Which New Antibiotics Are Urgently Needed; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jean, S.S.; Lee, W.S.; Lam, C.; Hsu, C.W.; Chen, R.J.; Hsueh, P.R. Carbapenemase-producing Gram-negative bacteria: Current epidemics, antimicrobial susceptibility and treatment options. Future Microbiol. 2015, 10, 407–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Duin, D.; Doi, Y. The global epidemiology of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Virulence 2017, 8, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopotsa, K.; Osei Sekyere, J.; Mbelle, N.M. Plasmid evolution in carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae: A review. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1457, 61–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partridge, S.R.; Kwong, S.M.; Firth, N.; Jensen, S.O. Mobile Genetic Elements Associated with Antimicrobial Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00088-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Potron, A.; Nordmann, P. OXA-48-like carbapenemases: The phantom menace. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Heritier, C.; Tolun, V.; Nordmann, P. Emergence of oxacillinase-mediated resistance to imipenem in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.E.; Holmes, A.; Peck, R.; Livermore, D.M.; Hope, W. OXA-48-Like beta-Lactamases: Global Epidemiology, Treatment Options, and Development Pipeline. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0021622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Al Maskari, Z.; Al Rashdi, F.; Bernabeu, S.; Nordmann, P. NDM-1-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated in the Sultanate of Oman. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Dortet, L.; Bernabeu, S.; Nordmann, P. Genetic features of blaNDM-1-positive Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 5403–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, D.; Toleman, M.A.; Giske, C.G.; Cho, H.S.; Sundman, K.; Lee, K.; Walsh, T.R. Characterization of a new metallo-beta-lactamase gene, bla(NDM-1), and a novel erythromycin esterase gene carried on a unique genetic structure in Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 14 from India. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 5046–5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman Qamar, M.; Lopes, B.S.; Hassan, B.; Khurshid, M.; Shafique, M.; Atif Nisar, M.; Mohsin, M.; Nawaz, Z.; Muzammil, S.; Aslam, B.; et al. The present danger of New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase: A threat to public health. Future Microbiol. 2020, 15, 1759–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Diaz, M.; Ellaby, N.; Turton, J.; Woodford, N.; Tomas, M.; Ellington, M.J. NDM-1 carbapenemase resistance gene vehicles emergent on distinct plasmid backbones from the IncL/M family. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 620–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A. Resistance plasmid families in Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 2227–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Seiffert, S.N.; Schwendener, S.; Perreten, V.; Endimiani, A. Differentiation of IncL and IncM Plasmids Associated with the Spread of Clinically Relevant Antimicrobial Resistance. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potron, A.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Derepressed transfer properties leading to the efficient spread of the plasmid encoding carbapenemase OXA-48. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikhan, N.F.; Petty, N.K.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Beatson, S.A. BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): Simple prokaryote genome comparisons. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getino, M.; de la Cruz, F. Natural and Artificial Strategies To Control the Conjugative Transmission of Plasmids. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getino, M.; Riley, P.; Arkell, P.; Baker, D.; Ravi, A.; van Vliet, A.H.M.; La Ragione, R.M. University of Surrey, Guildford, UK, 2022, manuscript in preparation.
- Golebiewski, M.; Kern-Zdanowicz, I.; Zienkiewicz, M.; Adamczyk, M.; Zylinska, J.; Baraniak, A.; Gniadkowski, M.; Bardowski, J.; Ceglowski, P. Complete nucleotide sequence of the pCTX-M3 plasmid and its involvement in spread of the extended-spectrum beta-lactamase gene blaCTX-M-3. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 3789–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, L.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P.; Carta, C.; Carattoli, A. Complete sequencing of an IncH plasmid carrying the blaNDM-1, blaCTX-M-15 and qnrB1 genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 1645–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Villa, L.; Poirel, L.; Bonnin, R.A.; Nordmann, P. Evolution of IncA/C blaCMY-(2)-carrying plasmids by acquisition of the blaNDM-(1) carbapenemase gene. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 783–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Morooka, N.; Yamamoto, Y.; Fujita, K.; Isono, K.; Choi, S.; Ohtsubo, E.; Baba, T.; Wanner, B.L.; Mori, H.; et al. Highly accurate genome sequences of Escherichia coli K-12 strains MG1655 and W3110. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2006, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, Y.; Peirano, G.; Pitout, J.D.D. Complete Genome Sequence of Escherichia coli J53, an Azide-Resistant Laboratory Strain Used for Conjugation Experiments. Genome Announc. 2018, 6, e00433-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S. GitHub: 2010. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc (accessed on 16 November 2022).
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, D.E.; Lu, J.; Langmead, B. Improved metagenomic analysis with Kraken 2. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseemann, T. GitHub. Available online: https://github.com/tseemann/mlst (accessed on 16 November 2022).
- Jolley, K.A.; Maiden, M.C. BIGSdb: Scalable analysis of bacterial genome variation at the population level. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseemann, T. GitHub. Available online: https://github.com/tseemann/abricate (accessed on 16 November 2022).
- Feldgarden, M.; Brover, V.; Gonzalez-Escalona, N.; Frye, J.G.; Haendiges, J.; Haft, D.H.; Hoffmann, M.; Pettengill, J.B.; Prasad, A.B.; Tillman, G.E.; et al. AMRFinderPlus and the Reference Gene Catalog facilitate examination of the genomic links among antimicrobial resistance, stress response, and virulence. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; Garcia-Fernandez, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Moller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.; Nash, J.H.E. MOB-suite: Software tools for clustering, reconstruction and typing of plasmids from draft assemblies. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, e000206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| E. coli Recipient | Type | Phylogroup | Source | Year | Country | CF (log10 T/R) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MG1655 (RifR) | Commensal | A | Human | 1922 | US | −2.1 ± 0.2 |
| SAP2531 (RifR) | Pathogenic | A | Human | 2018 | UK | −3.8 ± 0.7 |
| SAP2592 (RifR) | Pathogenic | B1 | Human | 2018 | UK | −3.4 ± 0.6 |
| NCTC 12241 (RifR) | Pathogenic | B2 | Human | 1946 | US | N.D. |
| NCTC 13441 (NxR) | Pathogenic | B2 | Human | 2003 | UK | N.D. |
| SAP2492 (RifR) | Pathogenic | B2 | Human | 2018 | UK | N.D. |
| SAP2188 (NxR) | Pathogenic | C | Avian | 2018 | UK | N.D. |
| SAP2526 (NxR) | Pathogenic | D | Human | 2018 | UK | −4.4 ± 0.4 |
| SAP2573 (RifR) | Pathogenic | E | Human | 2018 | UK | N.D. |
| SAP2485 (RifR) | Pathogenic | F | Human | 2018 | UK | −3.6 ± 0.2 |
| SAP2180 (RifR) | Pathogenic | G | Avian | 2018 | UK | N.D. |
| Donor | Plasmid | Recipient | CF (log10 T/R) |
| E. coli SAP1756 | pSAP1756 | E. coli MG1655 (RifR) | −2.1 ± 0.2 |
| E. coli SAP1756 | pSAP1756 | S. marcescens NCTC 13382 (RifR) | −3.0 ± 0.2 |
| E. coli SAP1756 | pSAP1756 | K. pneumoniae NCTC 9633 (RifR) | −3.6 ± 0.4 |
| E. coli SAP1756 | pSAP1756 | E. cloacae NCTC 13380 (RifR) | −4.0 ± 0.1 |
| E. coli SAP1756 | pSAP1756 | Y. enterocolitica NCTC 12982 (RifR) | −2.4 ± 0.3 |
| Donor | Plasmid | Recipient | CF (log10 T/D) |
| E. coli MG1655 (RifR) | pSAP1756 | E. coli MG1655 (NxR) | −2.4 ± 0.2 |
| S. marcescens NCTC 13382 (RifR) | pSAP1756 | E. coli MG1655 (NxR) | −2.3 ± 0.4 |
| K. pneumoniae NCTC 9633 (RifR) | pSAP1756 | E. coli MG1655 (NxR) | −2.5 ± 0.7 |
| E. cloacae NCTC 13380 (RifR) | pSAP1756 | E. coli MG1655 (NxR) | −1.9 ± 0.2 |
| Y. enterocolitica NCTC 12982 (RifR) | pSAP1756 | E. coli MG1655 (NxR) | −1.8 ± 0.5 |
| Species | Isolate | Plasmid | Inc | AMR Gene | D/R | Selection | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | SAP1756 | pSAP1756 | IncM2 | blaNDM-1 | D | Mer0.25 | This work |
| E. coli | SAP2180 | R | Nx50 | This work | |||
| E. coli | SAP2188 | R | Nx50 | This work | |||
| E. coli | SAP2485 | R | Rif50 | This work | |||
| E. coli | SAP2492 | R | Rif50 | [19] | |||
| E. coli | SAP2526 | R | Nx50 | [19] | |||
| E. coli | SAP2531 | R | Rif50 | [19] | |||
| E. coli | SAP2573 | R | Rif50 | [19] | |||
| E. coli | SAP2592 | R | Nx50 | [19] | |||
| E. cloacae | NDM-1_1 | pNDM-1_1 | IncM2 | blaNDM-1 | D | Mer0.25 | [13] |
| Citrobacter | NDM-1_2 | pNDM-1_2 | IncM2 | blaNDM-1 | D | Mer0.25 | [13] |
| K. pneumoniae | NDM-1_3 | pNDM-1_3 | IncM2 | blaNDM-1 | D | Mer0.25 | [13] |
| E. cloacae | NDM-1_4 | pNDM-1_4 | IncM2 | blaNDM-1 | D | Mer0.25 | [13] |
| E. coli | NDM-1_5 | pNDM-1_5 | IncM2 | blaNDM-1 | D | Mer0.25 | [13] |
| E. coli | OXA-48_1 | pOXA-48_1 | IncL | blaOXA-48 | D | Mer0.25 | This work |
| K. pneumoniae | OXA-48_2 | pOXA-48_2 | IncL | blaOXA-48 | D | Mer0.25 | This work |
| E. cloacae | OXA-48_3 | pOXA-48_3 | IncL | blaOXA-48 | D | Mer0.25 | This work |
| Citrobacter | OXA-48_4 | pOXA-48_4 | IncL | blaOXA-48 | D | Mer0.25 | This work |
| K. oxytoca | OXA-48_5 | pOXA-48_5 | IncL | blaOXA-48 | D | Mer0.25 | This work |
| E. coli | MG1655 | pCTX-M-3 | IncM2 | blaCTX-M-3 | D | Ctx2 | [20] |
| K. pneumoniae | TCKpnC | pNDM-MAR | IncH | blaNDM-1 | D | Mer0.25 | [21] |
| K. pneumoniae | Kp7 | pNDM-KN | IncA/C | blaNDM-1 | D | Ctx2 | [22] |
| E. coli | MG1655 | R | Nx50/Rif50 | [23] | |||
| E. coli | J53 | R | NaN3100 | [24] | |||
| S. marcescens | NCTC 13382 | R | Rif50 | ||||
| K. pneumoniae | NCTC 9633 | R | Rif50 | ||||
| E. cloacae | NCTC 13380 | R | Rif50 | ||||
| Y. enterocolitica | NCTC 12982 | R | Rif50 | ||||
| E. coli | NCTC 12241 | R | Rif50 | ||||
| E. coli | NCTC 13441 | R | Nx50 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Getino, M.; López-Díaz, M.; Ellaby, N.; Clark, J.; Ellington, M.J.; La Ragione, R.M. A Broad-Host-Range Plasmid Outbreak: Dynamics of IncL/M Plasmids Transferring Carbapenemase Genes. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111641
Getino M, López-Díaz M, Ellaby N, Clark J, Ellington MJ, La Ragione RM. A Broad-Host-Range Plasmid Outbreak: Dynamics of IncL/M Plasmids Transferring Carbapenemase Genes. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(11):1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111641
Chicago/Turabian StyleGetino, María, María López-Díaz, Nicholas Ellaby, John Clark, Matthew J. Ellington, and Roberto M. La Ragione. 2022. "A Broad-Host-Range Plasmid Outbreak: Dynamics of IncL/M Plasmids Transferring Carbapenemase Genes" Antibiotics 11, no. 11: 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111641
APA StyleGetino, M., López-Díaz, M., Ellaby, N., Clark, J., Ellington, M. J., & La Ragione, R. M. (2022). A Broad-Host-Range Plasmid Outbreak: Dynamics of IncL/M Plasmids Transferring Carbapenemase Genes. Antibiotics, 11(11), 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111641






