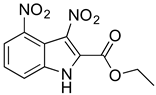
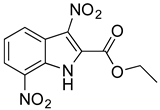
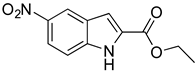
Abstract
The discovery of new classes of antibiotics is slow, and it is being greatly outpaced by the development of bacterial resistance. This disparity places us in an increasingly vulnerable position because we are running out of safe and effective therapeutic options to treat antibiotic-resistant infections. This is exemplified by the emergence and persistence of hospital-acquired and community-associated methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), which has markedly narrowed our options for treating life-threatening staph infections. Thus, there is an urgent need to develop novel, potent, preventive, and therapeutic agents. In our current study, we performed a whole-cell screening assay of synthetic libraries for antibacterial activity and identified a novel molecule, MZ-01. MZ-01 exhibited potent bactericidal activity against Gram-positive bacterial pathogens, including MRSA, Streptococcus pyogenes, and Streptococcus pneumoniae, at low concentrations. MZ-01 killed and lysed both the late exponential phase of an S. aureus population and bacteria inside mammalian cells. Furthermore, MZ-01 exhibited low cytotoxicity. These results indicate that MZ-01 is a promising scaffold to guide the development of novel, potent antibacterial agents against multidrug-resistant Gram-positive bacterial pathogens such as MRSA.
1. Introduction
Bacterial resistance to antibiotics is a serious threat to public health worldwide. Staphylococcus aureus is one of six major pathogens, including Enterococcus faecium, S. aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter spp., that are responsible for the majority of antibiotic-resistant infections in the US [1,2,3], and result in tens of millions of infections annually [4]. The persistence of multidrug-resistant S. aureus, especially methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), is a serious public health concern [5,6]; in 2017, MRSA caused nearly 20,000 deaths in the US (CDC, 2019). MRSA isolates are responsible for at least 40% of all hospital-acquired MRSA (HA-MRSA) infections [7], whereas the more virulent community-acquired MRSA (CA-MRSA) has emerged and spread worldwide [8,9,10].
In addition to being a concern for human health in healthcare and community settings, significant concerns regarding MRSA in food animals have emerged after the identification of MRSA among Dutch swine farms in 2005 [11]. Livestock-associated MRSA (LA-MRSA) isolates are genetically distinct from human isolates [12]. Most LA-MRSA from swine can be assigned by multilocus sequence typing (MLST) to a single sequence type, ST398 [13]. ST398 MRSA has been detected on many pig farms in different countries, including the US [14,15,16,17]. In the US, 49% of the animals and 45% of the workers examined on farms in Iowa and Illinois carried ST398 MRSA [18]. People working in these barns or in close contact with pigs are at significant risk for ST398 LA-MRSA colonization [12,16,18,19,20,21]. As such, these individuals are at increased risk of developing drug-resistant S. aureus infections, and sporadic cases of serious disease have been reported [13,22,23,24]. Furthermore, ST398 MRSA has been found in retail meat products, including ground pork and ground beef, in Europe, Canada, and the US [25,26,27,28]. The rise of MRSA in food animals increasingly threatens food safety and public health because LA-MRSA isolates are now emerging as causes of human disease and death [29,30,31,32].
Several antibiotics, including linezolid and daptomycin, are approved for the treatment of MRSA and are still part of our first and second lines of therapy; vancomycin, linezolid, and clindamycin are used for the treatment of MRSA pneumonia [33]. However, there has been a rise in multidrug resistance against these antibiotics, which further limits our therapeutic options [34,35,36,37,38,39,40]. There are several new antibiotics in the pipeline, but they are mostly limited to existing classes and thus have cross-resistance, which highlights the need for the development of novel antibiotic classes [41,42].
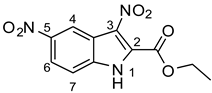
As part of our ongoing efforts to identify new therapies against S. aureus, we performed a whole-cell screening assay of synthetic libraries and identified a novel compound: a 3,5-dinitroindole-2-carboxylate derivative, termed MZ-01. In this study, we validated the compound MZ-01 in vitro. MZ-01 exhibited potent bactericidal activity against Gram-positive bacterial pathogens, including S. aureus (e.g., MRSA), Streptococcus pyogenes, and Streptococcus pneumoniae at low concentrations. Yet, even at high concentrations, MZ-01 did not kill Gram-negative bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Importantly, MZ-01 had low cytotoxicity against eukaryotic cell lines. Overall, these results suggest that MZ-01 is a promising compound for the development of selective antibacterial agents for Gram-positive bacterial infections.
2. Results
2.1. MZ-01 Had Potent Antibacterial Activity against Gram-Positive Bacterial Pathogens, Including S. aureus (e.g., MRSA), S. pyogenes, and S. pneumoniae
In order to identify new antibacterial agents, we screened a small compound library (approximately 5000 compounds) and found that MZ-01 exhibits bactericidal activity at low concentrations against MRSA WCUH29 (MIC: 2.67 μg/mL) and against the clinical human S. aureus isolates (MIC50: 4 μg/mL), including USA100 HA-MRSA NRS382, USA200 HA-MRSA NRS383, USA300 CA-MRSA NR384, USA400 CA-MRSA MW2, and methicillin-sensitive S. aureus (MSSA) (Table 1). Moreover, MZ-01 showed bactericidal activity against Gram-positive S. pyogenes and S. pneumoniae (MIC: 5.33 μg/mL), weak antibacterial activity against Gram-positive M. abscessus, and no activity against Gram-negative P. aeruginosa and K. pneumoniae at 128 μg/mL (Table 1).

Table 1.
Antibacterial profile of MZ-01.
MZ-01 also appeared to have weak activity against E. coli at 106.67 μg/mL; however, null mutation of the AcrAB efflux pump increased the susceptibility of E. coli to MZ-01 (Table 1), suggesting a specific mechanism of action. These results suggest that MZ-01 has the potential to be developed into a Gram–positive-selective or broad-spectrum antibacterial agent.
2.2. MZ-01 Had Potent Bactericidal Activity against MRSA
To further evaluate the antibacterial activity of MZ-01, we performed time-dependent killing assays by adding different doses (2, 4, 8, 16, 32, or 64 × MIC) of MZ-01 into the early and late exponential phases of an S. aureus population, respectively. MZ-01 exhibited potent bactericidal activity against MRSA WCUH29 in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 1A,C); after 24 h exposure to approximate 6.4 log10 CFUs of the early exponential phases of S. aureus, no viable bacteria were recovered, indicating that MZ-01 at 32 × MIC concentration could kill the bacterial population. In this experiment, Vancomycin (Van) was used as a positive control. Vancomycin killed WCUH29 bacterial cells at 4 to 8 × MIC after 24 h of exposure to the early exponential phase of culture (Figure 1B). Notably, 16 to 32 × MIC of MZ-01 effectively killed and lysed the S. aureus population in late exponential phase after 24 h of exposure to WCUH29, whereas more bacteria were viable after exposure to 16 × MIC of vancomycin for 24 h (Figure 1D).
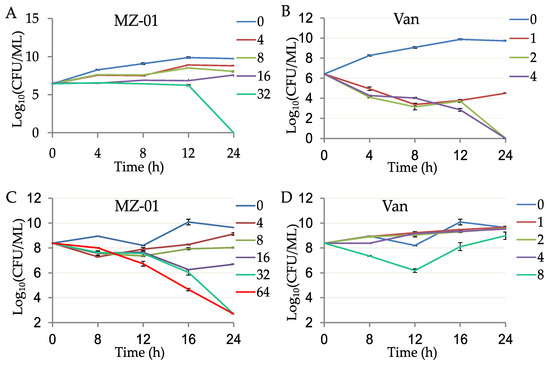
Figure 1.
Time-dependent killing of MRSA by MZ-01. MRSA WCUH29 was grown in TSB to early (A,B) and late (C,D) exponential phase and were exposed to different doses of antibacterial agents. An aliquot of the culture was taken from each tube at different time points after exposing to the compounds, and a serial dilution was performed. The diluted culture was incubated at 37 °C, and the average values of Log10 CFU/mL were determined from triplicate experiments. The unit of MZ-01 and Van (vancomycin) is μg/mL.
2.3. MZ-01 Induces Low Frequency of Resistant Mutations
To determine the frequency of bacterial resistance to MZ-01, we harvested the bacterial cells from the stationary growth of MRSA (WCUH29 strain) and spread them onto TSA plates containing 8 × MIC, 4 × MIC, or 2 × MIC of MZ-01, and incubated for 48 h at 37 °C. We were unable to obtain mutants of S. aureus resistant to MZ-01 even when plating 1010 CFU onto the media containing 8 × MIC and 4 × MIC of the compound. Only six colonies of S. aureus were obtained when plating 1010 CFU onto TSA plates with 2 × MIC of MZ-01 after 48 h of incubation at 37 °C. The frequency of resistance to MZ-01 is therefore estimated to be between 10−9 and 10−10. In addition, only two colonies appeared in 2-fold increased MIC, whereas the rest of the colonies showed similar MIC compared to the control, suggesting that MZ-01 may have multiple targets.
2.4. MZ-01 Has Low Cytotoxicity
To validate the lead compound, we conducted cytotoxicity assays using two mammalian cell lines, Vero monkey kidney cells, and A549 human lung cancer epithelial cells, in triplicate experiments as described [43]. The cells were incubated in tissue culture flasks at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere until a confluent monolayer was achieved. The cells were exposed to different doses of compounds for 24 h. Cell viability was determined using the CellTiter 96® Aqueous Non-Radioactive Cell Proliferation Assay; DMSO was used as a negative control. MZ-01 induced less than 5% Vero cell death at 117 μg/mL (400 μM), whereas a positive control compound, ID2551, caused more than 80% cell death (Figure 2).
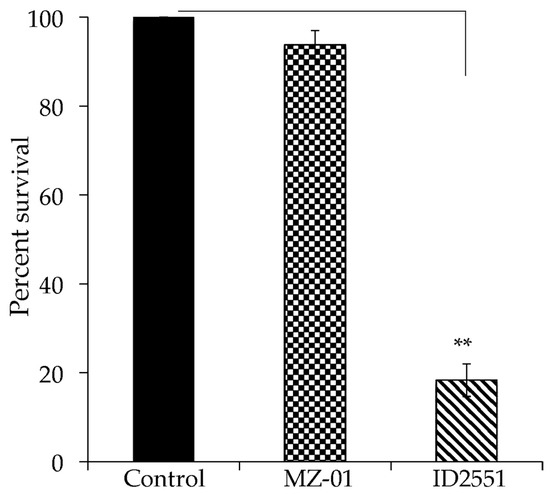
Figure 2.
Effect of compounds on cell viability. The monolayer of Vero cells was cultured in RPMI 1640 with 10% FBS and exposed to 400 μM of compounds in DMSO. Control cells were exposed to DMSO vehicle control. Cell viability was measured after 24 h treatment and is expressed as an average of at least three experiments ± standard deviation. The symbol ‘**’ indicates a significant difference between the control and treated cells (p < 0.01).
2.5. MZ-01 Kills S. aureus Inside of A549 Epithelial Cells
To assess the activity of MZ-01 in vivo, we examined the efficacy of MZ-01 against MRSA in epithelial cells. A549 cells were infected with MRSA; 1 h after infection, the extracellular bacteria were killed with gentamicin/lysostaphin as described [44]. Infected cells were washed, exposed to 100 μg/mL MZ-01 or vancomycin, and collected in RPMI1640 with 10% FBS 6 or 24 h after treatment. The cells were then lysed, diluted, and plated onto TSA plates to determine viable CFU. No morphological changes were observed in cells after treatment with different antibiotics, including vancomycin. Moreover, 24 h after exposure to the same concentration of MZ-01, A549 cells exhibited no remarkable difference compared to DMSO control (Figure 3A). However, similar to vancomycin, MZ-01 caused significantly decreased viable bacterial cells (MRSA WCUH29) inside of A549 cells 24 h after treatment compared to those treated for 6 h (Figure 3B).
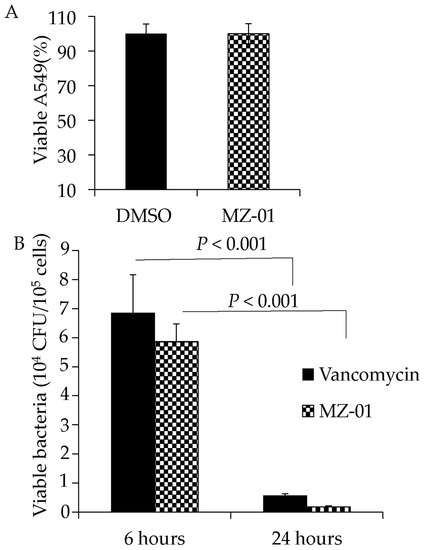
Figure 3.
Examination of cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity in human lung epithelial A549 cells. (A) Effect of MZ-01 on the viability of A549 cells. The epithelial cells (A549) were incubated in RPMI 1640 medium with 10% FBS. Monolayers of A549 cells (2 × 105 cells well−1) were exposed to MZ-01 in DMSO. Control cells were exposed to DMSO vehicle control. Cell viability was measured after 24 h treatment and is expressed as an average of at least three experiments ± standard deviation. (B) Recovery of viable MRSA from A549 cells at different time points after treatment with MZ-01 or control vancomycin. Monolayers of A549 cells (2 × 105 cells well−1) were infected by approximately 3 × 106 cfu of WCUH29. The extracellular bacteria were removed 1 h after infection. Cell viability was measured at different time points after treatment and is expressed as an average of at least three experiments ± standard deviation.
2.6. Identification of Key Groups for Activity of MZ-01
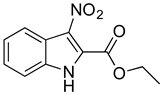
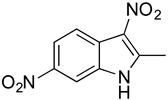
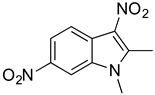
To identify key functional groups for MZ-01 activity, we performed pilot SAR studies. Six analogs were selected to identify sites amenable to modification and were examined against MRSA (Table 2). N-methylation at the indole in MZ-04 abolished activity against MRSA compared to MZ-01 and MZ-03. Repositioning of the C5 nitro group to either the C4 or C7 position in MZ-05 and MZ-06, respectively, was not tolerated compared to MZ-01 (Table 2). Removal of the C3 nitro group completely abolished activity in MZ-07, whereas removal of the C5 nitro group in MZ-02 still led to activity that was far less potent than the activity of MZ-01. The shown MIC values are the averages from triplicate experiments.

Table 2.
Activity of MZ-01 analogs against MRSA WCUH29.
3. Discussion
In this study, we employed the whole-cell screening assays of the compound library collected by Dr. Noland’s laboratory and identified a novel compound, 3,5-dinitroindole (MZ-01) [45,46], with moderate bactericidal activities against Gram-positive bacterial pathogens, including MRSA, low cytotoxicity to eukaryotic cells, and low resistance frequency in MRSA. Altogether, these findings suggest that MZ-01 has the potential to be developed into a potent anti-Gram-positive bacterial pathogen agent. Furthermore, our data showed that MZ-01 possesses weak activity against Gram-negative bacteria E. coli and A. baumannii, suggesting that it may be possible to expand its spectrum. In addition, the effect of efflux pump (acrAB) deletion on MZ-01′s MIC for E. coli is fairly small, which is a desirable characteristic.
MZ-01 possesses a biologically significant indole backbone [47] with two aromatic nitro groups. Although nitroaromatic groups are generally undesirable in drug discovery because of toxicological problems resulting from the metabolic reduction of the nitro group to the corresponding amine [48], some nitroaromatic compounds are used as anti-infection drugs (chloramphenicol, PA-824, metronidazole, and nitrofurantoin), as well as to treat trypanosomatid disease, helminth infections, Parkinson’s disease, angina, and insomnia [49,50,51,52,53]. Taken together, our pilot studies and previous literature strongly support that 3,5-dinitroindole-2-carboxylate derivatives have a remarkable potential to be developed into a new class of antibacterial.
The target of MZ-01 remains to be determined, and we are in the process of identifying the potential mechanism of action for MZ-01 using whole-genome sequencing-resistant mutants and transcriptomics analysis. Null mutation of efflux pump protein AcrAB increased E. coli susceptibility to MZ-01, suggesting a specific mechanism of action. We are in the progress of determining its mechanism of action by whole-genomic DNA sequencing analysis of resistant mutants and examining the impact of MZ-01 on global gene transcription profiles using RNA-Seq technologies. It has been reported that the use of nitroaromatic compounds as anti-infective drugs (chloramphenicol, PA-824, metronidazole, nitrofurantoin, etc.) are often prodrugs and their mode of action is involved in bacterial nitroreductases and/or oxidoreductases [54,55,56]. Our results revealed that the frequency of resistance (FOR) is low, less than 10−9 in S. aureus. This suggests that if activation is required for MZ-01 to inhibit bacterial growth by any enzymes, the enzyme is likely necessary for growth.
Preliminary SAR activity of several pairs of analogs (MZ-01 vs. MZ-02; MZ-03 vs. MZ-04; MZ-01 vs. MZ-07) provides some insights into medicinal chemistry options, which can be analyzed with in silico methods to design new analogs. Meanwhile, additional analogs can be purchased from molecular diversity vendors to augment the internal medicinal chemistry initiatives. These analogs will enable us to perform detailed structure-activity relationship studies in vivo.
Antibacterial drug discovery is extremely difficult because of poor cellular accumulation of compounds due to limited penetration and/or active efflux [57,58]. Although the availability of numerous bacterial genomes and advanced bioinformatics technologies provides powerful tools for identifying a variety of new drug targets, target-directed rational drug design has not been fruitful in antibacterial drug discovery [58]. With results from more than 20 years of study, researchers still have limited success in transforming novel lead compounds into drugs [57,58]. Through our pilot studies, we have demonstrated that MZ-01 is a promising compound that will require further studies to elucidate its mechanism of action and to conduct a detailed SAR analysis and synthesize analogs to further improve its antibacterial activity.
In conclusion, we identified that MZ-01 possesses good antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacterial pathogens, including MRSA. Our finding suggests that MZ-01 is a promising compound for the development of selective antibacterial agents for Gram-positive bacterial infections.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids, and Growth Media
S. aureus strains used in this study include MRSA isolates USA100 HA-MRSA NRS382, USA200 HA-MRSA NRS383, USA300 CA-MRSA NR384, USA400 CA-MRSA MW2, and 1371 (USA300), and methicillin-sensitive S. aureus MSSA isolate MSA553. USA300 (1371) and MSA553 isolates were kindly provided by Drs. Richard Goering and Patrick Schlievert, respectively. The S. aureus cells were cultured in Trypticase soy broth (TSB) at 37 °C with shaking. S. pyogenes 90-226, S. pnuemoniae N1387, and E. faecalis V583 strains were kindly provided by Drs. Paul Cleary and Gary Dunny. M. abscessus (ATCC 19977) and A. baumannii (ATCC 19606) were kindly provided by Dr. Michio Kurosu. E. coli (ATCC25922), K. pneumonia (ATCC13883), and P. aeruginosa (ATCC 27853) were kindly provided by Dr. Christine Salomon. E. coli MG1655 wild type and acrAB knockout mutant strains were kindly provided by Dr. Vincent Tam.
4.2. Antibiotics and Chemical Compounds
Antibiotics, including amoxicillin, chloramphenicol, erythromycin, and vancomycin, were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. MZ-01, MZ-02, MZ-03, MZ-04, MZ-05, MZ-06, and MZ-07 compounds were from Dr. Noland’s laboratory. These compounds were synthesized as previously described [45,46].
4.3. Eukaryotic Cell Culture
Vero monkey kidney epithelial cells (ATCC CCL-81) were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Invitrogen, CA, USA). Cultures of Vero cells were maintained in a medium containing penicillin (5 µg/mL) and streptomycin (100 µg/mL) (Invitrogen, CA, USA). Assays were performed in RPMI 1640 medium with different doses of tested compounds. A549 cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 as described [43,44].
4.4. MIC and MBC Assays
S. aureus strains were grown in Trypticase soy broth (TSB) at 37 °C overnight and were diluted to ~105 CFU/mL in MHB for MIC assays with a 96-well microtiter format. Serial dilutions of the compounds were prepared in MHB broth in a final assay volume of 100 μL. Fifty microliters of 105 CFU/mL bacteria were added to the serially diluted antibiotics. The MIC was the concentration at which the antibiotic prevented turbidity in the well after incubation for 18 h at 37 °C, as described [59]. The MBC assay was conducted by dropping 10 μL of overnight culture (from the wells with 4×, 2×, and 1 × MIC in the 96-well plates of MIC assay) onto TSA. The MBC was the concentration at which the antibiotic killed the bacterial cells in the well after incubation for 18 h at 37 °C. The MIC and MBC assays were repeated at least three times, respectively.
4.5. Kinetic Time-Killing Assays
Kinetic time-killing assays for antimicrobial agents were conducted based on the CLSI guidelines. The MRSA WCUH29 strain was grown into early and late exponential phase, respectively, in MHB at 37 °C with shaking (225 rpm) and exposed to different concentrations of antibacterial agents. The bacterial solution (50 μL) was collected from the culture at multiple time points and diluted in fresh TSB and plated onto TSA, and incubated overnight at 37 °C for viable CFU. The time-killing assay was repeated at least three times.
4.6. Cytotoxicity Assay with Vero and A549 Cells
We conducted cytotoxicity assays using two mammalian cell lines, Vero monkey kidney cells and A549 human lung cancer epithelial cells, in triplicate experiments as described [43]. The cells were incubated in tissue culture flasks at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere until a confluent monolayer was achieved. Briefly, all cells were grown in 96-well plates to 90% confluence. To test the cytotoxicity, monolayer cells were exposed to different doses of tested compounds and incubated at 37 °C with 5%CO2 for 24 h. At the end of the experiment, cell viability was determined using the CellTiter 96® Aqueous Non-Radioactive Cell Proliferation Assay (Promega, MI, USA) as per the manufacturer’s instructions. DMSO was used as a negative control. Each experiment was repeated at least three times, and all of the percentages of cell death related to control were calculated and statistically analyzed by Student’s t-test.
To determine the potential antibacterial activity of MZ-01 in vivo, we examined the efficacy of MZ-01 against MRSA in epithelial cells. The human epithelial A549 cells were infected with MRSA. The extracellular bacteria were killed with gentamicin/lysostaphin 1 h after infection, as described [44]. Then, the infected cells were washed and collected at 6 or 24 h after exposure to 100 μg/mL MZ-01 or vancomycin in RPMI1640 with 10% FBS. The cells were lysed, diluted, and plated onto TSA plates for viable CFU.
4.7. Data Analysis
Independent samples were statistically analyzed using Student’s t-test with an alpha level ≤ 0.05 considered significant.
Author Contributions
J.Y. performed antibacterial assays, examined the cytotoxicity of the lead compounds, and contributed to writing the manuscript. C.B. prepared samples for biological testing and contributed to writing the manuscript. W.N. provided the compound library. T.J.J. contributed to editing the manuscript. Y.J. conceived and designed the project, wrote the manuscript, and directed the implementation of the whole cell screening and validating of compounds. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by grant AI078951 (to Y. Ji) from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease and by a grant from the EZID-Signature Research Program from the College of veterinary medicine at the University of Minnesota USDA General Agricultural Research fund (MIN-63-119 to Y. Ji).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the main text, figures, and tables.
Acknowledgments
We want to thank Courtney Aldrich and Peter Dosa for their helpful suggestions. We want to thank Michelle Ji and Nansea Ji for their suggestions and assistance in editing. The MRSA isolate MW2 was obtained through the Network of Antimicrobial Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus (NARSA) program supported under NIAID/NIH contract #HHSN272200700055C.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Vestergaard, M.; Frees, D.; Ingmer, H. Antibiotic Resistance and the MRSA Problem. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global Shortage of Innovative Antibiotics Fuels Emergency and Spread of Drug-Resistance; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Larru, B.; Gong, W.; Vendetti, N.; Sullivan, K.V.; Localio, R.; Zaoutis, T.E.; Gerber, J.S. Bloodstream Infections in Hospitalized Children: Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Susceptibilities. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2016, 35, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daum, R.S.; Spellberg, B. Progress Toward a Staphylococcus aureus Vaccine. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourtis, A.P.; Hatfield, K.; Baggs, J.; Mu, Y.; See, I.; Epson, E.; Nadle, J.; Kainer, M.A.; Dumyati, G.; Petit, S.; et al. Vital Signs: Epidemiology and Recent Trends in Methicillin-Resistant and in Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Infections—United States. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2019, 68, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mera, R.M.; Suaya, J.A.; Amrine-Madsen, H.; Hogea, C.S.; Miller, L.A.; Lu, E.P.; Sahm, D.F.; O’Hara, P.; Acosta, C.J. Increasing role of Staphylococcus aureus and community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in the United States: A 10-year trend of replacement and expansion. Microb. Drug Resist. 2011, 17, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidron, A.I.; Edwards, J.R.; Patel, J.; Horan, T.C.; Sievert, D.M.; Pollock, D.A.; Fridkin, S.K.; National Healthcare Safety Network Team; Participating National Healthcare Safety Network Facilities. NHSN annual update: Antimicrobial-resistant pathogens associated with healthcare-associated infections: Annual summary of data reported to the National Healthcare Safety Network at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2006–2007. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2008, 29, 996–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, L.; Mu, Y.; Belflower, R.; Scott, J.; Ray, S.; Dumyati, G.; Felsen, C.; Petit, S.; Yousey-Hindes, K.; Nadle, J.; et al. Risk Factors for Invasive Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection After Recent Discharge From an Acute-Care Hospitalization, 2011–2013. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yeh, A.J.; Cheung, G.Y.; Villaruz, A.E.; Tan, V.Y.; Joo, H.S.; Chatterjee, S.S.; Yu, Y.; Otto, M. Basis of virulence in a Panton-Valentine leukocidin-negative community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 211, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLeo, F.R.; Chambers, H.F. Reemergence of antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the genomics era. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2464–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrup, L.B.; Hansen, J.E.; Pedersen, K. Occurrence and Survival of Livestock-Associated MRSA in Pig Manure and on Agriculture Fields. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderhaeghen, W.; Hermans, K.; Haesebrouck, F.; Butaye, P. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) in Food Production Animals. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 606–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.C.; Pearson, N. The Emergence of Staphylococcus aureus ST398. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2010, 11, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köck, R.; Harlizius, J.; Bressan, N.; Laerberg, R.; Wieler, L.H.; Witte, W.; Deurenberg, R.H.; Voss, A.; Becker, K.; Friedrich, A.W. Prevalence and molecular characteristics of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) among pigs on German farms and import of livestock-related MRSA into hospitals. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 28, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crombé, F.; Willems, G.; Dispas, M.; Hallin, M.; Denis, O.; Suetens, C.; Gordts, B.; Struelens, M.; Butaye, P. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Among Pigs in Belgium. Microb. Drug Resist. 2012, 18, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirolo, M.; Visaggio, D.; Gioffrè, A.; Artuso, I.; Gherardi, M.; Pavia, G.; Samele, P.; Ciambrone, L.; Di Natale, R.; Spatari, G.; et al. Unidirectional animal-to-human transmission of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST398 in pig farming; evidence from a surveillance study in southern Italy. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynaga, E.; Navarro, M.; Vilamala, A.; Roure, P.; Quintana, M.; Garcia-Nuñez, M.; Figueras, R.; Torres, C.; Lucchetti, G.; Sabrià, M. Prevalence of colonization by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST398 in pigs and pig farm workers in an area of Catalonia, Spain. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dressler, A.E.; Scheibel, R.P.; Wardyn, S.; Harper, A.L.; Hanson, B.M.; Kroeger, J.S.; Diekema, D.J.; Bender, J.B.; Gray, G.C.; Smith, T.C. Prevalence, antibiotic resistance and molecular characterization of Staphylococcus aureus in pigs at agricultural fairs in the USA. Vet. Rec. 2012, 170, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.E.; Ronco, T.; Stegger, M.; Sieber, R.; Fertner, M.E.; Martin, H.L.; Farre, M.; Toft, N.; Larsen, A.R.; Pedersen, K. MRSA CC398 in dairy cattle and veal calf farms indicates spillover from pig production. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardyn, S.E.; Forshey, B.M.; Farina, S.A.; Kates, A.E.; Nair, R.; Quick, M.K.; Wu, J.Y.; Hanson, B.M.; O’Malley, S.M.; Shows, H.W.; et al. Swine Farming Is a Risk Factor for Infection With and High Prevalence of Carriage of Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Graells, C.; Antoine, J.; Larsen, J.; Catry, B.; Skov, R.; Denis, O. Livestock veterinarians at high risk of acquiring methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST398. Epidemiol. Infect. 2011, 140, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekkelenkamp, M.B.; Sekkat, M.; Carpaij, N.; Troelstra, A.; Bonten, M.J. Endocarditis due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus originating from pigs. Ned. Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2006, 150, 2442–2447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rasigade, J.P.; Laurent, F.; Hubert, P.; Vandenesch, F.; Etienne, J. Lethal necrotizing pneumonia caused by an ST398 Staphylococcus aureus strain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, C.; Aspiroz, C.; Ezpeleta, A.I.; Gómez-Sanz, E.; Zarazaga, M.; Torres, C. Empyema caused by MRSA ST398 with atypical resistance profile, Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 138–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agersø, Y.; Hasman, H.; Cavaco, L.M.; Pedersen, K.; Aarestrup, F.M. Study of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Danish pigs at slaughter and in imported retail meat reveals a novel MRSA type in slaughter pigs. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 157, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fessler, A.T.; Kadlec, K.; Hassel, M.; Hauschild, T.; Eidam, C.; Ehricht, R.; Monecke, S.; Schwarz, S. Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Food and Food Products of Poultry Origin in Germany. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7151–7157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weese, J.S.; Reid-Smith, R.; Rousseau, J.; Avery, B. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) contamination of retail pork. Can. Vet. J. 2010, 51, 749–752. [Google Scholar]
- O’Brien, A.M.; Hanson, B.M.; Farina, S.A.; Wu, J.Y.; Simmering, J.E.; Wardyn, S.E.; Forshey, B.M.; Kulick, M.E.; Wallinga, D.B.; Smith, T.C. MRSA in Conventional and Alternative Retail Pork Products. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graveland, H.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Bergs, K.; Heesterbeek, H.; Heederik, D. Persistence of livestock associated MRSA CC398 in humans is dependent on intensity of animal contact. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cleef, B.A.; Graveland, H.; Haenen, A.P.; van de Giessen, A.W.; Heederik, D.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Kluytmans, J.A. Persistence of livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in field workers after short-term occupational exposure to pigs and veal calves. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 1030–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkade, E.; van Benthem, B.; den Bergh, M.K.; van Cleef, B.; van Rijen, M.; Bosch, T.; Kluytmans, J. Dynamics and determinants of Staphylococcus aureus carriage in livestock veterinarians: A prospective cohort study. J. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, e11–e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Frana, T.S.; Beahm, A.R.; Hanson, B.M.; Kinyon, J.M.; Layman, L.L.; Karriker, L.A.; Ramirez, A.; Smith, T.C. Isolation and characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from pork farms and visiting veterinary students. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalmers, S.J.; Wylam, M.E. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection and Treatment Options. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2069, 229–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, C.P.V.; Mejias, A.; Leber, A.; Sanchez, P.J. A decade of antimicrobial resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: A single center experience. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, S.; Mizutani, T.; Hiramatsu, K.; Kikuchi, K. Rapid Acquisition of Linezolid Resistance in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Role of Hypermutation and Homologous Recombination. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decousser, J.W.; Desroches, M.; Bourgeois-Nicolaos, N.; Potier, J.; Jehl, F.; Lina, G.; Cattoir, V.; Vandenesh, F.; Doucet-Populaire, F.; Microbs Study Group. Susceptibility trends including emergence of linezolid resistance among coagulase-negative staphylococci and meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from invasive infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 46, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrel, M.; Perencevich, E.N.; David, M.Z. USA300 Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus, United States, 2000–2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1973–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiest, D.J. Treatment failure resulting from resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to daptomycin. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 655–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiya, H.; Haruki, Y.; Uchida, T.; Wada, T.; Shiota, S.; Ishida, T.; Ogawa, H.; Murase, T.; Otsuka, F. Emergence of Daptomycin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus during Treatment. Intern. Med. 2016, 55, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, A.; Conrad, M.; Haselbeck, R.J.; Kedar, G.C.; Brown-Driver, V.; Finn, J.; Silverman, J.A. Regulation of mprF by antisense RNA restores daptomycin susceptibility to daptomycin-resistant isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spellberg, B.; Shlae, D. Prioritized current unmet needs for antibacterial therapies. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 96, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattoir, V.; Felden, B. Future Antibacterial Strategies: From Basic Concepts to Clinical Challenges. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Ji, Y. Involvement of alpha5beta1-integrin and TNF-alpha in Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin-induced death of epithelial cells. Cell. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1809–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, N.; Yang, J.; Ji, Y. Determining Impact of Growth Phases on Capacity of Staphylococcus aureus to Adhere to and Invade Host Cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2069, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noland, W.E.; Rush, K.R. Nitration of Indoles. V. Nitration of Electronegatively Substituted Indoles. Synthesis of the Four bz,3-Dinitroindoles. J. Org. Chem. 1966, 31, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noland, W.E.; Smith, L.R.; Rush, K.R. Nitration of Indoles. III. Polynitration of 2-Alkylindoles. J. Org. Chem. 1965, 30, 3457–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sá Alves, F.R.; Barreiro, E.J.; Fraga, C.A. From nature to drug discovery: The indole scaffold as ‘privileged structure’. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straus, J. The Nitroaromatic Group in Drug Design, Pharmacology and Toxicology. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1979, 18, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanska, J.Z.; Gralewska, R.; Starosciak, B.J.; Kazimierczuk, Z. Antimicrobial activity of substituted azoles and their nucleosides. Die Pharm. 1999, 54, 879–884. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, S.; Wyllie, S. Nitro drugs for the treatment of trypansomatid diseases: Past, present, and future prospects. Trends Parasitol. 2014, 30, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, D.D. Tolcapone: Review of its pharmacology and use as adjunctive therapy in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Interv. Aging 2009, 4, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorkin, E.M.; Clissold, S.P.; Brogden, R.N. Nifedipine. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic efficacy, in ischaemic heart disease, hypertension and related cardiovascular disorders. Drugs 1985, 30, 182–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattila, M.A.; Larni, H.M. Flunitrazepam: A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use. Drugs 1980, 20, 353–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisson, G.; Goodwin, A.; Raudonikiene, A.; Hughes, N.J.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Berg, D.E.; Hoffman, P.S. Enzymes associated with reductive activation and action of nitazoxanide, nitrofurans, and metronidazole in Helicobacter pylori. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2116–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haver, H.L.; Chua, A.; Ghode, P.; Lakshminarayana, S.B.; Singhal, A.; Mathema, B.; Wintjens, R.; Bifani, P. Mutations in genes for the F420 biosynthetic pathway and a nitroreductase enzyme are the primary resistance determinants in spontaneous in vitro-selected PA-824-resistant mutants of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5316–5323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crofts, T.S.; Sontha, P.; King, A.O.; Wang, B.; Biddy, B.A.; Zanolli, N.; Gaumnitz, J.; Dantas, G. Discovery and Characterization of a Nitroreductase Capable of Conferring Bacterial Resistance to Chloramphenicol. Cell Chem. Biol. 2019, 26, 559–570.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, L.L. Challenges of antibacterial discovery. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 71–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, D.J.; Gwynn, M.N.; Holmes, D.J.; Pompliano, D.L. Drugs for bad bugs: Confronting the challenges of antibacterial discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Fox, B.; Lonetto, M.L.; Etherton, M.R.; Payne, D.J.; Holmes, D.J.; Rosenberg, M.; Ji, Y. Identification of antimicrobial targets using a comprehensive genomic approach. Pharmocogenomics 2004, 5, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).