Mini-Review: Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli from Farm Animal-Associated Sources
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Prevalence of AR E. coli from Farm Animal-Associated Sources
2.1. AR E. coli from Farm Animals
2.1.1. Food Animals and Products
2.1.2. Animal Waste
2.2. AR E. coli in Waste Treatment Plants
| Resistance to Antibiotics | ARGs | Contents of AR E. coli | Sources | Location | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ampicillin and chloramphenicol | bla and cat | 3 × 104 CFU/mL | Municipal wastewater | Italy | [71] |
Ampicillin and trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole | NN | NN | Influent wastewater | Norway | [67] |
| β-lactams and tetracycline | NN | 1.25 × 105 CFU/mL in winter and 1.25 × 103 CFU/mL in summer | Upstream and downstream from the effluent discharge point | Poland | [68] |
| Aminoglycosides, sulfonamides, and quinolones | aac-Ib, aacC2, aadA1, blaCTX-M, oqxB, qnrS, sul1, sul2, dfrA7, tetA, and tetG | NN | Municipal wastewater treatment plants | China | [72] |
| Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole and tetracycline | blaCTX-M-1, blaTEM, tetA, and tetB | 1.49–2.11 × 105 CFU/ml | Urban wastewater treatment facility | America | [69] |
Ampicillin, nalidixic acid, tetracycline, cotrimoxazole, and streptomycin | Cit, Int1, Tn3, CTX-M1, IMP, and qnrS | NN | Municipal and animal wastewater | Slovakia | [70] |
Neomycin, florfenicol, norfloxacin, amoxicillin, colistin, chlortetracycline, and sulfamethoxazole | NN | 3.0 × 103–2.1 × 105 CFU/mL | Aerobic digestion and waste stabilization pond | Thailand | [63] |
2.3. AR E. coli in the Aquatic Environment
2.4. Modes of HGT in AR E. coli
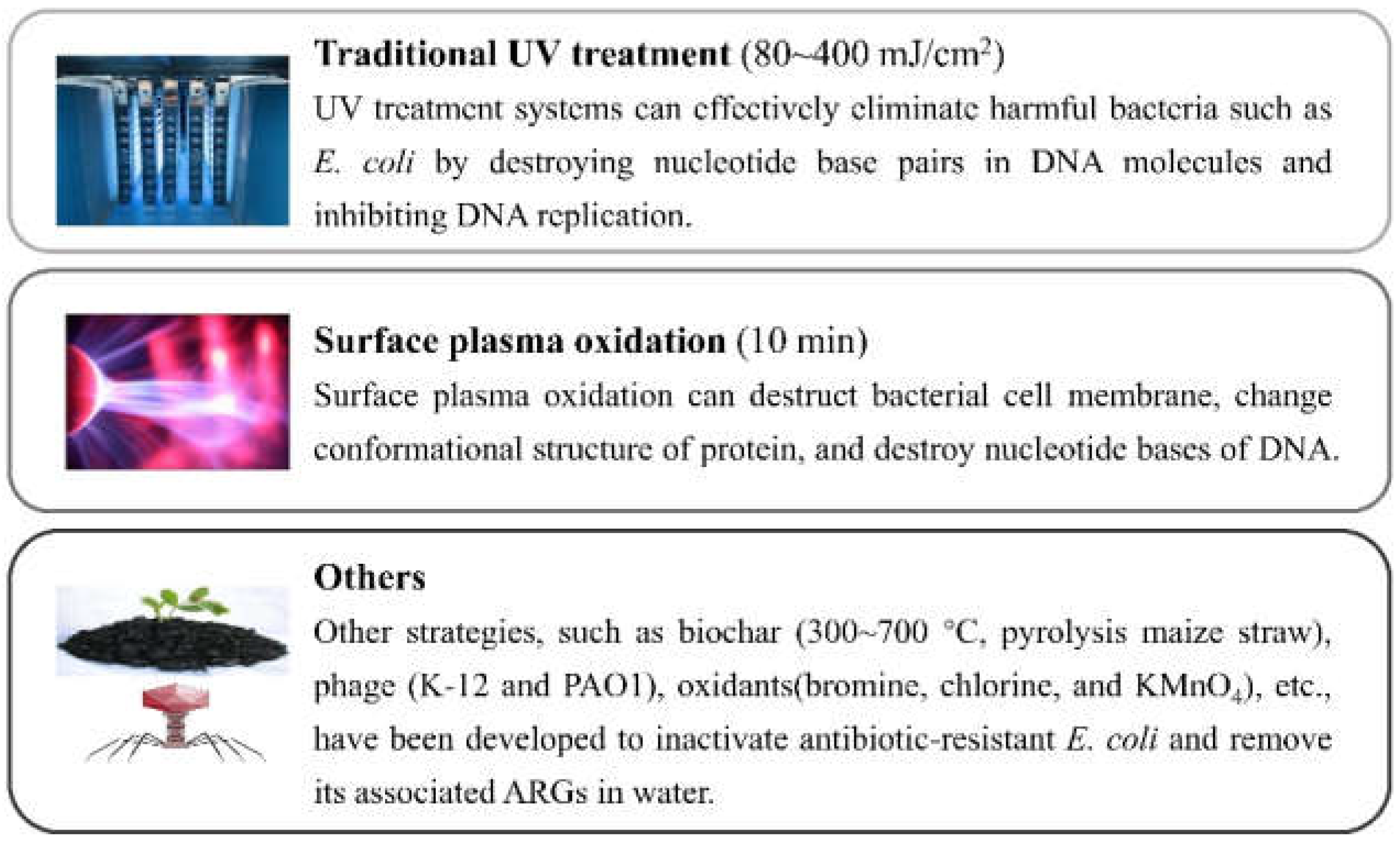
3. Disinfection of AR E. coli and Its ARGs
3.1. Traditional UV Treatment
3.2. Surface Plasma Oxidation
3.3. Others
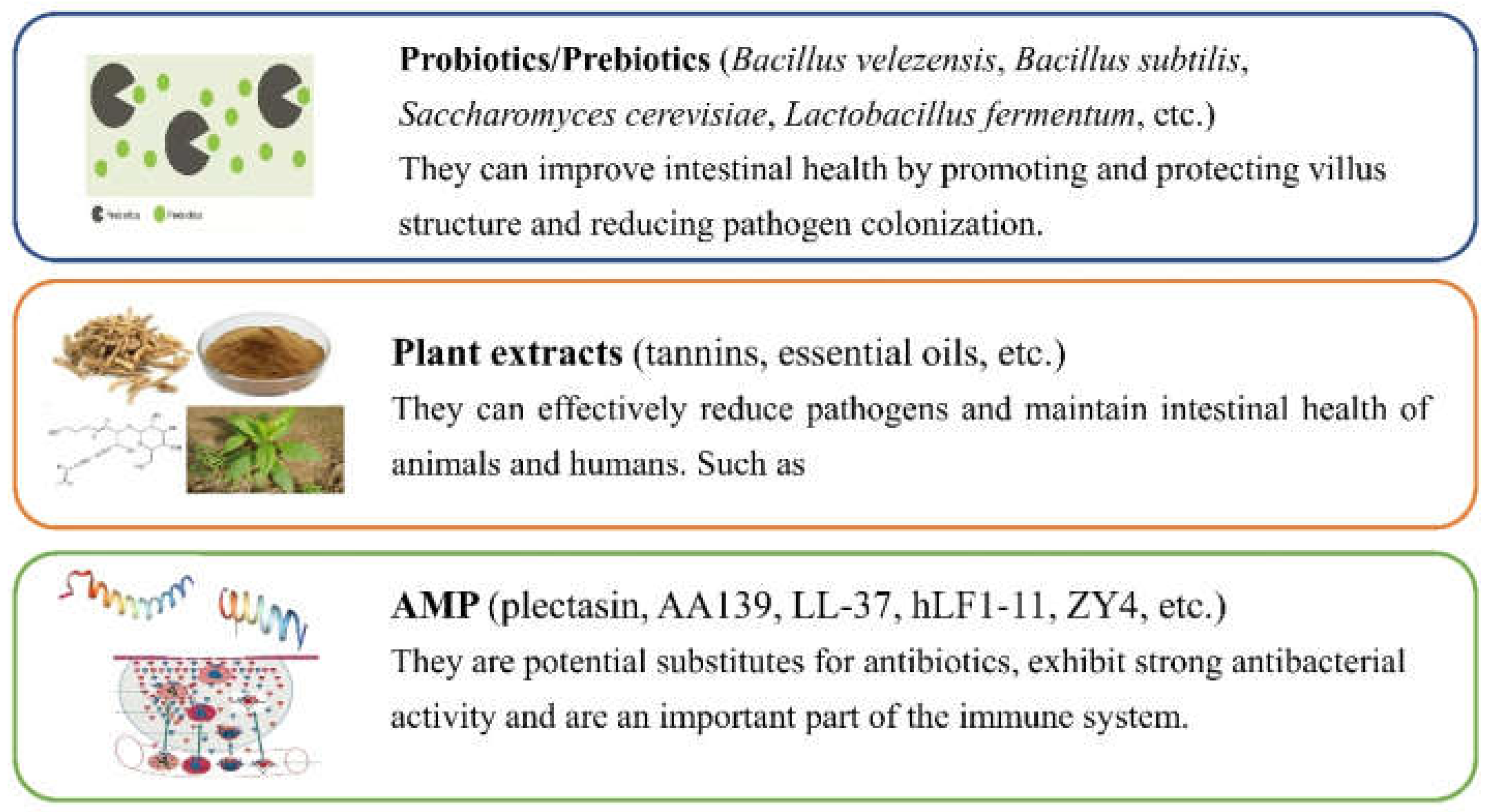
4. Alternatives to Antibiotics to Combat AR E. coli from the Farm Animal-Associated Sources
4.1. Probiotics/Prebiotics
4.2. Plant Extracts
4.3. AMPs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bernadether, T.R.; Douglas, R.C.; Gaspary, O.M.; Murugan, S.; Joram, B. Comparison of the prevalence of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli isolates from commercial-layer and free-range chickens in Arusha district, Tanzania. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 10, 1422–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, J.W.; Huang, H.H.; Chang, S.M.; Scaria, J.; Chiu, Y.L.; Chen, C.M.; Ko, W.C.; Wang, J.L. Antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli and sequence type 131 in fecal colonization in dogs in Taiwan. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.S.; Nayak, B.B.; Kumar, S.H. High prevalence of multiple antibiotic-resistant, extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli in fresh seafood sold in retail markets of Mumbai, India. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, S.; Kudva, V.; Shetty, K.; Shetty, V. Prevalence and characterization of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in ready-to-eat street foods. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewers, C.; Antao, E.M.; Diehl, I.; Philipp, H.C.; Wieler, L.H. Intestine and environment of the chicken as reservoirs for extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli strains with zoonotic potential. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutson, K. Nobody is talking about environmental monitoring. In Food Safety Lessons for Cannabis-Infused Edibles; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 111–137. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Y.; Jang, W.; Carolyn, J. A brief overview of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and its plasmid O157. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 20, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhao, W.; Shi, Z.D.; Gu, H.R.; Zhang, X.T.; Ji, X.; Zou, X.T.; Gong, J.S.; Yao, W. Accumulation of antibiotics and heavy metals in meat duck deep litter and their role in persistence of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli in different flocks on one duck farm. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorbara, M.T.; Dubin, K.; Littmann, E.R.; Moody, T.U.; Fontana, E.; Seok, R.; Leiner, I.M.; Taur, Y.; Peled, J.U.; van den Brink, M.R.M.; et al. Inhibiting antibiotic-resistant Enterobacteriaceae by microbiota-mediated intracellular acidification. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Bejar, B.; de Blas Martin, I.G.; Arevalo-Villena, M.; Perez, A.B. High prevalence of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli isolates from retail poultry products in Spain. Animals 2021, 11, 3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manishimwe, R.; Moncada, P.M.; Musanayire, V.; Shyaka, A.; Scott, H.M.; Loneragan, G.H. Antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli and Salmonella from the feces of food animals in the east province of Rwanda. Animals 2021, 11, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.J.; Kim, S.J.; Moon, D.C.; Mechesso, A.F.; Choi, J.H.; Kang, H.Y.; Boby, N.; Yoon, S.S.; Lim, S.K. Antimicrobial resistance in Escherichia coli isolates from healthy food animals in South Korea, 2010–2020. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, S.B.; Marshall, B. Antibacterial resistance worldwide: Causes, challenges and responses. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S122–S129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinthaler, F.F.; Posch, J.; Feierl, G.; Wust, G.; Haas, D.; Ruckenbauer, G.; Mascher, F.; Marth, E. Antibiotic resistance of E. coli in sewage and sludge. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1685–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hamelsveld, S.; Adewale, M.E.; Kurenbach, B.; Godsoe, W.; Harding, J.S.; Remus-Emsermann, M.N.P.; Heinemann, J.A. Prevalence of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from urban and agricultural streams in Canterbury, New Zealand. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fnz104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Administration, D. Standards for Growing, Harvesting, Packing, and Holding of Produce for Human Consumption; Deparment of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration: College Park, MD, USA, 2015.
- Van Driel, A.; Notermans, D.; Meima, A.; Mulder, M.; Donker, G.; Stobberingh, E.; Verbon, A. Antibiotic resistance of Escherichia coli isolated from uncomplicated UTI in general practice patients over a 10-year period. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 2151–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, D.K.; Taneja, N.K.; Dp, S.; Chakotiya, A.; Patel, P.; Taneja, P.; Sachdev, D.; Gupta, S.; Sanal, M.G. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of biofilm forming, antimicrobial resistant, pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from Indian dairy and meat products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 336, 108899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, D.C.; Livermore, D.M.; Papa, I.; Hall, L.M. Resistance among Escherichia coli to sulphonamides and other antimicrobials now little used in man. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 56, 962–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brynildsen, M.P.; Winkler, J.A.; Spina, C.S.; MacDonald, I.C.; Collins, J.J. Potentiating antibacterial activity by predictably enhancing endogenous microbial ROS production. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, S.; White, D.G.; Zhao, S.; McDermott, P.; Walker, R.; Meng, J. Characterization of multiple-antimicrobial-resistant Escherichia coli isolates from diseased chickens and swine in China. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 3483–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Feng, C.; Gao, M.; Wang, L. Prevalence of veterinary antibiotics and antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli in the surface water of a livestock production region in northern China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIver, K.S.; Amoako, D.G.; Abia, A.L.K.; Bester, L.A.; Chenia, H.Y.; Essack, S.Y. Molecular epidemiology of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli from farm-to-fork in intensive poultry production in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schink, A.K.; Kadlec, K.; Kaspar, H.; Mankertz, J.; Schwarz, S. Analysis of extended-spectrum-beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli isolates collected in the GERM-Vet monitoring programme. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messerer, M.; Fischer, W.; Schubert, S. Investigation of horizontal gene transfer of pathogenicity islands in Escherichia coli using next-generation sequencing. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, T.L.; Callaway, T.R.; Norman, K.N.; Scott, H.M.; Loneragan, G.H.; Ison, S.A.; Beier, R.C.; Harhay, D.M.; Norby, B.; Nisbet, D.J. Transferability of antimicrobial resistance from multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from cattle in the USA to E. coli and Salmonella Newport recipients. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2017, 11, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blahna, M.T.; Zalewski, C.A.; Reuer, J.; Kahlmeter, G.; Foxman, B.; Marrs, C.F. The role of horizontal gene transfer in the spread of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole resistance among uropathogenic Escherichia coli in Europe and Canada. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 57, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambrecht, E.; Van Coillie, E.; Boon, N.; Heyndrickx, M.; Van de Wiele, T. Transfer of antibiotic resistance plasmid from commensal E. coli towards human intestinal microbiota in the M-SHIME: Effect of E. coli dosis, human individual and antibiotic use. Life 2021, 11, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vines, J.; Cusco, A.; Napp, S.; Alvarez, J.; Saez-Llorente, J.L.; Rosas-Rodoreda, M.; Francino, O.; Migura-Garcia, L. Transmission of similar mcr-1 carrying plasmids among different Escherichia coli lineages isolated from livestock and the farmer. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Sun, M.; Zhao, Y.; Jiao, W.; Xia, B.; Liu, M.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, D.; Huang, R.; et al. Targeted inactivation of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a soil-lettuce system by combined polyvalent bacteriophage and biochar treatment. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Li, H.; Kang, Z.; Zhong, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, G.; Wang, T. Surface plasma induced elimination of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli and resistance genes: Antibiotic resistance, horizontal gene transfer, and mechanisms. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 275, 119185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Su, H.; Xu, W.; Hu, X.; Xu, Y.; Wen, G.; Cao, Y. Removal of antibiotic resistance genes and inactivation of antibiotic-resistant bacteria by oxidative treatments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kang, Z.; Jiang, E.; Song, R.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, G.; Wang, T.; Jia, H.; Zhu, L. Plasma induced efficient removal of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli and antibiotic resistance genes, and inhibition of gene transfer by conjugation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.M.; Xu, L.M.; Wang, X.C.; Zhuang, K.; Liu, Q.Q. Effects of ultraviolet disinfection on antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli from wastewater: Inactivation, antibiotic resistance profiles and antibiotic resistance genes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mandal, S.; Panda, A.K.; Murugan, C.; Xu, X.; Senthil Kumar, N.; Jin, F. Antimicrobial peptides: Novel source and biological function with a special focus on entomopathogenic nematode/bacterium symbiotic complex. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 555022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Ding, L.; Dong, Q.; Wang, X.; Wei, H.; Hu, C.; Ma, C.; Yan, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Degen, A.A. Effects of root extracts of three traditional Chinese herbs as dietary supplements on dry matter intake, average daily gain, rumen fermentation and ruminal microbiota in early weaned yak calves. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2021, 278, 115002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabelo-Ruiz, M.; Ariza-Romero, J.J.; Zurita-Gonzalez, M.J.; Martin-Platero, A.M.; Banos, A.; Maqueda, M.; Valdivia, E.; Martinez-Bueno, M.; Peralta-Sanchez, J.M. Allium-based phytobiotic enhances egg production in laying hens through microbial composition changes in ileum and cecum. Animals 2021, 11, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, S.Y.; Penuela-Sierra, L.M.; Ospina, M.A. Effects of oregano (Lippia origanoides) essential oil supplementation on the performance, egg quality, and intestinal morphometry of Isa Brown laying hens. Vet. World 2021, 14, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rima, M.; Rima, M.; Fajloun, Z.; Sabatier, J.M.; Bechinger, B.; Naas, T. Antimicrobial peptides: A potent alternative to antibiotics. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Ge, C.; Yao, H. Antimicrobial peptides from black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) as potential antimicrobial factors representing an alternative to antibiotics in livestock farming. Animals 2021, 11, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.A.; Lee, W.H.; Zhang, Y. Efficacy of OH-CATH30 and its analogs against drug-resistant bacteria In vitro and in mouse models. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 3309–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaïri, A.; Ferrières, L.; Latour-Lambert, P.; Beloin, C.; Tangy, F.; Ghigo, J.-M.; Hani, K. In vitro activities of dermaseptins K4 S4 and K4K20S4 against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa planktonic growth and biofilm formation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 2221–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechinger, B.; Juhl, D.W.; Glattard, E.; Aisenbrey, C. Revealing the mechanisms of synergistic action of two magainin antimicrobial peptide. Front. Med. Technol. 2020, 2, 615494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büyükkiraz, M.; Kesmen, Z. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs): A promising class of antimicrobial compounds. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 1573–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizman, M.; Avgustin, J.A.; Zdovc, I.; Golob, M.; Trkov, M.; Ciglenecki, U.J.; Biasizzo, M.; Kirbis, A. Antimicrobial resistance and molecular characterization of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases and other Escherichia coli isolated from food of animal origin and human intestinal isolates. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, G.S.; Waits, K.; Nordstrom, L.; Grande, H.; Weaver, B.; Papp, K.; Horwinski, J.; Koch, B.; Hungate, B.A.; Liu, C.M.; et al. Antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli from retail poultry meat with different antibiotic use claims. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcazar, J.L. How do bacteriophages promote antibiotic resistance in the environment? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azam, M.; Mohsin, M.; Sajjad Ur, R.; Saleemi, M.K. Virulence-associated genes and antimicrobial resistance among avian pathogenic Escherichia coli from colibacillosis affected broilers in Pakistan. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2019, 51, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornsey, M.; Betts, J.W.; Mehat, J.W.; Wareham, D.W.; van Vliet, A.H.M.; Woodward, M.J.; La Ragione, R.M. Characterization of a colistin-resistant avian pathogenic Escherichia coli ST69 isolate recovered from a broiler chicken in Germany. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.M.; El-Shall, N.A.; Khalil, D.S.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Swelum, A.A.; Mahmoud, A.H.; Ebaid, H.; Komany, A.; Sammour, R.H.; Sedeik, M.E. Incidence, pathotyping, and antibiotic susceptibility of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli among diseased broiler chicks. Pathogens 2020, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, H.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Zhu, G.; Xia, P.; Cui, L.; Li, J.; et al. ClbG in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli contributes to meningitis development in a mouse model. Toxins 2021, 13, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aklilu, E.; Harun, A.; Singh, K.K.B. Molecular characterization of blaNDM, blaOXA-48, mcr-1 and blaTEM-52 positive and concurrently carbapenem and colistin resistant and extended spectrum beta-lactamase producing Escherichia coli in chicken in Malaysia. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, T.; Le Thi, H.; Thanh, P.N.; Minh, D.T.N.; Hoang, O.N.; Hoai, P.H.; Yamaguchi, T.; Jinnai, M.; Do, P.N.; Van, C.D.; et al. Abundance of colistin-resistant Escherichia coli harbouring mcr-1 and extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing E. coli co-harbouring blaCTX-M-55 or -65 with blaTEM isolates from chicken meat in Vietnam. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, H.M.; Al Naiemi, N.; Elsohaby, I.; Mahmoud, A.F.A.; Salem, G.A.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C. Prevalence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacterales in retail sheep meat from Zagazig city, Egypt. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabala, R.F.; Usui, M.; Tamura, Y.; Abd-Elghany, S.M.; Sallam, K.I.; Elgazzar, M.M. Prevalence of colistin-resistant Escherichia coli harbouring mcr-1 in raw beef and ready-to-eat beef products in Egypt. Food Control 2021, 119, 107436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Khattak, S.; Ali, R.; Nawaz, N.; Ullah, K.; Khan, S.B.; Ali, M.; Patching, S.G.; Mustafa, M.Z. Prevalence and molecular characterization of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli O157:H7 from dairy milk in the Peshawar region of Pakistan. J. Food Saf. 2021, 41, e12941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Flaherty, E.; Borrego, C.M.; Balcazar, J.L.; Cummins, E. Human exposure assessment to antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli through drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.H.; Kwon, J.Y.; Shin, S.B.; Choi, W.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Ha, K.S. Antibiotic resistance in shellfish and major inland pollution sources in the drainage basin of Kamak Bay, Republic of Korea. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checcucci, A.; Trevisi, P.; Luise, D.; Modesto, M.; Blasioli, S.; Braschi, I.; Mattarelli, P. Exploring the animal waste resistome: The spread of antimicrobial resistance genes through the use of livestock manure. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, M.M.; Barraud, O.; Kerouredan, M.; Gaschet, M.; Stalder, T.; Oswald, E.; Dagot, C.; Ploy, M.C.; Brugere, H.; Bibbal, D. Comparison of the incidence of pathogenic and antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli strains in adult cattle and veal calf slaughterhouse effluents highlighted different risks for public health. Water Res. 2016, 88, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, T.L.B.; Schmidt, S. Assessment of three indigenous South African herbivores as potential reservoirs and vectors of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2017, 63, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.U.; Zhang, H.; Huang, S.; Iqbal, M.K.; Mehmood, K.; Luo, H.; Li, J. Characteristics of integrons and associated gene cassettes in antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from free-ranging food animals in China. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 1902–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandee, S.; Chan, R.; Chiemchaisri, W.; Chiemchaisri, C. Alteration of antibiotic-resistant phenotypes and minimal inhibitory concentration of Escherichia coli in pig farming: Comparison between closed and open farming systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juraschek, K.; Deneke, C.; Schmoger, S.; Grobbel, M.; Malorny, B.; Kasbohrer, A.; Schwarz, S.; Meemken, D.; Hammerl, J.A. Phenotypic and genotypic properties of fluoroquinolone-resistant, qnr-carrying Escherichia coli isolated from the German food chain in 2017. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Hiroki, H.; Xie, H.; Nishiyama, M.; Sakamoto, S.H.; Uemura, R.; Nukazawa, K.; Ogura, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Kobayashi, I. Antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from dairy cows and their surrounding environment on a livestock farm practicing prudent antimicrobial use. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2022, 240, 113930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, D.; Wallace, R.M.; Rwego, I.B.; Gillespie, T.R.; Chapman, C.A.; Singer, R.S.; Goldberg, T.L. Antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli and class 1 integrons in humans, domestic animals, and wild primates in rural Uganda. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01632-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwermer, C.U.; Krzeminski, P.; Wennberg, A.C.; Vogelsang, C.; Uhl, W. Removal of antibiotic resistant E. coli in two Norwegian wastewater treatment plants and by nano- and ultra-filtration processes. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaźmierczak, B.; Osińska, A.; Korzeniewska, E.; Harnisz, M.; Niestępski, S.; Jachimowicz, P.; Jadwiszczak, P.; Kutyłowska, M.; Miller, U. The occurrence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, including Escherichia coli, in municipal wastewater and river water. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 100, 00061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandon, B.; Jennifer, S.; Rachelle, B.; Caitlin, C.; Elizabeth, L.; Munoz-Price, L.S.; Krassimira, R.H.; Troy, S. Antibiotic resistance patterns of Escherichia coli isolates from the clinic through the wastewater pathway. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2021, 238, 113863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregova, G.; Kmet, V.; Szaboova, T. New insight on antibiotic resistance and virulence of Escherichia coli from municipal and animal wastewater. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanotto, C.; Bissa, M.; Illiano, E.; Mezzanotte, V.; Marazzi, F.; Turolla, A.; Antonelli, M.; De Giuli Morghen, C.; Radaelli, A. Identification of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Chemosphere 2016, 164, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Tian, T.; Yang, Q.; Riaz, L. Transfer potentials of antibiotic resistance genes in Escherichia spp. strains from different sources. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerlin, H.N.; Pola, C.C.; McLamore, E.S.; Gentry, T.; Karthikeyan, R.; Gomes, C.L. Prevalence of Escherichia coli and antibiotic-resistant bacteria during fresh produce production (romaine lettuce) using municipal wastewater effluents. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 660047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bong, C.W.; Low, K.Y.; Chai, L.C.; Lee, C.W. Prevalence and diversity of antibiotic resistant Escherichia coli from anthropogenic-impacted larut river. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 794513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, S.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Y. Research progress on distribution, migration, transformation of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in aquatic environment. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 1195–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamelin, K.; Bruant, G.; El-Shaarawi, A.; Hill, S.; Edge, T.A.; Fairbrother, J.; Harel, J.; Maynard, C.; Masson, L.; Brousseau, R. Occurrence of virulence and antimicrobial resistance genes in Escherichia coli isolates from different aquatic ecosystems within the St. Clair River and Detroit River areas. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2007, 73, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laroche, E.; Petit, F.; Fournier, M.; Pawlak, B. Transport of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli in a public rural karst water supply. J. Hydrol. 2010, 392, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jia, A.; Wan, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, K.; Peng, H.; Dong, Z.; Hu, J. Occurrences of three classes of antibiotics in a natural river basin: Association with antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 14317–14325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malema, M.S.; Abia, A.L.K.; Tandlich, R.; Zuma, B.; Mwenge Kahinda, J.M.; Ubomba-Jaswa, E. Antibiotic-resistant pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from rooftop rainwater-harvesting tanks in the eastern cape, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhr, A.E.; Gohar, M.K.; Atta, A.H. Impact of some ecological factors on fecal contamination of drinking water by diarrheagenic antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli in Zagazig city, Egypt. Int. J. Microbiol. 2016, 2016, 6240703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Hodgers, L.; Masters, N.; Sidhu, J.P.; Katouli, M.; Toze, S. Occurrence of intestinal and extraintestinal virulence genes in Escherichia coli isolates from rainwater tanks in Southeast Queensland, Australia. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7394–7400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Shuai, X.; Lin, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Chen, H. Prevalence of multi-resistant plasmids in hospital inhalable particulate matter (PM) and its impact on horizontal gene transfer. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 270, 116296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, J.; Qiu, Z.; Jin, M.; Shen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Li, J.W. Horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in a membrane bioreactor. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 167, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Thomsen, L.E.; Olsen, J.E. Antimicrobial-induced horizontal transfer of antimicrobial resistance genes in bacteria: A mini-review. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinayamohan, P.; Pellissery, A.; Venkitanarayanan, K. Role of horizontal gene transfer in the dissemination of antimicrobial resistance in food animal production. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 47, 100882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loayza, F.; Graham, J.P.; Trueba, G. Factors obscuring the role of E. coli from domestic animals in the global antimicrobial resistance crisis: An evidence-based review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Abbas, M.; Rehman, M.U.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Gong, S.; Yang, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, M.; Cheng, A. Dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) via integrons in Escherichia coli: A risk to human health. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Walsh, T.; Yi, L.; Zhang, R.; Spencer, J.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.; Dong, B.; Huang, X.; et al. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: A microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, D.P.; Hillman, K.; Fenlon, D.R.; Low, J.C. Transfer of antibiotic resistance between commensal and pathogenic members of the Enterobacteriaceae under ileal conditions. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 95, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Su, B.; Chen, R.; Lin, J.; Lin, Z.; Wang, D.; Yu, Y. A study on the role that quorum sensing play in antibiotic-resistant plasmid conjugative transfer in Escherichia coli. Ecotoxicology 2018, 27, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiltunen, T.; Virta, M.; Laine, A.L. Antibiotic resistance in the wild: An eco-evolutionary perspective. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, J.; Slawson, R. Potential repair of Escherichia coli DNA following exposure to UV radiation from both medium- and low-pressure UV sources used in drinking water treatment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 3293–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, L.; Fiorentino, A.; Anselmo, A. Advanced treatment of urban wastewater by UV radiation: Effect on antibiotics and antibiotic-resistant E. coli strains. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Huang, J.J.; Xi, J.; Hu, H.; Zhu, Y. Effect of ultraviolet irradiation and chlorination on ampicillin-resistant Escherichia coli and its ampicillin resistance gene. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2016, 10, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Song, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, T.; Jia, H.; Zhu, L. Inhibited conjugative transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in antibiotic resistant bacteria by surface plasma. Water Res. 2021, 204, 117630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.R.; Cho, I.H.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Strategies to minimize antibiotic resistance. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 4274–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.R.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, L.W.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Educational effectiveness, target, and content for prudent antibiotic use. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 214021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchil, R.R.; Kohli, G.S.; Katekhaye, V.M.; Swami, O.C. Strategies to combat antimicrobial resistance. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, ME01–ME04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, H.M.; Huque, K.S.; Kamaruddin, K.M.; Beg, M. Global restriction of using antibiotic growth promoters and alternative strategies in poultry production. Sci. Prog. 2018, 101, 52–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenmakers, K. How China is getting its farmers to kick their antibiotics habit. Nature 2020, 586, S60–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, K.; Li, C.L.; Wang, J.; Qi, G.H.; Gao, J.; Zhang, H.J.; Wu, S.G. Effects of dietary supplementation with bacillus subtilis, as an alternative to antibiotics, on growth performance, serum immunity, and intestinal health in broiler chickens. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 786878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, R.; Keharia, H.; Bose, A.; Pandit, N.; Doshi, J.; Rao, S.V.R.; Paul, S.S.; Raju, M. Genome assisted probiotic characterization and application of Bacillus velezensis ZBG17 as an alternative to antibiotic growth promoters in broiler chickens. Genomics 2021, 113, 4061–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, R.M.; Hassan, F.U.; Saeed, M.; Rafeeq, M.; Zahra, N.; Fraz, A.; Saeed, S.; Khan, M.A.; Mahgoub, H.A.M.; Farag, M.R.; et al. Role of yeast and yeast-derived products as feed additives in broiler nutrition. Anim. Biotechnol. 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Anno, M.; Reggi, S.; Caprarulo, V.; Hejna, M.; Sgoifo Rossi, C.A.; Callegari, M.L.; Baldi, A.; Rossi, L. Evaluation of tannin extracts, leonardite and tributyrin supplementation on diarrhoea incidence and gut microbiota of weaned piglets. Animals 2021, 11, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakheel, M.M.; Alkandari, F.A.H.; Mueller-Harvey, I.; Woodward, M.J.; Rymer, C. Antimicrobial in vitro activities of condensed tannin extracts on avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oussalah, M.; Caillet, S.; Saucier, L.; Lacroix, M. Inhibitory eVects of selected plant essential oils on the growth of four pathogenic bacteria: E. coli O157:H7, Salmonella typhimurium, Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes. Food Control 2007, 18, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd, E.; Ismail, M. Tackling experimental colisepticaemia in broiler chickens using phytobiotic essential oils and antibiotic alone or in combination. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2014, 15, 110–115. [Google Scholar]
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Saad, A.M.; Salem, H.M.; Ashry, N.M.; Abo Ghanima, M.M.; Shukry, M.; Swelum, A.A.; Taha, A.E.; El-Tahan, A.M.; et al. Essential oils and their nanoemulsions as green alternatives to antibiotics in poultry nutrition: A comprehensive review. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Mandal, G.P.; Patra, A.K.; Kumar, P.; Samanta, I.; Pradhan, S.; Samanta, A.K. Different essential oils in diets of broiler chickens: 2. Gut microbes and morphology, immune response, and some blood profile and antioxidant enzymes. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2018, 236, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nibbering, P.H.; Ravensbergen, E.; Welling, M.M.; van Berkel, L.A.; van Berkel, P.H.; Pauwels, E.K.; Nuijens, J.H. Human lactoferrin and peptides derived from its N terminus are highly effective against infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mygind, P.H.; Fischer, R.L.; Schnorr, K.M.; Hansen, M.T.; Sonksen, C.P.; Ludvigsen, S.; Raventos, D.; Buskov, S.; Christensen, B.; De Maria, L.; et al. Plectasin is a peptide antibiotic with therapeutic potential from a saprophytic fungus. Nature 2005, 437, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwangi, J.; Yin, Y.; Wang, G.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lai, R. The antimicrobial peptide ZY4 combats multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, A.G.; Huang, J.X.; Neve, S.; Zuegg, J.; Edwards, I.A.; Cain, A.K.; Boinett, C.J.; Barquist, L.; Lundberg, C.V.; Steen, J.; et al. An amphipathic peptide with antibiotic activity against multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, J.; Liu, G.; Ke, C.; Fan, W.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Dixon, W.; Song, M.; Cao, Y.; Xiao, H. Inhibitory effects of a novel antimicrobial peptide from kefir against Escherichia coli. Food Control 2016, 65, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Santos, A.C.; Novais, C.; Peixe, L.; Freitas, A.R. Enterococcus spp. as a producer and target of bacteriocins: A double-edged sword in the antimicrobial resistance crisis context. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prada-Prada, S.; Flórez-Castillo, J.; Farfán-García, A.; Guzmán, F.; Hernández-Peñaranda, I. Antimicrobial activity of Ib-M peptides against Escherichia coli O157: H7. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lin, C.; Sung, C.; Fang, J. Antibacterial activities of bacteriocins: Application in foods and pharmaceuticals. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.Y.; Graca, T.; Avillan, J.J.; Zhao, Z.; Call, D.R. Microcin PDI inhibits antibiotic-resistant strains of Escherichia coli and shigella through a mechanism of membrane disruption and protection by homotrimer self-immunity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e00371-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divyashree, M.; Mani, M.K.; Reddy, D.; Kumavath, R.; Ghosh, P.; Azevedo, V.; Barh, D. Clinical applications of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs): Where do we stand now? Protein Pept. Lett. 2020, 27, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Yan, Z.B.; Meng, Y.M.; Hong, X.Y.; Shao, G.; Ma, J.J.; Cheng, X.R.; Liu, J.; Kang, J.; Fu, C.Y. Antimicrobial peptides: Mechanism of action, activity and clinical potential. Mil. Med. Res. 2021, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sources | Resistance to Antibiotics | ARGs | Location | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eggs | Florophenicol | NN | Slovenia | [45] |
| Turkey | ampicillin, ampicillin–sulbactam, cefazolin, and tetracycline | uidA | America | [46] |
| Broiler chicken | Colistin, ampicillin, tetracycline, and chloramphenicol | strA, strB, and blaTEM-135 | Germany | [49] |
| Fresh seafood in retail markets | Cephalosporins cefotaxime, cefpodoxime, ceftazidime, imipenem, cefoxitin, and meropenem | blaCTX-M, blaSHV, blaTEM, blaOXA, blaNDM, and blaVIM | India | [3] |
| Raw beef | Colistin and cefotaxime | mcr-1 and ECTX-M-28 | Egypt | [55] |
| Ready-to-eat beef products | Colistin and cefotaxime | mcr-1 and blaTEM-116 | Egypt | [55] |
| Milk | Amoxicillin–clavulanic acid, ampicillin, ceftriaxone, kanamycin, streptomycin, trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole, and vancomycin | blaCTX-M, blaTEM-1, blaNDM-1, blaOXA-48, blaVIM, and blaSHV | Pakistan | [56] |
| Malaysian broiler chicken | Carbapenem and colistin | mcr-1, blaTEM-52, blaNDM, blaOXA-48, and blaIMP | Malaysia | [52] |
| Vietnam broiler chicken | Colistin | blaCTX-M, mcr-1, blaTEM, and blaCMY-2 | Vietnam | [53] |
| Retail mutton | Trimethoprim, sulfamethoxazole, aminoglycosides, quinolones, and nitrofurantoin | blaCTX-M, blaTEM, and blaSHV | Egypt | [54] |
| Sources | Resistance to Antibiotics | ARGs | Strategies | Location | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Veal calf | Tetracycline, ampicillin, sulfonamides, streptomycin, and trimethoprim | intI1 and intI2 | NN | French | [60] |
| South African herbivores | Gentamicin, tobramycin, ceftazidime, and aztreonam | NN | Antibiotics used in human medicine should be avoided in veterinary medicine | South Africa | [61] |
| Free-grazing food animals | Ampicillin, ceftriaxone, chloramphenicol, gentamicin, streptomycin, sulfonamide, tetracycline, etc. | dfrA, orfF, aadA, sul1, and qacEΔ1 | NN | China | [62] |
| Meat duck deep litter | Ceftiofur, enrofloxacin, ofloxacin, and gentamicin | NN | The deep litter should be treated with appropriate antibiotic resistant bacteria | China | [8] |
| Dog | Cefazolin and fluoroquinolone | blaSHV, blaTEM, blaOXA, and blaCTX-M | NN | Taiwan, China | [2] |
| Intensively produced poultry | Ampicillin, tetracycline, nalidixic acid, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and chloramphenicol | blaCTX-M, sul1, tetA, and tetB | NN | South Africa | [23] |
| Open pig farm | Chlortetracycline, tetracycline, tilmicosin, amoxicillin, and doxycycline | NN | Legislation to clarify the boundary between antibiotics for human use and antibiotics for veterinary use | Thailand | [63] |
| Deer and Pigs | Ciprofloxacin and nalidixic acid | qnrS and qnrB | NN | Germany | [64] |
| Cow farm | Tetracycline | tetA, tetB, and tetM | Veterinarian supervisor, administration history for all individuals, and the rearing environment is strictly managed | Japan | [65] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, C.; Kong, L.; Liao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wu, Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, X. Mini-Review: Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli from Farm Animal-Associated Sources. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1535. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111535
Xu C, Kong L, Liao Y, Tian Y, Wu Q, Liu H, Wang X. Mini-Review: Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli from Farm Animal-Associated Sources. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(11):1535. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111535
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Chunming, Lingqiang Kong, Yonghong Liao, Yuan Tian, Qi Wu, Haosi Liu, and Xiumin Wang. 2022. "Mini-Review: Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli from Farm Animal-Associated Sources" Antibiotics 11, no. 11: 1535. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111535
APA StyleXu, C., Kong, L., Liao, Y., Tian, Y., Wu, Q., Liu, H., & Wang, X. (2022). Mini-Review: Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli from Farm Animal-Associated Sources. Antibiotics, 11(11), 1535. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111535







