Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, a Pathogen of Increasing Relevance to Dermatologists: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
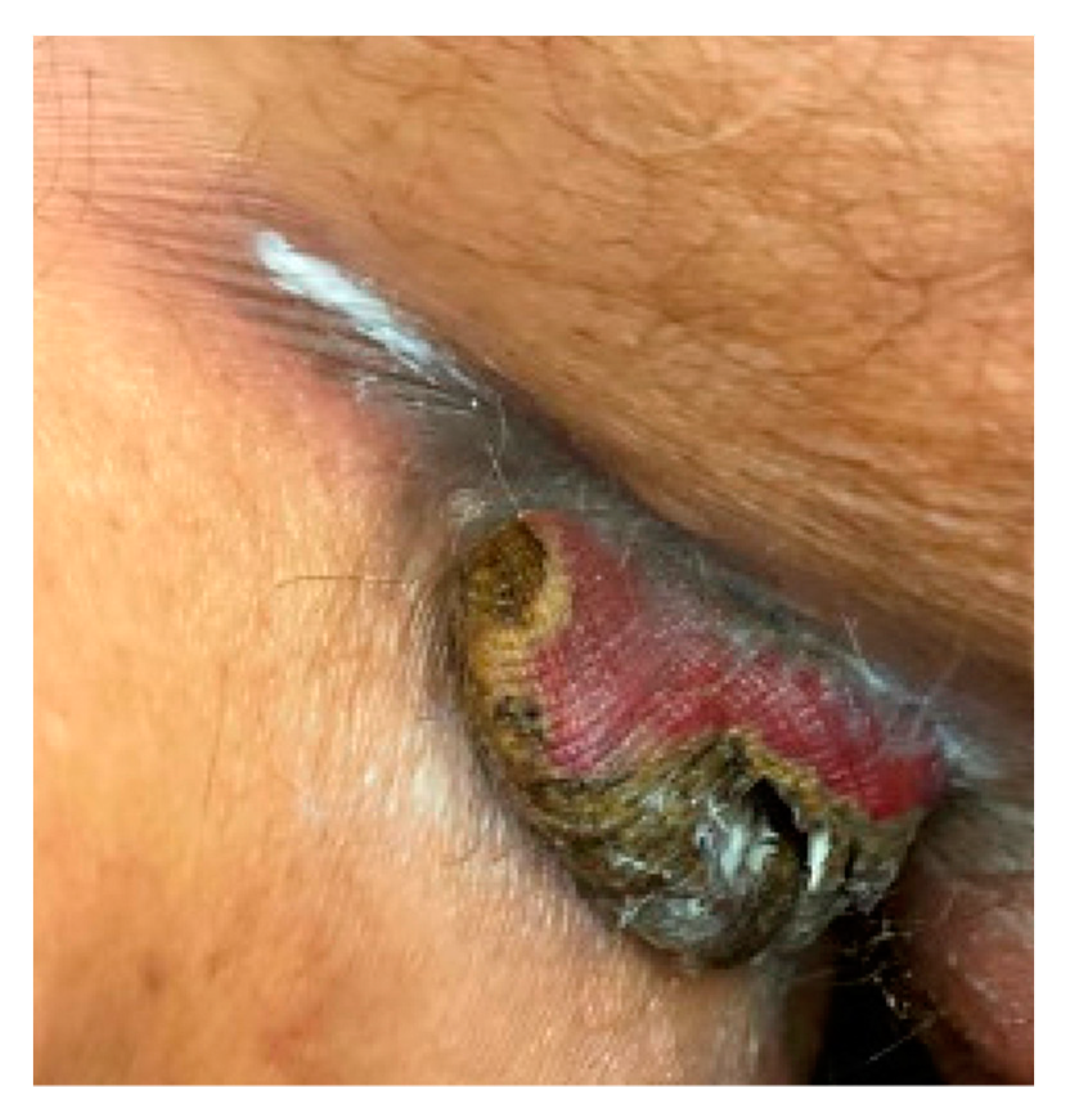
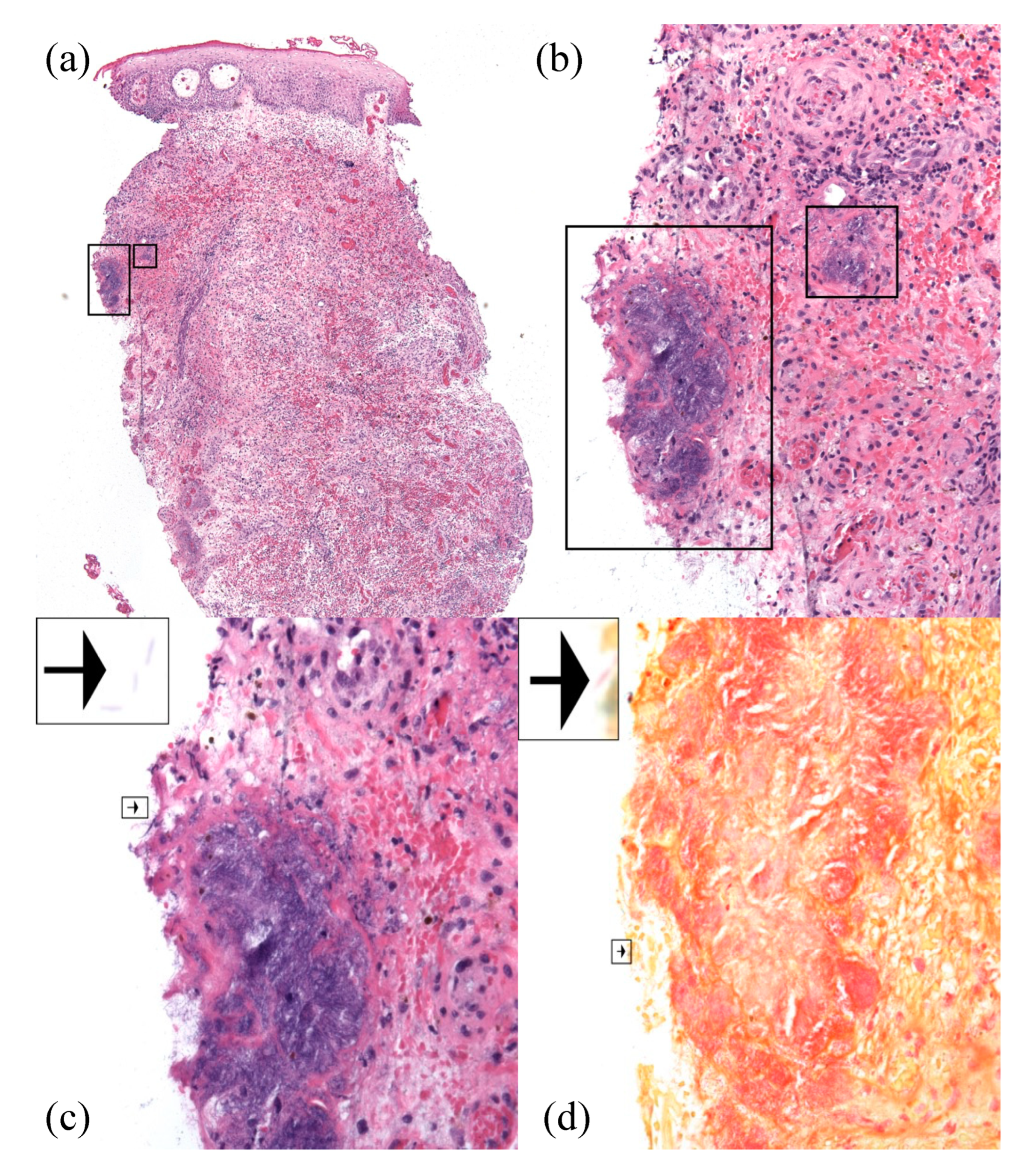
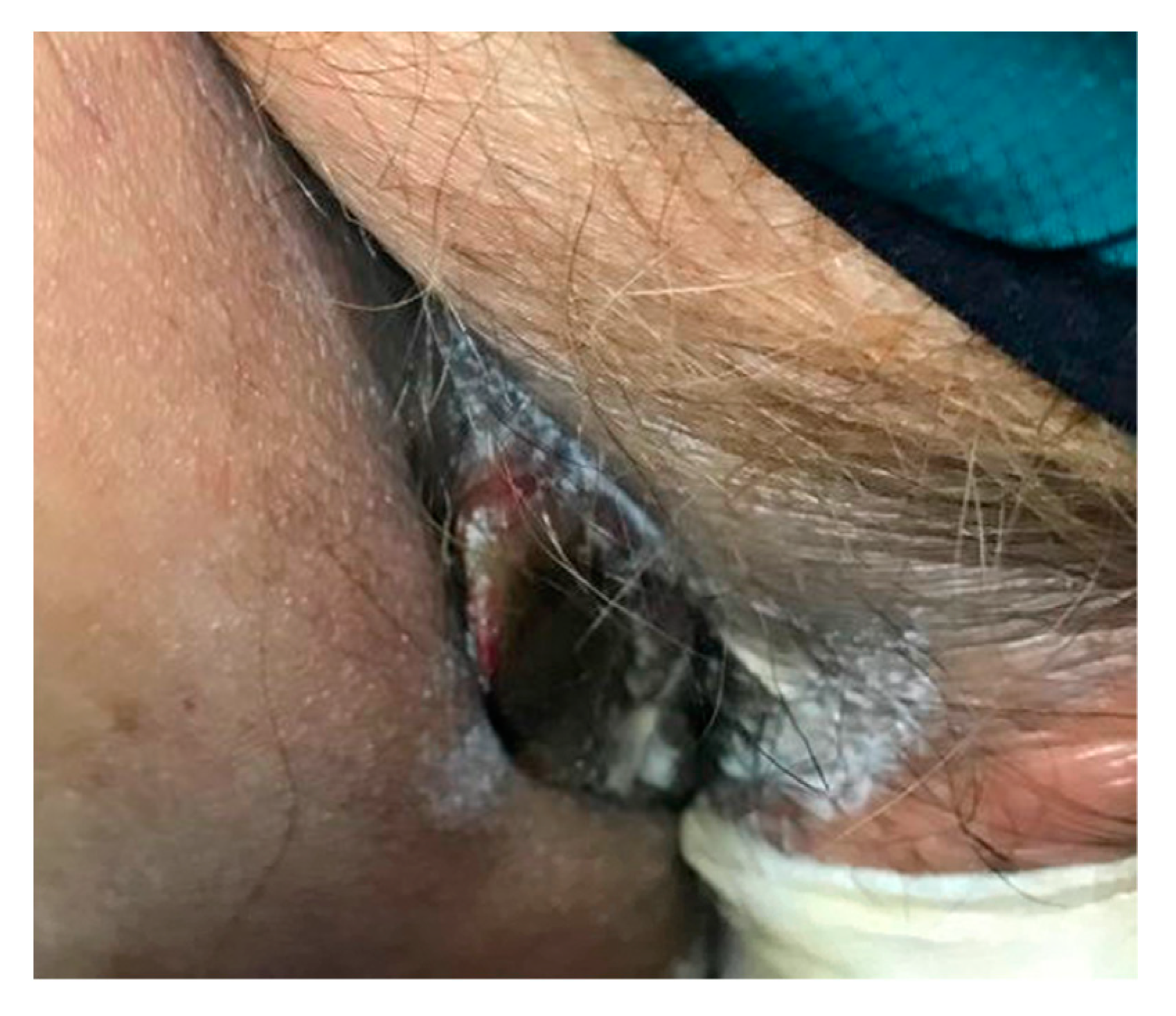
2. Case Report
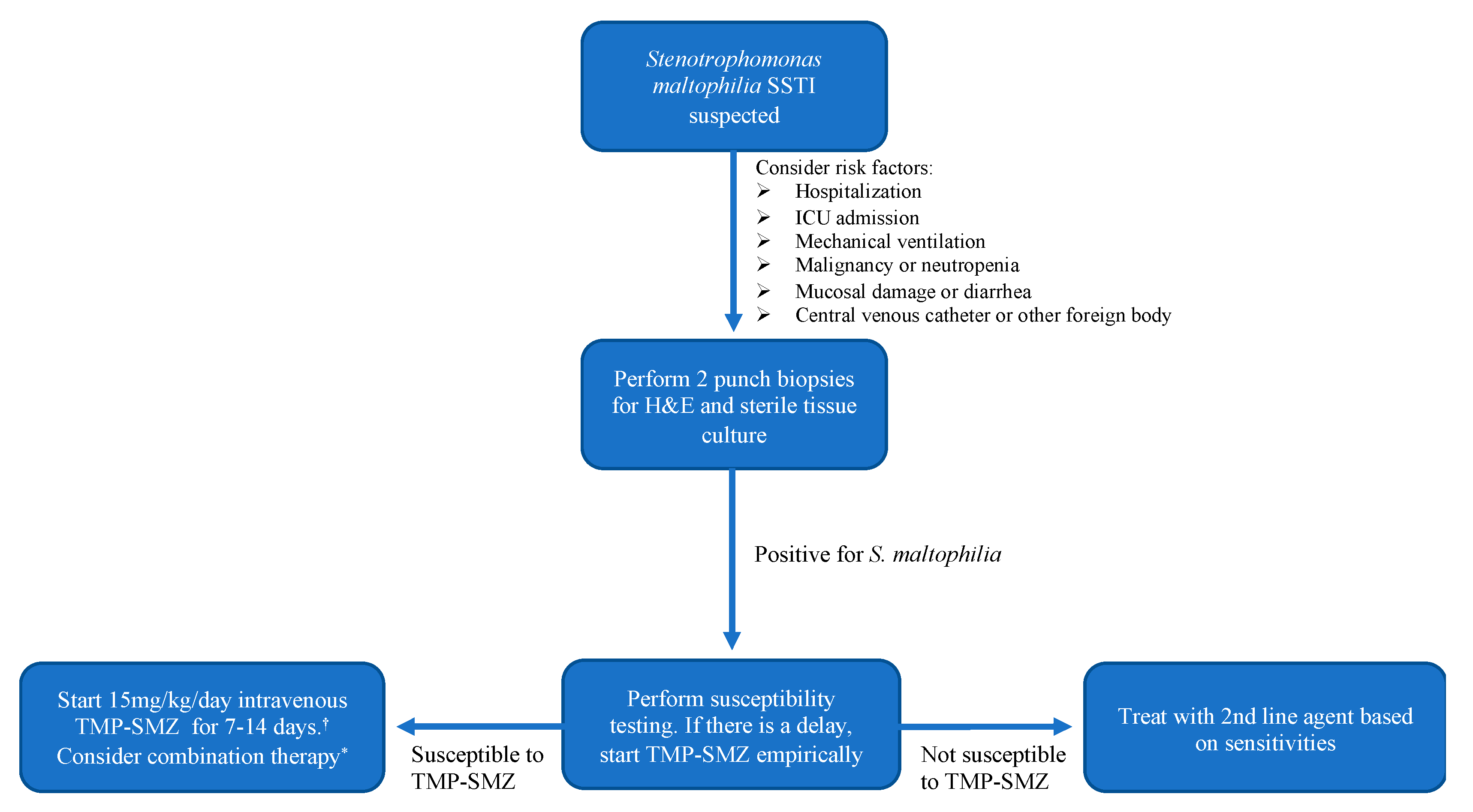
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Skin and soft tissue infection | SSTI |
| Intensive care unit | ICU |
| Hematoxylin and eosin stain | H&E |
| Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole | TMP-SMZ |
References
- Baumrin, E.; Piette, E.W.; Micheletti, R.G. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: An emerging multidrug-resistant opportunistic pathogen in the immunocompromised host. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr-2017-221053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senol, E. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: The significance and role as a nosocomial pathogen. J. Hosp. Infect. 2004, 57, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdar, A.; Rolston, K.V. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: Changing spectrum of a serious bacterial pathogen in patients with cancer. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 1602–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apisarnthanarak, A.; Fraser, V.J.; Dunne, W.M.; Little, J.R.; Hoppe-Bauer, J.; Mayfield, J.L.; Polish, L.B. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Intestinal Colonization in Hospitalized Oncology Patients with Diarrhea. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 37, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falagas, M.E.; Kastoris, A.C.; Vouloumanou, E.K.; Rafailidis, P.I.; Kapaskelis, A.M.; Dimopoulos, G. Attributable mortality of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infections: A systematic review of the literature. Future Microbiol. 2009, 4, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paez, J.I.; Tengan, F.M.; Barone, A.A.; Levin, A.S.; Costa, S.F. Factors associated with mortality in patients with bloodstream infection and pneumonia due to Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 27, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paez, J.I.G.; Costa, S.F. Risk factors associated with mortality of infections caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: A systematic review. J. Hosp. Infect. 2008, 70, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwa, A.L.; Low, J.G.; Lim, T.P.; Leow, P.C.; Kurup, A.; Tam, V.H. Independent predictors for mortality in patients with positive Stenotrophomonas maltophilia cultures. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2008, 37, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Samonis, G.; Karageorgopoulos, D.E.; Maraki, S.; Levis, P.; Dimopoulou, D.; Spernovasilis, N.A.; Kofteridis, D.P.; Falagas, M.E. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infections in a general hospital: Patient characteristics, antimicrobial susceptibility, and treatment outcome. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, S.C.; Mokaddas, E.M. The increase in carbapenem use and emergence of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia as an important nosocomial pathogen. J. Chemother 1999, 11, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elting, L.S.; Khardori, N.; Bodey, G.P.; Fainstein, V. Nosocomial infection caused by Xanthomonas maltophilia: A case-control study of predisposing factors. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 1990, 11, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbina, T.; Razazi, K.; Ourghanlian, C.; Woerther, P.L.; Chosidow, O.; Lepeule, R.; de Prost, N. Antibiotics in Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safdar, A.; Rodriguez, G.H.; Balakrishnan, M.; Tarrand, J.J.; Rolston, K.V. Changing trends in etiology of bacteremia in patients with cancer. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect Dis. 2006, 25, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adegoke, A.A.; Stenström, T.A.; Okoh, A.I. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia as an Emerging Ubiquitous Pathogen: Looking Beyond Contemporary Antibiotic Therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muder, R.R.; Harris, A.P.; Muller, S.; Edmond, M.; Chow, J.W.; Papadakis, K.; Wagener, M.W.; Bodey, G.P.; Steckelberg, J.M. Bacteremia due to Stenotrophomonas (Xanthomonas) maltophilia: A prospective, multicenter study of 91 episodes. Clin. Infect Dis. 1996, 22, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.H.; Chi, C.Y.; Chen, H.P.; Chen, T.L.; Lai, C.J.; Fung, C.P.; Yu, K.W.; Wong, W.W.; Liu, C.Y. Clinical characteristics and prognostic factors of patients with Stenotrophomonas maltophilia bacteremia. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2004, 37, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sader, H.S.; Jones, R.N. Antimicrobial susceptibility of uncommonly isolated non-enteric Gram-negative bacilli. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 25, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belzer, A.; Weiss, E.; Etaee, F.; Bunick, C.G.; Damsky, W.; Nelson, C.A. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, a Pathogen of Increasing Relevance to Dermatologists: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1398. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101398
Belzer A, Weiss E, Etaee F, Bunick CG, Damsky W, Nelson CA. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, a Pathogen of Increasing Relevance to Dermatologists: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(10):1398. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101398
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelzer, Annika, Emma Weiss, Farshid Etaee, Christopher G. Bunick, William Damsky, and Caroline A. Nelson. 2022. "Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, a Pathogen of Increasing Relevance to Dermatologists: A Case Report and Review of the Literature" Antibiotics 11, no. 10: 1398. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101398
APA StyleBelzer, A., Weiss, E., Etaee, F., Bunick, C. G., Damsky, W., & Nelson, C. A. (2022). Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, a Pathogen of Increasing Relevance to Dermatologists: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Antibiotics, 11(10), 1398. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101398






