The Impact of Patient-Reported Penicillin or Cephalosporin Allergy on the Occurrence of the Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Primary Knee and Hip Arthroplasty
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
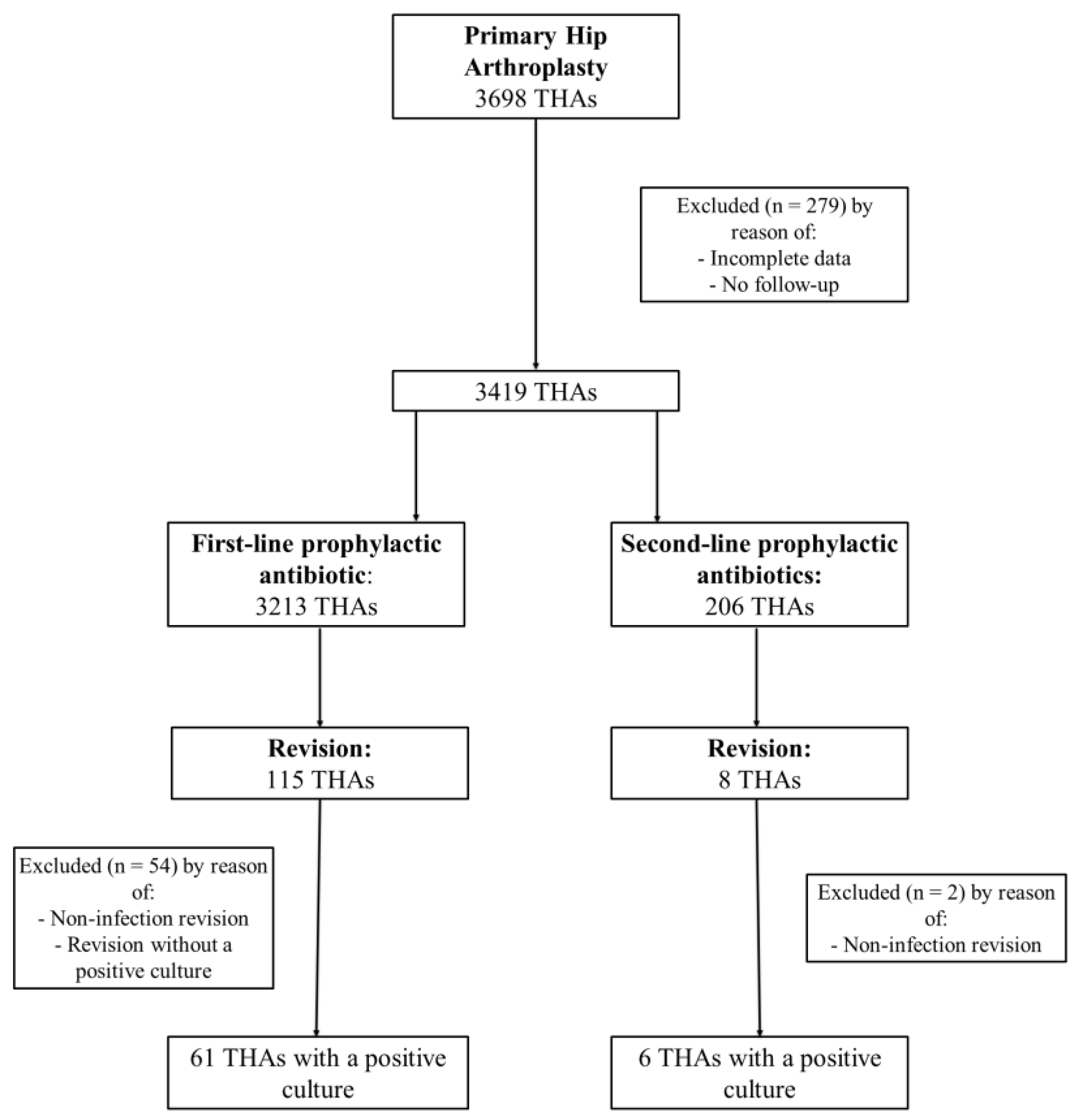
2.1. THA Group
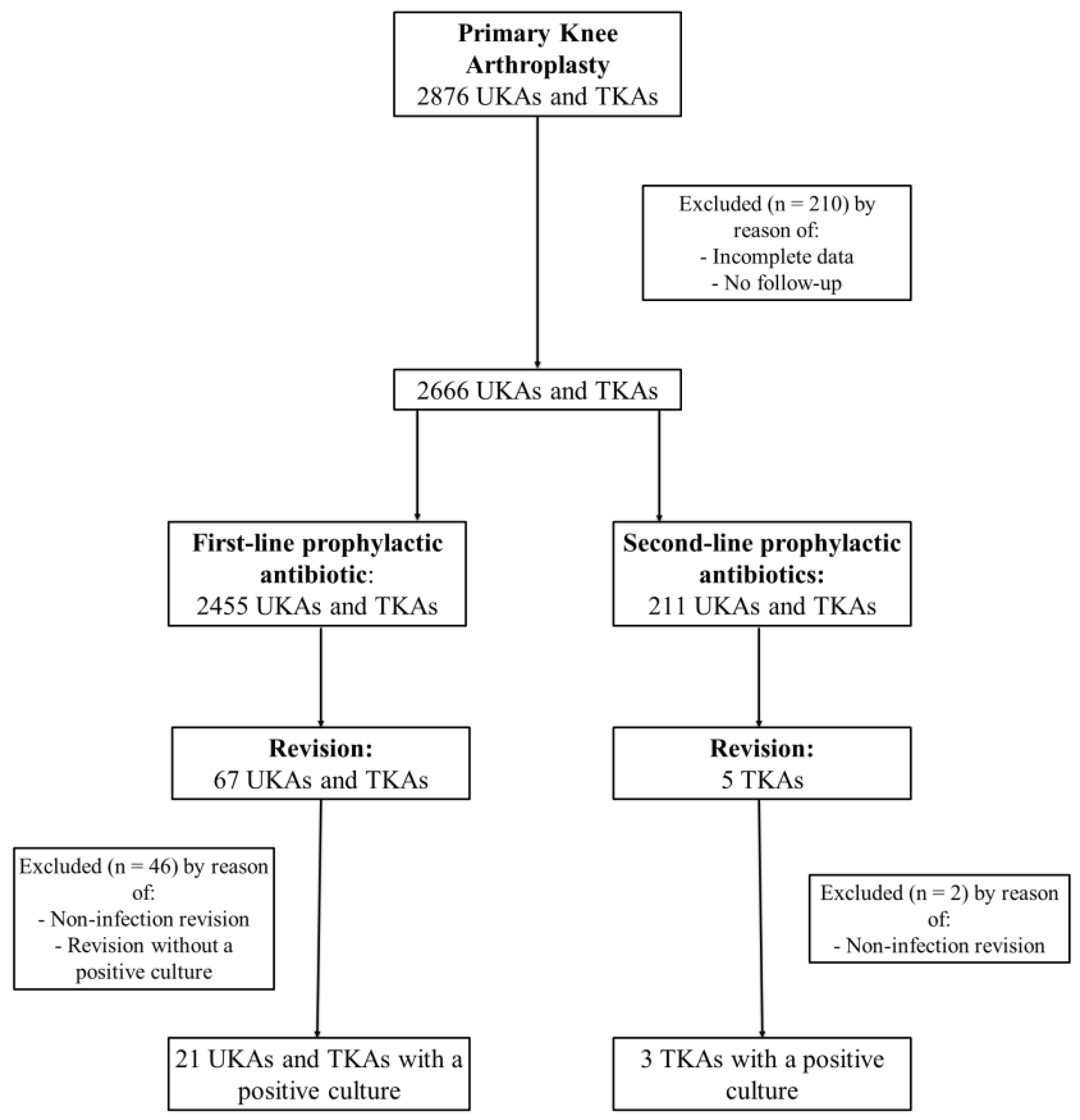
2.2. UKA/TKA Group
2.3. Revision and PJI Rate
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Surgical Treatment
4.2. Prophylactic Antibiotic Treatment
4.3. Microbiology
4.4. Outcome Measures
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dobson, P.F.; Reed, M.R. Prevention of infection in primary THA and TKA. EFORT Open Rev. 2020, 5, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meehan, J.; Jamali, A.A.; Nguyen, H. Prophylactic antibiotics in hip and knee arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2009, 91, 2480–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratzler, D.W.; Dellinger, E.P.; Olsen, K.M.; Perl, T.M.; Auwaerter, P.G.; Bolon, M.K.; Fish, D.N.; Napolitano, L.M.; Sawyer, R.G.; Slain, D.; et al. Clinical practice guidelines for antimicrobial prophylaxis in surgery. Surg. Infect. 2013, 14, 73–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboltins, C.A.; Berdal, J.E.; Casas, F.; Corona, P.S.; Cuellar, D.; Ferrari, M.C.; Hendershot, E.; Huang, W.; Kuo, F.C.; Malkani, A.; et al. Hip and Knee Section, Prevention, Antimicrobials (Systemic): Proceedings of International Consensus on Orthopedic Infections. J. Arthroplast。 2019, 34, S279–S288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyles, C.C.; Hevesi, M.; Osmon, D.R.; Park, M.A.; Habermann, E.B.; Lewallen, D.G.; Berry, D.J.; Sierra, R.J. 2019 John Charnley Award: Increased risk of prosthetic joint infection following primary total knee and hip arthroplasty with the use of alternative antibiotics to cefazolin. Bone Jt. J. 2019, 101 B, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevoska, S.; Himmelbauer, F.; Stiftinger, J.; Stadler, C.; Gotterbarm, T.; Heyse, T.J.; Klasan, A. Significant Difference in Antimicrobial Resistance of Coagulase Negative Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Septic Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty Between Two Major Orthopedic Centers. J. Arthroplast。 2022, 37, S306–S312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenthal, K.G.; Li, Y.; Banerji, A.; Yun, B.J.; Long, A.A.; Walensky, R.P. The Cost of Penicillin Allergy Evaluation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 1019–1027.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, A.H.; Kelmer, G.; MacDonald, J.H.; Clance, M.R.; King, P.J. The Impact of Patient-Reported Penicillin Allergy on Risk for Surgical Site Infection in Total Joint Arthroplasty. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2019, 27, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, N.R.; Moverman, M.A.; Puzzitiello, R.N.; Menendez, M.E.; Barnes, C.L.; Kavolus, J.J. Preoperative Allergy Testing for Patients Reporting Penicillin and Cephalosporin Allergies is Cost-Effective in Preventing Infection after Total Knee and Hip Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast。 2021, 36, 700–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, V.J.; Iloanya, M.C.; Sanchez, F.L.; Billings, C.R.; O’Brien, M.J.; Savoie, F.H.; Sherman, W.F. Is Patient-reported Penicillin Allergy Independently Associated with Increased Risk of Prosthetic Joint Infection after Total Joint Arthroplasty of the Hip, Knee, and Shoulder? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2020, 478, 2699–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefánsdóttir, A.; Johansson, D.; Knutson, K.; Lidgren, L.; Robertsson, O. Microbiology of the infected knee arthroplasty: Report from the Swedish Knee Arthroplasty Register on 426 surgically revised cases. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 41, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchalter, D.B.; Nduaguba, A.; Teo, G.M.; Kugelman, D.; Aggarwal, V.K.; Long, W.J. Cefazolin remains the linchpin for preventing acute periprosthetic joint infection following primary total knee arthroplasty. Bone Jt. Open 2022, 3, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertsson, O.; Thompson, O.; W-Dahl, A.; Sundberg, M.; Lidgren, L.; Stefánsdóttir, A. Higher risk of revision for infection using systemic clindamycin prophylaxis than with cloxacillin: A report from the Swedish Knee Arthroplasty Register on 78,000 primary total knee arthroplasties for osteoarthritis. Acta Orthop. 2017, 88, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inglis, J.M.; Caughey, G.E.; Smith, W.; Shakib, S. Documentation of penicillin adverse drug reactions in electronic health records: Inconsistent use of allergy and intolerance labels. Intern. Med. J. 2017, 47, 1292–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacFadden, D.R.; LaDelfa, A.; Leen, J.; Gold, W.L.; Daneman, N.; Weber, E.; Al-Busaidi, I.; Petrescu, D.; Saltzman, I.; Devlin, M.; et al. Impact of Reported Beta-Lactam Allergy on Inpatient Outcomes: A Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubiano, J.A.; Adkinson, N.F.; Phillips, E.J. Penicillin Allergy Is Not Necessarily Forever Jason. JAMA 2017, 318, 82–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trubiano, J.A.; Thursky, K.A.; Stewardson, A.J.; Urbancic, K.; Worth, L.J.; Jackson, C.; Stevenson, W.; Sutherland, M.; Slavin, M.A.; Grayson, M.L.; et al. Impact of an Integrated Antibiotic Allergy Testing Program on Antimicrobial Stewardship: A Multicenter Evaluation. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDanel, D.L.; Azar, A.E.; Dowden, A.M.; Murray-Bainer, S.; Noiseux, N.O.; Willenborg, M.; Clark, C.R.; Callaghan, J.J.; Haleem, A. Screening for Beta-Lactam Allergy in Joint Arthroplasty Patients to Improve Surgical Prophylaxis Practice. J. Arthroplast。 2017, 32, S101–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, J.; Pavlos, R.; James, I.; Phillips, E. Improving the Effectiveness of Penicillin Allergy De-labeling. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2015, 3, 365–374.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonomo, A.; Nucera, E.; Pecora, V.; Rizzi, A.; Aruanno, A.; Pascolini, L.; Ricci, A.G.; Colagiovanni, A.; Schiavino, D. Cross-reactivity and tolerability of cephalosporins in patients with cell-mediated allergy to penicillins. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 24, 331–337. [Google Scholar]
- Campagna, J.D.; Bond, M.C.; Schabelman, E.; Hayes, B.D. The use of cephalosporins in penicillin-allergic patients: A literature review. J. Emerg. Med. 2012, 42, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, A.; Sánchez, A.; Luque, S.; Mur, I.; Puig, L.; Crusi, X.; González, J.C.; Sorlí, L.; González, A.; Horcajada, J.P.; et al. Intraoperative bacterial contamination and activity of different antimicrobial prophylaxis regimens in primary knee and hip replacement. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, S.; Al-Obaidi, B.; Jardine, A.; Jonas, S.; Al-Hadithy, N.; Satish, V. A comparative study of 5 different antibiotic prophylaxis regimes in 4500 total knee replacements. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2020, 11, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornero, E.; Garcí-Ramiro, S.; Martínez-Pastor, J.C.; Bori, G.; Bosch, J.; Morata, L.; Sala, M.; Basora, M.; Mensa, J.; Soriano, A. Prophylaxis with teicoplanin and cefuroxime reduces the rate of prosthetic joint infection after primary arthroplasty. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.B.; Wynne, R.; Joshi, A.; Liu, H.; Good, R.P. Is it time to include vancomycin for routine perioperative antibiotic prophylaxis in total joint arthroplasty patients? J. Arthroplast。 2012, 27, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyllianakis, M.E.; Karageorgos, A.C.; Marangos, M.N.; Saridis, A.G.; Lambiris, E.E. Antibiotic prophylaxis in primary hip and knee arthroplasty. Comparison between cefuroxime and two specific antistaphylococcal agents. J. Arthroplast。 2010, 25, 1078–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, V.K.; Bakhshi, H.; Ecker, N.U.; Parvizi, J.; Gehrke, T.; Kendoff, D. Organism profile in periprosthetic joint infection: Pathogens differ at two arthroplasty infection referral centers in Europe and in the United States. J. Knee Surg. 2014, 27, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kheir, M.M.; Tan, T.L.; Azboy, I.; Tan, D.D.; Parvizi, J. Vancomycin Prophylaxis for Total Joint Arthroplasty: Incorrectly Dosed and Has a Higher Rate of Periprosthetic Infection Than Cefazolin. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2017, 475, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feder, O.I.; Yeroushalmi, D.; Lin, C.C.; Galetta, M.S.; Meftah, M.; Lajam, C.M.; Slover, J.D.; Schwarzkopf, R.; Bosco, J.A.; Macaulay, W.B. Incomplete Administration of Intravenous Vancomycin Prophylaxis is Common and Associated With Increased Infectious Complications after Primary Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast。 2021, 36, 2951–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skyrman, S.; Bartek, J.; Haghighi, M.; Fornebo, I.; Skoglund, T.; Jakola, A.S.; von Vogelsang, A.C.; Förander, P. Preoperative antibiotic prophylaxis regimen in brain tumour surgery in Sweden: A quasi-experimental study. Acta Neurochir. 2020, 162, 2849–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surat, G.; Bernsen, D.; Schimmer, C. Antimicrobial stewardship measures in cardiac surgery and its impact on surgical site infections. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2021, 16, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvizi, J.; Tan, T.L.; Goswami, K.; Higuera, C.; Della Valle, C.; Chen, A.F.; Shohat, N. The 2018 Definition of Periprosthetic Hip and Knee Infection: An Evidence-Based and Validated Criteria. J. Arthroplast。 2018, 33, 1309–1314.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevoska, S.; Himmelbauer, F.; Stiftinger, J.; Stadler, C.; Pisecky, L.; Gotterbarm, T.; Klasan, A. Significant Difference in Antimicrobial Resistance of Bacteria in Septic Revision between Total Knee Arthroplasty and Total Hip Arthroplasty. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, R.; Cantón, R.; Brown, D.F.J.; Giske, C.G.; Heisig, P.; Macgowan, A.P.; Mouton, J.W.; Nordmann, P.; Rodloff, A.C.; Rossolini, G.M.; et al. EUCAST expert rules in antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Cefuroxime (n = 3213) | Non-Cefuroxime (n = 206) | p-Value (Significant < 0.05) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age, years (SD) | 65.9 (12.1) | 67.8 (11.4) | 0.028 |
| Gender, n (%): | |||
| Female | 1707 (53.1) | 146 (70.9) | <0.001 |
| Male | 1506 (46.9) | 60 (29.1) | |
| Laterality, n (%): | |||
| Left | 1503 (46.8) | 103 (50.0) | 0.370 |
| Right | 1681 (52.3) | 103 (50.0) | |
| Both | 29 (0.9) | 0 | |
| Mean BMI, kg/m2 (SD) | 28.0 (4.8) | 29.2 (5.4) | 0.001 |
| Mean ASA score | 2.1 | 2.4 | |
| ASA score, n (%): | |||
| I | 508 (15.8) | 16 (7.8) | 0.002 |
| II | 1953 (60.8) | 104 (50.5) | 0.003 |
| III | 733 (22.8) | 84 (40.8) | <0.001 |
| IV | 19 (0.6) | 2 (1.0) | 0.500 |
| Median Follow-up, months (IQR) | 15.9 (39.1) | 15.4 (35.1) | 0.833 |
| Variable | Cefuroxime (n = 2455) | Non-Cefuroxime (n = 211) | p-Value (Significant < 0.05) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age, years (SD) | 68.7 (9.9) | 69.1 (9.6) | 0.572 |
| Gender, n (%): | |||
| Female | 1492 (60.8) | 163 (77.3) | <0.001 |
| Male | 963 (39.2) | 48 (22.7) | |
| Laterality, n (%): | |||
| Left | 1188 (48.4) | 105 (49.8) | 0.700 |
| Right | 1243 (50.6) | 106 (50.2) | |
| Both | 24 (1.0) | 0 | |
| Arthroplasty, n (%) | |||
| TKA | 1668 (67.9) | 164 (77.7) | 0.003 |
| UKA | 787 (32.1) | 47 (22.3) | |
| Mean BMI, kg/m2 (SD) | 29.9 (5.4) | 30.3 (6.1) | 0.307 |
| Mean ASA score | 2.2 | 2.8 | |
| ASA score, n (%): | |||
| I | 212 (8.6) | 11 (5.2) | 0.085 |
| II | 1591 (64.8) | 125 (59.2) | 0.110 |
| III | 645 (26.3) | 73 (34.6) | 0.009 |
| IV | 7 (0.3) | 2 (1.0) | 0.110 |
| Median Follow-up, months (IQR) | 13.1 (23.6) | 13.5 (23.8) | 0.757 |
| Group | Variable | Cefuroxime | Non-Cefuroxime | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UKA/TKA | Revision rate, n (%) | 67/2455 (2.7) | 5/211 (2.4) | 0.757 |
| PJI rate, n (%) | 21/2455 (0.9) | 3/211 (1.4) | 0.403 | |
| THA | Revision rate, n (%) | 115/3213 (3.6) | 8/206 (3.9) | 0.820 |
| PJI rate, n (%) | 61/3123 (2.0) | 6/206 (2.9) | 0.309 |
| Group | Prophylactic Antibiotic | 1 Month | 3 Months | <1 Year | >1 Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UKA/TKA | Cefuroxime (n = 21), n (%) | 7 (33.3) | 5 (23.8) | 5 (23.8) | 4 (19.1) |
| Non-cefuroxime (n = 3), n (%) | 1 (33.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (66.7) | |
| THA | Cefuroxime (n = 61), n (%) | 33 (54.1) | 12 (36.4) | 2 (3.3) | 14 (23.0) |
| Non-cefuroxime (n = 6), n (%) | 3 (50.0) | 1 (16.7) | 2 (33.3) | 0 (0.0.) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stevoska, S.; Behm-Ferstl, V.; Zott, S.; Stadler, C.; Schieder, S.; Luger, M.; Gotterbarm, T.; Klasan, A. The Impact of Patient-Reported Penicillin or Cephalosporin Allergy on the Occurrence of the Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Primary Knee and Hip Arthroplasty. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101345
Stevoska S, Behm-Ferstl V, Zott S, Stadler C, Schieder S, Luger M, Gotterbarm T, Klasan A. The Impact of Patient-Reported Penicillin or Cephalosporin Allergy on the Occurrence of the Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Primary Knee and Hip Arthroplasty. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(10):1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101345
Chicago/Turabian StyleStevoska, Stella, Verena Behm-Ferstl, Stephanie Zott, Christian Stadler, Sophie Schieder, Matthias Luger, Tobias Gotterbarm, and Antonio Klasan. 2022. "The Impact of Patient-Reported Penicillin or Cephalosporin Allergy on the Occurrence of the Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Primary Knee and Hip Arthroplasty" Antibiotics 11, no. 10: 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101345
APA StyleStevoska, S., Behm-Ferstl, V., Zott, S., Stadler, C., Schieder, S., Luger, M., Gotterbarm, T., & Klasan, A. (2022). The Impact of Patient-Reported Penicillin or Cephalosporin Allergy on the Occurrence of the Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Primary Knee and Hip Arthroplasty. Antibiotics, 11(10), 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101345






