Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Var Boulardii CNCM I–1079 Reduces Expression of Genes Involved in Inflammatory Response in Porcine Cells Challenged by Enterotoxigenic E. Coli and Influences Bacterial Communities in an In Vitro Model of the Weaning Piglet Colon
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
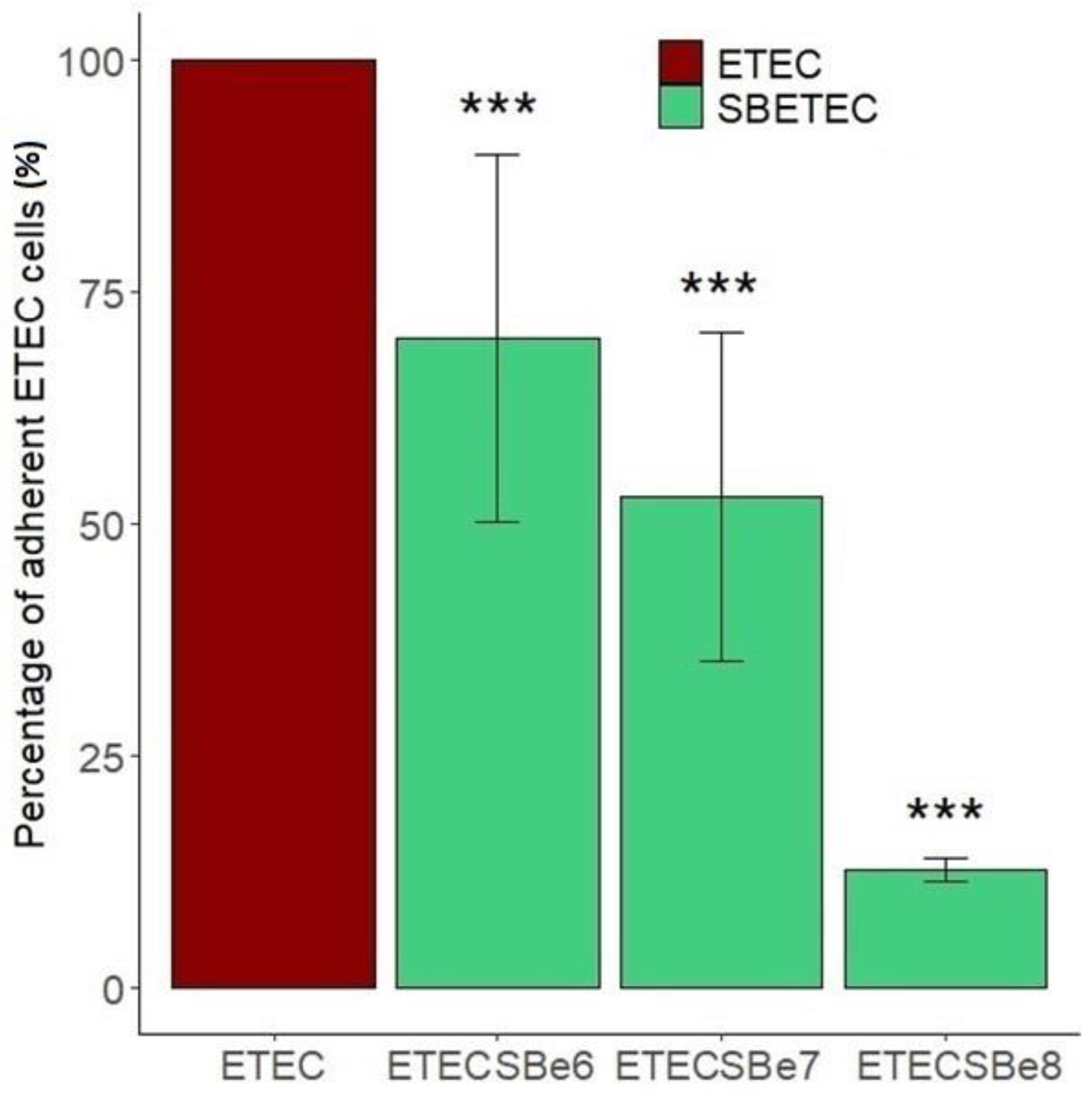
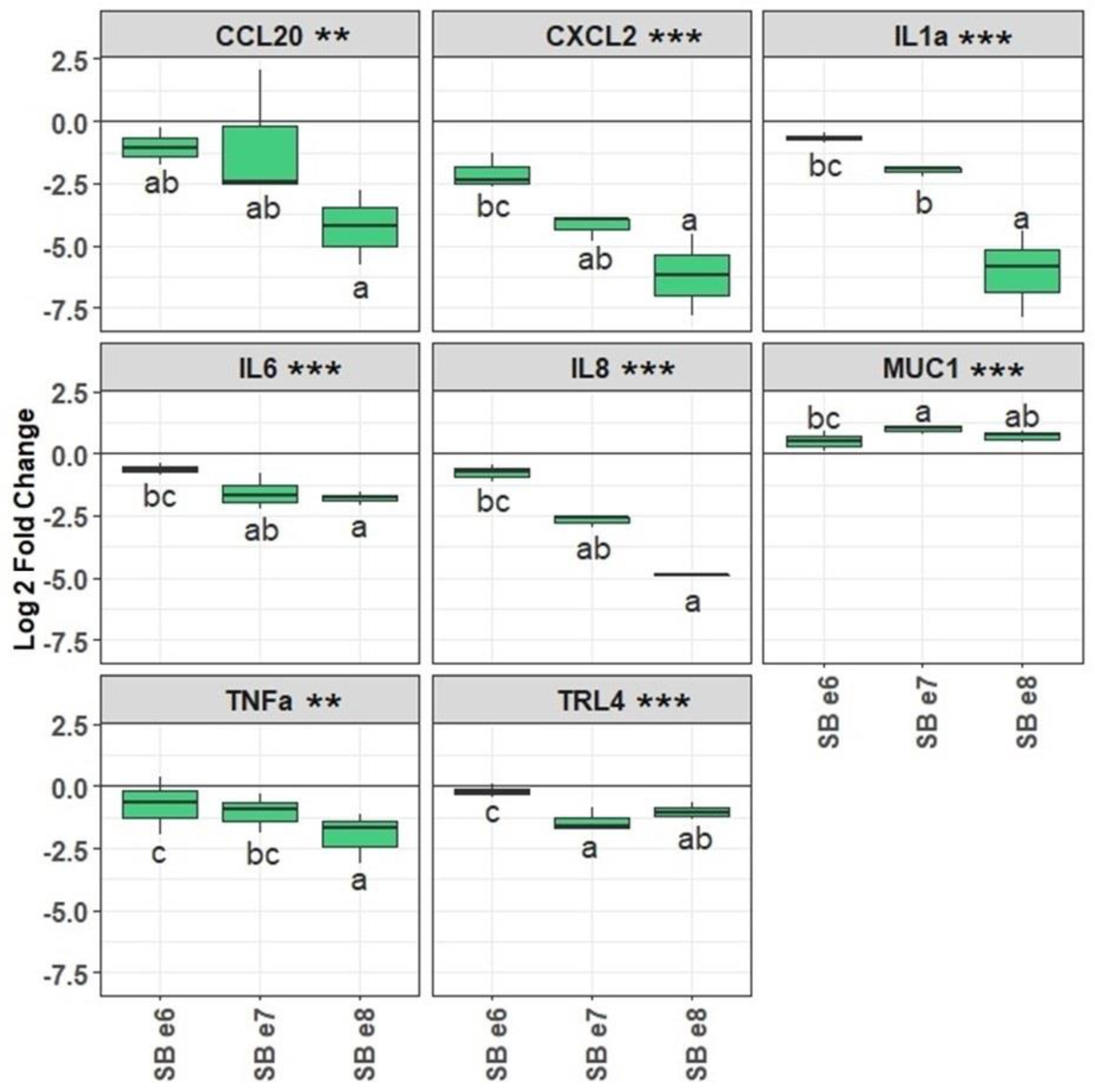
2.1. SB CNCM I-1079 Inhibits ETEC Adhesion and ETEC-Induced Inflammatory Response on IPEC-J2 Intestinal Cells
2.2. Live SB CNCM I-1079 Impacts Microbiota Composition and Activity of the Mpigut-IVM Challenged with a Feed Deprivation Stress, a Dietary Change and an ETEC Strain
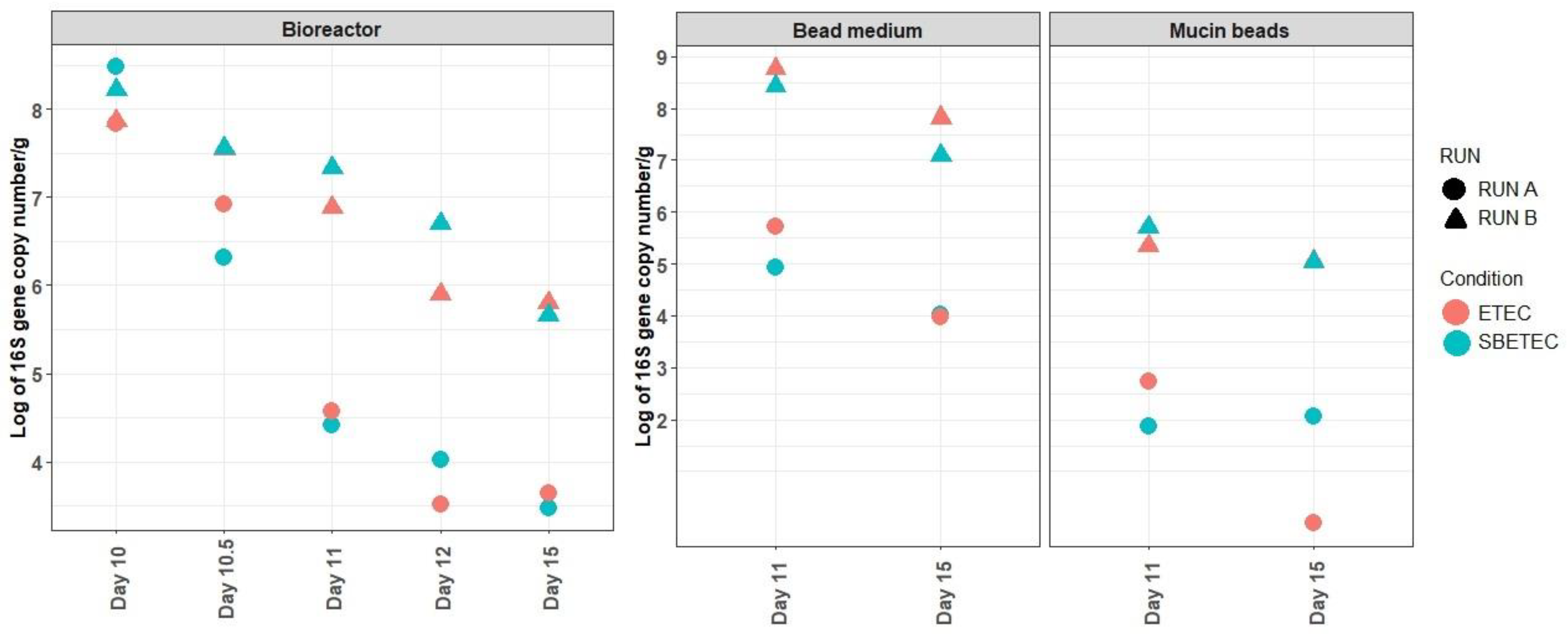
2.2.1. Effects of SB on ETEC Colonization in the MPigut-IVM
2.2.2. Effects of SB on Gut Microbiota Activity
2.2.3. Effects of SB on Microbiota Composition
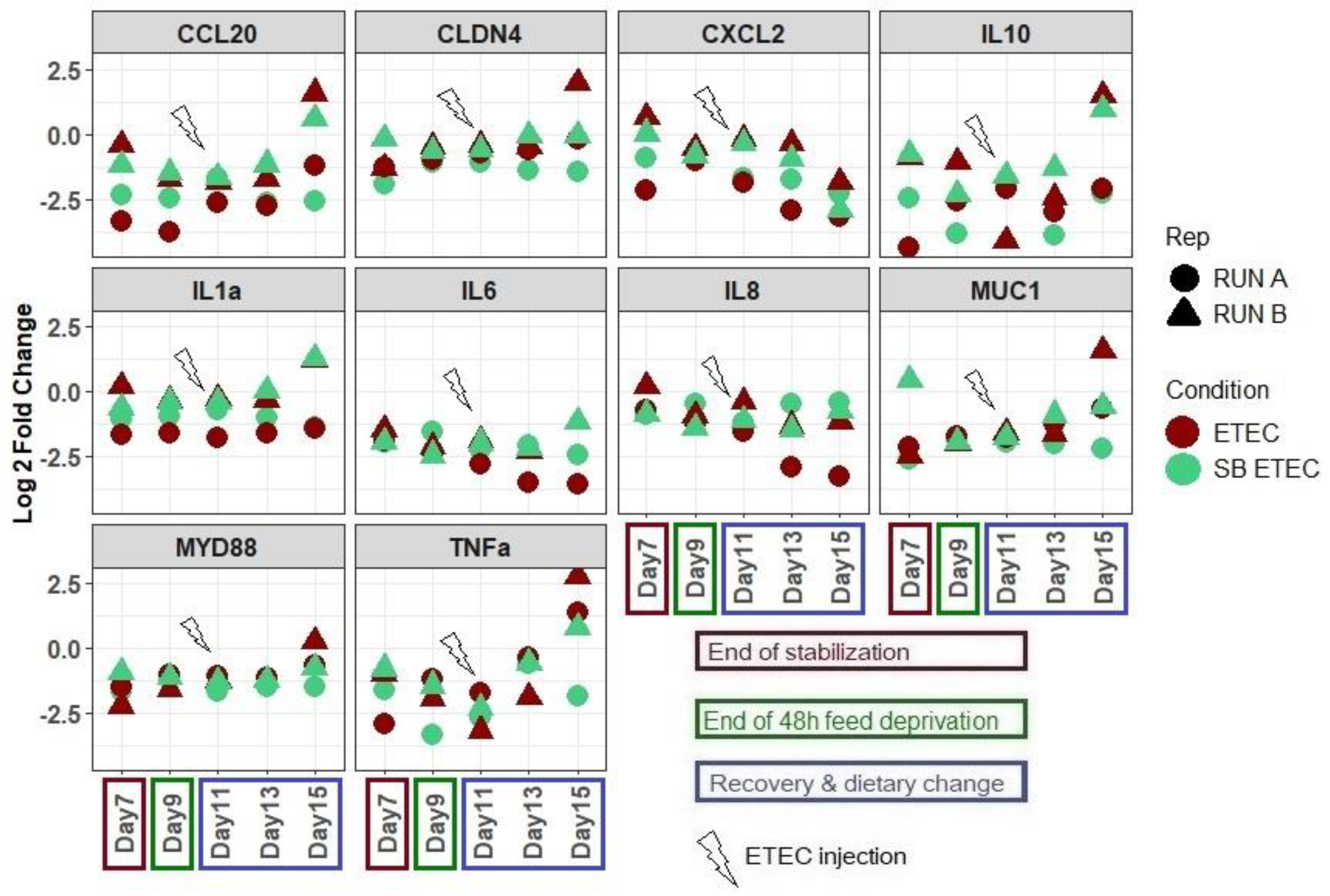
2.3. SB Live Yeast Supplementation to ETEC-Challenged Mpigut-IVM Leads to Changes in Gene Expression Profile of IPI-2I Intestinal Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
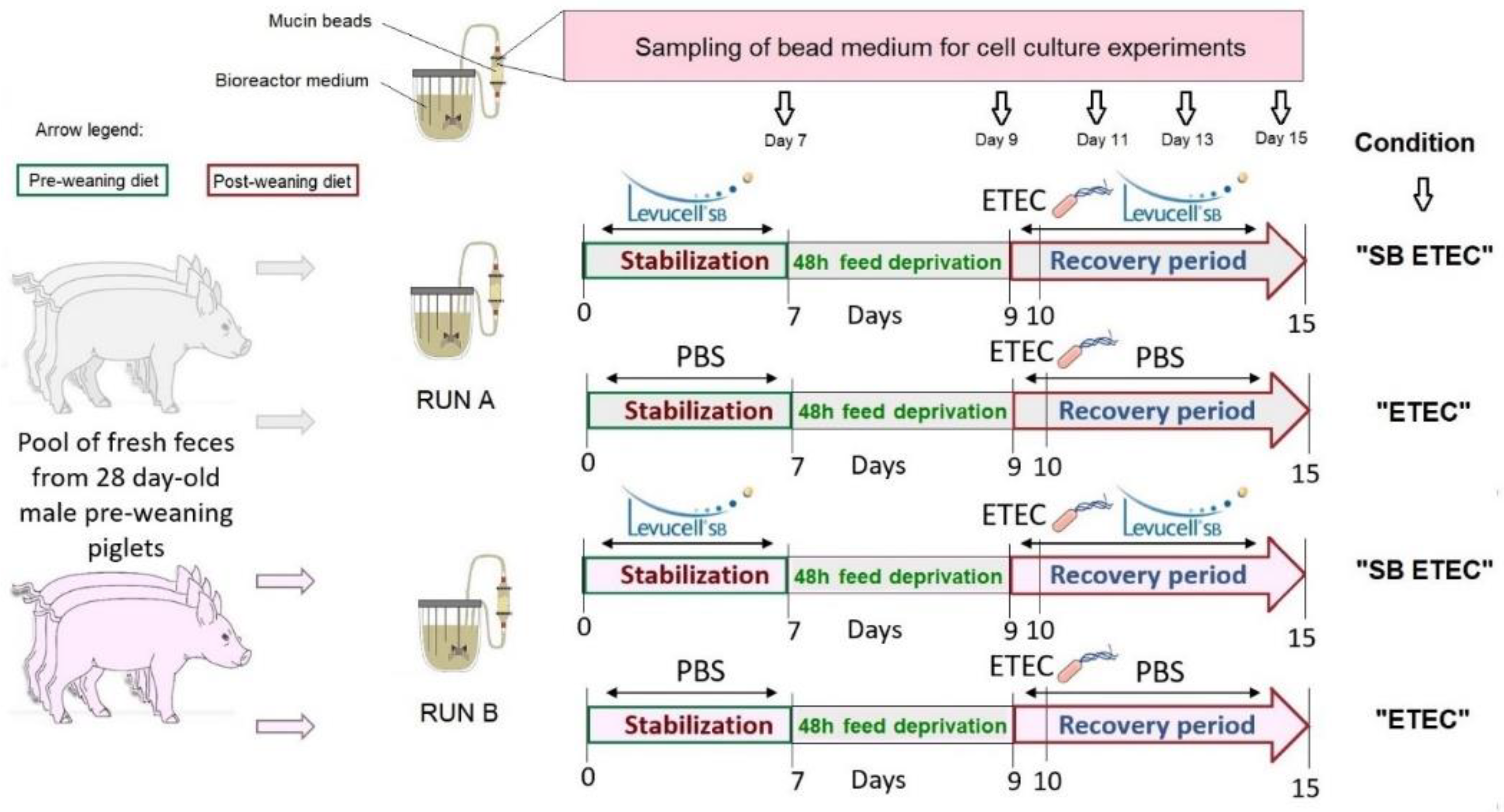
4.1. MPigut-IVM In Vitro Experiments
4.1.1. Fecal Samples Collection and Treatments
4.1.2. MPigut-IVM Parameters
4.1.3. Mucin Bead Production and Compartment
4.1.4. In Vitro Fermentation Procedures
4.1.5. ETEC Culture Conditions and Challenge Procedure in The MPigut-IVM
4.1.6. SB CNCM I-1079 Supplementation
4.1.7. DNA Extraction from MPigut-IVM Samples
4.1.8. Microbial Quantification by qPCR
4.1.9. MiSeq 16S rDNA Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analysis
4.1.10. Quantification of Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs) by Gas Chromatography
4.2. Porcine Intestinal Cell Line Experiments
4.2.1. Adhesion Assay of ETEC on IPEC-J2 Cells
4.2.2. Incubation of ETEC-challenged MPigut-IVM Samples with an Intestinal Porcine Cell Line
4.2.3. RNA Isolation from Cell IPEC-J2 and IPI2-I lysates
4.2.4. RT-qPCR on Porcine Intestinal Cell RNA Extracts
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rhouma, M.; Fairbrother, J.M.; Beaudry, F.; Letellier, A. Post weaning diarrhea in pigs: Risk factors and non-colistin-based control strategies. Acta Vet. Scand. 2017, 59, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fairbrother, J.M.; Nadeau, E.; Gyles, C.L. Escherichia coli in postweaning diarrhea in pigs: An update on bacterial types, pathogenesis, and prevention strategies. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2005, 6, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubreuil, J.D.; Isaacson, R.E.; Schifferli, D.M. Animal Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. EcoSal Plus 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girard, M.; Thanner, S.; Pradervand, N.; Hu, D.; Ollagnier, C.; Bee, G. Hydrolysable chestnut tannins for reduction of postweaning diarrhea: Efficacy on an experimental ETEC F4 model. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gresse, R.; Chaucheyras-Durand, F.; Fleury, M.A.; Van de Wiele, T.; Forano, E.; Blanquet-Diot, S. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Postweaning Piglets: Understanding the Keys to Health. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 851–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert Consensus Document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiros, T.G.; Luise, D.; Derakhshani, H.; Petri, R.; Trevisi, P.; D’Inca, R.; Auclair, E.; van Kessel, A.G. Effect of live yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae supplementation on the performance and cecum microbial profile of suckling piglets. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García, G.R.; Dogi, C.A.; Poloni, V.L.; Fochesato, A.S.; De Moreno de Leblanc, A.; Cossalter, A.M.; Payros, D.; Oswald, I.P.; Cavaglieri, L.R. Beneficial effects of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RC016 in weaned piglets: In vivo and ex vivo analysis. Benef. Microbes 2019, 10, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Heugten, E.; Funderburke, D.W.; Dorton, K.L. Growth performance, nutrient digestibility, and fecal microflora in weanling pigs fed live yeast. J. Anim. Sci. 2003, 81, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, A.G.; Chattin, S.E.; Robbins, C.M.; Golden, D.A. Effects of a direct-fed yeast culture on enteric microbial populations, fermentation acids, and performance of weanling pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 1998, 76, 2138–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, L.; Xu, Q.; Wu, C.; Luo, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, B.; Auclair, E.; Kiros, T.; Fang, Z.; Lin, Y.; et al. Effects of dietary live yeast supplementation on growth performance, diarrhoea severity, intestinal permeability and immunological parameters of weaned piglets challenged with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 118, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Badia, R.; Zanello, G.; Chevaleyre, C.; Lizardo, R.; Meurens, F.; Martínez, P.; Brufau, J.; Salmon, H. Effect of Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. Boulardii and β-galactomannan oligosaccharide on porcine intestinal epithelial and dendritic cells challenged in vitro with Escherichia coli F4 (K88). Vet. Res. 2012, 43, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanello, G.; Meurens, F.; Berri, M.; Chevaleyre, C.; Melo, S.; Auclair, E.; Salmon, H. Saccharomyces cerevisiae decreases inflammatory responses induced by F4+ enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in porcine intestinal epithelial cells. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2011, 141, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brousseau, J.-P.; Talbot, G.; Beaudoin, F.; Lauzon, K.; Roy, D.; Lessard, M. Effects of probiotics Pediococcus acidilactici strain MA18/5M and Saccharomyces cerevisiae subsp. boulardii strain SB-CNCM I-1079 on fecal and intestinal microbiota of nursing and weanling piglets. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 93, 5313–5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanello, G.; Berri, M.; Dupont, J.; Sizaret, P.Y.; d’Inca, R.; Salmon, H.; Meurens, F. Saccharomyces cerevisiae modulates immune gene expressions and inhibits ETEC-mediated ERK1/2 and p38 signaling pathways in intestinal epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gresse, R.; Chaucheyras-Durand, F.; Garrido, J.J.; Denis, S.; Jiménez-Marín, A.; Beaumont, M.; Van de Wiele, T.; Forano, E.; Blanquet-Diot, S. Pathogen Challenge and Dietary Shift Alter Microbiota Composition and Activity in a Mucin-Associated in vitro Model of the Piglet Colon (MPigut-IVM) Simulating Weaning Transition. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gresse, R.; Chaucheyras-Durand, F.; Denis, S.; Beaumont, M.; Van de Wiele, T.; Forano, E.; Blanquet-Diot, S. Weaning-associated feed deprivation stress causes microbiota disruptions in a novel mucin-containing in vitro model of the piglet colon (MPigut-IVM). J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 12, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, B.; Fekete, P.Z. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in veterinary medicine. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 295, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, M.D. Impact of antibiotic use in the swine industry. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2014, 19, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trckova, M.; Faldyna, M.; Alexa, P.; Zajacova, Z.S.; Gopfert, E.; Kumprechtova, D.; Auclair, E.; D’Inca, R. The effects of live yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae on postweaning diarrhea, immune response, and growth performance in weaned piglets1. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisi, P.; Latorre, R.; Priori, D.; Luise, D.; Archetti, I.; Mazzoni, M.; D’Inca, R.; Bosi, P. Effect of feed supplementation with live yeast on the intestinal transcriptome profile of weaning pigs orally challenged with Escherichia coli F. Animals 2017, 11, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Vallance, B.A.; Boyer, L.; Bergstrom, K.S.; Walker, J.; Madsen, K.; O’Kusky, J.R.; Buchan, A.M.; Jacobson, K. Saccharomyces boulardii ameliorates Citrobacter rodentium-induced colitis through actions on bacterial virulence factors. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G295–G306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Czerucka, D.; Dahan, S.; Mograbi, B.; Rossi, B.; Rampal, P. Saccharomyces boulardii Preserves the Barrier Function and Modulates the Signal Transduction Pathway Induced in Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli-Infected T84 Cells. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 5998–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castagliuolo, I.; Riegler, M.F.; Valenick, L.; LaMont, J.T.; Pothoulakis, C. Saccharomyces boulardii Protease Inhibits the Effects of Clostridium difficile Toxins A and B in Human Colonic Mucosa. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mumy, K.L.; Chen, X.; Kelly, C.P.; McCormick, B.A. Saccharomyces boulardii interferes with Shigella pathogenesis by postinvasion signaling events. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G599–G609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Huang, X.; Fang, S.; He, M.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, C.; Huang, L. Unraveling the Fecal Microbiota and Metagenomic Functional Capacity Associated with Feed Efficiency in Pigs. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Investigations of Bacteroides spp. towards next-generation probiotics. Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Huang, X.; Wang, P.; Yan, Z.; Sun, W.; Zhao, S.; Gun, S. Longitudinal development of the gut microbiota in healthy and diarrheic piglets induced by age-related dietary changes. Microbiology 2019, 8, e923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bin, P.; Tang, Z.; Liu, S.; Chen, S.; Xia, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, H.; Zhu, G. Intestinal microbiota mediates Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-induced diarrhea in piglets. BMC Veter. Res. 2018, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schroeder, B.; Duncker, S.; Barth, S.; Bauerfeind, R.; Gruber, A.D.; Deppenmeier, S.; Breves, G. Preventive Effects of the Probiotic Escherichia coli Strain Nissle 1917 on Acute Secretory Diarrhea in a Pig Model of Intestinal Infection. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2006, 51, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secher, T.; Brehin, C.; Oswald, E. Early settlers: Which E. coli strains do you not want at birth? Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2016, 311, G123–G129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Macfarlane, S.; Macfarlane, G.T. Regulation of short-chain fatty acid production. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2003, 62, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saegusa, S.; Totsuka, M.; Kaminogawa, S.; Hosoi, T. Candida albicans and Saccharomyces cerevisiae induce interleukin-8 production from intestinal epithelial-like Caco-2 cells in the presence of butyric acid. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 41, 227–235. [Google Scholar]
- Rajput, I.R.; Ying, H.; Yajing, S.; Arain, M.A.; Weifen, L.; Ping, L.; Bloch, D.M.; Wenhua, L. Saccharomyces boulardii and Bacillus subtilis B10 modulate TLRs and cytokines expression patterns in jejunum and ileum of broilers. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173917. [Google Scholar]
- Angulo, M.; Reyes-Becerril, M.; Cepeda-Palacios, R.; Ramírez, D.T.; Esteban, M.Á.; Angulo, C. Probiotic effects of marine Debaryomyces hansenii CBS 8339 on innate immune and antioxidant parameters in newborn goats. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 2339–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Qian, J.; Li, J. Saccharomyces boulardii alleviates ulcerative colitis carcinogenesis in mice by reducing TNF-α and IL-6 levels and functions and by rebalancing intestinal microbiota. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Alexander, C.; Steelman, A.J.; Warzecha, C.M.; De Godoy, M.R.; Swanson, K.S. Effects of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation product on fecal characteristics, nutrient digestibility, fecal fermentative end-products, fecal microbial populations, immune function, and diet palatability in adult dogs. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 1586–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppi, A. Swine enteric colibacillosis: Diagnosis, therapy and antimicrobial resistance. Porc. Health Manag. 2017, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devriendt, B.; Stuyven, E.; Verdonck, F.; Goddeeris, B.; Cox, E. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (K88) induce proinflammatory responses in porcine intestinal epithelial cells. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huijsdens, X.W.; Linskens, R.K.; Mak, M.; Meuwissen, S.G.M.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.J.E.; Savelkoul, P.H.M. Quantification of Bacteria Adherent to Gastrointestinal Mucosa by Real-Time PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 4423–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Lee, C.; Kim, J.; Hwang, S. Group-specific primer and probe sets to detect methanogenic communities using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 89, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohene-Adjei, S.; Chaves, A.V.; McAllister, T.A.; Benchaar, C.; Teather, R.M.; Forster, R.J. Evidence of Increased Diversity of Methanogenic Archaea with Plant Extract Supplementation. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 56, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-W.; Nam, Y.-D.; Sung, Y.; Kim, K.-H.; Roh, S.W.; Yoon, J.-H.; An, K.-G.; Bae, J.-W. Quantitative real time PCR assays for the enumeration of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the Saccharomyces sensu stricto complex in human feces. J. Microbiol. Methods 2007, 71, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madoroba, E.; Van Driessche, E.; De Greve, H.; Mast, J.; Ncube, I.; Read, J.; Beeckmans, S. Prevalence of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli virulence genes from scouring piglets in Zimbabwe. Trop. Anim. Heal. Prod. 2009, 41, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudié, F.; Auer, L.; Bernard, M.; Mariadassou, M.; Cauquil, L.; Vidal, K.; Maman, S.; Hernandez-Raquet, G.; Combes, S.; Pascal, G. FROGS: Find, Rapidly, OTUs with Galaxy Solution. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahé, F.; Rognes, T.; Quince, C.; de Vargas, C.; Dunthorn, M. Swarm: Robust and fast clustering method for amplicon-based studies. PeerJ 2014, 2, e593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Mills, D.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, L.; Mariadassou, M.; O’Donohue, M.; Klopp, C.; Hernandez-Raquet, G. Analysis of large 16S rRNA Illumina data sets: Impact of singleton read filtering on microbial community description. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, e122–e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, J.M.; Chen, W.; Chu, P.; Berschneider, H.M.; Argenzio, R.A.; Paradiso, A.M. L-glutamine and L-asparagine stimulate Na+-H+ exchange in porcine jejunal enterocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 1994, 266, G828–G838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaeffer, B.; Bottreau, E.; Velge, P.; Pardon, P. Epithelioid and fibroblastic cell lines derived from the ileum of an adult histocompatible miniature boar (d/d haplotype) and immortalized by SV40 plasmid. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 62, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mariani, V.; Palermo, S.; Fiorentini, S.; Lanubile, A.; Giuffra, E. Gene expression study of two widely used pig intestinal epithelial cell lines: IPEC-J2 and IPI-2I. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 131, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gresse, R.; Garrido, J.J.; Jiménez-Marín, A.; Denis, S.; Van de Wiele, T.; Forano, E.; Blanquet-Diot, S.; Chaucheyras-Durand, F. Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Var Boulardii CNCM I–1079 Reduces Expression of Genes Involved in Inflammatory Response in Porcine Cells Challenged by Enterotoxigenic E. Coli and Influences Bacterial Communities in an In Vitro Model of the Weaning Piglet Colon. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10091101
Gresse R, Garrido JJ, Jiménez-Marín A, Denis S, Van de Wiele T, Forano E, Blanquet-Diot S, Chaucheyras-Durand F. Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Var Boulardii CNCM I–1079 Reduces Expression of Genes Involved in Inflammatory Response in Porcine Cells Challenged by Enterotoxigenic E. Coli and Influences Bacterial Communities in an In Vitro Model of the Weaning Piglet Colon. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(9):1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10091101
Chicago/Turabian StyleGresse, Raphaële, Juan J. Garrido, Angeles Jiménez-Marín, Sylvain Denis, Tom Van de Wiele, Evelyne Forano, Stéphanie Blanquet-Diot, and Frédérique Chaucheyras-Durand. 2021. "Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Var Boulardii CNCM I–1079 Reduces Expression of Genes Involved in Inflammatory Response in Porcine Cells Challenged by Enterotoxigenic E. Coli and Influences Bacterial Communities in an In Vitro Model of the Weaning Piglet Colon" Antibiotics 10, no. 9: 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10091101
APA StyleGresse, R., Garrido, J. J., Jiménez-Marín, A., Denis, S., Van de Wiele, T., Forano, E., Blanquet-Diot, S., & Chaucheyras-Durand, F. (2021). Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Var Boulardii CNCM I–1079 Reduces Expression of Genes Involved in Inflammatory Response in Porcine Cells Challenged by Enterotoxigenic E. Coli and Influences Bacterial Communities in an In Vitro Model of the Weaning Piglet Colon. Antibiotics, 10(9), 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10091101







