Testudines as Sentinels for Monitoring the Dissemination of Antibiotic Resistance in Marine Environments: An Integrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. General Mechanisms by Which Bacteria Develops Antibiotic Resistance
1.2. Antibiotics and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in Marine Environments
2. Methods Used to Evaluate Turtles Are Sentinels for Monitoring AR in Marine Environments
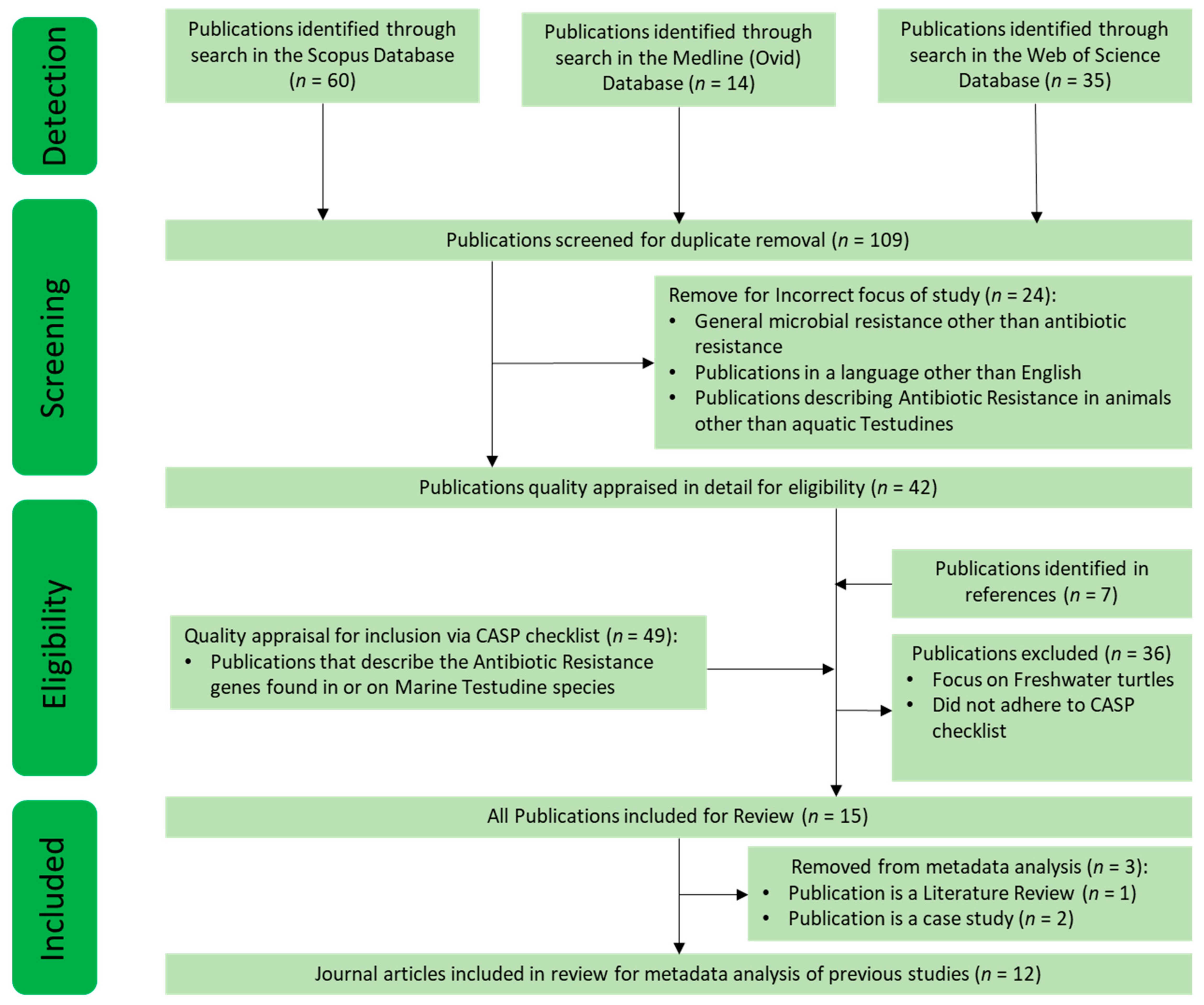
2.1. Systematic Literature Search Strategy, INCLUSION and Exclusion CRITERIA, and Quality Assessment
2.2. Quantitative Evaluation of Compiled Data
3. Results and Discussion of Data on Using Turtles for Monitoring AR in Marine Environments
3.1. An Overview on the Systematic Search of the Literature on Using Sea Turtles for Monitoring AR
3.2. Distribution of Studies on AR in Marine Environments by Geographical Site and Turtle Species
3.2.1. AR in Turtles in Marine Environments and the Potential Influence of Geographical Location
3.2.2. AR in Marine Environments and the Potential Influence of Differences in Turtle Species
3.3. Detection and Quantification of AR Profiles in Marine Environments
3.3.1. Present Challenges in Detecting ARB in Marine Turtles
3.3.2. Quantitative Evaluation of Phenotypic AR Patterns in Marine Turtles
3.3.3. Quantitative Evaluation of Anthropogenic Sources of AR in Marine Turtles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hawkey, P.M. Molecular epidemiology of clinically significant antibiotic resistance genes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153 (Suppl. 1), S406–S413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydnor, E.R.M.; Perl, T.M. Hospital epidemiology and infection control in acute-care settings. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 141–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacios, O.; Blasco, L.; Bleriot, I.; Fernandez-Garcia, L.; González Bardanca, M.; Ambroa, A.; López, M.; Bou, G.; Tomás, M. Strategies to Combat Multidrug-Resistant and Persistent Infectious Diseases. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collignon, P.; Beggs, J.J.; Walsh, T.R.; Gandra, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Anthropological and socioeconomic factors contributing to global antimicrobial resistance: A univariate and multivariable analysis. Lancet Planet. Health 2018, 2, e398–e405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Liu, X.; Li, L.; Shi, J.; Guo, W.; Xue, J. Temporal dynamics of antibiotic resistant genes and their association with the bacterial community in a water-sediment mesocosm under selection by 14 antibiotics. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruden, A.; Pei, R.; Storteboom, H.; Carlson, K.H. Antibiotic Resistance Genes as Emerging Contaminants: Studies in Northern Colorado. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7445–7450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fri, J.; Njom, H.A.; Ateba, C.N.; Ndip, R.N. Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Gene Characteristics of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Isolated from Healthy Edible Marine Fish. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 9803903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre, A.A.; Gardner, S.C.; Marsh, J.C.; Delgado, S.G.; Limpus, C.J.; Nichols, W.J. Hazards associated with the consumption of sea turtle meat and eggs: A review for health care workers and the general public. EcoHealth 2006, 3, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figgener, C.; Bernardo, J.; Plotkin, P.T. Beyond trophic morphology: Stable isotopes reveal ubiquitous versatility in marine turtle trophic ecology. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 1947–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, N.S.; Martins, A.S.; Faust, D.R.; Sakai, H.; Bianchini, A.; da Silva, C.C.; Aguirre, A.A. Cadmium in tissues of green turtles (Chelonia mydas): A global perspective for marine biota. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulson, J.R.; Mahmoud, I.Y.; Al-Musharafi, S.K.; Al-Bahry, S.N. Antibiotic resistant bacteria in the environment as bio-indicators of pollution. Open Biotechnol. J. 2016, 10, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahasan, M.S.; Waltzek, T.B.; Huerlimann, R.; Ariel, E. Comparative analysis of gut bacterial communities of green turtles (Chelonia mydas) pre-hospitalization and post-rehabilitation by high-throughput sequencing of bacterial 16S rRNA gene. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 207, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, S.A.; Ramachandran, A.; Perron, G.G. Antibiotic pollution in the environment: From microbial ecology to public policy. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bahry, S.; Mahmoud, I.; Elshafie, A.; Al-Harthy, A.; Al-Ghafri, S.; Al-Amri, I.; Alkindi, A. Bacterial flora and antibiotic resistance from eggs of green turtles Chelonia mydas: An indication of polluted effluents. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munita, J.M.; Arias, C.A. Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 481–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikaido, H. Multidrug resistance in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 119–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raleigh, E.A.; Low, K.B. Conjugation. In Brenner’s Encyclopedia of Genetics, 2nd ed.; Maloy, S., Hughes, K., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; pp. 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkin, S.; Colwell, R.R. Oceans and Health: Pathogens in the Marine Environment; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2005; Volume 233. [Google Scholar]
- Whitman, W.B.; Coleman, D.C.; Wiebe, W.J. Prokaryotes: The unseen majority. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6578–6583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Handelsman, J. Toward a census of bacteria in soil. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2006, 2, e92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowieson, A.; Kluenter, A. Contribution of exogenous enzymes to potentiate the removal of antibiotic growth promoters in poultry production. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2019, 250, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kümmerer, K. Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—A review—Part II. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, M. Occurrence and removal of antibiotic resistance genes in municipal wastewater and rural domestic sewage treatment systems in eastern China. Environ. Int. 2013, 55, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, L.; Manaia, C.; Merlin, C.; Schwartz, T.; Dagot, C.; Ploy, M.; Michael, I.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes spread into the environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazda, M.; Kumirska, J.; Stepnowski, P.; Mulkiewicz, E. Antibiotic resistance genes identified in wastewater treatment plant systems—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, D.L.; LaPara, T.M. Effect of temperature on the fate of genes encoding tetracycline resistance and the integrase of class 1 integrons within anaerobic and aerobic digesters treating municipal wastewater solids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 9128–9133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinthaler, F.; Posch, J.; Feierl, G.; Wüst, G.; Haas, D.; Ruckenbauer, G.; Mascher, F.; Marth, E. Antibiotic resistance of E. coli in sewage and sludge. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1685–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee-Sanford, J.C.; Mackie, R.I.; Koike, S.; Krapac, I.G.; Lin, Y.-F.; Yannarell, A.C.; Maxwell, S.; Aminov, R.I. Fate and transport of antibiotic residues and antibiotic resistance genes following land application of manure waste. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 1086–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolhouse, M.; Ward, M.; van Bunnik, B.; Farrar, J. Antimicrobial resistance in humans, livestock and the wider environment. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquillo, M.G.; Hernandez, J.C.A. Antibiotic and synthetic growth promoters in animal diets: Review of impact and analytical methods. Food Control. 2017, 72, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuong, N.V.; Padungtod, P.; Thwaites, G.; Carrique-Mas, J.J. Antimicrobial usage in animal production: A review of the literature with a focus on low-and middle-income countries. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenni, P.; Ancona, V.; Caracciolo, A.B. Ecological effects of antibiotics on natural ecosystems: A review. Microchem. J. 2018, 136, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.A.; French, D.P.; Brooks, J.M. Optimising the value of the critical appraisal skills programme (CASP) tool for quality appraisal in qualitative evidence synthesis. Res. Methods Med. Health Sci. 2020, 1, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahasan, M.S.; Picard, J.; Elliott, L.; Kinobe, R.; Owens, L.; Ariel, E. Evidence of antibiotic resistance in Enterobacteriales isolated from green sea turtles, Chelonia mydas on the Great Barrier Reef. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 120, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bahry, S.N.; Mahmoud, I.Y.; Al-Zadjali, M.; Elshafie, A.; Al-Harthy, A.; Al-Alawi, W. Antibiotic resistant bacteria as bio-indicator of polluted effluent in the green turtles, Chelonia mydas in Oman. Mar. Environ. Res. 2011, 71, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bahry, S.N.; Al-Zadjali, M.A.; Mahmoud, I.Y.; Elshafie, A.E. Biomonitoring marine habitats in reference to antibiotic resistant bacteria and ampicillin resistance determinants from oviductal fluid of the nesting green sea turtle, Chelonia mydas. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 1308–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alduina, R.; Gambino, D.; Presentato, A.; Gentile, A.; Sucato, A.; Savoca, D.; Filippello, S.; Visconti, G.; Caracappa, G.; Vicari, D.; et al. Is Caretta Caretta a Carrier of Antibiotic Resistance in the Mediterranean Sea? Antibiotics 2020, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delli Paoli Carini, A.; Ariel, E.; Picard, J.; Elliott, L. Antibiotic Resistant Bacterial Isolates from Captive Green Turtles and in Vitro Sensitivity to Bacteriophages. Int. J. Microbiol. 2017, 2017, 5798161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, M.; Giacopello, C.; Bottari, T.; Fisichella, V.; Rinaldo, D.; Mammina, C. Antibiotic Resistance of Gram Negatives isolates from loggerhead sea turtles (Caretta caretta) in the central Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1363–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Serrano, I.; Santos, J.P.; Bilocq, F.; Pereira, N.; de Santos Loureiro, N.; Tavares, L.; Pirnay, J.P.; De Vos, D. Pseudomonads from wild free-living sea turtles in Príncipe Island, Gulf of Guinea. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 81, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D.W.; Fernandes, M.R.; Sellera, F.P.; Costa, D.G.C.; Bracarense, A.P.L.; Lincopan, N. Genetic background of CTX-M-15-producing Enterobacter hormaechei ST114 and Citrobacter freundii ST265 co-infecting a free-living green turtle (Chelonia mydas). Zoonoses Public Health 2019, 66, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, A.; Dipineto, L.; Fioretti, A.; Hochscheid, S. Loggerhead sea turtles as sentinels in the western Mediterranean: Antibiotic resistance and environment-related modifications of Gram-negative bacteria. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prichula, J.; Pereira, R.I.; Wachholz, G.R.; Cardoso, L.A.; Tolfo, N.C.C.; Santestevan, N.A.; Medeiros, A.W.; Tavares, M.; Frazzon, J.; d’Azevedo, P.A.; et al. Resistance to antimicrobial agents among enterococci isolated from fecal samples of wild marine species in the southern coast of Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 105, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavala-Norzagaray, A.A.; Aguirre, A.A.; Velazquez-Roman, J.; Flores-Villasenor, H.; Leon-Sicairos, N.; Ley-Quinonez, C.P.; Hernandez-Diaz, L.D.J.; Canizalez-Roman, A. Isolation, characterization, and antibiotic resistance of Vibrio spp. in sea turtles from Northwestern Mexico. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirth, H.F. Synopsis of the Biological Data on the Green Turtle Chelonia Mydas (Linnaeus 1758); Fish and Wildlife Service, US Department of the Interior: Falls Church, VA, USA, 1997; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Witherington, B.; Kubilis, P.; Brost, B.; Meylan, A. Decreasing annual nest counts in a globally important loggerhead sea turtle population. Ecol. Appl. 2009, 19, 30–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasg, I.; Elligsen, M.; MacFadden, D.; Daneman, N. Predictive utility of swab screening for vancomycin-resistant enterococcus in selection of empiric antibiotics for Enterococcus sterile-site infections: A retrospective cohort study. CMAJ Open 2017, 5, E632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Qadir, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Endo, T.; Zahoor, A. Global, regional, and country level need for data on wastewater generation, treatment, and use. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 130, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuskopf, L.; Sheehan, M.; Whelan, A. Developing a Sampling and Analysis Quality Plan for the Cleveland Bay Sewage Treatment Plant. Aust. Water Assoc. Water J. 2020, 5, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faridahanim, A.; Shamila, A.; Mohd, I.; Shaikhah, S. Metals in tropical seagrass-accumulation of mercury and lead. World Appl. Sci. J. 2014, 32, 1468–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, J.M.; Vieira, S.; Jimenez, V.; Rio, J.C.; Rebelo, R. Stable isotopes reveal dietary differences and site fidelity in juvenile green turtles foraging around São Tomé Island, West Central Africa. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 600, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, T.; Aoki, S.; Kameda, K.; Hazel, J.; Reich, K.; Kamezaki, N. Site fidelity, ontogenetic shift and diet composition of green turtles Chelonia mydas in Japan inferred from stable isotope analysis. Endanger. Species Res. 2014, 25, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyneken, J.; Lohmann, K.J.; Musick, J.A. The Biology of Sea Turtles; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.-M.; Zhong, L.-L.; Zhang, X.-F.; Hu, H.-T.; Li, Y.-Q.; Yang, X.-R.; Feng, L.-Q.; Huang, X.; Tian, G.-B. NDM-1-producing Citrobacter freundii, Escherichia coli, and Acinetobacter baumannii identified from a single patient in China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5073–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Grady, K.A.; Krause, V. An outbreak of salmonellosis linked to a marine turtle. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1999, 30, 324–327. [Google Scholar]
- Warwick, C.; Arena, P.C.; Steedman, C. Health implications associated with exposure to farmed and wild sea turtles. JRSM Short Rep. 2013, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, P.M.; Steffes, Z.J. Emerging infectious diseases of chelonians. Vet. Clin. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2013, 16, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento-Ramirez, J.M.; van der Voort, M.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Dieguez-Uribeondo, J. Unravelling the microbiome of eggs of the endangered sea turtle Eretmochelys imbricata identifies bacteria with activity against the emerging pathogen Fusarium falciforme. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogomolni, A.L.; Gast, R.J.; Ellis, J.C.; Dennett, M.; Pugliares, K.R.; Lentell, B.J.; Moore, M.J. Victims or vectors: A survey of marine vertebrate zoonoses from coastal waters of the Northwest Atlantic. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2008, 81, 13–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, B.M. Sea turtle husbandry. In The Biology of Sea Turtles; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; Volume 2, pp. 411–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, R.J.; Thompson, M.B. Experimental analysis of the impact of foxes on freshwater turtle populations. Conserv. Biol. 2005, 19, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edet, U.; Antai, S.; Brooks, A.; Asitok, A.; Enya, O.; Japhet, F. An Overview of Cultural, Molecular and Metagenomic Techniques in Description of Microbial Diversity. J. Adv. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, S.K.; Castro-Nallar, E.; Pérez-Losada, M.; Toma, I.; McCaffrey, T.A.; Hoffman, E.P.; Siegel, M.O.; Simon, G.L.; Johnson, W.E.; Crandall, K.A. Metataxonomic and Metagenomic Approaches vs. Culture-Based Techniques for Clinical Pathology. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcock, B.P.; Raphenya, A.R.; Lau, T.T.; Tsang, K.K.; Bouchard, M.; Edalatmand, A.; Huynh, W.; Nguyen, A.-L.V.; Cheng, A.A.; Liu, S. CARD 2020: Antibiotic resistome surveillance with the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D517–D525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Turtle Species | Food Sources in Marine Environments | Geographical Site & Presumed ARB Source, Biological Sample, and Dominant Bacterial Isolate | MDRB |
|---|---|---|---|
| Green (Chelonia mydas) | Juveniles: Shrimp, crabs, clams, mussels, fish, squid.Adults: Seagrass, algae | NW Indian Ocean & Arabian sea, fresh eggs, Psuedomonas spp, (n = 30). [14] | + |
| Gulf of Oman Arabian sea, oviductal fluid, Citrobacter spp, (n = 40). [35] | + | ||
| Gulf of Oman Arabian sea, oviductal fluid, Citrobacter spp, (n = 20). [36] | + | ||
| Pacific Ocean (Rehabilitation centres, NE Australia), ocular swabs, Vibrio spp, (n = 7). [38] | + | ||
| Atlantic Ocean (South coast of Brazil), cloacal or rectal swabs, Enteroccus spp, (n = 6). [43] | + | ||
| Pacific Ocean (Baja California & Sinaloa Mexico), nasopharyngeal & oral swabs, Vibrio spp, (n = 42). [44] | + | ||
| Pacific Ocean (Rehabilitation centres & wild, NE Australia), cloacal swabs, Citrobacter spp, (n = 73). [34] | + | ||
| Loggerhead (Caretta caretta) | Juveniles & adults: Shrimp, crabs, clams, mussels, fish, squid. | Mediterranean Sea (Rehabilitation centre in Italy), internal organs, cloacal, oral & skin swabs, Aeromonas & Citrobacter spp, (n = 20). [37] | + |
| Central Mediterranean Sea (Italy), cloacal, oral & skin swabs, Proteus & Citrobacter spp, (n = 19). [39] | + | ||
| West Mediterranean Sea (Italy), oral & cloacal swabs, Pseudomonas & Citrobacter spp, (n = 35). [42] | + | ||
| Leatherback (Dermochelys coriacea) | Juveniles & adults: Jellyfish, other soft-bodied animals, algae. | Atlantic Ocean (Gulf of Guinea, Principe Island), oral & cloacal swabs, Pseudomonas spp, (n = 10 Leatherback & n = 2 Green). [40] | - |
| Olive Ridley (Lepidochelys olivacea) | Juveniles & adults: Shrimp, crabs, clams, mussels, fish, squid. | Pacific Ocean (Sinaloa Mexico), nasopharyngeal & oral swabs, Vibrio spp, (n = 22). [44] | + |
| Hawksbill (Eretmochelys imbricate) | Juveniles and adults: Sponges, squid, shrimp, anemones. | Atlantic Ocean (South coast of Brazil), cloacal or rectal swabs, Enteroccus spp, (n = 2). [43] | + |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drane, K.; Huerlimann, R.; Power, M.; Whelan, A.; Ariel, E.; Sheehan, M.; Kinobe, R. Testudines as Sentinels for Monitoring the Dissemination of Antibiotic Resistance in Marine Environments: An Integrative Review. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10070775
Drane K, Huerlimann R, Power M, Whelan A, Ariel E, Sheehan M, Kinobe R. Testudines as Sentinels for Monitoring the Dissemination of Antibiotic Resistance in Marine Environments: An Integrative Review. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(7):775. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10070775
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrane, Kezia, Roger Huerlimann, Michelle Power, Anna Whelan, Ellen Ariel, Madoc Sheehan, and Robert Kinobe. 2021. "Testudines as Sentinels for Monitoring the Dissemination of Antibiotic Resistance in Marine Environments: An Integrative Review" Antibiotics 10, no. 7: 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10070775
APA StyleDrane, K., Huerlimann, R., Power, M., Whelan, A., Ariel, E., Sheehan, M., & Kinobe, R. (2021). Testudines as Sentinels for Monitoring the Dissemination of Antibiotic Resistance in Marine Environments: An Integrative Review. Antibiotics, 10(7), 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10070775






