Antimicrobial Resistance Determinants in Genomes and Plasmids from Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Isolates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
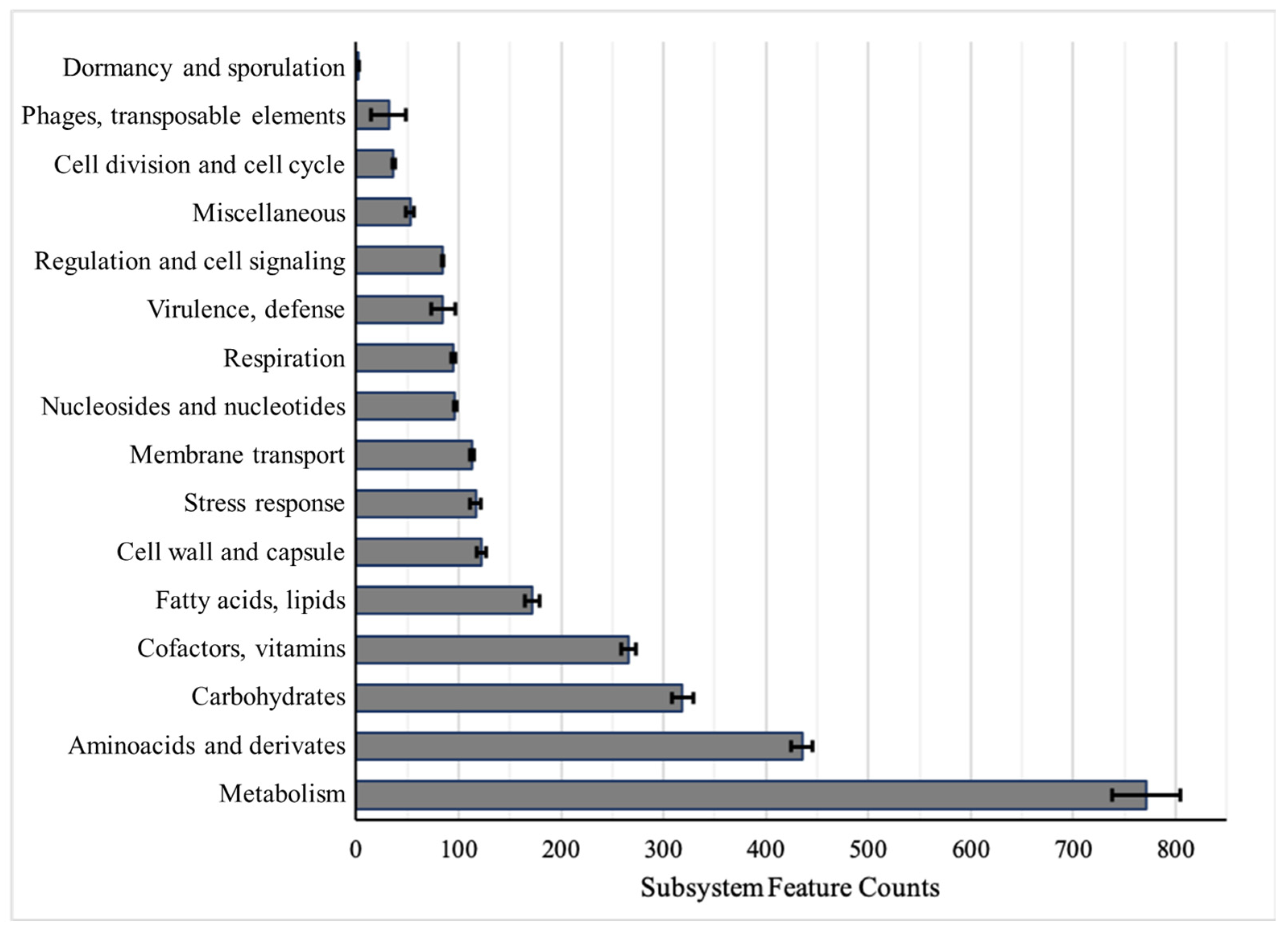
2.1. Genomic Annotations and Subsystem Categories
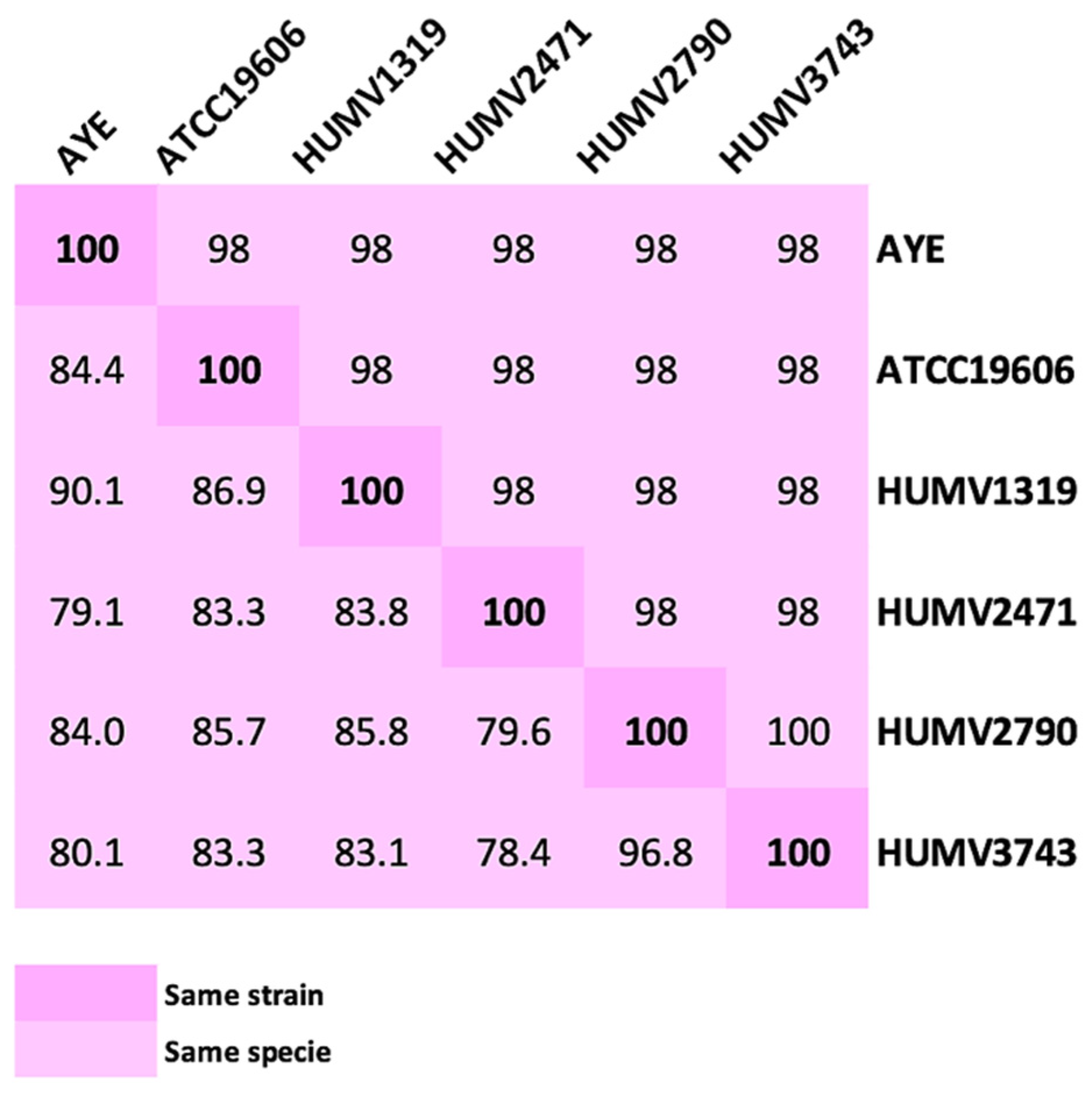
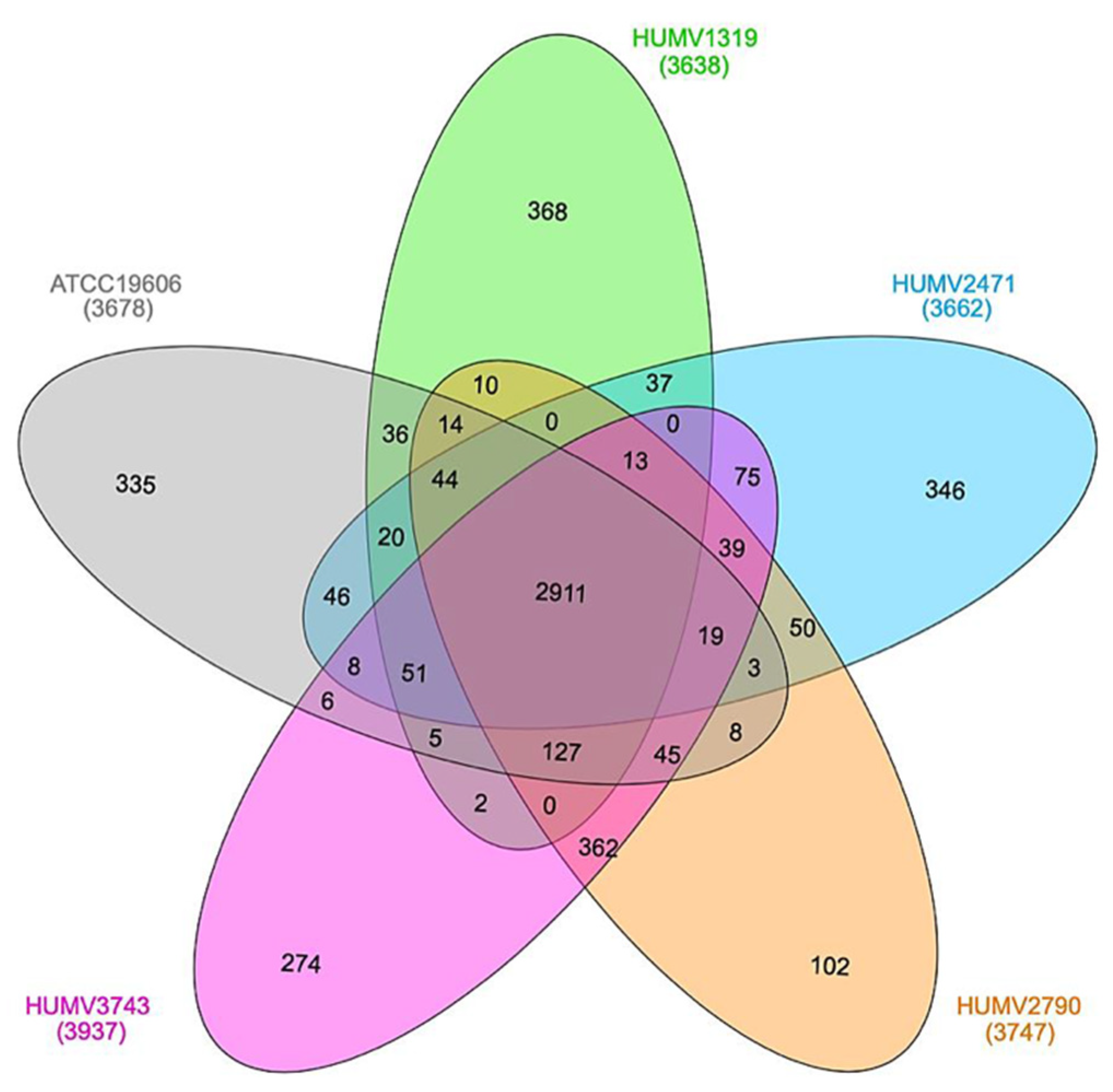
2.2. Strain Comparison and Pan-Genome Analysis
2.3. Susceptibility of A. baumannii to Antimicrobial Agents
2.4. Antimicrobial Resistance Determinants
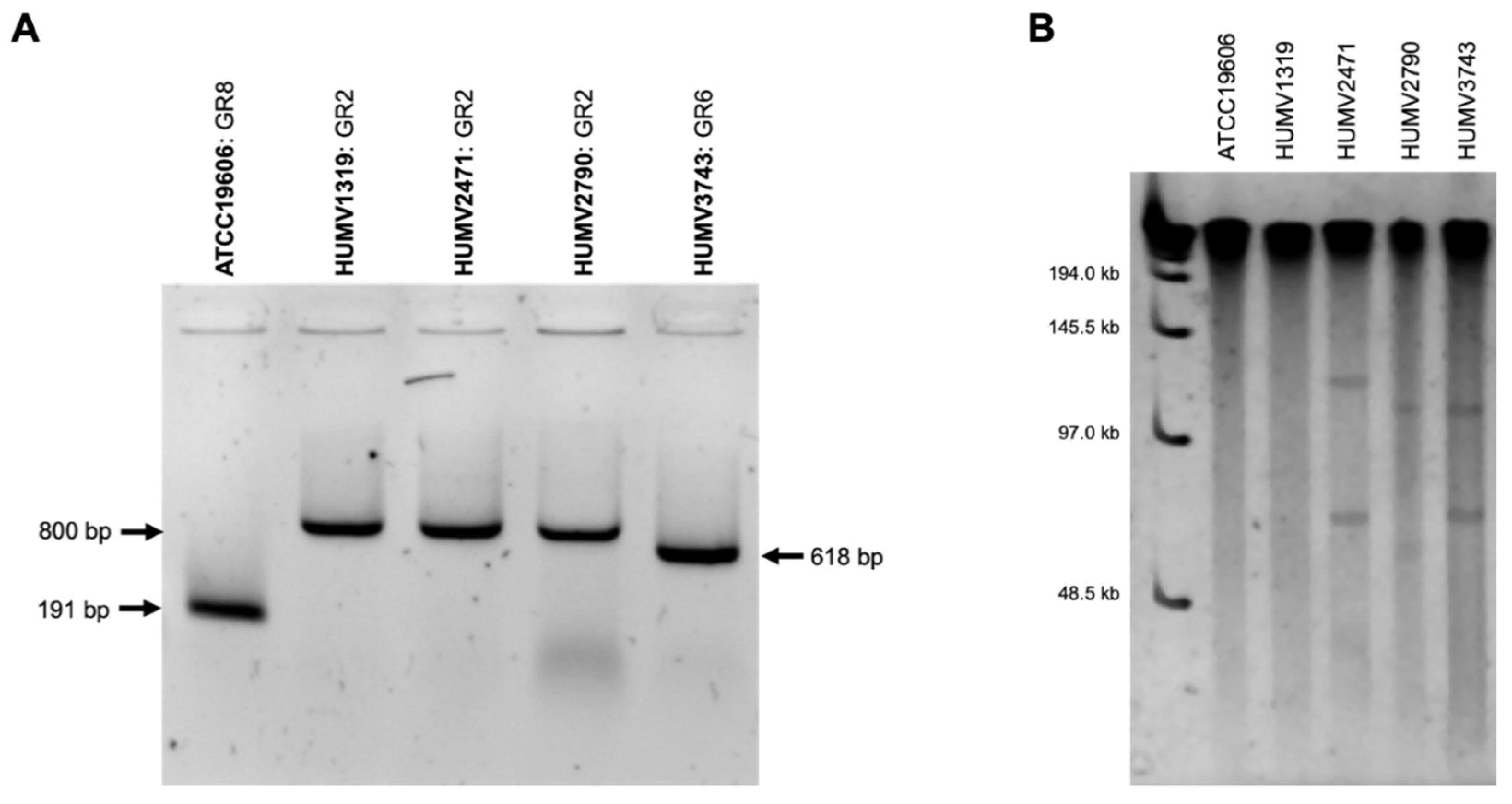
2.5. Plasmid Prediction and Analysis
2.6. Virulence Factors
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains
4.2. Antibiotic Susceptibility Assays
4.3. DNA Isolation and Sequencing
4.4. Genomic Assembly and Annotation
4.5. Plasmid Prediction and Identifications
4.6. Strain Comparison and Pan-Genome Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, S.N.; Khan, A.U. Breaking the Spell: Combating Multidrug Resistant ‘Superbugs’. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergogne-Bérézin, E.; Towner, K. Acinetobacter spp. as Nosocomial Pathogens: Microbiological, Clinical, and Epidemiological Features. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 9, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkshoorn, L.; Nemec, A.; Seifert, H. An increasing threat in hospitals: Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, P.; Paluchowska, P. Acinetobacter baumannii: Biology and drug resistance—Role of carbapenemases. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2016, 54, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Peleg, A.Y.; Seifert, H.; Paterson, D.L. Acinetobacter baumannii: Emergence of a Successful Pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 538–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, F.; Ponce-Terashima, R.; Adams, M.D.; Bonomo, R.A. Are we closing in on an “elusive enemy”? The current status of our battle with Acinetobacter baumannii. Virulence 2011, 2, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Z.; Livermore, D.M.; Nikaido, H. Role of efflux pump (s) in intrinsic resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Active efflux as a contributing factor to b-lactam resistance. Antimicrob. Agent Chemother. 1994, 38, 1732–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.; Nielsen, T.B.; Bonomo, R.A.; Pantapalangkoor, P.; Luna, B.; Spellberg, B. Clinical and Pathophysiological Overview of Acinetobacter Infections: A Century of Challenges. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 409–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia, R.; Arroyo, L.A.; Conde, M.; Aldana, J.M.; Torres, M.-J.; Fernández-Cuenca, F.; Garnacho-Montero, J.; Cisneros, J.M.; Ortiz, C.; Pachón, J.; et al. Nosocomial Outbreak of Infection With Pan-Drug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a Tertiary Care University Hospital. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2009, 30, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goic-Barisic, I.; Music, M.S.; Kovacic, A.; Tonkic, M.; Hrenovic, J. Pan Drug-Resistant Environmental Isolate of Acinetobacter baumannii from Croatia. Microb. Drug Resist. 2017, 23, 494–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lean, S.S.; Yeo, C.C. Small, Enigmatic Plasmids of the Nosocomial Pathogen, Acinetobacter baumannii: Good, Bad, Who Knows? Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partridge, S.R.; Kwong, S.M.; Firth, N.; Jensen, S.O. Mobile Genetic Elements Associated with Antimicrobial Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00088-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertini, A.; Poirel, L.; Mugnier, P.D.; Villa, L.; Nordmann, P.; Carattoli, A. Characterization and PCR-Based Replicon Typing of Resistance Plasmids in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4168–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, M.D.; Chan, E.R.; Molyneaux, N.D.; Bonomo, R.A. Genomewide Analysis of Divergence of Antibiotic Resistance Determinants in Closely Related Isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3569–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallenet, D.; Nordmann, P.; Barbe, V.; Poirel, L.; Mangenot, S.; Bataille, E.; Dossat, C.; Gas, S.; Kreimeyer, A.; Lenoble, P.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Acinetobacters: Three Genomes for Three Lifestyles. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subashchandrabose, S.; Smith, S.; DeOrnellas, V.; Crepin, S.; Kole, M.; Zahdeh, C.; Mobley, H.L.T. Acinetobacter baumannii Genes Required for Bacterial Survival during Bloodstream Infection. mSphere 2016, 1, e00013–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, A.Y.; de Breij, A.; Adams, M.D.; Cerqueira, G.M.; Mocali, S.; Galardini, M.; Nibbering, P.H.; Earl, A.; Ward, D.V.; Paterson, D.L.; et al. The Success of Acinetobacter Species; Genetic, Metabolic and Virulence Attributes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro-Díez, M.; Chapartegui-González, I.; Redondo-Salvo, S.; Leigh, C.; Merino, D.; Segundo, D.S.; Fernández, A.; Navas, J.; Icardo, J.M.; Acosta, F.; et al. Human neutrophils phagocytose and kill Acinetobacter baumannii and A. pittii. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro-Díez, M.; Chapartegui-González, I.; Suberbiola, B.; Ocejo-Vinyals, J.G.; López-Hoyos, M.; Ramos-Vivas, J. Gene expression profiling in human neutrophils after infection with Acinetobacter baumannii in vitro. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro-Díez, M.; Navascués-Lejarza, T.; Remuzgo-Martínez, S.; Navas, J.; Icardo, J.M.; Acosta, F.; Martìnez-Martìnez, L.; Ramos-Vivas, J. Acinetobacter baumannii and A. pittii clinical isolates lack adherence and cytotoxicity to lung epithelial cells in vitro. Microbes Infect. 2016, 18, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapartegui-González, I.; Lázaro-Díez, M.; Bravo, Z.; Navas, J.; Icardo, J.M.; Ramos-Vivas, J. Acinetobacter baumannii maintains its virulence after long-time starvation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 8.1. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 1 June 2018).
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 28th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standars Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018; ISBN 1-56238-838. [Google Scholar]
- Lean, S.-S.; Yeo, C.C.; Suhaili, Z.; Thong, K.-L. Comparative Genomics of Two ST 195 Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii with Different Susceptibility to Polymyxin Revealed Underlying Resistance Mechanism. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahl, J.W.; Gillece, J.D.; Schupp, J.M.; Waddell, V.G.; Driebe, E.M.; Engelthaler, D.M.; Keim, P. Evolution of a Pathogen: A Comparative Genomics Analysis Identifies a Genetic Pathway to Pathogenesis in Acinetobacter. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancilla-Rojano, J.; Castro-Jaimes, S.; Ochoa, S.A.; Bobadilla del Valle, M.; Luna-Pineda, V.M.; Bustos, P.; Laris-González, A.; Arellano-Galindo, J.; Parra-Ortega, I.; Hernández-Castro, R.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequences of Five Acinetobacter baumannii Strains From a Child With Leukemia M2. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.-F.; Lan, C.-Y. Antimicrobial resistance inAcinetobacter baumannii: From bench to bedside. World J. Clin. Cases 2014, 2, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, A.G.; Waglechner, N.; Nizam, F.; Yan, A.; Azad, M.A.; Baylay, A.J.; Bhullar, K.; Canova, M.J.; De Pascale, G.; Ejim, L.; et al. The Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 3348–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid Prokaryotic Genome Annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, N.C.; Wareham, D.W. Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: Mechanisms of virulence and resistance. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 35, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, I.; Espinal, P.; Vila-Farrés, X.; Vila Estapé, J. The Acinetobacter baumannii Oxymoron: Commensal Hospital Dweller Turned Pan-Drug-Resistant Menace. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, S.E.; Deshpande, L.M.; Davis, A.P.; Mendes, R.E.; Castanheira, M. Aminoglycoside-modifying enzyme and 16S ribosomal RNA methyltransferase genes among a global collection of Gram-negative isolates. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 16, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boo, T.W.; Walsh, F.; Crowley, B. Molecular characterization of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter species in an Irish university hospital: Predominance of Acinetobacter genomic species 3. J. Med Microbiol. 2009, 58, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, W.; Zhang, X.; Hou, M.; Han, D.; Li, Y.; Xiong, W. Draft genome sequence of an OXA-23, OXA-66, ADC-25 and TEM-1D co-producing Acinetobacter baumannii ST195 isolated from a patient with neonatal pneumonia in China. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 16, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumbo, C.; Fernández-Moreira, E.; Merino, M.; Poza, M.; Mendez, J.A.; Soares, N.C.; Mosquera, A.; Chaves, F.; Bou, G. Horizontal Transfer of the OXA-24 Carbapenemase Gene via Outer Membrane Vesicles: A New Mechanism of Dissemination of Carbapenem Resistance Genes in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3084–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, Y.; Murray, G.L.; Peleg, A.Y. Acinetobacter baumannii: Evolution of Antimicrobial Resistance—Treatment Options. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 36, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamsizadeh, Z.; Nikaeen, M.; Esfahani, B.N.; Mirhoseini, S.H.; Hatamzadeh, M.; Hassanzadeh, A. Detection of antibiotic resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in various hospital environments: Potential sources for transmission of Acinetobacter infections. Environ. Heal. Prev. Med. 2017, 22, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila, J.; Ruiz, J.; Goni, P.; Marcos, A.; Jimenez de Anta, T. Mutation in the gyrA gene of quinolone-resistant clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 1201–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, J.; Ruiz, J.; Goni, P.; De Anta, T.J. Quinolone-resistance mutations in the topoisomerase IV parC gene of Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1997, 39, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.P.; Sutton, G.; DePew, J.; Krishnakumar, R.; Choi, Y.; Huang, X.-Z.; Beck, E.; Harkins, D.M.; Kim, M.; Lesho, E.P.; et al. A novel method of consensus pan-chromosome assembly and large-scale comparative analysis reveal the highly flexible pan-genome of Acinetobacter baumannii. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, K.; Kenyon, J.J.; Hamidian, M.; Schultz, M.B.; Pickard, D.J.; Dougan, G.; Hall, R. Five decades of genome evolution in the globally distributed, extensively antibiotic-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii global clone 1. Microb. Genom. 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrer, L.; Khodursky, R.F.; Johnson, J.R.; Hiasa, H.; Khodursky, A. Analysis of mutational patterns in quinolone resistance-determining regions of GyrA and ParC of clinical isolates. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 53, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhu, N.T.K.; Riordan, D.W.; Nhu, T.D.H.; Thanh, D.P.; Thwaites, G.; Lan, N.P.H.; Wren, B.W.; Baker, S.; Stabler, R.A. The induction and identification of novel Colistin resistance mutations in Acinetobacter baumannii and their implications. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Walsh, T.R.; Yi, L.-X.; Zhang, R.; Spencer, J.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.; Dong, B.; Huang, X.; et al. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: A microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyne, S.; Courvalin, P.; Périchon, B. Efflux-Mediated Antibiotic Resistance in Acinetobacter spp. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Wang-Kan, X.; Neuberger, A.; van Veen, H.W.; Pos, K.M.; Piddock, L.J.V.; Luisi, B.F. Multidrug efflux pumps: Structure, function and regulation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.D.; Goglin, K.; Molyneaux, N.; Hujer, K.M.; Lavender, H.; Jamison, J.J.; MacDonald, I.J.; Martin, K.M.; Russo, T.; Campagnari, A.A.; et al. Comparative Genome Sequence Analysis of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 8053–8064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahl, J.W.; Johnson, J.K.; Harris, A.D.; Phillippy, A.M.; Hsiao, W.W.; Thom, K.A.; Rasko, D.A. Genomic comparison of multi-drug resistant invasive and colonizing Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from diverse human body sites reveals genomic plasticity. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, M.S.; Haft, D.H.; Harkins, D.M.; Perez, F.; Hujer, K.M.; Bajaksouzian, S.; Benard, M.F.; Jacobs, M.R.; Bonomo, R.A.; Adams, M.D. New Insights into Dissemination and Variation of the Health Care-Associated Pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii from Genomic Analysis. mBio 2014, 5, e00963-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nocera, P.P.; Rocco, F.; Giannouli, M.; Triassi, M.; Zarrilli, R. Genome organization of epidemic Acinetobacter baumannii strains. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouts, D.E.; Brinkac, L.; Beck, E.; Inman, J.; Sutton, G. PanOCT: Automated clustering of orthologs using conserved gene neighborhood for pan-genomic analysis of bacterial strains and closely related species. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heberle, H.; Meirelles, G.V.; da Silva, F.R.; Telles, G.P.; Minghim, R. InteractiVenn: A web-based tool for the analysis of sets through Venn diagrams. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T. The enveomics collection: A toolbox for specialized analyses of microbial genomes and metagenomes. Peer J. Prepr. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Auch, A.F.; Klenk, H.-P.; Göker, M. Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Dong, Y.; Yang, Z.-L.; Luo, H.; Zhang, X.; Gao, F. Complete Sequence of pABTJ2, A Plasmid from Acinetobacter baumannii MDR-TJ, Carrying Many Phage-like Elements. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2014, 12, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Millan, A.; MacLean, R.C. Fitness Costs of Plasmids: A Limit to Plasmid Transmission. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touchon, M.; Cury, J.; Yoon, E.-J.; Krizova, L.; Cerqueira, G.C.; Murphy, C.; Feldgarden, M.; Wortman, J.; Clermont, D.; Lambert, T.; et al. The Genomic Diversification of the Whole Acinetobacter Genus: Origins, Mechanisms, and Consequences. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 6, 2866–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vielva, L.; de Toro, M.; Lanza, V.F.; de la Cruz, F. PLACNETw: A web-based tool for plasmid reconstruction from bacterial genomes. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3796–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsey, C.W.; Tomaras, A.P.; Actis, L.A. Sequence and organization of pMAC, an Acinetobacter baumannii plasmid harboring genes involved in organic peroxide resistance. Plasmid 2006, 56, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; Mcgettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST.org website and their applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.; Blin, K.; Duddela, S.; Krug, D.; Kim, H.U.; Bruccoleri, R.; Lee, S.Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; Müller, R.; Wohlleben, W.; et al. AntiSMASH 3.0—A comprehensive resource for the genome mining of biosynthetic gene clusters. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W237–W243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zankari, E.; Hasman, H.; Cosentino, S.; Vestergaard, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Larsen, M.V. Identification of acquired antimicrobial resistance genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, L.J.; Julien, P.; Kuhn, M.; von Mering, C.; Muller, J.; Doerks, T.; Bork, P. eggNOG: Automated construction and annotation of orthologous groups of genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 36, D250–D254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, S.; Forslund, K.; Szklarczyk, D.; Trachana, K.; Roth, A.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Gabaldón, T.; Rattei, T.; Creevey, C.; Kuhn, M.; et al. eggNOG v4.0: Nested orthology inference across 3686 organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D231–D239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Strains | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATCC19606 | HUMV1319 | HUMV2471 | HUMV2790 | HUMV3743 | ||
| Contigs | 96 | 110 | 108 | 118 | 176 | |
| Size (bp) | 3,914,294 | 3,916,888 | 3,810,872 | 3,935,804 | 4,006,761 | |
| % GC | 39.1 | 39 | 38.9 | 39 | 39 | |
| Subsystems | 462 | 451 | 453 | 453 | 451 | |
| CDS | RAST | 3689 | 3703 | 3556 | 3706 | 3882 |
| Prokka | 3667 | 3680 | 3542 | 3689 | 3886 | |
| tRNA | 64 | 63 | 64 | 62 | 63 | |
| mRNA | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| rRNA | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | |
| MLST | Oxford | ST921 | ST106 | ST350 | ST218 | |
| Pasteur | ST52 | ST3 | ST49 | ST2 | ST2 | |
| COL | MER | AMP * | GEN | CIP | TET ** | ERY | Resistance Profile | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC | ATCC19606 | 2 | 4 | >64 | 4 | >0.25 | 1 | >128 | MAE |
| HUMV1319 | 2 | >16 | >64 | >128 | >4 | 8 | >128 | MAGPTE | |
| HUMV2471 | 2 | >16 | >64 | >128 | >4 | 16 | 32 | MAGPTE | |
| HUMV2790 | 8 | 4 | >64 | 8 | >4 | >32 | >128 | CMAGPTE | |
| HUMV3743 | 4 | >16 | >64 | >128 | >4 | >32 | 64 | CMAGPTE | |
| MIC50 | 2 | >16 | >64 | >32 | >4 | 16 | >128 | ||
| MIC90 | >8 | >16 | >64 | >32 | >4 | >32 | >128 | ||
| Range (mg/L) | 0.125–8 | 0.25–16 | 1–64 | 0.5–32 | 0.06–4 | 0.5–32 | 2–128 |
| STRAINS | ANTIMICROBIAL CLASSES RESISTANCE GENES | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMINOGLYCOSIDES | β-LACTAM | SULFONAMIDES | ||
| ampC | OXA | |||
| ATCC19606 | ant(3′’)-IIa | ADC-2 | OXA-51 (98) | sul |
| OXA-51 (386) | ||||
| HUMV1319 | aac(6’)-Ib’ | ADC-7 | OXA-24 OXA-51 (71) OXA-51 (385) | sul |
| ant(2’’)-Ia | ||||
| ant(3’’)-IIa | ||||
| aph(3’)-VI | ||||
| aph(3’)-VIa | ||||
| HUMV2471 | ant(2’’)-Ia ant(3’’)-IIa | ADC-39 | OXA-24 | |
| OXA-51 (98) | ||||
| OXA-51 (386) | ||||
| HUMV2790 | ant(3’’)-IIa aph(3’’)-Ib aph(6)-Id | ADC-25 | OXA-51 (66) OXA-51 (109) | sul |
| HUMV3743 | aac(3)-IIa ant(3’’)-IIa aph(3’’)-Ib aph(3’)-VIa aph(6)-Id | ADC-25 | OXA-51 (66) OXA-51 (109) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chapartegui-González, I.; Lázaro-Díez, M.; Redondo-Salvo, S.; Navas, J.; Ramos-Vivas, J. Antimicrobial Resistance Determinants in Genomes and Plasmids from Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Isolates. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10070753
Chapartegui-González I, Lázaro-Díez M, Redondo-Salvo S, Navas J, Ramos-Vivas J. Antimicrobial Resistance Determinants in Genomes and Plasmids from Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Isolates. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(7):753. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10070753
Chicago/Turabian StyleChapartegui-González, Itziar, María Lázaro-Díez, Santiago Redondo-Salvo, Jesús Navas, and José Ramos-Vivas. 2021. "Antimicrobial Resistance Determinants in Genomes and Plasmids from Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Isolates" Antibiotics 10, no. 7: 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10070753
APA StyleChapartegui-González, I., Lázaro-Díez, M., Redondo-Salvo, S., Navas, J., & Ramos-Vivas, J. (2021). Antimicrobial Resistance Determinants in Genomes and Plasmids from Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Isolates. Antibiotics, 10(7), 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10070753









