Abstract
Antibiotic-resistant Enterobacteriaceae are regularly detected in livestock. As pathogens, they cause difficult-to-treat infections and, as commensals, they may serve as a source of resistance genes for other bacteria. Slaughterhouses produce significant amounts of wastewater containing antimicrobial-resistant bacteria (AMRB), which are released into the environment. We analyzed the wastewater from seven slaughterhouses (pig and poultry) for extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-carrying and colistin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. AMRB were regularly detected in pig and poultry slaughterhouse wastewaters monitored here. All 25 ESBL-producing bacterial strains (19 E. coli and six K. pneumoniae) isolated from poultry slaughterhouses were multidrug-resistant. In pig slaughterhouses 64% (12 of 21 E. coli [57%] and all four detected K. pneumoniae [100%]) were multidrug-resistant. Regarding colistin, resistant Enterobacteriaceae were detected in 54% of poultry and 21% of pig water samples. Carbapenem resistance was not detected. Resistant bacteria were found directly during discharge of wastewaters from abattoirs into water bodies highlighting the role of slaughterhouses for environmental surface water contamination.
1. Introduction
Antimicrobials are essential to treat bacterial infections. The emergence and spread of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) has been recognized globally as a serious threat to public health [1]. Moreover, antimicrobial consumption can lead to alterations in the human microbiota and select for antimicrobial-resistant bacteria (AMRB). AMRB and partially metabolized antimicrobials are excreted into the wastewater with urine and feces and may end up in surface waters and cropland via the sewage system [2].
Among the most critical antibiotic-resistant bacteria, extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Enterobacterales are listed on the WHO’s “Global priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria to guide research, discovery and development of new antibiotics” [3]. ESBL-producing bacteria excrete enzymes that hydrolyze 3rd- and 4th-generation cephalosporins, such as cefotaxime, and were described for the first time in 1983 [4]. There are different ESBL variants. The first were TEM and SHV. The prevalence of these enzymes has since declined, while at the same time isolates producing CTX-M-type β-lactamases have spread worldwide. ESBL are plasmid mediated [5]. ESBL-producing Enterobacterales show a high zoonotic potential [3].
Industrial agriculture, in its present form, relies heavily on the widespread use of antimicrobials to improve animal health, welfare and productivity. Antimicrobials are administered to livestock either as therapeutics (to treat individual animals) or in a metaphylactic approach, i.e., the presence of clinical illness in a small number of animals triggers drug administration of the whole herd or flock [6].
Although an overall decline in sales of veterinary antibiotics could be observed between 2011 and 2018 [7], the broad administration of antibiotic substances—for example in pig husbandry—is still ongoing. Tetracyclines, amoxicillin, macrolides and colistin are most frequently used in pork production. Studies reported in the German poultry sector indicated that broilers treated for 10 days with one active compound within their 39-day production period in 2011 [8] and between 2014 and 2017 showed no change of antimicrobial usage [9].
Of particular concern is the emergence of 3MRGN, i.e., Gram-negative bacteria that are resistant against three of the most important antimicrobial classes. They occur not only in healthcare settings [10], but also in poultry [11,12] and swine production chains [13]. In addition, Enterobacterales often carry mobilizable colistin resistance (mcr) genes [14,15]. Colistin resistance is of particular importance, as the agent had to be reintroduced into human medicine—despite nephrotoxic and neurotoxic properties—for therapy of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae [16]. Consequently, the WHO included colistin into the group of the “highest priority critically important antimicrobials” for human medicine [17].
Throughout our manuscript, isolates exhibiting resistance to at least three antimicrobial classes are considered to be multidrug-resistant (MDR).
In 2017, more than 1.5 million tons of poultry and almost 5.5 million tons of pigs were slaughtered in Germany [18]. The slaughtering process produces large amounts of wastewater, potentially contaminated with bacteria resistant against antimicrobials (several 1000 L per 1000 kg live weight) [19]. In this regard, wastewater represents a source for environmental pollution with antibiotic-resistant/MDR bacteria, possibly driven by inadequate treatment in the in-house wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) [20].
The aim of this study was to evaluate the occurrence and diversity of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria (Enterobacterales and Staphylococcus aureus) in wastewater of seven slaughterhouses at two time points. Besides species identification, molecular similarity analyses and phenotypic resistance testing were performed. In addition, whole-genome sequencing and bioinformatics analysis were carried out for selected isolates.
2. Results
2.1. Isolates
For the two sampling time points and all slaughterhouse wastewater outlets, bacterial growth was detected on CHROMID ESBL plates. Growth on the colistin plates was present for all samples obtained in November, but only for two in December (Table 1).

Table 1.
Growth on selective media.
No growth was detected on the culture media specific for MRSA nor for carbapenem-resistant bacteria (NDM/OXA-48) (Table 1). According to color and morphology of the colonies, Escherichia (E.) coli, Klebsiella (K.) spp., Enterobacter (E.) spp. and Citrobacter (C.) spp. suspect colonies were subcultured, and in total, 55 isolates were further analyzed in the VITEK2 MS system (Table 2).

Table 2.
Bacteria with antimicrobial resistance confirmed by Vitek 2 MS and selective media of origin.
Putative ESBL-producing E. coli isolates were found at both time points from all slaughterhouse wastewater samples. Putative ESBL-producing K. pneumoniae isolates were found in four of seven samples collected in November and only in two of six samples obtained in December (57% and 33%, respectively). On the colistin-containing media, E. coli grew in three of seven November samples and only from one slaughterhouse (F) in December. Putative colistin-resistant K. pneumoniae colonies were present only in the samples from slaughterhouse D in November. Moreover, in November, two Raoultella (R.) ornithinolytica isolates were detected in samples from slaughterhouse A. In two samples from November (slaughterhouses E and G) E. cloacae was detected. In December, no samples at all were obtained from slaughterhouse G due to operational reasons (Table 2).
2.2. Similarity Analysis
Based on RAPD, different patterns (“fingerprints”) were detected for the isolates from samples of different slaughterhouse effluents. By contrast, highly similar patterns were regularly found for bacterial isolates from the same slaughterhouse samples at the individual sampling times. Highly similar patterns were shared between the duplicate samples as well as between samples originating from different selective plates (ESBL and COLISTIN). This was most pronounced for E. coli from slaughterhouse F, with four of five E. coli showing highly similar patterns (Figure 1). Note, however, that no consistent patterns were evident for bacterial isolates between the two sampling points.
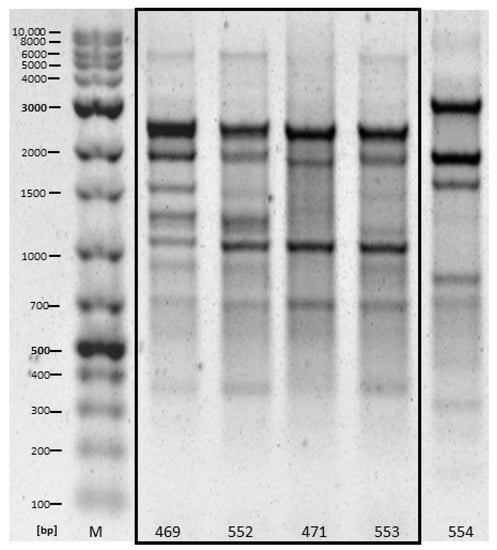
Figure 1.
RAPD patterns of five E. coli isolates obtained from slaughterhouse D in November 2020, highly similar patterns are framed by the box. Samples 469 and 471 originated from COLISTIN plates (duplicate 1 and 2, respectively), while 552 and 553 originated from ESBL plates (duplicate 1 and 2, respectively). Sample 554 originated from an ESBL plate of duplicate 2.
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST)
Except for the two R. ornithinolytica strains, all isolates were resistant to piperacillin. Furthermore, the majority of isolates were additionally resistant to the 2nd- and 3rd-Gen cephalosporins cefuroxime (95% [n = 52]), cefotaxime (89% [n = 49]) and ceftazidime (95% [n = 52]). Twenty-nine isolates were resistant to ciprofloxacin (53%), while five isolates (9%) were resistant to gentamicin and 26 (47%) were resistant to tetracycline. All isolates were susceptible to meropenem and imipenem. Twenty (36%) isolates exhibited a resistance against colistin, which is a last-resort antibiotic. It is noticeable that 43 (78%) of 55 isolates examined exhibited resistance against three or more antimicrobial classes and can, therefore, be specified as phenotypically multidrug-resistant (MDR). For all K. pneumoniae (n = 10) and 31 E. coli (78%) isolates, a MDR phenotype was determined, respectively. Twenty-three MDR E. coli were obtained in November 2020, while eight were isolated in December 2020. Similarly, MDR K. pneumoniae were mainly obtained in November (seven isolates vs. three isolates in December). Details are given in Table 3.

Table 3.
Results of the VITEK2 MS (species allocation), phenotypic resistance profiles of 55 putative ESBL-producing isolates and derived confirmation of an ESBL production as well as MDR status. Sampling months were November (N) and December (D) 2020. Selective media of origin were ESBL (E) and COLISTIN (C). Isolates subjected to whole genome sequencing are indicated with asterisks.
2.4. Whole-Genome Sequencing
Two different phylotypes were identified among the three whole-genome sequenced E. coli isolates. The isolates with the numbers 469 and 472 belong to phylotype A and the isolate 622 to phylotype B1. The following sequence types (ST) appeared: E. coli: ST4981 (isolates 469, 472) and ST533 (isolate 622); K. pneumoniae: ST29 (isolate 558); C. freundii: ST248 (isolate 620). Genes encoding for various proteins associated with antibiotic resistance, e.g., blaCTX-M-15, tet(34) and mcr-1.1, were detected, thus matching our phenotypic findings. To further compare phenotypic and genotypic resistance data, the antibiotic classes aminoglycosides, β-lactams and polypeptides (colistin) were included in our subsequent analysis (Figure 2). For colistin resistance, our pheno- and genotypic results concorded. Possessors of mcr-1.1 (numbers: 469; 472; 622) were phenotypically colistin-resistant, whereas bacteria without the resistance gene (numbers: 558; 620) were susceptible. Similarly, different genes encoding β-lactam resistance, such as blaCTX-M-15, blaTEM-181 and blaSHV-187 occurred. Phenotypically, all five isolates were resistant against β-lactam antibiotics. In addition, various resistance genes encoding for multiple drug resistance were found (e.g., marA, tolC, emrK).
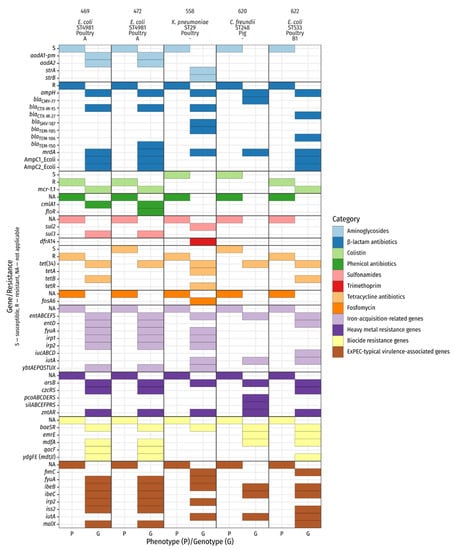
Figure 2.
Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of sequenced isolates. Genotypic data represent selected results from ABRicate (ARG-ANNOT, BacMet, Ecoli_VF). The header lists isolate number, species, sequence type, origin of isolation, and E. coli phylotype. mrdA is annotated as Penicillin_Binding_Protein_Ecoli in the ARG-ANNOT database.
To gain insight into the virulence of the selected isolate, we investigated virulence-associated genes related to pathogenic bacteria. The main focus laid on hypermucoviscosity, iron acquisition and resistance against heavy metals and biocides. In relation to hypermucoviscosity, we found rmp, which is associated with hypermucoviscosity and different genes which play a role in iron re-uptake, such as yersiniabactin, enterobactin, and aerobactin synthesis (irp1, irp2, fyuA, ybtAEPQSTUX (469, 472, 558), entABCDEFS (all isolates; but 558 and 620 missing entD), and iucABCD (622), iutA (558, 620, 622)). Furthermore, we noticed genes conferring resistance against heavy metals (zntAR, arsB (all isolates), czc system (469, 472, 622), pcoABCDERS (620), silABCEFPRS (620)) and biocides (emrE (620, 622), mdfA (469, 472, 620, 622), ydgEF(mdtJI) (469, 472, 622), qacF (469, 472), baeSR (all isolates)) transpired. We detected several extra-intestinal pathogenic E. coli (ExPEC)-typical virulence-associated genes e.g., iutA (558, 620,622), fimC (558, 622), fyuA (469, 472, 558) and irp2 (469, 472, 522). Some of them were present in all three E. coli isolates (malX, ibeB/C, iss2) (details are given in Figure 2).
3. Discussion
We investigated wastewater from seven German slaughterhouses at two time points for the occurrence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Our results clearly demonstrate that these germs are present in wastewater, and thus may lead to contamination of downstream water bodies and agricultural settings. Since antibiotic-resistant bacteria apparently survive the passage through the in-slaughterhouse treatment plant, the procedure may not be suitable to prevent bacterial spill-over effects into the environment.
The presence of enterobacteria in wastewater is not surprising as most of them are part of the healthy animal microbiota and are able to colonize the gastrointestinal tract. Savin et al. recently demonstrated the presence of such bacteria in two German poultry and pig slaughterhouses. The authors examined water samples along the process chain for ESBL-producing Enterobacterales and colistin-resistant bacteria in two poultry and two pork slaughterhouses. They found the respective pathogens on all levels [13,14,20,21]. Note, however, that in this study, only a small proportion of the investigated isolates originated from wastewater. Here, we received a total of 55 ESBL-carrying or colistin-resistant isolates.
Two sources for the isolated pathogens can be considered. On the one hand, a slaughterhouse-specific microbial flora could have established itself, from which bacteria are continuously washed off and released into the environment. On the other hand, the microorganisms could originate from the animals currently slaughtered. To test this, we compared the isolates from the two time points of the respective slaughterhouses. The fact that RAPD analysis regularly revealed highly similar patterns within a sampling location at one sampling time point, but never disclosed matches in patterns between sampling events at one location may suggest that the slaughtered animal species is crucial to the bacterial composition of the wastewater released by the abattoir.
3.1. Resistance Data
Overall, we detected high levels of MDR bacteria in all slaughterhouse wastewater samples. All K. pneumoniae isolates were multidrug-resistant and 78% of E. coli samples demonstrated such phenotypes. In wastewater samples from poultry slaughterhouses, we found 100% of 25 examined isolates to be MDR (19 E. coli and six K. pneumoniae), i.e., isolates exhibited resistance against three or more antimicrobial classes. Thus, our results match recently published findings, reporting a similarly high level of MDR bacteria overall [13,14,20,21].
Of 25 E. coli and K. pneumoniae isolates in wastewater samples from four pig slaughterhouses, 64% were MDR. For E. coli 57% (12 of 21) isolates exhibited a MDR phenotype, and thus, we can confirm the results of Savin et al. [21]. To the best of our knowledge, we provide here data on the occurrence of MDR K. pneumoniae in wastewater from German pig slaughterhouses for the first time. All K. pneumoniae isolates investigated were MDR (n = 4). The significantly lower proportion of MDR bacteria in wastewater from pig slaughterhouses in our study may be due to the lower frequency of antibiotic treatment in pigs [7,8,9,22].
All isolates were susceptible to the carbapenems meropenem and imipenem. Studies from Asia and Africa report high levels of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales [23,24]. These findings are not surprising, since carbapenems are not approved for use in livestock in the European Union (EU) and similar results have been reported by others (reviewed in [25]). In contrast, 20 of the 55 examined isolates (36%) exhibited resistance against colistin, which is a last-resort antibiotic for humans. Colistin has been used in veterinary medicine in recent decades in the EU, leading to selective pressure and the evolution of colistin-resistant bacteria [26]. Colistin is predominantly used in pig and cattle production to control enteric infections caused by E. coli and Salmonella or for metaphylactic treatment [27,28], while for the poultry sector, there are no relevant indications other than colibacillosis [29]. Similar to the prevalence of MDR bacteria, differences in the proportions of colistin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae between samples from poultry and swine slaughterhouses were observed. For 25 pig slaughterhouse isolates (21 E. coli and four K. pneumoniae) 16% (n = 4) were colistin-resistant (one E. coli and three K. pneumoniae), while of 25 analyzed poultry slaughterhouse isolates, 56% (n = 14) were resistant against this last-resort antibiotic. Both values are significantly higher than those previously reported for the pig and poultry sectors, respectively. Irrgang et al. published colistin resistance data for E. coli isolates between 2010 and 2015 of about 5% in broilers, 10% in turkeys and approx. 3% in pigs [30]. However, in a recently published study by Savin et al., similar orders of magnitude of colistin-resistant E. coli along the slaughterhouse process chain (pig: 45.0%, poultry: 52.8%) were reported. The authors mention that this might be due to co-selection through other antimicrobials that are often used in pigs, e.g., macrolides, lincosamides and tetracyclines or a linkage to their selective isolation procedure [21].
3.2. Sequencing Data
Analysis of the whole-genome sequence data revealed broad agreement of phenotypic and genotypic results. For the phenotypic resistances observed, genotypic resistance determinants were always found as well (Figure 2). Details of the individual whole-genome sequenced E. coli are summarized below.
E. coli ST4981
In a recent investigation of irrigation water in Switzerland with a focus on antibiotic-resistant bacteria, ESBL-producing E. coli of sequence type ST4981 were detected, among others [31]. For this ST, only the virulence genes gad (glutamate decarboxylase) and iss (increased serum survival) were detected. These two virulence factors were also present in our two whole-genome sequenced ST4981 isolates in addition to others (Figure 2). Additionally, blaCTX-M-15 was detected in all isolates. CTX-M-15 has been reported globally in all major ecological niches (humans, animals, and environment). CTX-M-15 is an excellent example for the public health threat that involves the circulation of resistant Enterobacterales in different ecological niches in the “One Health” context [32]. The combination of ST4981 and CTX-M-15-carrying E. coli has already been detected in fecal samples from piglets with diarrhea [33]. Both of our isolates belonged to phylogroup A, which is predominantly associated with commensal E. coli [34].
E. coli ST533
In 2009, Bonnedahl et al. detected ST533 in a sample of “offshore” gulls [35]. The authors conclude that higher resistance levels in “city-dump” gulls can be explained by greater exposure to human activities, especially higher antibiotic pressure. In a study of ESBL/AmpC-producing E. coli obtained along the poultry chain between 2008 und 2013, two isolates of sequence type ST533 were found.
ST533 was also detected as part of a study of urine samples from dogs and cats in Switzerland. Like the ST533 isolate of the present study, the corresponding isolate was assigned to phylogroup B1 (commonly associated with commensal strains [34]) and carried a bla gene of the CTX-M type, too. However, unlike the present isolate, it was CTX-M-15 [36]. blaCTX-M-27 is a CTX-M type that has recently been found increasingly. It is present in humans, animals, and environment, especially in E. coli ST131 [37,38,39,40] and also in the ST533 isolate of the present study. Interestingly, occurrence of CTX-M-27 has been reported in a study on ESBL-producers in slaughterhouse workers. Dohmen et al. found CTX-M-27 in combination with plasmid rep/inc-types IncFIA-FIB-FII [41], thus matching our findings (IncFIA-FIB-FII).
K. pneumoniae ST29
Sequence type 29 has already been identified in K. pneumoniae in several studies in different regions of the world in samples of animal origin. These include slaughterhouse effluents in Pakistan [23] and poultry meat imported from the Netherlands in Ghana [24]. In the Pakistan study, nearly 10% of K. pneumoniae isolates were carbapenem-resistant, and ST29 accounted for over 50%. However, all isolates were colistin-sensitive. In the Ghanaian study, all K. pneumoniae isolates were carbapenem-sensitive regardless of their origin (predominantly The Netherlands, Brazil, and the U.S.). The ST29 isolate of the present study, like the ST29 representatives of the above studies, carried a bla gene of CTX-M-15 type and was carbapenem-sensitive, like the Ghanaian (Dutch) isolate. However, it showed phenotypical and genotypical colistin resistance, which was not addressed in the Ghanaian study.
Hypervirulence in K. pneumoniae (hvKP) has been reported worldwide as a contributor to serious infections and outcomes in pathogens, both in hospitals and the community [42] and is often accompanied with a hypermucoviscous phenotype that confers resistance to phagocytosis and intracellular killing [43]. Moura et al. reported a ST29 isolate exhibiting a hypermucoviscous phenotype. In addition, in that strain, the same plasmids replicons as in the ST29 isolate of the present study were detected (IncFII and IncFIB) [44]. Therefore, we decided to perform a hypermucoviscosity test with all K. pneumoniae isolates. However, none of our isolates exhibited a hypermucoviscous phenotype.
C. freundii ST248
The C. freundii isolate in the present study had only a few resistance determinants (blaCMY-77, qnrB18). So far, no reports are available linking this ST to clinical manifestations or remarkable resistance traits. Only in a study from China—dealing with carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae—was this ST detected. However, the C. freundii ST248 isolates in that study were carbapenem-susceptible [45].
3.3. Wastewater Treatment
According to the Directive 2010/75/EU of the European Union on industrial emissions (integrated pollution prevention and control), the use of best available techniques is prescribed for the treatment of wastewater and according to Decision (EU) 2016/902 of the European Union [46], this means that the following requirements are imposed on the wastewater for the point of discharge into the water body: Biochemical Oxygen Demand in 5 days (BOD5), Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD), Ammonium Nitrogen (NH4-N), Total Nitrogen and Total Phosphorus. Microbiological requirements are not specified.
Recently, Pärnänen et al. showed that wastewater treatment decreased antimicrobial resistance genes (ARG) [47]. They also found lower levels of ARG in effluents from northern European countries compared to southern European countries. Reasons for this may be differences in antibiotic consumption and temperature. However, this study aimed at the detection of ARG in wastewater samples and not on the examination of individual isolates.
In contrast, other “isolate-based” studies showed that WWTP do not lead to the reduction of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria in wastewater or achieve this task only insufficiently [2,48]. The present study lacks insight into the condition prior to wastewater treatment but the numerous detections of multidrug-resistant pathogens of various species after treatment suggest that the reduction of antibiotic-resistant bacteria may be insufficient.
Karkman et al. reviewed that urban WWTPs are among the main sources of both AMRB and antibiotic-resistance genes since they provide unique interfaces between human society and the environment as sewage from households and hospitals contain antibiotics and bacteria of human origin, potentially providing a selective pressure for AMRB and ARGs prior to their release into the environment [49]. While hardly any studies have been published on slaughterhouse WWTP, it must be assumed that similarly favorable conditions for the development of resistant bacteria exist in wastewater released from abattoirs. Some authors report that the conditions in urban WWTPs may be favorable for the selection of ARB which, in turn, can transfer the resistance determinants to susceptible bacteria (reviewed in [49,50]), indicating the need for further research on this topic. These concerns mentioned should be addressed before large-scale investments are made in wastewater treatment plants worldwide.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sampling Locations and Sample Collection
Samples were collected by two Greenpeace e.V. collection teams from Greenpeace e.V. on the same two days in November and December 2020, respectively. They were taken from seven slaughterhouses (four pig and three poultry slaughterhouses) directly from the outlet of the WWTP of the slaughterhouse, i.e., immediately before discharge to the receiving water body/river (for slaughterhouse E the outlet of the effluent was below the water surface in the receiving water body). Approximately 500 mL were collected in a sterile plastic container (Carl Roth GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany) and transported refrigerated to the Friedrich-Loeffler-Institute (FLI). Each location was sampled at two different times (two days) and samples were taken in duplicate each. In December, no samples could be obtained from Slaughterhouse G due to operational reasons (26 samples total).
4.2. Isolation of Bacteria and Identification
In the laboratory, 100 mL of water samples were first pre-filtered using a sterilized gauze (PZN: 04046708, FESMED Verbandmittel GmbH, Frankenberg/Sa., Germany) to remove the fine particles. The pre-filtered water was free from any macro-particles, sediment and most fine particles. Thereafter, each sample was filtered using the EZ-Fit filtration system with 0.45 µm pore size filter membranes (merckmillipore, Darmstadt, Germany). After filtration, filter membranes were transferred to 10 mL TSB (Carl Roth GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany) containing 2 µg/mL cefotaxime (VWR International, Darmstadt, Germany) followed by overnight incubation at 37 °C and shaking at 200 rpm. Depending on the turbidity level, dilution of the overnight cultures followed (up to 10,000 fold dilution). For each sample, 100 µL of the dilutions were plated on chromogenic media CHROMID CARB/OXA, CHROMID ESBL, CHROMID Colistin, and CHROMID MRSA agar plates (bioMérieux, Nürtingen, Germany), and incubated overnight at 37 °C. Putative antibiotic-resistant colonies of E. coli (red-purple colonies) and KEC (Klebsiella spp., Enterobacter spp., Citrobacter spp. (blue colonies)) were subcultivated until pure cultures were achieved. Single pure colonies were picked for further verification and characterization.
4.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST)
Bacterial species were initially identified by MALDI-TOF MS (VITEK2 MS, bioMérieux, Nürtingen, Germany). AST was carried out using VITEK2 (bioMérieux, Nürtingen, Germany). Testing was performed using software version 9.02 and AST-N223 card, according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The AST card used for the VITEK2 included an ESBL confirmation test. Second- and third-generation cephalosporins (ceftazidime, cefotaxime and cefuroxime) were used alone or in combination with clavulanic acid. A reduction of growth in the presence of clavulanic acid was considered indicative of ESBL production.
In addition, 96-well plate broth microdilution was performed for determination of minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of veterinary important antimicrobial compounds, e.g., colistin. A single inoculum adjusted to a McFarland standard of 0.5 in 0.9% NaCl was used. Fifty µL of the suspension were diluted in 11.5 mL of Mueller-Hinton II broth (Oxoid, Wesel, Germany). One hundred microliters of the broth were then transferred to Merlin MICRONAUT S 96-well antimicrobial susceptibility testing plates for farm animals (“Großtiere 4”) (Merlin, Bornheim-Hersel, Germany). The results were assessed visually after incubation at 37 °C for 18–24 h. Growth was considered when turbidity was present at the bottom of the well. The tests were considered as valid only if growth in the internal growth control was observed.
MIC Breakpoints were set according to the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) breakpoint tables for interpretation of MICs and zone diameters (Version 11.0, 2021. http://www.eucast.org) (last accessed on 8 May 2021).
4.4. Similarity Analysis
The randomly amplified polymorphic deoxyribonucleic acid analysis by PCR (RAPD-PCR) involves the amplification of random segments of genomic DNA using short arbitrary primers. It is used for bacterial identification on the strain or isolate level [51,52]. DNA was extracted using the MasterPure™ DNA Purification Kit for Blood, Version II (Lucigen, Middleton, WI, USA). PCR reactions included 2.5 μL of DNA template mixed with 10 μL primer 1 (5′-AAGAGCCCGT-3′) and 2 (5′-GCGATCCCCA-3′) (10 μ/L) (Eurofins, Hamburg, Germany), 12.5 μL nuclease-free water (ad 50 μL) and 25 μL Master Mix (DreamTaq™ Green PCR Master-Mix, Fisher Scientific, Schwerte, Germany). PCR was performed under the following cycling conditions: initial denaturation 15 min @ 95 °C; 35 cycles of denaturation 1 min @ 94 °C, annealing 1 min @ 36 °C and elongation 2 min @ 72 °C and a final elongation 10 min @ 72 °C. Amplified products were separated by electrophoresis on 1.5% agarose gels and stained with GelRed (VWR International, Darmstadt, Germany). A 1 kb ladder (VWR International, Darmstadt, Germany) was used as molecular mass marker. Patterns were determined visually.
4.5. Hypermucoviscosity
Hypermucoviscosity experiments were performed using the string test. Strings of five mm or longer, which formed after stretching on the tip of a sterile inoculation loop were defined positive [42]. Experiments were performed with three technical replicates and three biological replicates.
4.6. Sequence Analysis
According to the resistance profiles, five particularly resistant isolates were selected and subjected to whole-genome sequencing (WGS). Sequences of three E. coli, one C. freundii, and one K. pneumoniae were generated using the Illumina NextSeq 550 platform (Microbial Genome Sequencing Center, Pittsburgh, PA, USA [MiGS]). DNA was extracted using the MasterPure™ DNA Purification Kit for Blood, Version II (s. above). After quantification and initial quality control, DNA was shipped to MiGS. MiGS performed library preparation as published elsewhere [53] followed by sequencing using 2 × 150 bp paired-end reads.
Raw sequencing reads were adapter-trimmed (k-mer-based trimming using 23-mers down to 11-mers at the right end using the included adapter references; additional trimming by paired read overlap), contaminant-filtered (k-mer-based removal of phiX174 sequences), and quality-trimmed (trimming on both sites for regions with quality < 3; removal of poly G tails ≥ 10 bp; maximum number of Ns after trimming: 0; minimum average quality after trimming: 18; minimum length: 32 bp, filtering reads with entropy below 0.5 to remove low-complexity reads) using BBDuk from BBTools v. 38.89 (http://sourceforge.net/projects/bbmap/) (accessed on 1 February 2021). Both trimmed reads and raw reads were quality controlled using FastQC v. 0.11.9 (http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/) (accessed on 1 February 2021). De novo genome assemblies were conducted by employing the assembly pipeline shovill v. 1.1.0 (https://github.com/tseemann/shovill) (accessed on 1 February 2021) in combination with SPAdes v. 3.15.0 [54]. As part of the pipeline, trimmed reads were subsampled to assemble at a maximum coverage of 100×. Besides the polishing step as part of the shovill pipeline, assemblies underwent an additional polishing step. For this, all trimmed reads were mapped back to the contigs using BWA v. 0.7.17 [55]. The obtained SAM/BAM files were sorted and duplicates marked with SAMtools v. 1.11 [56]. Finally, variants were called with Pilon v. 1.23 [57]. The polished assemblies were checked for suspicious assembly metrics (e.g., high count of contigs and genome size, high N50/N90, low L50/L90). Additionally, CheckM v. 1.1.3 [58] was employed to estimate genome completeness and contamination. The in-silico multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) and antibiotic resistance/virulence gene detection were carried out using mlst v. 2.19.0 (https://github.com/tseemann/mlst) (accessed on 1 February 2021) and ABRicate v. 1.0.0 (https://github.com/tseemann/abricate) (accessed on 1 February 2021), respectively. Both tools rely on 3rd party public databases (e.g., PubMLST [59], VFDB [60], ResFinder [61], PlasmidFinder [62], BacMet [63], ARG-ANNOT [64], Ecoli_VF (https://github.com/phac-nml/ecoli_vf) (accessed on 1 February 2021)).
5. Conclusions
Even if a reduction during wastewater treatment occurs, it has to be assumed that significant bacterial loads are present in the production areas of the slaughterhouses. This fact is alarming in two respects: first, it results in the possibility of the pathogens entering downstream water sources and, thus, the environment and the food chain and second, the pathogens pose a risk to the employees of the slaughterhouse.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: D.Z., and K.S.; Methodology: T.H.-B., S.E.H., P.K.L., J.A.B., D.Z. and K.S.; Data analysis: T.H.-B., S.E.H., P.K.L., L.B. and K.S.; Writing—original draft preparation: T.H.-B., P.K.L., L.B. and K.S.; Writing—review and editing: all authors; Supervision: T.H.-B. and K.S. Project administration: T.H.-B., D.Z. and K.S.; Funding acquisition: D.Z. and K.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data for this study have been deposited in the European Nucleotide Archive (ENA) at EMBL-EBI under accession number PRJEB44418 (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/ena/browser/view/PRJEB44418) (accessed on 1 February 2021).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- World Health Organization. Antimicrobial Resistance Global Report on Surveillance; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Verburg, I.; Garcia-Cobos, S.; Leal, L.H.; Waar, K.; Friedrich, A.W.; Schmitt, H. Abundance and Antimicrobial Resistance of Three Bacterial Species Along a Complete Wastewater Pathway. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, Research, and Development of New Antibiotics: The Who Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knothe, H.; Shah, P.; Krcmery, V.; Antal, M.; Mitsuhashi, S. Transferable Resistance to Cefotaxime, Cefoxitin, Cefamandole and Cefuroxime in Clinical Isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Serratia marcescens. Infection 1983, 11, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, K.; Bradford, P.A. Epidemiology of Β-Lactamase-Producing Pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00047-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolhouse, M.; Ward, M.; van Bunnik, B.; Farrar, J. Antimicrobial Resistance in Humans, Livestock and the Wider Environment. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency—European Surveillance of Veterinary Antimicrobial Consumption. “Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 31 European Countries in 2018”. EMA-ESVAC, 2020. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/report/sales-veterinary-antimicrobial-agents-31-european-countries-2018-trends-2010-2018-tenth-esvac-report_en.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- van Rennings, L.; von Münchhausen, C.; Hartmann, M.; Ottilie, H.; Honscha, W.; Käsbohrer, A.; Kreienbrock, L. [Antibiotic Usage and Antibiotic Sales in Germany in 2011—The Situation of Drug Usage in Veterinary Medicine]. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2014, 127, 366–374. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- German Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture. “Pressemitteilung Nr. 157/2019.” German Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture. 2019. Available online: https://www.bmel.de/SharedDocs/Pressemitteilungen/DE/2019/157-reserve-antibiotika.html (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Huebner, N.O.; Dittmann, K.; Henck, V.; Wegner, C.; Kramer, A. Epidemiology of Multidrug Resistant Bacterial Organisms and Clostridium Difficile in German Hospitals in 2014: Results from a Nationwide One-Day Point Prevalence of 329 German Hospitals. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaak, H.; van Hoek, A.H.A.M.; Hamidjaja, R.A.; van der Plaats, R.Q.J.; Kerkhof-de Heer, L.; Husman, A.M.D.; Schets, F.M. Distribution, Numbers, and Diversity of Esbl-Producing E. coli in the Poultry Farm Environment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135402. [Google Scholar]
- Ghodousi, A.; Bonura, C.; Di Noto, A.M.; Mammina, C. Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase, Ampc-Producing, and Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Escherichia coli in Retail Broiler Chicken Meat, Italy. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2015, 12, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savin, M.; Bierbaum, G.; Hammerl, J.A.; Heinemann, C.; Parcina, M.; Sib, E.; Voigt, A.; Kreyenschmidt, J. Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Antimicrobial Residues in Wastewater and Process Water from German Pig Slaughterhouses and Their Receiving Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savin, M.; Bierbaum, G.; Blau, K.; Parcina, M.; Sib, E.; Smalla, K.; Schmithausen, R.; Heinemann, C.; Hammerl, J.A.; Kreyenschmidt, J. Colistin-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Isolated from Process Waters and Wastewater from German Poultry and Pig Slaughterhouses. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 575391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X.; Wang, S.; Ren, H.; Shen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, S. Rapid Rise of the Esbl and Mcr-1 Genes in Escherichia coli of Chicken Origin in China, 2008–2014. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzopardi, E.A.; Boyce, D.E.; Thomas, D.W.; Dickson, W.A. Colistin in Burn Intensive Care: Back to the Future? Burns 2013, 39, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization—Advisory Group on Integrated Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance. Critically Important Antimicrobials for Human Medicine, 5th ed.; WHO—AGISAR: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Statistisches Bundesamt. “Viehbestand und Tierische Erzeugung 2017, Fachserie 3 Reihe 4.” Destatis. 2018. Available online: https://www.destatis.de/DE/Themen/Branchen-Unternehmen/Landwirtschaft-Forstwirtschaft-Fischerei/Tiere-Tierische-Erzeugung/Publikationen/Downloads-Tiere-und-tierische-Erzeugung/viehbestand-tierische-erzeugung-2030400177005.html (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Mittal, G.S. Characterization of the Effluent Wastewater from Abattoirs for Land Application. Food Rev. Int. 2004, 20, 229–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savin, M.; Bierbaum, G.; Hammerl, J.A.; Heinemann, C.; Parcina, M.; Sib, E.; Voigt, A.; Kreyenschmidt, J. Eskape Bacteria and Extended-Spectrum-Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated from Wastewater and Process Water from German Poultry Slaughterhouses. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2020, 86, e02748-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savin, M.; Bierbaum, G.; Kreyenschmidt, J.; Schmithausen, R.M.; Sib, E.; Schmoger, S.; Käsbohrer, A.; Hammerl, J.A. Clinically Relevant Escherichia coli Isolates from Process Waters and Wastewater of Poultry and Pig Slaughterhouses in Germany. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaekel, F.; May, T.; Seiler, J.; Hartmann, M.; Kreienbrock, L. Antibiotic Drug Usage in Pigs in Germany—Are the Class Profiles Changing? PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, T.H.; Aslam, B.; Arshad, M.I.; Alvi, R.F.; Muzammil, S.; Yasmeen, N.; Aslam, M.A.; Khurshid, M.; Rasool, M.H.; Baloch, Z. Emergence of Bla (Ndm-1) Harboring Klebsiella pneumoniae St29 and St11 in Veterinary Settings and Waste of Pakistan. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 3033–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eibach, D.; Dekker, D.; Boahen, K.G.; Akenten, C.W.; Sarpong, N.; Campos, C.B.; Berneking, L.; Aepfelbacher, M.; Krumkamp, R.; Owusu-Dabo, E.; et al. Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in Local and Imported Poultry Meat in Ghana. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 217, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kock, R.; Daniels-Haardt, I.; Becker, K.; Mellmann, A.; Friedrich, A.W.; Mevius, D.; Schwarz, S.; Jurke, A. Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae in Wildlife, Food-Producing, and Companion Animals: A Systematic Review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyanwu, M.U.; Jaja, I.F.; Nwobi, O.C. Occurrence and Characteristics of Mobile Colistin Resistance (Mcr) Gene-Containing Isolates from the Environment: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catry, B.; Cavaleri, M.; Baptiste, K.; Grave, K.; Grein, K.; Holm, A.; Jukes, H.; Liebana, E.; Lopez Navas, A.; Mackay, D.; et al. Use of Colistin-Containing Products within the European Union and European Economic Area (Eu/Eea): Development of Resistance in Animals and Possible Impact on Human and Animal Health. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 46, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhouma, M.; Beaudry, F.; Thériault, W.; Letellier, A. Colistin in Pig Production: Chemistry, Mechanism of Antibacterial Action, Microbial Resistance Emergence, and One Health Perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolakos, I.; Piccirillo, A. A Review on the Current Situation and Challenges of Colistin Resistance in Poultry Production. Avian Pathol. 2018, 47, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irrgang, A.; Roschanski, N.; Tenhagen, B.A.; Grobbel, M.; Skladnikiewicz-Ziemer, T.; Thomas, K.; Roesler, U.; Kasbohrer, A. Prevalence of Mcr-1 in E. coli from Livestock and Food in Germany, 2010–2015. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gekenidis, M.-T.; Qi, W.; Hummerjohann, J.; Zbinden, R.; Walsh, F.; Drissner, D. Antibiotic-Resistant Indicator Bacteria in Irrigation Water: High Prevalence of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase (Esbl)-Producing Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmeira, J.D.; Haenni, M.; Metayer, V.; Madec, J.Y.; Ferreira, H.M.N. Epidemic Spread of Inci1/Pst113 Plasmid Carrying the Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase (Esbl) Blactx-M-8 Gene in Escherichia coli of Brazilian Cattle. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 243, 108629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.-C.; Yeh, K.-S. Characteristics of Extended-Spectrum Β-Lactamase–Producing Escherichia coli Isolated from Fecal Samples of Piglets with Diarrhea in Central and Southern Taiwan in 2015. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clermont, O.; Christenson, J.K.; Denamur, E.; Gordon, D.M. The Clermont Escherichia coli Phylo-Typing Method Revisited: Improvement of Specificity and Detection of New Phylo-Groups. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnedahl, J.; Drobni, M.; Gauthier-Clerc, M.; Hernandez, J.; Granholm, S.; Kayser, Y.; Melhus, Å.; Kahlmeter, G.; Waldenström, J.; Johansson, A.; et al. Dissemination of Escherichia coli with Ctx-M Type Esbl between Humans and Yellow-Legged Gulls in the South of France. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, H.; Zweifel, C.; Wittenbrink, M.M.; Stephan, R. Esbl-Producing Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Isolated from Dogs and Cats in Switzerland. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 162, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cormier, A.; Zhang, P.L.C.; Chalmers, G.; Weese, J.S.; Deckert, A.; Mulvey, M.; McAllister, T.; Boerlin, P. Diversity of Ctx-M-Positive Escherichia coli Recovered from Animals in Canada. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 231, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, M.R.; Sellera, F.P.; Cunha, M.P.V.; Lopes, R.; Cerdeira, L.; Lincopan, N. Emergence of Ctx-M-27-Producing Escherichia coli of St131 and Clade C1-M27 in an Impacted Ecosystem with International Maritime Traffic in South America. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, H.; Doijad, S.; Falgenhauer, L.; Fritzenwanker, M.; Imirzalioglu, C.; Chakraborty, T. Bla(Ctx-M-27)-Encoding Escherichia coli Sequence Type 131 Lineage C1-M27 Clone in Clinical Isolates, Germany. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1754–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccirilli, A.; Pompilio, A.; Rossi, L.; Segatore, B.; Amicosante, G.; Rosatelli, G.; Perilli, M.; Di Bonaventura, G. Identification of Ctx-M-15 and Ctx-M-27 in Antibiotic-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria Isolated from Three Rivers Running in Central Italy. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohmen, W.; Van Gompel, L.; Schmitt, H.; Liakopoulos, A.; Heres, L.; Urlings, B.A.; Mevius, D.; Bonten, M.J.M.; Heederik, D.J.J. Esbl Carriage in Pig Slaughterhouse Workers Is Associated with Occupational Exposure. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 2003–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shon, A.S.; Bajwa, R.P.S.; Russo, T.A. Hypervirulent (Hypermucoviscous) Klebsiella pneumoniae: A New and Dangerous Breed. Virulence 2013, 4, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Marr, C.M. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00001-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, Q.; Esposito, F.; Fernandes, M.R.; Espinoza-Muñoz, M.; Souza, T.A.; Santos, S.R.; Cerdeira, L.; Cassettari, V.; Lincopan, N. Genome Sequence Analysis of a Hypermucoviscous/Hypervirulent and Mdr Ctx-M-15/K19/St29 Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Human Infection. Pathog. Dis. 2017, 75, ftx121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, K.; Chen, W.; Chen, J.; Zheng, J.; Liu, C.; Cheng, L.; Zhou, W.; Shen, H.; Cao, X. Epidemiological Characteristics of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Collected from 17 Hospitals in Nanjing District of China. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Commission Implementing Decision (Eu) 2016/902 of 30 May 2016 Establishing Best Available Techniques (Bat) Conclusions, under Directive 2010/75/Eu of the European Parliament and of the Council, for Common Waste Water and Waste Gas Treatment/Management Systems in the Chemical Sector. In C(2016)3127; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2016; Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32016D0902 (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Parnanen, K.M.M.; Narciso-da-Rocha, C.; Kneis, D.; Berendonk, T.U.; Cacace, D.; Do, T.T.; Elpers, C.; Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Henriques, I.; Jaeger, T.; et al. Antibiotic Resistance in European Wastewater Treatment Plants Mirrors the Pattern of Clinical Antibiotic Resistance Prevalence. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau9124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flach, C.F.; Genheden, M.; Fick, J.; Larsson, D.G.J. A Comprehensive Screening of Escherichia coli Isolates from Scandinavia’s Largest Sewage Treatment Plant Indicates No Selection for Antibiotic Resistance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11419–11428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karkman, A.; Do, T.T.; Walsh, F.; Virta, M.P.J. Antibiotic-Resistance Genes in Waste Water. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manaia, C.M.; Rocha, J.; Scaccia, N.; Marano, R.; Radu, E.; Biancullo, F.; Cerqueira, F.; Fortunato, G.; Iakovides, I.C.; Zammit, I.; et al. Antibiotic Resistance in Wastewater Treatment Plants: Tackling the Black Box. Environ. Int. 2018, 115, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravelo, C.; Magariños, B.; López-Romalde, S.; Toranzo, A.E.; Romalde, J.L. Molecular Fingerprinting of Fish-Pathogenic Lactococcus garvieae Strains by Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA Analysis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocco, L.; Valentino, I.V.; Scapigliati, G.; Stingo, V. Rapd-Pcr Analysis for Molecular Characterization and Genotoxic Studies of a New Marine Fish Cell Line Derived from Dicentrarchus Labrax. Cytotechnology 2014, 66, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baym, M.; Kryazhimskiy, S.; Lieberman, T.D.; Chung, H.; Desai, M.M.; Kishony, R. Inexpensive Multiplexed Library Preparation for Megabase-Sized Genomes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128036. [Google Scholar]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. Spades: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and Accurate Short Read Alignment with Burrows-Wheeler Transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; Proc, G.P.D. The Sequence Alignment/Map Format and Samtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.D.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An Integrated Tool for Comprehensive Microbial Variant Detection and Genome Assembly Improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. Checkm: Assessing the Quality of Microbial Genomes Recovered from Isolates, Single Cells, and Metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-Access Bacterial Population Genomics: Bigsdb Software, the Pubmlst.Org Website and Their Applications [Version 1; Peer Review: 2 Approved]. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zheng, D.D.; Jin, Q.; Chen, L.H.; Yang, J. Vfdb 2019: A Comparative Pathogenomic Platform with an Interactive Web Interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D687–D692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zankari, E.; Hasman, H.; Cosentino, S.; Vestergaard, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Larsen, M.V. Identification of Acquired Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; Garcia-Fernandez, A.; Larsen, M.V.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Hasman, H. In Silico Detection and Typing of Plasmids Using Plasmidfinder and Plasmid Multilocus Sequence Typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, C.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Rensing, C.; Kristiansson, E.; Larsson, D.G.J. Bacmet: Antibacterial Biocide and Metal Resistance Genes Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D737–D743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.K.; Padmanabhan, B.R.; Diene, S.M.; Lopez-Rojas, R.; Kempf, M.; Landraud, L.; Rolain, J.M. Arg-Annot, a New Bioinformatic Tool to Discover Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Bacterial Genomes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).