Use of an Insulation Layer on the Connection Tracks of a Biosensor with Coplanar Electrodes to Increase the Normalized Impedance Variation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Aspect
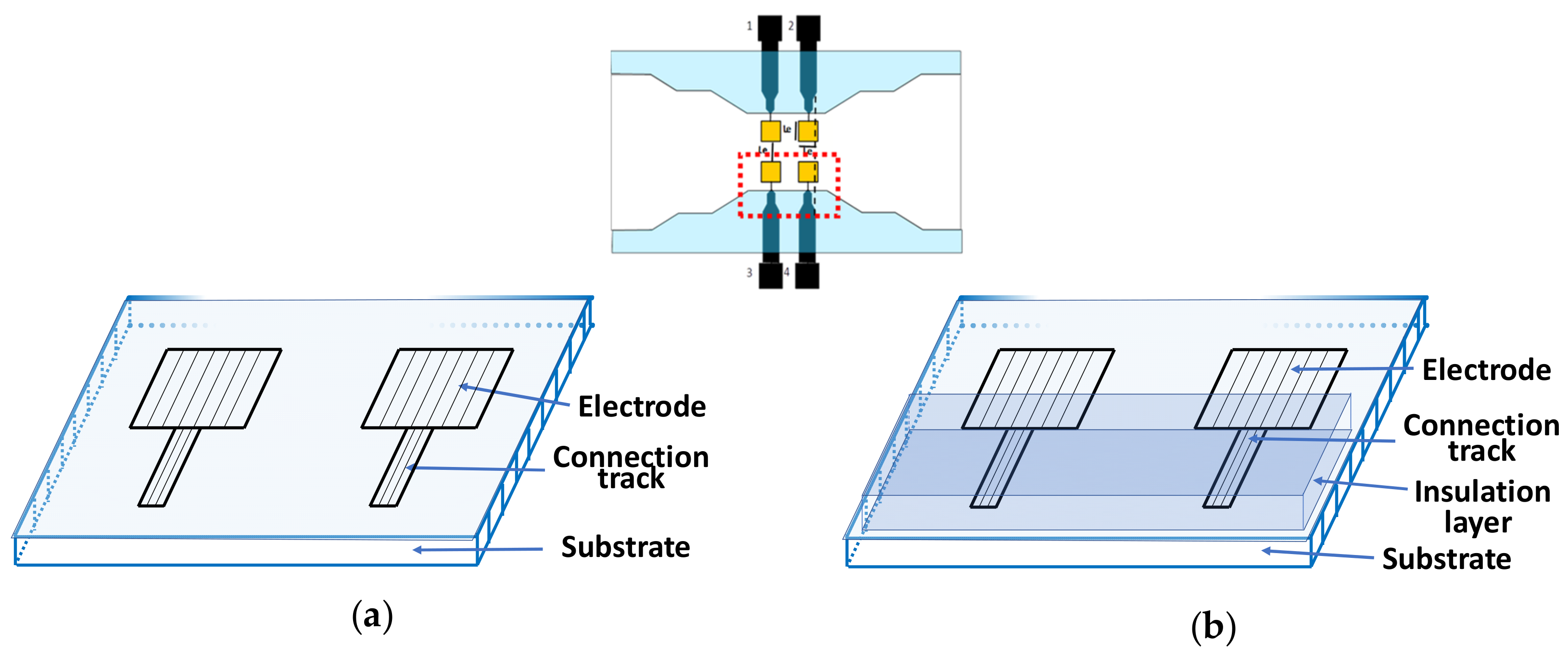
2.1. Electrodes Structure
2.2. Electrical Model
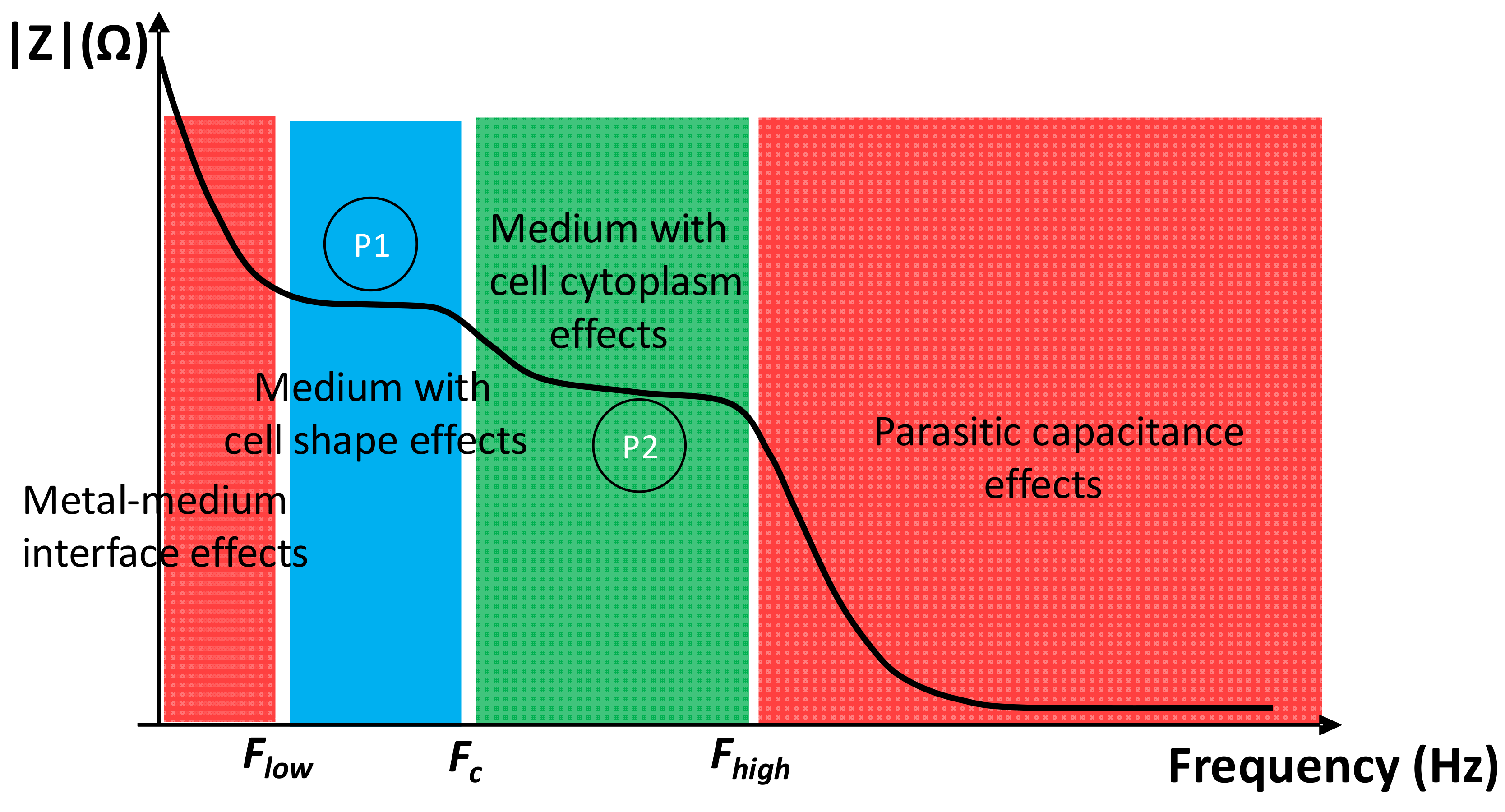
2.3. Cutoff Frequencies
2.4. Normalized Impedance Variation
3. Simulations
3.1. Simulations Setup
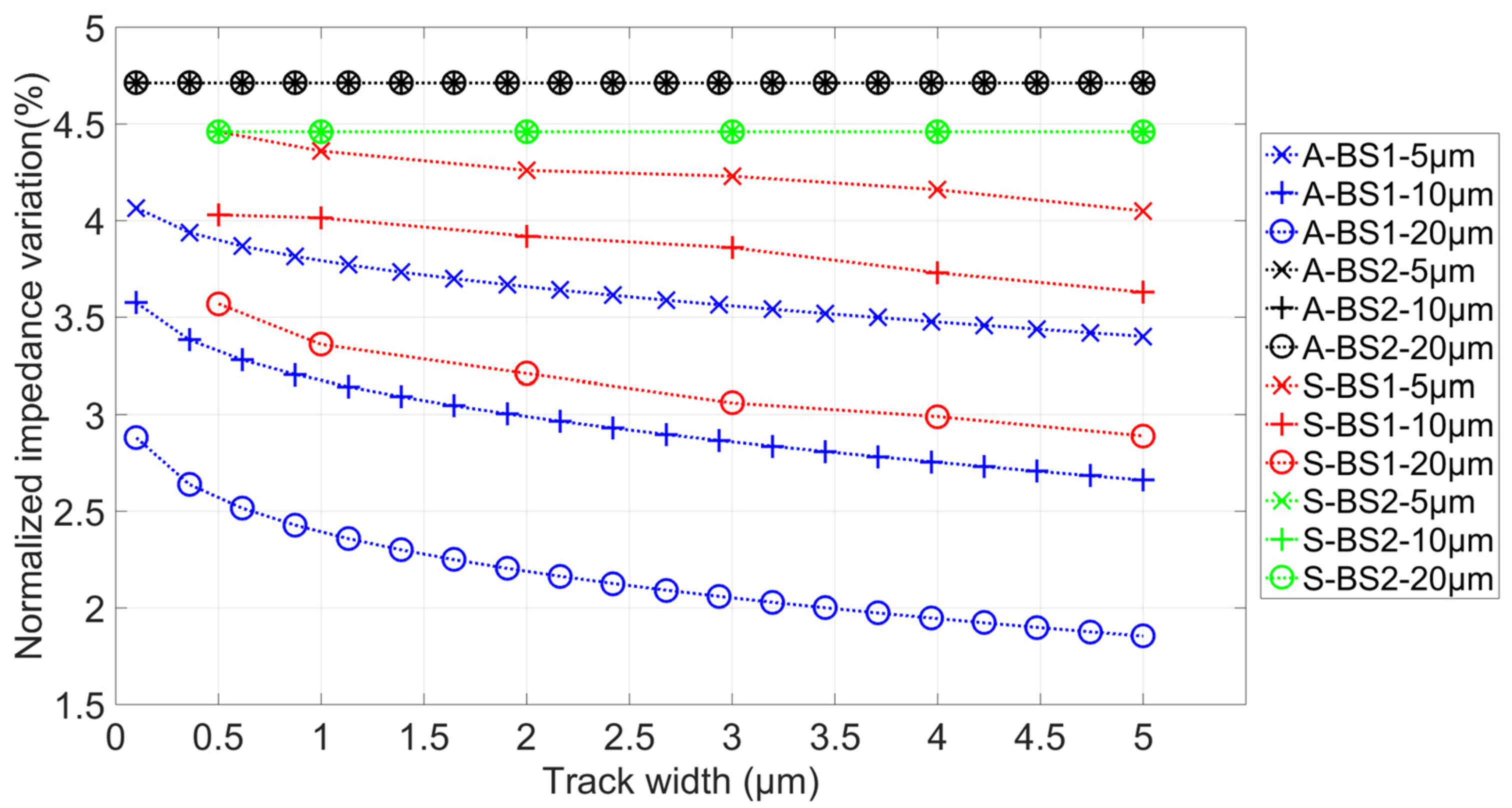
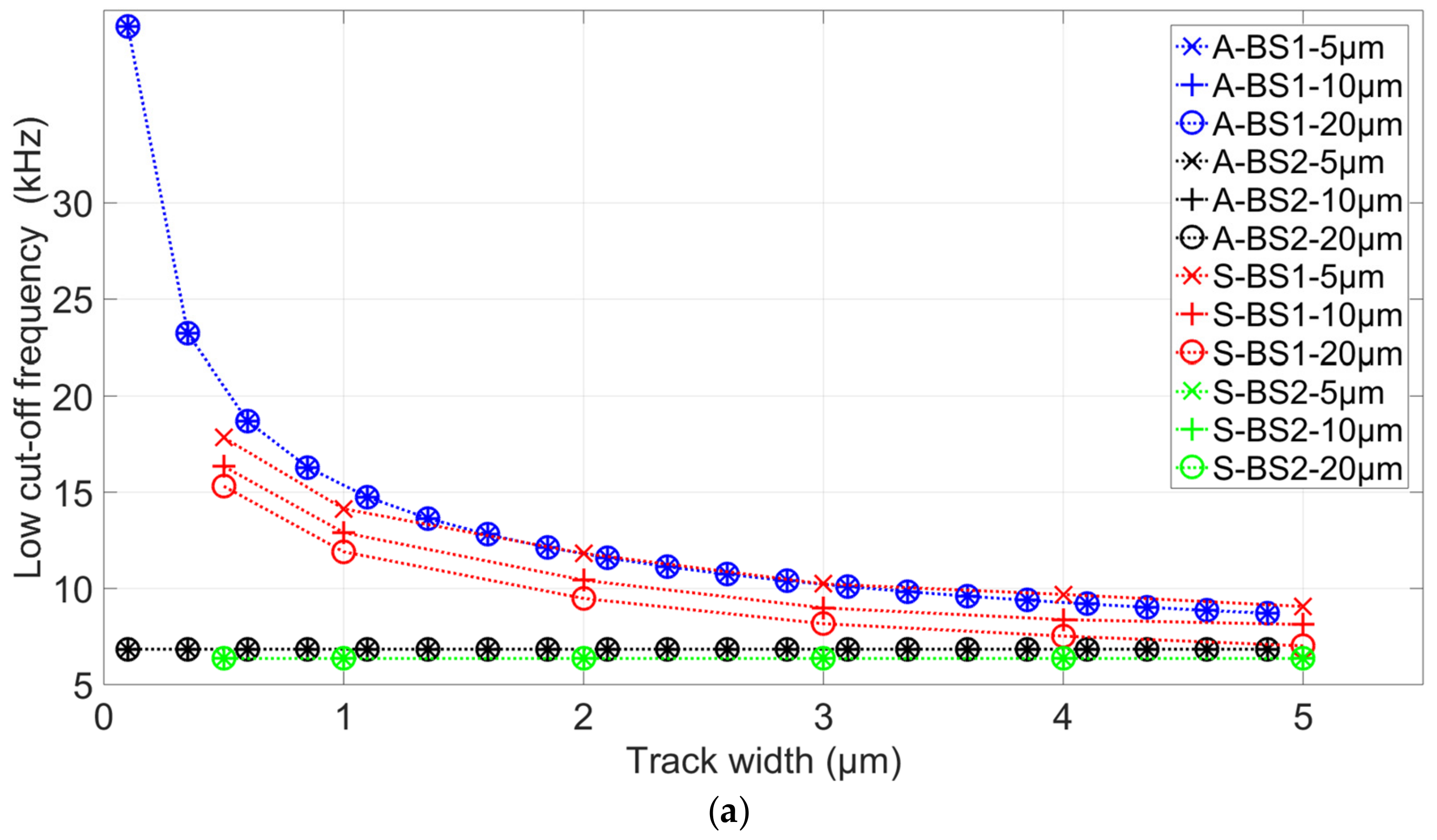
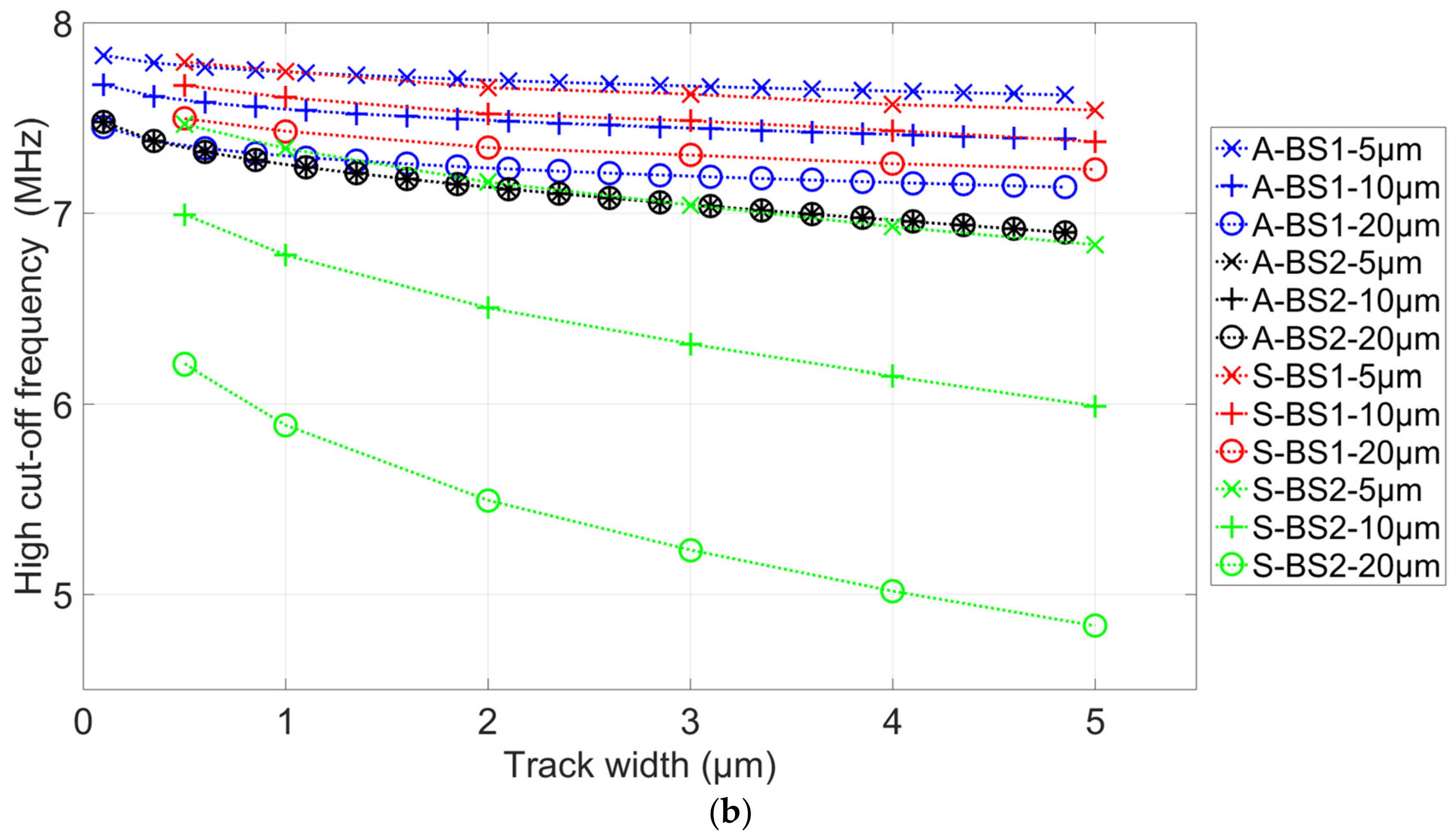
3.2. Simulation Results
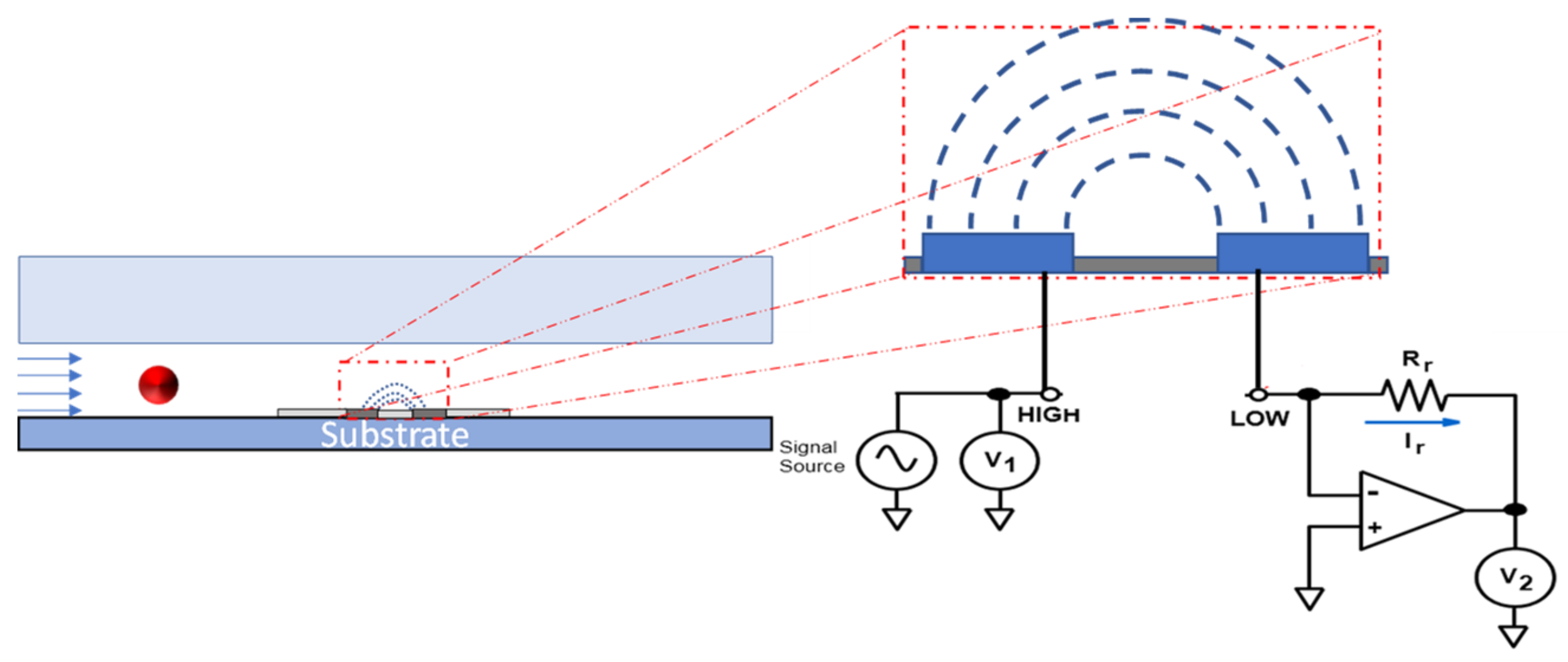
4. Material and Methods
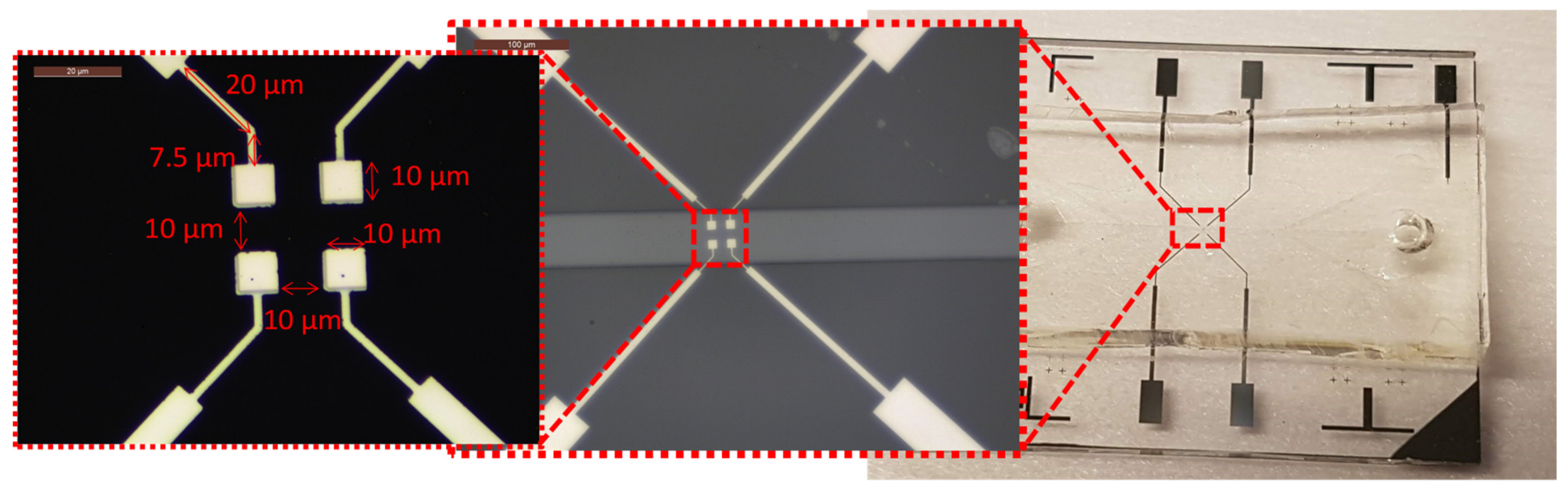
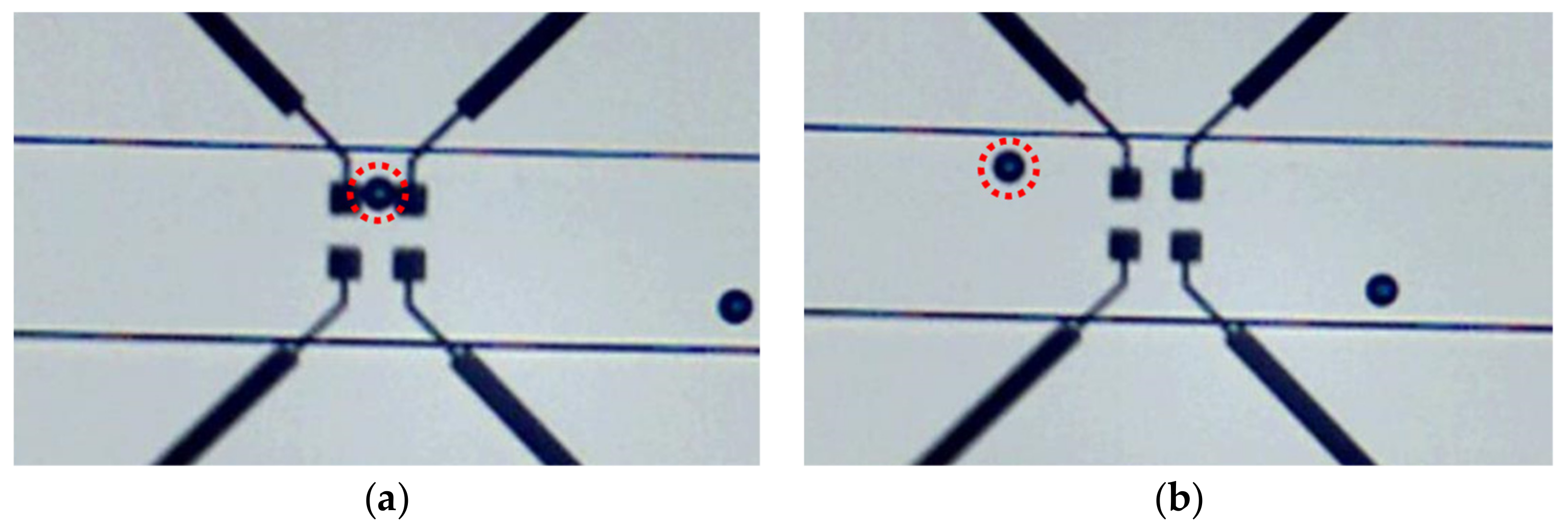
4.1. Sensors Fabrication
4.2. Samples Preparation
4.3. Experimental Setup
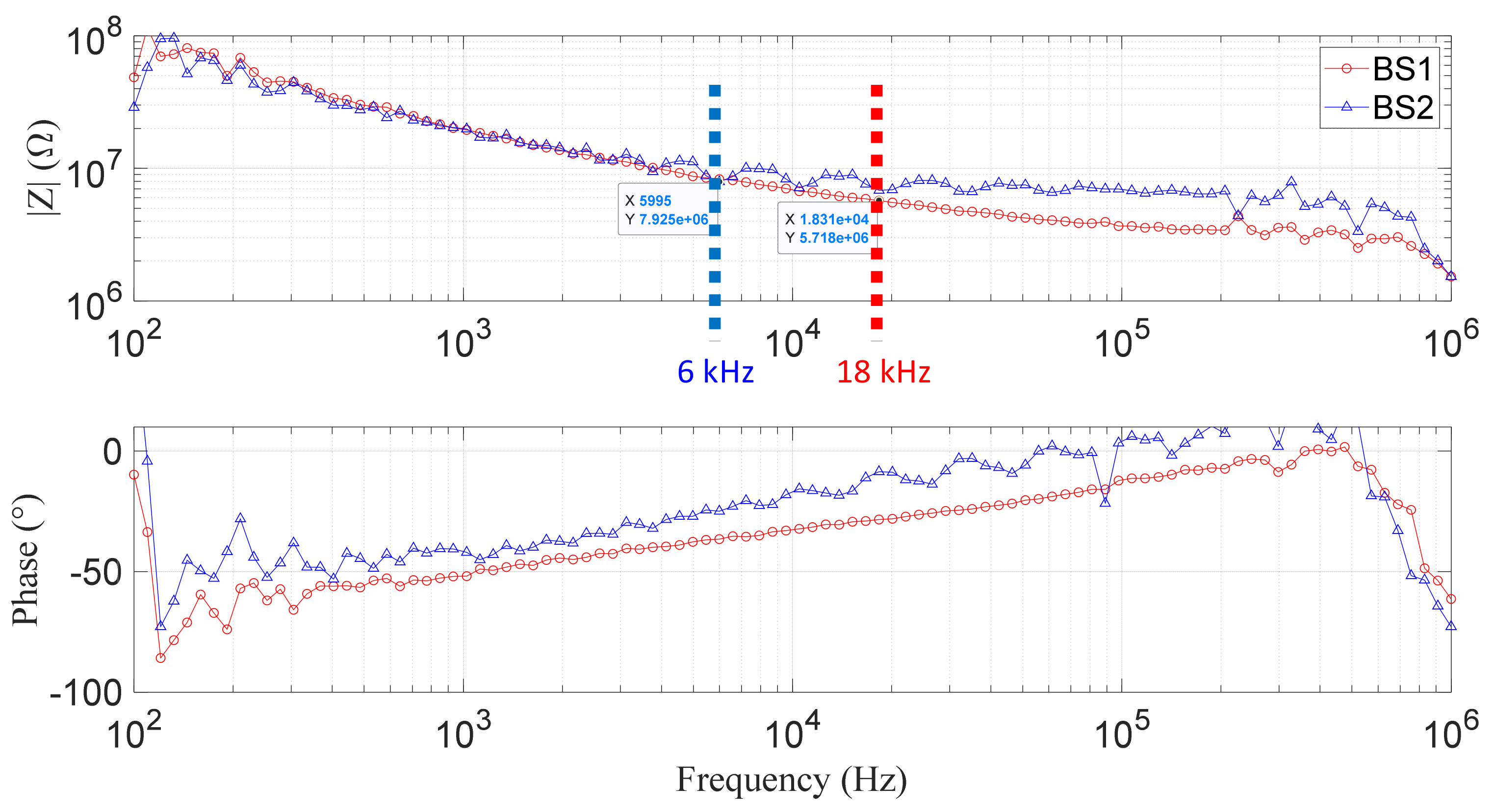
4.4. Experimental Results
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B

Appendix C

References
- Kolluri, N.; Klapperich, C.M.; Cabodi, M. Towards lab-on-a-chip diagnostics for malaria elimination. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, A.K.; Sapkota, A.; Wen, J.; Li, J.; Takei, M. Linear relationship between cytoplasm resistance and hemoglobin in red blood cell hemolysis by electrical impedance spectroscopy eight-parameter equivalent circuit. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 119, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Lum, J.; Callaway, Z.; Lin, J.; Bottje, W.; Li, Y. A label-free impedance immunosensor using screen-printed interdigitated electrodes and magnetic nanobeads for the detection of E. coli O157:H7. Biosensors 2015, 5, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.I.; Joo, Y.D.; Han, K.H. An electrorotation technique for measuring the dielectric properties of cells with simultaneous use of negative quadrupolar dielectrophoresis and electrorotation. Analyst 2013, 138, 1529–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudel, J.; Nadi, M.; Elmazria, O.; Kourtiche, D. An electrical model optimization for single cell flow impedance spectroscopy. Int. J. Smart Sens. Intell. Syst. 2016, 9, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qiang, Y.; Alvarez, O.; Du, E. Electrical impedance microflow cytometry with oxygen control for detection of sickle cells. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 2392–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rho, J.; Jang, W.; Hwang, I.; Lee, D.; Lee, C.H.; Chung, T.D. Multiplex immunoassays using virus-tethered gold microspheres by DC impedance-based flow cytometry. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhaob, X.T.; Luo, D.Y.C.N.; Jiang, M.; Wei, C.; Long, R.; Yue, W.T.; Wang, J.B.; Chen, J. Tumor cell characterization and classification based on cellular specific membrane capacitance and cytoplasm conductivity. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 57, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, Y.R.; Bürgel, S.C.; Misun, P.M.; Hierlemann, A.; Frey, O. Electrical impedance spectroscopy for microtissue spheroid analysis in hanging-drop networks. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araujo, A.L.A.; Claudel, J.; Nadi, M.; Kourtiche, D. Detection and characterization of biological cells by impedance spectroscopy. Proc. Int. Conf. Sens. Technol. ICST 2019, 2018, 309–314. [Google Scholar]
- Kokkinos, C.; Economou, A.; Prodromidis, M.I. Electrochemical immunosensors: Critical survey of different architectures and transduction strategies. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 88–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, D.; Luo, Y.; Li, H.; Deng, B.; Huang, S.B.; Chiu, T.K.; Wu, M.H.; Long, R.; Hu, H.; et al. A microfluidic system for cell type classification based on cellular size-independent electrical properties. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2272–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta-Nuñez, L.F.E.; Gutierrez-Iglesias, G.; Martinez-Cuazitl, A.; Mata-Miranda, M.M.; Alvarez-Jiménez, V.D.; Sánchez-Monroy, V.; Golberg, A.; González-Díaz, C.A. A biosensor capable of identifying low quantities of breast cancer cells by electrical impedance spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furst, A.L.; Francis, M.B. Impedance-based detection of bacteria. Chem. Rev. 2018, 119, 700–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, E.; Ha, S.; Diez-Silva, M.; Dao, M.; Suresh, S.; Chandrakasan, A.P. Electric impedance microflow cytometry for characterization of cell disease states. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 3903–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asphahani, F.; Zhang, M. Cellular impedance biosensors for drug screening and toxin detection. Analyst 2007, 132, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoneman, M.R.; Kosempa, M.; Gregory, W.D.; Gregory, C.W.; Marx, J.J.; Mikkelson, W.; Tjoe, J.; Raicu, V. Correction of electrode polarization contributions to the dielectric properties of normal and cancerous breast tissues at audio/radiofrequencies. Phys. Med. Biol. 2007, 52, 6589–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterworth, A.; Blues, E.; Williamson, P.; Cardona, M.; Gray, L.; Corrigan, D.K. SAM composition and electrode roughness affect performance of a DNA biosensor for antibiotic resistance. Biosensors 2019, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, H.; Sun, T.; Holmes, D.; Gawad, S.; Green, N.G. Single cell dielectric spectroscopy. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, M.; Li, Y.; Srinivasan, B.; Tung, S. A label-free, microfluidics and interdigitated array microelectrode-based impedance biosensor in combination with nanoparticles immunoseparation for detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in food samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 128, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, S.K.; Singh, P.K.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Khademhosseini, A.; Xu, Q.; Sonkusale, S.R. All electronic approach for high-throughput cell trapping and lysis with electrical impedance monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, K.; Gawad, S.; Renaud, P. Impedance spectroscopy flow cytometry: On-chip label-free cell differentiation. Cytom. Part A 2005, 65, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabuncu, A.C.; Stacey, M.; Craviso, G.L.; Semenova, N.; Vernier, P.T.; Leblanc, N.; Chatterjee, I.; Zaklit, J. Dielectric properties of isolated adrenal chromaffin cells determined by microfluidic impedance spectroscopy. Bioelectrochemistry 2018, 119, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Liu, Q. Biomedical Sensors and Measurement; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Price, D.T.; Rahman, A.R.A.; Bhansali, S. Design rule for optimization of microelectrodes used in electric cell-substrate impedance sensing (ECIS). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2071–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luiz, A.; de Araujo, A.; Claudel, J.; Kourtiche, D.; Nadi, M. Influence of Electrode Connection Tracks on Biological Cell Measurements by Impedance. Sensors 2019, 19, 2839. [Google Scholar]
- Schwan, H.P. Electric characteristics of tissues. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 1963, 1, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keysight Tehnologies. Impedance Measurement Handbook: A Guide to Measurement Technology and Techniques, 6th ed.; Application Note; Keysight Tehnologies: Santa Rosa, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]


| Component | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Cdl | Capacitance of the double-layer effect between the electrode and the medium | F |
| Cm | Medium capacity | F |
| Rm | Medium resistance | Ω |
| Rcy | Cymiddlelasmic cell resistance | Ω |
| Cmem | Membrane cell capacity | F |
| Csub | Capacitance of substrate under electrode | F |
| Csubp | Capacitance of substrate under connection tracks | F |
| Rp | Parasitic resistance of the connection track for the biosensor BS1 | Ω |
| Cdlp | Double-layer capacitance of the connection track for the biosensor BS1 | F |
| Cp | Parasitic capacitance of the connection track for the biosensor BS1 | F |
| CISO | Insulation capacitance of the connection track for the biosensor BS2 | F |
| Component | Description | Constant Values | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Φ | Volume fraction (ratio between the cell volume/measurement volume) | 0.03 | - |
| K | Shape factor | 8.38 | µm |
| σm | Medium conductivity | 1 | S/m |
| σcyt | Cell cymiddlelasm conductivity | 1 | S/m |
| εm | Medium permittivity | 78 × 8.85 × 10−12 | F/m |
| r | Cell radius | From 3 to 9 | µm |
| Cmem,s | Cell membrane surface capacitance | 1 | µF/cm2 |
| Kp | Connection track shape factor | From 2.3 to 22.5 | µm |
| εsub | Substrate permittivity | 4.2 × 8.85 × 10−12 | F/m |
| C0 | Superficial double-layer capacitance | 0.01 | F/m2 |
| Aele | Electrode area | 100 | µm² |
| Ap | Connection track area | From 0.5 to 100 | µm² |
| Material | Conductivity [S/m] | Relative Permittivity |
|---|---|---|
| Glass substrate | 10−13 | 4.2 |
| Medium (tap water) | 0.03 | 78 |
| Insulation (Si02) | 10−13 | 4.1 |
| Cell cymiddlelasm | 1 | 78 |
| Cell membrane | 10−13 | 847 with 750 nm thickness (fixed to obtain 1 µF/cm²) |
| Polystyrene beads | 10−13 | 2.4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alves de Araujo, A.L.; Claudel, J.; Kourtiche, D.; Nadi, M. Use of an Insulation Layer on the Connection Tracks of a Biosensor with Coplanar Electrodes to Increase the Normalized Impedance Variation. Biosensors 2019, 9, 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9030108
Alves de Araujo AL, Claudel J, Kourtiche D, Nadi M. Use of an Insulation Layer on the Connection Tracks of a Biosensor with Coplanar Electrodes to Increase the Normalized Impedance Variation. Biosensors. 2019; 9(3):108. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9030108
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlves de Araujo, Arthur Luiz, Julien Claudel, Djilali Kourtiche, and Mustapha Nadi. 2019. "Use of an Insulation Layer on the Connection Tracks of a Biosensor with Coplanar Electrodes to Increase the Normalized Impedance Variation" Biosensors 9, no. 3: 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9030108
APA StyleAlves de Araujo, A. L., Claudel, J., Kourtiche, D., & Nadi, M. (2019). Use of an Insulation Layer on the Connection Tracks of a Biosensor with Coplanar Electrodes to Increase the Normalized Impedance Variation. Biosensors, 9(3), 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9030108





