Suppressing Non-Specific Binding of Proteins onto Electrode Surfaces in the Development of Electrochemical Immunosensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
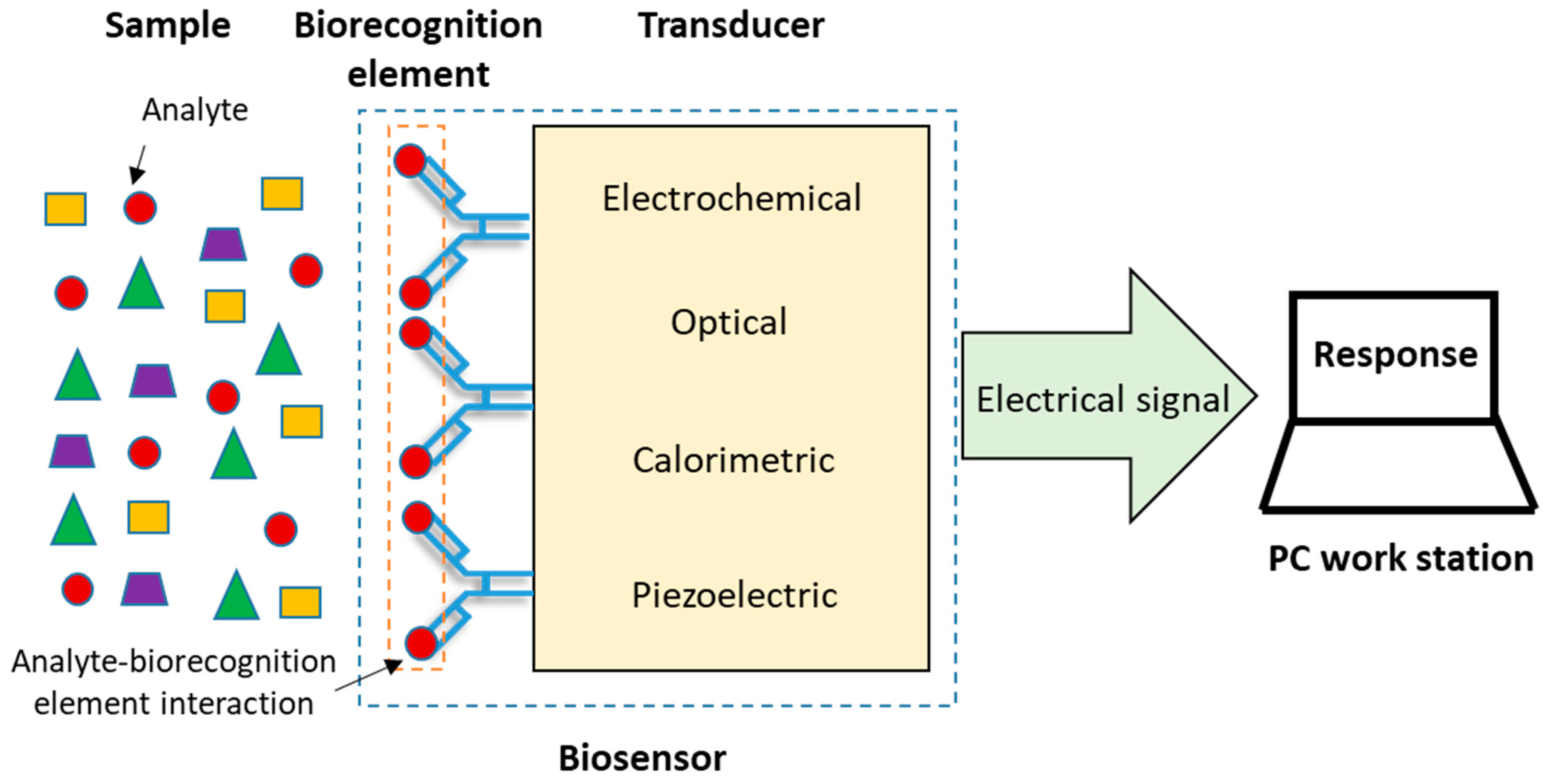
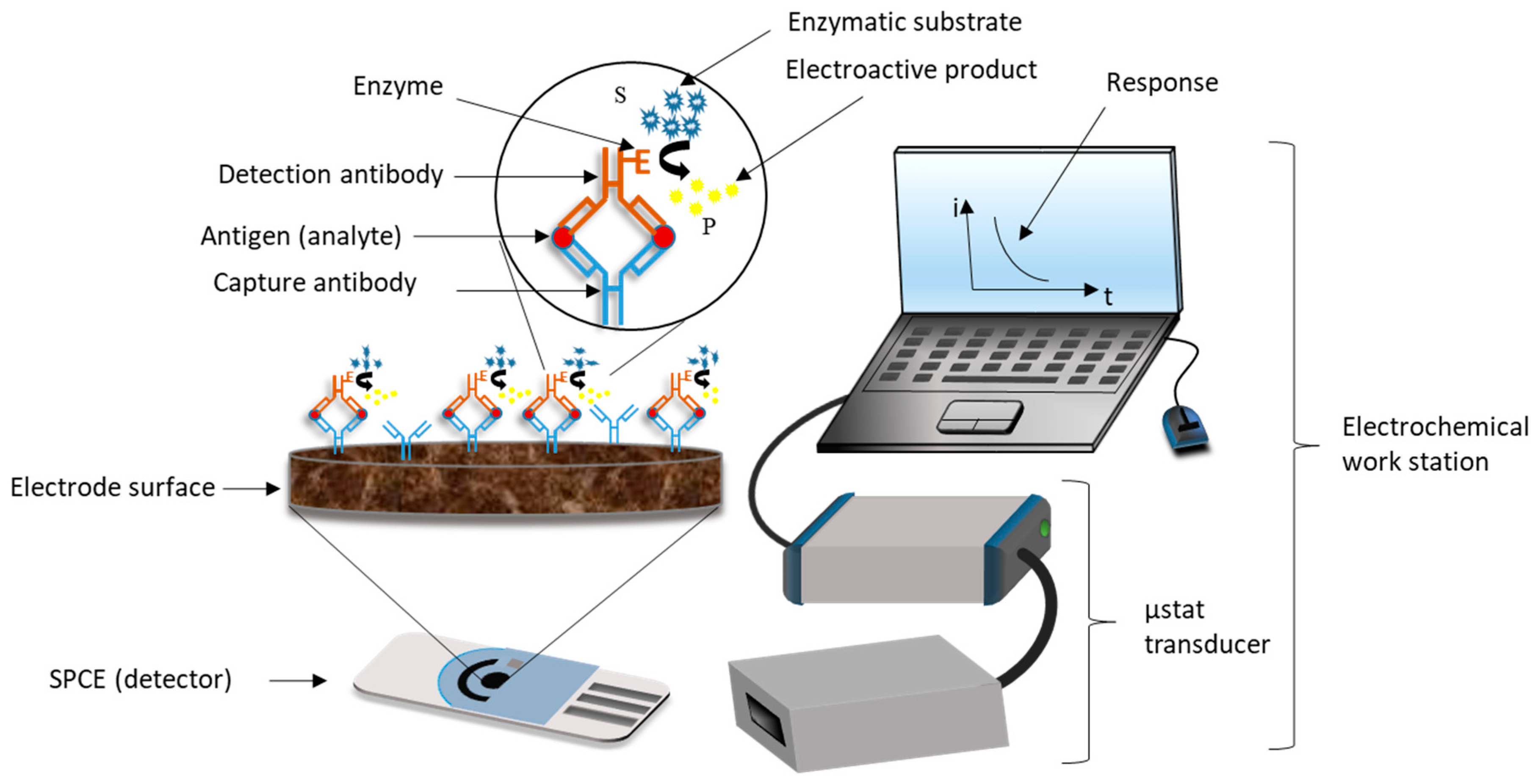
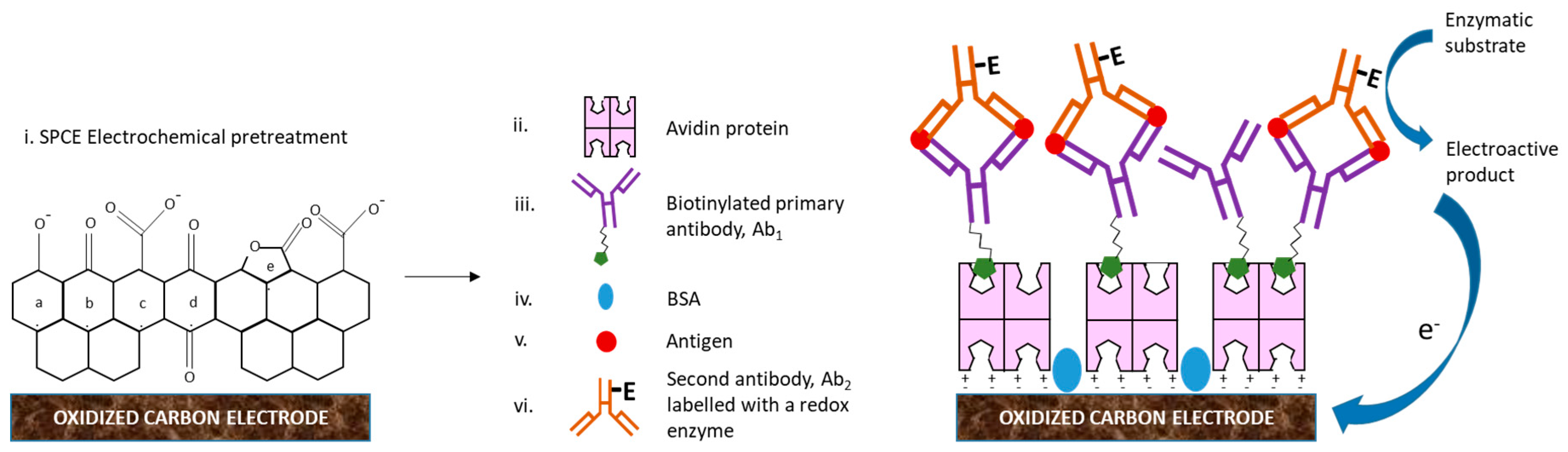
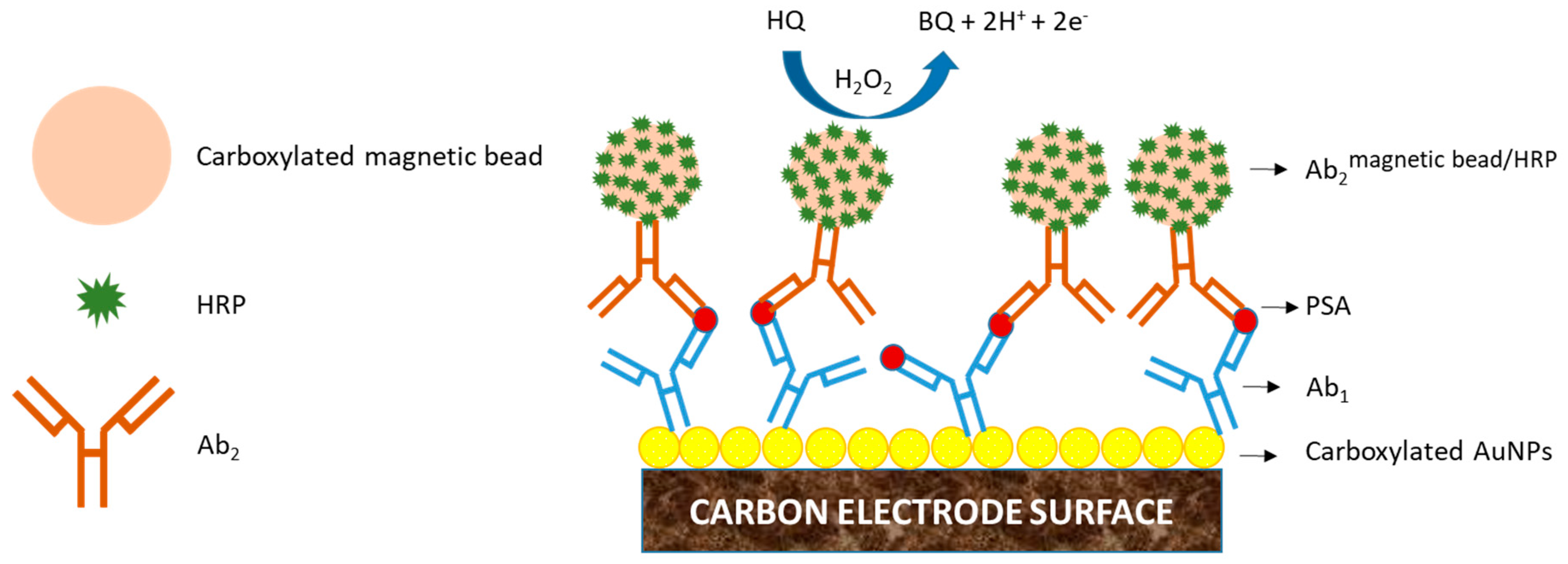
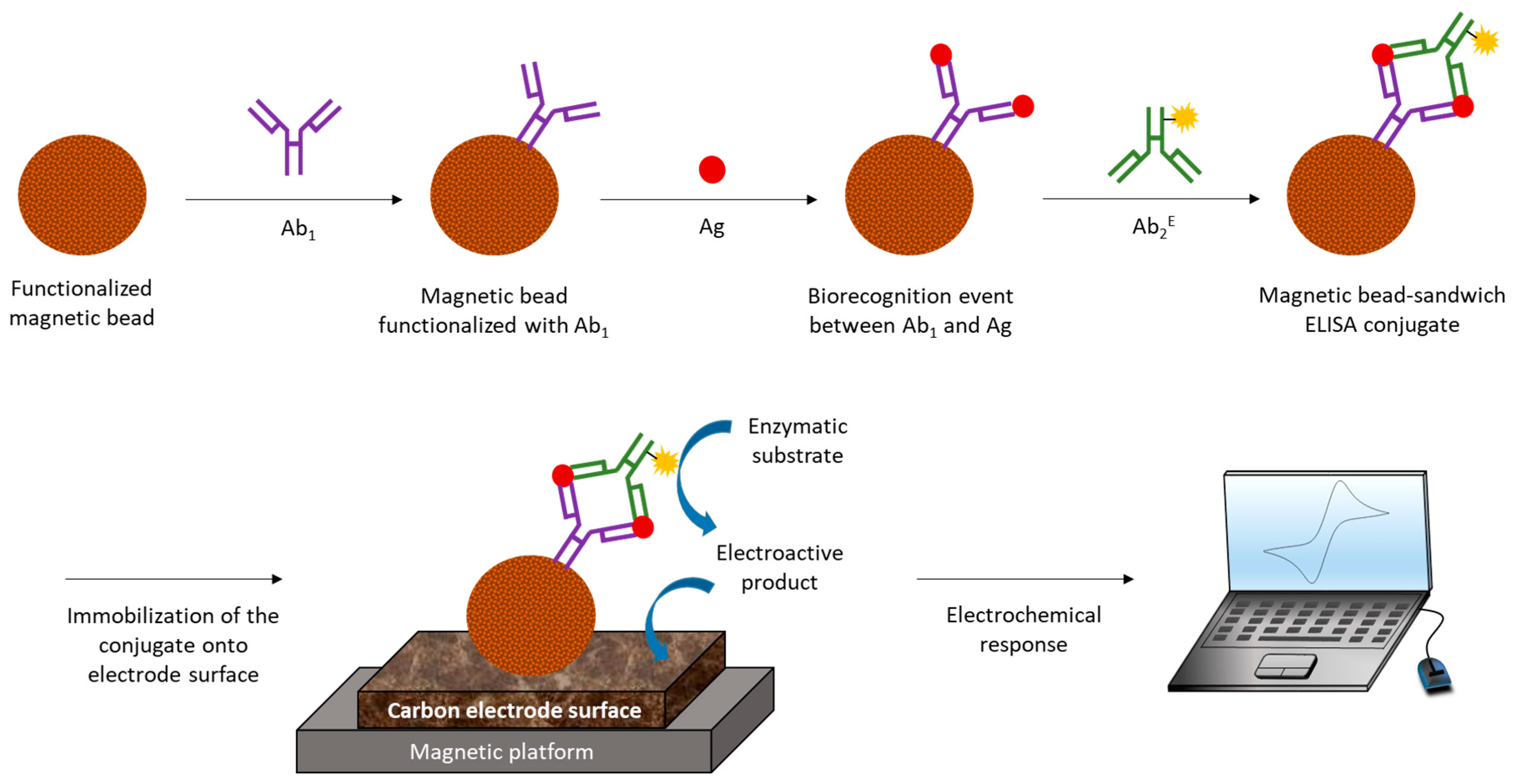
2. Electrochemical Immunosensors, EIs
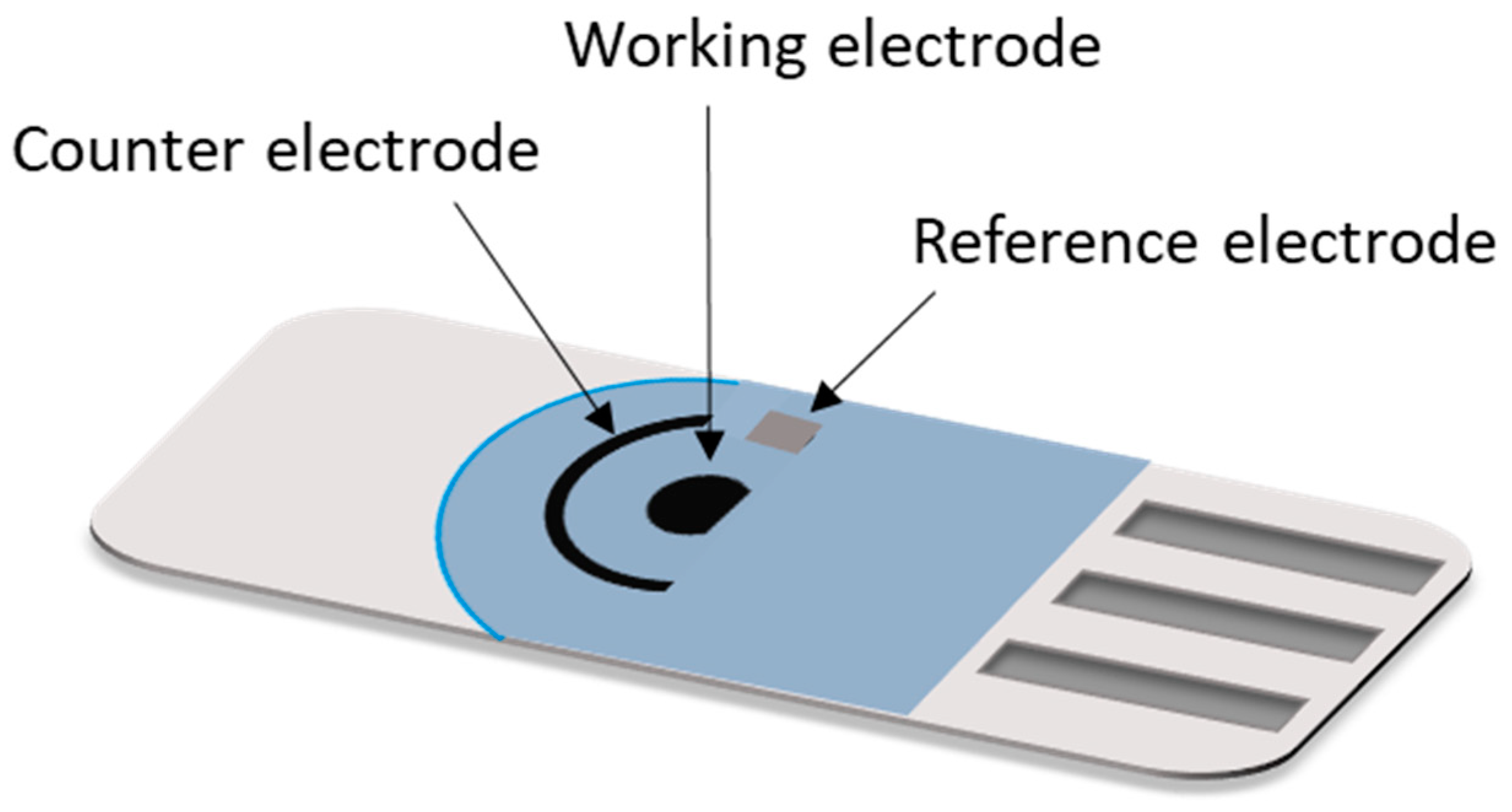
3. Screen Printed Electrodes, SPEs
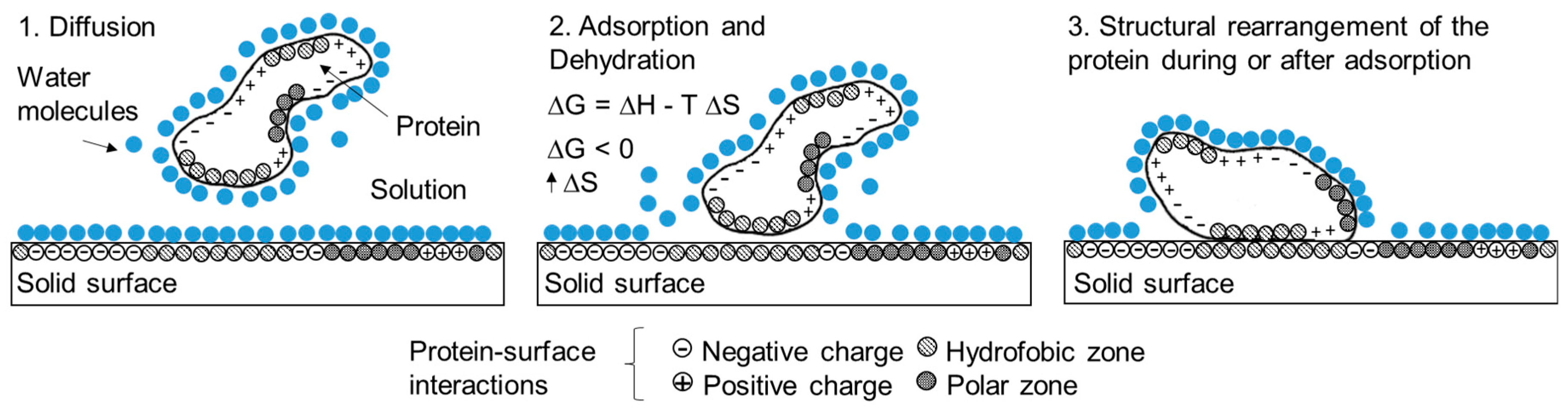
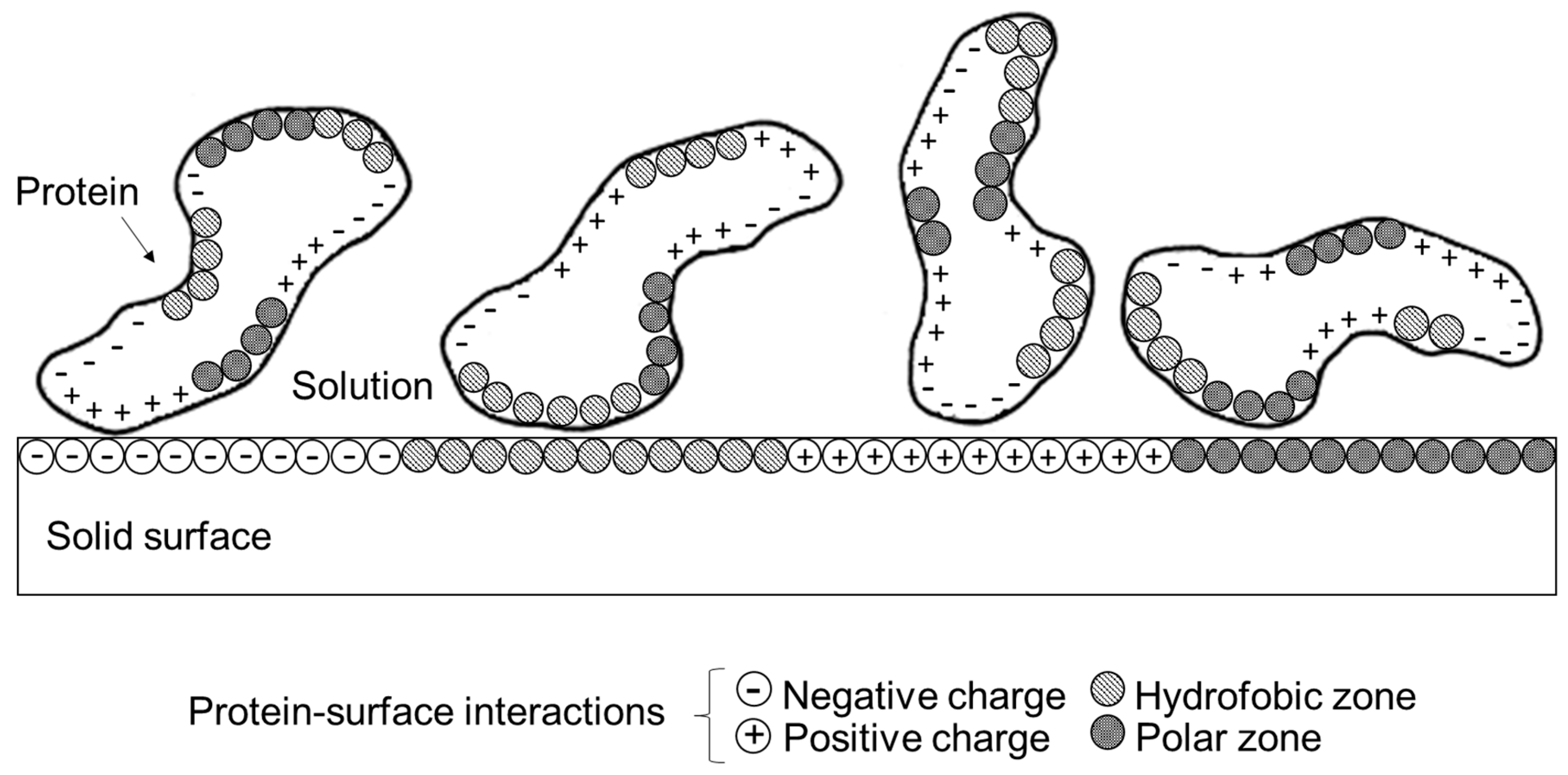
4. Understanding Protein Adsorption on Solid Surfaces to Improve Electrochemical Response
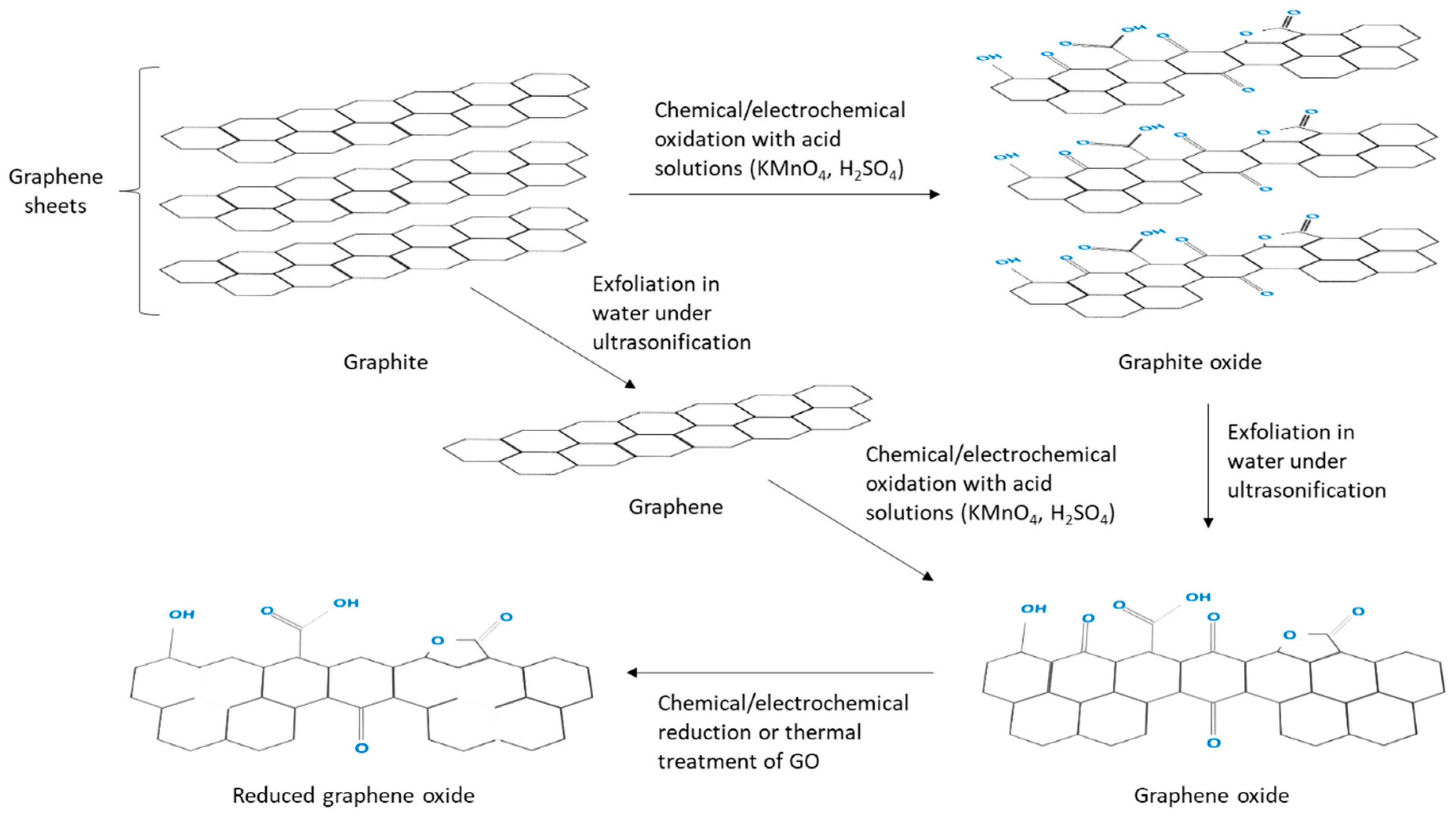
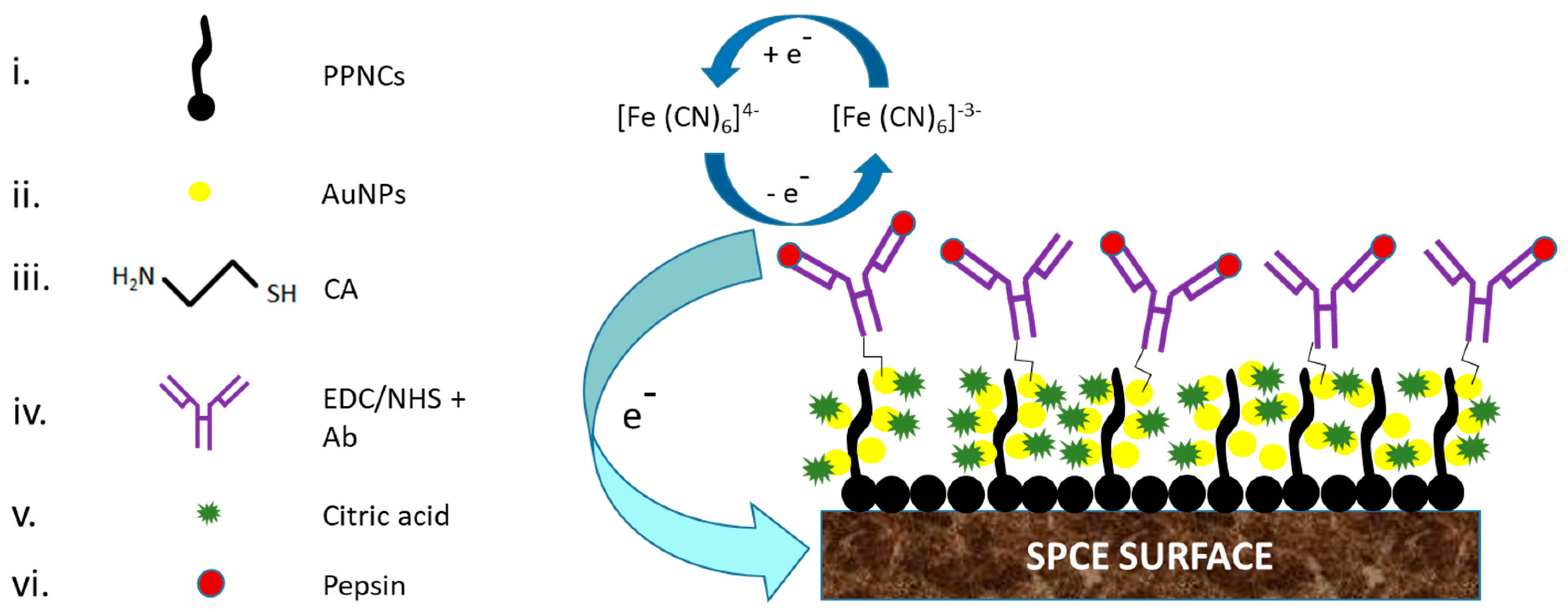
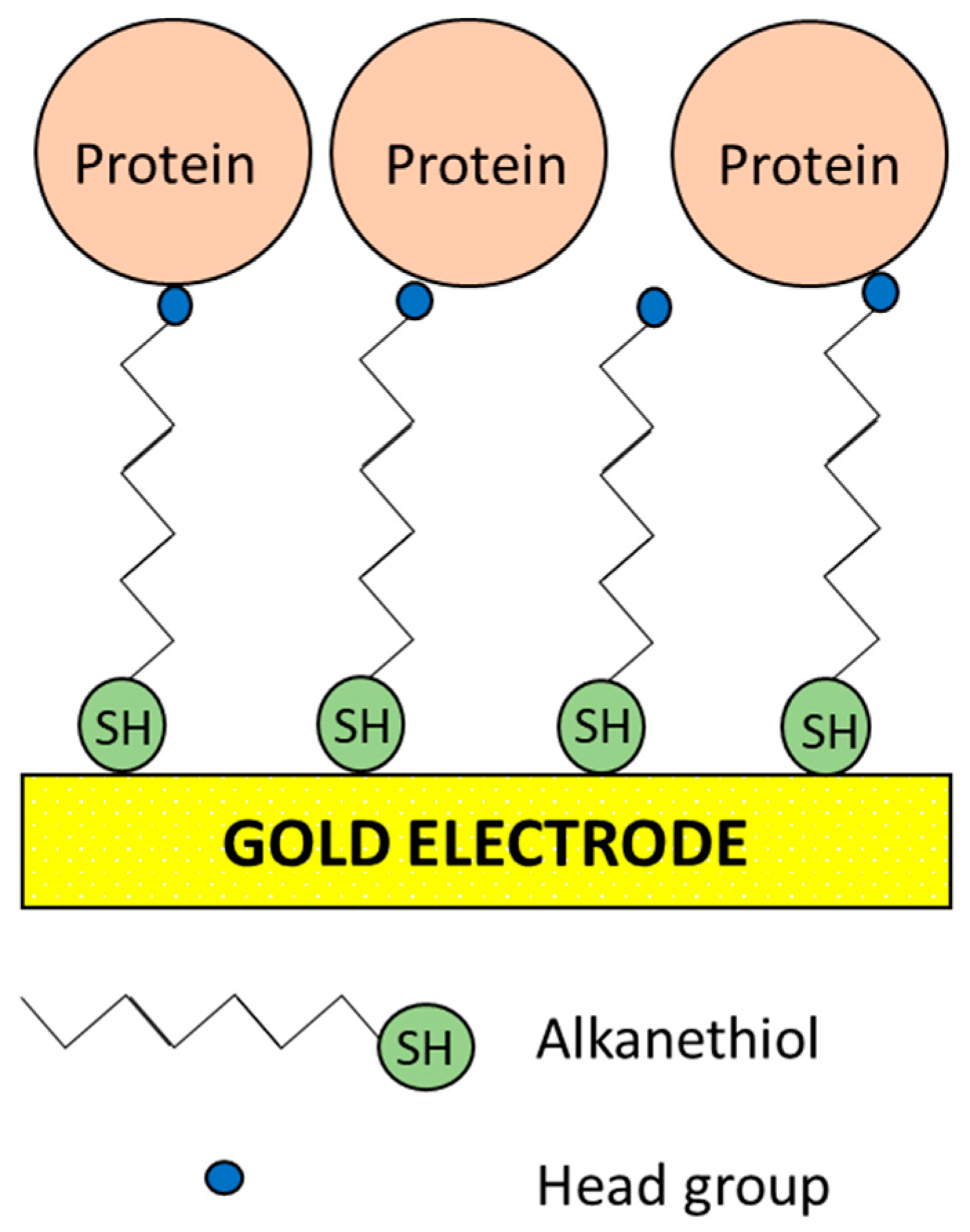
5. Strategies to Suppress Non-Specific Binding of Antibodies in EIs
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
- Portability for point of care testing applications
- Low cost disposable EIs
- High sensitivity and specificity to the target molecule
- Rapid clinical analysis
- Low sample and reagent consumption
- Easy to use
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, M.; Gu, Y.; Yun, Y.; Li, M.; Jin, X.; Wang, S. Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Immunosensing. Sensors 2017, 17, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadır, E.B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. Applications of electrochemical immunosensors for early clinical diagnostics. Talanta 2015, 132, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-H.; Wang, S. Sensors and biosensors for the determination of small molecule biological toxins. Sensors 2008, 8, 6045–6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piro, B.; Reisberg, S. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Immunosensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistry, K.K.; Layek, K.; Mahapatra, A.; RoyChaudhuri, C.; Saha, H. A review on amperometric-type immunosensors based on screen-printed electrodes. Analyst 2014, 139, 2289–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopinath, S.C.B.; Tang, T.-H.; Citartan, M.; Chen, Y.; Lakshmipriya, T. Current aspects in immunosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 57, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thévenot, D.R.; Toth, K.; Durst, R.A.; Wilson, G.S. Electrochemical biosensors: Recommended definitions and classification. Pure Appl. Chem. 1999, 71, 2333–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, G. Electrochemical Sensors for Clinic Analysis. Sensors 2008, 8, 2043–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Yao, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, D.; Gao, F.; Wang, P. Proximity hybridization-regulated catalytic DNA hairpin assembly for electrochemical immunoassay based on in situ DNA template-synthesized Pd nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 969, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zhou, F.; Chen, S.; Yao, Y.; Wu, J.; Yin, D.; Geng, D.; Wang, P. Proximity hybridization triggered rolling-circle amplification for sensitive electrochemical homogeneous immunoassay. Analyst 2017, 142, 4308–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liu, Q. Biomedical Sensors and Measurement; Zhejiang University Press: Hangzhou, China; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 199–214. ISBN 978-7-308-08269-3. [Google Scholar]
- Neethirajan, S.; Ragavan, V.; Weng, X.; Chand, R. Biosensors for Sustainable Food Engineering: Challenges and Perspectives. Biosensors 2018, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damborský, P.; Švitel, J.; Katrlík, J. Optical biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, F.; Zhu, A.; Shi, H. Recent Advances in Optical Biosensors for Environmental Monitoring and Early Warning. Sensors 2013, 13, 13928–13948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarocka, U.; Sawicka, R.; Góra-Sochacka, A.; Sirko, A.; Zagórski-Ostoja, W.; Radecki, J.; Radecka, H. Electrochemical immunosensor for detection of antibodies against influenza A virus H5N1 in hen serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 55, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Escosura-Muñiz, A.; Merkoçi, A. Electrochemical detection of proteins using nanoparticles: Applications to diagnostics. Expert Opin. Med. Diagn. 2010, 4, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, G.; Westmacott, K.; Honeychurch, K.C.; Crew, A.; Pemberton, R.M.; Hart, J.P. Recent Advances in the Fabrication and Application of Screen-Printed Electrochemical (Bio)Sensors Based on Carbon Materials for Biomedical, Agri-Food and Environmental Analyses. Biosensors 2016, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tadigadapa, S. Calorimetric biosensors with integrated microfluidic channels. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 19, 1733–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo-Dinh, T.; Cullum, B. Biosensors and biochips: Advances in biological and medical diagnosis. Anal. Chem. 2000, 366, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janshoff, A.; Galla, H.-J.; Steinem, C. Piezoelectric mass-sensing devices as biosensors—An alternative to optical biosensors? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2000, 39, 4004–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiteri, R.; Grattarola, M.; Butt, H.-J.; Skládal, P. Micromechanical cantilever-based biosensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 79, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presnova, G.V.; Rybcova, M.Y.; Egorov, A.M. Electrochemical Biosensors Based on Horseradish Peroxidase. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2008, 78, 2482–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.W.; Park, J.M.; Bernhardt, R.; Pyun, J.C. Immunosensor with a controlled orientation of antibodies by using NeutrAvidin–protein A complex at immunoaffinity layer. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 126, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokkinos, C.; Economou, A.; Prodromidis, M.I. Electrochemical immunosensors: Critical survey of different architectures and transduction strategies. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 88–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronkainen, N.J.; Halsall, H.B.; Heineman, W.R. Electrochemical biosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1747–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, K.; Ricciardi, C. Biosensors. In Encyclopedia of Food and Health, 1st ed.; Caballero, B., Finglas, P.M., Toldrá, F., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 1, pp. 430–436. ISBN 978-0-12-384947-2. [Google Scholar]
- Piro, B.; Shi, S.; Reisberg, S.; Noël, V.; Anquetin, G. Comparison of Electrochemical Immunosensors and Aptasensors for Detection of Small Organic Molecules in Environment, Food Safety, Clinical and Public Security. Biosensors 2016, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García Merino, A. Monoclonal antibodies. Basic features. Neurologia 2011, 26, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Byrne, H.; O’Kennedy, R.J. Antibodies and antibody-derived analytical biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieshaber, D.; MacKenzie, R.; Vörös, J.; Reimhult, E. Electrochemical Biosensors—Sensor Principles and Architectures. Sensors 2008, 8, 1400–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moina, C.; Ybarra, G. Fundamentals and Applications of Immunosensors. In Advances in Immunoassay Technology; Chiu, N.H.L., Christopoulos, T.K., Eds.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 65–69. ISBN 978-953-51-0440-7. [Google Scholar]
- Felix, F.S.; Angnes, L. Electrochemical immunosensors—A powerful tool for analytical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.S.; Rahman, M.R.T.; Lou, Z.; Tang, Y.; Raqib, S.M.; Jothi, J.S. Review: Advancements and application of immunosensors in the analysis of food contaminants. Nusant. Biosci. 2014, 6, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, B.; Chen, G.; Tang, D. Redox and catalysis “all-in-one” infinite coordination polymer for electrochemical immunosensor of tumor markers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, I.-H.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Kang, M.; Paik, J.K.; Ku, S.; Cho, H.-M.; Irudayaraj, J.; Kim, D.-H. Current Technologies of Electrochemical Immunosensors: Perspective on Signal Amplification. Sensors 2018, 18, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arduini, F.; Micheli, L.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G.; Piermarini, S.; Ricci, F.; Volpe, G. Electrochemical biosensors based on nanomodified screen-printed electrodes: Recent applications in clinical analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, F.; Volpe, G.; Micheli, L.; Palleschi, G. A review on novel developments and applications of immunosensors in food analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 605, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, F.; Adornetto, G.; Palleschi, G. A review of experimental aspects of electrochemical immunosensors. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 84, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viguier, C.; Crean, C.; O’Kennedy, R. Trends and perspectives in immunosensors. In Antibodies Applications and New Developments; Meulenberg, E.P., Ed.; Bentham Science: Emirate of Sharjah, UAE, 2012; Volume 25, pp. 184–208. ISBN 978-1-60805-586-9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Electrochemical Biosensors: Towards Point-of-Care Cancer Diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1887–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahammad, A.J.S.; Lee, J.-J.; Rahman, M.A. Electrochemical Sensors Based on Carbon Nanotubes. Sensors 2009, 9, 2289–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Nanoparticle-Based Electrochemical Bioassays of Proteins. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, B.D.; Kumar, S.; Pandey, C.M. Nanomaterials based biosensors for cancer biomarker detection. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 704, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renedo, O.D.; Alonso-Lomillo, M.A.; Martínez, M.J.A. Recent developments in the field of screen-printed electrodes and their related applications. Talanta 2007, 73, 202–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Miranda Ferrari, A.; Foster, C.W.; Kelly, P.J.; Brownson, D.A.C.; Banks, C.E. Determination of the Electrochemical Area of Screen-Printed Electrochemical Sensing Platforms. Biosensors 2018, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Li, Y.-T.; Li, D.-W.; Long, Y.-T. Recent developments and applications of screen-printed electrodes in environmental assays—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 734, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fähnrich, K.A.; Pravda, M.; Guilbault, G.G. Disposable amperometric immunosensor for the detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) using screen printed electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 18, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, R.A.S.; Lima, J.L.F.C.; Quinaz, M.B. Recent developments, characteristics and potential applications of screen-printed electrodes in pharmaceutical and biological analysis. Talanta 2016, 146, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taleat, Z.; Khoshroo, A.; Mazloum-Ardakani, M. Screen-printed electrodes for biosensing: A review (2008–2013). Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 865–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanjul-Bolado, P.; Hernández-Santos, D.; Lamas-Ardisana, P.J.; Martín-Pernía, A.; Costa-García, A. Electrochemical characterization of screen-printed and conventional carbon paste electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 3635–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Ho, J.C.; Takahashi, T.; Yerushalmi, R.; Takei, K.; Ford, A.C.; Chueh, Y.-L.; Javey, A. Toward the Development of Printable Nanowire Electronics and Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 3730–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, A.; Marty, J.L. Disposable Screen Printed Electrochemical Sensors: Tools for Environmental Monitoring. Sensors 2014, 14, 10432–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, K.; Vestergaard, M.C.; Tamiya, E. Printable Electrochemical Biosensors: A Focus on Screen-Printed Electrodes and Their Application. Sensors 2016, 16, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rama, E.C.; Costa-García, A. Screen-printed Electrochemical Immunosensors for the Detection of Cancer and Cardiovascular Biomarkers. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 1700–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C. Electrochemical Based Biosensors. Biosensors 2012, 2, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tudorache, M.; Bala, C. Biosensors based on screen-printing technology, and their applications in environmental and food analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 388, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Multiplexed Electrochemical Immunosensors for Clinical Biomarkers. Sensors 2017, 17, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devarakonda, S.; Singh, R.; Bhardwaj, J.; Jang, J. Cost-Effective and Handmade Paper-Based Immunosensing Device for Electrochemical Detection of Influenza Virus. Sensors 2017, 17, 2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cate, D.M.; Adkins, J.A.; Mettakoonpitak, J.; Henry, C.S. Recent developments in paper-based microfluidic devices. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windmiller, J.R.; Wang, J. Wearable Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors: A Review. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandodkar, A.J.; Jia, W.; Wang, J. Tattoo-Based Wearable Electrochemical Devices: A Review. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diederich, A.; Lösche, M. Novel biosensoric devices based on molecular protein hetero-multilayer films. Adv. Biophys. 1997, 34, 205–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, B.L.; Jordan, C.E.; Komguth, S.; Corn, R.M. Control of the Specific Adsorption of Proteins onto Gold Surfaces with Poly(L-lysine) Monolayers. Anal. Chem. 1995, 67, 4452–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sołoducho, J.; Cabaj, J.; Świst, A. Structure and Sensor Properties of Thin Ordered Solid Films. Sensors 2009, 9, 7733–7752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, M.; Estevez, M.-C.; Alvarez, M.; Otte, M.A.; Sepulveda, B.; Lechuga, L.M. Direct Detection of Protein Biomarkers in Human Fluids Using Site-Specific Antibody Immobilization Strategies. Sensors 2014, 14, 2239–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, J.D.; Hlady, V.; Wei, A.P. Adsorption of complex proteins at interfaces. Pure Appl. Chem. 1992, 64, 1777–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzeciakiewicz, H.; Esteves-Villanueva, J.; Soudy, R.; Kaur, K.; Martic-Milne, S. Electrochemical Characterization of Protein Adsorption onto YNGRT-Au and VLGXE-Au Surfaces. Sensors 2015, 15, 19429–19442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferhan, A.R.; Jackman, J.A.; Sut, T.N.; Cho, N.-J. Quantitative Comparison of Protein Adsorption and Conformational Changes on Dielectric-Coated Nanoplasmonic Sensing Arrays. Sensors 2018, 18, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q. Protein Adsorption in Microengraving Immunoassays. Sensors 2015, 15, 26236–26250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabe, M.; Verdes, D.; Seeger, S. Understanding protein adsorption phenomena at solid surfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 162, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggiero, C.; Mantelli, M.; Curtis, A.; Rolfe, P. Protein–Surface Interactions-An Energy-Based Mathematical Model. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 42, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, K.C.; Puleo, D.A.; Bizios, R. Protein-Surface Interactions. In An Introduction to Tissue-Biomaterial Interactions: Tissue-Biomaterial, 1st ed.; Dee, K.C., Puleo, D.A., Bizios, R., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 37–52. ISBN 9780471253945. [Google Scholar]
- Demanèche, S.; Chapel, J.-P.; Monrozier, L.J.; Quiquampoix, H. Dissimilar pH-dependent adsorption features of bovine serum albumin and α-chymotrypsin on mica probed by AFM. Colloids Surf. B 2009, 70, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremer, M.G.E.G.; Duval, J.; Norde, W.; Lyklema, J. Electrostatic interactions between immunoglobulin (IgG) molecules and a charged sorbent. Colloids Surf. A 2004, 250, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakides, T.R. Molecular Events at Tissue–Biomaterial Interface. In Host Response to Biomaterials: The Impact of Host Response on Biomaterial Selection, 1st ed.; Badylak, S.F., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2015; pp. 81–116. ISBN 9780128005002. [Google Scholar]
- Poncin-Epaillard, F.; Vrlinic, T.; Debarnot, D.; Mozetic, M.; Coudreuse, A.; Legeay, G.; El Moualij, B.; Zorzi, W. Surface treatment of polymeric materials controlling the adhesion of biomolecules. J. Funct. Biomater. 2012, 3, 528–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, P.; Farrar, D.; Perry, C.C. Interpretation of Protein Adsorption: Surface-Induced Conformational Changes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 8168–8173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, J.D.; Hlady, V. Protein Adsorption and Materials Biocompatibility: A Tutorial Review and Suggested Hypotheses. Adv. Polym. Sci. 1986, 79, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertz, C.F.; Santore, M.M. Adsorption and Reorientation Kinetics of Lysozyme on Hydrophobic Surfaces. Langmuir 2002, 18, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noinville, S.; Bruston, F.; El Amri, C.; Baron, D.; Nicolas, P. Conformation, Orientation, and Adsorption Kinetics of Dermaseptin B2 onto Synthetic Supports at Aqueous/Solid Interface. Biophys. J. 2003, 85, 1196–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norde, W. Driving forces for protein adsorption at solid surfaces. Macromol. Symp. 1996, 103, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.J.; Clegg, R.E.; Leavesley, D.I.; Pearcy, M.J. Mediation of biomaterial–cell interactions by adsorbed proteins: A review. Tissue Eng. 2005, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, R.J.; Jones, R.A.L.; Sferrazza, M. Adsorption and displacement of a globular protein on hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces. Colloids Surf. B 2002, 23, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertz, C.F.; Santore, M.M. Effect of Surface Hydrophobicity on Adsorption and Relaxation Kinetics of Albumin and Fibrinogen: Single-Species and Competitive Behavior. Langmuir 2001, 17, 3006–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartošík, M.; Doneux, T.; Pechan, Z.; Ostatná, V.; Paleček, E. Electrochemical detection of proteins. Encycl. Anal. Chem. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, K.; Sakiyama, T.; Imamura, K. On the adsorption of proteins on solid surfaces, a common but very complicated phenomenon. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2001, 91, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockris, J.; Reddy, A.K.N. Modern Electrochemistry 2B: Electrodics in Chemistry, Engineering, Biology, and Environmental Science, 2nd ed.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 1933–1948. ISBN 0-306-46324-5. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, L.C., Jr.; Lyons, C. Electrode systems for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1962, 102, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shedge, H.Y. Specific and Non-Specific Binding of Proteins and Nucleic Acids on Chemically Modified Reticulated Vitreous Carbon Electrodes. Master’s Thesis, Clemson University, Clemson, SC, USA, May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, A.; Cheng, K. The principles and applications of avidin-based nanoparticles in drug delivery and diagnosis. J. Control. Release 2017, 245, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermanson, G.T. Bioconjugate Techniques, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 465–505. ISBN 978-0-12-382239-0. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, A.; Barve, A.; Zhao, Z.; Jin, W.; Cheng, K. Comparison of avidin, neutravidin, and streptavidin as nanocarriers for efficient siRNA Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 1517–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orelma, H.; Johansson, L.S.; Filpponen, I.; Rojas, O.J.; Laine, J. Generic Method for Attaching Biomolecules via Avidin−Biotin Complexes Immobilized on Films of Regenerated and Nanofibrillar Cellulose. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 2802–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasinszki, T.; Krebsz, M.; Tung, T.T.; Losic, D. Carbon Nanomaterial Based Biosensors for Non-Invasive Detection of Cancer and Disease Biomarkers for Clinical Diagnosis. Sensors 2017, 17, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balcer, H.I.; Spiker, J.O.; Kang, K.A. Effects of Blocking Buffers and Plasma Proteins on the Protein C Biosensor Performance. In Oxygen Transport to Tissue XXIV. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 1st ed.; Dunn, J.F., Swartz, H.M., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; Volume 530, pp. 133–141. ISBN 978-1-4613-4912-9. [Google Scholar]
- Korotkaya, E.V. Biosensors: Design, classification, and applications in the food industry. Foods Raw Mater. 2014, 2, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Analytical Electrochemistry, 3rd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 130–136. ISBN 13 978-0-471-67879-3. [Google Scholar]
- Saka, C. Overview on the surface functionalization mechanism and determination of surface functional groups of plasma treated carbon nanotubes. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2017, 48, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, G.F.; Moore, E.J. Electrochemical immunosensors for food analysis: A review of recent developments. Anal. Lett. 2016, 50, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Tirado, E.; González-Cortés, A.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Carbon nanotubes functionalized by click chemistry as scaffolds for the preparation of electrochemical immunosensors. Application to the determination of TGF-beta 1 cytokine. Analyst 2016, 141, 5730–5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlili, C.; Cella, L.N.; Myung, N.V.; Shetty, V.; Mulchandani, A. Single-walled carbon nanotube chemoresistive label-free immunosensor for salivary stress biomarkers. Analyst 2010, 135, 2637–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanginario, A.; Miccoli, B.; Demarchi, D. Carbon Nanotubes as an Effective Opportunity for Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment. Biosensors 2017, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuila, T.; Bose, S.; Khanra, P.; Mishra, A.K.; Kim, N.H.; Lee, J.H. Recent advances in graphene-based biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 4637–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Li, G.; Deng, P.; Liang, J. Preparation of Cu2O-Reduced Graphene Nanocomposite Modified Electrodes towards Ultrasensitive Dopamine Detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.-H.; Chen, C.-W.; Lin, Y.-K.; Yeh, Y.-C.; Hsu, C.-C.; Fan, Y.-J.; Yu, I.-S.; Chen, J.-Z. Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma Jet Processed Carbon-Based Electrochemical Sensor Integrated with a 3D-Printed Microfluidic Channel. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, B534–B541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.-J. Simultaneous detection of tumor cell apoptosis regulators Bcl-2 and Bax through a dual-signal-marked electrochemical immunosensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 7674–7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.A.; Ahmed, M.U. Electrochemical immunosensors and their recent nanomaterial-based signal amplification strategies: A review. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 24995–25014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, H.; Ghourchian, H.; Eskandari, K.; Zeinali, M. Magnetic nanocomposite of anti-human IgG/COOH-multiwalled carbon nanotubes/Fe3O4 as a platform for electrochemical immunoassay. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 421, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, H.; Du, B.; Wei, Q. Facile synthesis of cuprous oxide nanowires decorated graphene oxide nanosheets nanocomposites and its application in label-free electrochemical immunosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthi, V.S.P.K.S.A.; Das, A.B.; Saxena, U. Recent advances in biosensor development for the detection of cancer biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 91, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzinger, M.; Le Goff, A.; Cosnier, S. Synergetic Effects of Combined Nanomaterials for Biosensing Applications. Sensors 2017, 17, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, S.; Perez-Potti, A. Applications of Nanomaterials for Immunosensing. Biosensors 2018, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Jia, X.; Han, J.; Ma, J.; Ma, Z. Electrochemical immunosensor for simultaneous detection of multiplex cancer biomarkers based on graphene nanocomposites. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 50, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Hong, S.; Jang, J. Label-free detection of influenza viruses using a reduced graphene oxide-based electrochemical immunosensor integrated with a microfluidic platform. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, S.S.; Lonkar, S.; Singh, K.K.; Swaminathan, S.; Abdala, A. Recent advances in graphene based gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 218, 160–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, X.; Chen, P. Biological and chemical sensors based on graphene materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2283–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Cheng, J.; Tang, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, J. Self-assembled graphene-enzyme hierarchical nanostructures for electrochemical biosensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 3366–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Dai, Z.; Lin, Y.; Du, D. Electrochemical Immunoassays Based on Graphene: A Review. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummers, W.S., Jr.; Offeman, R.E. Preparation of Graphitic Oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Cote, L.J.; Kim, F.; Yuan, W.; Shull, K.R.; Huang, J. Graphene oxide sheets at interfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 8180–8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suvarnaphaet, P.; Pechprasarn, S. Graphene-Based Materials for Biosensors: A Review. Sensors 2017, 17, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.C. Application and Uses of Graphene Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide. In Applications of Graphene and Graphene-Oxide Based Nanomaterials, 1st ed.; Ray, S.C., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 39–55. ISBN 978-0-323-37521-4. [Google Scholar]
- Haque, A.-M.J.; Park, H.; Sung, D.; Jon, S.; Choi, S.-Y.; Kim, K. An Electrochemically Reduced Graphene Oxide-Based Electrochemical Immunosensing Platform for Ultrasensitive Antigen Detection. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 1871–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auffan, M.; Rose, J.; Bottero, J.-Y.; Lowry, G.V.; Jolivet, J.-P.; Wiesner, M.R. Towards a definition of inorganic nanoparticles from an environmental, health and safety perspective. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Morrin, A.; Killard, A.J.; Smyth, M.R. Application of Nanoparticles in Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors. Electroanalysis 2006, 18, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, P.; Li, F.; Chu, Q.; Li, Y.; Dong, Y. An ultrasensitive sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor based on the signal amplification strategy of mesoporous core-shell Pd@Pt nanoparticles/amino group functionalized graphene nanocomposite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omidfar, K.; Zarei, H.; Gholizadeh, F.; Larijani, B. A high-sensitivity electrochemical immunosensor based on mobile crystalline material-41-polyvinyl alcohol nanocomposite and colloidal gold nanoparticles. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 421, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, R.; Zhu, J.-J. Fabrication of a novel electrochemical immunosensor based on the gold nanoparticles/colloidal carbon nanosphere hybrid material. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 7814–7817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, S.; Cheng, W.; Rana, R.K.; Zhu, J.-J. Functionalization of poly(o-phenylenediamine) with gold nanoparticles as a label-free immunoassay platform for the detection of human enterovirus 71. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 183, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, V.; Chikkaveeraiah, B.V.; Patel, V.; Gutkind, J.S.; Rusling, J.F. Ultrasensitive Immunosensor for Cancer Biomarker Proteins Using Gold Nanoparticle Film Electrodes and Multienzyme-Particle Amplification. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Liu, C.-M.; Dong, S.-L.; Du, C.-X.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Li, L.-H.; Wei, Y. Enhanced conductivity of rGO/Ag NPs composites for electrochemical immunoassay of prostate-specific antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chikkaveeraiah, B.V.; Bhirde, A.A.; Morgan, N.Y.; Eden, H.S.; Chen, X. Electrochemical Immunosensors for Detection of Cancer Protein Biomarkers. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6546–6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zani, A.; Laschi, S.; Mascini, M.; Marrazza, G. A New Electrochemical Multiplexed Assay for PSA Cancer Marker Detection. Electroanalysis 2010, 23, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, S.; Jiang, S. Protein interactions with oligo(ethylene glycol) (OEG) self-assembled monolayers: OEG stability, surface packing density and protein adsorption. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2007, 18, 1415–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotchen, C.E.; Maybury, I.J.; Nelson, G.W.; Foord, J.S.; Holdway, P.; Marken, F. Amplified Electron Transfer at Poly- Ethylene-Glycol (PEG) Grafted Electrodes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 11260–11268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Wu, H.; Chen, S.; Lu, Y.; Shen, H.; Jia, N. Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of hemoglobin immobilized in poly(ethylene glycol) grafted multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 7078–7084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.-J.; Sun, N.; Cui, M.; Ji, X.-P. The selectivity of triethylene glycol modified glassy carbon electrode for charged and uncharged pieces. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2015, 26, 1421–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Jin, J.; Jiang, W. A study of polyethylene glycol backfilling for enhancing target recognition using QCM-D and DPI. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 6217–6224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokanathan, A.R.; Zhang, S.; Regina, V.R.; Cole, M.A.; Ogaki, R.; Dong, M.; Besenbacher, F.; Meyer, R.L.; Kingshott, P. Mixed poly (ethylene glycol) and oligo (ethylene glycol) layers on gold as nonfouling surfaces created by backfilling. Biointerphases 2011, 6, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Kumar, P.; Park, D.-S.; Shim, Y.-B. Electrochemical Sensors Based on Organic Conjugated Polymers. Sensors 2008, 8, 118–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teles, F.R.R.; Fonseca, L.P. Applications of polymers for biomolecule immobilization in electrochemical biosensors. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2008, 28, 1530–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Lee, Y.J.; Eun, Y.-G.; Lee, G.-J. Label-Free Detection of Salivary Pepsin Using Gold Nanoparticle/Polypyrrole Nanocoral Modified Screen-Printed Electrode. Sensors 2018, 18, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimhult, E.; Höök, F. Design of Surface Modifications for Nanoscale Sensor Applications. Sensors 2015, 15, 1635–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braiek, M.; Rokbani, K.B.; Chrouda, A.; Mrabet, B.; Bakhrouf, A.; Maaref, A.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. An Electrochemical Immunosensor for Detection of Staphylococcus aureus Bacteria Based on Immobilization of Antibodies on Self-Assembled Monolayers-Functionalized Gold Electrode. Biosensors 2012, 2, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Fu, Y.; Fang, W.; Li, Y. Electrochemical Impedance Immunosensor Based on Self-Assembled Monolayers for Rapid Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 with Signal Amplification Using Lectin. Sensors 2015, 15, 19212–19224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delamar, M.; Hitmi, R.; Pinson, J.; Saveant, J.M. Covalent Modification of Carbon Surfaces by Grafting of Functionalized Aryl Radicals Produced from Electrochemical Reduction of Diazonium Salts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 5883–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukerma, K.; Chehimi, M.M.; Pinson, J.; Blomfield, C. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Evidence for the Covalent Bond between an Iron Surface and Aryl Groups Attached by the Electrochemical Reduction of Diazonium Salts. Langmuir 2003, 19, 6333–6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, M.-C.; Chaussé, A.; Cabet-Deliry, E.; Chehimi, M.M.; Pinson, J.; Podvorica, F.; Vautrin-Ul, C. Organic Layers Bonded to Industrial, Coinage, and Noble Metals through Electrochemical Reduction of Aryldiazonium Salts. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 3450–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gam-Derouich, S.; Carbonnier, B.; Turmine, M.; Lang, P.; Jouini, M.; Ben Hassen-Chehimi, D.; Chehimi, M.M. Electrografted aryl diazonium initiators for surface-confined photopolymerization: A new approach to designing functional polymer coatings. Langmuir 2010, 26, 11830–11840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahouche-Chergui, S.; Gam-Derouich, S.; Mangeney, C.; Chehimi, M.M. Aryl diazonium salts: A new class of coupling agents for bonding polymers, biomacromolecules and nanoparticles to surfaces. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4143–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Integrated Affinity Biosensing Platforms on Screen-Printed Electrodes Electrografted with Diazonium Salts. Sensors 2018, 18, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.; Ling, C.; Ma, Q.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, C. Sensitive electrochemical immunosensor array for the simultaneous detection of multiple tumor markers. Analyst 2012, 137, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gam-Derouich, S.; Jouini, M.; Ben Hassen-Chehimi, D.; Chehimi, M.M. Aryl diazonium salt surface chemistry and graft photopolymerization for the preparation of molecularly imprinted polymer biomimetic sensor layers. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 73, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.K.; Agarwal, G.S.; Rao, V.K.; Upadhyay, S.; Merwyn, S.; Gopalan, N.; Rai, G.P.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; Prakash, S. Amperometric immunosensor based on gold nanoparticles/alumina sol–gel modified screen-printed electrodes for antibodies to Plasmodium falciparum histidine rich protein-2. Analyst 2010, 135, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Pamidi, P.V.A.; Rogers, K.R. Sol−Gel-Derived Thick-Film Amperometric Immunosensors. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coradin, T.; Boissière, M.; Livage, J. Sol-gel Chemistry in Medicinal Science. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lev, O.; Wu, Z.; Bharathi, S.; Glezer, V.; Modestov, A.; Gun, J.; Rabinovich, L.; Sampath, S. Sol−Gel Materials in Electrochemistry. Chem. Mater. 1997, 9, 2354–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.A.; Azahar, M.; Malhotra, B.D. Electrochemical Urea Biosensor Based on Sol-gel Derived Nanostructured Cerium Oxide. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2012, 358, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Contreras-Naranjo, J.E.; Aguilar, O. Suppressing Non-Specific Binding of Proteins onto Electrode Surfaces in the Development of Electrochemical Immunosensors. Biosensors 2019, 9, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9010015
Contreras-Naranjo JE, Aguilar O. Suppressing Non-Specific Binding of Proteins onto Electrode Surfaces in the Development of Electrochemical Immunosensors. Biosensors. 2019; 9(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleContreras-Naranjo, Jesús E., and Oscar Aguilar. 2019. "Suppressing Non-Specific Binding of Proteins onto Electrode Surfaces in the Development of Electrochemical Immunosensors" Biosensors 9, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9010015
APA StyleContreras-Naranjo, J. E., & Aguilar, O. (2019). Suppressing Non-Specific Binding of Proteins onto Electrode Surfaces in the Development of Electrochemical Immunosensors. Biosensors, 9(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9010015