Review on SERS of Bacteria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Bacteria and the Antimicrobial Properties of Ag/Au Nanoparticles (NPs)
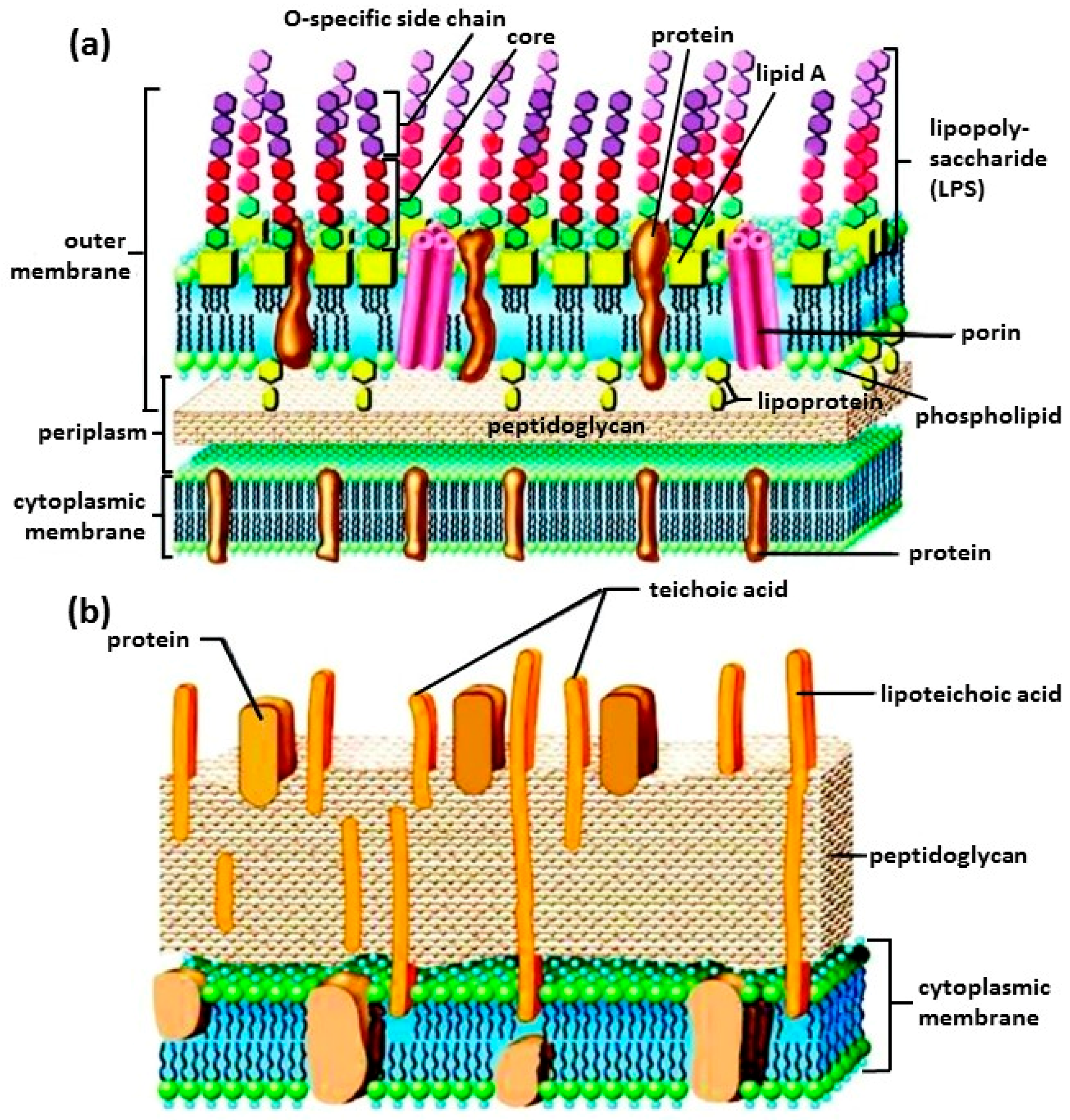
2.1.1. Structure of Bacteria
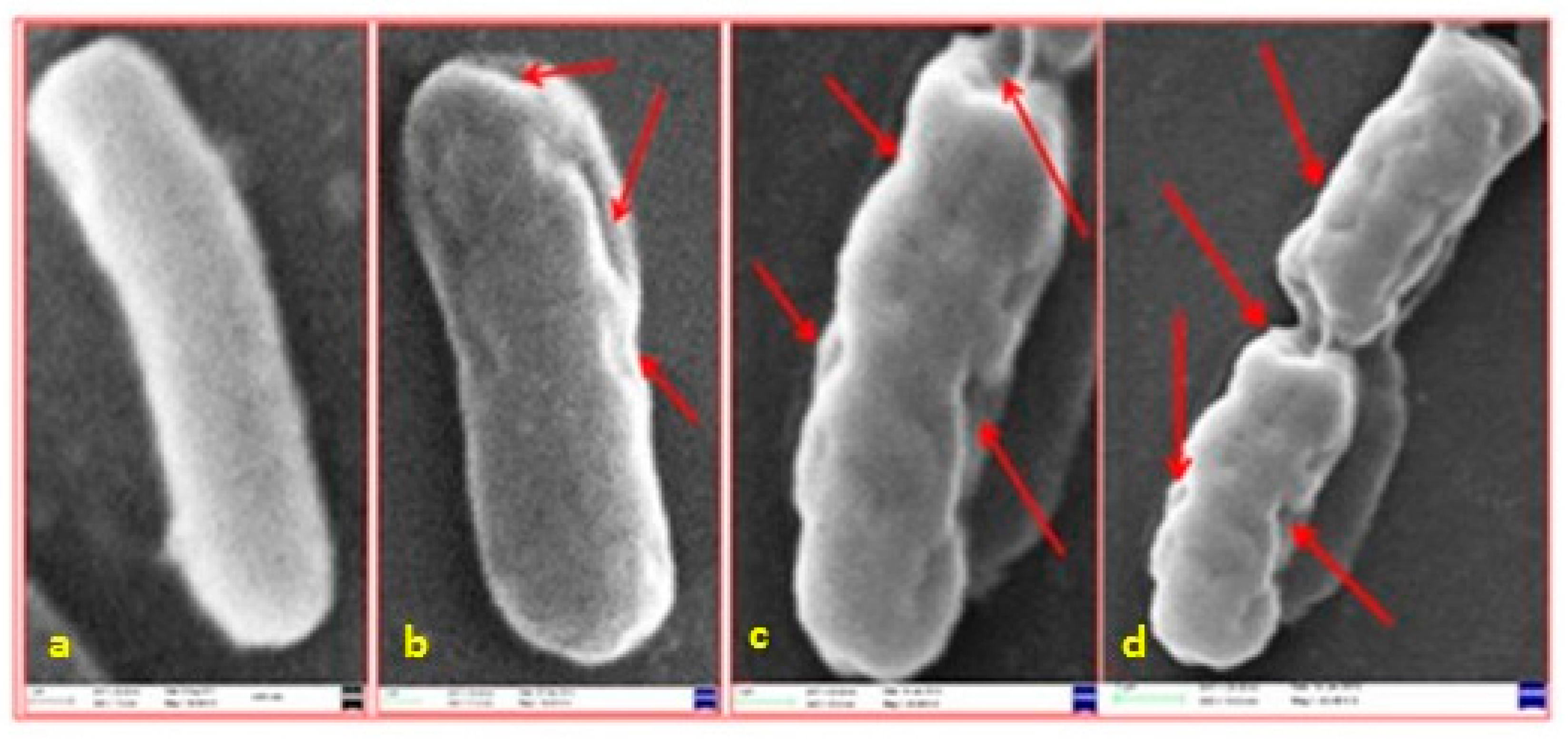
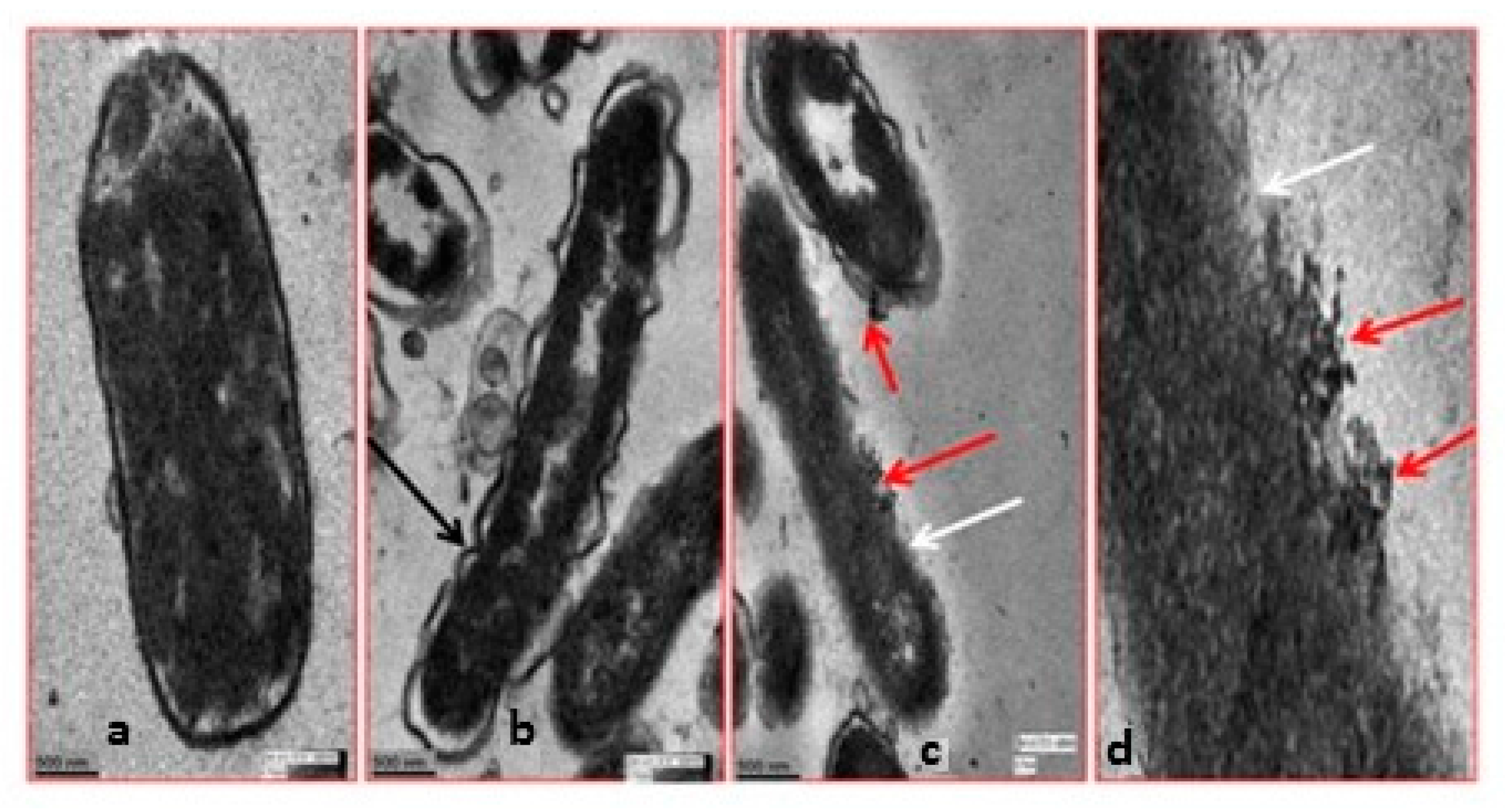
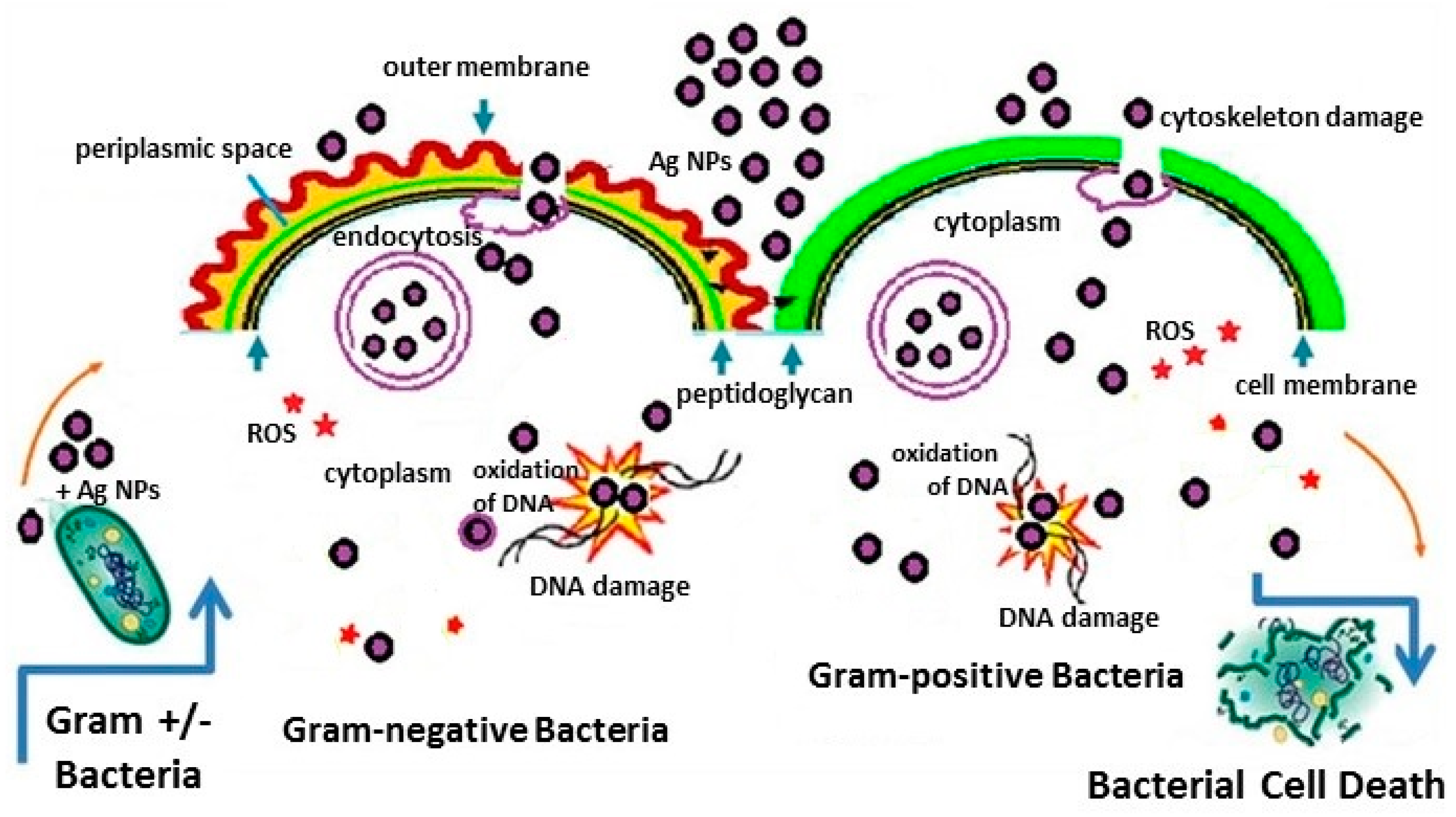
2.1.2. Antimicrobial Activity of Ag/Au NPs: Interaction of Ag/Au NPs with Bacteria
2.2. Methods and Substrates Used to Obtain SERS Spectra of Bacteria
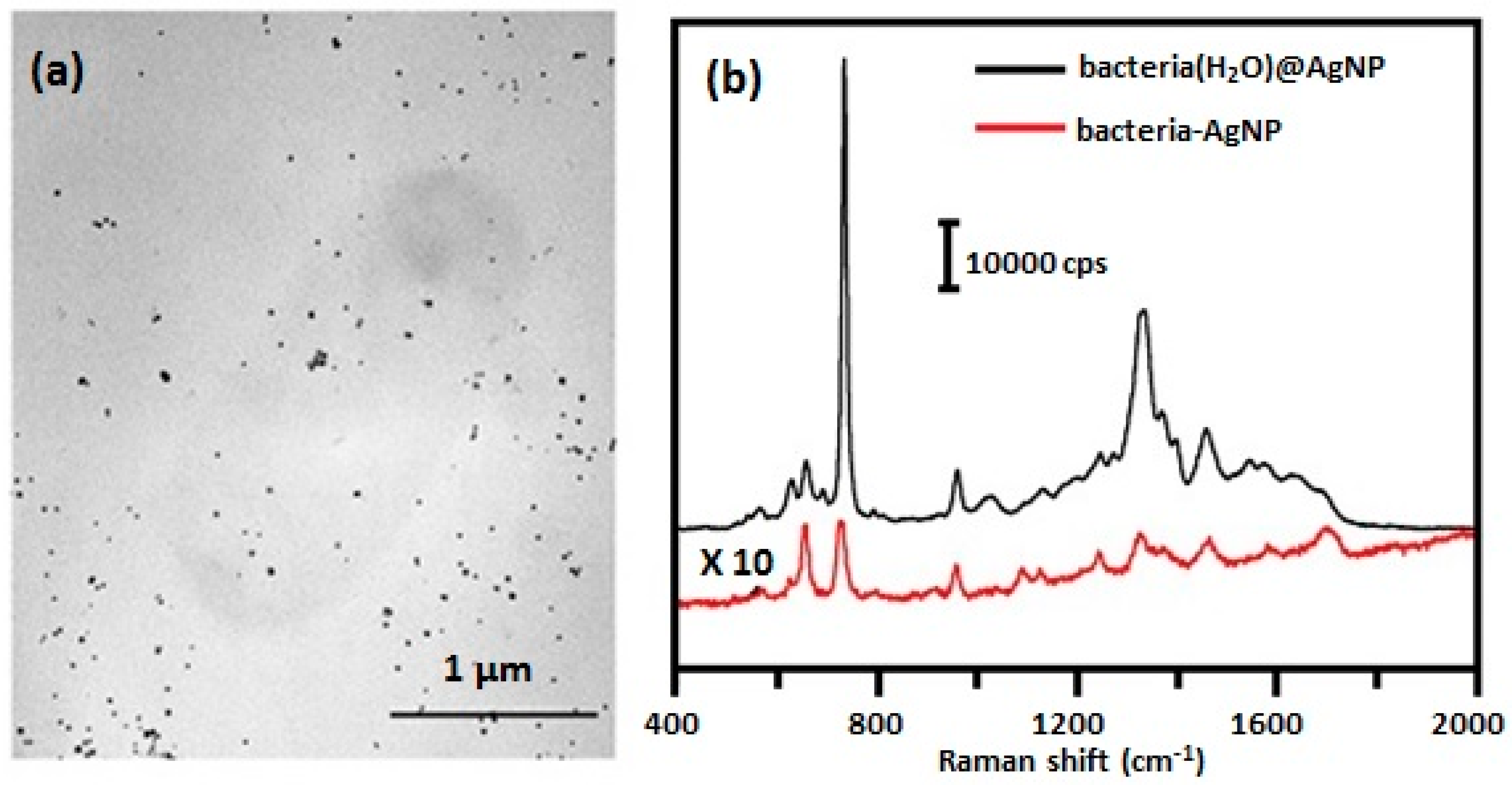
2.2.1. SERS Spectra Obtained by Forming Colloidal Silver/Gold on/inside the Bacteria
2.2.2. SERS Spectra Obtained by Placing Bacteria Directly on a SERS-Active Surface
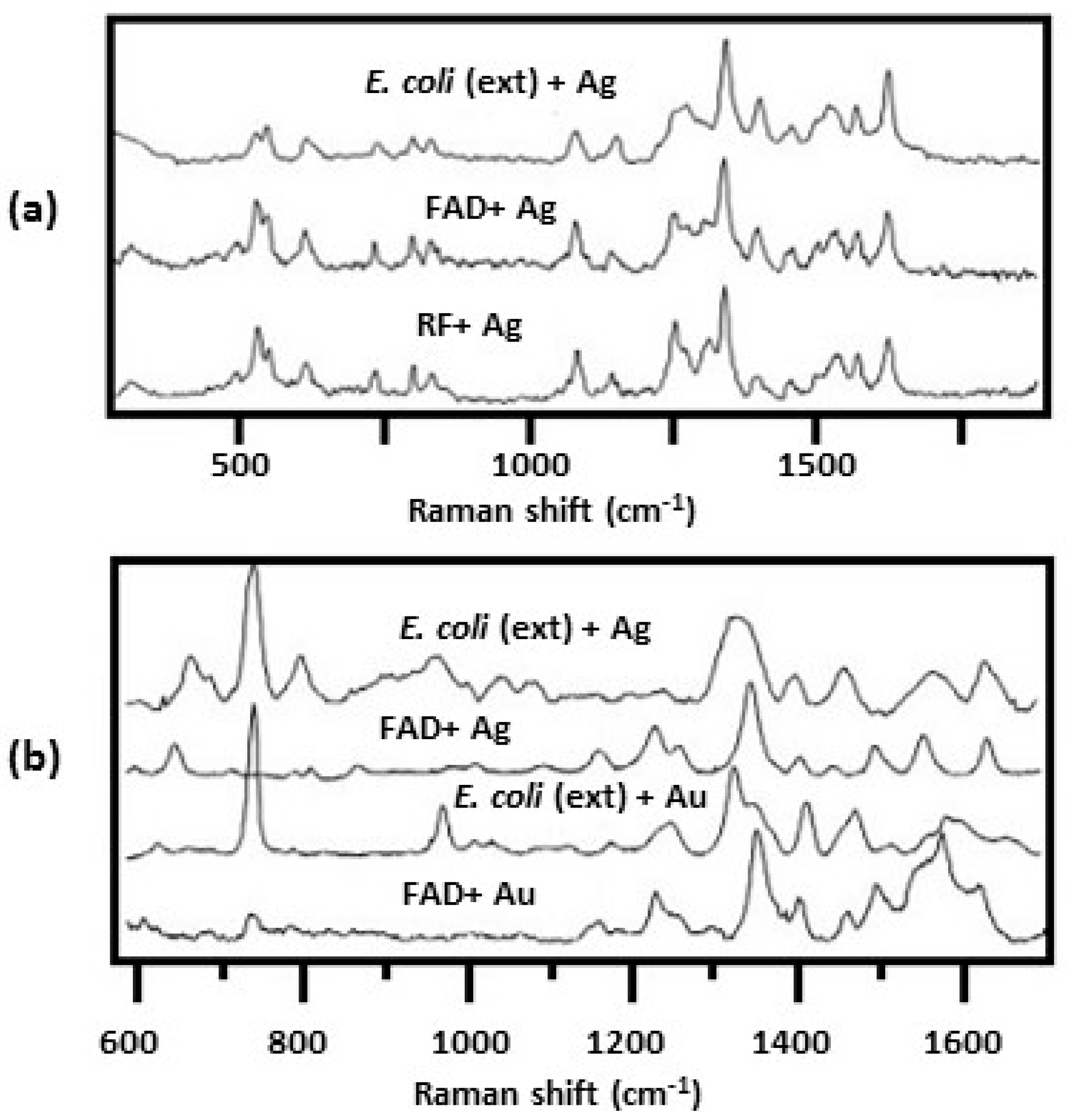
2.2.3. SERS Spectra Obtained by Mixing Colloids with Bacterial Suspensions
2.3. Factors Affecting SERS Spectral Features Obtained for Bacteria
2.3.1. Effect of Laser Excitation Wavelength and Colloid Type
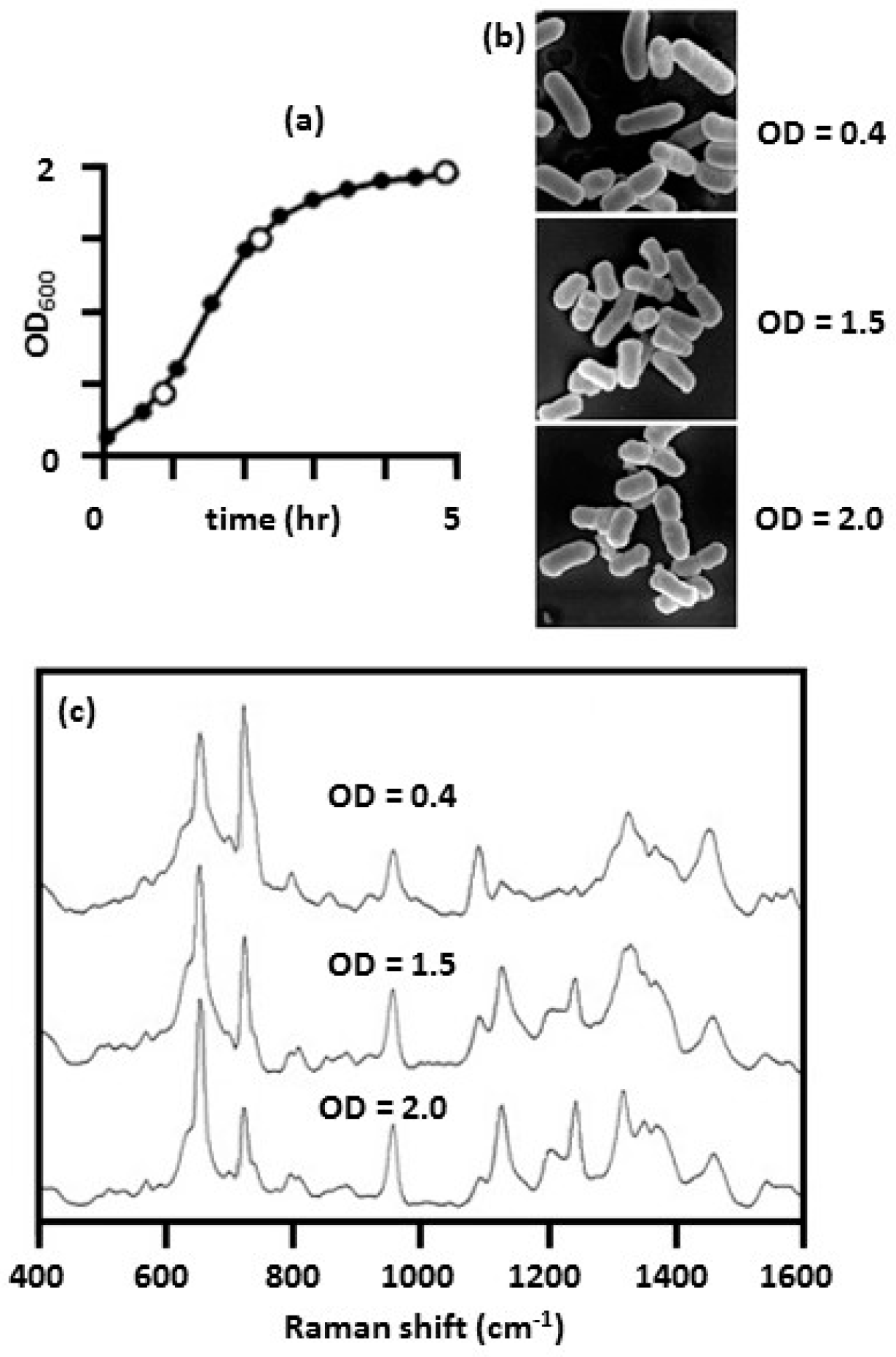
2.3.2. Bacterial Growth Phase
2.3.3. Stress/Environmental Factors
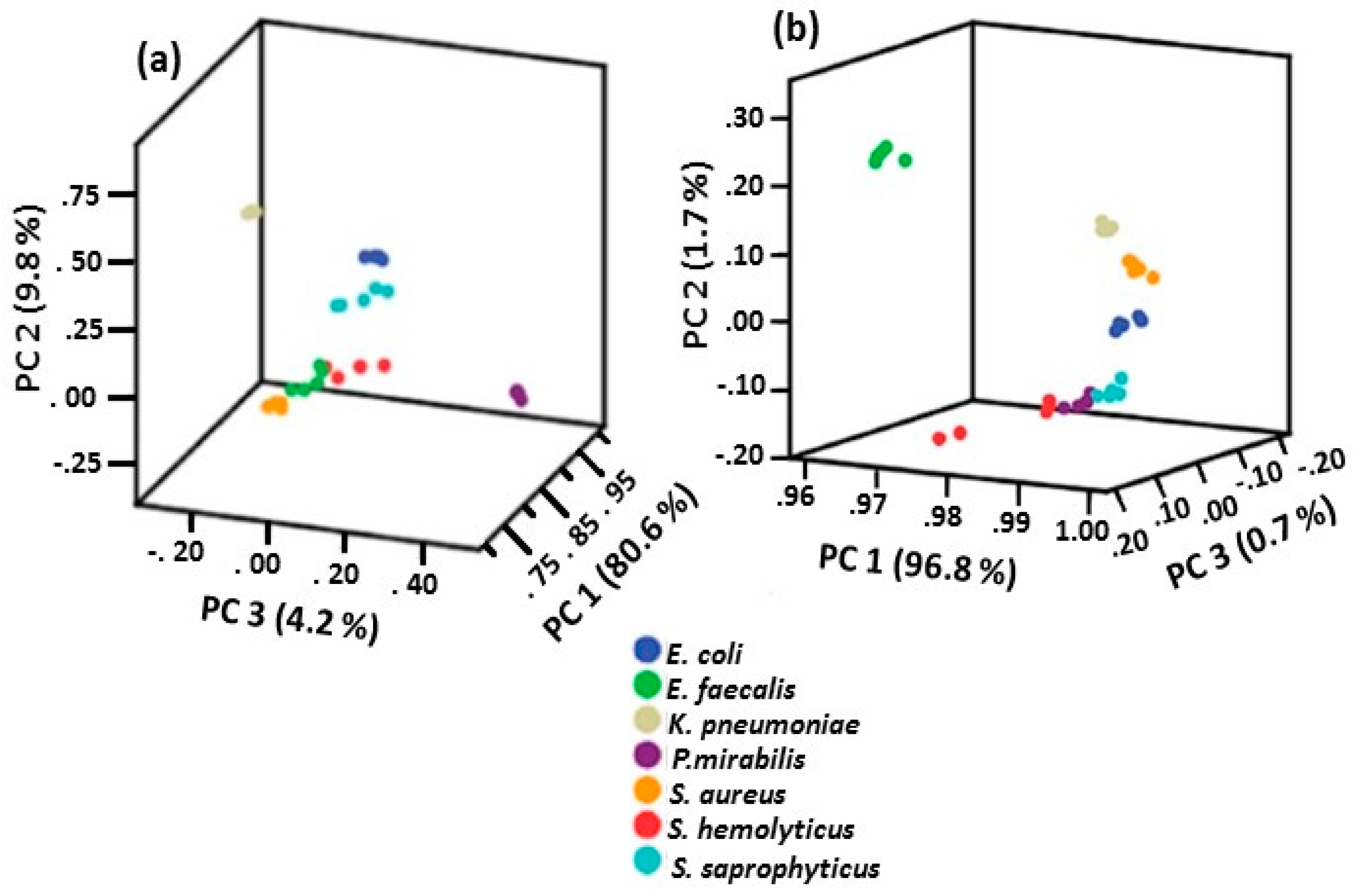
2.4. Principal Component Analysis
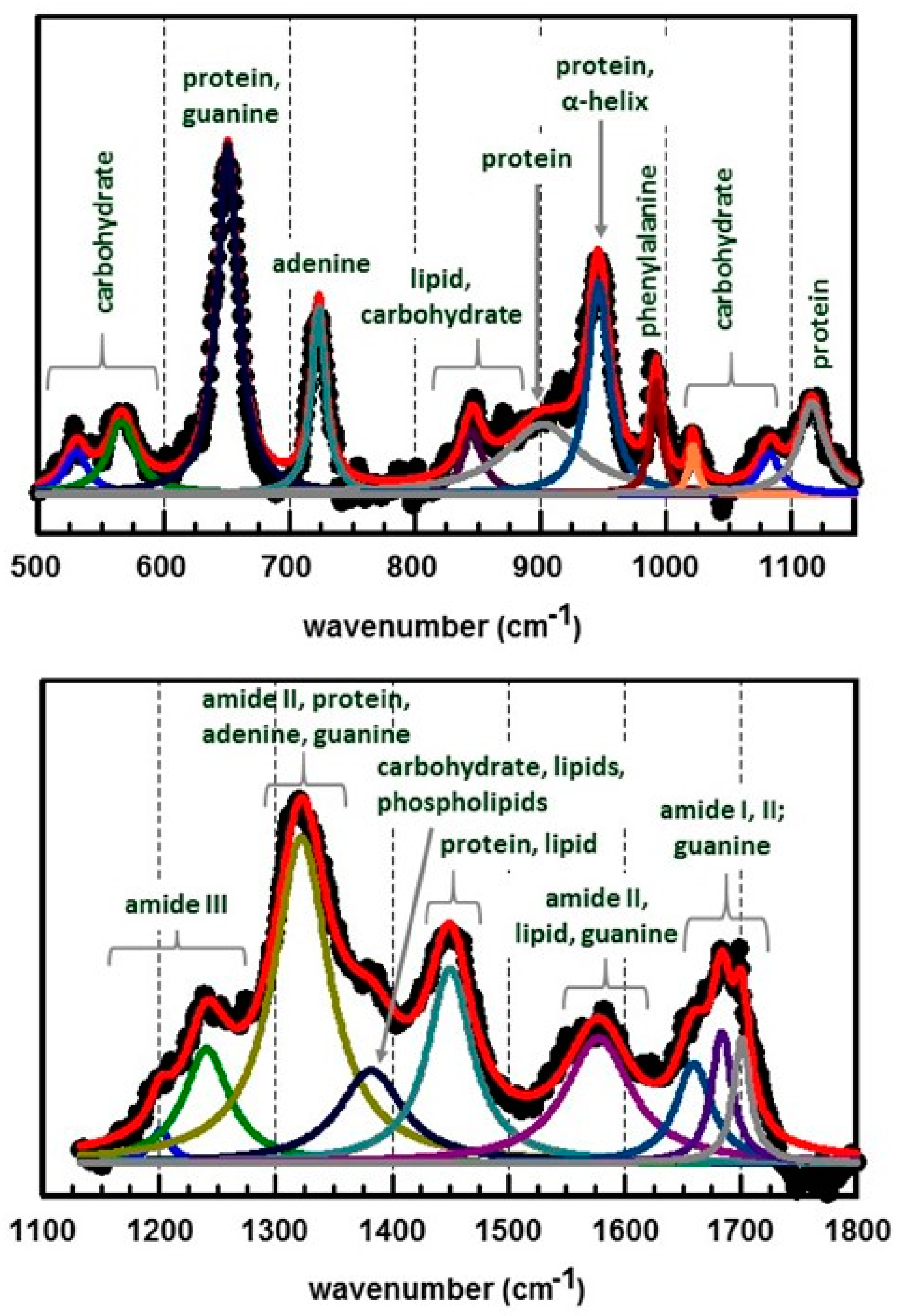
2.4.1. Peak Assignments of Bacterial Spectral Features
2.4.2. Summary of PCA Results Obtained for Bacteria
3. Conclusions
- Method used to obtain SERS spectra, i.e., internal/external colloid formation, placement of bacterial suspension on top of a SERS-active surface, or mixing Ag/Au NPs with bacteria
- Use of capped or uncapped Ag/Au NPs when using the mixing protocol
- Laser excitation wavelength used to generate the spectra
- Growth phase of the bacteria
- Bacterial interactions with the environment
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mosier-Boss, P.A. Review of SERS Substrates for Chemical Sensing. Nanomater 2017, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemire, J.A.; Harrison, J.J.; Turner, R.J. Antimicrobial Activity of Metals: Mechanisms, Molecular Targets, and Applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowan, M.K.; Bunn, J. Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Mishra, B.; Epand, R.F.; Epand, R.M. High-Quality 3D Structures Shine Light on Antibacterial, Anti-Biofilm and Antiviral Activities of Human Cathelicidin LL-37 and its Fragments. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1838, 2160–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartholomew, J.W.; Mittwer, T. The Gram Stain. Bacteriol. Rev. 1952, 16, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Yun, Y.-S. Bacterial Biosorbents and Biosorption. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 266–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beveridge, T.J. Structures of Gram-Negative Cell Walls and Their Derived Membrane Vesicles. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 4725–4733. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hughes, D.E. The Bacterial Cytoplasmic Membrane. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1962, 29, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Talaro, K.; Talaro, A. Foundations in Microbiology; William C. Brown Publishers: Dubuque, IA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Breakwell, D.P.; Moyes, R.B.; Reynolds, J. Differential Staining of Bacteria: Capsule Stain. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schembri, M.A.; Dalsgaard, D.; Klemm, P. Capsule Shields the Function of Short Bacterial Adhesins. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, M.K.; Deshmukh, S.D.; Ingle, A.P.; Gade, A.K. Silver Nanoparticles: The Powerful Nanoweapon against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Kong, Y.; Kunda, S.; Cirillo, J.D.; Liang, H. Antibacterial Activities of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles against Escherichia coli and bacillus Calmette-Guérin. J. Nanobiotech. 2012, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakai, T.C.; Kumar, A.; Majumdar, R.S.; Yadav, V. Mechanistic Basis of Antimicrobial Actions of Silver Nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-F.; Liu, Z.-G.; Shen, W.; Gurunathan, S. Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, Properties, Applications, and Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnihotri, S.; Mukherji, S.; Mukherji, S. Size-Controlled Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized over the Range 5–100 nm Using the Same Protocol and their Antibacterial Efficacy. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 3974–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Park, J.C.; Jeon, G.E.; Kim, C.S.; Seo, J.H. Effect of the Size and Shape of Silver Nanoparticles on Bacterial Growth and Metabolism by Monitoring Optical Density and Fluorescence Intensity. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2017, 22, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, N.; Marcato, P.D.; De Conti, R.; Alves, O.L.; Costa, F.T.M.; Brocchi, M. Potential Use of Silver Nanoparticles on Pathogenic Bacteria, Their Toxicity and Possible Mechanisms of Action. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2010, 21, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyasi, S.; Majhi, R.K.; Kumar, S.; Mishra, M.; Ghosh, A.; Suar, M.; Satyam, P.V.; Mohapatra, H.; Goswami, C.; Goswami, L. Polysaccharide-Capped Silver Nanoparticles Inhibit Biofilm Formation and Eliminate Multi-Drug-Resistant Bacteria by Disrupting Bacterial Cytoskeleton with Reduced Cytotoxicity towards Mammalian Cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, R.; Pal, A.; Chaudhuri, A.N. Antimicrobial Effect of Silver Nanoparticle on Pathogenic Organisms Isolated from East Kolkata Wetland. Int. J. Appl. Res. 2015, 1, 745–752. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Li, S.; Luo, J.; Wang, R.; Ding, W. Enhancement of the Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles against Phytopathogenic Bacterium Ralstonia solanacearum by Stabilization. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 7135852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, S.; Duffy, B.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Stobie, N.; McHale, P. Enhancement of the Antibacterial Properties of Silver Nanoparticles Using Beta-Cyclodextrin as a Capping Agent. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 36, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, M.A.; Khan, H.M.; Khan, A.A.; Ahmad, M.K.; Mahdi, A.A.; Pal, R.; Cameotra, S.S. Interaction of Silver Manoparticles with Escherichia coli and Their Cell Envelope Biomolecules. J. Basic Microbiol. 2014, 54, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotakadi, V.S.; Gaddam, S.A.; Venkata, S.K.; Sai Gopal, D.V.R. New Generation of Bactericidal Silver Nanoparticles against Different Antibiotic Resistant Escherichia coli Strains. Appl. Nanosci. 2015, 5, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyoti, K.; Baunthiyal, M.; Singh, A. Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Urtica. dioica Linn. Leaves and their Synergistic Effects with Antibiotics. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2016, 9, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L.Q. The Antimicrobial Activity of Nanoparticles: Present Situation and Prospects for the Future. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marotta, N.E.; Bottomley, L.A. Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering of Bacterial Cell Culture Growth Media. Appl. Spectrosc. 2010, 64, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premasiri, W.R.; Gebregziabher, Y.; Ziegler, L.D. On the Difference between Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Spectra of Cell Growth Media and Whole Bacterial Cells. Appl. Spectrosc. 2011, 65, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosier-Boss, P.A.; Sorensen, K.C.; George, R.D.; Obraztsova, A. SERS Substrates Fabricated Using Ceramic Filters for the Detection of Bacteria. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 153, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efrima, S.; Bronk, B.V. Silver Colloids Impregnating or Coating Bacteria. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 5947–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiri, L.; Bronk, B.V.; Shabtai, Y.; Czégé, J.; Efrima, S. Silver Metal Induced Surface Enhanced Raman of Bacteria. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2002, 208, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiri, L.; Bronk, B.V.; Shabtai, Y.; Eichler, J.; Efrima, S. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy as a Tool for Probing Specific Biochemical Components in Bacteria. Appl. Spectrosc. 2004, 58, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, R.M.; Brooker, A.; Goodacre, R. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy for Bacterial Discrimination Utilizing a Scanning Electron Microscope with a Raman Spectroscopy Interface. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 5198–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efrima, S.; Zeiri, L. Understanding SERS of Bacteria. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2009, 40, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Mungroo, N.; Daikuara, L.; Neethirajan, S. Label-Free NIR-SERS Discrimination and Detection of Foodborne Bacteria by in Situ Synthesis of Ag Colloids. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, R.E.; Cotton, T.M. Surface-Enhanced Resonance Raman and Electrochemical Investigation of Glucose Oxidase Catalysis at a Silver Electrode. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 2815–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Canstein, H.; Ogawa, J.; Shimizu, S.; Lloyd, J.R. Secretion of Flavins by Shewanella. Species and Their Role in Extracellular Electron Transfer. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, D.; Ivleva, N.P.; Mircescu, N.E.; Niessner, R.; Haisch, C. SERS Detection of Bacteria in Water by in Situ Coating with Ag Nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dina, N.E.; Zhou, H.; Colniţă, A.; Leopold, N.; Szoke-Nagy, T.; Coman, C.; Haisch, C. Rapid Single-Cell Detection and Identification of Pathogens by Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Analyst 2017, 142, 1782–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dina, N.E.; Colniţă, A.; Leopold, N.; Haisch, C. Rapid Single-Cell Detection and Identification of Bacteria by Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Procedia Technol. 2017, 27, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Cortés, S.; García-Ramos, J.V. SERS of AMP on Different Silver Colloids. J. Mol. Struct. 1992, 274, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colniță, A.; Dina, N.E.; Leopold, N.; Vodnar, D.C.; Bogdan, D.; Porav, S.A.; David, L. Characterization and Discrimination of Gram-Positive Bacteria Using Raman Spectroscopy with the Aid of Principal Component Analysis. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, T.D.; Fritchie, C.J., Jr. The Crystal Structure of a Riboflavin-Metal Complex: Riboflavin Silver Perchlorate Hemihydrate. J. Biol. Chem. 1973, 248, 2337–2343. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Macpherson, A.M.D.; Ottaway, J.M. Rapid Determination of Riboflavin in Yeast Preparations by Reaction with Silver Ions. Analyst 1978, 103, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benecky, M.; Yu, T.J.; Watters, K.L.; McFarland, J.T. Metal-Flavin Complexation: A Resonance Raman Investigation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1980, 626, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, K.E.; Homrighausen, D.; DePalma, G.; Nakatsu, C.H.; Irudayaraj, J. Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) for the Discrimination of Arthrobacter. Strains Based on Variations in Cell Surface Composition. Analyst 2012, 137, 4280–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, J.K.; Caldwell, T.P.; Christensen, K.A.; Chumanov, G. Monitoring the Kinetics of Bacillus subtilis Endospore Germination via Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 1724–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodelόn, G.; Montes-Garcia, V.; Lόpez-Puente, V.; Hill, E.H.; Hamon, C.; Sanz-Ortiz, M.N.; Rodal-Cedeira, S.; Costas, C.; Celiksoy, S.; Pérez-Juste, I.; et al. Detection and Imaging of Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Communities by Surface-Enhanced Resonance Raman Scattering. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schkolnik, G.; Schmidt, M.; Mazza, M.G.; Harnisch, F.; Musat, N. In Situ Analysis of a Silver Nanoparticle-Precipitating Shewanella Biofilm by Surface Enhanced Confocal Raman Microscopy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, P.; Malvadkar, N.; Cetinkaya, M.; Wang, H.; Allara, D.L.; Demirel, M.C. Surface-Enhanced Raman Detection on Metalized Nanostructured Poly(p-xylylene) Films. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 3562–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamińska, A.; Witkowska, E.; Kowalska, A.; Skoczyńska, A.; Ronkiewicz, P.; Szymborski, T.; Waluk, J. Rapid Detection and Identification of Bacterial Meningitis Pathogens in Ex Vivo Clinical Samples by SERS Method and Principal Component Analysis. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 4521–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-C.; Yang, Y.-M.; Liao, P.-H.; Chen, D.-W.; Lin, H.-P.; Chang, H.-C. A Filter-Like AuNPs@MS SERS Substrate for Staphylococcus aureus Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 53, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.-H.; Liu, C.-Y.; Wu, S.-B.; Liu, N.-W.; Peng, C.-Y.; Chan, T.-H.; Hsu, C.-F.; Wang, J.-K.; Wang, Y.-L. Highly Raman-Enhancing Substrates Based on Silver Nanoparticle Arrays with Tunable Sub-10 nm Gaps. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.-T.; Lin, Y.-H.; Hung, C.-S.; Liu, T.-J.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.-C.; Tsai, T.-H.; Wang, H.-H.; Wang, D.-W.; Wang, J.-K.; et al. A High Speed Detection Platform Based on Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering for Monitoring Antibiotic-Induced Chemical Changes in Bacteria Cell Wall. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.-Y.; Tsai, K.-T.; Wang, H.-H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.-H.; Chao, Y.-C.; Chang, H.-H.; Lin, C.-H.; Wang, J.-K.; Wang, Y.-L. Functionalized Arrays of Raman-Enhancing Nanoparticles for Capture and Culture-Free Analysis of Bacteria in Human Blood. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premasiri, W.R.; Moir, D.T.; Klempner, M.S.; Krieger, N.; Jones, G., II; Ziegler, L.D. Characterization of the Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) of Bacteria. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premasiri, W.R.; Lee, J.C.; Sauer-Budge, A.; Théberge, R.; Costello, C.E.; Ziegler, L.D. The Biochemical Origins of the Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectra of Bacteria: A Metabolomics Profiling by SERS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 4631–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premasiri, W.R.; Chen, Y.; Williamson, P.M.; Bandarage, D.C.; Pyles, C.; Ziegler, D. Rapid Urinary Tract Infection Diagnostics by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS): Identification and Antibiotic Susceptibilities. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 3043–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Pang, S.; Pearson, B.; Chujo, Y.; McLandsborough, L.; Fan, M.; He, L. Rapid Concentration Detection and Differentiation of Bacteria in Skimmed Milk Using Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering Mapping on 4-Mercaptophenylboronic Acid Functionalized Silver Dendrites. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 2229–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uusitalo, S.; Kögler, M.; Välimaa, A.-L.; Petäjä, J.; Kontturi, V.; Siitonen, S.; Laitinen, R.; Kinnunen, M.; Viitala, T.; Hiltunen, J. Stability Optimization of Microbial Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Detection with Immunomagnetic Separation Beads. Opt. Eng. 2017, 56, 037102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polosetti, S.; Baig, N.F.; Morales-Soto, N.; Shrout, J.D.; Bohn, P.W. Spatial Mapping of Pyocyanin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Bacterial Communities Using Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering. Appl. Spectrosc. 2017, 71, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith-Palmer, T.; Douglas, C.; Fredericks, P. Rationalizing the SER Spectra of Bacteria. Vib. Spectrosc. 2010, 53, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jayaseelan, S.; Ramaswamy, D.; Dharmaraj, S.W. Pyocyanin: Production, Applications, Challenges and New Insights. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Zhou, H.; Haisch, C.; Niessner, R.; Ying, Y. Reproducible E. coli Detection Based on Label-Free SERS and Mapping. Talanta 2016, 146, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Félix-Rivera, H.; González, R.; Del Mar Rodríguez, G.; Primera-Pedrozo, O.M.; Ríos-Velázquez, C.; Hernández-Rivera, S.P. Improving SERS Detection of Bacillus thuringiensis Using Silver Nanoparticles Reduced with Hydroxylamine and with Citrate Capped Borohydride. Int. J. Spectrosc. 2011, 2011, 989504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laucks, M.L.; Sengupta, A.; Junge, K.; Davis, E.J.; Swanson, B.D. Comparison of Psychro-active Artic Marine Bacteria and Common Mesophillic Bacteria Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2005, 59, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, A.; Laucks, M.L.; Dildine, N.; Drapala, E.; Davis, E.J. Bioaerosol Characterization by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS). J. Aerosol Sci. 2005, 36, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, A.; Laucks, M.L.; Davis, E.J. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy of Bacteria and Pollen. Appl. Spectrosc. 2005, 59, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahraman, M.; Yazici, M.M.; Şahin, F.; Bayrak, O.F.; Çulha, M. Reproducible Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Spectra of Bacteria on Aggregated Silver Nanoparticles. Appl. Spectrosc. 2007, 61, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahraman, M.; Yazici, M.M.; Şahin, F.; Çulha, M. Convective Assembly of Bacteria for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Langmuir 2008, 24, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avci, E.; Kaya, N.S.; Ucankus, G.; Çulha, M. Discrimination of Urinary Tract Infection Pathogens by Means of Their Growth Profiles Using Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 8233–8241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çulha, M.; Kahraman, M.; Çam, D.; Sayin, I.; Keseroğlu, K. Rapid Identification of Bacteria and Yeast Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Surf. Interface Anal. 2010, 42, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, M.; Keseroğlu, K.; Çulha, M. On Sample Preparation for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) of Bacteria and the Source of Spectral Features of the Spectra. Appl. Spectrosc. 2011, 65, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cam, D.; Keseroğlu, K.; Kahraman, M.; Sahin, F.; Çulha, M. Multiplex Identification of Bacteria in Bacterial Mixtures with Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2010, 41, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athamneh, A.I.M.; Senger, R.S. Peptide-Guided Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Probes for Localized Cell Composition Analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7805–7808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosier-Boss, P.A.; Sorensen, K.C.; George, R.D.; Sims, P.C.; Obraztsova, A. SERS Substrates Fabricated Using Ceramic Filters for the Detection of Bacteria: Eliminating the Citrate Interference. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 180, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larmour, I.A.; Faulds, K.; Graham, D. SERS Activity and Stability of the Most Frequently Used Silver Colloids. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2012, 43, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willets, K.A. Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) for Probing Internal Cellular Structure and Dynamics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escoriza, M.F.; Van Briesen, J.M.; Stewart, S.; Maier, J. Raman Spectroscopic Discrimination of Cell Response to Chemical and Physical Inactivation. Appl. Spectrosc. 2007, 61, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, K. On Lines and Planes of Closest Fit to Systems of Points in Space. Philos. Mag. 1901, 2, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotelling, H. Analysis of a Complex of Statistical Variables into Principal Components. J. Edu. Psychol. 1933, 24, 498–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosier-Boss, P.A.; Lieberman, S.H.; Newbery, R. Fluorescence Rejection in Raman Spectroscopy by Shifted-Spectra, Edge Detection, and FFT Filtering Techniques. Appl. Spectrosc. 1995, 49, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppels, G.J.; De Mul, F.F.M.; Otto, C.; Greve, J.; Robert-Nicoud, M.; Arndt-Jovin, D.J.; Jovin, T.M. Studying Single Living Cells and Chromosomes by Confocal Raman Microspectroscopy. Nature 1990, 347, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.E.; Griffiths, R.I.; Thompson, I.P.; Bailey, M.J.; Whiteley, A.S. Raman Microscopic Analysis of Single Microbial Cells. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 4452–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badr, Y.; Mahmoud, M.A. Effect of Silver Nanowires on the Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectra (SERS) of the RNA Bases. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectroc. 2006, 63, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podstawka, E.; Ozaki, Y.; Proniewicz, L.M. Adsorption of S-S Containing Proteins on a Colloidal Silver Surface Studied by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2004, 58, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krimm, S.; Bandekar, J. Vibrational Spectroscopy and Conformation of Peptides, Polypeptides, and Proteins. Adv. Protein Chem. 1986, 38, 181–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivleva, N.P.; Wagner, M.; Szkola, A.; Horn, H.; Niessner, R.; Haisch, C. Label-Free in Situ SERS Imaging of Biofilms. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 10184–10194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notingher, I. Raman Spectroscopy Cell-Based Biosensors. Sensors 2007, 7, 1343–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, I.S.; Premasiri, W.R.; Moir, D.T.; Ziegler, L.D. Barcoding Bacterial Cells: A SERS Based Methododology for Pathogen Identification. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2008, 39, 1660–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
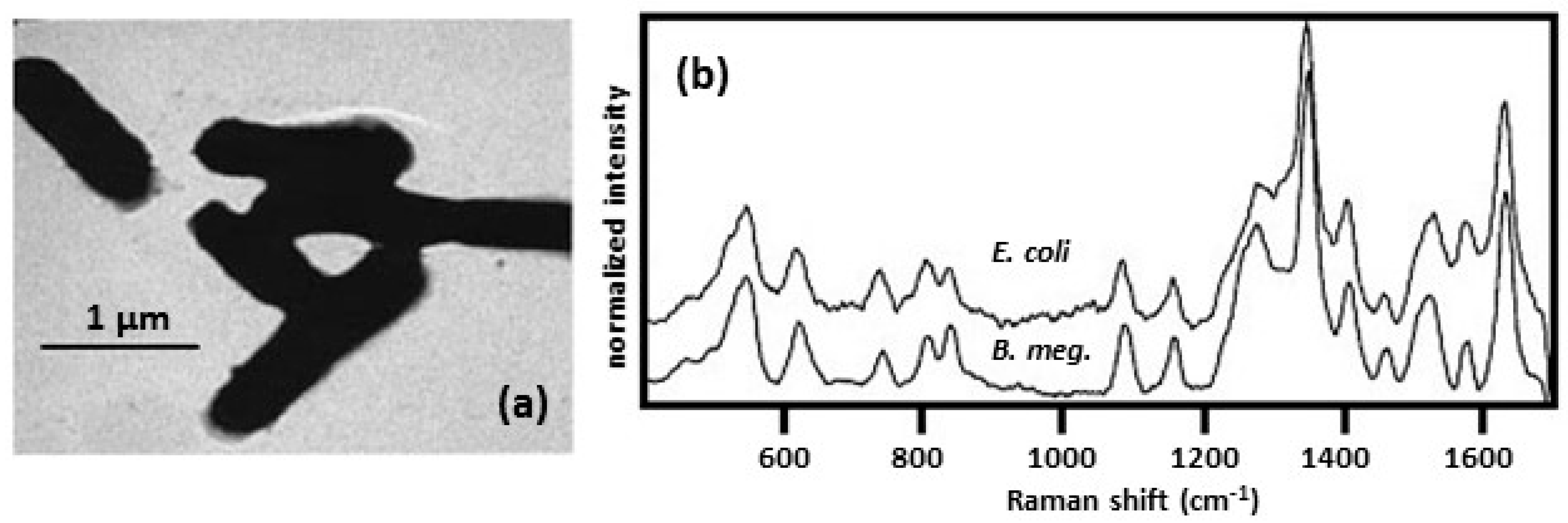
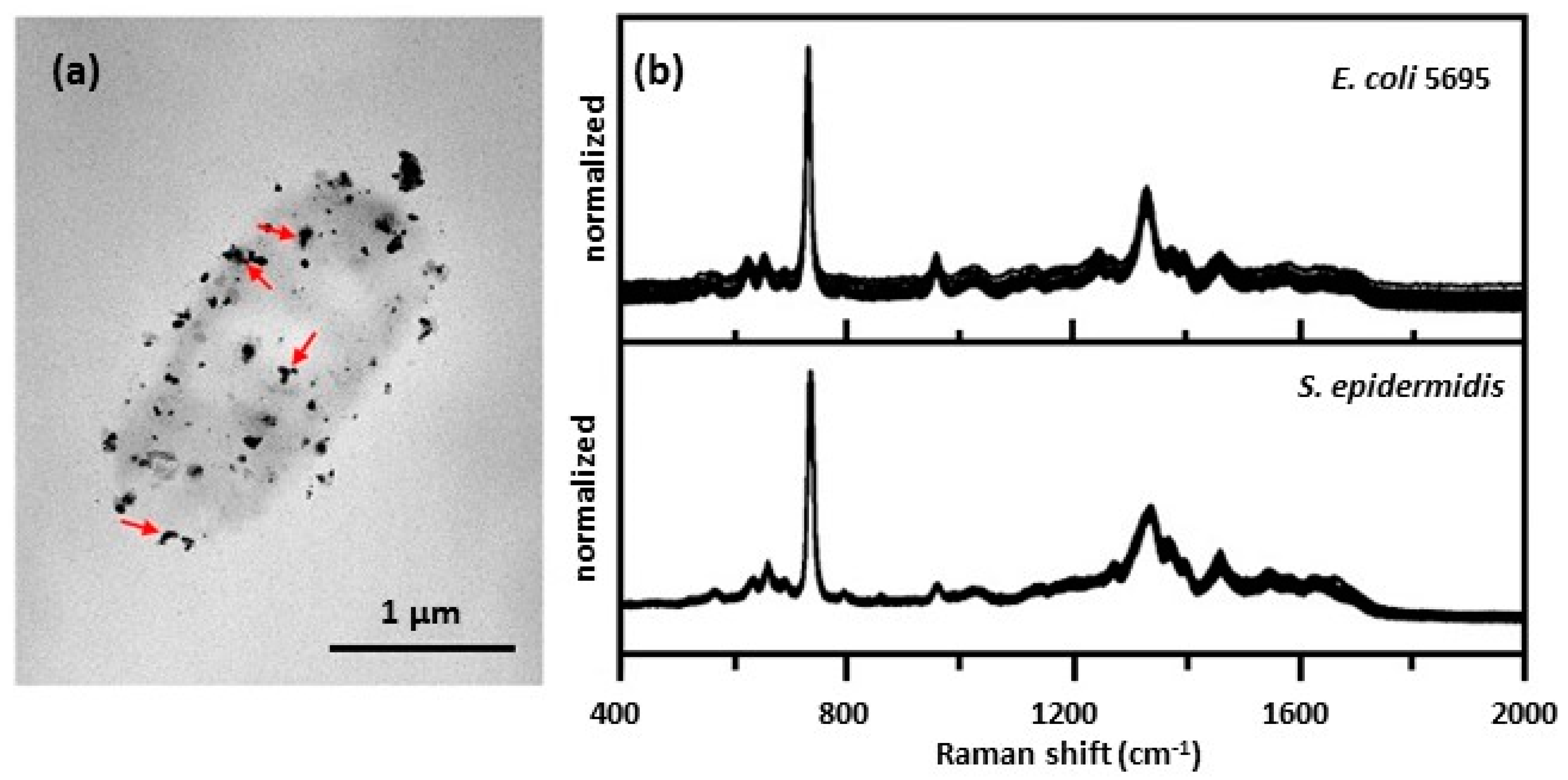
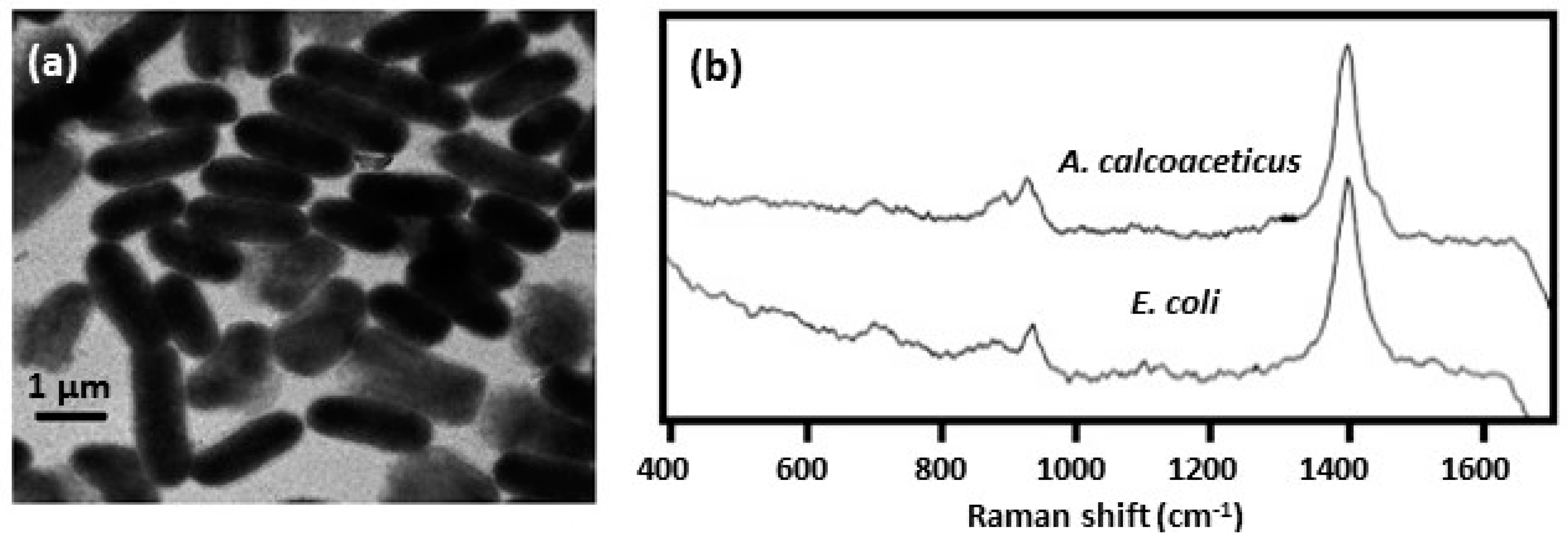
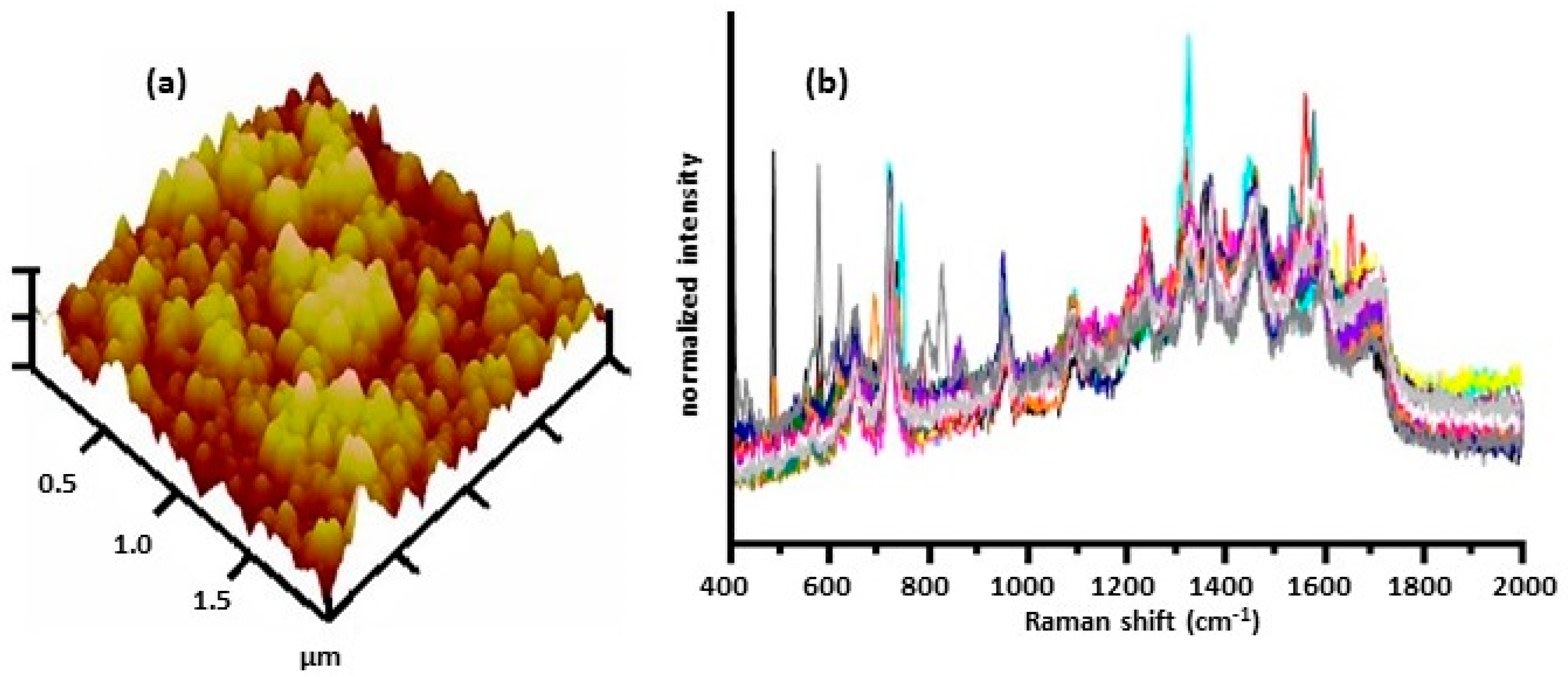



| SERS Method | SERS Substrate | Bacterial Species and References |
|---|---|---|
| external wall colloid | borohydride used to reduce Ag on the cell wall; treated cells placed on a microscope slide | Escherichia coli [30,31,32,34,35] |
| Bacillus megaterium [30,31,32,34] | ||
| Acinetobacter calcoaceticus [31,32] | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa [31,32,35] | ||
| Listeria innocua [35] | ||
| Listeria monocytogenes [35] | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus [35] | ||
| external wall colloid | borohydride used to reduce Au on the cell wall; treated cells placed on a glass slide | Escherichia coli [34] |
| external wall colloid | borohydride used to reduce Ag on the cell wall; treated cells placed on an Al SEM sample stub | Escherichia coli [33] |
| Bacillus subtilis [33] | ||
| external wall colloid | hydroxylamine used to reduce Ag on the cell wall; treated cells placed on a glass slide or a poly-l-lysine coated glass slide | Escherichia coli [38,39,40] |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis [38,39] | ||
| Aeromonas [39,40] | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa [39] | ||
| Proteus mirabilis [39] | ||
| Lactobacillus casei [39,40] | ||
| Morganella morganii [40] | ||
| Listeria monocytogenes [40] | ||
| Lactococcus lactis [40] | ||
| external wall colloid | hydroxylamine used to reduce Ag on the cell wall; treated cells placed on a MgF2 slide | Lactobacillus casei [42] |
| Listeria monocytogenes [42] | ||
| internal colloid | borohydride used to reduce Ag inside the cell; treated cells placed on a glass slide | Escherichia coli [33,34] |
| Acinetobacter calcoaceticus [33,34] |
| SERS Substrate | Bacterial Species and Reference |
|---|---|
| roughened Au coated glass slide | Anthrobacter [46] |
| Ag NPs (H2 reduction of Ag2O) immobilized on Ag mirrored glass slide | Bacillus subtilis [47] |
| Au@pNIPAM hydrogels; mesostructured Au@TiO2; micropatterned Au@SiO2 supercrystal arrays | Pseudomonas aeruginosa [48] |
| Ag NPs formed by the bacteria on a Ag/AgCl solid interface | Shewanella oneidensis [49] |
| thin Au film deposited onto a PPX-Cl surface using thermal evaporation | Escherichia coli [50] |
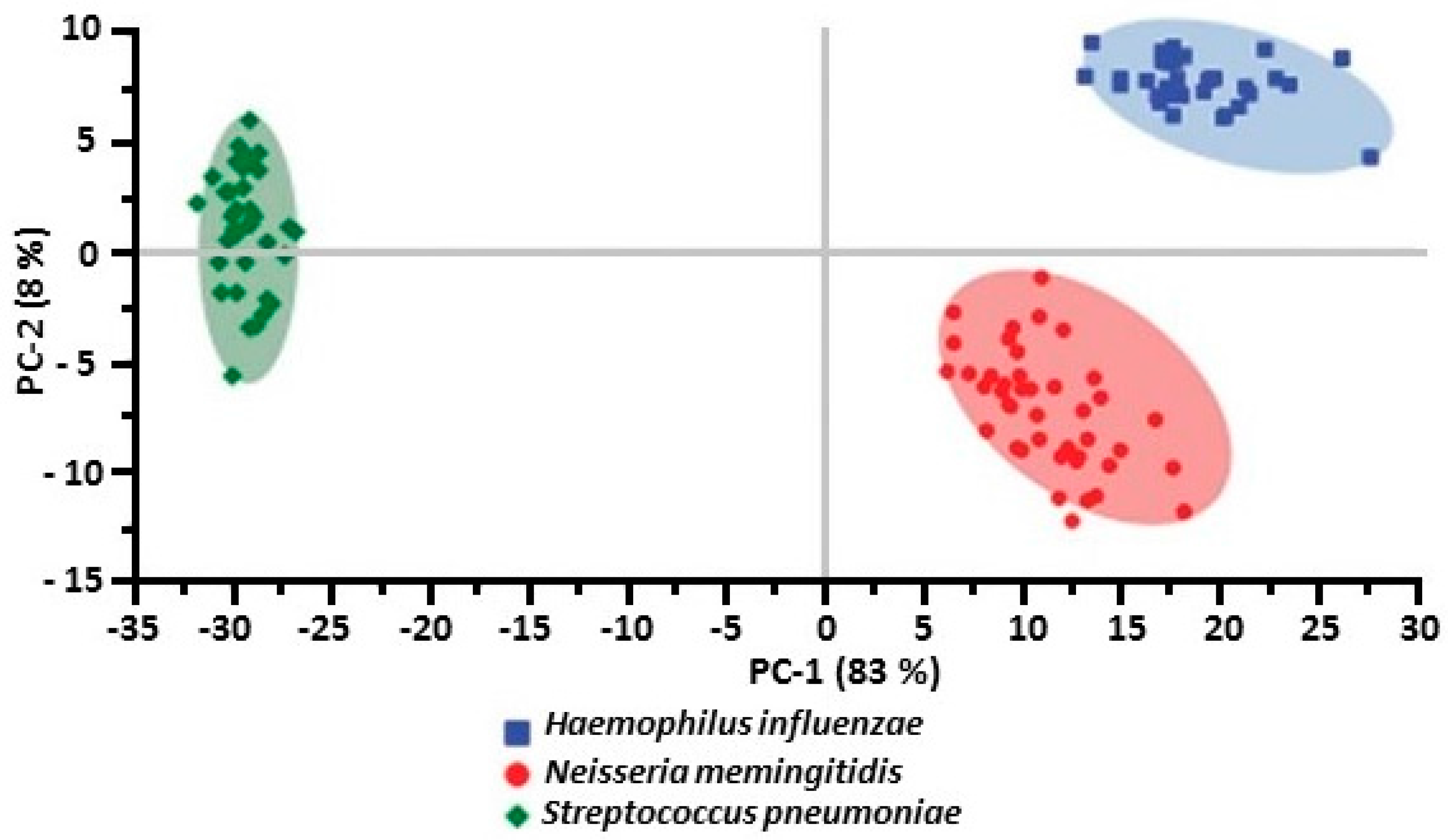
| Ag/Au film on 3 and 0.3 μm pore size, polycarbonate membranes | Haemoplilus influenzae [51] |
| Neisseria meningitidis [51] | |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae [51] | |
| filter made of borohydride generated Au NPs embedded in mesoporous silica | Staphylococcus aureus [52] |
| Staphylococcus aureus [54] | |
| Enterococcus feacalis [54] | |
| Listeria monocytogen [54] | |
| Escherichia coli [54] | |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae [54] | |
| Serratia marcescens [54] | |
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis [54] | |
| Mycobacterium gordonae [54] | |
| electrodeposited Ag NPs in AAO channels [53] | |
| electrodeposited Ag NPs in AAO channels [53]; coat array with vancomycin | Escherichia coli [55] |
| Enterococcus feacalis [55] | |
| Lactobacillus plantarum [5] | |
| borohydride generated Au NP-covered SiO2 substrate | Escherichia coli [56,57] |
| Bacillus cereus [56] | |
| Bacillus anthracis [56,57] | |
| Bacillus subtilis [56] | |
| Bacillus thuringiensis [56] | |
| Salmonella typhimurium [56] | |
| Staphylococcus aureus [57] | |
| Streptococcus agalactiae [57] | |
| Streptococcus pneumonia [57] | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa [57] | |
| Pseudomonas putida [57] | |
| Enterococcus faecium [57] | |
| Enterococcus feacalis [57] | |
| Acinetobacter baumannii [57] | |
| 4-mercaptophenylboronic acid functionalized Ag dendrites | Salmonella enterica [59] |
| Immunomagnetic separation followed by concentration on a SERS substrate | Listeria innocua [60] |
| SERS Substrate | Bacterial Species and Reference |
|---|---|
| hydroxylamine-generated Ag NPs; mixture placed on a glass slide | Escherichia coli [38,64] |
| hydroxylamine-generated Ag NPs; mixture placed in a glass capillary tube | Bacillus thuringiensis [65] |
| citrate capped, borohydride-generated Ag NPs; mixture placed in a glass capillary tube | Bacillus thuringiensis [65] |
| borohydride-generated Ag NPs; SERS obtained of mixture | Escherichia coli [66,67,68] |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa [66,67,68] | |
| Artic psychro-active marine bacteria [66] | |
| Salmonella typhimurium [68] | |
| borohydride-generated Ag NPs; mixture placed on CaF2 slides | Escherichia coli [69] |
| Bacillus megaterium [69] | |
| hydroxylamine-generated Ag NPs; mixture placed on CaF2 slides | Escherichia coli [71] |
| Enterococcus faecalis [71] | |
| Staphylococcus aureus [71] | |
| Staphylococcus saprophyticus [71] | |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae [71] | |
| citrate-generated Ag NPs; mixture placed on CaF2 slides | Escherichia coli [69,72,73,74] |
| Bacillus megaterium [69,73] | |
| Shigella sonnei [72,74] | |
| Erwinia amylovara [72,74] | |
| Proteus vulgaris [72,74] | |
| Staphylacoccus cohnii [72] | |
| Staphylacoccus aureus [72] | |
| citrate-generated Ag NPs; mixture placed on glass slides | Escherichia coli [70] |
| Staphylacoccus cohnii [70] | |
| Ag NPs conjugated with synthetic peptides (pgSERS probes) | Escherichia coli [75] |
| citrate-generated Ag NPs; mixture filtered onto a ceramic filter | Escherichia coli [76] |
| Shewanella putrefaciens [76] | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa [76] |
© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mosier-Boss, P.A. Review on SERS of Bacteria. Biosensors 2017, 7, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7040051
Mosier-Boss PA. Review on SERS of Bacteria. Biosensors. 2017; 7(4):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7040051
Chicago/Turabian StyleMosier-Boss, Pamela A. 2017. "Review on SERS of Bacteria" Biosensors 7, no. 4: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7040051
APA StyleMosier-Boss, P. A. (2017). Review on SERS of Bacteria. Biosensors, 7(4), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7040051




