An Electrochemical Enzyme Biosensor for 3-Hydroxybutyrate Detection Using Screen-Printed Electrodes Modified by Reduced Graphene Oxide and Thionine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Apparatus
2.2. Reagents and Solutions
2.3. Samples
2.4. Procedures
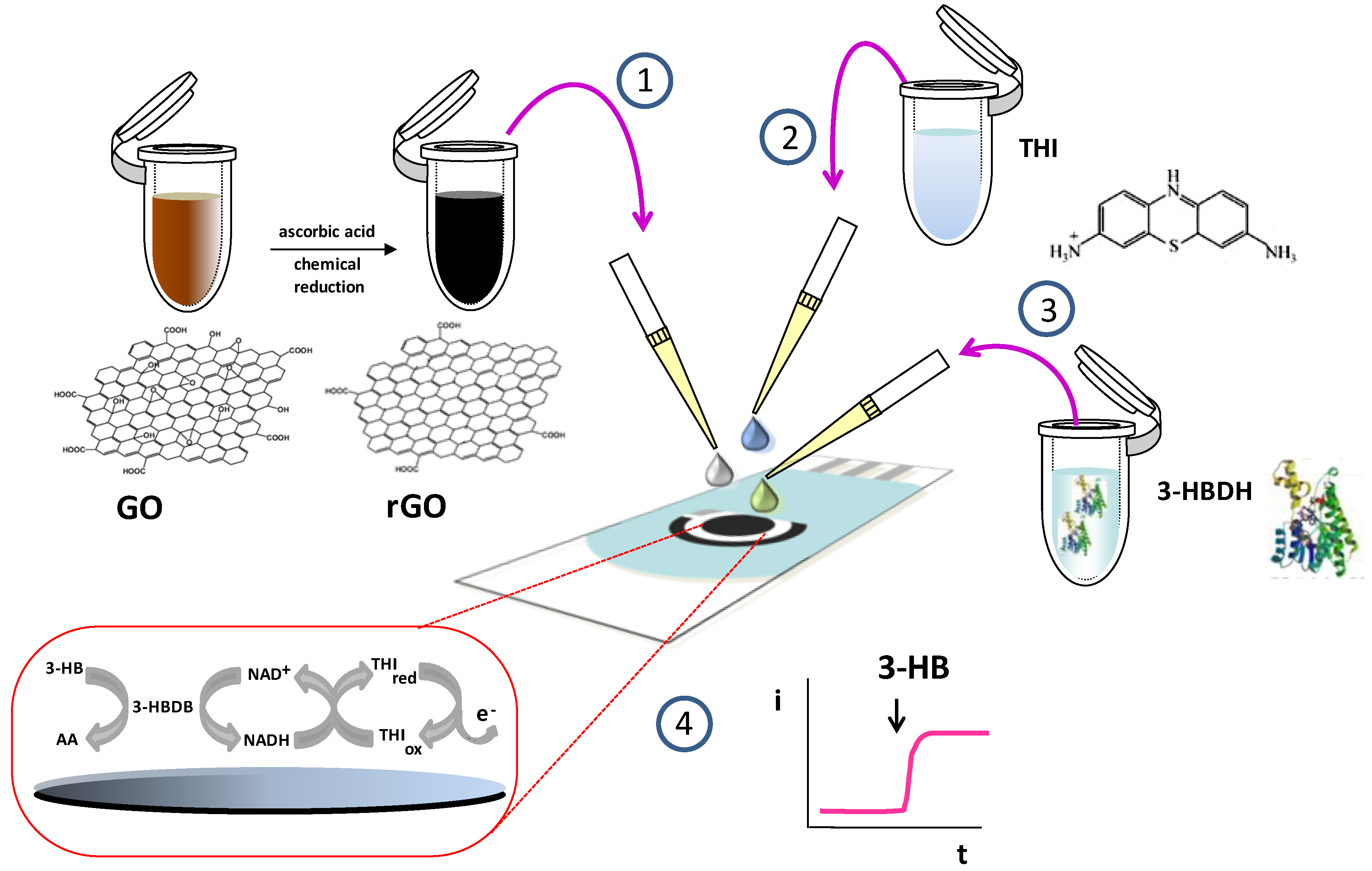
2.4.1. Preparation of Enzyme Biosensors
2.4.2. Analysis of Human Serum
3. Results and Discussion
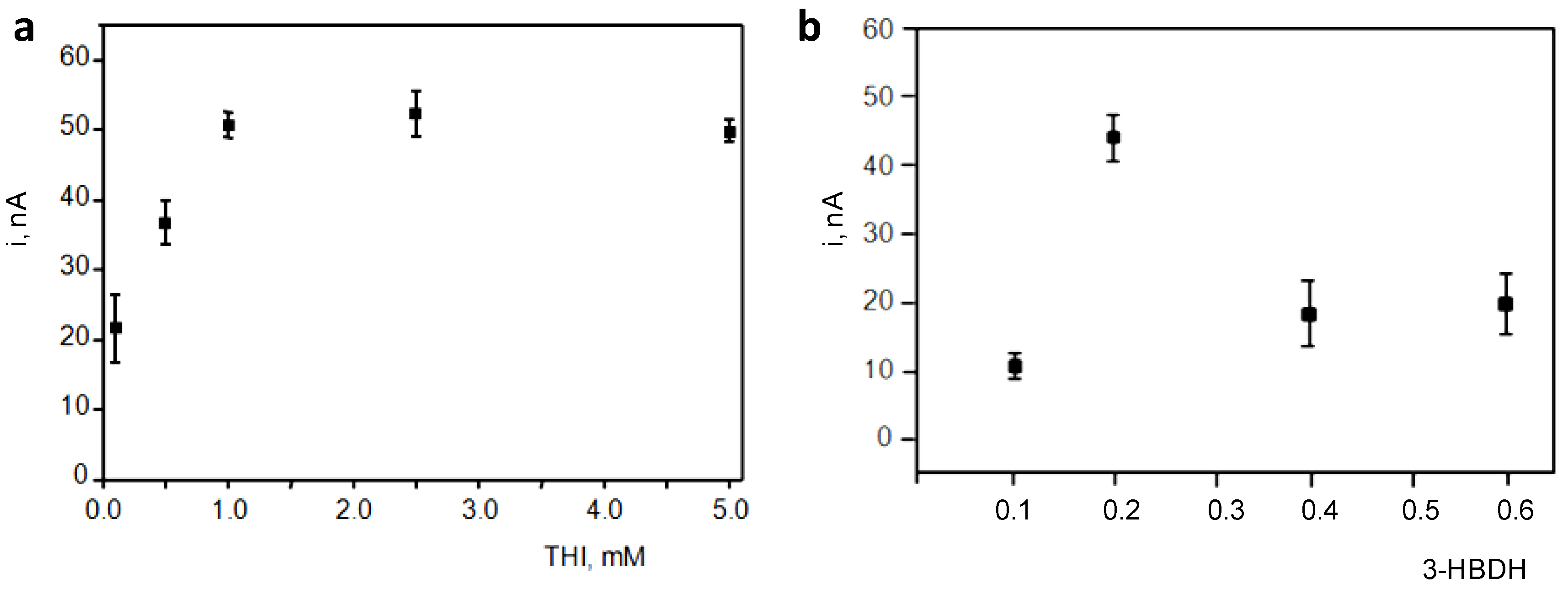
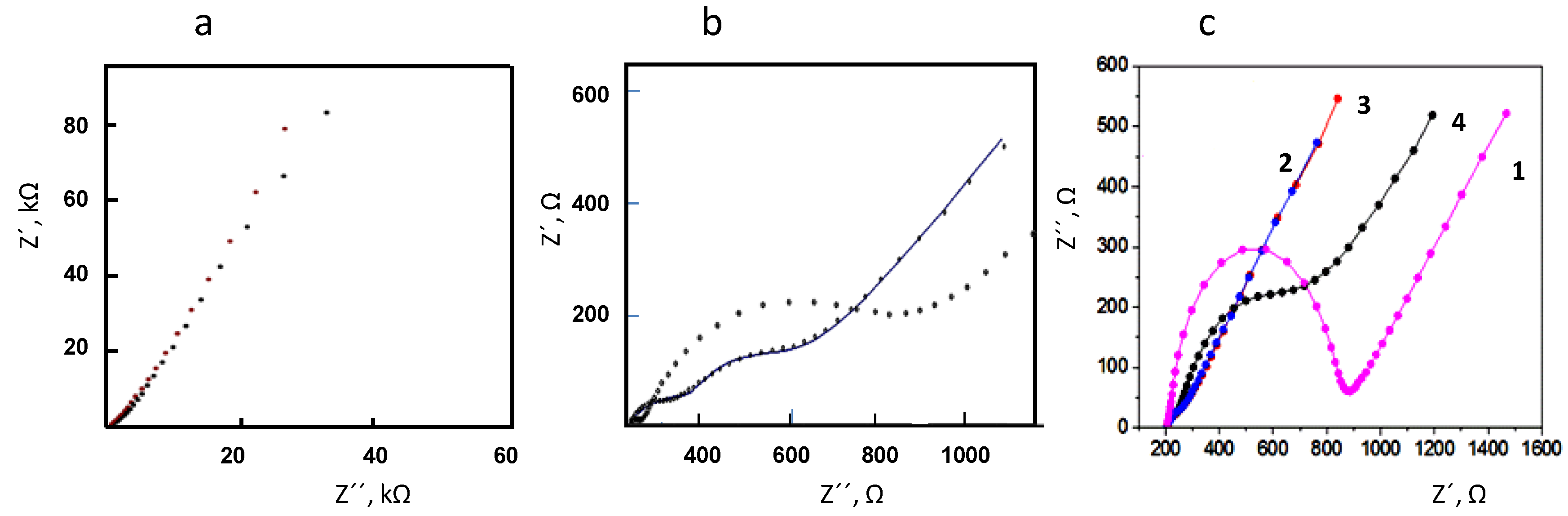
3.1. Optimization of the Variables Involved in the Preparation and Performance of the Biosensor
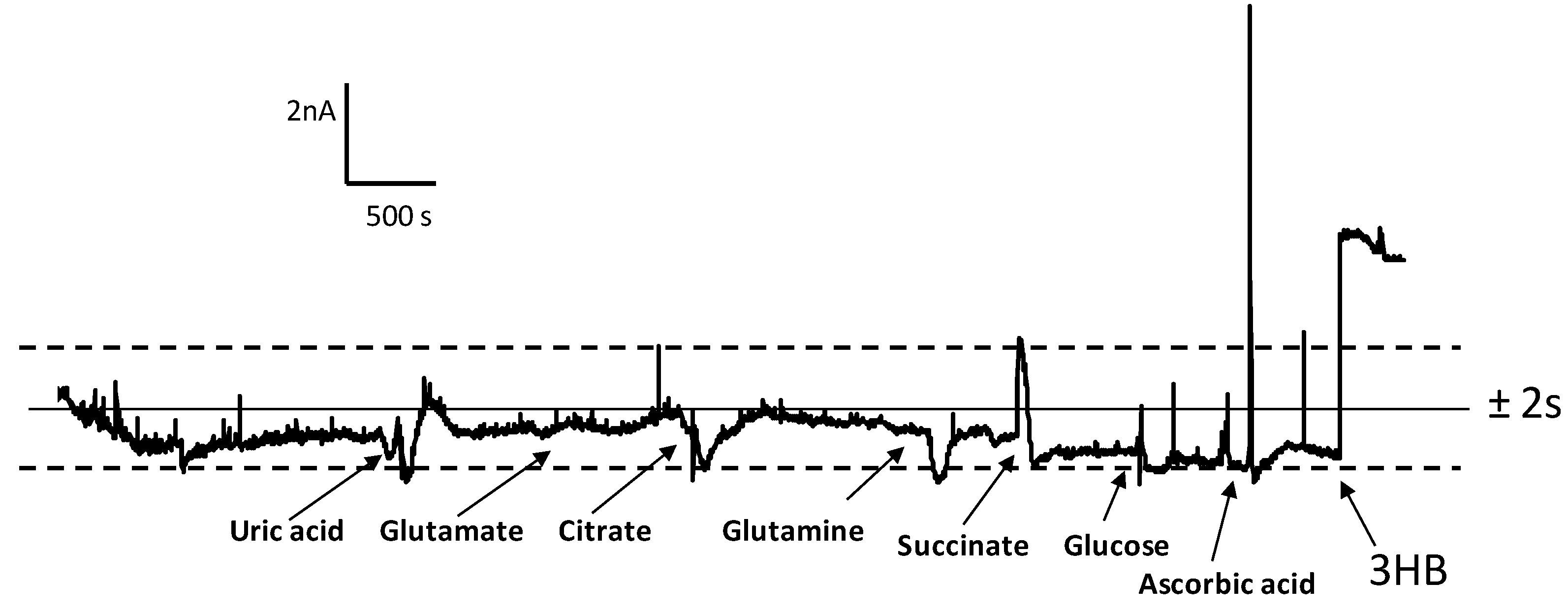
3.2. Analytical Figures of Merit of the Biosensor
3.3. Determination of 3-HB in Spiked Human Serum
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wallace, T.M.; Matthews, D.R. Recent advances in the monitoring and management of diabetic ketoacidosis. QJM 2004, 97, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laffel, L. Use of a point-of-care beta-hydroxybutyrate sensor for detection of ketonemia in dogs. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 1999, 15, 412–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Gallego, E.; Guirro, M.; Riera-Borrull, M.; Hernández-Aguilera, A.; Mariné-Casadó, R.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Beltrán-Debón, R.; Sabench, F.; Hernández, M.; Castillo, D.; et al. Mapping of the circulating metabolome reveals α-ketoglutarate as a predictor of morbid obesity-associated non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; He, Q.; Tan, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Graphene-Based Electrochemical Sensors. Small 2013, 9, 1160–1172. [Google Scholar]
- Lawal, A.T. Synthesis and utilisation of graphene for fabrication of electrochemical sensors. Talanta 2015, 131, 424–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bari, C.; Goñi-Urtiaga, A.; Pita, M.; Shleev, S.; Toscano, M.D.; Sainz, R.; De Lacey, A.L. Fabrication of high surface area graphene electrodes with high performance towards enzymatic oxygen reduction. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 191, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumera, M.; Ambrosi, A.; Bonanni, A.; Chng, E.L.K.; Poh, H.L. Graphene for electrochemical sensing and biosensing. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 29, 954–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Shen, G.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, J.; Guo, S. Reduction of graphene oxide via L-ascorbic acid. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 1112–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.M.; Feng, H.B.; Lu, J.; Li, J.H. Preparation structure and electrochemical properties of reduced graphene sheet films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 2782–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorsand, F.; Azizi, M.D.; Naeemy, A.; Larijani, B.; Omidfar, K. An electrochemical biosensor for 3-hydroxybutyrate detection based on screen-printed modifed by coenzyme functionalized carbon nanotubes. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 2327–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, R.C.H.; Hon, P.Y.T.; Mak, W.C.; Law, L.Y.; Huc, J.; Renneberg, R. Biosensor for rapid determination of 3-hydrybutyrate using bienzyme system. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Ma, N.Z.; Wang, Y. A new handheld biosensor for monitoring blood ketones. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 109, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrow, N.J.; Sanghera, G.S.; Walters, S.J.; Watkin, J.L. Development of a commercial amperometric biosensor electrodefor the ketone d-3-hydroxybutyrate. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 1617–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimomura, T.; Sumiya, T.; Ono, M.; Ito, T.; Hanaoka, T. A novel, disposable, screen-printed amperometric biosensor for ketone 3-β-hydroxybutyrate fabricated using a 3-β-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase—Mesoporous silica conjugate. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.C.; Hennek, J.W.; Ainla, A.; Kumar, A.A.; Lan, W.J.; Im, J.; Smith, B.S.; Zhao, M.; Whitesides, G.M. A paper-based “pop-up” electrochemical device for analysis of beta-hydroxybutyrate. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 6326–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veerapandian, M.; Hunter, R.; Neethirajan, S. Ruthenium dye sensitized graphene oxide electrode for on-farm rapiddetection of beta-hydroxybutyrate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 228, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Wang, S.-H.; Liu, C.-C. An electrochemical biosensor of the ketone 3-β-hydroxybutyrate for potential diabetic patient management. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 129, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Aksay, I.A.; Lin, Y. Graphene based electrochemical sensors and biosensors: A Review. Electroanalysis 2009, 22, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yu, P.; Ma, Y. Stable dispersions of graphene and highly conducting graphene films: A new approach to creating colloids of graphene monolayers. Chem. Commun. 2009, 30, 4527–4529. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Jiang, H.; Zhai, J.; Liu, B.; Dong, S. A simple route to incorporate redox mediator into carbon nanotubes/Nafion composite film and its application to determine NADH at low potential. Talanta 2007, 74, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Merino, M.J.; Guardia, L.; Paredes, J.L.; Villar-Rodil, S.; Solís-Fernández, P.; Martínez-Alonso, A.; Tascón, J.M.D. Vitamin C is an ideal substitute for hydrazine in the reduction of graphene oxide suspensions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 6426–6432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-García, G.; Agüí, L.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Multiplexed electrochemical immunosensing of obesity-related hormones at grafted graphene-modified electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 202, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, C.J.; Spoors, J.A.; Cooper, J.M.; Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Mullen, W.H. Amperometric biosensor for rapid measurement of 3-hydroxybutyrate in undiluted whole blood and plasma. Anal. Chim. Acta 1990, 237, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beta Hydroxybutyrate (beta HB) Assay Kit (Colorimetric) (ab83390). Available online: http://www.abcam.com/beta-hydroxybutyrate-beta-hb-assay-kit-colorimetric-ab83390.html (accessed on 10 November 2017).
- Picoprobe β Hydroxybutyrate (beta HB) Assay Kit (Fluorometric) (ab180876). Available online: http://www.abcam.com/picoprobe-beta-hydroxybutyrate-beta-hb-assay-kit-fluorometric-ab180876.html (accessed on 10 November 2017).



| Electrode | Biosensor Fundamentals | Technique/E Detec. | Linear Range /LOD, mM | Sample | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-HBDB/NAD+/SWCNTs/SPCE | 3-HB + NAD+ (3-HBDH)→NADH. Detect. NADH | CV/−150 mV vs. Ag/AgCl | 0.01–0.1/0.009 | human serum | [10] |
| Clark electrode | 3-HB + NAD+ (3-HBDH)→NADH NADH+O2(SHL)→NAD+ Detect. O2 consumption | amperom.−600mV vs. Ag/AgCl | 0.008–0.8/0.0039 | spiked human serum | [11] |
| 3-HBDB/NAD+/Fe(CN)64−/CMC/SPCE | 3-HB + NAD+ (3-HBDH)→NADH Detect. NADH with Fe(CN)64- | amperom. +300 mV vs. Ag/AgCl | 0.014–5.3/0.014 | human serum | [12] |
| 1,10-PQ/NAD+/3-HBDH/SPCE | 3-HB + NAD+ (3-HBDH)→NADH Detect. NADH with 1,10-PD | +200 mV vs. Ag/AgCl | 0–6/- | spiked blood | [13] |
| 3-HBDH–FSM8.0/NAD+/MB/SPCE | 3-HB + NAD+ (3-HBDH)→NADH Detect. NADH with MB | amperom. −50 mV vs. Ag/AgCl | 0.03–8/0.0292 | - | [14] |
| 1,10-PD/NAD+/3-HBDH/EPAD | 3-HB + NAD+ (3-HBDH)→NADH Detect. NADH with 1,10-PD | amperom. +200 mV | 0–6/0.3 | spiked whole blood | [15] |
| 3-HBDH/[Ru(bpy)3]2+/GO/NAD+/SPCE | 3-HB + NAD+ (3-HBDH) → NADH. Detect. NADH with [Ru(bpy)3]2+ | amperom. +60 mV vs. Ag/AgCl | 0.2–2.0/- | bovine serum | [16] |
| SPIrCE | 3-HB + NAD+ (3-HBDH)→NADH Detect. NADH | amperom. +200 mV vs. Ag/AgCl (T = 37.5 °C) | 0–10/- | bovine serum | [17] |
| 3-HBDH/THI/rGO/SPCE | 3-HB + NAD+ (3-HBDH)→NADH Detect. NADH with THI | amperom. 0 mV vs. Ag | 0.003–0.4/0.001 | spiked human serum | This work |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-García, G.; Pérez-Julián, E.; Agüí, L.; Cabré, N.; Joven, J.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. An Electrochemical Enzyme Biosensor for 3-Hydroxybutyrate Detection Using Screen-Printed Electrodes Modified by Reduced Graphene Oxide and Thionine. Biosensors 2017, 7, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7040050
Martínez-García G, Pérez-Julián E, Agüí L, Cabré N, Joven J, Yáñez-Sedeño P, Pingarrón JM. An Electrochemical Enzyme Biosensor for 3-Hydroxybutyrate Detection Using Screen-Printed Electrodes Modified by Reduced Graphene Oxide and Thionine. Biosensors. 2017; 7(4):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7040050
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-García, Gonzalo, Elena Pérez-Julián, Lourdes Agüí, Naomí Cabré, Jorge Joven, Paloma Yáñez-Sedeño, and José Manuel Pingarrón. 2017. "An Electrochemical Enzyme Biosensor for 3-Hydroxybutyrate Detection Using Screen-Printed Electrodes Modified by Reduced Graphene Oxide and Thionine" Biosensors 7, no. 4: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7040050
APA StyleMartínez-García, G., Pérez-Julián, E., Agüí, L., Cabré, N., Joven, J., Yáñez-Sedeño, P., & Pingarrón, J. M. (2017). An Electrochemical Enzyme Biosensor for 3-Hydroxybutyrate Detection Using Screen-Printed Electrodes Modified by Reduced Graphene Oxide and Thionine. Biosensors, 7(4), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7040050







