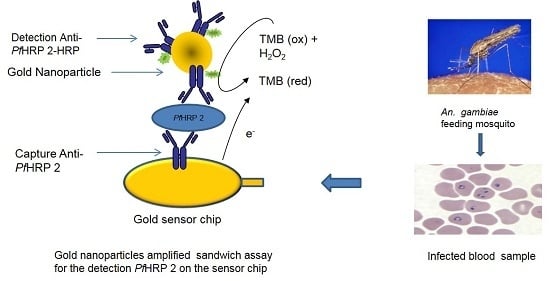
Development of an Immunosensor for PfHRP 2 as a Biomarker for Malaria Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sensors Fabrication and Electrochemical Measurements
2.3. SEM and AFM Scan of the SPGE
2.4. Immunoassay Development (ELISA)
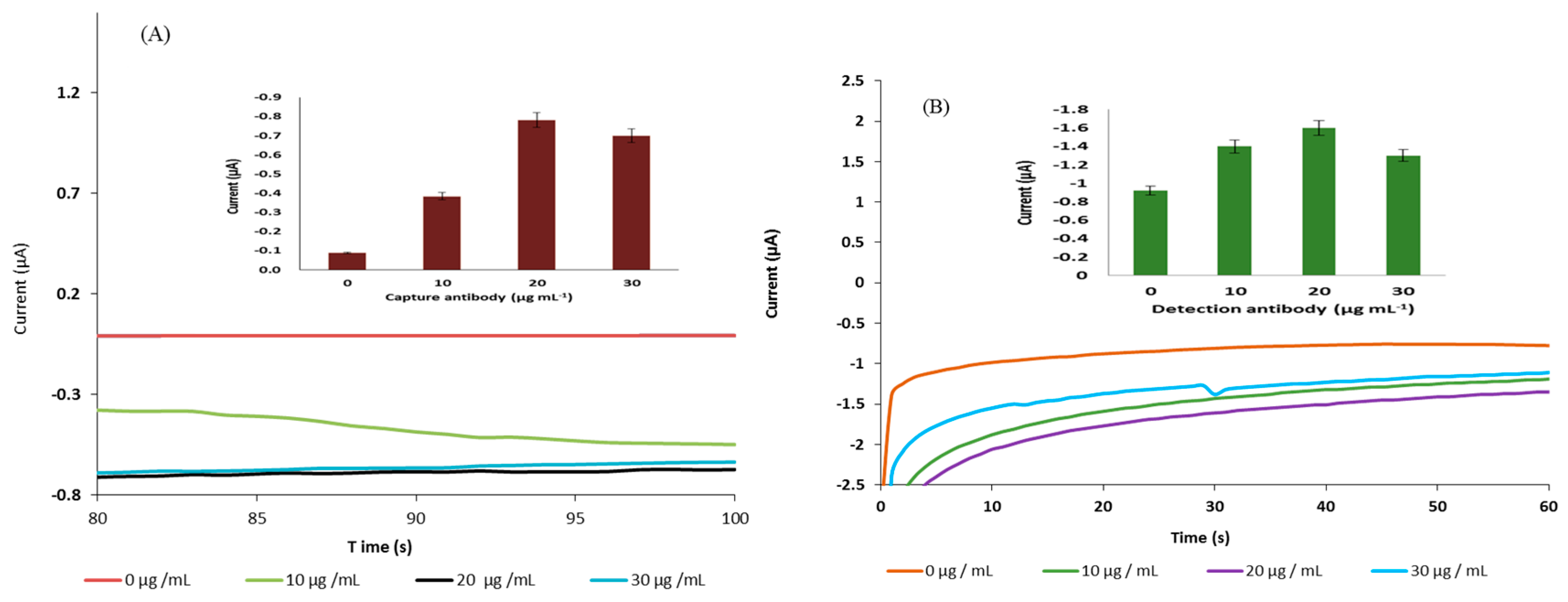
2.5. Optimisation of Capture and Detection Antibody on the Sensor’s Surface
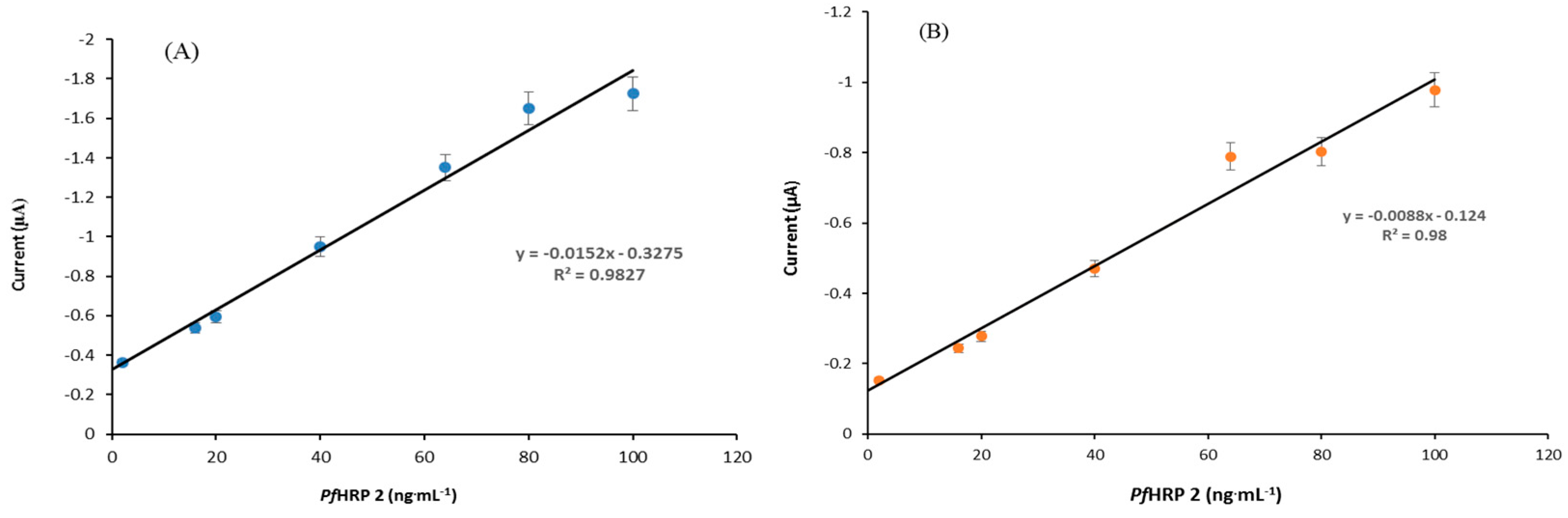
2.6. Standard Curve and Limit of Detection
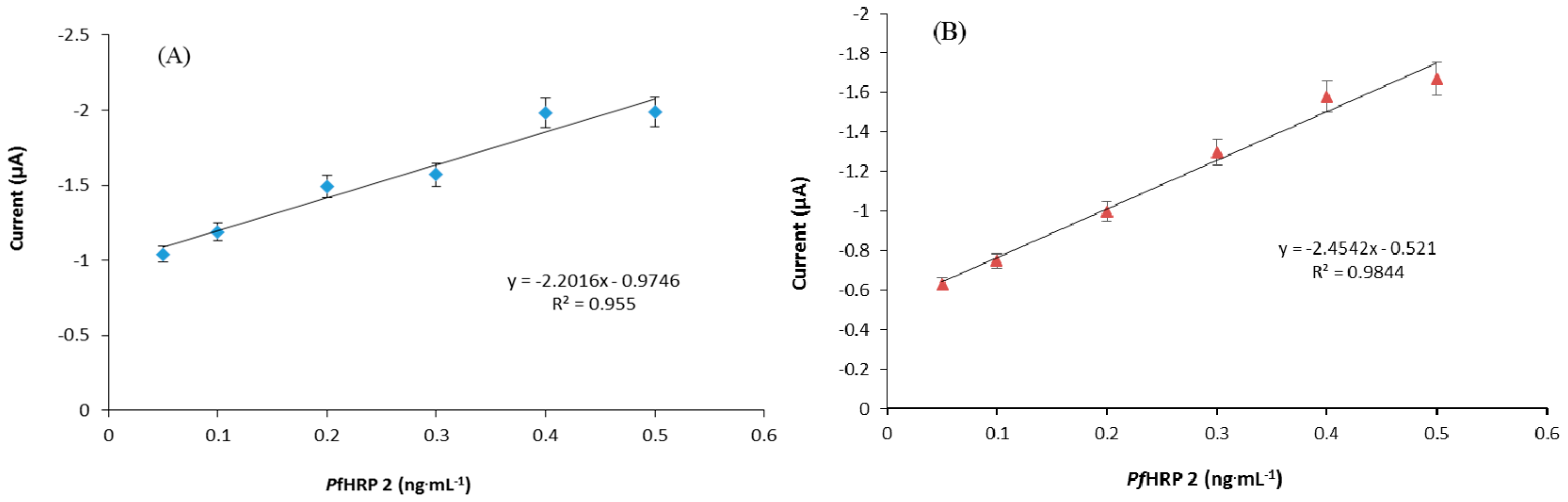
2.7. Signal Amplification Using Gold Nanoparticle
2.8. Human Serum Assay
3. Results and Discussion
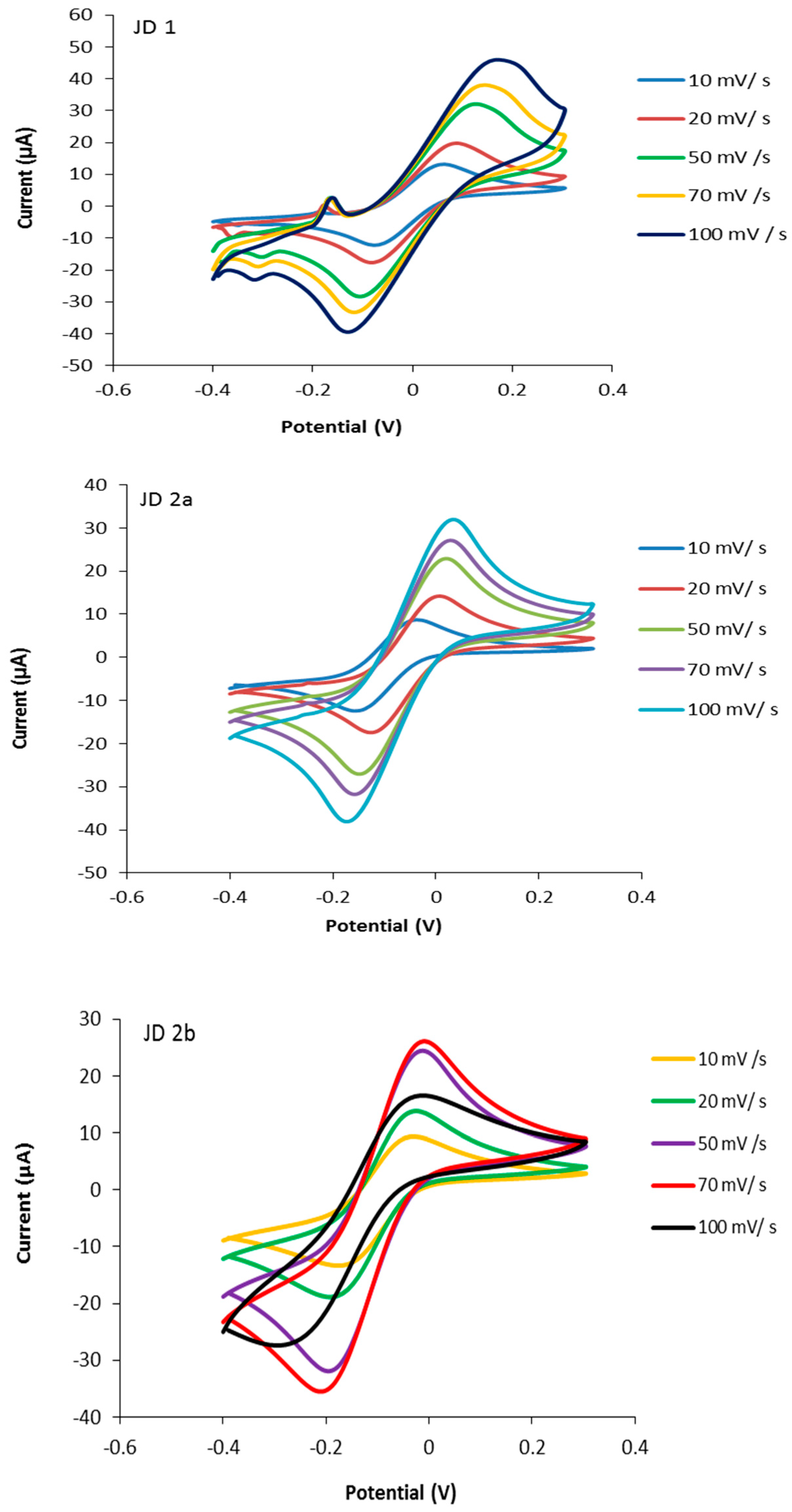
3.1. Characterisation of the Screen-Printed Electrodes
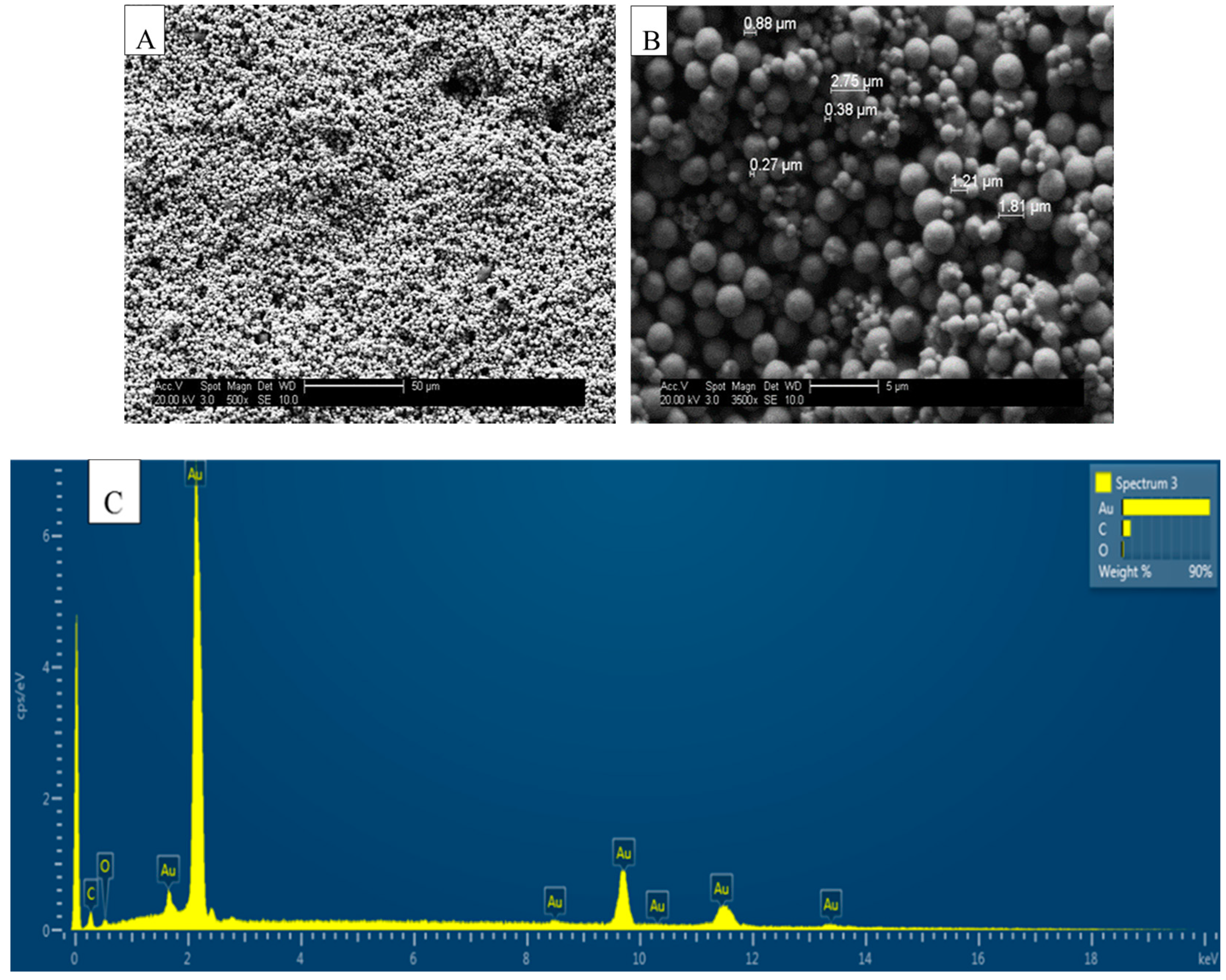
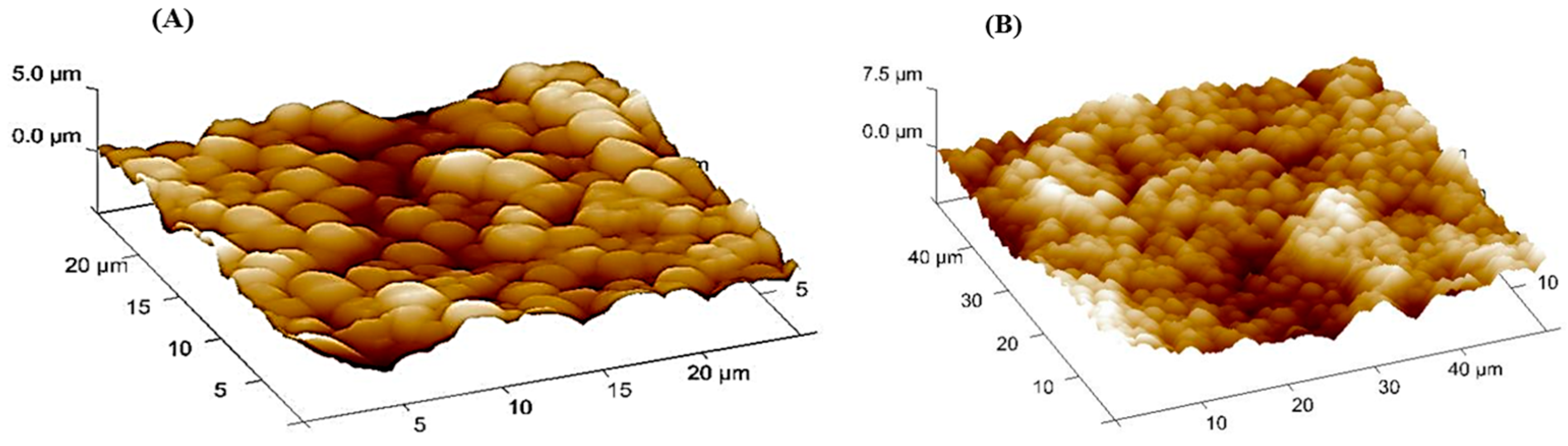
3.2. SEM, ESEM and AFM of Bare SPGE
3.3. Development of the Immunoassay
3.4. Development of PfHRP 2 Immunosensor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noppadon, T.; Chatnapa, D.; Polrat, W.; Srivicha, K. Malaria diagnosis: A brief review. Korean J. Parasitol. 2009, 47, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Malaria Fact Sheet. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs094/en/ (accessed on 1 May 2017).
- Malaria Treatment. Available online: http://www.who.int/malaria/publications/treatment/en/ (accessed on 1 May 2017).
- Kifude, C.M.; Rajasekariah, H.G.; Sullivan, D.J.; Stewart, V.A.; Angov, E.; Martin, S.K.; Diggs, C.L.; Waitumbi, J.N. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein 2 in blood, plasma, and serum. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2008, 15, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, S.; Vallejo, A.F.; Quintero, J.P.; Arévalo-Herrera, M.; Cancino, M.; Ferro, S. Field evaluation of an automated RDT reader and data management device for Plasmodium falciparum/Plasmodium vivax malaria in endemic areas of Colombia. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirev, P.; Feldman, A.; Kongkasuriyachai, D.; Scholl, P.; Sullivan, D.; Kumar, N. Detection of malaria parasites in blood by laser desorption mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 3262–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholl, P.F.; Kongkasuriyachai, D.; Demirev, P.A.; Feldman, A.B.; Lin, J.S.; Sullivan, D.J., Jr.; Kumar, N. Rapid detection of malaria infection in vivo by laser desorption mass spectrometry. The Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2004, 71, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diagnoses, C.G. Maiera Consultative Group on Diagnoses and Diagnostics. A Research Agenda for Malaria Eradication: Diagnoses and Diagnostics. PLoS. Med. 2011, 8, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Redd, S.; Kazembe, P.; Luby, S.; Nwanyanwu, O.; Hightower, A.; Ziba, C.; Wirima, J.; Chitsulo, L.; Franco, C.; Olivar, M. Clinical algorithm for treatment of Plasmodium falciparum malaria in children. Lancet 2006, 347, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corran, P.; Coleman, P.; Riley, E.; Drakeley, C. Serology: A robust indicator of malaria transmission intensity? Trends Parasitol. 2007, 23, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias, N.; Subirats, M.; Trevisi, P.; Ramírez-Olivencia, G.; Castán, P.; Puente, S.; Toro, C. Performance of a new gelled nested PCR test for the diagnosis of imported malaria: Comparison with microscopy, rapid diagnostic test, and real-time PCR. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 2587–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vekemans, J.; Marsh, K.; Greenwood, B.; Leach, A.; Kabore, W.; Soulanoudjingar, S.; Asante, K.P.; Ansong, D.; Evans, J.; Sacarlal, J.; et al. Assessment of severe malaria in a multicenter, phase III, RTS, S/AS01 malaria candidate vaccine trial: Case definition, standardization of data collection and patient care. Malar. J. 2011, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merwyn, S.; Gopalan, N.; Singh, A.K.; Rai, G.P.; Agarwal, G.S. Monoclonal antibodies against recombinant histidine-rich protein 2 of Plasmodium falciparum and their use in malaria diagnosis. Hybridoma 2011, 30, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellems, T.E.; Howard, R.J. Homologous genes encode two distinct histidine-rich proteins in a cloned isolate of Plasmodium falciparum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 6065–6069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, E.L.; Marletta, M.A. Heme binding to the histidine-rich protein II from Plasmodium falciparum. Biochemistry 2005, 25, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desakorn, V.; Dondorp, A.M.; Silamut, K.; Pongtavornipinyo, W.; Sahassananda, D.; Chotivanich, K.; Pitisuttithum, P.; Smithyman, A.; Day, N.P.; Day, N.P.; White, N.J. Stage-dependent production and release of histidine-rich protein 2 by Plasmodium falciparum. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 99, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, D.J., Jr.; Gluzman, I.Y.; Goldberg, D.E. Plasmodium hemozin formation mediated by histidine-rich proteins. Science 1996, 271, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, D.J.; Gluzman, I.Y.; Russell, D.G.; Goldberg, D.E. On the molecular mechanism of chloroquine’s antimalarial action. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 11865–11870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, E.P.; Marsh, K.; Saul, A.J.; Wellems, T.E.; Taylor, D.W.; Maloy, W.L.; Howard, R.J. Comparative analysis of the Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich proteins HRP-I, HRP-II and HRP-III in malaria parasites of diverse origin. Parasitology 1987, 95, 209–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkes, M.; Conroy, A.L.; Opoka, R.O.; Namasopo, S.; Liles, W.C.; John, C.C.; Kain, K.C. Use of a three-band HRP2/pLDH combination rapid diagnostic test increases diagnostic specificity for falciparum malaria in Ugandan children. Malar. J. 2014, 2875, 13–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leke, R.F.; Djokam, R.R.; Mbu, R.; Leke, R.J.; Fogako, J.; Megnekou, R.; Metenou, S.; Sama, G.; Zhou, Y.; Cadigan, T.; et al. Detection of the Plasmodium falciparum Antigen Histidine-Rich Protein 2 in Blood of Pregnant Women: Implications for Diagnosing Placental Malaria. J. Clin. Microbial. 1999, 37, 2992–2996. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Peng, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Tang, S. Evaluation of wondfo rapid diagnostic kit (Pf-HRP2/PAN-pLDH) for diagnosis of malaria by using nano-gold immunochromatographic assay. Acta Parasitol. 2014, 59, 2670–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouattara, A.; Doumbo, S.; Saye, R.; Beavogui, A.H.; Traoré, B.; Djimdé, A.; Niangaly, A.; Kayentao, K.; Diallo, M.; Doumbo, O.K.; et al. Use of a pLDH-based dipstick in the diagnostic and therapeutic follow-up of malaria patients in Mali. Malar. J. 2011, 10, 1475–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, E.S.; Kim, T.S.; Nam, H.W. Western blot diagnosis of vivax malaria with multiple stage-specific antigens of the parasite. Korean J. Parasitol. 2001, 39, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikarwar, B.; Sharma, P.K.; Srivastava, A.; Agarwal, G.S.; Boopathi, M.; Singh, B.; Jaiswal, Y.K. Surface plasmon resonance characterization of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies of malaria for biosensor applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 60, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tothill, I.E. Biosensors for cancer markers diagnosis. Seminars in cell & developmental biology. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2009, 20, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Noh, M.F.; Tothill, I.E. Development and characterisation of disposable gold electrodes, and their use for lead (II) analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 386, 2095–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Gosser, D.K.J. Cyclic Voltammetry: Simulation and Analysis of Reaction Mechanisms; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Salam, F.; Tothill, I.E. Detection of Salmonella typhimurium using an electrochemical immunosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2630–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrin, A.; Killard, A.J.; Smyth, R.M. Electrochemical Characterization of Commercial and Home-Made Screen-Printed Carbon Electrodes. Anal. Lett. 2007, 36, 2021–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, T.R.; Adams, R.N. Voltammetry at inert electrodes: II. Correlation of experimental results with theory for voltage and controlled potential scanning, controlled potential electrolysis, and chronopotentiometric techniques. Anal. Chim. Acta 1961, 25, 482–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S.K.; Singh, P.S.; Malhotra, B.D.; Marks, R.S.; Cullen, D.C.; Karube, I.; Lowe, C.R.; Weetall, H.H. Handbook of Biosensors and Biochips; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 342–377. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, C.O.; Tothill, I.E. Development of an electrochemical immunosensor for aflatoxin M1 in milk with focus on matrix interference. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2452–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanjul-Bolado, P.; González-García, M.B.; Costa-García, A. Amperometric detection in TMB/HRP-based assays. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 382, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, G.; Draisci, R.; Palleschi, G.; Compagnone, D. 3, 3′, 5, 5′-Tetramethylbenzidine as electrochemical substrate for horseradish peroxidase based enzyme immunoassays: A comparative study. Analyst 1998, 123, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillehoj, P.B.; Huang, M.C.; Truong, N.; Ho, C.M. Rapid electrochemical detection on a mobile phone. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2950–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, J.F.; Okoth, S.A.; Fontecha, G.A.; Torres, R.E.; Banegas, E.I.; Matute, M.L.; Bucheli, S.T.; Goldman, I.F.; de Oliveira, A.M.; Barnwell, J.W.; et al. Prevalence of PfHRP2 and PfHRP3 gene deletions in Puerto Lempira, Honduras. Malar. J. 2015, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzakah, E.; Kang, K.; Ni, C.; Tang, S.X.; Wang, J.H.; Wang, J.F. Comparative performance of aldolase and lactate dehydrogenase rapid diagnostic tests in Plasmodium vivax detection. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, M.F.; Baker, J.; Lee, N.; Luchavez, J.; Ariey, F.; Nhem, S.; McCarthy, J.S. Circulating antibodies against Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich proteins 2 interfere with antigen detection by rapid diagnostic tests. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.K.; Rao, V.K.; Agarwal, G.S.; Rai, G.P.; Gopalan, N.; Prakash, S.; Sharma, S.K.; Vijayaraghavan, R. Highly sensitive amperometric immunosensor for detection of Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein 2 in serum of humans with malaria: Comparison with a commercial kit. J. Clin. Microbial. 2008, 46, 3759–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.K.; Agarwal, G.S.; Rao, V.K.; Upadhyay, S.; Merwyn, S.; Gopalan, N.; Rai, G.P.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; Prakash, S. Amperometric immunosensor based on gold nanoparticles/alumina sol-gel modified screen-printed electrodes for antibodies to Plasmodium falciparum histidine rich protein-2. Analyst 2010, 135, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza Castilho, M.; Laube, T.; Yamanaka, H.; Alegret, S.; Pividori, M. Magneto immunoassays for Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein 2 related to malaria based on magnetic nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 5570–5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gikunoo, E.; Abera, A.; Woldesenbet, E. A novel carbon nanofibers grown on glass microballoons immunosensor: A tool for early diagnosis of malaria. Sensors 2014, 14, 14686–14699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brince, P.K.; Kumar, S.; Tripathy, S.; Vanjari, S.R.K.; Singh, V.; Singh, S.G. A highly sensitive self- assembled monolayer modified copper doped zinc oxide nanofiber interface for detection of Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein-2: Targeted towards rapid, early diagnosis of malaria. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, G.; Nagarajan, S.; Lapidus, L.J.; Lillehoj, P.B. Enzyme-free electrochemical immunosensor based on methylene blue and the electro-oxidation of hydrazine on Pt nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Analyte | Assay Principle | Range | Detection Limit | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PfHRP 2 | SPR | - | 5.6 pg∙mL−1 | [25] |
| PfHRP 2 | Carbon SPE modified with MWCN and Au/MWCN | - | 8 ng∙mL−1 | [37] |
| PfHRP 2 | Carbon SPE modified with AuNPs/Al2O3sol–gel | - | - | [41] |
| PfHRP 2 | Graphite–epoxy composite magneto electrodes | - | 0.36 ng∙mL−1 | [42] |
| PfHRP 2 | Polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic chips | - | 16 ng∙mL−1 | [43] |
| PfHRP 2 | Carbon nanofiber forest grown on glass microballons | 0.01–10 ng∙mL−1 | 0.025 ng∙mL−1 | [44] |
| PfHRP 2 | Mercaptopropylphosphonic acid functionalized copper doped zinc oxide nanofibers | 10 ag∙mL−1–10 µg∙mL−1 | 6.8 ag∙mL−1 | [45] |
| PfHRP 2 | Low electrocatalytic indium tin oxide (ITO) on glass electrodes; APTES-glutaraldehyde modified | 1 pg∙mL−1–100 ng∙mL−1 | 2.2 pg∙mL−1 | [46] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hemben, A.; Ashley, J.; Tothill, I.E. Development of an Immunosensor for PfHRP 2 as a Biomarker for Malaria Detection. Biosensors 2017, 7, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7030028
Hemben A, Ashley J, Tothill IE. Development of an Immunosensor for PfHRP 2 as a Biomarker for Malaria Detection. Biosensors. 2017; 7(3):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7030028
Chicago/Turabian StyleHemben, Aver, Jon Ashley, and Ibtisam E. Tothill. 2017. "Development of an Immunosensor for PfHRP 2 as a Biomarker for Malaria Detection" Biosensors 7, no. 3: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7030028
APA StyleHemben, A., Ashley, J., & Tothill, I. E. (2017). Development of an Immunosensor for PfHRP 2 as a Biomarker for Malaria Detection. Biosensors, 7(3), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7030028