A Label-Free and Ultrasensitive Immunosensor for Detection of Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin Based on Graphene FETs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
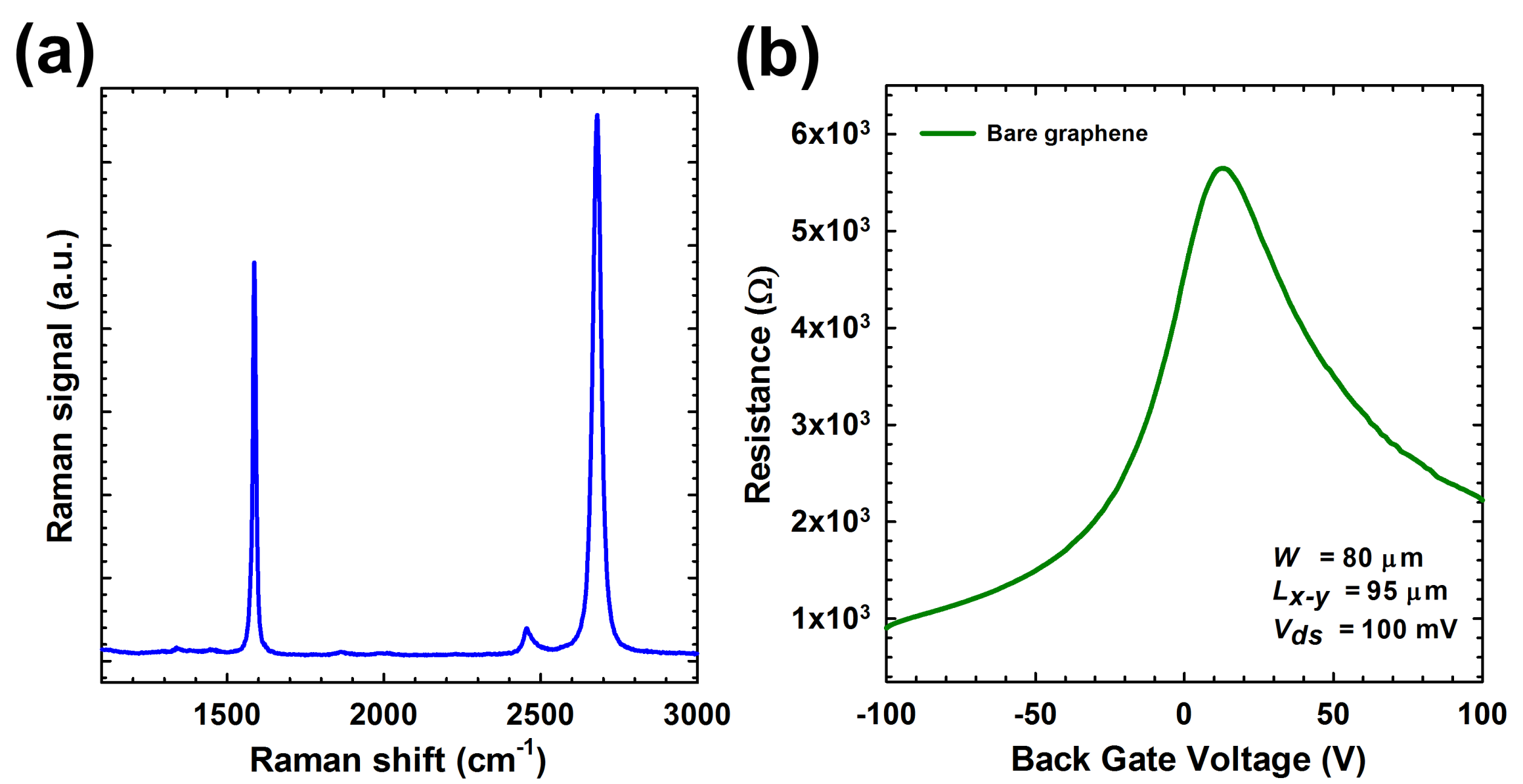
2.2. Characterization of BG-gFET
2.3. Sensor Test and Data Analysis
2.4. Wet Transfer of Graphene
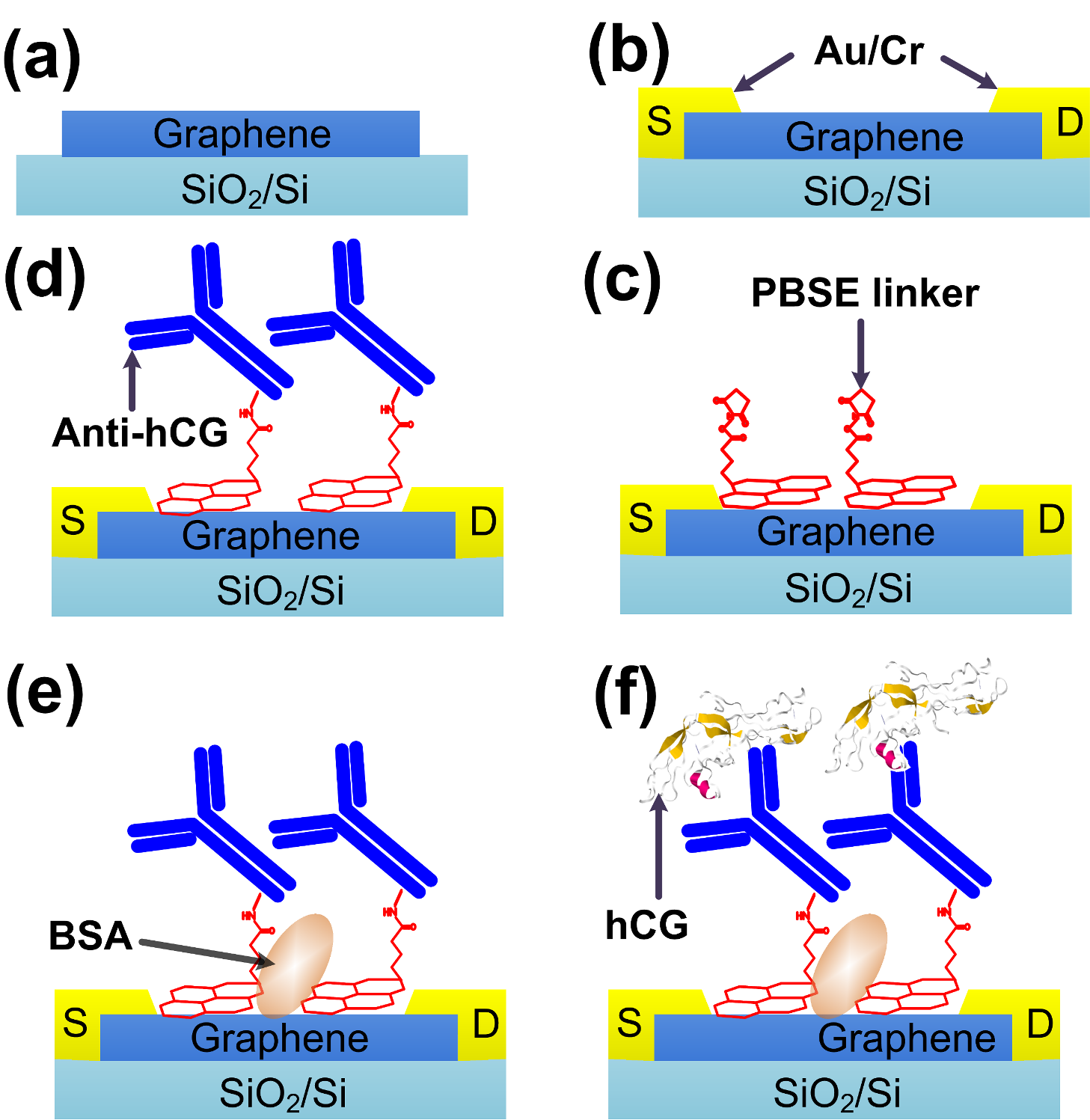
2.5. Materials Fabrication of hCG Biosensor
3. Results and Discussion
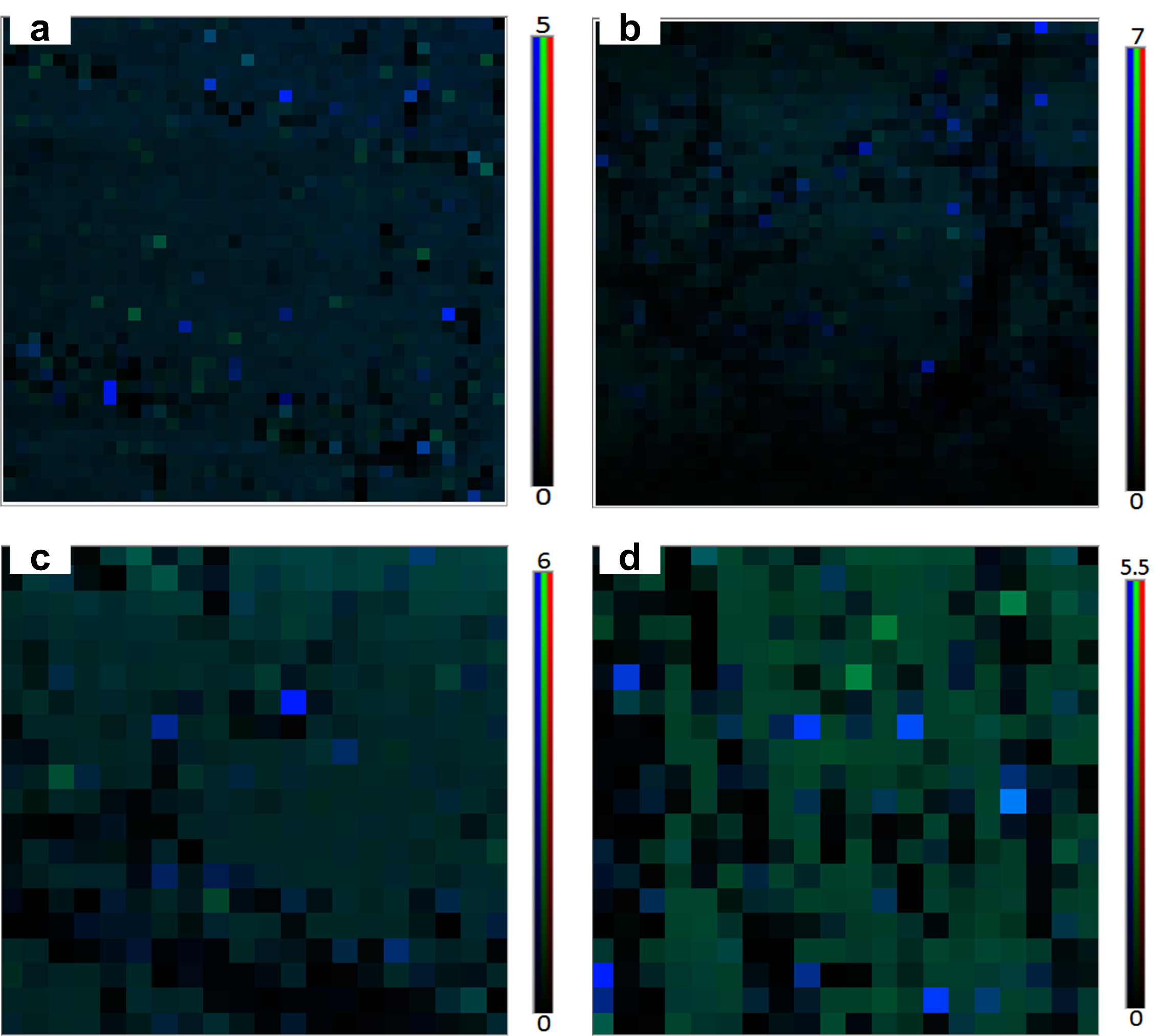
3.1. Assessment of Surface Morphology
3.2. Qualitavie Assessment of Graphene and Surface Modification
3.3. Dependence of hCG Concentration
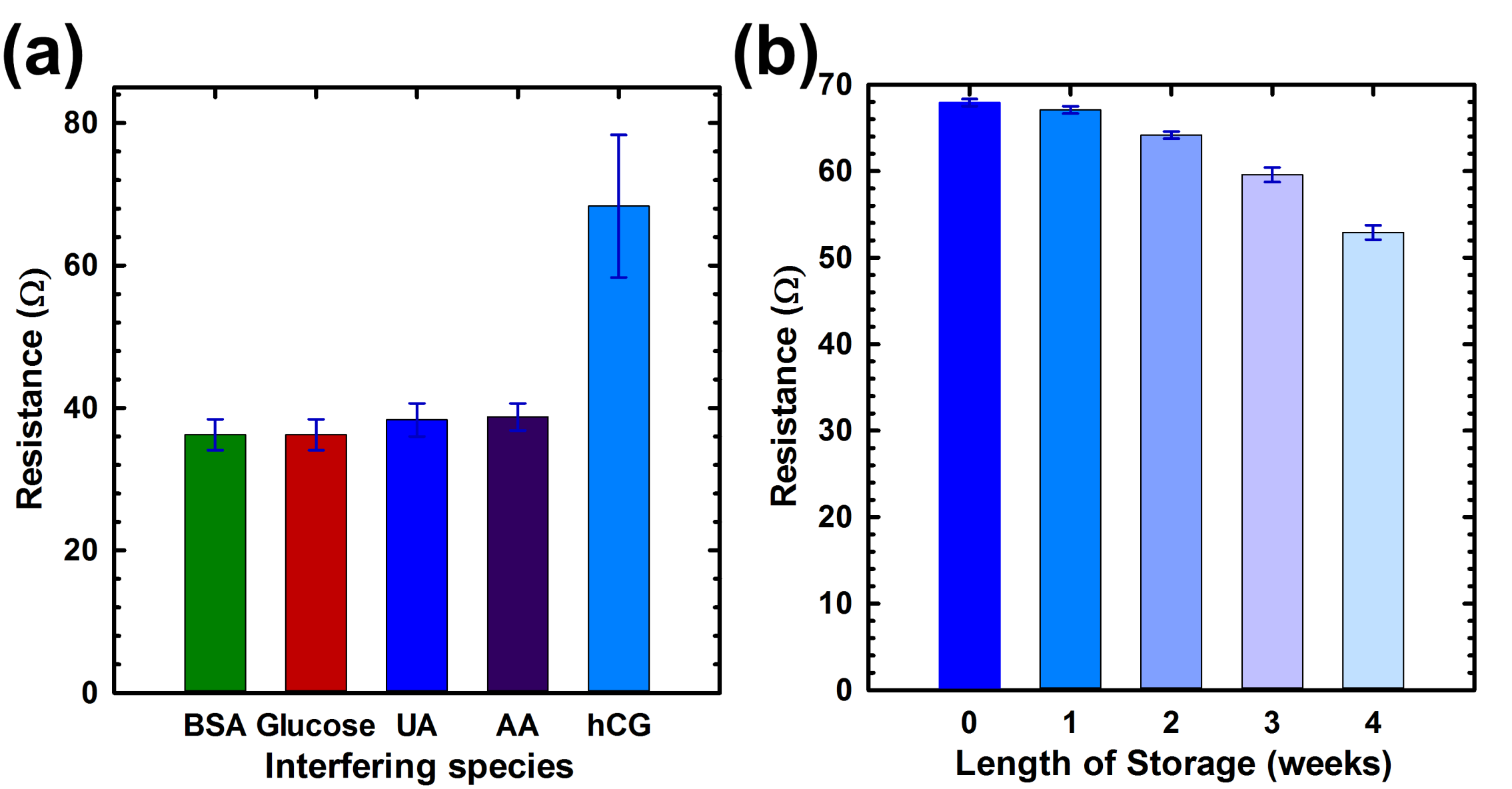
3.4. Slectivity, Stability, Reproducibility and Reusability
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chetcuti, A.F.; Wong, D.K.; Stuart, M.C. An indirect perfluorosulfonated ionomer-coated electrochemical immunosensor for the detection of the protein human chorionic gonadotrophin. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 4088–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenman, U.-H.; Tiitinen, A.; Alfthan, H.; Valmu, L. The classification, functions and clinical use of different isoforms of HCG. Hum. Reprod. Update 2006, 12, 769–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, R.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y.; Ou, C.; Cao, S.; Li, X. Amperometric immunosensors based on layer-by-layer assembly of gold nanoparticles and methylene blue on thiourea modified glassy carbon electrode for determination of human chorionic gonadotrophin. Talanta 2008, 74, 1330–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Mao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, T.; Chen, M.; Yu, F.; Fu, W. A novel piezoelectric quartz micro-array immunosensor based on self-assembled monolayer for determination of human chorionic gonadotropin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 19, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y.; Cao, S.; Guan, S.; Fu, P.; Min, L. A novel immunosensor based on gold nanoparticles and poly-(2,6-pyridinediamine)/multiwall carbon nanotubes composite for immunoassay of human chorionic gonadotrophin. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 51, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartiainen, J.; Alfthan, H.; Lehtovirta, P.; Stenman, U.H. Elevated hCG and a high proportion of hCGβ in serum preceding the diagnosis of trophoblastic disease by seven months. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2002, 109, 589–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Liang, X.; Liu, Q.; Liang, A.; Jiang, Z. A novel nanocatalytic sers detection of trace human chorionic gonadotropin using labeled-free vitoria blue 4R as molecular probe. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergveld, P. Development, operation, and application of the ion-sensitive field-effect transistor as a tool for electrophysiology. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1972, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Moraes, A.C.M.; Kubota, L.T. Recent trends in field-effect transistors-based immunosensors. Chemosensors 2016, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pumera, M. Graphene in biosensing. Mater. Today 2011, 14, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuila, T.; Bose, S.; Khanra, P.; Mishra, A.K.; Kim, N.H.; Lee, J.H. Recent advances in graphene-based biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 4637–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, N.; Berry, V. Graphene-based single-bacterium resolution biodevice and DNA transistor: Interfacing graphene derivatives with nanoscale and microscale biocomponents. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 4469–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Kim, Y.H.; Cheon, D.S.; Seo, T.S. Micropatterned reduced graphene oxide based field-effect transistor for real-time virus detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 186, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, S.; Burwell, G.; Castaing, A.; Gonzalez, D.; Conlan, R.; Guy, O. Epitaxial graphene immunosensor for human chorionic gonadotropin. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 190, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.-H.; Kumar, V.; Moyano, D.R.; Wen, S.-H.; Parashar, V.; Hsiao, S.-H.; Srivastava, A.; Saxena, P.S.; Huang, K.-P.; Chang, C.-C.; et al. High-performance and high-sensitivity applications of graphene transistors with self-assembled monolayers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, J.; Vishnubhotla, R.; Vrudhula, A.; Johnson, A.C. Scalable production of high-sensitivity, label-free DNA biosensors based on back-gated graphene field effect transistors. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 8700–8704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Kang, H.; Naylor, C.H.; Streller, F.; Ducos, P.; Serrano, M.D.; Ping, J.; Zauberman, J.; Carpick, R.W.; Wang, Y.-J.; et al. Scalable production of sensor arrays based on high-mobility hybrid graphene field effect transistors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 27546–27552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Pan, G.; Suhail, A.; Islam, K.; Avent, N.; Davey, P. Deep UV hardening of photoresist for shaping of graphene and lift-off fabrication of back-gated field effect biosensors by ion-milling and sputter deposition. Carbon 2017, 118, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cai, W.; An, J.; Kim, S.; Nah, J.; Yang, D.; Piner, R.; Velamakanni, A.; Jung, I.; Tutuc, E.; et al. Large-area synthesis of high-quality and uniform graphene films on copper foils. Science 2009, 324, 1312–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suk, J.W.; Kitt, A.; Magnuson, C.W.; Hao, Y.; Ahmed, S.; An, J.; Swan, A.K.; Goldberg, B.B.; Ruoff, R.S. Transfer of CVD-grown monolayer graphene onto arbitrary substrates. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6916–6924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, K.; Chand, R.; Han, D.; Shin, I.-S.; Kim, Y.-S. An electrochemical assay for restriction endonuclease activity using graphene monolayer. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, B261–B264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, A.; Islam, K.; Li, B.; Jenkins, D.; Pan, G. Reduction of polymer residue on wet–transferred cvd graphene surface by deep UV exposure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 183103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Pan, G.; Jamil, N.Y.; Al Taan, L.; Awan, S.; Avent, N. Shielding technique for deposition of au electrical contacts on graphene by sputtering. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2015, 33, 030601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuoriluoto, M.; Orelma, H.; Zhu, B.; Johansson, L.-S.; Rojas, O.J. Control of protein affinity of bioactive nanocellulose and passivation using engineered block and random copolymers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 5668–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schedin, F.; Geim, A.; Morozov, S.; Hill, E.; Blake, P.; Katsnelson, M.; Novoselov, K. Detection of individual gas molecules adsorbed on graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Kwon, O.S.; Lee, S.H.; Song, H.S.; Park, T.H.; Jang, J. Ultrasensitive flexible graphene based field-effect transistor (fet)-type bioelectronic nose. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5082–5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, O.S.; Park, S.J.; Hong, J.-Y.; Han, A.-R.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.S.; Oh, J.H.; Jang, J. Flexible fet-type vegf aptasensor based on nitrogen-doped graphene converted from conducting polymer. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 1486–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bartolomeo, A.; Giubileo, F.; Romeo, F.; Sabatino, P.; Carapella, G.; Iemmo, L.; Schroeder, T.; Lupina, G. Graphene field effect transistors with niobium contacts and asymmetric transfer characteristics. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 475202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bartolomeo, A.; Santandrea, S.; Giubileo, F.; Romeo, F.; Petrosino, M.; Citro, R.; Barbara, P.; Lupina, G.; Schroeder, T.; Rubino, A. Effect of back-gate on contact resistance and on channel conductance in graphene-based field-effect transistors. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2013, 38, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.F.; Iqbal, M.Z.; Iqbal, M.W.; Iermolenko, V.M.; Khalil, H.W.; Nam, J.; Kim, K.S.; Noh, H.; Eom, J. Stable and reversible doping of graphene by using KNO3 solution and photo-desorption current response. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 50040–50046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, S.; Hashim, U.; Gopinath, S.C.; Poopalan, P.; Ramayya, H.; Omar, M.I.; Haarindraprasad, R.; Veeradasan, P. A point-of-care immunosensor for human chorionic gonadotropin in clinical urine samples using a cuneated polysilicon nanogap lab-on-chip. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, K.; Suhail, A.; Pan, G. A Label-Free and Ultrasensitive Immunosensor for Detection of Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin Based on Graphene FETs. Biosensors 2017, 7, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7030027
Islam K, Suhail A, Pan G. A Label-Free and Ultrasensitive Immunosensor for Detection of Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin Based on Graphene FETs. Biosensors. 2017; 7(3):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7030027
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Kamrul, Ahmed Suhail, and Genhua Pan. 2017. "A Label-Free and Ultrasensitive Immunosensor for Detection of Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin Based on Graphene FETs" Biosensors 7, no. 3: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7030027
APA StyleIslam, K., Suhail, A., & Pan, G. (2017). A Label-Free and Ultrasensitive Immunosensor for Detection of Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin Based on Graphene FETs. Biosensors, 7(3), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7030027




