Lipid Bilayer Membrane in a Silicon Based Micron Sized Cavity Accessed by Atomic Force Microscopy and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Instruments
2.2. Fabrication and Functionalization of Micron-Sized Cavity
2.3. Preparation of Large Unilamellar Vesicles and Lipid Bilayer Membrane
2.4. Atomic Force Microscopy
2.5. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
3. Results and Discussion
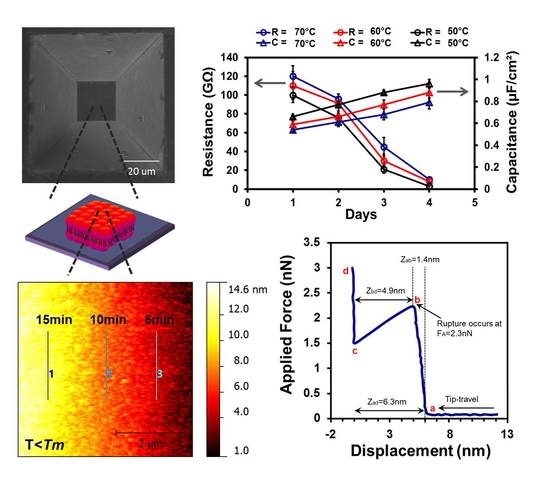
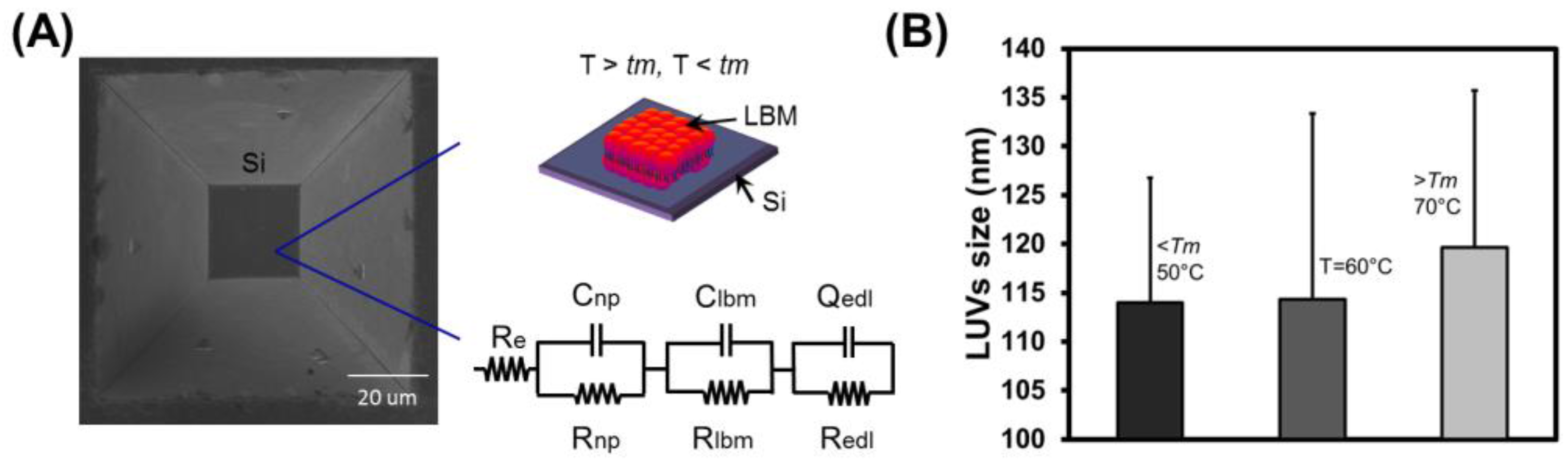
3.1. Fabrication of Micron-Sized Cavity in Si and Lipid Bilayers
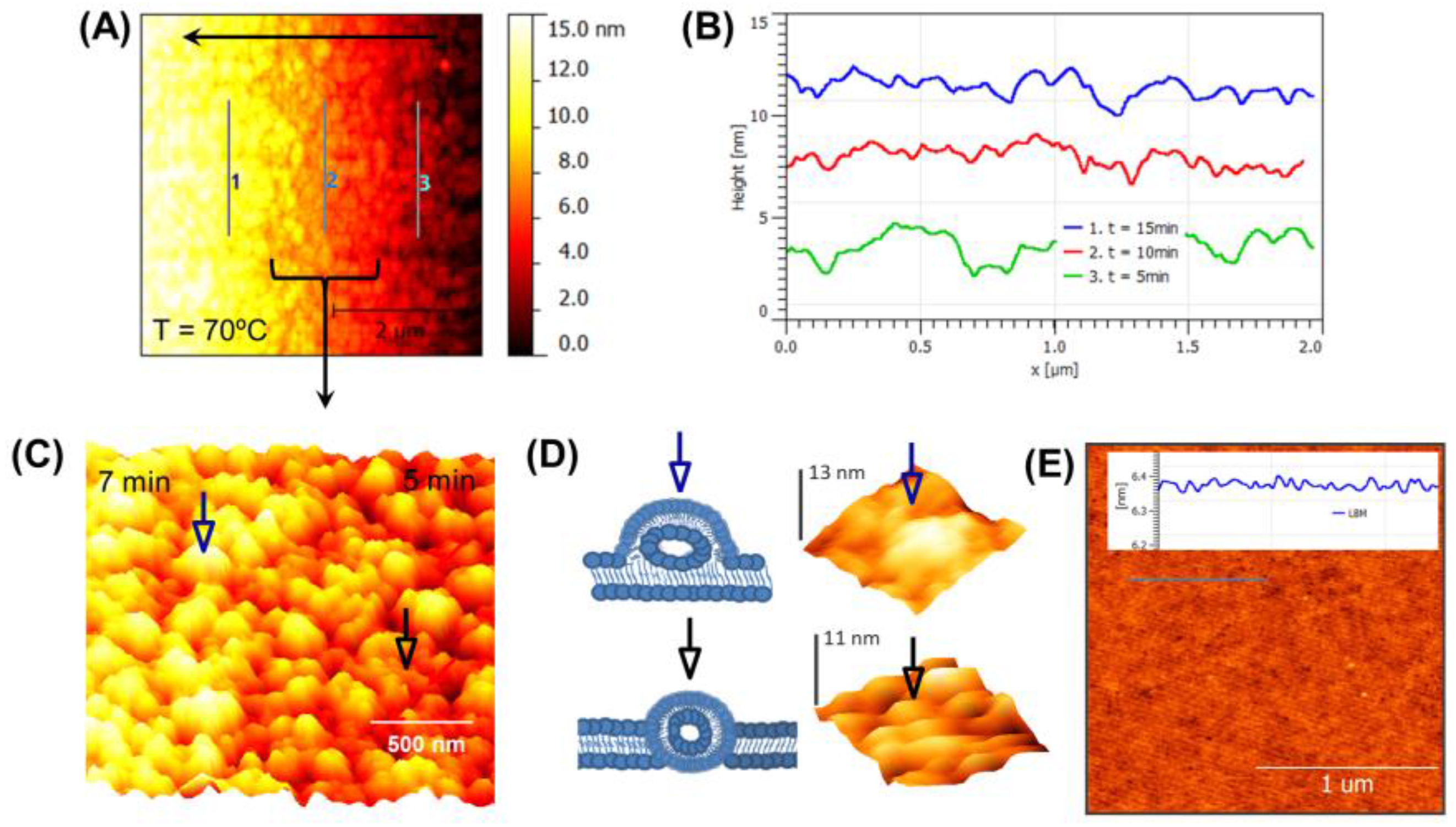
3.2. Real-Time Monitoring of SLB above Tm
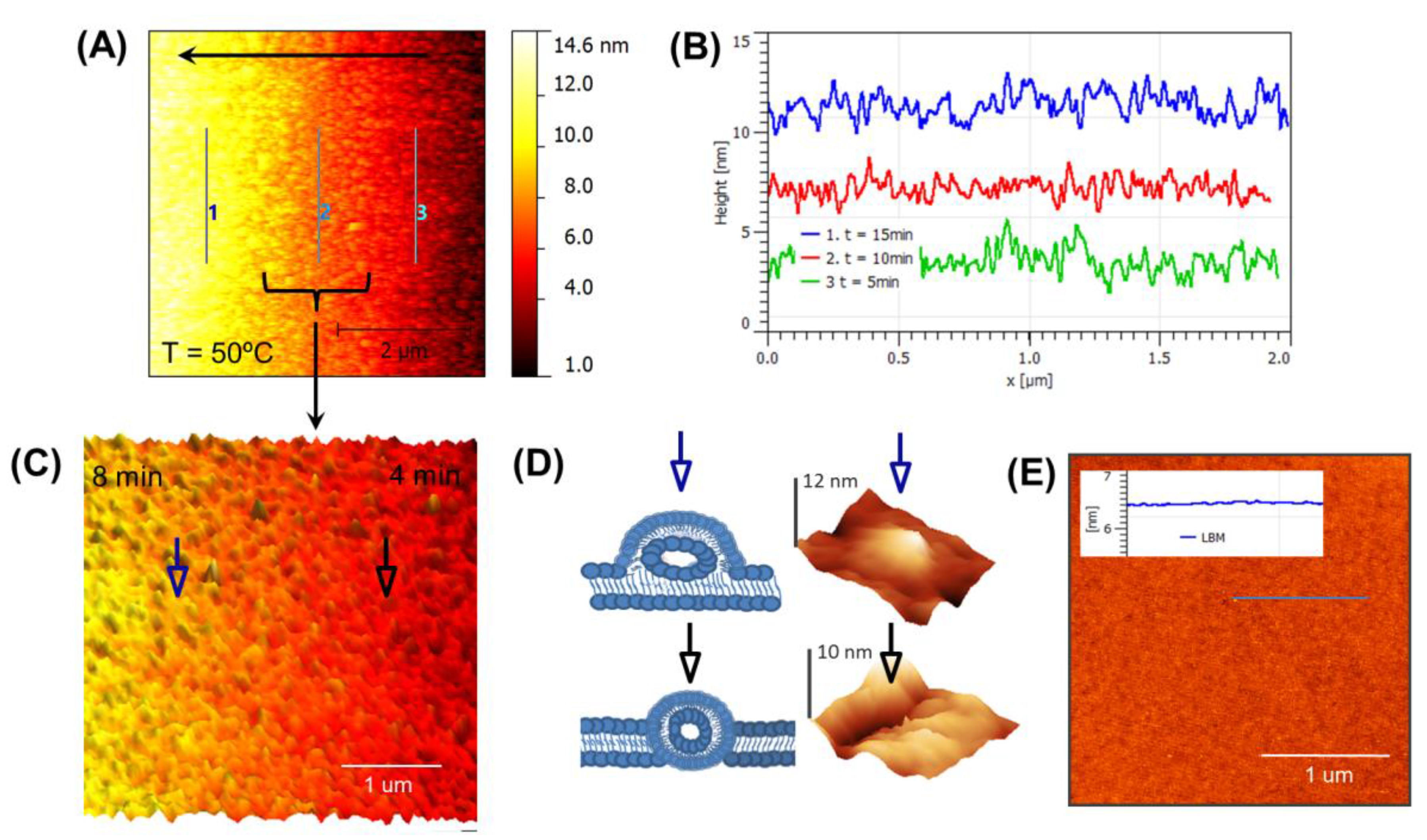
3.3. Real-Time Monitoring of SLB below Tm
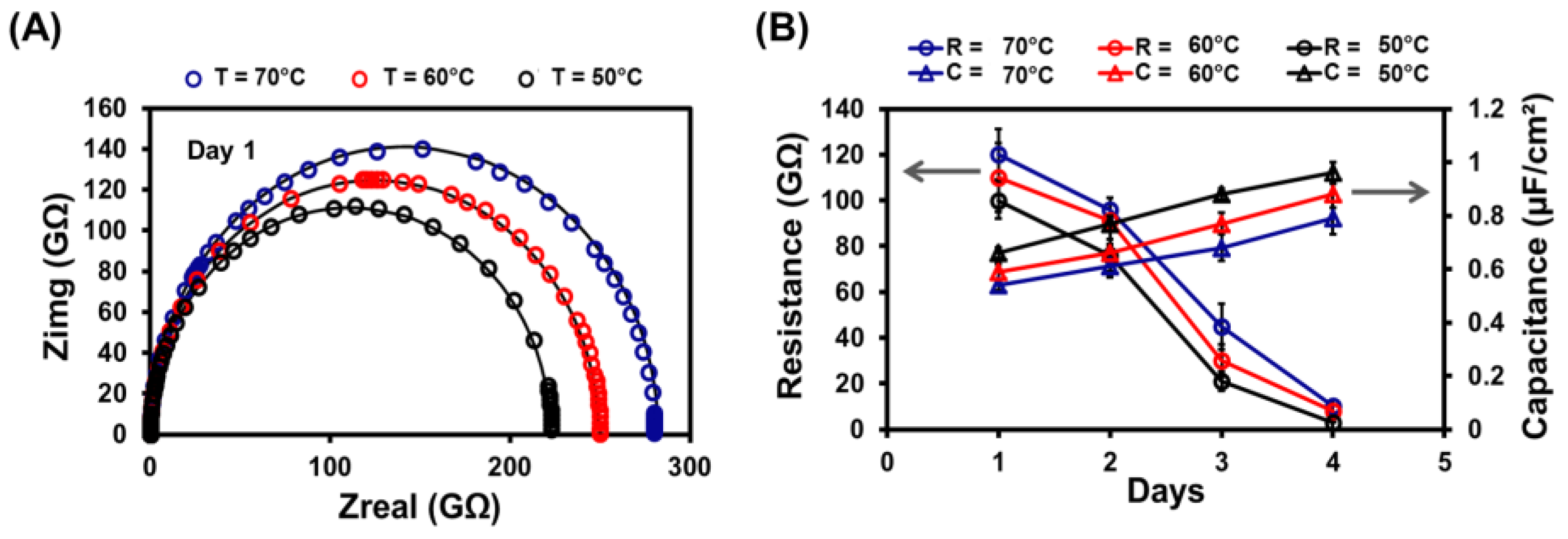
3.4. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
3.5. Stability of Lipid Bilayer Membrane
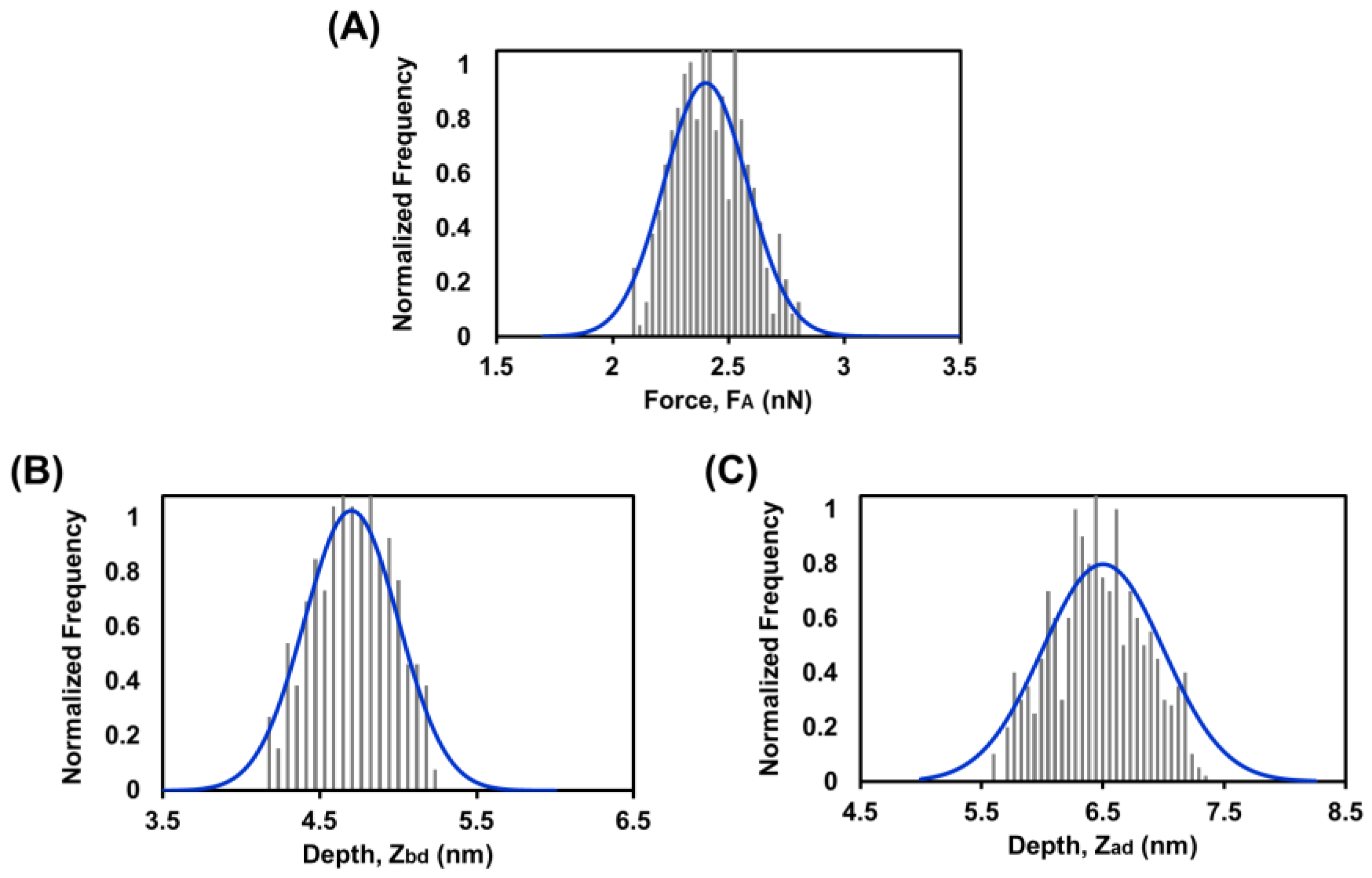
3.6. Force Spectroscopy Study of SLB below Tm
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, M.S.; Dosoky, N.S.; Williams, J.D. Engineering lipid bilayer membranes for protein studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 21561–21597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingeot-Leclercq, M.P.; Deleu, M.; Brasseur, R.; Dufrene, Y.F. Atomic force microscopy of supported lipid bilayers. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1654–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reviakine, I.; Brisson, A. Formation of supported phospholipid bilayers from unilamellar vesicles investigated by atomic force microscopy. Langmuir 2000, 16, 1806–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hane, F.; Drolle, E.; Gaikwad, R.; Faught, E.; Leonenko, Z. Amyloid-β aggregation on model lipid membranes: An atomic force microscopy study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 26, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.C.; Blanchette, C.D.; Ratto, T.V.; Longo, M.L. Lipid domains in supported lipid bilayer for atomic force microscopy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2007, 400, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wacklin, H.P.; Thomas, R.K. Spontaneous formation of asymmetric lipid bilayers by adsorption of vesicles. Langmuir 2007, 23, 7644–7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Janmey, P.A.; Sharp, K.A.; Finkel, T.H. Improved method of preparation of supported planar lipid bilayers as artificial membranes for antigen presentation. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2011, 74, 1174–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picas, L.; Suarez-Germa, C.; Teresa Montero, M.; Hernandez-Borrell, J. Force spectroscopy study of langmuir-blodgett asymmetric bilayers of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylglycerol. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 3543–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrent-Burgues, J.; Oncins, G.; Sanz, F. Study of mixed Langmuir and Langmuir-Blodgett films of dissimilar components by AFM and force spectroscopy. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 321, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenhert, S.; Sun, P.; Wang, Y.; Fuchs, H.; Mirkin, C.A. Massively Parallel Dip-Pen Nanolithography of Heterogeneous Supported Phospholipid Multilayer Patterns. Small 2007, 3, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirtz, M.; Corso, R.; Sekula-Neuner, S.; Fuchs, H. Comparative Height Measurements of Dip-Pen Nanolithography-Produced Lipid Membrane Stacks with Atomic Force, Fluorescence, and Surface-Enhanced Ellipsometric Contrast Microscopy. Langmuir 2011, 27, 11605–11608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirtz, M.; Oikonomou, A.; Georgiou, T.; Fuchs, H.; Vijayaraghavan, A. Multiplexed biomimetic lipid membranes on graphene by dip-pen nanolithography. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirtz, M.; Brglez, J.; Fuchs, H.; Niemeyer, C.M. Selective Binding of DNA Origami on Biomimetic Lipid Patches. Small 2015, 11, 5752–5758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, F.; Hirtz, M.; Greiner, A.M.; Weschenfelder, M.; Waterkotte, B.; Bastmeyer, M.; Fuchs, H. Interdigitated Multicolored Bioink Micropatterns by Multiplexed Polymer Pen Lithography. Small 2013, 9, 3266–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jass, J.; Tjarnhage, T.; Puu, G. From liposomes to supported, planar bilayer structures on hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces: An atomic force microscopy study. Biophys. J. 2000, 79, 3153–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellana, E.T.; Cremer, P.S. Solid supported lipid bilayers: From biophysical studies to sensor design. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2006, 61, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailor, M.J.; Park, J.H. Hybrid nanoparticles for detection and treatment of cancer. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 3779–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, H.; Nieto, A.; Ma, F.; Freeman, W.R.; Sailor, M.J.; Cheng, L. Tunable sustained intravitreal drug delivery system for daunorubicin using oxidized porous silicon. J. Control Release 2014, 178, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seantier, B.; Breffa, C.; Felix, O.; Decher, G. In Situ Investigations of the Formation of Mixed Supported Lipid Bilayers Close to the Phase Transition Temperature. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Trefna, H.; Persson, M.; Kasemo, B.; Svedhem, S. Formation of supported lipid bilayers on silica: Relation to lipid phase transition temperature and liposome size. Soft Matt. 2014, 10, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Kirat, K.; Morandat, S.; Dufrene, Y.F. Nanoscale analysis of supported lipid bilayers using atomic force microscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1798, 750–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morandat, S.; Azouzi, S.; Beauvais, E.; Mastouri, A.; El Kirat, K. Atomic force microscopy of model lipid membranes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 1445–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giocondi, M.C.; Yamamoto, D.; Lesniewska, E.; Milhiet, P.E.; Ando, T.; Le Grimellec, C. Surface topography of membrane domains. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1798, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goksu, E.I.; Vanegas, J.M.; Blanchette, C.D.; Lin, W.C.; Longo, M.L. AFM for structure and dynamics of biomembranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2009, 1788, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binnig, G.; Quate, C.F. Atomic Force Microscope. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 56, 930–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.S.; Williams, J.D. Fabrication of solid state nanopore in thin silicon membrane using low cost multistep chemical etching. Materials 2015, 8, 7389–7400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauscher, M.; Dietrich, S. Wetting Phenomena in Nanofluidics. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2008, 38, 143–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Dosoky, N.S.; Berdiev, B.K.; Williams, J.D. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for black lipid membranes fused with channel protein supported on solid-state nanopore. Eur. Biophys. J. 2016, 45, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, R.P.; Berat, R.; Brisson, A.R. Formation of solid-supported lipid bilayers: An integrated view. Langmuir 2006, 22, 3497–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimhult, E.; Hook, F.; Kasemo, B. Temperature dependence of formation of a supported phospholipid bilayer from vesicles on SiO2. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 66, 051905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerner, Z.; Pajkossy, T. Impedance of rough capacitive electrodes: The role of surface disorder. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1998, 448, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Kisiel, K.; Jung, J.; Ulanski, J.; Tondelier, D.; Geffroy, B.; Bonnassieux, Y.; Horowitz, G. Persistent photoexcitation effect on the poly(3-hexylthiophene) film: Impedance measurement and modeling. Synth. Met. 2012, 162, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiskopf, D.; Schmitt, E.K.; Kluhr, M.H.; Dertinger, S.K.; Steinem, C. Micro-BLMs on highly ordered porous silicon substrates: Rupture process and lateral mobility. Langmuir 2007, 23, 9134–9139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tantawi, K.H.; Berdiev, K.B.; Cerro, R.; Williams, J.D. Porous silicon membrane for investigation of transmembrane proteins. Superlattices Microstruct. 2013, 58, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantawi, K.H.; Cerro, R.; Berdiev, K.B.; Matrin, M.E.; Patel, D.; Williams, J.D. Investigation of transmembrane protein fused in lipid bilayer membranes supported on porous silicon. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2013, 37, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romer, W.; Steinem, C. Impedance analysis and single-channel recordings on nano-black lipid membranes based on porous alumina. Biophys. J. 2004, 86, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, C.F.; Li, M.G.; Yan, J.W.; Mao, B.W. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and atomic force microscopic studies of electrical and mechanical properties of nano-black lipid membranes and size dependence. Langmuir 2012, 28, 14739–14746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumowicz, M.; Petelska, A.D.; Figaszewski, Z.A. Impedance analysis of a phosphatidylcholine-phosphatidylethanolamine system in bilayer lipid membranes. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 5024–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumowicz, M.; Kotynska, J.; Petelska, A.; Figaszewski, Z. Impedance analysis of phosphatidylcholine membranes modified with valinomycin. Eur. Biophys. J. 2006, 35, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ma, S.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bi, H.; Zhang, L.; Han, X. High Impedance Droplet-Solid Interface Lipid Bilayer Membranes. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 2094–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, B.M.; Polans, J.; Comer, J.; Sridhar, S.; Wendel, D.; Aksimentiev, A.; Bashir, R. Lipid bilayer coated Al2O3 nanopore sensors: Towards a hybrid biological solid-state nanopore. Biomed. Microdevices 2011, 13, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalsi, S.; Powl, A.M.; Wallace, B.A.; Morgan, H.; De Planque, M.R.R. Shaped apertures in photoresist films enhance the lifetime and mechanical stability of suspended lipid bilayers. Biophys. J. 2014, 106, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeger, H.M.; Di Cerbo, A.; Alessandrini, A.; Facci, P. Supported lipid bilayers on mica and silicon oxide: Comparison of the main phase transition behavior. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 8926–8933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picas, L.; Rico, F.; Scheuring, S. Direct measurement of the mechanical properties of lipid phases in supported bilayers. Biophys. J. 2012, 102, L01–L03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, M.S.; Dosoky, N.S.; Patel, D.; Weimer, J.; Williams, J.D. Lipid Bilayer Membrane in a Silicon Based Micron Sized Cavity Accessed by Atomic Force Microscopy and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. Biosensors 2017, 7, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7030026
Khan MS, Dosoky NS, Patel D, Weimer J, Williams JD. Lipid Bilayer Membrane in a Silicon Based Micron Sized Cavity Accessed by Atomic Force Microscopy and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. Biosensors. 2017; 7(3):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7030026
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Muhammad Shuja, Noura Sayed Dosoky, Darayas Patel, Jeffrey Weimer, and John Dalton Williams. 2017. "Lipid Bilayer Membrane in a Silicon Based Micron Sized Cavity Accessed by Atomic Force Microscopy and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy" Biosensors 7, no. 3: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7030026
APA StyleKhan, M. S., Dosoky, N. S., Patel, D., Weimer, J., & Williams, J. D. (2017). Lipid Bilayer Membrane in a Silicon Based Micron Sized Cavity Accessed by Atomic Force Microscopy and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. Biosensors, 7(3), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7030026