Composite Hydrogels with Engineered Microdomains for Optical Glucose Sensing at Low Oxygen Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
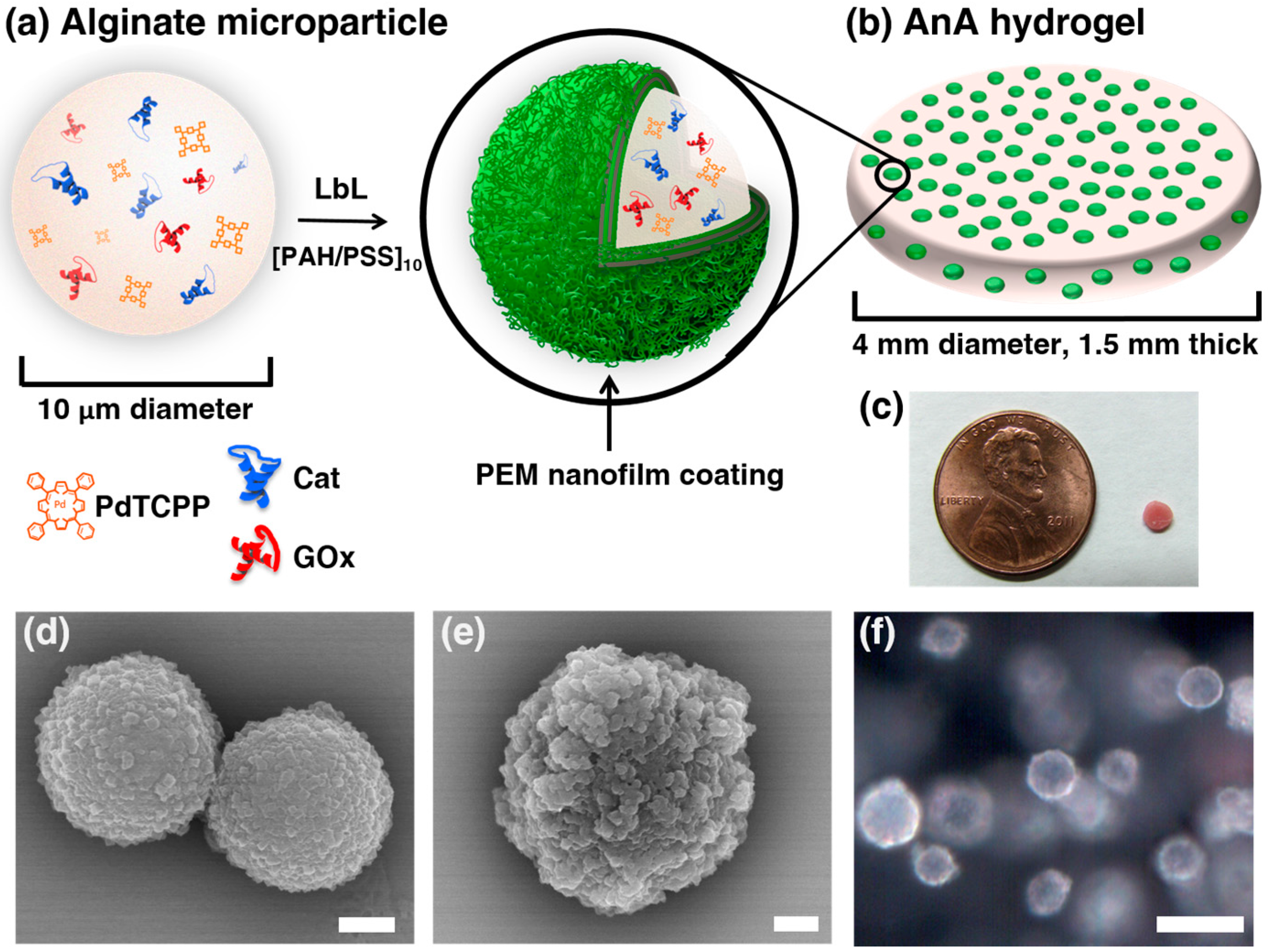
2.2. Alginate Microparticle Synthesis
2.3. Layer-by-Layer (LbL) Deposition on Alginate Microparticles
2.4. AnA Fabrication: Alginate Microparticles Embedded in Alginate Hydrogel
2.5. Diffusion Measurements
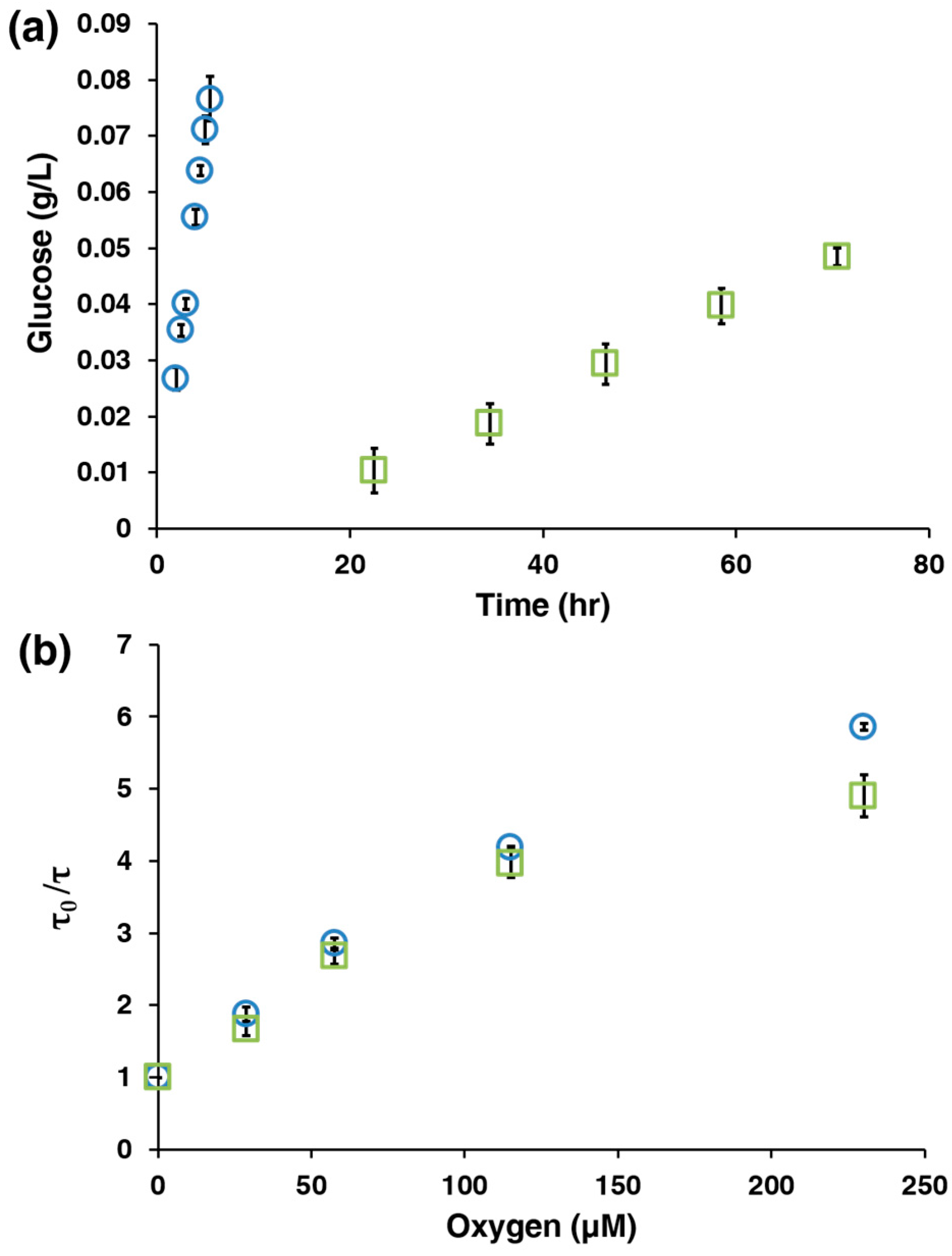
2.6. Oxygen and Glucose Challenges
2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy of Alginate
2.8. Darkfield and Hyperspectral Imaging of AnA Hydrogels
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the AnA Hydrogels
3.2. AnA Hydrogel Response
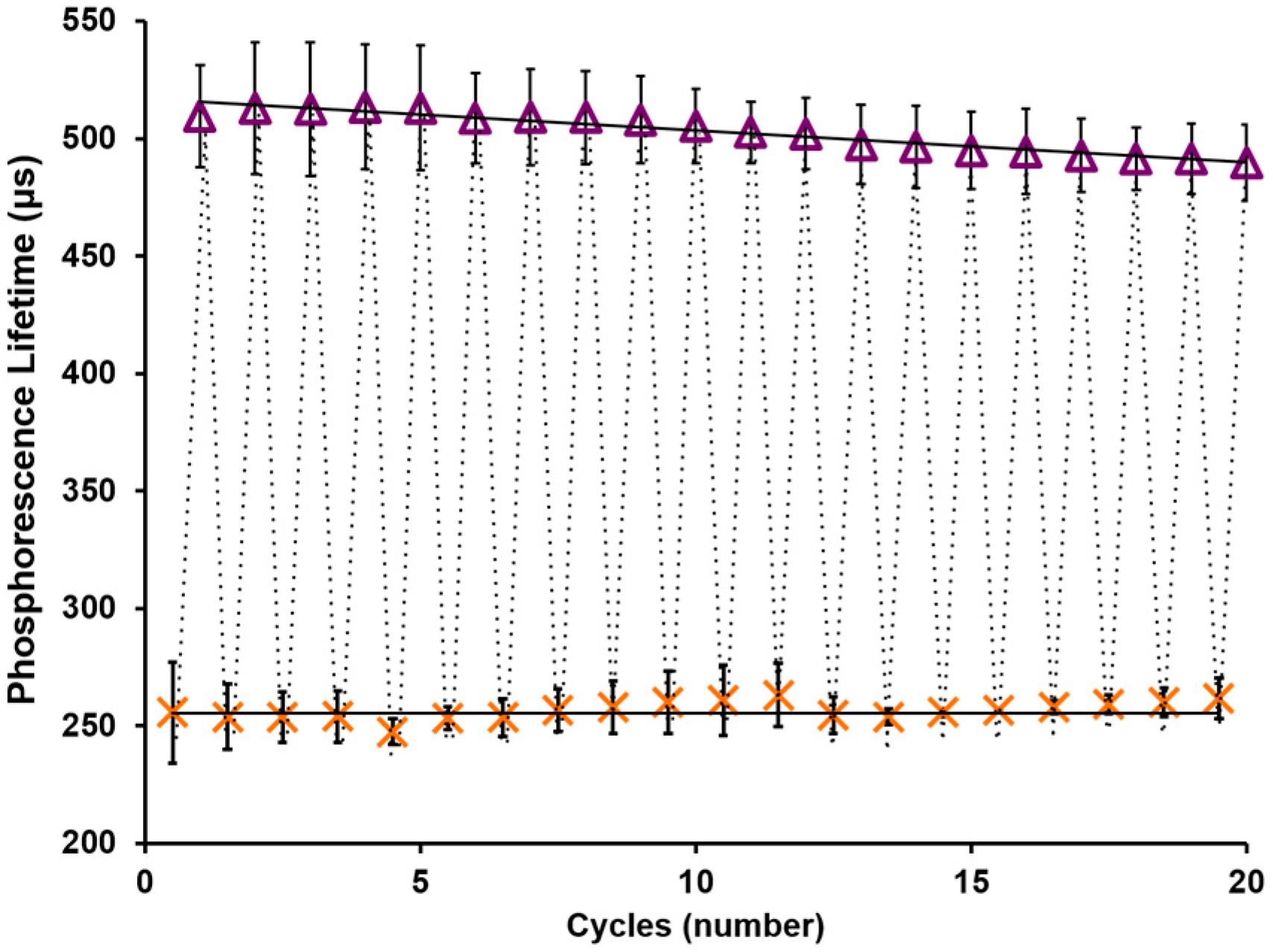
3.3. AnA Hydrogel Stability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thompson, S.; James, M.; Wiebe, N.; Hemmelgarn, B.; Manns, B.; Klarenbach, S.; Tonelli, M.; Network, A.K.D. Cause of death in patients with reduced kidney function. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 2504–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andre, F.; Booy, R.; Bock, H.; Clemens, J.; Datta, S.; John, T.; Lee, B.; Lolekha, S.; Peltola, H.; Ruff, T. Vaccination greatly reduces disease, disability, death and inequity worldwide. Bull. World Health Organ. 2008, 86, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, N.M.; Becker, M.H.; Janz, N.K.; Lorig, K.; Rakowski, W.; Anderson, L. Self-management of chronic disease by older adults a review and questions for research. J. Aging Health 1991, 3, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, G. In search of a germ theory equivalent for chronic disease. Prev. Chron. Dis. 2012, 9, 110301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, J.R.; Cleveland, J.L. Targeting lactate metabolism for cancer therapeutics. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3685–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sousa Vieira, E.E.; Bispo, J.A.M.; Fernandes, A.B.; Silveira, L. Biomarkers of Chronic Kidney Disease in the Urine of Diabetic/Hypertensive Patients by Means of Raman Spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the SPIE BIOS, San Francisco, CA, USA, 7 March 2016.
- Burge, M.R.; Mitchell, S.; Sawyer, A.; Schade, D.S. Continuous glucose monitoring: The future of diabetes management. Diabetes Spectr. 2008, 21, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, H.; Mühlemann, H. Telemetry of plaque ph from interdental area. Helv. Odontol. Acta 1966, 10, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guinovart, T.; Parrilla, M.; Crespo, G.A.; Rius, F.X.; Andrade, F.J. Potentiometric sensors using cotton yarns, carbon nanotubes and polymeric membranes. Analyst 2013, 138, 5208–5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Emaminejad, S.; Nyein, H.Y.Y.; Challa, S.; Chen, K.; Peck, A.; Fahad, H.M.; Ota, H.; Shiraki, H.; Kiriya, D. Fully integrated wearable sensor arrays for multiplexed in situ perspiration analysis. Nature 2016, 529, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogasawara, K.; Tsuru, T.; Mitsubayashi, K.; Karube, I. Electrical conductivity of tear fluid in healthy persons and keratoconjunctivitis sicca patients measured by a flexible conductimetric sensor. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 1996, 234, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Valdés-Ramírez, G.; Bandodkar, A.J.; Jia, W.; Martinez, A.G.; Ramírez, J.; Mercier, P.; Wang, J. Non-invasive mouthguard biosensor for continuous salivary monitoring of metabolites. Analyst 2014, 139, 1632–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, N.; Lähdesmäki, I.; Parviz, B.A. A contact lens with an integrated lactate sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 162, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, S.; Kudo, H.; Saito, T.; Ogawa, M.; Saito, H.; Otsuka, K.; Funakubo, A.; Mitsubayashi, K. A flexible and wearable biosensor for tear glucose measurement. Biomed. Microdevices 2007, 9, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Liao, Y.; Lingley, A.; Afanasiev, A.; Lähdesmäki, I.; Otis, B.; Parviz, B. A contact lens with integrated telecommunication circuit and sensors for wireless and continuous tear glucose monitoring. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2012, 22, 075007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/advisorycommittees/committeesmeetingmaterials/medicaldevices/medicaldevicesadvisorycommittee/clinicalchemistryandclinicaltoxicologydevicespanel/ucm517251.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2016).
- Morais, J.M.; Papadimitrakopoulos, F.; Burgess, D.J. Biomaterials/tissue interactions: Possible solutions to overcome foreign body response. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, M.C.; Meyerhoff, M.E. Implantable chemical sensors for real-time clinical monitoring: Progress and challenges. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2002, 6, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrara, S.; Ghoreishizadeh, S.; Olivo, J.; Taurino, I.; Baj-Rossi, C.; Cavallini, A.; Op de Beeck, M.; Dehollain, C.; Burleson, W.; Moussy, F.G. Fully integrated biochip platforms for advanced healthcare. Sensors 2012, 12, 11013–11060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budgett, D.M.; Hu, A.P.; Si, P.; Pallas, W.T.; Donnelly, M.G.; Broad, J.W.; Barrett, C.J.; Guild, S.-J.; Malpas, S.C. Novel technology for the provision of power to implantable physiological devices. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 102, 1658–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrus, L.P.; Unruh, R.; Wisniewski, N.A.; McShane, M.J. Characterization of lactate sensors based on lactate oxidase and palladium benzoporphyrin immobilized in hydrogels. Biosensors 2015, 5, 398–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unruh, R.M.; Roberts, J.R.; Nichols, S.P.; Gamsey, S.; Wisniewski, N.A.; McShane, M.J. Preclinical evaluation of poly (hema-co-acrylamide) hydrogels encapsulating glucose oxidase and palladium benzoporphyrin as fully implantable glucose sensors. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2015, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumosa, L.S.; Routh, T.L.; Lin, J.T.; Lucisano, J.Y.; Gough, D.A. Permeability of subcutaneous tissues surrounding long-term implants to oxygen. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 8287–8296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, E.W.; Grant, P.S.; Zhu, H.; McShane, M.J. Microscale enzymatic optical biosensors using mass transport limiting nanofilms. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.Q.; McShane, M.J. Modeling of spherical fluorescent glucose microsensor systems: Design of enzymatic smart tattoos. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gough, D.A. The implantable glucose sensor: An example of bioengineering design. Introd. Bioeng. 2001, 44, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, A.; Nagaraja, A.T.; You, Y.-H.; Roberts, J.R.; McShane, M.J. Cross-linked nanofilms for tunable permeability control in a composite microdomain system. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 71781–71790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.-H.; Nagaraja, A.; Biswas, A.; Marks, H.; Coté, G.L.; McShane, M.J. Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors 2015, Busan, Korea, 1–4 November 2015.
- Srivastava, R.; Brown, J.; Zhu, H.; McShane, M.J. Stabilization of glucose oxidase in alginate microspheres with photoreactive diazoresin nanofilm coatings. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 91, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikartovská, A.; Bučko, M.; Mislovičová, D.; Pätoprstý, V.; Lacík, I.; Gemeiner, P. Improvement of the stability of glucose oxidase via encapsulation in sodium alginate-cellulose sulfate-poly (methylene-co-guanidine) capsules. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2007, 41, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.Q.; Srivastava, R.; McShane, M.J. Encapsulation of glucose oxidase and an oxygen-quenched fluorophore in polyelectrolyte-coated calcium alginate microspheres as optical glucose sensor systems. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 21, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roberts, J.R.; Ritter, D.W.; McShane, M.J. A design full of holes: Functional nanofilm-coated microdomains in alginate hydrogels. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 3195–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, A.; Nagaraja, A.T.; McShane, M.J. Fabrication of nanocapsule carriers from multilayer-coated vaterite calcium carbonate nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 21193–21201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papkovsky, D.B.; Ponomarev, G.V.; Trettnak, W.; O’Leary, P. Phosphorescent complexes of porphyrin ketones: Optical properties and application to oxygen sensing. Anal. Chem. 1995, 67, 4112–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Baker, M.F.; Au-Yeung, K.Y.; Wisniewski, N.A.; Gamsey, S.; Morelli-Alvarez, L.; Mills, J.L.; Campos, M.; Helton, K.L. The first-in-man “Si Se Puede” study for the use of micro-oxygen sensors (moxys) to determine dynamic relative oxygen indices in the feet of patients with limb-threatening ischemia during endovascular therapy. J. Vasc. Surg. 2015, 61, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocchitta, G.; Spanu, A.; Babudieri, S.; Latte, G.; Madeddu, G.; Galleri, G.; Nuvoli, S.; Bagella, P.; Demartis, M.I.; Fiore, V. Enzyme biosensors for biomedical applications: Strategies for safeguarding analytical performances in biological fluids. Sensors 2016, 16, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleppe, K. The effect of hydrogen peroxide on glucose oxidase from aspergillus niger*. Biochemistry 1966, 5, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoni, T.; Santianni, D.; Manzoni, A.; Zanardi, S.; Mascini, M. Enzyme electrode for glucose determination in whole blood. Talanta 1997, 44, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, P.H.; Gough, D.A. Time-dependent inactivation of immobilized glucose oxidase and catalase. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1987, 29, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Non-Crosslinked | Crosslinked | |
|---|---|---|
| τ0 (μs) | 603 ± 16.3 | 588 ± 22.3 |
| Ksv (μM−1·O2) × 10−2 | 1.9 ± 0.072 | 2.3 ± 0.017 |
| Ambient O2 | ||
| Dynamic Range (mg/dL) | 5.7–330 | 87–350 |
| Sensitivity (μs × dL/mg) | 0.80 ± 0.11 | 0.075 ± 0.013 |
| Low O2 | ||
| Dynamic Range (mg/dL) | b--- | 2.6–350 |
| Sensitivity (μs × dL/mg) | b--- | 0.97 ± 0.054 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bornhoeft, L.R.; Biswas, A.; McShane, M.J. Composite Hydrogels with Engineered Microdomains for Optical Glucose Sensing at Low Oxygen Conditions. Biosensors 2017, 7, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7010008
Bornhoeft LR, Biswas A, McShane MJ. Composite Hydrogels with Engineered Microdomains for Optical Glucose Sensing at Low Oxygen Conditions. Biosensors. 2017; 7(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleBornhoeft, Lindsey R., Aniket Biswas, and Michael J. McShane. 2017. "Composite Hydrogels with Engineered Microdomains for Optical Glucose Sensing at Low Oxygen Conditions" Biosensors 7, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7010008
APA StyleBornhoeft, L. R., Biswas, A., & McShane, M. J. (2017). Composite Hydrogels with Engineered Microdomains for Optical Glucose Sensing at Low Oxygen Conditions. Biosensors, 7(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7010008





