Electrochemical, Electrochemiluminescence, and Photoelectrochemical Aptamer-Based Nanostructured Sensors for Biomarker Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Discussion
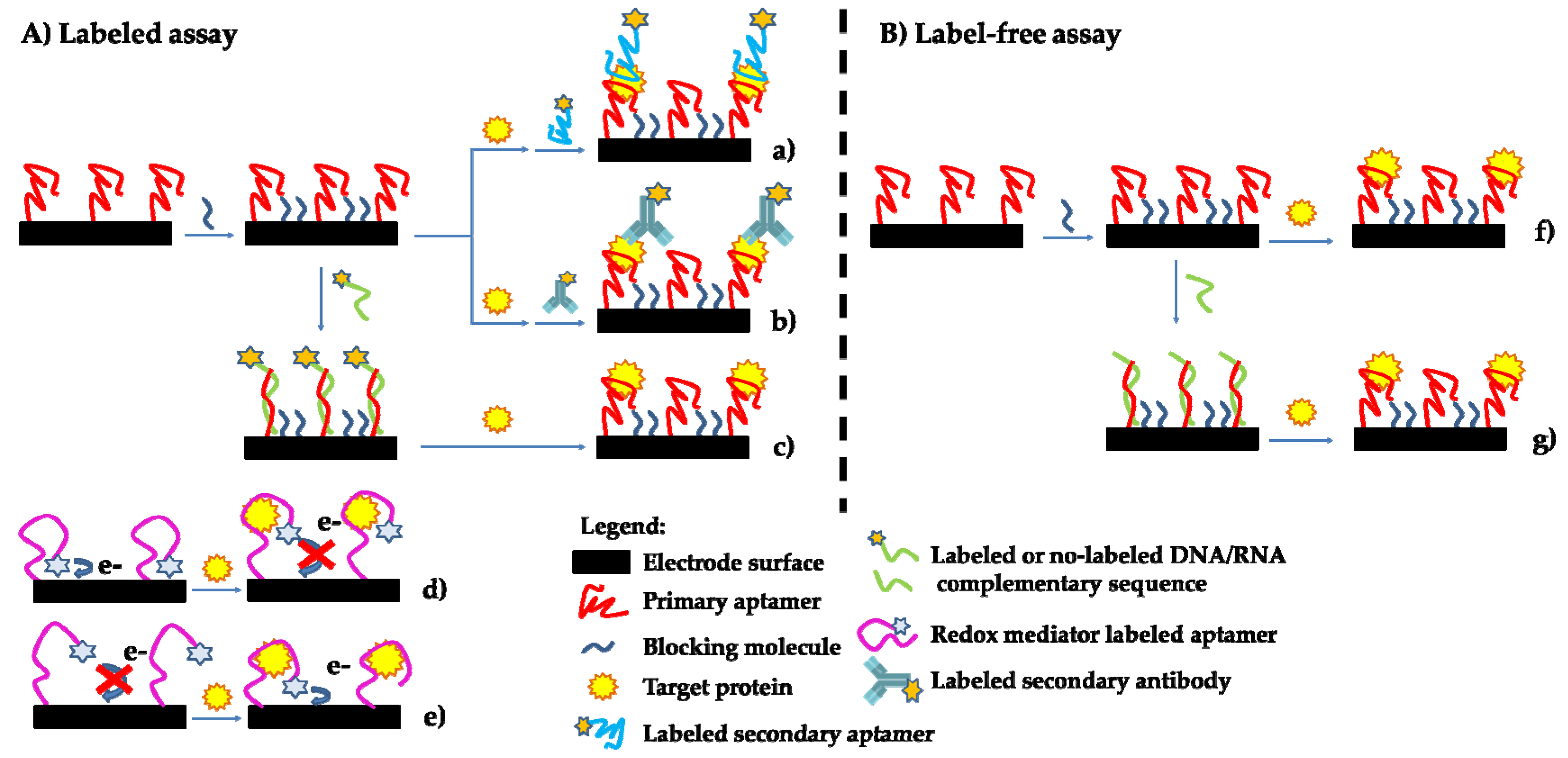
2.1. Aptasensor Formats
2.2. Electrochemical Aptasensors
2.3. Electrochemiluminescence Aptasensors
2.4. Photoelectrochemical Aptasensors
3. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buyse, M.; Sargent, D.J.; Grothey, A.; Matheson, A.; De Gramont, A. Biomarkers and surrogate end points—The challenge of statistical validation. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 7, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, N.L.; Hayes, D.F. Cancer biomarkers. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, J.A.; Weinstein, J.N. Biomarkers in cancer staging, prognosis and treatment selection. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, H.B. On a new substance occurring in the urine of a patient with mollities ossium. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1848, 138, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantzi, M.; Latosinska, A.; Fluhe, L.; Hupe, M.C.; Critselis, E.; Kramer, M.W.; Merseburger, A.S.; Mischak, H.; Vlahou, A. Developing proteomic biomarkers for bladder cancer: Towards clinical application. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2015, 12, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, M.J.; Sturgeon, C.M.; Sölétormos, G.; Barak, V.; Molina, R.; Hayes, D.F.; Diamandis, E.P.; Bossuyt, P. Validation of new cancer biomarkers: A position statement from the european group on tumor markers. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayeux, R. Biomarkers: Potential uses and limitations. NeuroRX 2004, 1, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahadır, E.B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. Applications of commercial biosensors in clinical, food, environmental, and biothreat/biowarfare analyses. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 478, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palchetti, I. Affinity biosensors for tumor-marker analysis. Bioanalysis 2014, 6, 3417–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.M.; Lee, S.; Ban, C. Aptamers and their biological applications. Sensors 2012, 12, 612–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palchetti, I.; Mascini, M. Nucleic acid biosensors for environmental pollution monitoring. Analyst 2008, 133, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascini, M.; Palchetti, I.; Tombelli, S. Nucleic acid and peptide aptamers: Fundamentals and bioanalytical aspects. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 1316–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyrin, E. Nucleic acid aptamer molecular recognition principles and application in liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 1531–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zu, Y. Aptamers and their applications in nanomedicine. Small 2015, 11, 2352–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Ragavan, K.V.; Thakur, M.S.; Raghavarao, K.S.M.S. Recent advances in nanoparticle based aptasensors for food contaminants. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 612–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, A.; Marty, J.L. Aptamer based electrochemical sensors for emerging environmental pollutants. Front. Chem. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thévenot, D.R.; Toth, K.; Durst, R.A.; Wilson, G.S. Electrochemical biosensors: Recommended definitions and classification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaconu, I.; Cristea, C.; Hârceagă, V.; Marrazza, G.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Săndulescu, R. Electrochemical immunosensors in breast and ovarian cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 425, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taleat, Z.; Ravalli, A.; Mazloum-Ardakani, M.; Marrazza, G. CA125 immunosensor based on poly-anthranilic acid modified screen-printed electrodes. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieshaber, D.; MacKenzie, R.; Vörös, J.; Reimhult, E. Electrochemical biosensors—Sensor principles and architectures. Sensors 2008, 8, 1440–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lisdat, F.; Schäfer, D. The use of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for biosensing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 1555–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, J.S.; Pourmand, N. Label-free impedance biosensors: Opportunities and challenges. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 1239–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravalli, A.; da Rocha, C.G.; Yamanaka, H.; Marrazza, G. A label-free electrochemical affisensor for cancer marker detection: The case of HER2. Bioelectrochemistry 2015, 106, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, S.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Q.; Wei, Y.; Ji, J.; Zhang, W. Progress of new label-free techniques for biosensors: A review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2016, 36, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascini, M. Aptamers in Bioanalysis; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.F.; Hesselberth, J.R.; Meyers, L.A.; Ellington, A.D. Aptamer database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D95–D100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zani, A.; Laschi, S.; Mascini , M.; Marrazza, G. A new electrochemical multiplexed assay for PSA cancer marker detection. Electroanalysis 2011, 23, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khafaji, Q.A.M.; Harris, M.; Tombelli, S.; Laschi, S.; Turner, A.P.F.; Mascini, M.; Marrazza, G. An electrochemical immunoassay for HER2 detection. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrero, M.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Electrochemical biosensors for the determination of cardiovascular markers: A review. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 1132–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palchetti, I.; Mascini, M. Electrochemical nanomaterial-based nucleic acid aptasensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 3103–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centi, S.; Tatini, F.; Ratto, F.; Gnerucci, A.; Mercatelli, R.; Romano, G.; Landini, I.; Nobili, S.; Ravalli, A.; Marrazza, G.; et al. In vitro assessment of antibody-conjugated gold nanorods for systemic injections. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2014, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravalli, A.; Marrazza, G. Gold and magnetic nanoparticles-based electrochemical biosensors for cancer biomarker determination. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 3307–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arduini, F.; Micheli, L.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G.; Piermarini, S.; Ricci, F.; Volpe, G. Electrochemical biosensors based on nanomodified screen-printed electrodes: Recent applications in clinical analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingarrón, J.M.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; González-Cortés, A. Gold nanoparticle-based electrochemical biosensors. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 5848–5866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsan, M.M.; Ghica, M.E.; Brett, C.M.A. Electrochemical sensors and biosensors based on redox polymer/carbon nanotube modified electrodes: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 881, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzinger, M.; Le Goff, A.; Cosnier, S. Nanomaterials for biosensing applications: A review. Front. Chem. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centi, S.; Messina, G.; Tombelli, S.; Palchetti, I.; Mascini, M. Different approaches for the detection of thrombin by an electrochemical aptamer-based assay coupled to magnetic beads. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 1602–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eksin, E.; Erdem, A.; Kuruc, A.P.; Kayi, H.; Öğünç, A. Impedimetric aptasensor based on disposable graphite electrodes developed for thrombin detection. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 2864–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Lin, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.F.; Le, X.C. Aptamer binding assays for proteins: The thrombin example—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 837, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florea, A.; Ravalli, A.; Cristea, C.; Săndulescu, R.; Marrazza, G. An optimized bioassay for Mucin1 detection in serum samples. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 1594–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Q.; Qian, C.; Hao, N.; Xu, L.; Yao, C. Electrochemical aptasensor for mucin 1 based on dual signal amplification of poly(o-phenylenediamine) carrier and functionalized carbon nanotubes tracing tag. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taleat, Z.; Cristea, C.; Marrazza, G.; Mazloum-Ardakani, M.; Săndulescu, R. Electrochemical immunoassay based on aptamer-protein interaction and functionalized polymer for cancer biomarker detection. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 717–718, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Wen, W.; Wang, Q.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, X.; Gu, H.; Wang, S. Novel electrochemical aptamer biosensor based on an enzyme-gold nanoparticle dual label for the ultrasensitive detection of epithelial tumour marker MUC1. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 53, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Ho, C.; Cheng, A.K.H.; Yu, H.Z. Immobilization of redox-labeled hairpin DNA aptamers on gold: Electrochemical quantitation of epithelial tumor marker mucin 1. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 110, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Hu, R.; Bao, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S. An insertion approach electrochemical aptasensor for mucin 1 detection based on exonuclease-assisted target recycling. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 71, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Qin, Y.; Deng, C.; Xiang, J.; Li, Y. A simple and sensitive impedimetric aptasensor for the detection of tumor markers based on gold nanoparticles signal amplification. Talanta 2015, 132, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, T.A.; Yoon, J.H.; Gurudatt, N.G.; Won, M.S.; Shim, Y.B. Ultrasensitive cytosensing based on an aptamer modified nanobiosensor with a bioconjugate: Detection of human non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Ye, D.; Zhao, Q.; Luo, J.; Zhang, S.; Kong, J. A novel aptasensor based on MUC-1 conjugated CNSs for ultrasensitive detection of tumor cells. Analyst 2014, 139, 4917–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.; Gurbuz, Y.; Niazi, J.H. Label-free capacitance based aptasensor platform for the detection of HER2/ErbB2 cancer biomarker in serum. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2015, 220, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, L.; Kim, S.E.; Cho, M.; Choe, W.; Nam, J.; Lee, D.W.; Lee, Y. Electrochemical detection of HER2 using single stranded DNA aptamer modified gold nanoparticles electrode. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2013, 186, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chandra, P.; Shim, Y.B. Ultrasensitive and selective electrochemical diagnosis of breast cancer based on a hydrazine—Au nanoparticle—Aptamer bioconjugate. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, W. Cascade signal amplification based on copper nanoparticle-reported rolling circle amplification for ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of the prostate cancer biomarker. ACS Appl. Mater. Int. 2016, 8, 2573–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavosi, B.; Salimi, A.; Hallaj, R.; Moradi, F. Ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor for PSA biomarker detection in prostate cancer cells using gold nanoparticles/PAMAM dendrimer loaded with enzyme linked aptamer as integrated triple signal amplification strategy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmasebi, F.; Noorbakhsh, A. Sensitive electrochemical prostate specific antigen aptasensor: Effect of carboxylic acid functionalized carbon nanotube and glutaraldehyde linker. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 1134–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souada, M.; Piro, B.; Reisberg, S.; Anquetin, G.; Noël, V.; Pham, M.C. Label-free electrochemical detection of prostate-specific antigen based on nucleic acid aptamer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahi, A.; Sattarahmady, N.; Heli, H. Label-free electrochemical aptasensing of the human prostate-specific antigen using gold nanospears. Talanta 2016, 156–157, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Goggins, S.; Frost, C.G.; Estrela, P. A novel immobilization strategy for electrochemical detection of cancer biomarkers: DNA-directed immobilization of aptamer sensors for sensitive detection of prostate specific antigens. Analyst 2015, 140, 2628–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolly, P.; Formisano, N.; Tkáč, J.; Kasák, P.; Frost, C.G.; Estrela, P. Label-free impedimetric aptasensor with antifouling surface chemistry: A prostate specific antigen case study. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2015, 209, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Wen, W.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S. Novel electrochemical aptamer biosensor based on gold nanoparticles signal amplification for the detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Electrochem. Commun. 2013, 37, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, H.; Zuo, C.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Zhong, M.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, H.; Yang, M. Electrochemical detection of carcinoembryonic antigen based on silver nanocluster/horseradish peroxidase nanocomposite as signal probe. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 176, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; Na, W.; Jang, J. One-pot synthesis of multidimensional conducting polymer nanotubes for superior performance field-effect transistor-type carcinoembryonic antigen biosensors. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 14335–14343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Dong, C. Label-free electrochemical aptasensor for carcino-embryonic antigen based on ternary nanocomposite of gold nanoparticles, hemin and graphene. Electroanalysis 2015, 28, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravalli, A.; Rivas, L.; De La Escosura-Muñiz, A.; Pons, J.; Merkoçi, A.; Marrazza, G. A DNA aptasensor for electrochemical detection of vascular endothelial growth factor. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 3411–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.; Gurbuz, Y.; Niazi, J.H. Capacitive aptamer–antibody based sandwich assay for the detection of VEGF cancer biomarker in serum. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2015, 209, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizi, M.A.; Shamsipur, M.; Farzin, L. A high sensitive electrochemical aptasensor for the determination of VEGF165 in serum of lung cancer patient. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamsipur, M.; Farzin, L.; Tabrizi, M.A.; Molaabasi, F. Highly sensitive label free electrochemical detection of VGEF165 tumor marker based on “signal off” and “signal on” strategies using an anti-VEGF165 aptamer immobilized BSA-gold nanoclusters/ionic liquid/glassy carbon electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.X.; Huang, K.J.; Liu, Y. Novel electrochemical dual-aptamer-based sandwich biosensor using molybdenum disulfide/carbon aerogel composites and Au nanoparticles for signal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 71, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yuan, Y.; biXie, S.; Chai, Y.; Yuan, R. Amplified amperometric aptasensor for selective detection of protein using catalase-functional DNA-PtNPs dendrimer as a synergetic signal amplification label. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 60, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Li, H.; Liang, H.; Qiang, W.; Xu, D. Disposable electrochemical aptasensor array by using in situ DNA hybridization inducing silver nanoparticles aggregate for signal amplification. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 2775–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, X.; Yang, X.; Sun, Q.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Shen, G.; Lu, J.; Shen, G.; Yu, R. Background eliminated signal-on electrochemical aptasensing platform for highly sensitive detection of protein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 66, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.J.; Shuai, H.L.; Zhang, J.Z. Ultrasensitive sensing platform for platelet-derived growth factor BB detection based on layered molybdenum selenide-graphene composites and Exonuclease III assisted signal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zheng, H.; Gao, X.; Lin, Z.; Chen, G. A label-free ultrasensitive electrochemical aptameric recognition system for protein assay based on hyperbranched rolling circle amplification. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 11418–11420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Zhang, S.; Ji, H.; Wang, M.; Peng, D.; Yan, F.; Fang, S.; Zhang, H.; Jia, C.; Zhang, Z. Protein-templated cobaltous phosphate nanocomposites for the highly sensitive and selective detection of platelet-derived growth factor-BB. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Shuai, H.L.; Huang, K.J. A label-free electrochemical aptasensor based on leaf-like vanadium disulfide-Au nanoparticles for the sensitive and selective detection of platelet-derived growth factor BB. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 8277–8284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Q.; Fu, W. An aptamer-based biosensing platform for highly sensitive detection of platelet-derived growth factor via enzyme-mediated direct electrochemistry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 759, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kufe, D.W. Mucins in cancer: Function, prognosis and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, C.; Schiff, R. HER2: Biology, detection, and clinical implications. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2011, 135, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Makarov, D.V.; Loeb, S.; Getzenberg, R.H.; Partin, A.W. Biomarkers for prostate cancer. Annu. Rev. Med. 2009, 60, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minton, J.P.; Martin, E.W. The use of serial CEA determinations to predict recurrence of colon cancer and when to do a second-look operation. Cancer 1978, 42, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci-Vitiani, L.; Lombardi, D.G.; Pilozzi, E.; Biffoni, M.; Todaro, M.; Peschle, C.; De Maria, R. Identification and expansion of human colon-cancer-initiating cells. Nature 2007, 445, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, N.; Gerber, H.-P.; LeCouter, J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, R.; Raines, E.W.; Bowen-Pope, D.F. The biology of platelet-derived growth factor. Cell 2016, 46, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelmann, I.; Liersch, R.; Kessler, T.; Mesters, R.M.; Berdel, W.E. Angiogenesis inhibition in cancer therapy: Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and their receptors: Biological functions and role in malignancy. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2010, 180, 51–81. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bard, A.J. Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence; Marecel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bock, L.C.; Griffin, L.C.; Latham, J.A.; Vermaas, E.H.; Toole, J.J. Selection of single-stranded DNA molecules that bind and inhibit human thrombin. Nature 1992, 355, 564–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macaya, R.F.; Schultze, P.; Smith, F.W.; Roe, J.A.; Feigon, J. Thrombin-binding DNA aptamer forms a unimolecular quadruplex structure in solution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 3745–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasset, D.M.; Kubik, M.F.; Steiner, W. Oligonucleotide inhibitors of human thrombin that bind distinct epitopes1. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 272, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Chai, Y.; Wang, H.; Bai, L.; Yuan, R. A signal-on electrochemiluminescence aptasensor based on the quenching effect of manganese dioxide for sensitive detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 56756–56761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Tian, D.; Gu, J.; Cui, H. A novel electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for protein based on a sensitive N-(aminobutyl)-N-ethylisoluminol-functionalized gold nanoprobe. Analyst 2011, 136, 3244–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Li, W.; Guo, Z.; Sha, Y.; Wang, S.; Su, X.; Jiang, X. Electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for the MUC1 protein based on multi-functionalized graphene oxide nanocomposite. Electroanalysis 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.N.; Zhuo, Y.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y.Q. New signal amplification strategy using semicarbazide as co-reaction accelerator for highly sensitive electrochemiluminescent aptasensor construction. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 11389–11397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, G.F.; Zhuo, Y.; Chai, Y.-Q.; Xiang, Y.; Yuan, R. The Ru complex and hollow gold nanoparticles branched-hydrogel as signal probe for construction of electrochemiluminescent aptasensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Xin, X.; Pang, X.; Pietraszkiewicz, M.; Hozyst, R.; Sun, X.; Wei, Q. Application of Europium multiwalled carbon nanotubes as novel luminophores in an electrochemiluminescent aptasensor for thrombin using multiple amplification strategies. ACS Appl. Mater. Int. 2015, 7, 12663–12670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Li, J.; Kang, T.; Cheng, S. Bi-functionalized aptasensor for ultrasensitive detection of thrombin. Talanta 2015, 138, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.N.; Zhang, X.; Zhuo, Y.; Chai, Y.Q.; Yuan, R. An amplified electrochemiluminescent aptasensor using Au nanoparticles capped by 3,4,9,10-perylene tetracarboxylic acid-thiosemicarbazide functionalized C60 nanocomposites as a signal enhancement tag. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2085–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.; Li, L.; Yin, Z.; Hou, X.; Zhu, J.J. Biobar-coded gold nanoparticles and DNAzyme-based dual signal amplification strategy for ultrasensitive detection of protein by electrochemiluminescence. ACS Appl. Mater. Int. 2015, 7, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Du, Y.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y. An off-on-off electrochemiluminescence approach for ultrasensitive detection of thrombin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 59, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Sun, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, L.; Qi, H.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, C. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence aptasensor for ultrasensitive detection of thrombin incorporating an auxiliary probe. Talanta 2014, 130, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-M.; Zhang, J.J.; Shi, G.F.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Y.Y.; Huang, K.J.; Chen, Y.H. Label-free electrochemiluminescence aptasensor using Ru(bpy)32+ functionalized dopamine-melanin colloidal nanospheres and gold nanoparticles as signal-amplifying tags. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 129, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Wang, C.; Yang, L.; Li, X.; Guo, L.; Qiu, B.; Lin, Z.; Chen, G. Hyperbranched rolling circle amplification based electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for ultrasensitive detection of thrombin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Gan, X.; Chai, Y.; Yuan, R. A novel electrochemiluminescence aptasensor based on in situ generated proline and matrix polyamidoamine dendrimers as coreactants for signal amplication. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 55, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Chai, Y.; Yuan, R.; Wang, H.; Bai, L. Highly enhanced electrochemiluminescence based on pseudo triple-enzyme cascade catalysis and in situ generation of co-reactant for thrombin detection. Analyst 2014, 139, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yang, F.; Tang, J.; He, P. A label-free electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for thrombin detection based on host–guest recognition between tris(bipyridine)ruthenium(II)-β-cyclodextrin and aptamer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, Y.; Ma, M.; Chai, Y.-Q.; Zhao, M.; Yuan, R. Amplified electrochemiluminescent aptasensor using mimicking bi-enzyme nanocomplexes as signal enhancement. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 809, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y.; Gao, A.; Lu, C.C.; He, X.W.; Yin, X.B. An electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for thrombin using graphene oxide to immobilize the aptamer and the intercalated probe. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 48, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, G.; Lu, L.; Gao, X.; Li, M.J.; Qiu, B.; Lin, Z.; Yang, H.; Chen, G. Magnetic graphene oxide-based electrochemiluminescent aptasensor for thrombin. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 89, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Cui, H. A label-free electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for thrombin based on novel assembly strategy of oligonucleotide and luminol functionalized gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 39, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Y.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y. Enhanced electrochemiluminescence quenching of CdS:Mn nanocrystals by CdTe QDs-doped silica nanoparticles for ultrasensitive detection of thrombin. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 2916–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Shan, Y.; Zhao, W.W.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y. Gold nanoparticle enhanced electrochemiluminescence of CdS thin films for ultrasensitive thrombin detection. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 4004–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Qi, H.; Gao, Q.; Yang, J.; Zhang, C. Nanomaterial-amplified “signal off/on” electrogenerated chemiluminescence aptasensors for the detection of thrombin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.-W.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.C.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y. Quantum dots: Electrochemiluminescent and photoelectrochemical bioanalysis. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9520–9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devadoss, A.; Sudhagar, P.; Terashima, C.; Nakata, K.; Fujishima, A. Photoelectrochemical biosensors: New insights into promising photoelectrodes and signal amplification strategies. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2015, 24, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.W.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y. Photoelectrochemical DNA biosensors. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 7421–7441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.W.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y. Photoelectrochemical bioanalysis: The state of the art. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S. Quantum dot-based photoelectric conversion for biosensing applications. Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 67, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voccia, D.; Palchetti, I. Photoelectrochemical biosensors for nucleic acid detection. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 3320–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finklea, H.O. Photoelectrochemistry: Introductory concepts. J. Chem. Educ. 1983, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J. Photoelectrochemical aptasensing of kanamycin using visible light-activated carbon nitride and graphene oxide nanocomposites. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9372–9375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenjuan, Y.; Le Goff, A.; Spinelli, N.; Holzinger, M.; Diao, G.W.; Shan, D.; Defrancq, E.; Cosnier, S. Electrogenerated trisbipyridyl Ru(II)-/nitrilotriacetic-polypyrene copolymer for the easy fabrication of label-free photoelectrochemical immunosensor and aptasensor: Application to the determination of thrombin and anti-cholera toxinantibody. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Ma, S.; Bao, J.; Tu, W.; Dai, Z. Using graphene-based plasmonic nanocomposites to quench energy from quantum dots for signal-on photoelectrochemical aptasensing. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11720–11724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alix-Panabieres, C.; Pantel, K. Challenges in circulating tumour cell research. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Bao, J.; Han, M.; Tu, W.; Dai, Z. Quantum dots sensitized titanium dioxide decorated reduced graphene oxide for visible light excited photoelectrochemical biosensing at a low potential. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Huang, T.; Lu, J. A photoelectrochemical aptasensor for mucin 1 based on DNA/aptamer linking of quantum dots and TiO2 nanotube arrays. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, L.; Zhu, W.; Xue, Y.; Liu, S. Construction of photoelectrochemical thrombin aptasensor via assembling multilayer of graphene-CdS nanocomposites. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Jin, X.; Zhang, S. A new photoelectrochemical aptasensor for the detection of thrombin based on functionalized graphene and CdSe nanoparticles multilayers. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 4929–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.T.; Zhang, J.J.; Gong, Y.; Ruan, X.J.; Liu, Y.M.; Chen, Y.H.; Ren, S.W. A competitive photoelectrochemical aptasensor for thrombin detection based on the use of TiO2 electrode and glucose oxidase label. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 759, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Guo, C.; Ma, H.; Zhao, D.; Li, Y.; Wu, D.; Wei, Q. Facile fabrication of an aptasensor for thrombin based on graphitic carbon nitride/TiO2 with high visible-light photoelectrochemical activity. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Z.; Bai, H.J.; Wang, G.L.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y. A photoelectrochemical sensor based on CdS-polyamidoamine nano-composite film for cell capture and detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 2045–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Jin, X.; Li, X. Aptamer based photoelectrochemical cytosensor with layer-by-layer assembly of CdSe semiconductor nanoparticles as photoelectrochemically active species. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3674–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Biomarker | Assay Strategy | Signal Amplification | Electrochemical Technique | LOD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MUC1 | Sandwich | Enzymatic | DPV | 0.07 nM | [41] |
| Sandwich | AuNPs/MWCNTs | DPV | 1 pM | [42] | |
| Mixed sandwich | MB | DPV | 0.62 ng/mL | [43] | |
| Switch-on | AuNPs | DPV | 2.2 nM | [44] | |
| Switch-off | − | CV | 50 nM | [45] | |
| Displacement | Exonuclease | SWV | 4 pM | [46] | |
| Displacement | AuNPs | EIS | 0.1 mM | [47] | |
| Cells | |||||
| Sandwich | AuNPs | Chronoamperometry | 8 cells/mL | [48] | |
| Label-free | CNSs | EIS | 40 cells/mL | [49] | |
| HER2 | Label-free | − | EIS | 0.2 ng/mL | [50] |
| Label-free | AuNPs | EIS | 10−5 ng/mL | [51] | |
| Mixed sandwich | AgNPs/AuNPs | SWV | 0.037 pg/mL | [52] | |
| 26 cells/mL | |||||
| PSA | Mixed sandwich | AuNPs | DPV | 0.02 fg/mL | [53] |
| Mixed sandwich | AuNPs/PAMAM dendrimer | DPV | 10 fg/mL | [54] | |
| EIS | 5 pg/mL | ||||
| Displacement | CNTs/Chitosan | DPV | 0.74 ng/mL | [55] | |
| Switch on/off | − | SWV | 1 ng/mL | [56] | |
| Label-free | Au nanospears | DPV | 50 pg/mL | [57] | |
| Label free | − | EIS | 0.5 pg/mL | [58] | |
| Label free | − | EIS | < 1 ng/mL | [59] | |
| CEA | Sandwich | AuNPs | DPV | 0.5 ng/mL | [60] |
| Mixed sandwich | AgNCs | SWV | 0.5 pg/mL | [61] | |
| Label-free | PPY/CNTs | FET | 1 fg/mL | [62] | |
| Label free | AuNPs/HGNs | DPV | 40 fg/mL | [63] | |
| VEGF | Sandwich | AuNPs | DPV | 30 nM | [64] |
| Mixed sandwich | − | Capacitance | From 400 to 800 pg/mL | [65] | |
| Label-free | mesoporous carbon/gold nanocomposite | EIS | 1 pg/mL | [66] | |
| Switch-off | AuNCs | DPV | 0.32 pM | [67] | |
| Label-free | EIS | 0.48 pM | |||
| PDGF-BB | Sandwich | AuNPs | DPV | 0.3 pM | [68] |
| Sandwich | PAMAM dendrimer | DPV | 0.02 pM | [69] | |
| Sandwich | AuNPs/AgNPs | DPV | 1.6 pg/mL | [70] | |
| Switch-on | Endonuclease | CV | 10 pg/mL | [71] | |
| Displacement | Endonuclease | DPV | 20 fM | [72] | |
| Displacement | − | DPV | 1.6 fM | [73] | |
| Label-free | Co3(PO4)2 nanocomposites | EIS | 3.7 pg/mL | [74] | |
| Label-free | AuNP and VS2 nanosheet | EIS | 0.4 pM | [75] | |
| Label-free | Graphene/AuNPs | CV | 1.7 pM | [76] | |
| Luminophore | LOD | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| CdTe | 0.03 fM | [92] |
| Ru complex and pNAMA-HGNPs hydrogel composites | 0.54 fM | [93] |
| Europium and MWCNT | 0.23 pM | [94] |
| CdSe | 2.7 aM | [95] |
| AuNPs/TSC-PTC/C60 | 3.3 fM | [96] |
| AuNPs-CdSeTe-ZnS | 0.28 fM | [97] |
| Eu3+-doped CdS nanocrystals | 1 aM | [98] |
| Ruthenium(II) complex | 2.0 × 10−15 M | [99] |
| Ru(bpy)32+/Dpa-mel CNSs | 2.2 × 10−13 M | [100] |
| Ru(phen)3 2+ | 1.2 aM | [101] |
| PAMAM / Ru(II) complex | 5.0 fM | [102] |
| GDH and hemin/G-quadruplex | 33 fM | [103] |
| tris(bipyridine) Ru(II)-β cyclodextrin | 0.1 pM | [104] |
| HGNPs/GOxNPs/PtNPs | 0.3 fM | [105] |
| Ru(phen)32+ | 0.4 pM | [106] |
| Ir(III) complex | 1.3 nM | [107] |
| luminol-AuNPs | 1.7 pM | [108] |
| CdS:MnNCs and CdTe/SiO2 NPs | 1 aM | [109] |
| CdS thin films and AuNPs | 100 aM | [110] |
| Ruthenium complex | 3 × 10−15 M | [111] |
| Biomarker | Label and Signal Generation Process | LOD | Photoactive Materials | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEA | RGO-AuNPs nanocomposites in RET process | 0.47 pg/mL | CdTe/ITO | [121] |
| HRP impeding the light absorbance and B-4-CHD inhibiting AA diffusion to the electrode surface | 1.38 pg/mL | CdSe/TiO2/RGO/ITO | [123] | |
| MUC1 | CdTe | 0.52 nM | TiO2 nanotube arrays | [124] |
| thrombin | Ru(NH3)63+ | 1 pM | Graphene-CdS/PEI/ITO | [125] |
| - | CdSe/PAA-Graphene/PDDA/ITO | [126] | ||
| Label-free; the analyte hinders the diffusion of the AA, inducing a photocurrent decrease | 1 × 10−13 mol/L | (NTA-pyrene) and (Ru(II)-pyrene) complex | [120] | |
| AuNPs–glucose oxidase | 1.9 × 10−13 mol/L | TiO2 | [127] | |
| Label-free | 1.2 × 10−13 mol/L | g-C3N4/TiO2/ITO | [128] | |
| SMMC-7721 human hepatoma carcinoma cells | Label-free; steric hindrances for the diffusion of AA to the surface of CdSe | 5.0 × 10 3 cells/mL | CdS-PAMAM nano-composite/ITO | [129] |
| Ramos cell | Label-free; steric hindrances for the diffusion of AA to the surface of CdSe | 84 cells/mL | CdSe/PDDA/ITO | [130] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ravalli, A.; Voccia, D.; Palchetti, I.; Marrazza, G. Electrochemical, Electrochemiluminescence, and Photoelectrochemical Aptamer-Based Nanostructured Sensors for Biomarker Analysis. Biosensors 2016, 6, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6030039
Ravalli A, Voccia D, Palchetti I, Marrazza G. Electrochemical, Electrochemiluminescence, and Photoelectrochemical Aptamer-Based Nanostructured Sensors for Biomarker Analysis. Biosensors. 2016; 6(3):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6030039
Chicago/Turabian StyleRavalli, Andrea, Diego Voccia, Ilaria Palchetti, and Giovanna Marrazza. 2016. "Electrochemical, Electrochemiluminescence, and Photoelectrochemical Aptamer-Based Nanostructured Sensors for Biomarker Analysis" Biosensors 6, no. 3: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6030039
APA StyleRavalli, A., Voccia, D., Palchetti, I., & Marrazza, G. (2016). Electrochemical, Electrochemiluminescence, and Photoelectrochemical Aptamer-Based Nanostructured Sensors for Biomarker Analysis. Biosensors, 6(3), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6030039








