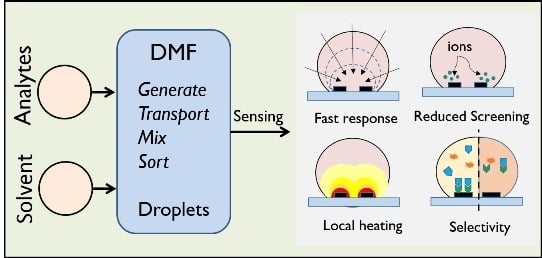
Droplet-based Biosensing for Lab-on-a-Chip, Open Microfluidics Platforms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
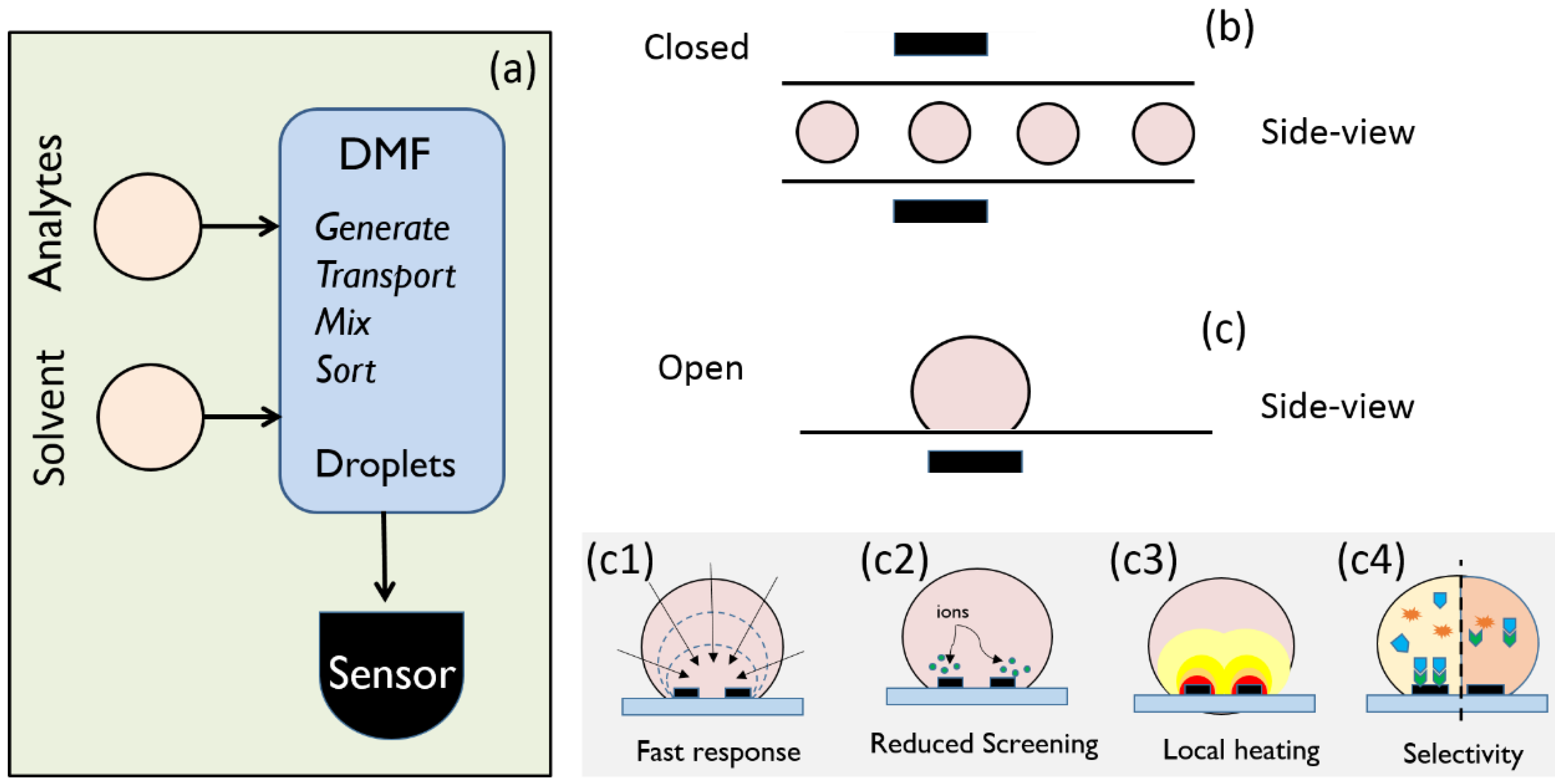
1.1. Response Time of Biosensors
1.2. Screening-Limited Sensitivity of Biosensors
1.3. The Importance of “Selectivity” for Integrated Biosensors
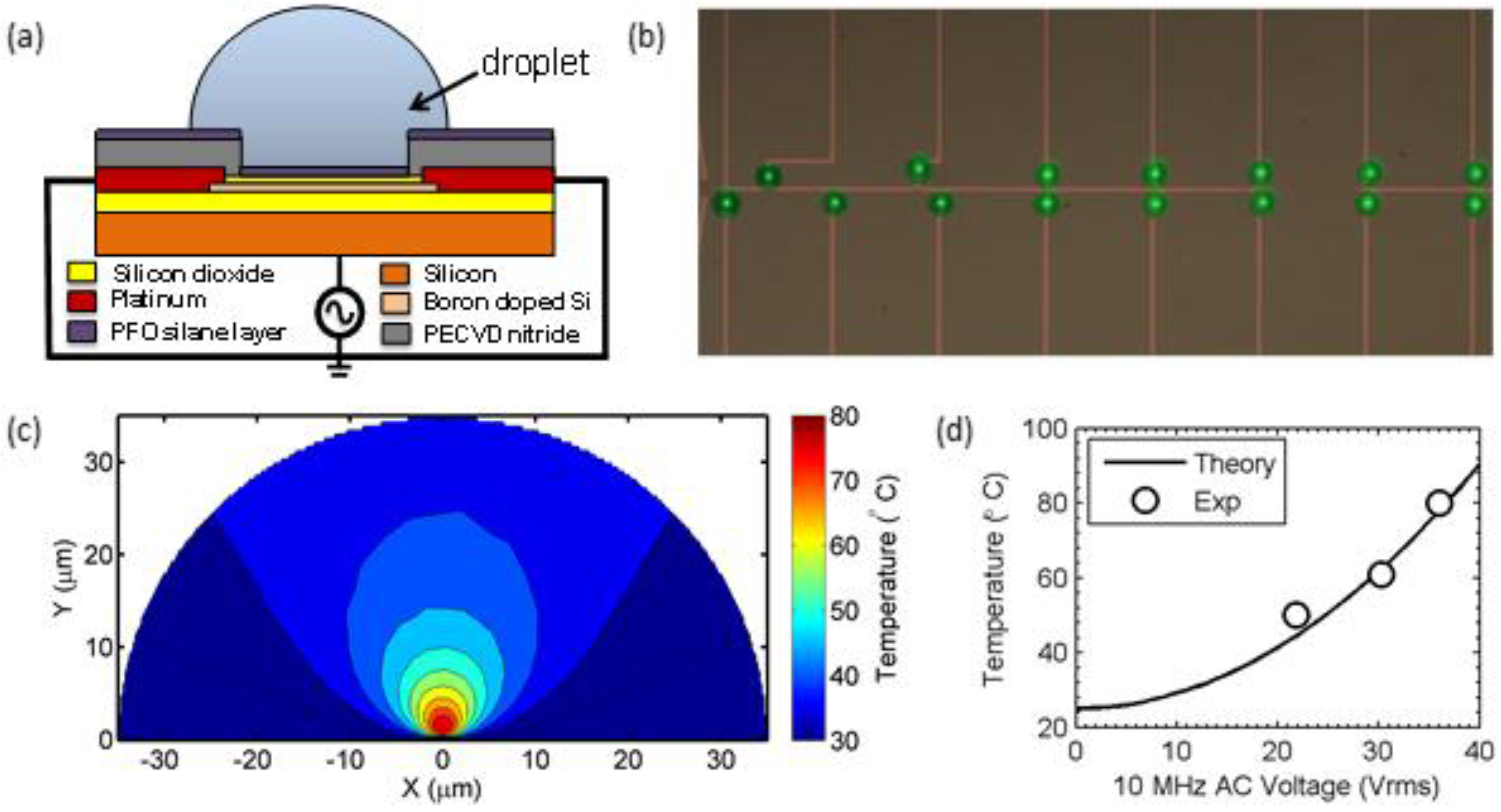
2. Droplet-Based Beating of diffusion Limit in Electrical Biosensors
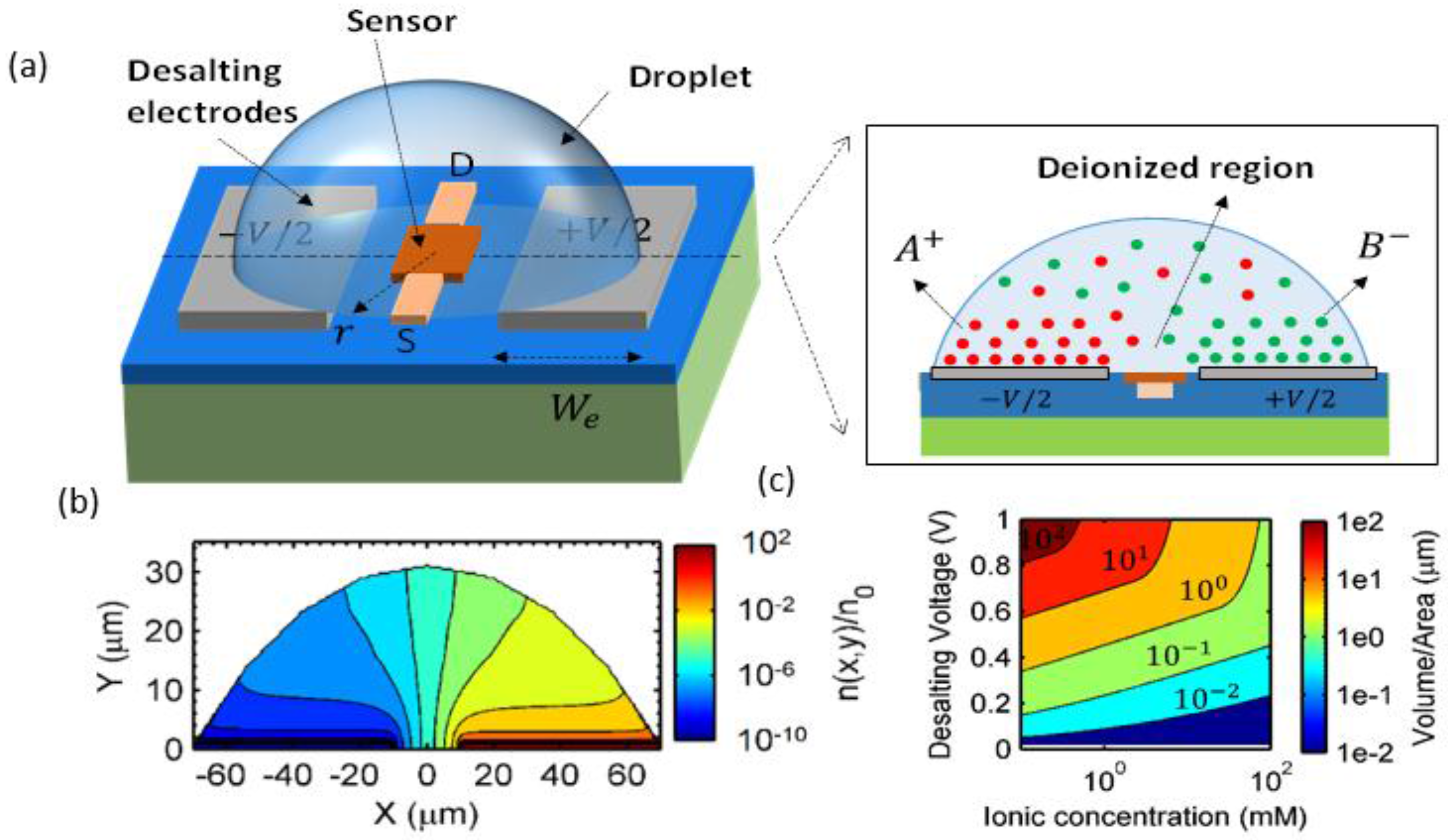
3. Droplets to Overcome Screening Limit
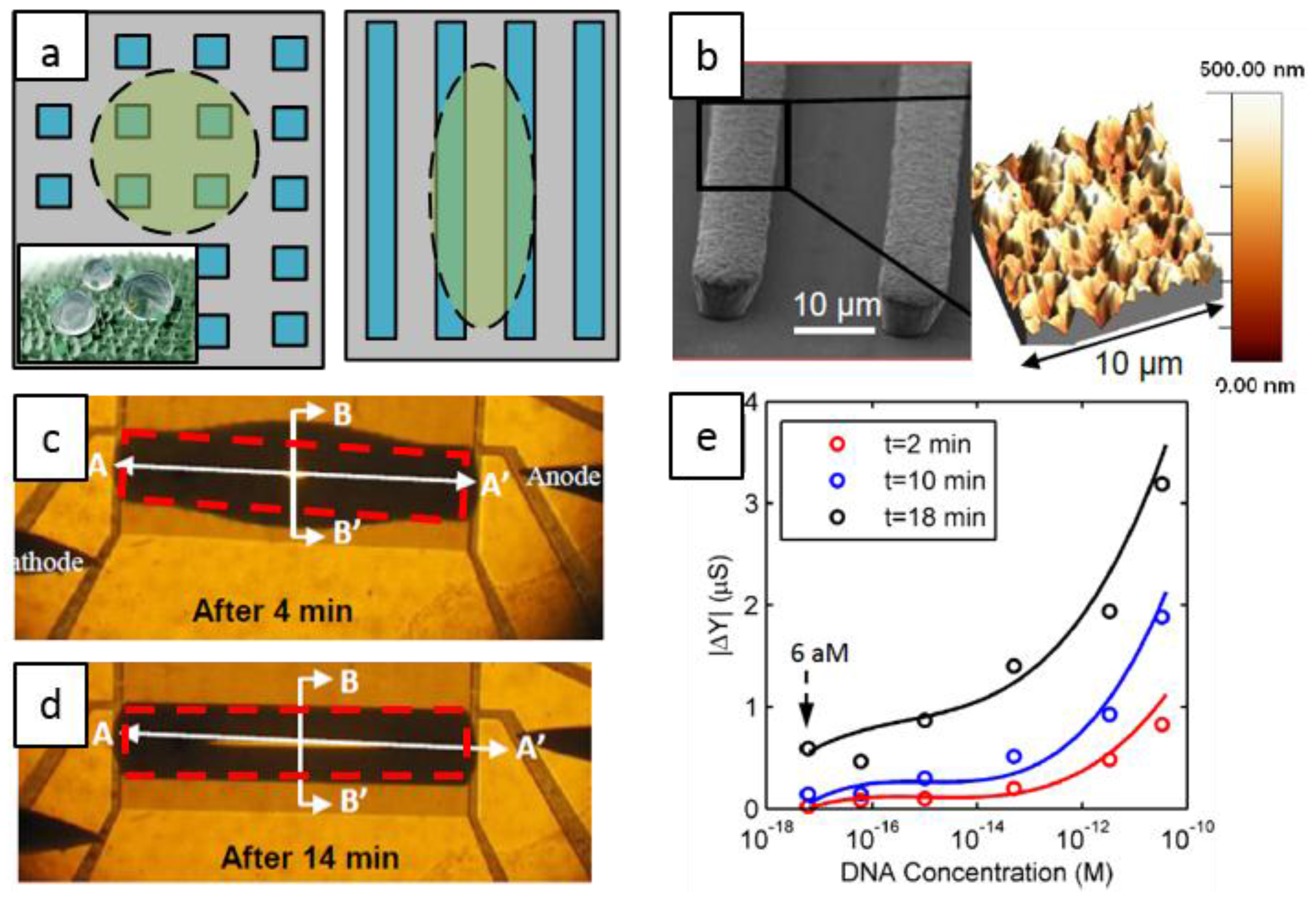
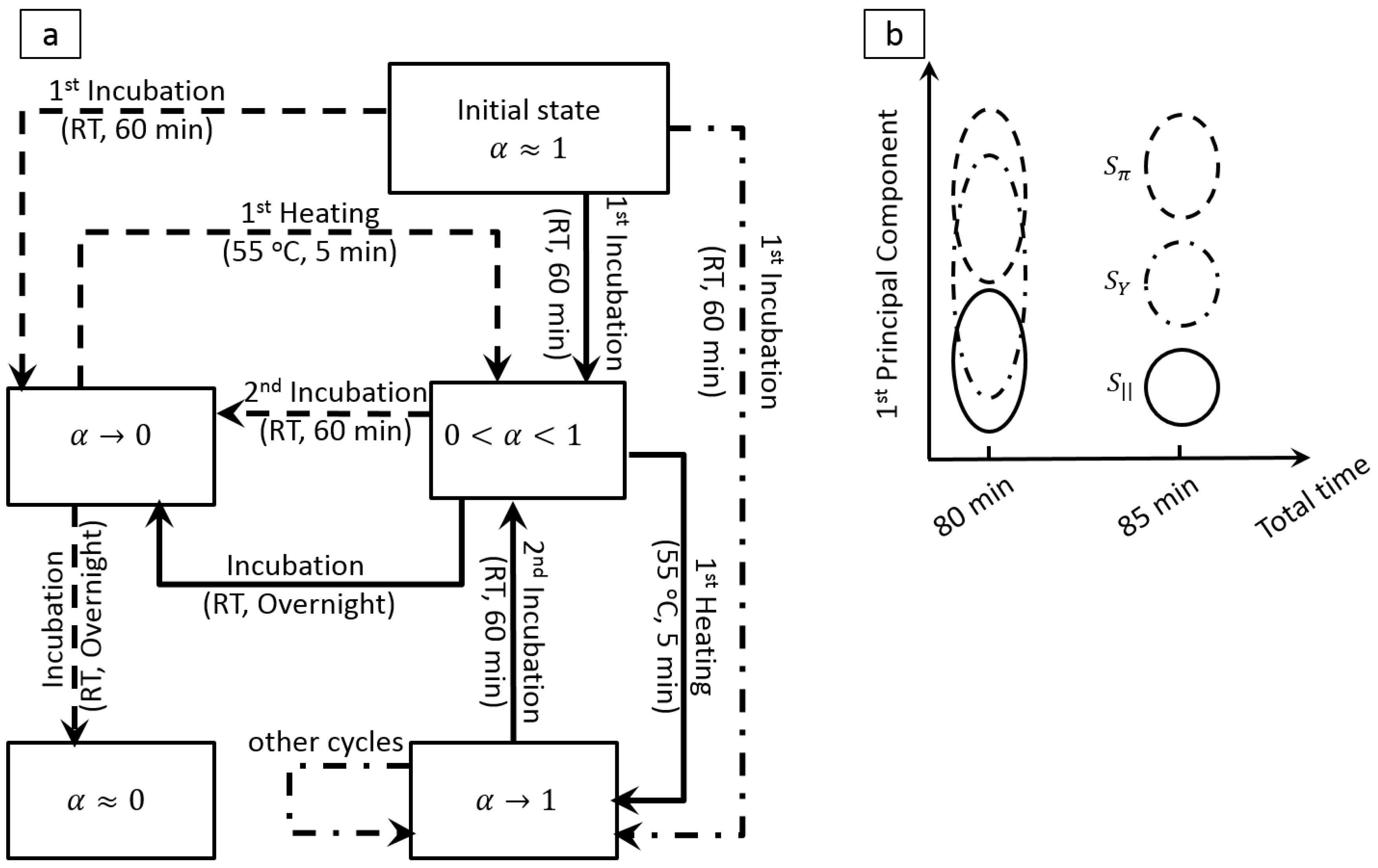
4. Selectivity in Droplet-Based Systems: DNA Hybridization as a Case-Study
5. Challenges and Outlook
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Damhorst, G.L.; Murtagh, M.; Rodriguez, W.R.; Bashir, R. Microfluidics and Nanotechnology for Detection of Global Infectious Diseases. Proc. IEEE 2015, 103, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damhorst, G.L.; Watkins, N.N.; Bashir, R. Micro- and nanotechnology for HIV/AIDS diagnostics in resource-limited settings. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Banada, P.P.; Chatni, M.R.; Lim, K.S.; Bhunia, A.K.; Ladisch, M.; Bashir, R. A multifunctional micro-fluidic system for dielectrophoretic concentration coupled with immuno-capture of low numbers of Listeria monocytogenes. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suehiro, J.; Ohtsubo, A.; Hatano, T.; Hara, M. Selective detection of bacteria by a dielectrophoretic impedance measurement method using an antibody-immobilized electrode chip. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 119, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sackmann, E.K.; Fulton, A.L.; Beebe, D.J. The present and future role of microfluidics in biomedical research. Nature 2014, 507, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malic, L.; Brassard, D.; Veres, T.; Tabrizian, M. Integration and detection of biochemical assays in digital microfluidic LOC devices. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 418–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.; Ng, A.H.C.; Fobel, R.; Wheeler, A.R. Digital microfluidics. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2012, 5, 413–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teh, S.-Y.; Lin, R.; Hung, L.-H.; Lee, A.P. Droplet microfluidics. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 198–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Angelis, F.; Gentile, F.; Mecarini, F.; Das, G.; Moretti, M.; Candeloro, P.; Coluccio, M.L.; Cojoc, G.; Accardo, A.; Liberale, C.; et al. Di Breaking the diffusion limit with super-hydrophobic delivery of molecules to plasmonic nanofocusing SERS structures. Nat. Photonics 2011, 5, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melli, M.; Scoles, G.; Lazzarino, M.; Al, M.E.T. Fast detection of biomolecules in diffusion-Limited regime using micromechanical pillars. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7928–7935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Dak, P.; Salm, E.; Dash, S.; Garimella, S.V.; Bashir, R.; Alam, M.A. Nanotextured superhydrophobic electrodes enable detection of attomolar-scale DNA concentration within a droplet by non-faradaic impedance spectroscopy. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 4248–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemna, E.W.M.; Segerink, L.I.; Wolbers, F.; Vermes, I.; van den Berg, A. Label-free, high-throughput, electrical detection of cells in droplets. Analyst 2013, 138, 4585–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Butte, M.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterned paper as a platform for inexpensive, low-volume, portable bioassays. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2007, 46, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Jones, T.B. Moving droplets between closed and open microfluidic systems. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 2201–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Chen, D.L.; Ismagilov, R.F. Reactions in droplets in microfluidic channels. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2006, 45, 7336–7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, J.; Ma, W.; Zheng, W. PCR microfluidic devices for DNA amplification. Biotechnol. Adv. 2006, 24, 243–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Dalton, C.; Crabtree, H.J.; Nilsson, G.; Kaler, K.V.I.S. Continuous dielectrophoretic cell separation microfluidic device. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, H.; Wheeler, A.R.; Garrell, R.L.; Loo, J.A.; Kim, C.-J.C. An integrated digital microfluidic chip for multiplexed proteomic sample preparation and analysis by MALDI-MS. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, Z.-X.; Luo, R.; Lü, S.-H.; Xu, A.-D.; Yang, Y.-J. Droplet-based micro oscillating-flow PCR chip. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2005, 15, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbulovic-Nad, I.; Au, S.H.; Wheeler, A.R. A microfluidic platform for complete mammalian cell culture. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer, N.R.; Hindson, B.J.; Wheeler, E.K.; Hall, S.B.; Rose, K.A.; Kennedy, I.M.; Colston, B.W. On-chip, real-time, single-copy polymerase chain reaction in picoliter droplets. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 8471–8475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sims, C.E.; Allbritton, N.L. Analysis of single mammalian cells on-chip. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, V.; Pamula, V.K.; Fair, R.B. An integrated digital microfluidic lab-on-a-chip for clinical diagnostics on human physiological fluids. Lab Chip 2004, 4, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, P.; Marchand, G.; Fouillet, Y.; Berthier, J.; Douki, T.; Hassine, F.; Gmouh, S.; Vaultier, M. Ionic liquid droplet as e-microreactor. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 4909–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, C.D.; Linder, V.; Sia, S.K. Commercialization of microfluidic point-of-care diagnostic devices. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2118–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.A. nanoHUB.org—Courses: Nanohub-U: Principles of Electronic Nanobiosensors. Available online: https://nanohub.org/courses/pen (accessed on 2 January 2016).
- Dittrich, P.S.; Tachikawa, K.; Manz, A. Micro total analysis systems. Latest advancements and trends. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 3887–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, C.; Li, C.-W.; Ji, S.; Yang, M. Microfluidics technology for manipulation and analysis of biological cells. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 560, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ali, J.; Sorger, P.K.; Jensen, K.F. Cells on chips. Nature 2006, 442, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, P.R.; Alam, M.A. Performance limits of nanobiosensors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 233120-1–233120-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothberg, J.M.; Hinz, W.; Rearick, T.M.; Schultz, J.; Mileski, W.; Davey, M.; Leamon, J.H.; Johnson, K.; Milgrew, M.J.; Edwards, M.; et al. An integrated semiconductor device enabling non-optical genome sequencing. Nature 2011, 475, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goluch, E.D.; Nam, J.-M.; Georganopoulou, D.G.; Chiesl, T.N.; Shaikh, K.A.; Ryu, K.S.; Barron, A.E.; Mirkin, C.A.; Liu, C. A bio-barcode assay for on-chip attomolar-sensitivity protein detection. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Zhu, Z.; Lei, J.; Geng, Y.; Ju, H. Sub-femtomolar electrochemical detection of DNA using surface circular strand-replacement polymerization and gold nanoparticle catalyzed silver deposition for signal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 39, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senapati, S.; Slouka, Z.; Shah, S.S.; Behura, S.K.; Shi, Z.; Stack, M.S.; Severson, D.W.; Chang, H.-C. An ion-exchange nanomembrane sensor for detection of nucleic acids using a surface charge inversion phenomenon. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 60, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, H.D.; Mirkin, C.A. The bio-barcode assay for the detection of protein and nucleic acid targets using DTT-induced ligand exchange. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergveld, P. Development, Operation, and Application of the Tool for Electrophysiology. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1972, BME-19, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, J.; Nair, P.R.; Alam, M.A. Theory of signal and noise in double-gated nanoscale electronic pH sensors. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 34516-1–34516-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dak, P.; Nair, P.; Go, J.; Alam, M.A. Extended-gate biosensors achieve fluid stability with no loss in charge sensitivity. In Proceedings of the IEEE Device Research Conference—Conference Digest, Notre Dame, IN, Canada, 23–26 June 2013; Volume 20, pp. 105–106.
- Lee, J.; Dak, P.; Lee, Y.; Park, H.; Choi, W.; Alam, M.A.; Kim, S. Two-dimensional Layered MoS2 Biosensors Enable Highly Sensitive Detection of Biomolecules. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toumazou, C.; Georgiou, P. Piet Bergveld—40 years of ISFET technology: From neuronal sensing to DNA sequencing. Electron. Lett. 2011, 47, S7–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, P.R.; Alam, M.A. Screening-limited response of nanobiosensors. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1281–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, E.; Wagner, R.; Sigworth, F.J.; Breaker, R.; Fahmy, T.M.; Reed, M.A. Importance of the Debye screening length on nanowire field effect transistor sensors. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 3405–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.; Ah, C.S.; Park, C.W.; Yang, J.-H.; Kim, T.; Ahn, C.-G.; Park, S.H.; Sung, G.Y. Direct label-free electrical immunodetection in human serum using a flow-through-apparatus approach with integrated field-effect transistors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 1767–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, G.S.; Zhong, Z. Detection beyond the Debye Screening Length in a High-Frequency Nanoelectronic Biosensor. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elnathan, R.; Kwiat, M.; Pevzner, A.; Engel, Y.; Burstein, L.; Khatchtourints, A.; Lichtenstein, A.; Kantaev, R.; Patolsky, F. Biorecognition Layer Engineering: Overcoming Screening Limitations of Nanowire-Based FET Devices. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5245–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaminathan, V.V.; Dak, P.; Reddy, B.; Salm, E.; Duarte-Guevara, C.; Zhong, Y.; Fischer, A.; Liu, Y.-S.; Alam, M.A.; Bashir, R. Electronic desalting for controlling the ionic environment in droplet-based biosensing platforms. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 053105-1–053105-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dak, P.; Alam, M.A. Electrostatic desalting of micro-droplets to enable novel chemical/biosensing applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE 72nd Device Research Conference, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 22–25 June 2014; Volume 232, pp. 275–276.
- Stern, E.; Vacic, A.; Rajan, N.K.; Criscione, J.M.; Park, J.; Ilic, B.R.; Mooney, D.J.; Reed, M.A.; Fahmy, T.M. Label-free biomarker detection from whole blood. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krivitsky, V.; Hsiung, L.-C.; Lichtenstein, A.; Brudnik, B.; Kantaev, R.; Elnathan, R.; Pevzner, A.; Khatchtourints, A.; Patolsky, F. Si nanowires forest-based on-chip biomolecular filtering, separation and preconcentration devices: Nanowires do it all. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4748–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, P.R.; Alam, M.A. Theory of “Selectivity” of label-free nanobiosensors: A geometro-physical perspective. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berdat, D.; Martin Rodríguez, A.C.; Herrera, F.; Gijs, M.A.M. Label-free detection of DNA with interdigitated micro-electrodes in a fluidic cell. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-S.; Banada, P.P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Bhunia, A.K.; Bashir, R. Electrical characterization of DNA molecules in solution using impedance measurements. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, E.; Willner, I. Probing Biomolecular Interactions at Conductive and Semiconductive Surfaces by Impedance Spectroscopy: Routes to Impedimetric Immunosensors, DNA-Sensors, and Enzyme Biosensors. Electroanalysis 2003, 15, 913–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-Y.; Park, S.-M. DNA hybridization sensors based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy as a detection tool. Sensors 2009, 9, 9513–9532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, S.J.; Pourmand, N. Label-Free Impedance Biosensors: Opportunities and Challenges. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 1239–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degefa, T.H.; Kwak, J. Electrochemical impedance sensing of DNA at PNA self assembled monolayer. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2008, 612, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafka, J.; Pänke, O.; Abendroth, B.; Lisdat, F. A label-free DNA sensor based on impedance spectroscopy. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 7467–7474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Cai, H.; He, P.; Fang, Y. Probing DNA Hybridization by Impedance Measurement Based on CdS-Oligonucleotide Nanocojugates. Electroanalysis 2004, 16, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neinhuis, C.; Barthlott, W. Characterization and distribution of water-repellent, self-cleaning plant surfaces. Ann. Bot. 1997, 79, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Kumari, N.; Garimella, S.V. Characterization of ultrahydrophobic hierarchical surfaces fabricated using a single-step fabrication methodology. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2011, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Garimella, S.V. Droplet evaporation dynamics on a superhydrophobic surface with negligible hysteresis. Langmuir 2013, 29, 10785–10795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bliznyuk, O. Directional Wetting on Patterned Surfaces. PhD Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, Netherland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Alam, M.A. Incubation-free detection of bacteria cells by using droplet-based impedance sensing. In Proceedings of the 73rd Annual Device Research Conference, Columbus, OH, USA, 21–24 June 2015; Volume 14, pp. 227–228.
- Ebrahimi, A.; Alam, M.A. Evaporation-enhanced impedance sensing for highly-sensitive differentiation of dsDNA from ssDNA. In Proceedings of the IEEE 71st Device Research Conference, South Bend, IN, USA, 23–26 June 2013; pp. 159–160.
- Ebrahimi, A.; Alam, M.A. Time-resolved PCA of “droplet impedance” identifies DNA hybridization at nM concentration. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 215, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dak, P.; Ebrahimi, A.; Alam, M.A. Non-faradaic impedance characterization of an evaporating droplet for microfluidic and biosensing applications. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 2469–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salm, E.; Guevara, C.; Dak, P.; Dorvel, B.R.; Reddy, B.; Alam, M.A.; Bashir, R. Ultralocalized thermal reactions in subnanoliter droplets-in-air. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3310–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilic, M.S.; Bazant, M.Z.; Ajdari, A. Steric effects in the dynamics of electrolytes at large applied voltages. I. Double-layer charging. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Tian, S.; Tiefenauer, L.; Nielsen, P.E.; Knoll, W. Simultaneously Amplified Electrochemical and Surface Plasmon Optical Detection of DNA Hybridization Based on Ferrocene—Streptavidin Conjugates. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 2756–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.-J.; Liu, Y.-J.; Wang, H.-B.; Wang, Y.-Y. A sensitive electrochemical DNA biosensor based on silver nanoparticles-polydopamine@graphene composite. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 118, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goda, T.; Singi, A.B.; Maeda, Y.; Matsumoto, A.; Torimura, M.; Aoki, H.; Miyahara, Y. Label-free potentiometry for detecting DNA hybridization using peptide nucleic acid and DNA probes. Sensors 2013, 13, 2267–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorgenfrei, S.; Chiu, C.; Gonzalez, R.L.; Yu, Y.-J.; Kim, P.; Nuckolls, C.; Shepard, K.L. Label-free single-molecule detection of DNA-hybridization kinetics with a carbon nanotube field-effect transistor. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Star, A.; Tu, E.; Niemann, J.; Gabriel, J.P.-C.; Joiner, S.; Valcke, C. Label-free detection of DNA hybridization using carbon nanotube network field-effect transistors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Lang, H.P.; Huber, F.; Bietsch, A.; Grange, W.; Certa, U.; McKendry, R.; Güntherodt, H.-J.; Hegner, M.; Gerber, C. Rapid and label-free nanomechanical detection of biomarker transcripts in human RNA. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2006, 1, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Yu, H.; Xu, P.; Xu, W.; Chen, W.; Chen, C.; Li, X. Real-time enzyme-digesting identification of double-strand DNA in a resonance-cantilever embedded micro-chamber. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.-Y.; Loan, P.T.K.; Hsu, C.-L.; Lee, Y.-H.; Wang, J.T.-W.; Wei, K.-H.; Lin, C.-T.; Li, L.-J. Label-free detection of DNA hybridization using transistors based on CVD grown graphene. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weizmann, Y.; Chenoweth, D.M.; Swager, T.M. DNA-CNT Nanowire Networks for DNA Detection. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 3238–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, W.; Jiang, S.; Xu, S.; Bai, C. Fabrication of Integrated Field-Effect Transistors and Detecting System Based on CVD Grown Graphene. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 196, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martı, M.T.; Tseng, Y.-C.; Ormategul, N.; Lionaz, I.; Eritja, R.; Bokor, J. Label-Free DNA Biosensors Based on Functionalized Carbon Nanotube Field Effect Transistors. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 530–536. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Wolf, L.K.; Georgiadis, R.M. Secondary structure effects on DNA hybridization kinetics: A solution versus surface comparison. Nucl. Acids Res. 2006, 34, 3370–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, A.; Lu, N.; Dai, P.; Li, T.; Pei, H.; Gao, X.; Yibin, G.; Yuelin, W.; Fan, C. Silicon-Nanowire-Based CMOS-Compatible Field-Effect Transistor Nanosensors for Ultrasensitive Electrical Detection of Nucleic Acids. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3974–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabani, A.; Zourob, M.; Allain, B.; Marquette, C.A.; Lawrence, M.F.; Mandeville, R. Bacteriophage-modified microarrays for the direct impedimetric detection of bacteria. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 9475–9482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, M.; Li, Y. Interdigitated array microelectrode based impedance biosensor coupled with magnetic nanoparticle-antibody conjugates for detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in food samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 2408–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannoor, M.S.; Tao, H.; Clayton, J.D.; Sengupta, A.; Kaplan, D.L.; Naik, R.R.; Verma, N.; Omenetto, F.G.; McAlpine, M.C. Graphene-based wireless bacteria detection on tooth enamel. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, O.K.; Liu, Y.; Shuaib, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Ladisch, M.R.; Bashir, R.; Bhunia, A.K. Targeted capture of pathogenic bacteria using a mammalian cell receptor coupled with dielectrophoresis on a biochip. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 3094–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltezos, G.; Johnston, M.; Scherer, A. Thermal management in microfluidics using micro-Peltier junctions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Li, Z.; Pisano, A.P.; Williams, R.S. Selective Surface Functionalization of Silicon Nanowires via Nanoscale Joule Heating. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 3106–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, J.J.; Sundaresan, S.G.; Geist, J.; Reyes, D.R.; Booth, J.C.; Rao, M.V.; Gaitan, M. Microwave dielectric heating of fluids in an integrated microfluidic device. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2007, 17, 2224–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issadore, D.; Humphry, K.J.; Brown, K.A.; Sandberg, L.; Weitz, D.; Westervelt, R.M. Microwave Dielectric Heating of Drops in Microfluidic Devices. Lab Chip. 2009, 9, 1701–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf, M.; Frey, U.; Taschini, S.; Hierlemann, A. Micro hot plate-based sensor array system for the detection of environmentally relevant gases. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 6801–6808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgakilas, A.G.; Haveles, K.S.; Sideris, E.G.; Konsta, A.A. Dielectric study of the double helix to single coil transition of DNA. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 1998, 5, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuletić, T.; Babić, S.D.; Grgičin, D.; Aumiler, D.; Rädler, J.; Livolant, F.; Tomić, S. Manning free counterion fraction for a rodlike polyion: Aqueous solutions of short DNA fragments in presence of very low added salt. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker-Jarvis, J.; Jones, C.A.; Riddle, B. Electrical Properties and Dielectric Relaxation of DNA in Solution; NIST Technical Note 1509; US Department of Commerce, National Institute of Standards and Technology: Boulder, CO, USA, 1998.
- Ma, H.; Wallbank, R.W.R.; Chaji, R.; Li, J.; Suzuki, Y.; Jiggins, C.; Nathan, A. An impedance-based integrated biosensor for suspended DNA characterization. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinwari, M.W.; Zhitomirsky, D.; Deen, I.A.; Selvaganapathy, P.R.; Deen, M.J.; Landheer, D. Microfabricated Reference Electrodes and their Biosensing Applications. Sensors 2010, 10, 1679–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salm, E.; Zhong, Y.; Reddy, B.; Duarte-guevara, C.; Swaminathan, V.; Liu, Y.; Bashir, R. Electrical detection of nucleic acid ampli fi cation using an on-chip quasi-reference electrode and a PVC refet. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 6968–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte-Guevara, C.; Swaminathan, V.V.; Burgess, M.; Reddy, B.; Salm, E.; Liu, Y.-S.; Rodriguez-Lopez, J.; Bashir, R. On-chip metal/polypyrrole quasi-reference electrodes for robust ISFET operation. Analyst 2015, 140, 3630–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dak, P.; Ebrahimi, A.; Swaminathan, V.; Duarte-Guevara, C.; Bashir, R.; Alam, M.A. Droplet-based Biosensing for Lab-on-a-Chip, Open Microfluidics Platforms. Biosensors 2016, 6, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6020014
Dak P, Ebrahimi A, Swaminathan V, Duarte-Guevara C, Bashir R, Alam MA. Droplet-based Biosensing for Lab-on-a-Chip, Open Microfluidics Platforms. Biosensors. 2016; 6(2):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleDak, Piyush, Aida Ebrahimi, Vikhram Swaminathan, Carlos Duarte-Guevara, Rashid Bashir, and Muhammad A. Alam. 2016. "Droplet-based Biosensing for Lab-on-a-Chip, Open Microfluidics Platforms" Biosensors 6, no. 2: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6020014
APA StyleDak, P., Ebrahimi, A., Swaminathan, V., Duarte-Guevara, C., Bashir, R., & Alam, M. A. (2016). Droplet-based Biosensing for Lab-on-a-Chip, Open Microfluidics Platforms. Biosensors, 6(2), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6020014