Abstract
The signal-to-noise ratio of planar ISFET pH sensors deteriorates when reducing the area occupied by the device, thus hampering the scalability of on-chip analytical systems which detect the DNA polymerase through pH measurements. Top-down nano-sized tri-gate transistors, such as silicon nanowires, are designed for high performance solid-state circuits thanks to their superior properties of voltage-to-current transduction, which can be advantageously exploited for pH sensing. A systematic study is carried out on rectangular-shaped nanowires developed in a complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS)-compatible technology, showing that reducing the width of the devices below a few hundreds of nanometers leads to higher charge sensitivity. Moreover, devices composed of several wires in parallel further increase the exposed surface per unit footprint area, thus maximizing the signal-to-noise ratio. This technology allows a sub milli-pH unit resolution with a sensor footprint of about 1 µm2, exceeding the performance of previously reported studies on silicon nanowires by two orders of magnitude.
1. Introduction
Reducing the size of electronic devices affects the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Structures with improved gate-to-channel coupling, indicated as multi-gate devices, were conceived for traditional solid-state systems to overcome this issue [1]. In particular, the feature of these devices, enhanced subthreshold swing, reduced short-channel effects such as drain-induced barrier lowering (DIBL) and, consequently, resulted in an improved scalability [2,3,4]. As a matter of fact, the introduction of multi-gate device architectures has so far effectively sustained Moore’s law and kept up the pace of technological advancement in the electronics industry.
In the field of bioanalytics, the large-scale integration of CMOS chips exposing arrays of liquid-gate FET pH-sensors has shown its potential in applications such as DNA sequencing [5], and holds the promise to innovate DNA quantification based on quantitative PCR [6,7,8]. If the paradigm of nanoscale multi-gate devices improved as well the SNR of liquid-gate sensors, it would be possible to reduce the sensor size and consequently increase the throughput of analytical systems.
Silicon-based multi-gate structures, commonly indicated as nanoribbons (SiNRs) and nanowires (SiNWs), have been proposed as bio and chemical sensors [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29] . Although a few works indicate that improved macromolecular sensing can be achieved with smaller devices [30], no consensus has been reached on the effect of size reduction on pH sensitivity as well as the role of device technology, device layout, bias and signal readout [31,32]. In what follows, we show that tri-gate silicon nanoribbons with rectangular cross-section exhibit an enhanced sensitivity vs. pH when decreasing their width below a few hundreds of nanometers. We perform noise characterization for devices of different size and biasing, proposing a multi-wire configuration to achieve higher SNR. The resolution that can be achieved with a sensor footprint of one micrometer square corresponds to a 0.8‰ shift in pH, which is equivalent to approximately 100 electrons in the case of silicon dioxide interfaces. This performance is two orders of magnitude better than the one obtained with planar devices [33,34].
We developed tri-gate devices on Silicon-On-Insulator (SOI) substrates based on self-aligned CMOS-compatible top-down processes, with accuracy down to 5 nm. The use of a semi-industrial process ensures a high level of control over process variations and enables the fabrication of high-density individually connected SiNRs with a well-defined orientation and a wide range of widths and lengths. Such features still represent a challenge for bottom-up technologies [35].
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Technology and Fabrication Process
The n+/p/n+ SiNRs are fabricated on SOI wafers and patterned by means of a top-down hybrid deep ultraviolet (DUV) and e-beam lithography followed by a reactive ion etching (RIE). The fabrication process was entirely developed at CEA-LETI. The wafers are composed of a 200 nm silicon layer on top of a 400 nm thick SiO2 insulating bulk oxide layer (BOX). The silicon top layer is first thinned by chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) and then by several steps of silicon thermal oxidation/desoxidation to obtain a 50 nm silicon top layer, which defines the thickness (tNR) of the SiNRs. Devices with feature sizes above 300 nm are patterned using deep ultraviolet (DUV), while e-beam lithography is employed for smaller dimensions. Once patterned, the undesired material is etched away by reactive ion etching (RIE). A high quality 3 nm SiO2 gate oxide is grown using thermal dry oxidation. In order to obtain n-type devices, the SiNRs are doped by boron implantation (1 × 1018 cm−3). A sacrificial polysilicon gate is used as a hard mask to dope the source and drain terminals with phosphorous (1 × 1019 cm−3), thus effectively defining the SiNR length. The entire chip surface, with the exception of the contact pads and the SiNR, is passivated by a multi-layer insulator composed of 50 nm of Si3N4, 300 nm of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) and 200 nm of phosphosilicate glass (PSG) (Figure 1b). This multilayer insulator is designed to withstand the liquid environment and to avoid the propagation of pin-holes in the passivation that could short-circuit the electrolyte with the contact lines [36].
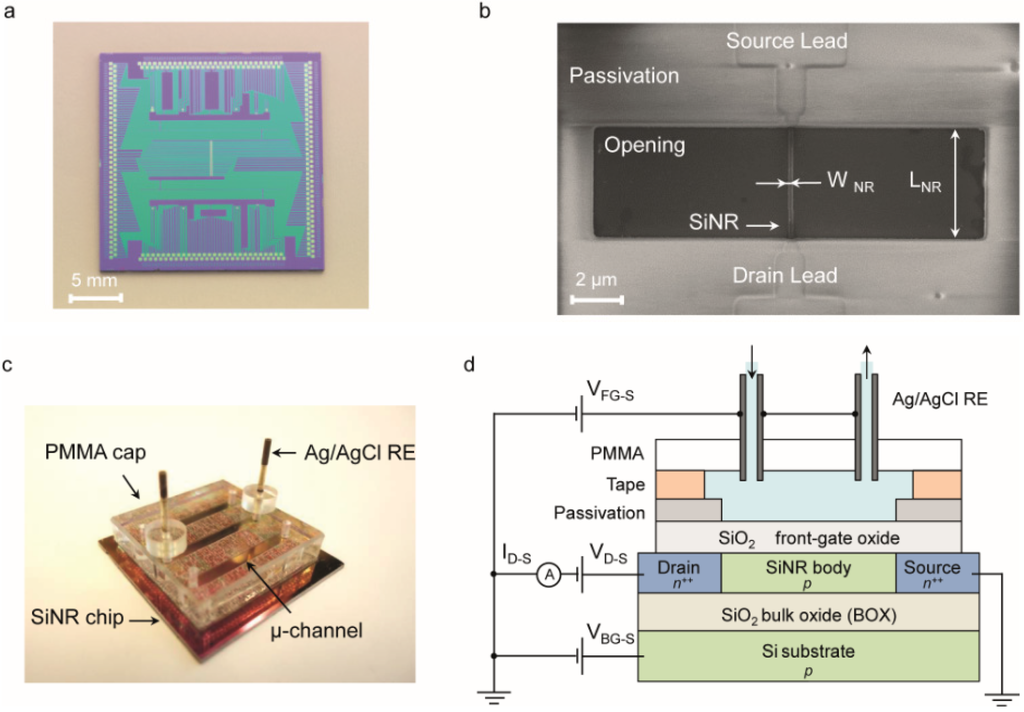
Figure 1.
(a) Optical image of the chip; (b) SEM image of a Silicon NanoRibbon (SiNR). Top view of a device with WNR = 87 nm and LNR = 4250 nm. The source and drain leads are passivated, while the body of the device is exposed. The length of each SiNR corresponds to the opening in the passivation; (c) Optical image of the microfluidics setup; (d) Cross section of the fabricated device and a sketch of the measurement setup (not to scale).
2.2. Ag/AgCl Reference Electrode Fabrication
The Ag/AgCl electrodes are obtained by a galvanostatic oxidation on silver tubes. The silver tubes are dipped in 0.1 M HNO3 for about 1 min, in order to clean and activate the surface, and then rinsed with deionized water. After the surface activation, the silver wire is connected to a working electrode (anode); a platinum wire is connected to a counter electrode (cathode) and both of them are dipped into a solution of 0.1 M KCl. A current density of 2.5 mA/cm2 is applied at the anode for a time that depends on the desired thickness of the AgCl layer (5 µm in this work). At the end of the oxidation, the Ag/AgCl tubes are dipped into a solution of 0.1 M KCl for at least 4 hours prior to use. The performances in terms of voltage drift have been compared with respect to commercial Ag/AgCl (see Supplementary Figure S10).
2.3. Microfluidics
The microchannels are obtained with a chemical-resistant double-coated tape (3M 9086), patterned by laser micromachining. The height of the channels is thereby defined by the thickness of the tape (190 μm). A poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) cap with holes drilled in the locations of inlets and outlets is placed on top of the tape to seal the channels, and the inlet and outlet tubes are inserted.
A syringe pump (Harvard Apparatus) is used to flux the solution of interest into the microfluidics. Due to the double-coated tape system, the microfluidics can easily be removed by incubating the chip in 2-Propanol alcohol overnight. The chip can, therefore, be cleaned more thoroughly and re-used. Figure 1b shows an SEM image of a used device after the cleaning procedure.
2.4. Electrical Characterization
The electrical characterization of the devices was performed by means of a semiconductor parameter analyzer (SPA, Agilent 4156C) used both in sweep and sampling modes, controlled by LabVIEW VIs and MATLAB scripts via a GPIB interface.
2.5. pH Sensing Experiments
The SiNR chips are cleaned by successive washing steps of ethanol/acetone/ethanol (10 min each), separated by rinsing with deionized water and drying with N2. After the cleaning procedure of the chip surface, the microfluidic module is mounted and the chip is ready for the experiment. The solutions at different pH are interspersed by 10 µM KCl (pHKCl ~6.8) injections. Each injection is 15 min long, at fixed flow rate of 5 µL/min. At the end of each injection, the syringe pump is stopped and the solution is changed.
The different pH solutions are prepared starting with 10 mM phosphate buffered saline (PBS) containing 100 mM KCl, which is added to stabilize the Ag/AgCl RE. The solutions are adjusted to the desired pH by adding either a strong acid (H2SO4) or a strong base (NaOH), so that the difference in the ionic strength of the solutions results to be negligible.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. pH Sensitivity of Single SiNR Devices as a Function of Their Width
The fabricated chip features 75 SiNRs with thickness (tNR) of 50 nm and different widths (WNR) and lengths (LNR) (Figure 1a,b). Devices with identical LNR and different WNR (and vice versa) were fabricated with the specific aim of studying the effect of size on the device noise and sensitivity, both in terms of ΔVTH/ΔpH and ΔID-S/ΔpH.
The SiNR chip is coupled with a microfluidic module that employs Ag/AgCl reference electrodes (REs) and allows subsequent injections of different solutions into sub-5 µL microchannels (Figure 1c) [37].
The SiNRs can be operated either by the solid-state back-gate or by the liquid front-gate (Figure 1d). The back-gating approach consists in applying a gate voltage (VBG-S) between the silicon substrate and the source terminal. Instead, in the case of front-gating, a voltage VFG-S is applied between the electrolyte solution, biased by Ag/AgCl REs, and the source terminal, while the back-gate is short-circuited with the source contact. As shown in our previous work [37], the front-gating configuration with grounded back-gate prevents from any parasitic coupling between the electrolyte solution and the environment.
Figure 2 shows the ID-S-VFG-S and ID-S-VD-S characteristics of a SiNR in front-gating bias. The SiNR shows a MOSFET behavior, with threshold voltage (VTH) of approximately 1.5 V and a sub-threshold swing (SS) of about 100 mV/dec. The VTH does not show any systematic trend vs. W. Typical ID-S,ON/ID-S,OFF ratio in virgin devices is of about 104, and can be as good as 106, while the leakage in Figure 2a (red curve) is more representative of a device that has been extensively used in liquid environment. Note that the leakage may have different sources, both inside and outside the active device area, but in any case does not affect our sensitivity data that is taken well above VTH. A slightly negative differential output resistance is sometimes observed at large VGS (Figure 2b) probably due to a small drift vs. time (also visible in Figure 3b and discussed later on), that lowers ID-S while sweeping the VD-S with an integration time of 20 ms and 151 bias points per ID-S-VD-S curve. A VDS of 1.5V was selected to maximize the absolute change of the drain current with the pH without incurring in reliability issues (see also Supplementary Figure S1) and because it is favorable in terms of SNR with respect to lower VDS values [38].
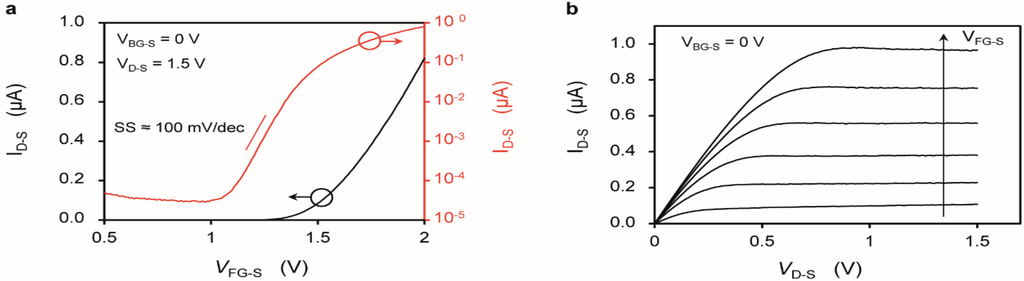
Figure 2.
(a,b) Characterization of a SiNR with length (LNR) of 2375 nm and a width (WNR) of 290 nm. The electrolyte is 100 µM KCl. (a) Drain current (ID-S) vs. gate voltage (VFG-S) plotted in linear (left y axis) and logarithmic (right y axis) scale; (b) Drain current (ID-S) vs. drain voltage (VD-S) plotted for different constant gate voltages (VFG-S), ranging from 1.5 V to 2.0 V, with a step of 0.1 V.
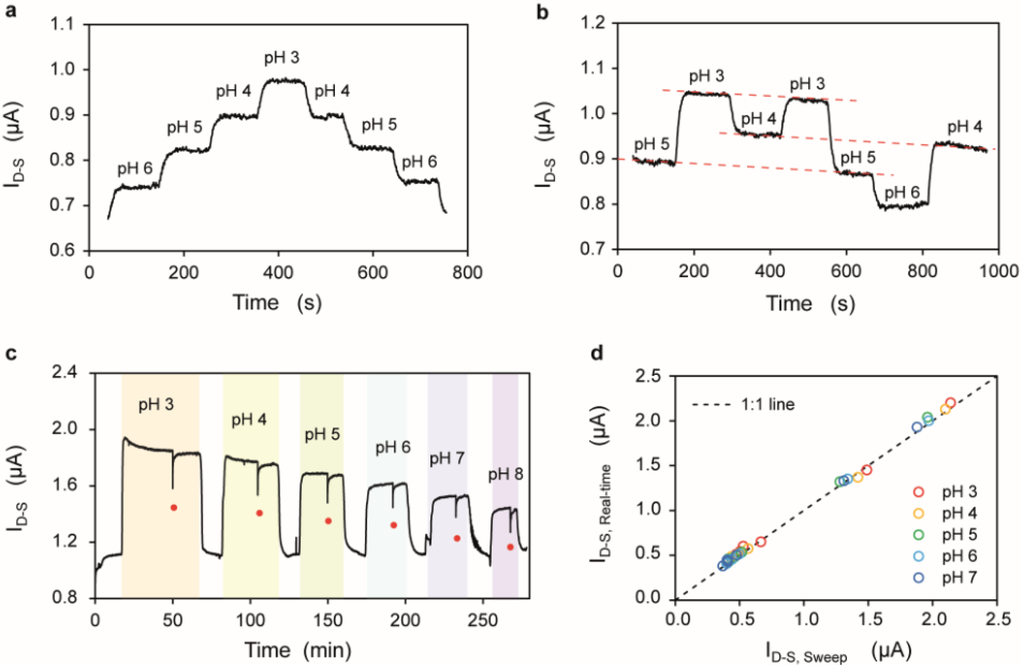
Figure 3.
(a) Drain current (ID-S) observed at fixed voltage bias upon injection of decreasing/increasing series of pH values; (b) Drain current (ID-S) observed at fixed voltage bias upon injection of randomize series of pH values. The three parallel red dotted lines highlight the drift affecting the ID-S; (c) Drain current (ID-S) measurement upon injection of solutions with different pH values and identical ionic strength. The red dots indicate when the ID-S-VFG-S characterization is performed; (d) Average ID-S observed at fixed polarization (ID-S,Real-time) vs. the ID-S extracted from the ID-S-VFG-S sweeps (ID-S, Sweep) from a set of SiNRs. A 1:1 line is plotted as reference. All measurements of the figure refer to the same device which has a WNR of 50 nm and a LNR of 2375 nm.
In our setup the liquid-gate terminal is common to all the devices while the source and drain contacts can be individually addressed for each SiNR device, allowing the current of the single devices to be measured independently.
Figure 3a shows the drain current of a SiNR measured in real-time upon the injection of solutions with decreasing and then increasing values of pH. According to the site binding theory [39,40,41], solutions with different pH values in contact with the gate oxide induce changes in the surface charge of the front-gate oxide as an effect of the deprotonation (protonation) of the silanol groups in the presence of OH− (H+) ions in the electrolyte. In particular, the surface of the front-gate oxide becomes negatively charged when it is in contact with electrolyte solutions with pH values higher than its isoelectric point (pI ≈ 2 in the case of SiO2). The change in surface charge affects the surface potential, which in turn modifies the conductance of the device when subjected to a constant voltage bias. The device is biased above threshold (VFG‑S − VTH ≈ 0.5 V) and in saturation regime (VD-S = 1.5 V), thus increasing the absolute value and the linearity of the current response in terms of ΔID-S/ΔpH with respect to the subthreshold regime (see Supplementary Figure S1). Moreover, the devices are biased to work in the saturation regime to maximize the dynamic range. As expected in the case of an n-type device, the drain current decreases with increasing pH, as more and more negative charges accumulate at the oxide surface, thus depleting the electrons in the channel. The device shows little hysteresis between the forward and backward pH sweeps (see Supplementary Figure S2). Non-monotonically increasing/decreasing pH series (Figure 3b) show that the conductance of the device depends on pH and experiences a linear drift, which does not show any relevant correlation with the pH values.
Figure 3c,d compares the device current evaluated either by keeping the device at a fixed voltage bias, or by performing a sequence of ID-S-VFG-S characteristics. Two conditioning injections at acidic and basic pH (pH 3 and pH 8, respectively) are performed at the beginning of the experiment in order to prime the front-gate oxide surface, and with the effect of improving the subthreshold slope (typically from between 150 and 200 mV/dec down to 100 mV/dec) and setting it to a stable value. For the rest of the entire experiment, the subthreshold slope remains constant, leading to a rigid shift of the ID-S-VFG-S characteristics upon pH injections (see Supplementary Figure S3). In order to cope with the dependence of the device current with the ionic force of the electrolyte (see Supplementary Figure S4), the pH solutions were prepared to have the same ionic strength (100 mM). The monitoring of the drift was performed by exposing the device to subsequent injections of a saline solution (10 µM KCl) alternated with the solutions at different pH.
In this experiment, the device has been kept at the above mentioned bias (VFG-S − VTH ≈ 0.5 V, VD-S = 1.5 V) (current vs. time plotted in Figure 3c), with the exception of the time points indicated by the red dots on the plot, when the device has been subjected to a series of three VFG-S sweeps (from 0 V to 2 V). The plot on Figure 3d shows a 1:1 correlation between the current measured at a fixed bias ID-S,Real-time (averaged over 5 min) and the current extracted from the ID-S-VFG-S corresponding to the same bias (ID-S, Sweep).
In our measurements the current drift is not affected by the size of the devices; rather, it can be ascribed to the wear out of the Ag/AgCl reference electrode, and possibly to the relatively thin nanowire top-oxide (3 nm).
The experiment described in Figure 3c has been performed on several nanowires to assess their pH sensitivity, both in terms of the change of the threshold voltage ΔVTH/ΔpH (Figure 4a,b) and in terms of the normalized current signal ΔI’D-S/ΔpH (Figure 4c,d), where I’D-S = ID-S/[(WNR + 2·tNR)/LNR] is the current normalized by the form factor. Figure 4a shows the shift of ID-S-VFG-S characteristics for one of the devices (WNR = 170 nm and LNR = 2375 nm). The threshold voltage of the n-type device increases due to the accumulated negative charges at the interface between the gate oxide and the electrolyte. The threshold voltage sensitivity ΔVTH/ΔpH for a set of SiNRs with different widths and identical length (LNR = 2375 nm) located close to each other on the chip area is shown in Figure 4b. The average voltage shift is about 30 mV/pH, in agreement with other previous works using SiO2 as gate oxide [42,43,44]. The voltage shift does not depend on the device width (Figure 4b), as shown previously [31], while it has a well-proven dependence on the buffer capacity of the gate insulator [39].
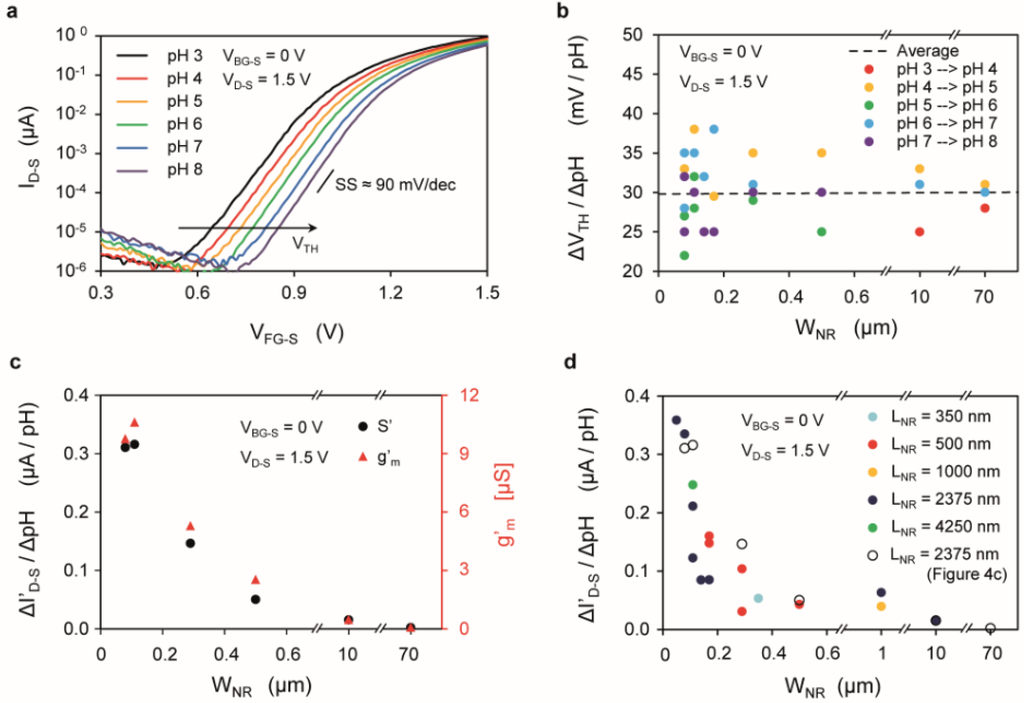
Figure 4.
(a) Drain current (ID-S) vs. front-gate voltage (VFG-S) characteristics for a device with WNR = 170 nm and LNR = 2375 nm exposed to different pH; (b) Threshold voltage shifts over different pH, calculated at ID-S = 1 nA and plotted against WNR; (c) pH sensitivity (ΔI’D-S/ΔpH) and normalized transconductance (g’m), plotted against the SiNR width (WNR). The length LNR of the devices is constant (LNR = 2375 nm); (d) Normalized-current sensitivity (S’ = ΔI’D-S/ΔpH) plotted against the SiNR width (WNR), for devices with different length (LNR), located on the same chip, all extracted at the same VFG-S − VTH = 0.5 V.
The sensitivity in terms of current signal as a function of the device width is shown in Figure 4c,d. In this analysis the effect of the source (RS) and drain (RD) parasitic series resistances on the performance of SiNRs devices has been taken into account by extracting their value and compensating for the corresponding voltage losses (see Supplementary Figure S5). The sensitivity of ΔI’D-S/ΔpH is not constant, but instead increases for decreasing width (WNR), due to the larger device transconductance g’m (Figure 4c). The sensitivity for devices with different widths and different lengths is plotted in Figure 4d as a function of the width, indicating that the length does not affect the sensitivity for the considered range (350–4250 nm). SiNRs with width below few hundreds of nanometers exhibit a higher transconductance.
Interestingly, this result is in contrast with other works [32], in which a linear dependence of the transconductancewith the factor (WNR + 2·tNR)/LNR is found. The enhancement of the transconductance with smaller WNR could be a signature of marked corner effects, typical of devices with high body doping and rectangular cross-section [45], as opposed to low-doped trapezoidal wires [32].
The next section analyzes the noise characteristics of the SiNRs, which is essential to evaluate the dependence of the sensor performance on their size and, ultimately, to determine the smallest pH change detectable per unit footprint surface.
3.2. Noise Characterization of the SiNRs
At low frequencies, the noise of SiNWs and SiNRs is dominated by flicker noise [22,25,46,47], which is characterized by a power spectral density that is proportional to f−γ where f is the frequency and 0.7 < γ < 1.3 [48]. The flicker noise leads to a degradation of the SNR that is more important for devices having smaller gate areas [49].
In what follows, we characterize the noise at different bias points for three SiNRs, ranging from 110 nm to 10 µm in width, by performing the fast Fourier transform (FFT) [50] of ID-S sampled at fS = 10 Hz. A spectral filtering technique [51] has been employed to compensate for the distortions caused by aliasing, which can impact the scaling exponents of f−γ noises (see Supplementary Figure S6) [51,52,53,54].
Figure 5a shows the current noise power spectral density (SID) for a SiNR (LNR = 2375 nm, WNR = 110 nm) biased in subthreshold (VFG-S = 0.9 V), weak inversion (VFG-S = 1.0 V and 1.1 V) and above threshold (VFG-S = 1.7 V), respectively. The SID of the silicon nanoribbon follows the expected 1/f behavior at low frequency, with larger noise at high VFG-S.
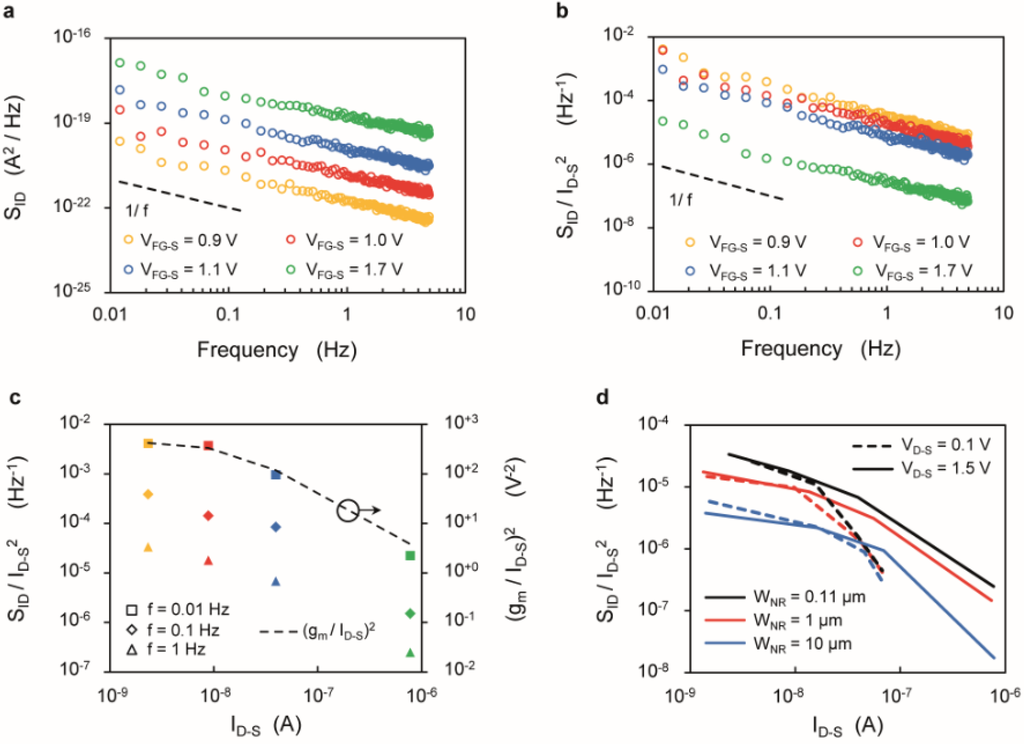
Figure 5.
(a–c) Noise characteristics of a SiNR with length LNR = 2375 nm, width WNR = 110 nm and drain voltage VD-S = 1.5 V. (a) Low-frequency drain current noise spectral density (SID) characteristics; (b) SID/ID-S2 plotted against frequency; (c) SID/ID-S2 plotted for different frequencies (f = 0.01 Hz, f = 0.1 Hz and f = 1 Hz) as a function of ID-S, compared with the (gm/ID‑S)2 ratio (dotted line, right axis); (d) SID/ID-S2 plotted as a function of ID-S for SiNRs with same length (LNR = 2375 nm) and different widths (WNR = 110 nm, WNR = 1 µm and WNR = 10 µm) biased to work in saturation (VD-S = 1.5 V, solid lines) and linear regime (VD-S = 0.1 V, dotted lines), at a frequency f = 1 Hz.
On the other hand, Figure 5b shows that when considering the ratio between noise power and squared signal, working above threshold leads to higher SNR. In support of this observation, Figure 5c reports SID/ID-S2 vs. ID-S for different sampling frequencies, showing that working at larger currents lead to smaller noise-to-signal ratio. These results are consistent with previously reported works [55], in which the SNR is maximized at the peak transconductance. Moreover, the plot shows that the quantity SID/ID-S2 and (gm/ID-S)2 follow the same trend vs. ID-S (see also Supplementary Figure S7), thus supporting the validity of the carrier-number fluctuation (ΔN) arising from the dynamic trapping and de-trapping of free carriers within the gate oxide as the dominating factor of the flicker noise [48,49].
Finally, Figure 5d compares the three SiNRs with different widths in terms of the SID/ID‑S2 factor. In the low current region, the SNR depends only weakly on the drain voltage. Instead, in strong inversion, the saturation regime ensures a lower noise-to-signal ratio.
In conclusion, since nano-sized transistors occupying smaller areas suffer more from intrinsic noise, those approaches aimed at increasing the array density of a chip by employing tinier pH sensors must take into account the degradation of the SNR, which would ultimately negatively affect the resolution in pH. In what follows, we show that multi-wire transistors can reduce this limit and thus allow smaller area per sensing pixel with improved resolution.
3.3. Multiple-Wire Devices
In this section, we show that devices consisting of multiple nanowires connected in parallel exceed the performance of single devices occupying the same footprint area, and we compare their performances with existing planar and tri-gate devices. In fact, multi-wires devices benefit, on one hand, from the enhanced sensitivity of narrower silicon structures and, on the other hand, from the lower noise provided by their larger interface area [56]. Moreover, previous works have shown the superior inter-device uniformity of multi-wire devices when compared to single SiNR [57]. As a consequence, multi-wire devices alleviate the variability of electrical parameters such as VTH, SS and gm.
The four common-source devices characterized in this work exhibit independent drain contacts for each finger, which allows us to compare the performance of the single-wire with that of two-, three- and four-wire devices (Figure 6, cartoon A, B, C and D respectively). The devices were biased above threshold (VFG‑S − VTH ≈ 1 V) and in saturation regime (VD‑S = 1.5 V). The results show an increase of the maximum transconductance with the number of SiNR fingers (Figure 6a). However, these values are smaller than the sum of the transconductance of individual wires, mainly due to the slightly different threshold voltage of the considered four wires, which results in a degradation of the average gm. As shown in Figure 4c, the current sensitivity is directly linked to the transconductance of the device and, therefore, it also increases with the number of fingers.
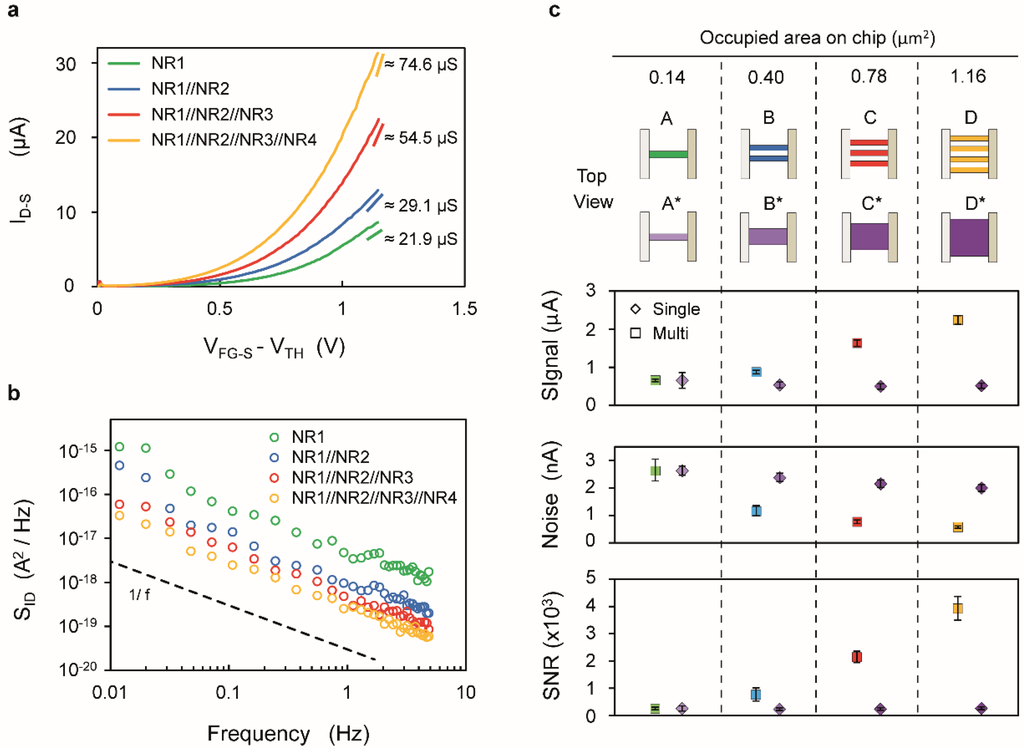
Figure 6.
(a–c) The SiNRs have dimensions as follows: WNR1,2 = 60 nm, WNR3,4 = 110 nm with LNR1,2,3,4 = 2375 nm. (a) Drain current (ID‑S) vs. overdrive voltage (VFG-S − VTH) characteristics; the value of the transconductance extracted at VFG‑S − VTH = 1.1 V is indicated on the right; (b) Low-frequency current noise spectral density (SID) characteristics (c) Signal, rms noise (as obtained by integrating SID over 1Hz bandwidth centered around 1Hz) and SNR values for multi-finger devices (□) and for single SiNR occupying the same area on chip (◊) with color-coded cartoon representation of the devices with the indication of the occupied area, considering a distance of 50 nm between fingers.
Figure 6b reports the current noise as a function of the frequency for devices with increasing number of fingers showing an improvement for devices featuring larger area, as expected from SID scaling rules. As for Figure 5, the spectra have been compensated for aliasing distortions (Figure S6, Supplementary). Figure 6c reports the Signal, Noise and SNR for devices of increasing occupied area featuring multiple nanowires (□). The Signal value corresponds to the measured gm of the device multiplied by ΔVTH/ΔpH (assumed to be 30 mV/pH, according to Figure 4b) and the related error bars are defined based on the variability over the timescale of an experiment (a few hours). The Noise value of multi-wire devices is obtained by calculating the square root of the integral of the noise spectrum SID in 1 Hz bandwidth centered at 1 Hz. The corresponding error bars are calculated from the prediction bounds of the interpolated spectrum (Figure S8, Supplementary).
The analysis of sensitivity and noise characteristics allows us to evaluate the resolution of the devices, i.e., the smallest detectable pH change. The resolution (δpH) is calculated as pH change giving a signal-to-noise ratio SNR = 3:
Since in Figure 4c we see that ΔIDS/ΔpH = gm ΔVTH/ΔpH, we can also compute
where is the voltage noise power spectral density. The noise-equivalent pH value is obtained by dividing the noise level (square root of the integral of the current noise spectra over the measurement frequency bandwidth) by the current sensitivity (ΔID‑S/ΔpH). A resolution of ~0.8‰ of pH change is achieved in a 1 Hz bandwidth, centered at 1 Hz, by a four-fingers device occupying approximately 1.16 µm2. In terms of the lowest detectable change of electron surface density at the gate interface, the achieved pH resolution corresponds to 1.78 × 10−17 C/µm2.
This result is close to the lowest reported value obtained with tri-gate nanowires (0.5‰ of a pH shift in a 1 Hz bandwidth centered at 10 Hz) employing a device with a 7 µm2 footprint [25]. Nevertheless, in the context of ever increasing array density of integrated pH sensors, the most indicative parameter is the resolution that can be achieved in a unit of occupied footprint area on the chip. In this regard, our results outperform the previous works (0.0008 pH vs. 0.0005·√(7) = 0.0013 pH change with 1 µm2 footprint device) [25], despite our more conservative choice of the SNR level to define the resolution (SNR = 3) and of a lower central frequency (fC) for the bandwidth (1 Hz vs. 10 Hz). When evaluated under the same conditions (SNR = 1, fC = 10 Hz), our system outperforms the state-of-the-art by two orders of magnitude.
In order to compare the performance of multi-wire design with single nanoribbon devices, the trend of single SiNRs of equivalent area (A*, B*, C* and D*) has been reported in Figure 6c (◊). In this case, the Signal values have been derived from Figure 4d, with the error bars taking into account the interpolation error of the fitted trend. The Noise values (◊ Noise plot Figure 6c) are evaluated on the basis of the noise characterization of single ribbon devices (Figure 5d, VD‑S = 1.5 V) and the corresponding error bars take into account the interpolation error (Figure S9, Supplementary). This suggests that the SNR of multi-wire devices increases with the area with a steeper trend than single nanoribbons and, in particular, a device occupying 1.16 µm2 is characterized by a SNR that is 15 times higher than the one of a single nanoribbon of identical footprint area.
Clearly, the resolution could be further improved by increasing the density of interconnected nanowires per device, and by sampling at higher frequencies [58]. Moreover, the employment of high-k gate dielectrics such as Al2O3 and HfO2 [16,31] would induce a larger change of surface potential upon a pH change, leading to a higher signal transduced by the sensor.
4. Conclusions
The performances including an improved sensitivity of nano-sized tri-dimensional silicon devices as detectors of surface charge in electrolyte environment have been investigated. The tri-gate configuration gives silicon nanoribbons undeniable advantages with respect to planar devices and, in particular, in this work we show that ribbons with width below a few hundreds of nanometers show enhanced conductivity properties, ultimately leading to higher sensitivity.
The enhanced performance characteristic of narrower wires can be combined with the lower noise granted by the larger gate area of multiple nanowires connected in parallel. Moreover, multi-wire devices assure improved inter-device uniformity in terms of the conductance characteristics.
In conclusion, we have shown that tri-dimensional, multi-wire devices constitute a successful approach to scale down the size of the single pH sensor, achieving unprecedented pH resolution per unit occupied footprint area. This feature is of particular interest in integrated pH-based bioanalytics on CMOS technology such as DNA sequencing and quantitative PCR, which lean toward sensor arrays of ever-increasing density. Our technology relies on highly-controlled top-down CMOS-compatible fabrication processes, which are required in large-scale integration.
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
This work has been funded by the Swiss Nano-Tera project ISyPeM (128852) and by the SNSF (Swiss National Science Foundation) project Bio3D (200021 140554). The authors wish to thank Federico Pittino for helpful discussions and Julien Buckley for his contribution to the design of the silicon nanoribbons.
Author Contributions
Enrico Accastelli and Carlotta Guiducci conceived and designed the experiments. Enrico Accastelli performed the experiments. Thomas Ernst was responsible for the fabrication of the devices. Enrico Accastelli, Paolo Scarbolo, Pierpaolo Palestri, Carlotta Guiducci, Luca Selmi equally contributed to analyze the data, devise extraction, compensation and normalization procedures for signal and noise. Enrico Accastelli and Carlotta Guiducci wrote the main part of the manuscript and all authors contributed to writing and revision of the manuscript. Carlotta Guiducci planned the project, directed the research and contributed for materials/analysis tools. All authors contributed to the discussion of the results and revised the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- James, D. Intel Ivy Bridge unveiled—The first commercial tri-gate, high-k, metal-gate CPU. In Proceedings of the IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 9–12 September 2012; pp. 1–4.
- Agrawal, N.; Kimura, Y.; Arghavani, R.; Datta, S. Impact of Transistor Architecture (Bulk Planar, Trigate on Bulk, Ultrathin-Body Planar SOI) and Material (Silicon or III-V Semiconductor) on Variation for Logic and SRAM Applications. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2013, 60, 3298–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colinge, J.P. FinFETs and Other Multi-Gate Transistors; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Moroz, V.; Damrongplasit, N.; Shin, C.; Liu, T.-J.K. Variation Study of the Planar Ground-Plane Bulk MOSFET, SOI FinFET, and Trigate Bulk MOSFET Designs. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2011, 58, 3294–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothberg, J.M.; Hinz, W.; Rearick, T.M.; Schultz, J.; Mileski, W.; Davey, M.; Leamon, J.H.; Johnson, K.; Milgrew, M.J.; Edwards, M.; et al. An integrated semiconductor device enabling non-optical genome sequencing. Nature 2011, 475, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte-Guevara, C.; Lai, F.-L.; Cheng, C.-W.; Reddy, B., Jr.; Salm, E.; Swaminathan, V.; Tsui, Y.-K.; Tuan, H.C.; Kalnitsky, A.; Liu, Y.-S.; et al. Enhanced Biosensing Resolution with Foundry Fabricated Individually Addressable Dual-Gated ISFETs. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 8359–8367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiducci, C.; Spiga, F.M. Another transistor-based revolution: On-chip qPCR. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 617–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toumazou, C.; Shepherd, L.M.; Reed, S.C.; Chen, G.I.; Patel, A.; Garner, D.M.; Wang, C.-J.A.; Ou, C.-P.; Amin-Desai, K.; Athanasiou, P.; et al. Simultaneous DNA amplification and detection using a pH-sensing semiconductor system. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunimovich, Y.L.; Shin, Y.S.; Yeo, W.-S.; Amori, M.; Kwong, G.; Heath, J.R. Quantitative real-time measurements of DNA hybridization with alkylated nonoxidized silicon nanowires in electrolyte solution. J. Anal. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 16323–16331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Wei, Q.Q.; Park, H.K.; Lieber, C.M. Nanowire nanosensors for highly sensitive and selective detection of biological and chemical species. Science 2001, 293, 1289–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfstroem, N.; Karlstroem, A.E.; Linnros, J. Silicon nanoribbons for electrical detection of biomolecules. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.P.A.; Zheng, G.; Lieber, C.M. Subthreshold Regime has the Optimal Sensitivity for Nanowire FET Biosensors. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Agarwal, A.; Trigg, A.D.; Singh, N.; Fang, C.; Tung, C.-H.; Fan, Y.; Buddharaju, K.D.; Kong, J. Silicon nanowire arrays for label-free detection of DNA. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 3291–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahm, J.; Lieber, C.M. Direct ultrasensitive electrical detection of DNA and DNA sequence variations using nanowire nanosensors. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, F.N.; Chang, H.-K.; Curreli, M.; Liao, H.-I.; Olson, C.A.; Chen, P.-C.; Zhang, R.; Roberts, R.W.; Sun, R.; Cote, R.J.; et al. Label-Free, Electrical Detection of the SARS Virus N-Protein with Nanowire Biosensors Utilizing Antibody Mimics as Capture Probes. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopfmacher, O.; Tarasov, A.; Fu, W.; Wipf, M.; Niesen, B.; Calame, M.; Schoenenberger, C. Nernst Limit in Dual-Gated Si-Nanowire FET Sensors. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2268–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; To, S.; You, L.; Sun, Y. Effect of Nanowire Number, Diameter, and Doping Density on Nano-FET Biosensor Sensitivity. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6661–6668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Kamins, T.I.; Nauka, K.; Williams, R.S. Sequence-specific label-free DNA sensors based on silicon nanowires. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, M.N.; Chen, S.; Carlen, E.T.; van den Berg, A. All-(111) Surface Silicon Nanowires: Selective Functionalization for Biosensing Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 3422–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, P.R.; Alam, M.A. Design considerations of silicon nanowire biosensors. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2007, 54, 3400–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patolsky, F.; Zheng, G.F.; Hayden, O.; Lakadamyali, M.; Zhuang, X.W.; Lieber, C.M. Electrical detection of single viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14017–14022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, N.K.; Duan, X.; Reed, M.A. Performance limitations for nanowire/nanoribbon biosensors. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 5, 629–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, E.; Klemic, J.F.; Routenberg, D.A.; Wyrembak, P.N.; Turner-Evans, D.B.; Hamilton, A.D.; LaVan, D.A.; Fahmy, T.M.; Reed, M.A. Label-free immunodetection with CMOS-compatible semiconducting nanowires. Nature 2007, 445, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, E.; Vacic, A.; Reed, M.A. Semiconducting Nanowire Field-Effect Transistor Biomolecular Sensors. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2008, 55, 3119–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, A.; Fu, W.; Knopfmacher, O.; Brunner, J.; Calame, M.; Schoenenberger, C. Signal-to-noise ratio in dual-gated silicon nanoribbon field-effect sensors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.U.; Chen, C.; Lin, K.H.; Fang, Y.; Lieber, C.M. Label-free detection of small-molecule-protein interactions by using nanowire nanosensors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3208–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.-J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, M.J.; Luo, Z.H.H.; Tay, G.K.I.; Lim, E.-J.A.; Kang, T.G.; Chen, Y. Silicon nanowire biosensor for highly sensitive and rapid detection of Dengue virus. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 146, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigante, S.; Scarbolo, P.; Wipf, M.; Stoop, R.L.; Bedner, K.; Buitrago, E.; Bazigos, A.; Bouvet, D.; Calame, M.; Schönenberger, C.; et al. Sensing with Advanced Computing Technology: Fin Field-Effect Transistors with High-k Gate Stack on Bulk Silicon. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4872–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buitrago, E.; Fernández-Bolaños, M.; Rigante, S.; Zilch, C.F.; Schröter, N.S.; Nightingale, A.M.; Ionescu, A.M. The top-down fabrication of a 3D-integrated, fully CMOS-compatible FET biosensor based on vertically stacked SiNWs and FinFETs. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfstrom, N.; Juhasz, R.; Sychugov, I.; Engfeldt, T.; Karlstrom, A.E.; Linnros, J. Surface charge sensitivity of silicon nanowires: Size dependence. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 2608–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedner, K.; Guzenko, V.A.; Tarasov, A.; Wipf, M.; Stoop, R.L.; Just, D.; Rigante, S.; Fu, W.; Minamisawa, R.A.; David, C.; et al. pH Response of Silicon Nanowire Sensors: Impact of Nanowire Width and Gate Oxide. Sens. Mater. 2013, 25, 567–576. [Google Scholar]
- Rajan, N.K.; Brower, K.; Duan, X.; Reed, M.A. Limit of detection of field effect transistor biosensors: Effects of surface modification and size dependence. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, J.; Cooper, E.B.; Gaudet, S.; Sorger, P.K.; Manalis, S.R. Electronic detection of DNA by its intrinsic molecular charge. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 14142–14146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentil, C.; Philippin, G.; Bockelmann, U. Signal enhancement in electronic detection of DNA hybridization. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Yan, H.; Lieber, C.M. A nanoscale combing technique for the large-scale assembly of highly aligned nanowires. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halté, C.; Delapierre, G.; Fournier, T.; Buckley, J.; Gely, M.; De Salvo, B.; Baron, T.; Vinet, F. Rapid Top-down Fabrication of Si Nanowire and Fully Automated Test Platform: Application to pH. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Wearable Micro and Nano Technologies for Personalized Health, Valencia, Spain, 21–23 May 2008.
- Accastelli, E.; Cappi, G.; Buckley, J.; Ernst, T.; Guiducci, C. Comparison between front- and back-gating of Silicon Nanoribbons in real-time sensing experiments. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Nanotechnology, Beijing, China, 5–8 August 2013; pp. 517–520.
- Pud, S.; Li, J.; Sibiliev, V.; Petrychuk, M.; Kovalenko, V.; Offenhäusser, A.; Vitusevich, S. Liquid and Back Gate Coupling Effect: Toward Biosensing with Lowest Detection Limit. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergveld, P.; VanHal, R.; Eijkel, J. The Remarkable Similarity between the Acid-Base Properties of ISFETs and Proteins and the Consequences for the Design of ISFET Biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1995, 10, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousse, L.; Bergveld, P. The role of buried OH sites in the response mechanism of inorganic-gate pH-sensitive ISFETs. Sens. Actuators 1984, 6, 65–78, (no A and B in Sensors and Actuators at that time). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, D.E.; Levine, S.; Healy, T.W. Site-binding model of the electrical double layer at the oxide/water interface. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1: Phys. Chem. Condens. Phases 1974, 70, 1807–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergveld, P. Thirty years of ISFETOLOGY—What happened in the past 30 years and what may happen in the next 30 years. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 88, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, W.M.; Cobbold, R. Basic Properties of the Electrolyte-SiO2-Si System—Physical and Theoretical Aspects. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1979, 26, 1805–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, X.T.; GhoshMoulick, R.; Eschermann, J.F.; Stockmann, R.; Offenhaeusser, A.; Ingebrandt, S. Fabrication and application of silicon nanowire transistor arrays for biomolecular detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 144, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossum, J.G.; Yang, J.W.; Trivedi, V.P. Suppression of corner effects in triple-gate MOSFETs. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2003, 24, 745–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Rim, T.; Kim, K.; Lee, U.; Baek, E.; Lee, H.; Baek, C.-K.; Meyyappan, M.; Deen, M.J.; Lee, J.-S. Silicon nanowire ion sensitive field effect transistor with integrated Ag/AgCl electrode: pH sensing and noise characteristics. Analyst 2011, 136, 5012–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuge, J.; Wang, R.; Huang, R.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, L.; Kim, D.-W.; Park, D.; Wang, Y. Investigation of Low-Frequency Noise in Silicon Nanowire MOSFETs. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2009, 30, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoen, E.; Claeys, C. On the flicker noise in submicron silicon MOSFETs. Solid State Electron. 1999, 43, 865–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghibaudo, G.; Roux, O.; Nguyen-Duc, C.; Balestra, F.; Brini, J. Improved Analysis of Low-Frequency Noise in Field-Effect Mos-Transistors. Phys. Status Solidi A Appl. Res. 1991, 124, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, F.J. On the use of windows for harmonic analysis with the discrete Fourier transform. Proc. IEEE 1978, 66, 51–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, J.W. Publisher’s note: Aliasing in 1/f(alpha) noise spectra: Origins, consequences, and remedies. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caloyannides, M.A. Microcycle Spectral Estimates of 1-F Noise in Semiconductors. J. Appl. Phys. 1974, 45, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, S.; Cranch, G.A.; Tikhomirov, A. Experimental evidence for the thermal origin of 1/f frequency noise in erbium-doped fiber lasers. Phys. Rev. A 2009, 79-5, 053802-1–053802-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasdin, N.J. Discrete Simulation of Colored Noise and Stochastic-Processes and 1/F(Alpha) Power-Law Noise Generation. Proc. IEEE 1995, 83, 802–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, N.K.; Routenberg, D.A.; Reed, M.A. Optimal signal-to-noise ratio for silicon nanowire biochemical sensors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 264107-1–264107-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clément, N.; Han, X.L.; Larrieu, G. Electronic transport mechanisms in scaled gate-all-around silicon nanowire transistor arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 263504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regonda, S.; Tian, R.; Gao, J.; Greene, S.; Ding, J.; Hu, W. Silicon multi-nanochannel FETs to improve device uniformity/stability and femtomolar detection of insulin in serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 45, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartagni, M.; Crescentini, M.; Rossi, M.; Morgan, H.; Sangiorgi, E. An AC and phase nanowire sensing for site-binding detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electron Device Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 15–17 December 2014; pp. 31.2.1–31.2.4.
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).