Sensing of Salivary Glucose Using Nano-Structured Biosensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
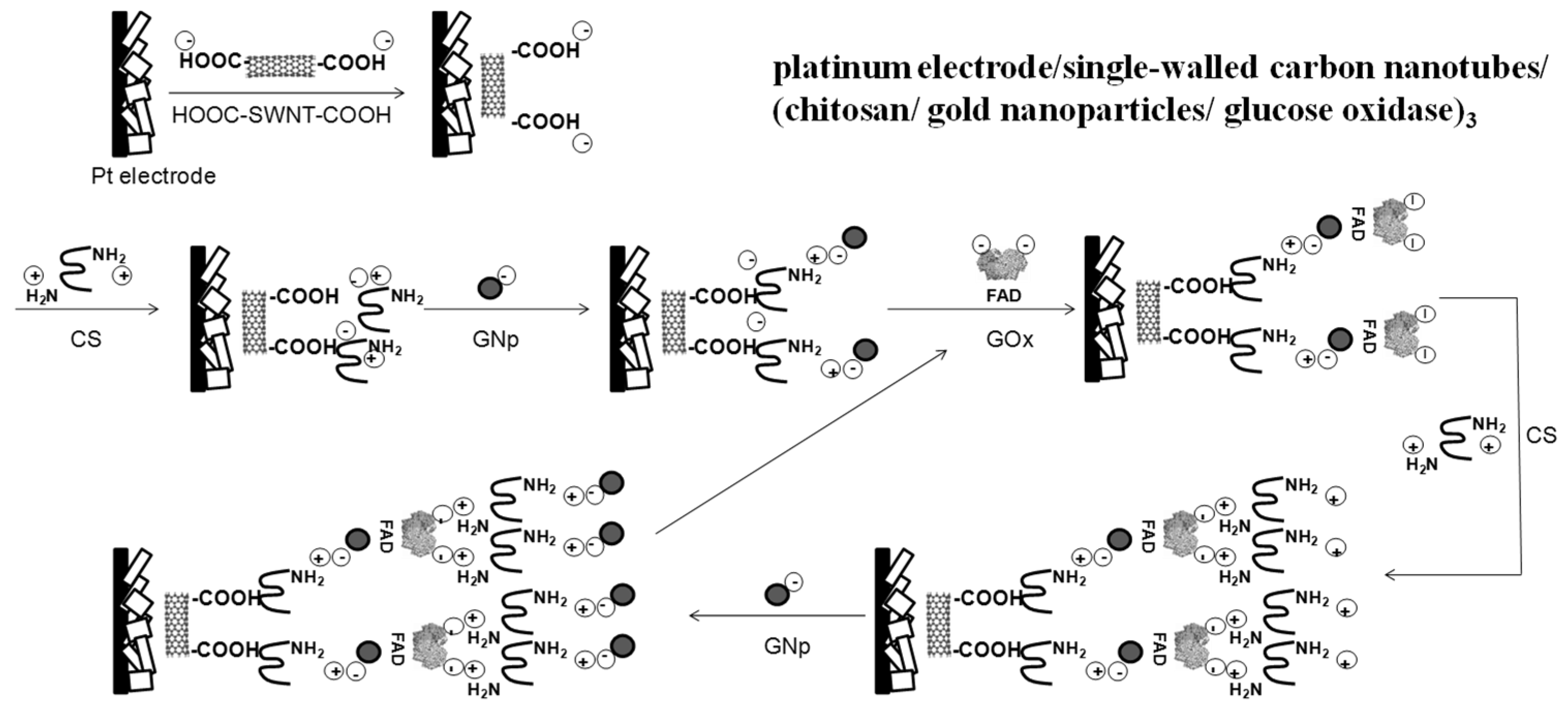
2.1. Sensor Fabrication
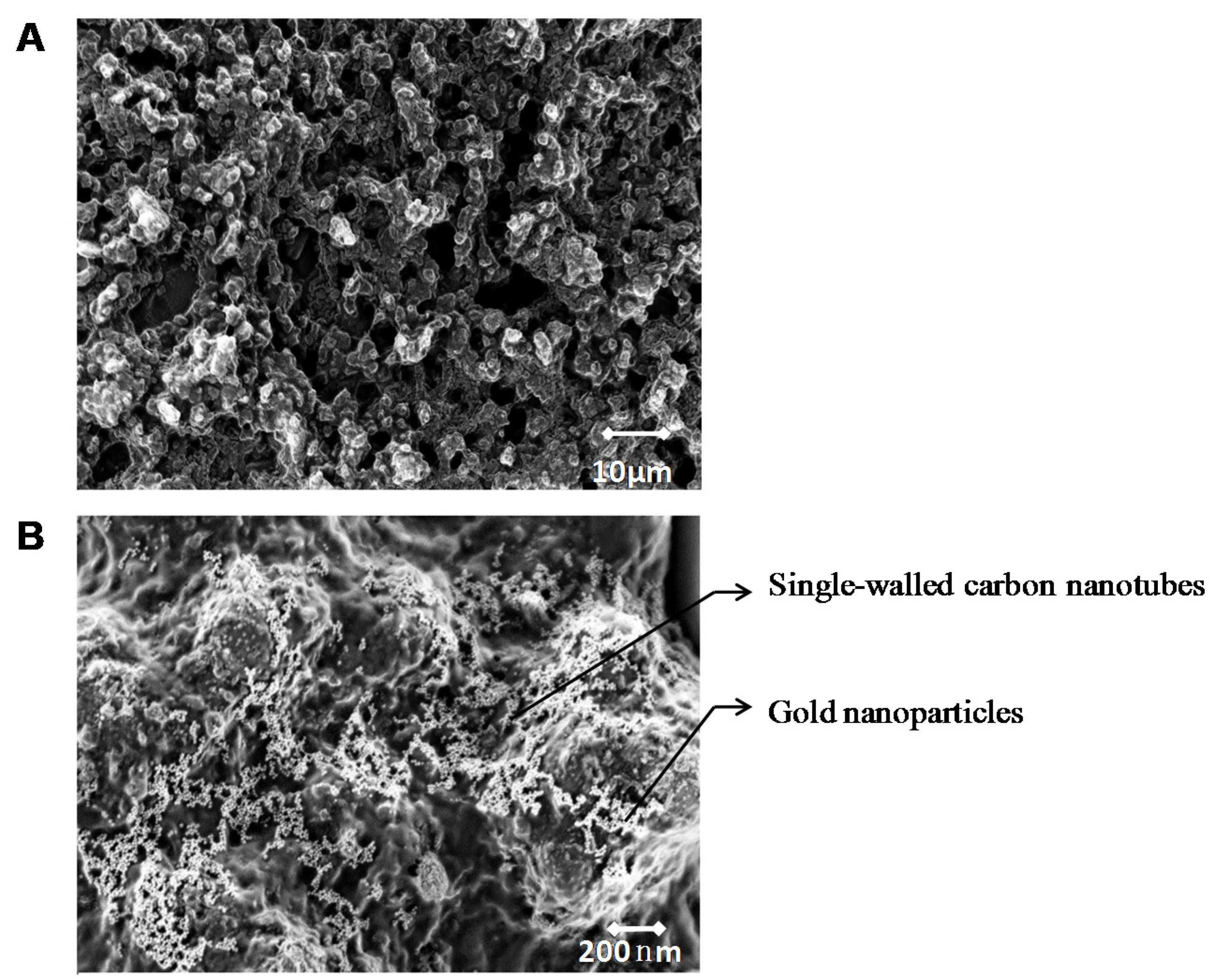
2.2. Micro-Fabrication Imaging
2.3. Sensor Measurement
2.4. Glucose Analysis with Reference Method
2.5. Blood Glucose and Salivary Glucose Monitoring Test
2.6. Saliva Collection Protocol
- (a)
- Wait for 5 min after rinsing mouth with water;
- (b)
- Minimize swallowing and hold saliva in mouth;
- (c)
- Place sterilized dental cotton sponge in mouth and chew until it is soaked with saliva (typically < 1 min);
- (d)
- Deposit sponge into syringe directly from the mouth without touching it to avoid contamination;
- (e)
- Insert plunger into syringe;
- (f)
- Squeeze saliva through pre-installed Westran S 0.2 μm polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane (Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC.) at the bottom of syringe and into sterilized tubes. Usually 1 ml of saliva samples is obtained through this process;
- (g)
- Use pipette to drop 100 μL saliva onto a sensor to cover all three electrodes;
- (h)
- Record measurement;
- (i)
- Dispose of sensor after washing out residual salivary specimen.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Layer-by-Layer Bio-Layer Construction
3.2. Number of Bio-Layers
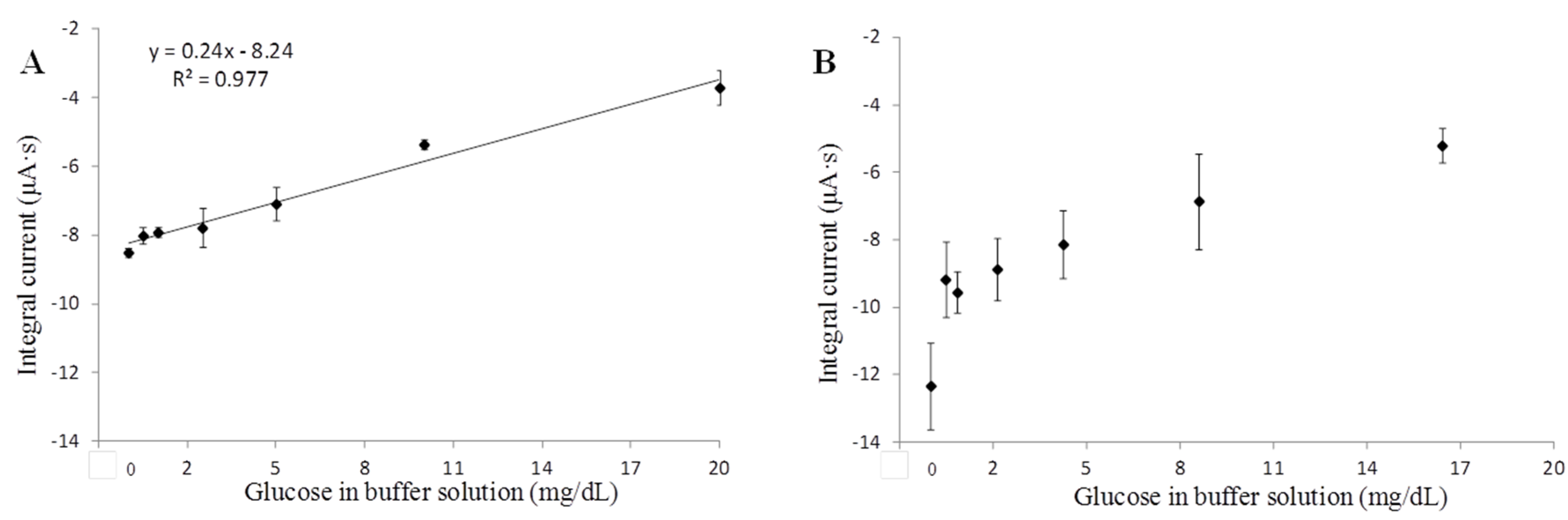
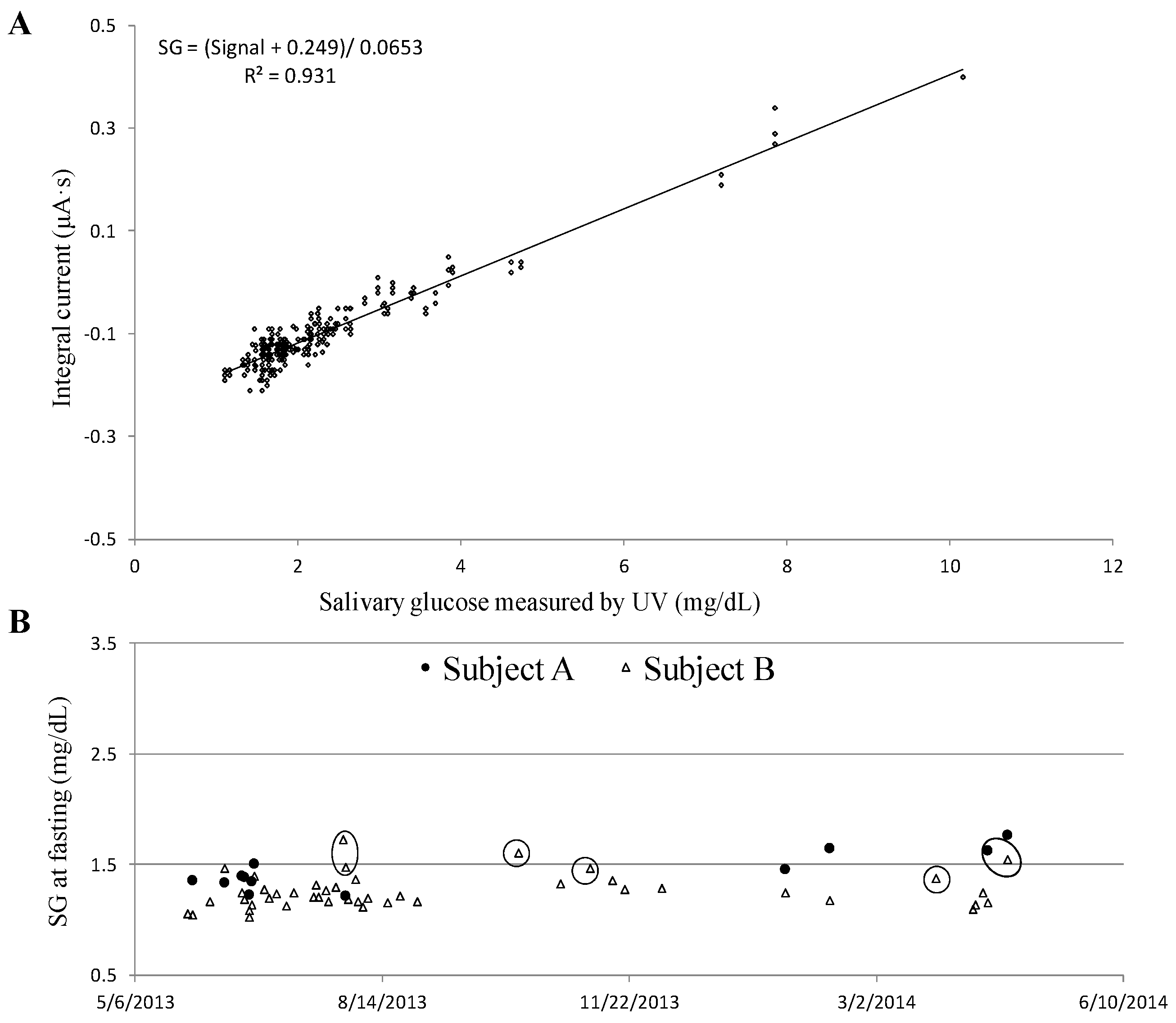
3.3. Glucose Sensing
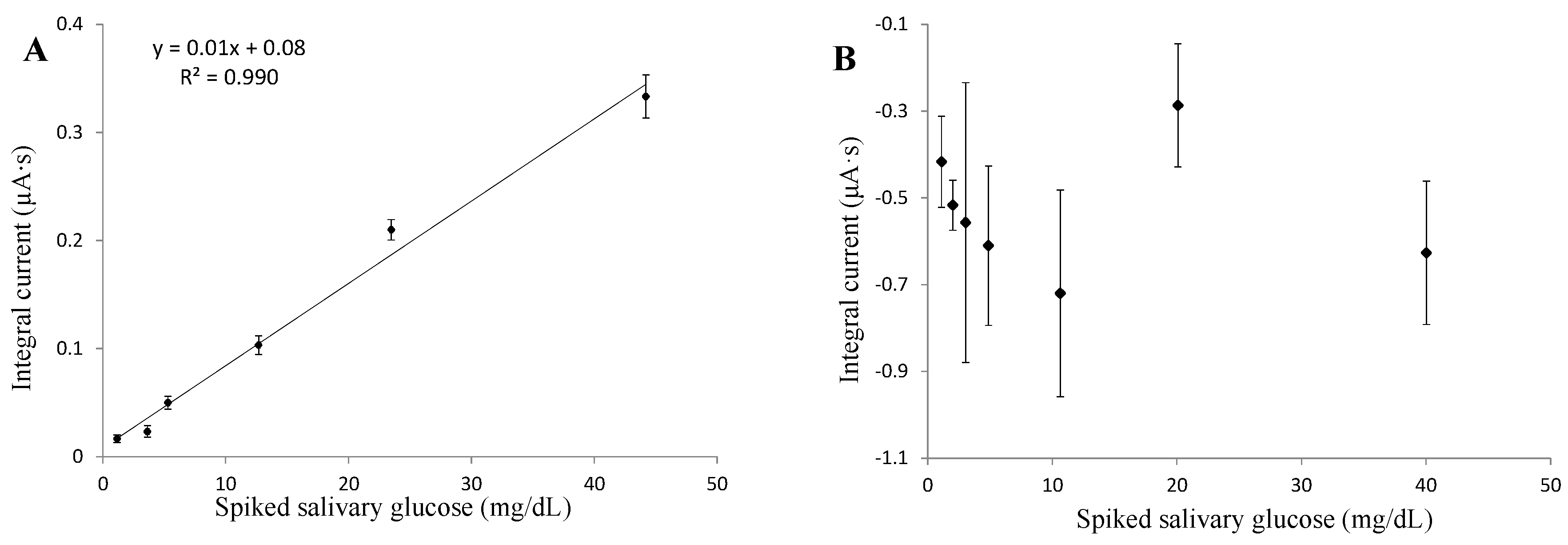
3.4. Glucose in Saliva
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Diabetes Statistics Report. 2014. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pubs/statsreport14/national-diabetes-report-web.pdf (accessed on 30 December 2015).
- Kaufman, E.; Lamster, I.B. The diagnostic application of saliva—A review. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 2002, 13, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, R.P.; Sharma, N.; Rathore, M.S.; Gupta, V.B.; Jain, S.; Agarwal, V.; Goyal, S. Noninvasive method for glucose level estimation by saliva. J. Diabetes Metab. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaii-Dizgah, I.; Mirzaii-Dizgah, M.R.; Mirzaii-Dizgah, M.H. Stimulated saliva glucose as a diagnostic specimen for diabetes mellitus. J. Arch. Mil. Med. 2013, 1, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsumori, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Kano, Y. A new approach to noninvasive measurement of blood glucose using saliva analyzing systems. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual International Conference of the Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Hong Kong, China, 29 October–1 Noverber 1998; pp. 1767–1770.
- Yamaguchi, M.; Mitsumori, M.; Kano, Y. Development of noninvasive procedure for monitoring blood glucose levels using saliva. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual International Conference of the Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Hong Kong, China, 29 October–1 Noverber 1998; pp. 1763–1766.
- Yeh, C.K.; Christodoulides, N.J.; Floriano, P.N.; Miller, C.S.; Ebersole, J.L.; Weigum, S.E.; Floriano, P.N.; Miller, C.S.; Ebersole, J.L.; Weigum, S.E.; et al. Current development of saliva/oral fluid-based diagnostics. Tex. Dent. J. 2010, 127, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zeller, H.; Novak, P.; Landgraf, R. Blood glucose measurement by infrared spectroscopy. Int. J. Artif. Organs 1989, 12, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- D’Auria, S.; Lakowicz, J.R. Enzyme fluorescence as a sensing tool: New perspectives in biotechnology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2001, 12, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Lin, M.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Liang, J.; Yao, H. In vivo blood glucose quantification using raman spectroscopy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mclntosh, T.S.; Davis, H.M.; Matthews, D.E. A liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method to measure stable isotopic tracer enrichments of glycerol and glucose in human serum. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 300, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahjudi, P.N.; Patterson, M.E.; Lim, S.; Yee, J.K.; Mao, C.S.; Lee, W.N. Measurement of glucose and fructose in clinical samples using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Clin. Biochem. 2010, 43, 198–207. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Electrochemical Glucose Biosensors. In Sensors, Biosensors and Their Biomedical Applications, 1st ed.; Zhang, X., Ju, H., Wang, J., Eds.; Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2008; Volume 3, pp. 57–69. [Google Scholar]
- Lubrano, G.J.; Guilbault, G.G. Glucose and l-amino acid electrodes based on enzyme membranes. Anal. Chim. Acta 1978, 97, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, E.H.; Lee, S.Y. Glucose biosensors: An overview of use in clinical practice. Sensors 2010, 10, 4558–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghindilis, L.A.; Atanasov, P.; Wilkins, E. Enzyme-catalyzed direct electron transfer: Fundamentals and analytical applications. Electroanalysis 1997, 9, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida Pdel, V.; Grégio, A.M.; Machado, M.A.; de Lima, A.A.; Azevedo, L.R. Saliva composition and functions: A comprehensive review. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2008, 9, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chou, J.; Tsai, Y.; Cheng, T.; Liao, Y.; Ye, G.; Yang, S. Fabrication of arrayed flexible screen-printed glucose biosensor based on microfluidic framework. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Hong, Y. Amperometric glucose sensor based on coimmobilization of glucose oxidase and poly(p-phenylenediamine) at a platinum microdisk electrode. Anal. Biochem. 2000, 280, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Z.; Deiss, F.; Liu, X.; Akbulut, O.; Whitesides, G.M. Integration of paper-based microfluidic devices with commercial electrochemical readers. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 3169–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Sun, S.; Liu, C.; Wei, S. An amperometric glucose biosensor based on a screen-printed electrode and os-complex mediator for flow injection analysis. Measurement 2011, 44, 1878–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohfuji, K.; Sato, N.; Hamada-sato, N.; Kobayashi, T.; Imada, C.; Okuma, H.; Watanabe, E. Construction of a glucose sensor based on a screen-printed electrode and a novel mediator pyocyanin from pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 19, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berisha, L.; Kalcher, K.; Hajrizi, A.; Arbneshi, T. A new biosensor for glucose based on screen-printed carbon electrodes modified with Tin (IV)-oxide. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 4, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, H.; Sode, K. A disposable electrochemical glucose sensor using catalytic subunit of novel thermostable glucose dehydrogenase. Open Biotechnol. J. 2007, 1, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polan, V.; Soukup, J.; Vytřas, K. Screen-printed carbon electrodes modified by rhodium dioxide and glucose dehydrogenase. Enzyme Res. 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, G.F.; Ohwa, M.; Wernet, W. Design of a stable charge transfer complex electrode for a third-generation amperometric glucose sensor. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 2939–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retama, J.R.; Cabarcos, E.L.; Mecerreyes, D.; López-ruiz, B. Design of an amperometric biosensor using polypyrrole-microgel composites containing glucose oxidase. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 20, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Hung, C.; Ke, J.; Zen, J. An electrochemically preanodized screen-printed carbon electrode for achieving direct electron transfer to glucose oxidase. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 10, 1094–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glucose Colorimetric/Fluorometric Assay Kit. 2014. Available online: http://www.biovision.com/manuals/K606.pdf (accessed on 22 January 2016).
- Du, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, M.L. An on-chip disposable salivary glucose sensor for diabetes control. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Whatman® Westran® PVDF Membranes. 2016. Available online: http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/aldrich/z671010?lang=en®ion=US (accessed on 22 January 2016).
- Costa, R.R.; Mano, J.F. Layer-by-layer self-assembly techniques for nanostructured devices in tissue engineering. In Nanomaterials in Tissue Engineering: Characterization, Fabrication and Applications, 1st ed.; Gaharwar, A.K., Sant, S., Hancock, M.J., Hacking, S.A., Eds.; Woodhead Pulishing Ltd: Cambridge, UK, 2013; Volume 4, pp. 88–118. [Google Scholar]
- Kumara, M.T.; Tripp, B.C.; Muralidharan, S. Layer-by-layer assembly of bioengineered flagella protein nanotubes. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2718–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubner, M.F.; Cohen, R.E. Layer-by-layer processed multilayers: Challenges and opportunities. In Multilayer Thin Films: Sequential Assembly of Nanocomposite Materials, 2nd ed.; Decher, G., Schlenoff, J.B., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2012; Volume 1, pp. 23–41. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, Y. Direct electron transfer of glucose oxidase promoted by carbon nanotubes is without value in certain mediator-free applications. Microchim. Acta 2012, 176, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andzane, J.; Tobin, J.M.; Li, Z.; Prikulis, J.; Baxendale, M.; Olin, H.; Holmes, J.D.; Erts, D. Selection of application specific single and multi walled carbon nanotubes by in situ characterization of conductive and field emission properties. AZojono-J. Nanotechnol. Online 2007, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.L.; Wang, J.N. Chemical sensing sensitivity of long-period grating sensor enhanced by colloidal gold nanoparticles. Sensors 2008, 8, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, M.L. Saliva Glucose Monitoring System. U.S. Patent US 14/153.647, 17 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Du, Y.; Wang, M.L. Noninvasive glucose monitoring using saliva nano-biosensor. Sens. Biosens. Res. 2015, 4, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Du, Y.; Wang, M.L. On-chip ultra-sensitive glucose sensing using multilayer films composed of single-walled carbon nanotubes-gold nanoparticles-and glucose oxidase. Sens. Biosens. Res. 2015, 4, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Petkova, G.A.; Záruba, C.K.; Zvátora, P.; Král, V. Gold and silver nanoparticles for biomolecule immobilization and enzymatic analysis. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Product Information. 2002. Available online: http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/content/dam/sigma-aldrich/docs/Sigma/Product_Information_Sheet/2/g6125pis.pdf (accessed on 22 January 2016).
- Ma, S.; Mu, J.; Qu, Y.; Jiang, L. Effect of refluxed sliver nanoparticles on inhibition and enhancement of enzymatic activity of glucose oxidase. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 345, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzgas, T.; Csöregi, E.; Emnéus, J.; Gorton, L.; Marko-Varga, G. Peroxidase-modified electrodes: Fundamentals and application. Anal. Chim. Acta 1996, 330, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paloma, Y.; Jordi, R.; Jose, M.P.; Xavier, R. Electrochemical sensing based on carbon nanotubes. Trends Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 939–953. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, M.; Maxwell, S.; Vogt, B.D.; La-Belle, J.T. Mesoporous carbon amperometric glucose sensors using inexpensive, commercial methacrylate-based binders. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 738, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diagnosing Diabetes and Learning about Prediabetes. 2014. Available online: http://www.diabetes.org/diabetes-basics/diagnosis/ (accessed on 2 March 2016).
- Bower, B.F.; Moore, R.E. The interpretation of laboratory tests 97 György Abel and Michael Laposata. In Clinical Laboratory Medicine, 2nd ed.; McClatchey, K.D., Ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Maywood, IL, USA, 2002; p. 339. [Google Scholar]


| Substrate | Electrode | Immobilization Method | Detection Range (mg/dL) | Reponse Time (Second) | Specimen | Generation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET | RuO2 | GOx /Nafion | 100–400 | 100 | buffer | 1st | [18] |
| PPy | Pt | PPD/GOx | 9–540 | N/A | buffer | 1st | [19] |
| Paper | Graphite | ferricyanide/GOx | up to 500 | 60 | buffer | 2nd | [20] |
| blood | |||||||
| PC | Graphite | HRP/PEGDGE/GOx | 9–540 | N/A | buffer | 2nd | [21] |
| /glutaraldehyde/BSA | |||||||
| PET | Carbon | pyocyanin/GOx | 18–360 | 120 | buffer | 2nd | [22] |
| soft drinks | |||||||
| Ceramic | Carbon | Tin(IV) oxide/GOx/Nafion | up to 200 | N/A | blood | 2nd | [23] |
| Unknown | Carbon | Rucoplex | 100–800 | 2 | blood | 2nd | [24] |
| /Ru(NH3)6Cl3 or K3Fe(CN)6 | |||||||
| /FADGDH/GOx | |||||||
| Ceramic | Carbon | Rhodium dioxide/ | 2nd | [25] | |||
| m-phenylenediamine/GOx | 10–500 | 25 | honey | ||||
| GDH/GOx/Nafion | 10–200 | 120 | |||||
| glutaraldehyde/BSA/GOx | 10–200 | 30 | syrup | ||||
| cellulose acetate/Nafion/GOx | 10–200 | 240 | |||||
| pyrrole/GOx | 50–250 | 35 | |||||
| Unknown | SEC | CTC/GOx/gel | 18–720 | N/A | buffer | 3rd | [26] |
| Ceramic | Pt | PPy-polystyrensulfonate | up to 180 | 11 | serum | 3rd | [27] |
| /PA/GOx | |||||||
| Aluminum | Carbon | CNT/GOx/Nafion | 1.8–16.2 | 20 | buffer | 3rd | [28] |
| Ceramic | Pt | SWNT/(chitosan/gold | 0.5–20 | 30 | buffer | 3rd | Current study |
| nanoparticles/GOx)3 | 1.1–45 | saliva |
| Amperometric Test | Pt/SWNT/(CS/GNp/GOx)3 | Pt/(CS/GNp/GOx)3 |
|---|---|---|
| Detection range (glucose in PBS) | 0–20 mg/dL | 0–20 mg/dL |
| a Repeatability | <10% | <20% |
| b Limit of detection (LOD) | 0.41 mg/dL | 4.94 mg/dL |
| c linearity | 0.98 | 0.78 |
| Subjects | Gender | Age | BG (mg/dL) | SG (mg/dL) | BG/SG Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | female | 20s | 92.7 | 1.43 | 64.8 |
| B | female | 20s | 85.2 | 1.22 | 69.8 |
| C | male | 40s | 96.5 | 1.39 | 69.6 |
| D | male | 50s | 114.6 | 1.99 | 57.6 |
| E | male | 50s | 108 | 2.4 | 45 |
| F | male | 50s | 101 | 1.46 | 69.2 |
| G | male | 50s | 99.7 | 1.43 | 69.7 |
| H | male | 20s | 91.6 | 1.55 | 59.1 |
| I | male | 20s | 100.3 | 1.73 | 58 |
| J | female | 20s | 91.6 | 1.05 | 87.2 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, M.L. Sensing of Salivary Glucose Using Nano-Structured Biosensors. Biosensors 2016, 6, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6010010
Du Y, Zhang W, Wang ML. Sensing of Salivary Glucose Using Nano-Structured Biosensors. Biosensors. 2016; 6(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Yunqing, Wenjun Zhang, and Ming L. Wang. 2016. "Sensing of Salivary Glucose Using Nano-Structured Biosensors" Biosensors 6, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6010010
APA StyleDu, Y., Zhang, W., & Wang, M. L. (2016). Sensing of Salivary Glucose Using Nano-Structured Biosensors. Biosensors, 6(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6010010






