Modified Electrodes Used for Electrochemical Detection of Metal Ions in Environmental Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
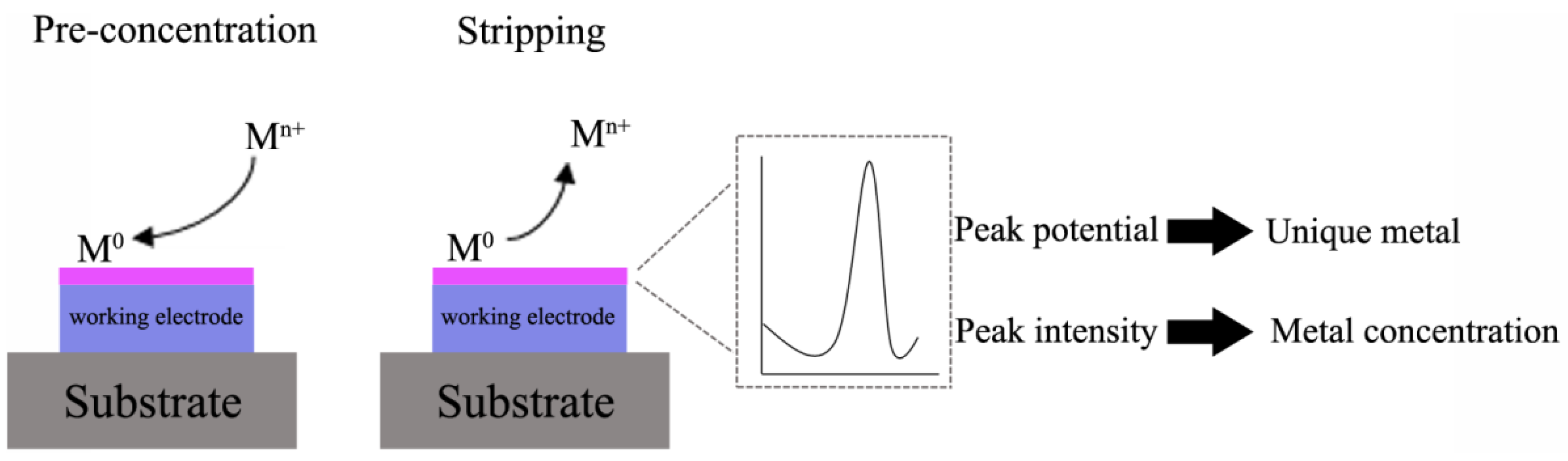
2. Generalities on Stripping Voltammetry
| Metals that can be determined by Anodic Stripping Voltammetry | ||
| Antimony | Gallium | Mercury |
| Arsenic | Germanium | Silver |
| Bismuth | Manganese | Thallium |
| Cadmium | Indium | Tin |
| Copper | Lead | Zinc |
| Species that can be determined by Cathodic Stripping Voltammetry | ||
| Arsenic | Iodide | Mercaptans |
| Chloride | Selenium | Thiocyanate |
| Bromide | Sulfide | Thio compounds |
| Metals that can be determined by Adsorptive Stripping Voltammetry | ||
| Aluminum | Nickel | Uranium |
| Cobalt | Chromium | Iron |
3. Electrode Materials
3.1. Mercury Electrodes
3.2. Gold and Silver Electrodes
3.3. Gold Nanoparticles-Modified Electrodes
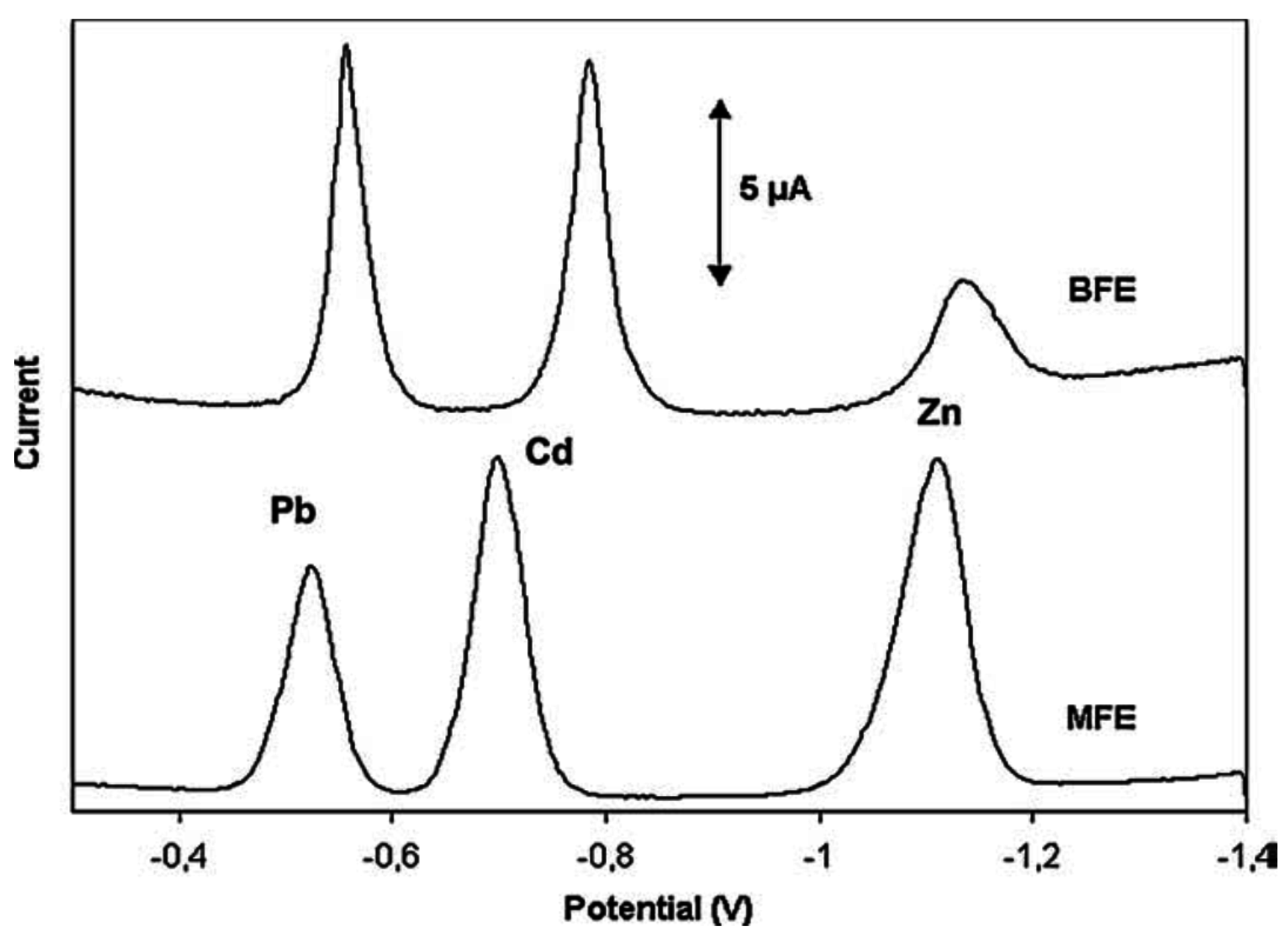
3.4. Bismuth Film Electrodes
| Medium | pH | Anodic Limit (V) | Cathodic Limit (V) | Potential Window (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1M HClO4 | 1.00 | −0.05 | −1.05 | 1.10 |
| 0.2M acetate buffer | 4.24 | −0.25 | −1.25 | 1.00 |
| 0.1 M NaOH | 12.17 | −0.55 | −1.55 | 1.00 |
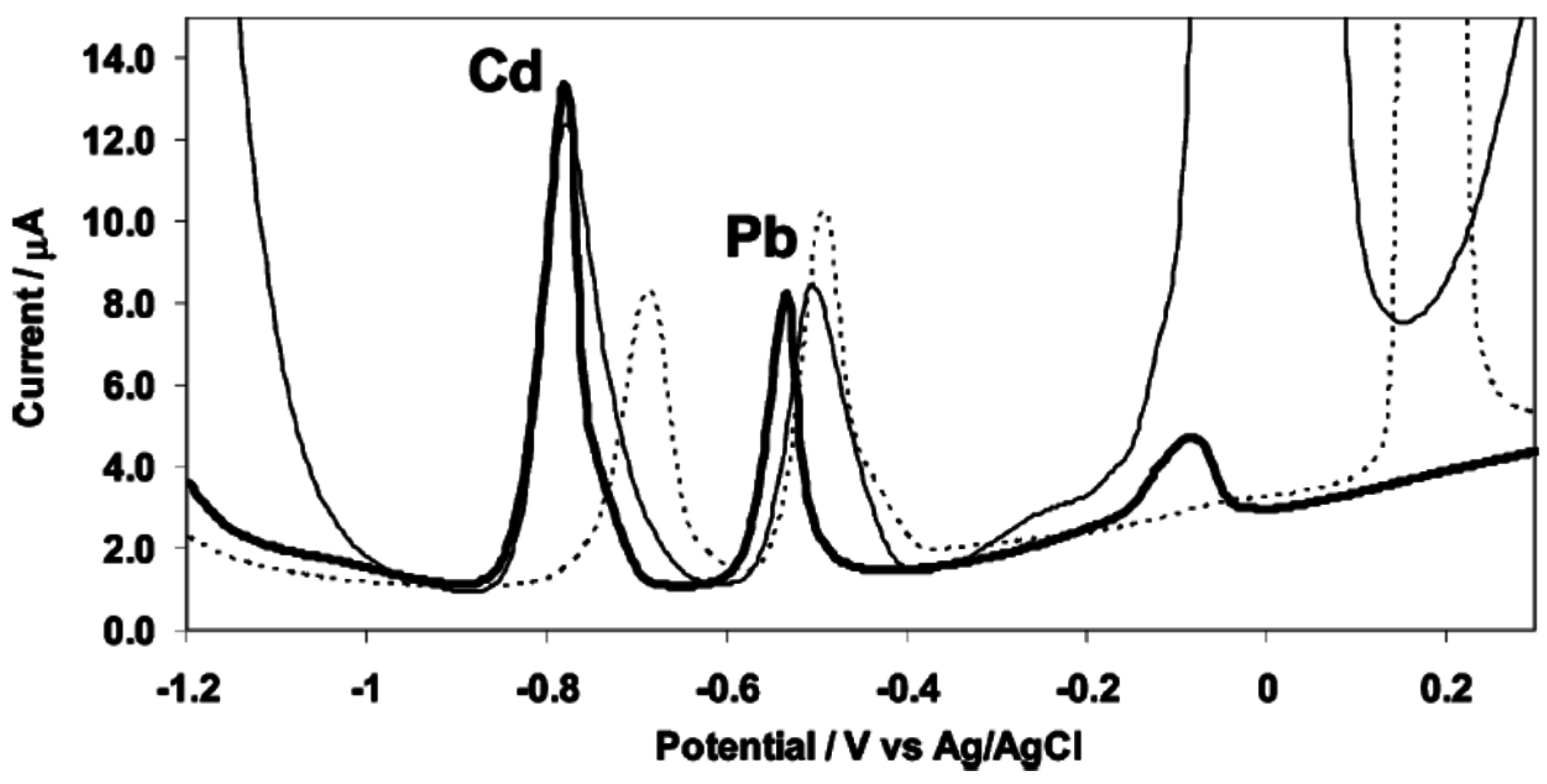
3.5. Antimony Film Electrodes
3.6. Bore Doped Diamond (BDD)
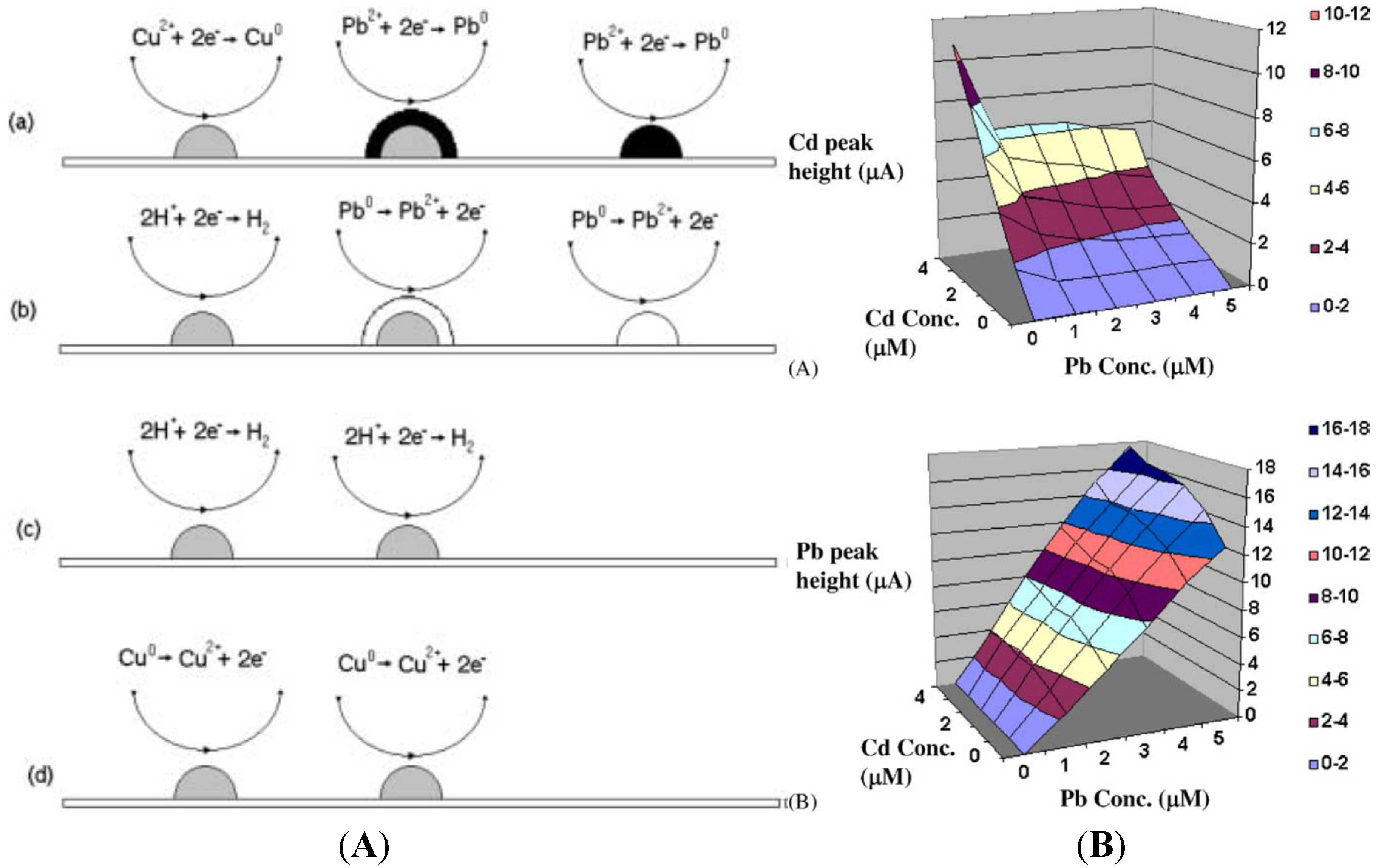
3.7. Diamond Like Carbon
4. Conducting Polymer-Modified Electrodes
4.1. Unmodified Conducting Polymers
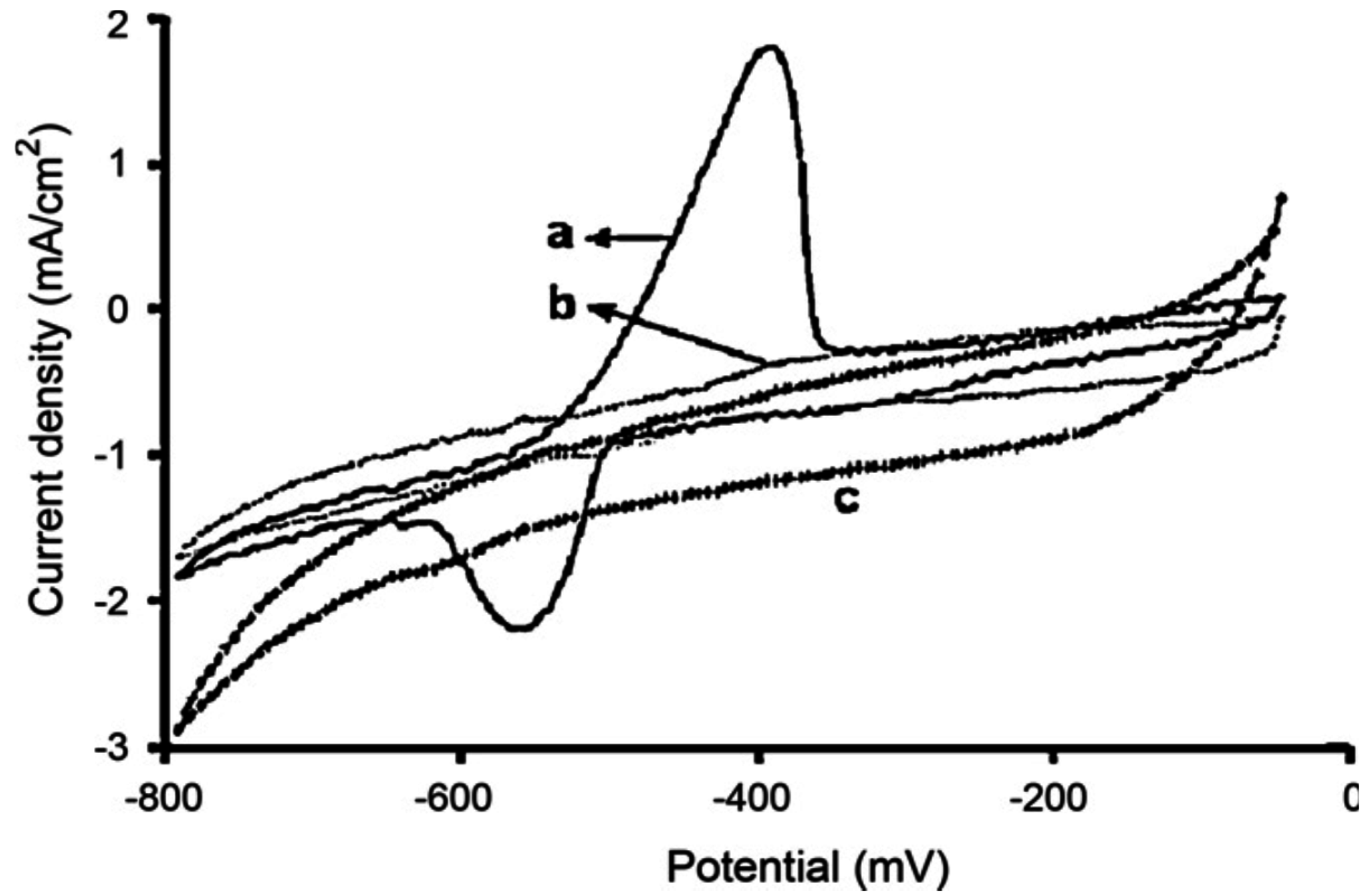
4.2. Modified Conducting Polymers
4.2.1. Doping and Copolymerization
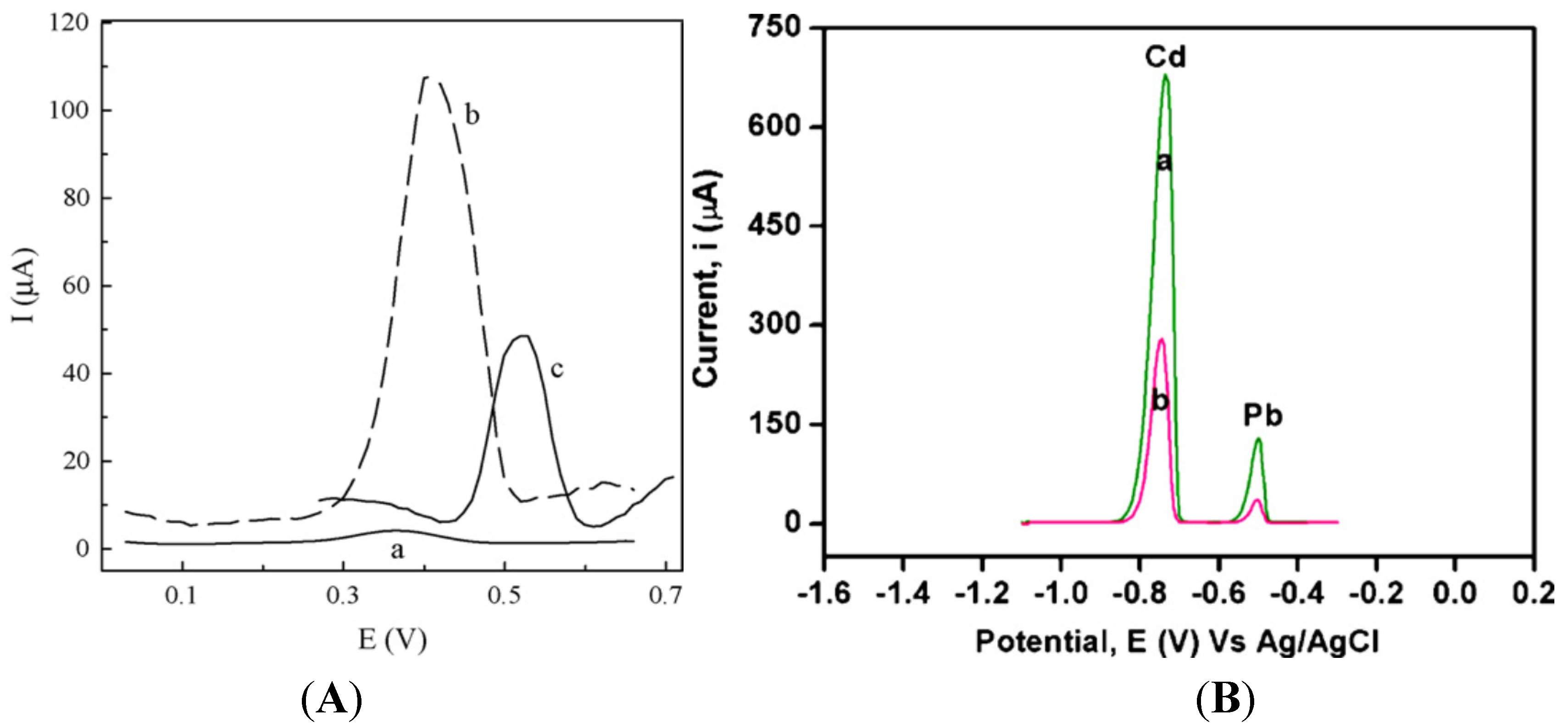
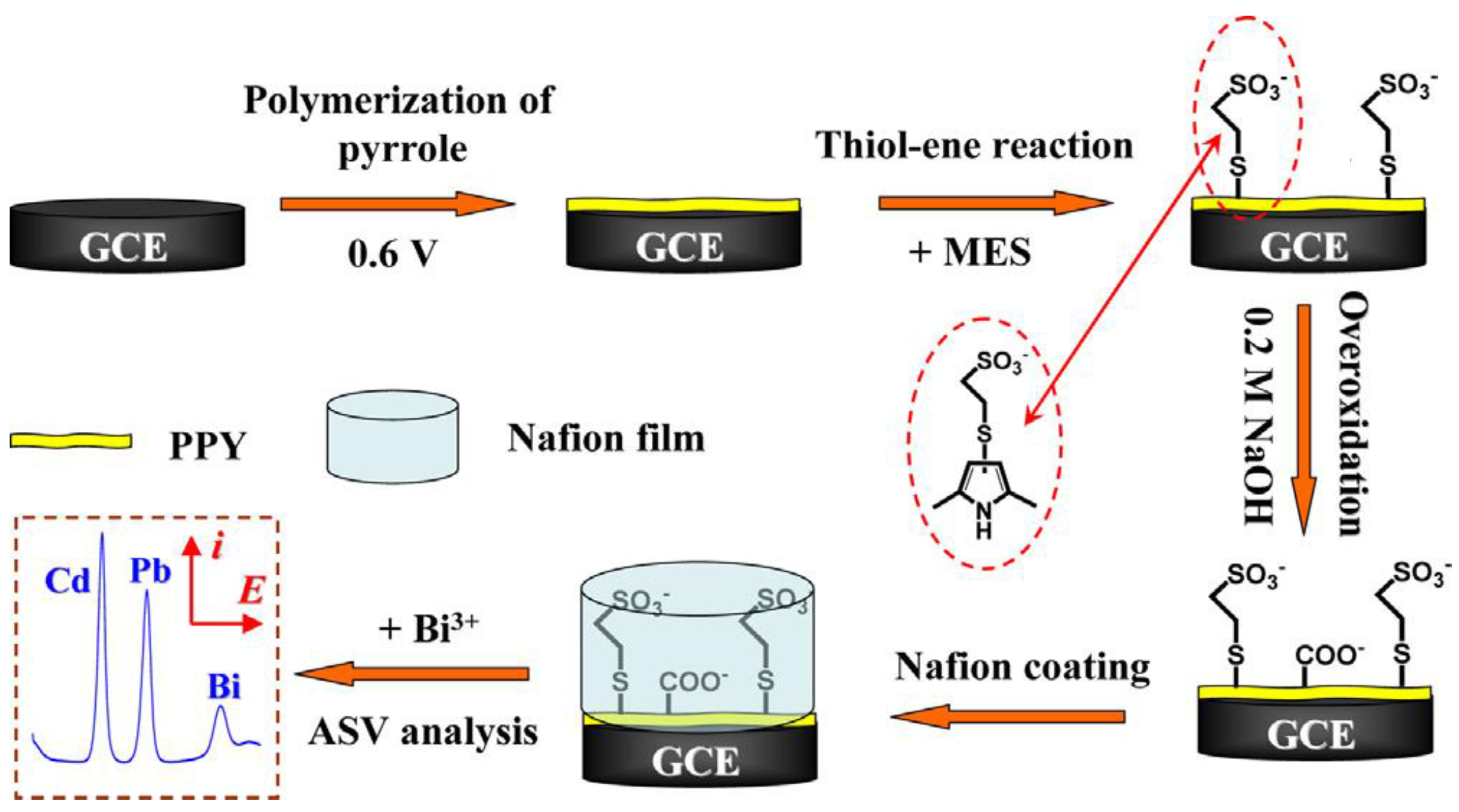
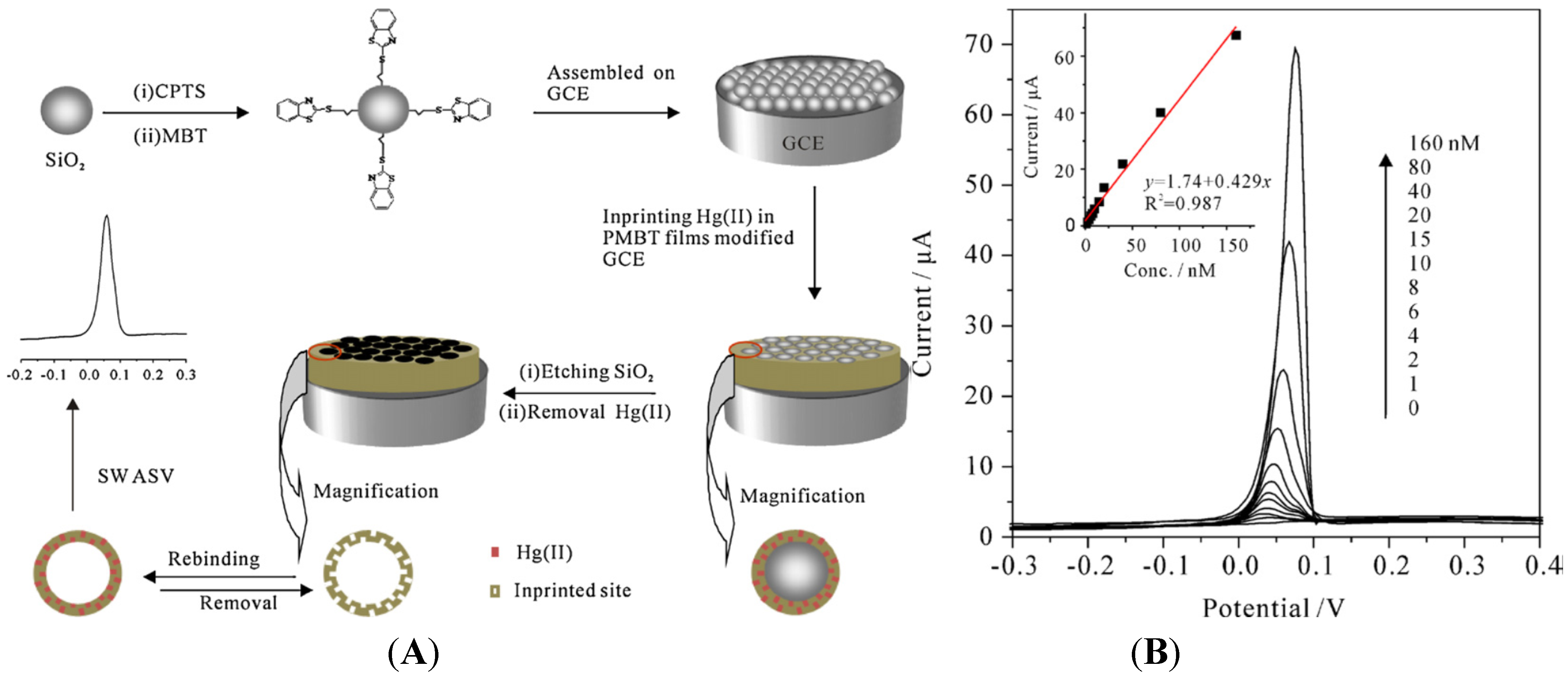
4.2.2. Grafting of a Complexing Agent
4.2.3. CNT-Modified Conducting Polymers
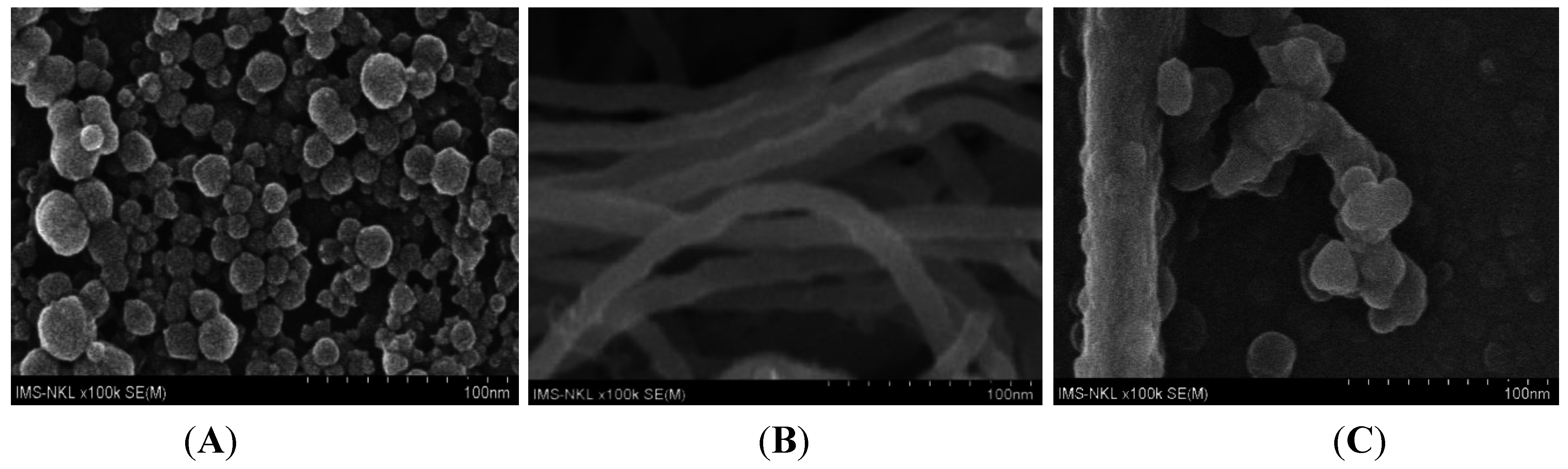
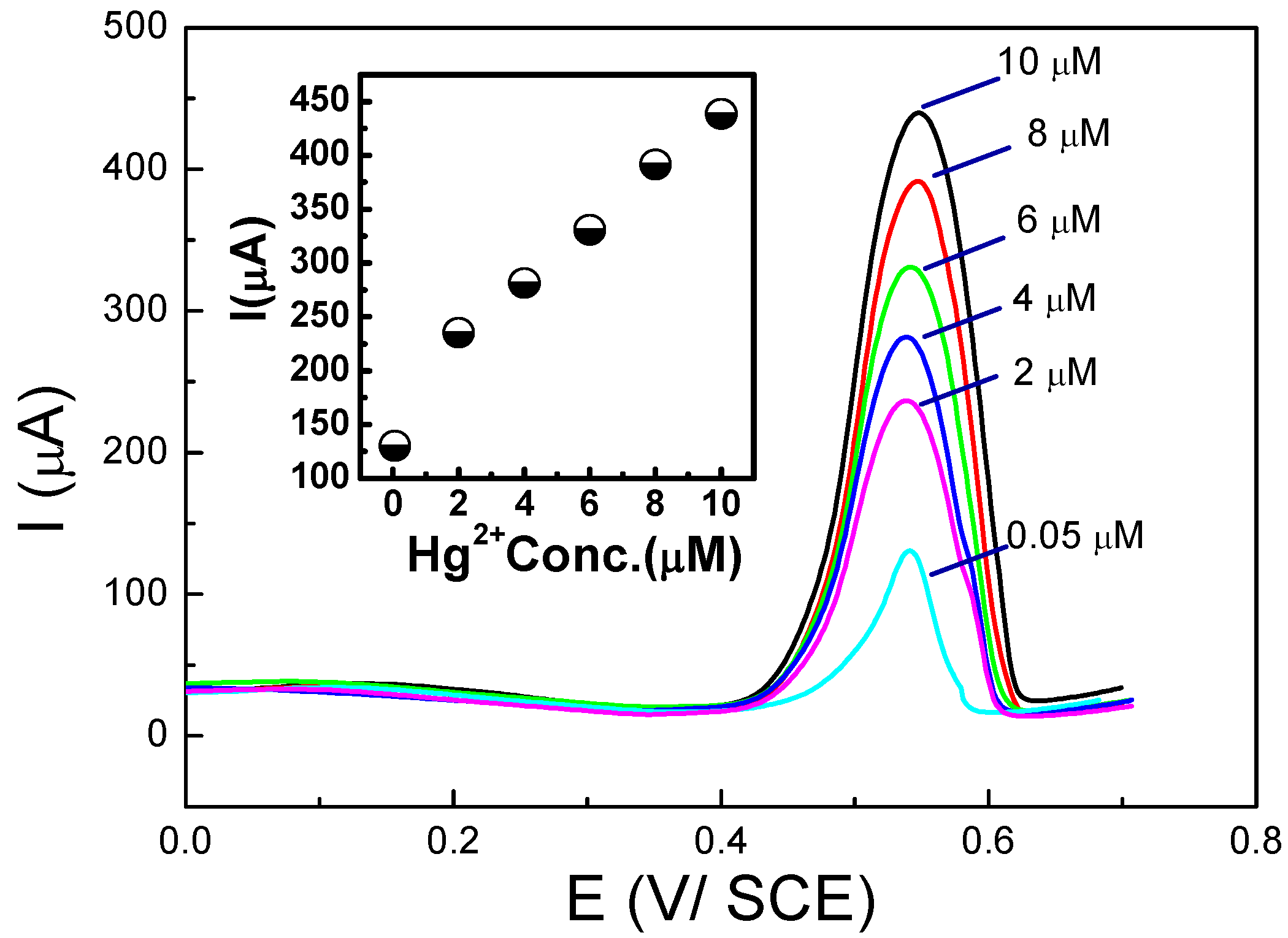
5. Electrodes Modified by Biomolecules
5.1. Enzymes

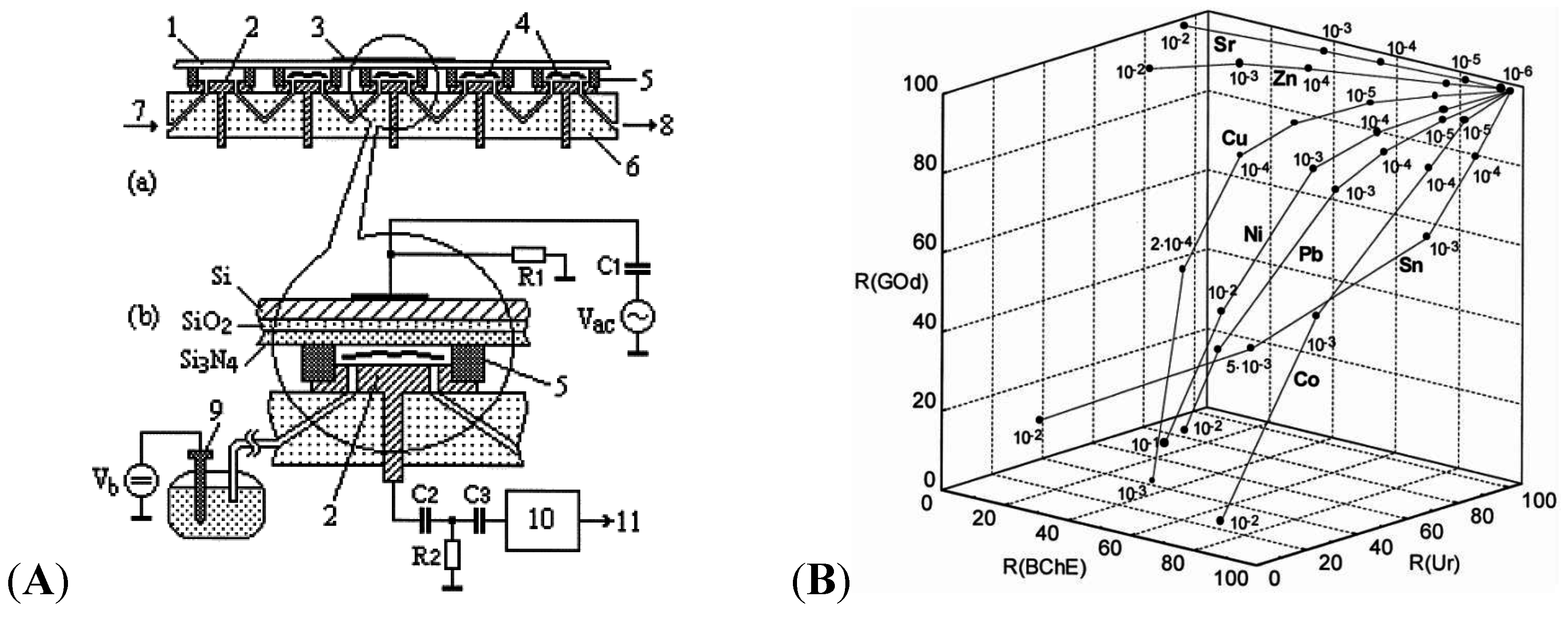
5.2. DNA
5.2.1. (T-Hg2+-T) Coordination Based Sensors
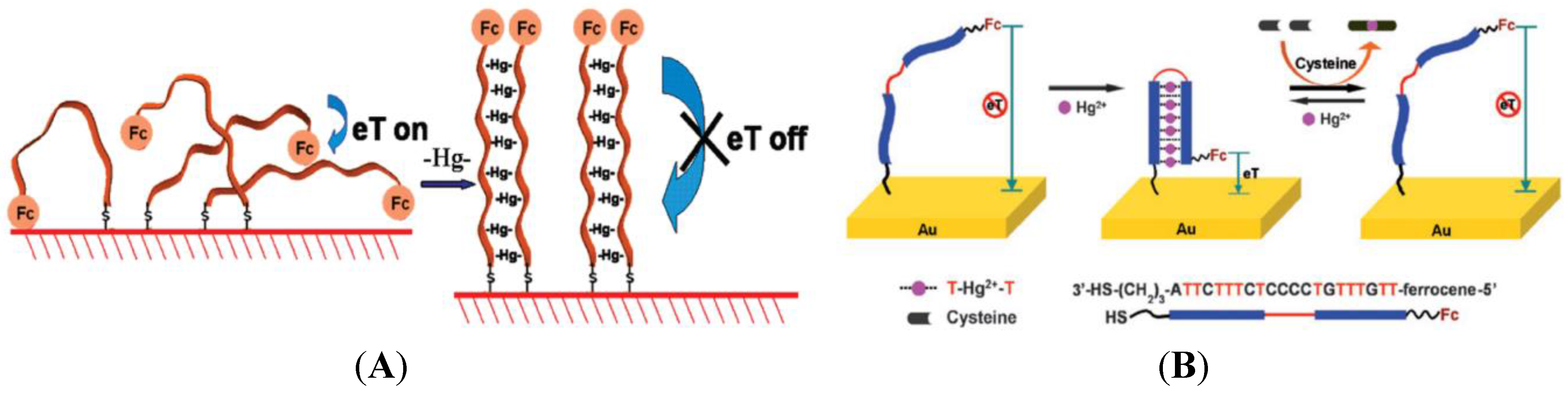
5.2.2. DNAzymes-Based Sensors
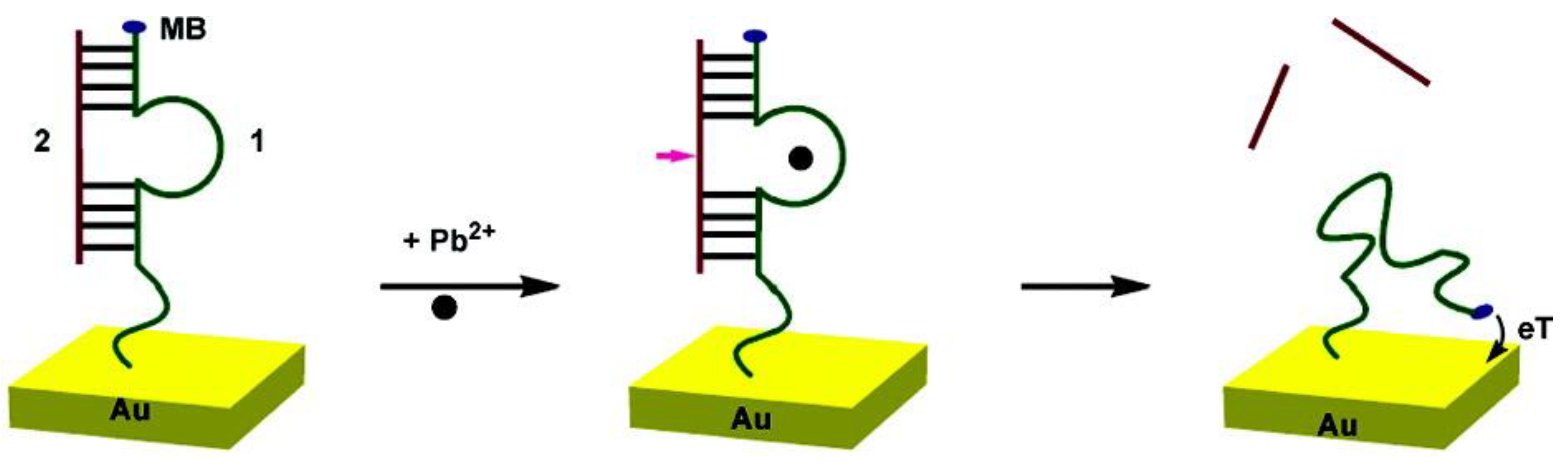
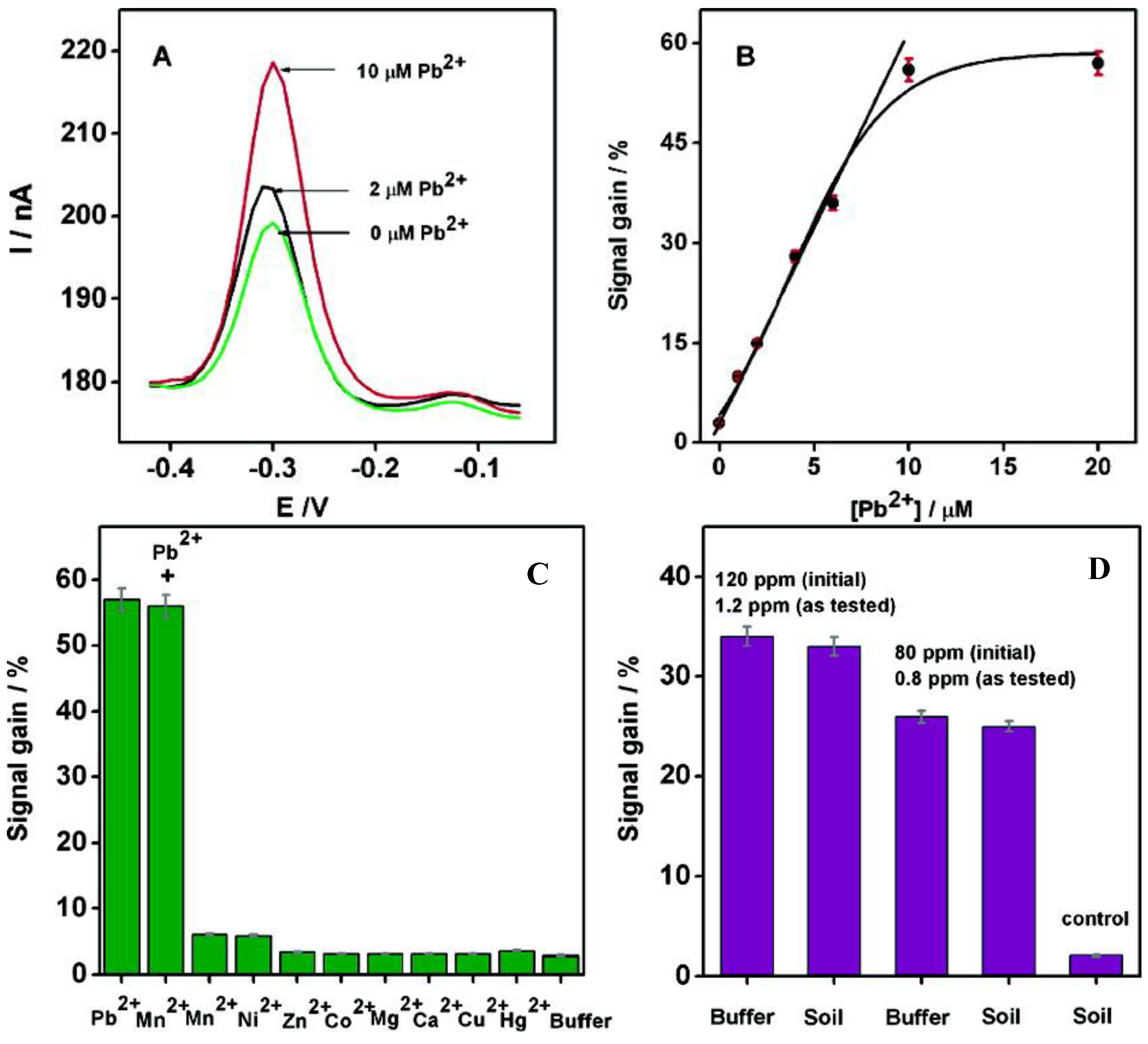
5.2.3. G-Quadruplex-Based Sensors
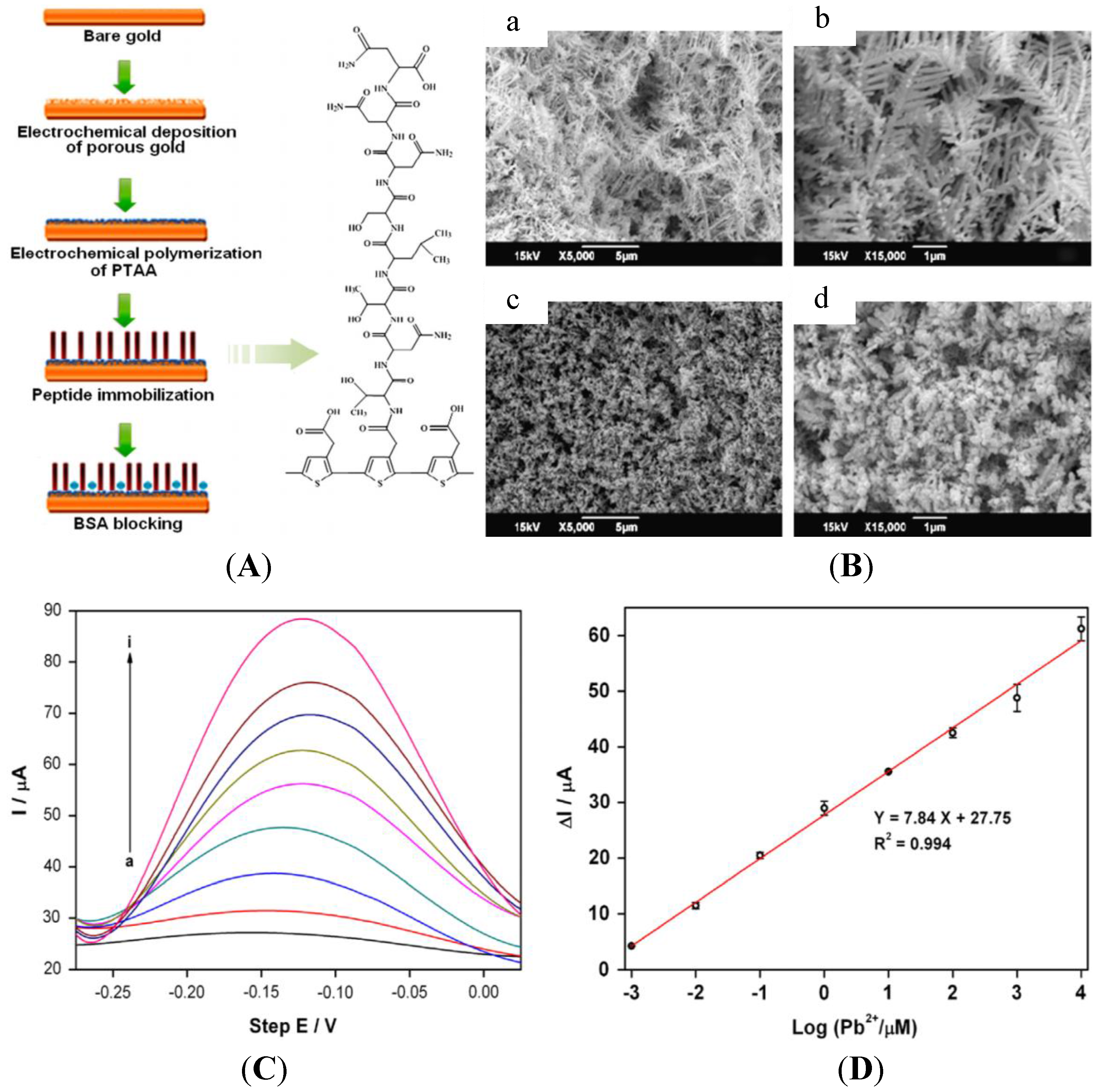
5.3. Peptides

5.4. Whole Cells


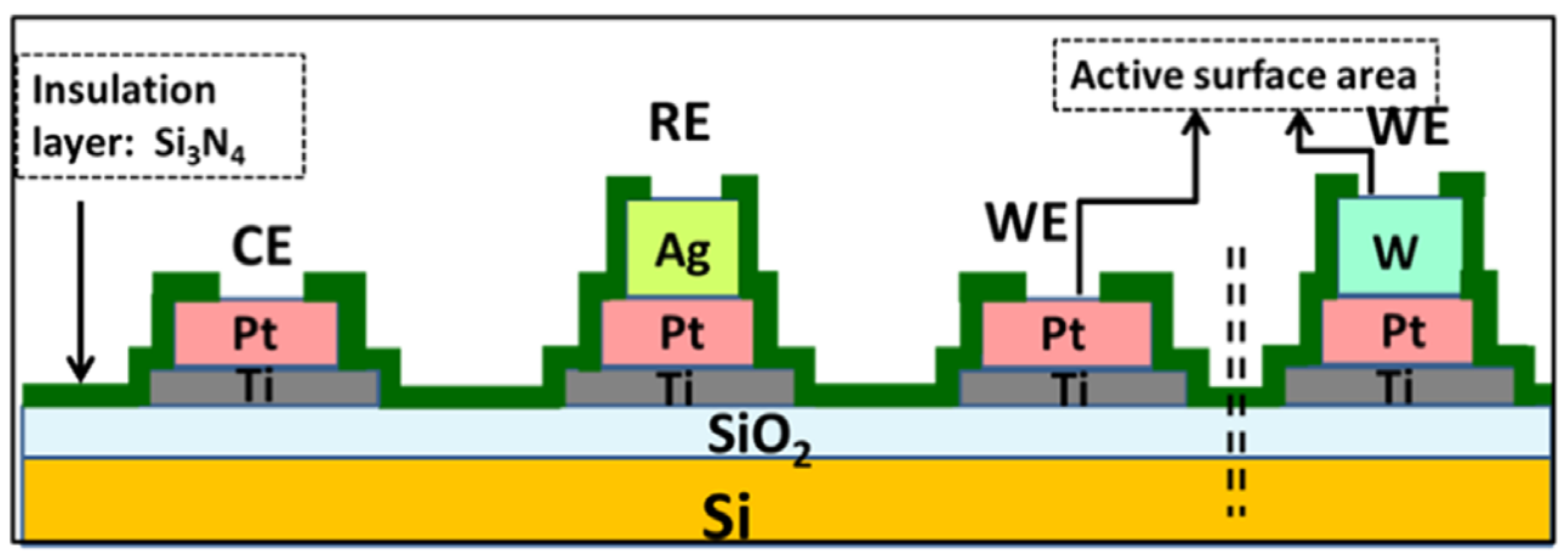

6. Conclusions and Perspectives
| Techniques | Advantages | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Metallic or carbon electrodes | Sub-ppb detection Easily miniaturisable On-field detection | Lack of specificity Lack of reproducibility Formation of intermetallic compounds Formation of biofilms and fouling |
| Chemically modified electrodes with CPs | Sub-ppb detection Specificity Anti-fouling | Sensibility Stability |
| Electrodes modified with biomolecules | Specificity | Costs Long-term stability Not yet available for on-field detection |
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Durkalec, M.; Szkoda, J.; Kolacz, R.; Opalinski, S.; Nawrocka, A.; Zmudzki, J. Bioaccumulation of lead, cadmium and mercury in roe deer and wild boars from areas with different levels of toxic metal pollution. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2015, 9, 205–212. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, E.H.; Day, J.A.; Palmer, C.D.; Price, W.J.; Smith, C.M.M.; Tyson, J.F. Atomic spectrometry update. Advances in atomic emission, absorption, and fluorescence spectrometry, and related techniques. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2005, 20, 562–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-Bayon, M.; DeNicola, K.; Caruso, J.A. Liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1000, 457–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Adeloju, S.B. Coupling of non-selective adsorption with selective elution for novel in-line separation and detection of cadmium by vapour generation atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 2015, 137, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, C.F.; Clough, R.; Drennan-Harris, L.R.; Hill, S.J.; Tyson, J.F. Atomic spectrometry update. Elemental speciation. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2011, 26, 1561–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, S.A.; Sharma, A.C.; Goponenko, A.V.; Ward, M.M. Photonic crystal aqueous metal cation sensing materials. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 1676–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunbabu, D.; Sannigrahi, A.; Jana, T. Photonic crystal hydrogel material for the sensing of toxic mercury ions (Hg2+) in water. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 2592–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Li, W.; Hu, X.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, D. Highly sensitive colorimetric sensing for heavy metal ions by strong polyelectrolyte photonic hydrogels. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 17193–17201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Zhang, J.T.; Xue, F.; Hong, Z.; Punihaole, D.; Asher, S.A. 2D Photonic Crystal Protein Hydrogel Coulometer for Sensing Serum Albumin Ligand Binding. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 4840–4847. [Google Scholar]
- Hutton, E.A.; van Elteren, J.T.; Ogorevc, B.; Smyth, M.R. Validation of bismuth film electrode for determination of cobalt and cadmium in soil extracts using ICP–MS. Talanta 2004, 63, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzitheodorou, E.; Economou, A.; Voulgaropoulos, A. Trace determination of chromium by square-wave adsorptive stripping voltammetry on bismuth film electrodes. Electroanalysis 2004, 16, 1745–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefala, G.; Economou, A.; Sofoniou, M. Determination of trace aluminium by adsorptive stripping voltammetry on a preplated bismuth-film electrode in the presence of cupferron. Talanta 2006, 68, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Hao, H.; Chen, Y.; Wan, P. Preparation of a preplated bismuth film on Pt electrode and its application for determination of trace aluminum(iii) by adsorptive stripping voltammetry. Electroanalysis 2011, 23, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, V.; Zehnalek, J.; Petrlova, J.; Potesil, D.; Sures, B.; Trnkova, L.; Kizek, R. Phytochelatin modified electrode surface as a sensitive heavy-metal ion biosensor. Sensors 2005, 5, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonil, Y.; Brand, M.; Kirowa-Eisner, E. Determination of sub-μg·L−1 concentrations of copper by anodic stripping voltammetry at the gold electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 1999, 387, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfil, Y.; Brand, M.; Kirowa-Eisner, E. Characteristics of subtractive anodic stripping voltammetry of Pb and Cd at silver and gold electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 464, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, M.; Eshkenazi, I.; Kirowa-Eisner, E. The Silver electrode in square-wave anodic stripping voltammetry. Determination of Pb2+ without removal of oxygen. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 4660–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirowa-Eisner, E.; Brand, M.; Tzur, D. Determination of sub-nanomolar concentrations of lead by anodic-stripping voltammetry at the silver electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 1999, 385, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfil, Y.; Kirowa-Eisner, E. Determination of nanomolar concentrations of lead and cadmium by anodic-stripping voltammetry at the silver electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 457, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simm, A.; Banks, C.; Compton, R.G. Sonoelectroanalytical detection of ultra-trace arsenic. Electroanalysis 2005, 17, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simm, A.; Banks, C.; Compton, R.G. The electrochemical detection of Arsenic(III) at a silver electrode. Electroanalysis 2005, 17, 1727–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Okajima, T.; Ohsaka, T. Selective detection of As(III) at the Au(111)-like polycrystalline gold electrode. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 9169–9176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Swain, G. Total inorganic arsenic detection in real water samples using anodic stripping voltammetry and a gold-coated diamond thin-film electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 593, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, C.; Nekrassova, O.; Compton, R.G. Reduction of hexavalent chromium at solid electrodes in acidic media: Reaction mechanism and analytical applications. Talanta 2005, 65, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kachoosangi, R.T.; Compton, R.G. Voltammetric determination of Chromium(VI) using a gold film modified carbon composite electrode. Sens. Actuators B 2013, 178, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Nekrassova, O.; Hyde, M.E.; Compton, R.G. Anodic stripping voltammetry of Arsenic(III) using gold nanoparticle-modified electrodes. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 5924–5929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jena, B.K.; Raj, C.R. Gold Nanoelectrode ensembles for the simultaneous electrochemical detection of ultratrace arsenic, mercury, and copper. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 4836–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jena, B.K.; Raj, C.R. Highly sensitive and selective electrochemical detection of sub-ppb level chromium (VI) using nano-sized gold particle. Talanta 2008, 76, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardegan, A.; Scopece, P.; Lamberti, F.; Meneghetti, M.; Moretto, L.M.; Ugo, P. Electroanalysis of trace inorganic arsenic with gold nanoelectrode ensembles. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, J.M.; Hocevar, S.B.; Farias, P.A.M.; Ogorevc, B. Bismuth-coated carbon electrodes for anodic stripping voltammetry. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 3218–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lu, J.; Kirgöz, U.A.; Hocevar, S.B.; Ogorevc, B. Insights into the anodic stripping voltammetric behavior of bismuth film electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 434, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, N.; Alberich, A.; Diaz-Cruz, J.M.; Arino, C.; Esteban, M. Coating methods, modifiers and applications of bismuth screen-printed electrodes. TrAC. Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 46, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, J.M.; Hocevar, S.B.; Ogorevc, B. Bismuth-coated screen-printed electrodes for stripping voltammetric measurements of trace lead. Electroanalysis 2001, 13, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, M.O.; de Suza, A.P.R.; Naozuka, J.; de Oliveira, P.V.; Bertotti, M. Bismuth modified gold microelectrode for Pb(II) determination in wine using alkaline medium. Electroanalysis 2009, 21, 1439–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetriadis, T.; Economou, A.; Voulgaropoulos, A. A study of pencil-lead bismuth-film electrodes for the determination of trace metals by anodic stripping voltammetry. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2004, 519, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadara, R.O.; Tothill, I.E. Stripping chronopotentiometric measurements of lead(II) and cadmium(II) in soils extracts and wastewaters using a bismuth film screen-printed electrode assembly. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 770–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Economou, A. Bismuth-film electrodes: Recent developments and potentialities for electroanalysis. TrAC. Trends Anal. Chem. 2005, 24, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, L.; Faria, R. The Influence of the Electrodeposition Conditions on the Electroanalytical Performance of the Bismuth Film Electrode for Lead Determination. Electroanalysis 2008, 20, 2259–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Pei, X.; Yue, W.; Bange, A.; Heineman, W.; Papautsky, I. Lab-on-a-Chip Sensor with Evaporated Bismuth Film Electrode for Anodic Stripping Voltammetry of Zinc. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 2586–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokkinos, C.; Economou, A.; Raptis, I.; Efstathiou, C.; Speliotis, T. Novel disposable bismuth-sputtered electrodes for the determination of trace metals by stripping voltammetry. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 2795–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinos, C.; Economou, A.; Raptis, I.; Speliotis, T. Disposable lithographically fabricated bismuth microelectrode arrays for stripping voltammetric detection of trace metals. Electrochem. Commun. 2011, 13, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinos, C.; Economou, A.; Raptis, I.; Speliotis, T. Disposable microfabricated bismuth microelectrode arrays for trace metal analysis by stripping voltammetry. Procedia Engineering 2011, 25, 880–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinos, C.; Economou, A.; Raptis, I. Microfabricated disposable lab-on-a-chip sensors with integrated bismuth microelectrode arrays for voltammetric determination of trace metals. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 710, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hocevar, S.B.; Svancara, I.; Ogorvc, B.; Vytras, K. Antimony Film Electrode for Electrochemical Stripping Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 8639–8643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhl, A.; Kestranek, W. The electrometric titration of acids and bases with the antimony indicator electrodes. Monatsh. Chem. 1923, 44, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebez, B.; Ogorevc, B.; Hocevar, S.B.; Veber, M. Functioning of antimony film electrode in acid media under cyclic and anodic stripping voltammetry conditions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 785, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokkinos, C.; Economou, A.; Raptis, I.; Speliotis, T. Novel disposable microfabricated antimony-film electrodes for adsorptive stripping analysis of trace Ni(II). Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopha, H.; Jovanovski, V.; Hocevar, S.B.; Ogorevc, B. In-situ plated antimony film electrode for adsorptive cathodic stripping voltammetric measurement of trace nickel. Electrochem. Commun. 2012, 20, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.L.; Zhu, J.Z.; Yang, S.Z.; Zhang, X.K.; Zhang, G.X. Electrochemical characterization of boron-doped polycrystalline diamond thin-film electrodes. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1995, 353, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaw, A.E.; Swain, M.G. A comparison of boron-doped diamond thin-film and Hg-coated glassy carbon electrodes for anodic stripping voltammetric determination of heavy metal ions in aqueous media. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 575, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manivannan, A.; Ramakrishnan, L.; Seehra, M.S.; Granite, E.; Butler, J.E.; Tryk, D.A.; Fujishima, A. Mercury detection at boron doped diamond electrodes using a rotating disk technique. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2005, 577, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragoe, D.; Sparatu, N.; Kawasaki, R.; Manivannan, A.; Sparatu, T.; Tryk, D.A.; Fujishima, A. Detection of trace levels of Pb2+ in tap water at boron-doped diamond electrodes with anodic stripping voltammetry. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 2437–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chooto, P.; Wararatananurak, P.; Innuphat, C. Determination of trace levels of Pb(II) in tap water by anodic stripping voltammetry with boron-doped diamond electrode. ScienceAsia 2010, 36, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saterlay, A.J.; Agra-Gutierrez, C.; Taylor, M.P.; Marken, F.; Compton, R.G. Sono-cathodic stripping voltammetry of lead at a polished boron-doped diamond electrode: Application to the determination of lead in river sediment. Electroanalysis 1999, 11, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, C.E.; Hyde, M.E.; Tomcik, P.; Jacobs, R.; Compton, R.G. Cadmium detection via boron-doped diamond electrodes: Surfactant inhibited stripping voltammetry. Talanta 2004, 62, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saterlay, A.J.; Foord, J.S.; Compton, R.G. Sono-cathodic stripping voltammetry of manganese at a polished boron-doped diamond electrode: Application to the determination of manganese in instant tea. Analyst 1999, 124, 1791–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saterlay, A.J.; Marken, F.; Foord, J.S.; Compton, R.G. Sonoelectrochemical investigation of silver analysis at a highly boron-doped diamond electrode. Talanta 2000, 53, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonthalia, P.; McGaw, A.E.; Show, Y.; Swain, M.G. Metal ion analysis in contaminated water samples using anodic stripping voltammetry and a nanocrystalline diamond thin-film electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 522, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tall, O.E.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Sigaud, M.; Vittori, O. Anodic stripping voltammetry of heavy metals at nanocrystalline boron-doped diamond electrode. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Yang, J.E.; Kim, J.P.; Bae, J.S.; Shim, Y.-B.; Won, M.-S. Simultaneous detection of Cd (II), Pb (II), Cu (II), and Hg (II) ions in dye waste water using a boron doped diamond electrode with DPASV. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, 31, 140–145. [Google Scholar]
- Sbartai, A.; Namour, P.; Errachid, A.; Krejci, J.; Sejnohova, R.; Renaud, L.; Larbi, H.M.; Loir, A.-S.; Garrelie, F.; Donnet, C.; et al. Electrochemical boron-doped diamond film microcells micromachined with femtosecond laser: Application to the determination of water framework directive metals. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 4805–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutton, L.; Newton, M.E.; Unwin, P.; MacPherson, J.V. Factors controlling stripping voltammetry of lead at polycrystalline boron doped diamond electrodes: New insights from high-resolution microscopy. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, C.; Wilkins, S.J.; Marken, F.; Compton, R.G. Simultaneous electrochemical detection and determination of lead and copper at boron-doped diamond film electrodes. Electroanalysis 2002, 14, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivannan, A.; Kawasaki, R.; Tryk, D.A.; Fujishima, A. Interaction of Pb and Cd during anodic stripping voltammetric analysis at boron-doped diamond electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 3313–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J. Diamond-like amorphous carbon. Mat. Sci. Eng. 2002, R37, 129–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, A.; Liu, E.; Tan, S.; Zhang, S.; Gao, J. Stripping voltammetric analysis of heavy metals at nitrogen doped diamond-like carbon film electrodes. Electroanalysis 2002, 14, 1294–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khun, N.W.; Liu, E. Linear sweep anodic stripping voltammetry of heavy metals from nitrogen doped tetrahedral amorphous carbon thin films. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 2890–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.X.; Liu, E. Nitrogenated diamond-like carbon films for metal tracing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 198, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadro, B.; Sikora, A.; Loir, A.; Errachid, A.; Garrelie, F.; Donnet, C.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Electrochemical performances of B doped and undoped diamond-like carbon (DLC) films deposited by femtosecond pulsed laser ablation for heavy metal detection using square wave anodic stripping voltammetric (SWASV) technique. Sens. Actuators. B 2011, 155, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickup, N.L.; Shapiro, J.S.; Wong, D.K.Y. Extraction of silver by polypyrrole films upon a base±acid treatment. Anal. Chim. Acta 1998, 364, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.Y.; Shiu, K.K. Preconcentration and electroanalysis of silver species at polypyrrole film modified glassy carbon electrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2001, 498, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zejli, H.; Izaoumen, N.; Bouchta, D.; El Kaoutit, M.; Temsamani, K.R. Electrochemically aided solid phase micro-extraction of mercury(II) at poly(3-methylthiophene) modified gold electrode. Anal. Lett. 2004, 37, 1737–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zejli, H.; Sharrock, P.; Hidalgo-Hidalgo de Cisneros, J.L.; Naranjo-Rodriguez, I.; Temsamani, K.R. Voltammetric determination of trace mercury at a sonogel-carbon electrode modified with poly-3-methylthiophene. Talanta 2006, 68, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Yasri, N.G.; Halabi, A.J.; Istamboulie, G.; Noguer, T. Chronoamperometric determination of lead ions using PEDOT:PSS modified carbon electrodes. Talanta 2011, 85, 2528–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, F.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Ye, B. Polyaniline Langmuir-Blodgett film modified glassy carbon electrode as a voltammetric sensor for determination of Ag+ ions. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 1795–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, E.; Zhao, X. Glassy carbon electrode modified by conductive polyaniline coating for determination of trace lead and cadmium ions in acetate buffer solution. Thin Solid Films 2011, 519, 5285–5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, M.C.; Oulahyane, M.; Mostefai, M.; Chehimi, M.M. Multiple internal reflection FT-IR spectroscopy (MIRFTIRS) study of the electrochemical synthesis and the redox process of poly(1,5-diaminonaphthalene). Synth. Met. 1998, 93, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilian, K. Affinity of some metal ions towards1,8-diaminonaphthalene conductive polymer. React. Funct. Polym. 2008, 68, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pałys, B.J.; Skompska, M.; Jackowska, K. Sensitivity of poly 1,8-diaminonaphthalene to heavy metal ions-electrochemical and vibrational spectra studies. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1997, 433, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.G.; Huang, M.R.; Li, S.X. Facile synthesis of poly(1,8-diaminonaphthalene) microparticles with a very high silver-ion adsorbability by a chemical oxidative polymerization. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 5363–5374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, M.S.; Yoon, J.H.; Shim, Y.B. Determination of selenium with a poly(1,8-diaminonaphthalene)-modified electrode. Electroanalysis 2005, 17, 1952–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, S.; el Rhazi, M.; Amine, A.; Curulli, A.; Palleschi, G. Carbon paste electrode bulk-modified with the conducting polymer poly(1,8-diaminonaphthalene): Application to lead determination. Microchim. Acta 2003, 143, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanganeh, A.R.; Amini, M.K. A potentiometric and voltammetric sensor based on polypyrrole film with electrochemically induced recognition sites for detection of silver ion. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 3822–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisak, G.; Wagner, M.; Kvarnstrom, C.; Bobacka, J.; Ivaska, A.; Lewenstam, A. Electrochemical behaviour of poly(benzopyrene) films doped with Eriochrome black T as Pb2+-sensitive sensors. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 2794–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, K.S.; Woo, S.B.; Jyoung, J.Y. Trace mercury determination by differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry using polythiophene-quinoline/glassy carbon modified electrode. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2003, 24, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerset, V.; Leaner, J.; Mason, R.; Iwuoha, E.; Morrin, A. Determination of inorganic mercury using a polyaniline and polyaniline-methylene blue coated screen-printed carbon electrode. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2010, 90, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerset, V.; Leaner, J.; Mason, R.; Iwuoha, E.; Morrin, A. Development and application of a poly(2,2'-dithiodianiline) (PDTDA)-coated screen-printed carbon electrode in inorganic mercury determination. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 4240–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philips, M.F.; Gopalan, A.L.; Lee, K.P. Development of a novel cyano group containing electrochemically deposited polymer film for ultrasensitive simultaneous detection of trace level cadmium and lead. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 237–238, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Joseph, A.; Ramamurthy, P.C.; Subramanian, S. Lead ion sensor with electrodes modified by imidazole-functionalized polyaniline. Microchim. Acta 2012, 177, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, Z.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, P.; Su, Z.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, Q.; Yau, S. Sensitive square wave anodic stripping voltammetric determination of Cd2+ and Pb2+ ions at Bi/Nafion/overoxidized 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate-tethered polypyrole/glassy carbon electrode. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 191, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.C.; Chen, X.; Guo, Z.; Xie, C.G.; Kong, L.T.; Liu, J.H.; Huang, X.J. Stripping voltammetric detection of mercury(II) based on a surface ion imprinting strategy in electropolymerized microporous poly(2-mercaptobenzothiazole) films modified glassy carbon electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 685, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Won, M.S.; Shim, Y.B. Characterization of an EDTA bonded conducting polymer modified electrode: Its application for the simultaneous determination of heavy metal ions. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitzmann, M.; Bucher, C.; Moutet, J.C.; Pereira, E.; Rivas, B.L.; Royal, G.; Saint-Aman, E. Complexation of poly(pyrrole-EDTA like) film modified electrodes: Application to metal cations electroanalysis. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 3082–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortina-Puig, M.; Munoz-Berbel, X.; del Valle, M.; Munoz, F.J.; Alonso-Lomillo, M.A. Characterization of an ion-selective polypyrrole coating and application to the joint determination of potassium, sodium and ammonium by electrochemical, impedance spectroscopy and partial least squares method. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 597, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthukumar, C.; Kesarkar, S.D.; Srivastava, D.N. Conductometric mercury [II] sensor based on polyaniline–cryptand-222 hybrid. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2007, 602, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evtugyn, G.A.; Stoikov, I.I.; Beljyakova, S.V.; Shamagsumova, R.V.; Stoikova, E.E.; Zhukov, A.Y.; Antipin, I.S.; Budnikov, H.C. Ag selective electrode based on glassy carbon electrode covered with polyaniline and thiacalix[4]arene as neutral carrier. Talanta 2007, 71, 1720–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, E.; Gu, D.; Wang, Y. Glassy carbon electrode coated with polyaniline-functionalized carbon nanotubes for detection of trace lead in acetate solution. Thin Solid Films 2011, 519, 5280–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmanipour, A.; Taher, M.A. An electrochemical sensor for stripping analysis of Pb(II) based on multiwalled carbon nanotube functionalized with 5-Br-PADAP. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2011, 15, 2695–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Tran, L.D.; Nguyen, H.L.; Nguyen, B.H.; Nguyen, V.H. Modified interdigitated arrays by novel poly(1,8-diaminonaphthalene)/carbon nanotubes composite for selective detection of mercury(II). Talanta 2011, 85, 2445–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Nguyen, T.M.; Ho, T.G.; Nguyen, N.T.; Reisberg, S.; Piro, B.; Pham, M.C. Design of interpenetrated network MWCNT/Poly(1,5-DAN) on interdigital electrode: Towards NO2 gas sensing. Talanta 2013, 115, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, H.D.; Nguyen, L.H.; Nguyen, T.D.; Nguyen, H.B.; Nguyen, T.L.; Tran, D.L. Anodic stripping voltammetric determination of Cd2+ and Pb2+ using interpenetrated MWCNT/P1,5-DAN as an enhanced sensing interface. Ionics 2015, 21, 571–578. [Google Scholar]
- Turdean, G.L. Design and development of biosensors for the detection of heavy metal toxicity. Int. J. Electrochem. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukla, A.L.; Kanjuk, N.I.; Starodub, N.F.; Shirshov, Y.M. Multienzyme electrochemical sensor array for determination of heavy metal ions. Sens. Actuators. B 1999, 57, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagal-Kestwal, D.; Karve, M.S.; Kakade, B.; Pillai, V.K. Invertase inhibition based electrochemical sensor for the detection of heavy metal ions in aqueous system: Application of ultra-microelectrode to enhance sucrose biosensor’s sensitivity. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, A.; Togashi, H. Highly selective oligonucleotide-based sensor for mercury(II) in aqueous solutions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 4300–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, N.N.; Tang, C.X.; He, X.W.; Yin, X.B. Tetrahedron-structured DNA and functional oligonucleotide for construction of an electrochemical DNA-based biosensor. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 7689–7691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor-Piperberg, G.; Tel-Vered, R.; Elbaz, J.; Willner, I. Nanoengineered electrically contacted enzymes on DNA scaffolds: Functional assemblies for the selective analysis of Hg2+ ions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 6878–6879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Shu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Jin, W.; Chen, X. An ultrasensitive electrochemical sensing platform for Hg2+ based on a density controllable metal-organic hybrid microarray. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Liu, H.; Zou, B.; Tian, D.; Huang, H. A fishnet electrochemical Hg2+ sensing strategy based on gold nanoparticle-bioconjugate andthymine-Hg2+-thymine coordination chemistry. Analyst 2012, 137, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Nie, H.; Jiang, J.; Shen, G.; Yu, R. Electrochemical sensor for mercury(II) based on conformational switch mediated by interstrand cooperative coordination. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5724–5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Kim, Y.R.; Oh, J.W.; Kim, T.H.; Mahajan, R.K.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, H. A regenerative electrochemical sensor based on oligonucleotide for the selective determination of mercury(II). Analyst 2009, 134, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, J.; Fu, L.; Tang, D.; Xu, M.; Chen, G.; Yang, H. Target-induced structure-switching DNA hairpins for sensitive electrochemical monitoring of mercury (II). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 39, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Chu, X.; Wang, H.; Shen, G.; Yu, R. Ultrasensitive electrochemical sensor for mercury (II) based on target-induced structure-switching DNA. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breaker, R.; Joyce, G. A DNA enzyme that cleaves RNA. Chem. Biol. 1994, 1, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Tian, R.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, C. Target-induced electronic switch for ultrasensitive detection of Pb2+ based on three dimensionally ordered macroporous Au-Pd bimetallic. Biosens. Biolectron. 2014, 53, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; He, S.; Xie, S.; Xu, X.; Liang, Z.; Meng, X.; Li, Q.; Zhu, Z. Electrochemical DNAzyme sensor for lead based on amplification of DNA-Au bio-bar codes. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 6323–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Tong, P.; Li, H.; Tang, J.; Zhang, L. Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of Pb2+ based on rolling circle amplification and quantum dots tagging. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocaña, C.; Malashikhina, N.; del Valle, M.; Pavlov, V. Label-free selective impedimetric detection of Cu2+ ions using catalytic DNA. Analyst 2013, 138, 1995–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Rowe, A.A.; Plaxco, K.W. Electrochemical detection of parts-per-billion lead via an electrode-bound DNAzyme assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 262–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Fang, W. Pb2+ induced DNA conformational switch from hairpin to G-quadruplex: Electrochemical detection of Pb2+. Analyst 2011, 136, 2367–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, C.; Tang, B. Crystal violet as a G-quadruplex-selective probe for sensitive amperometric sensing of lead. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 11909–11911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarczewska, M.; Kierzkowska, E.; Ziółkowski, R.; Górski, L.; Malinowska, E. Electrochemical oligonucleotide-based biosensor for the determination of lead ion. Bioelectrochem. 2015, 101, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Yuan, M.; Zhao, H. DNA Wrapped Metallic Single-walled Carbon Nanotube Sensor for Pb(II) Detection. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2014, 22, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, E.; Gooding, J.J. Peptide modified electrodes as electrochemical metal ion sensors. Electroanalysis 2006, 18, 1437–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viguier, B.; Zór, K.; Kasotakis, E.; Mitraki, A.; Clausen, C.H.; Svendsen, W.E.; Castillo-León, J. Development of an electrochemical metal-ion biosensor using self-assembled peptide nanofibrils. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 1594–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.; Cho, M.; Nam, J.D.; Choe, W.S.; Lee, Y. Highly sensitive electrochemical lead ion sensor harnessing peptide probe molecules on porous gold electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 48, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, N.; Prieto-Simón, B.; Cetó, X.; del Valle, M. Array of peptide-modified electrodes for the simultaneous determination of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Zn(II). Talanta 2014, 125, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daunert, S.; Barrett, G.; Feliciano, J.S.; Shetty, R.S.; Shrestha, S.; Smith-Spencer, W. Genetically engineered whole-cell sensing systems: Coupling biological recognition with reporter genes. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 2705–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, C.A.; Osma, J.F. Whole cell biosensors. In Biosensors: Recent Advances and Mathematical Challenges; Osma, J.F., Stoytcheva, M., Eds.; Omnia Science: Terrassa, Spain, 2014; pp. 51–96. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.; Ding, L.; Lei, J.; Ding, S.; Ju, H. Effective cell capture with tetrapeptide-functionalized carbon nanotubes and dual signal amplification for cytosensing and evaluation of cell surface carbohydrate. Anal. Chem. 2008, 280, 3867–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Yoav, H.; Almog, R.O.; Sverdlov, Y.; Sternheim, M.; Belkin, S.; Freeman, A.; Shacham-Diamand, Y. Modified working electrodes for electrochemical whole cell microchips. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 82, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, C.; Hu, N.; Zhou, J.; Du, L.; Wang, P. Microfabricated electrochemical cell-based biosensors for analysis of living cells in vitro. Biosensors 2012, 2, 127–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whole Cell Sensing Systems I, Reporter Cells and Devices, and Whole Cell Sensing System II, Applications. In Series: Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology; Belkin, S.; Gu, M.B. (Eds.) Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2010.
- Adam, V.; Chudobova, D.; Tmejova, K.; Cihalova, K.; Krizkova, S.; Guran, R.; Kominkova, M.; Zurek, M.; Kremplova, M.; Jimenez, A.M.; et al. An effect of cadmium and lead ions on Escherichia coli with the cloned gene for metallothionein (MT-3) revealed by electrochemistry. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 140, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Qin, H.; Liu, J.G.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Wu, D. A novel electrochemical method to evaluate the cytotoxicity of heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 271, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Cai, H.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, L.; Yang, M.; Wang, P. Detection of heavy metal toxicity using cardiac cell-based biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 3224–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafeman, D.G.; Parce, J.W.; McConnell, H.M. Light addressable potentiometric sensor for biochemical systems. Science 1988, 240, 1182–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, A.B.; Yoshinobu, T.; Iwasaki, H.; Sugihara, H.; Yukimasa, T.; Hirata, L.; Iwata, H. Investigation on light-addressable potentiometric sensor as a possible cell–semiconductor hybrid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 18, 1509–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brayner, R.; Couté, A.; Livage, J.; Perrette, C.; Sicard, C. Micro-algal biosensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 581–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsopela, A.; Lale, A.; Vanhove, E.; Reynes, O.; Séguy, I.; Temple-Boyer, P.; Juneau, P.; Izquierdo, R.; Launay, J. Integrated electrochemical biosensor based on algal metabolism for water toxicity analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 61, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouteau, C.; Dzyadevych, S.; Durrieu, C.; Chovelon, J.M. A bi-enzymatic whole cell conductometric biosensor for heavy metal ions and pesticides detection in water samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 21, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedri, H.; Durrieu, C. A self-assembled monolayers based conductometric algal whole cell biosensor for water monitoring. Microchim. Acta 2008, 163, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekaya, N.; Saiapina, O.; Ouada, H.B.; Lagarde, F.; Namour, P.; Ouada, H.B.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Bi-Enzymatic conductometric biosensor for detection of heavy metal ions and pesticides in water samples based on enzymatic inhibition in arthrospira platensis. J. Environ. Protect. 2014, 5, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, S.; Hodgkiss, J.; Plank, N.; Torsi, L.; Cowper, P.; Malliaras, G.; Braeken, Y.; Laurand, N.; Samuel, I.; Pomorska, A.; et al. Organic bioelectronics: General discussion. Faraday Discuss. 2014, 174, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramuz, M.; Hama, A.; Huerta, M.; Rivnay, J.; Leleux, P.; Owens, R.M. Combined optical and electronic sensing of epithelial cells using planar organic transistors. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 7083–7090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Lin, S.; Liu, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Du, W.; Li, X. Organic electrochemical transistor based biosensor for detecting marine diatoms in seawater medium. Sens. Actuators. B 2014, 203, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kergoat, L.; Piro, B.; Simon, D.T.; Pham, M.C.; Noël, V.; Berggren, M. Detection of glutamate and acetylcholine with organic electrochemical transistors based on conducting polymer/platinum nanoparticle composites. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5658–5664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandiello, E.; Sessolo, M.; Bolink, H.J. Aqueous electrolyte-gated ZnO transistors for environmental and biological sensing. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2014, 2, 10277–10281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemiroski, A.; Christodouleas, D.C.; Hennek, J.W.; Kumar, A.A.; Maxwell, E.J.; Fernández-Abedul, M.T.; Whitesides, G.M. Universal mobile electrochemical detector designed for use in resource-limited applications. PNAS 2014, 111, 11984–11989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
March, G.; Nguyen, T.D.; Piro, B. Modified Electrodes Used for Electrochemical Detection of Metal Ions in Environmental Analysis. Biosensors 2015, 5, 241-275. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios5020241
March G, Nguyen TD, Piro B. Modified Electrodes Used for Electrochemical Detection of Metal Ions in Environmental Analysis. Biosensors. 2015; 5(2):241-275. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios5020241
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarch, Gregory, Tuan Dung Nguyen, and Benoit Piro. 2015. "Modified Electrodes Used for Electrochemical Detection of Metal Ions in Environmental Analysis" Biosensors 5, no. 2: 241-275. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios5020241
APA StyleMarch, G., Nguyen, T. D., & Piro, B. (2015). Modified Electrodes Used for Electrochemical Detection of Metal Ions in Environmental Analysis. Biosensors, 5(2), 241-275. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios5020241






