The Scanning TMR Microscope for Biosensor Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
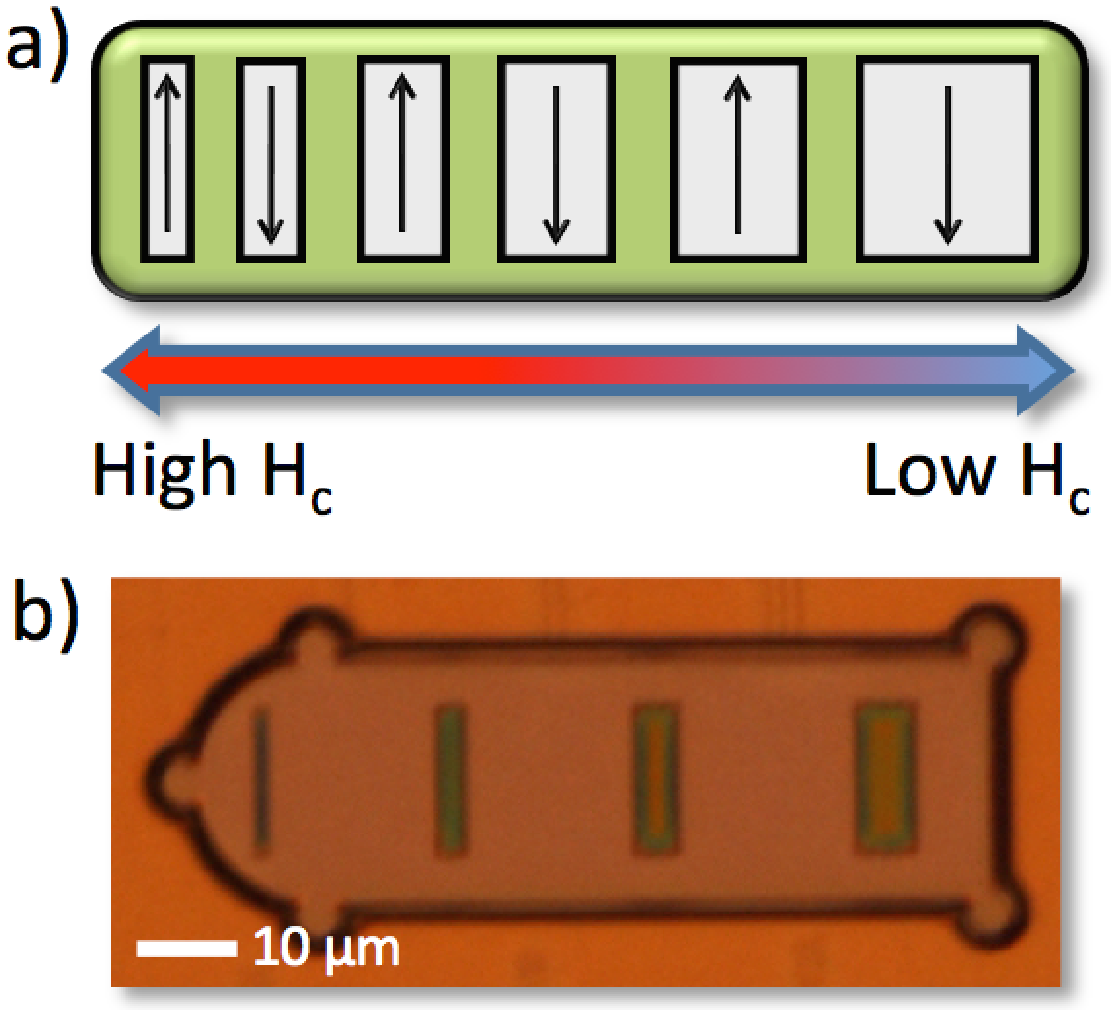
2. Instrument Design
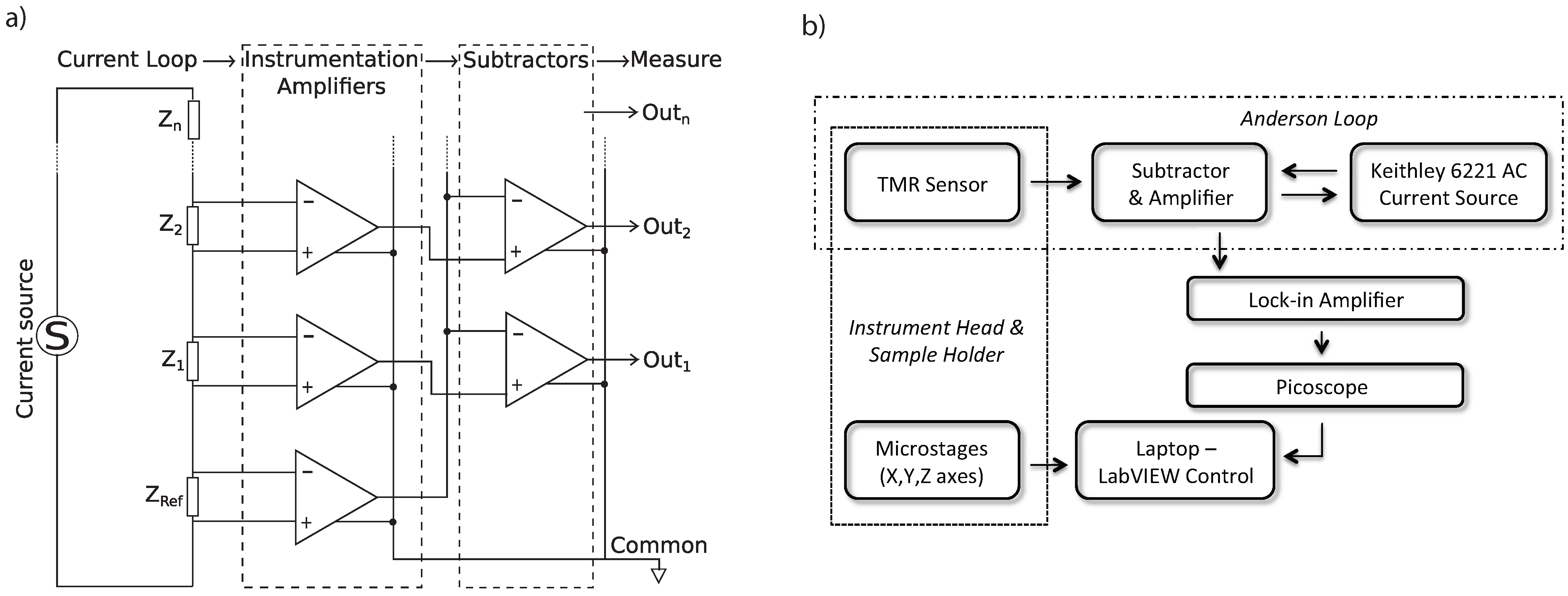
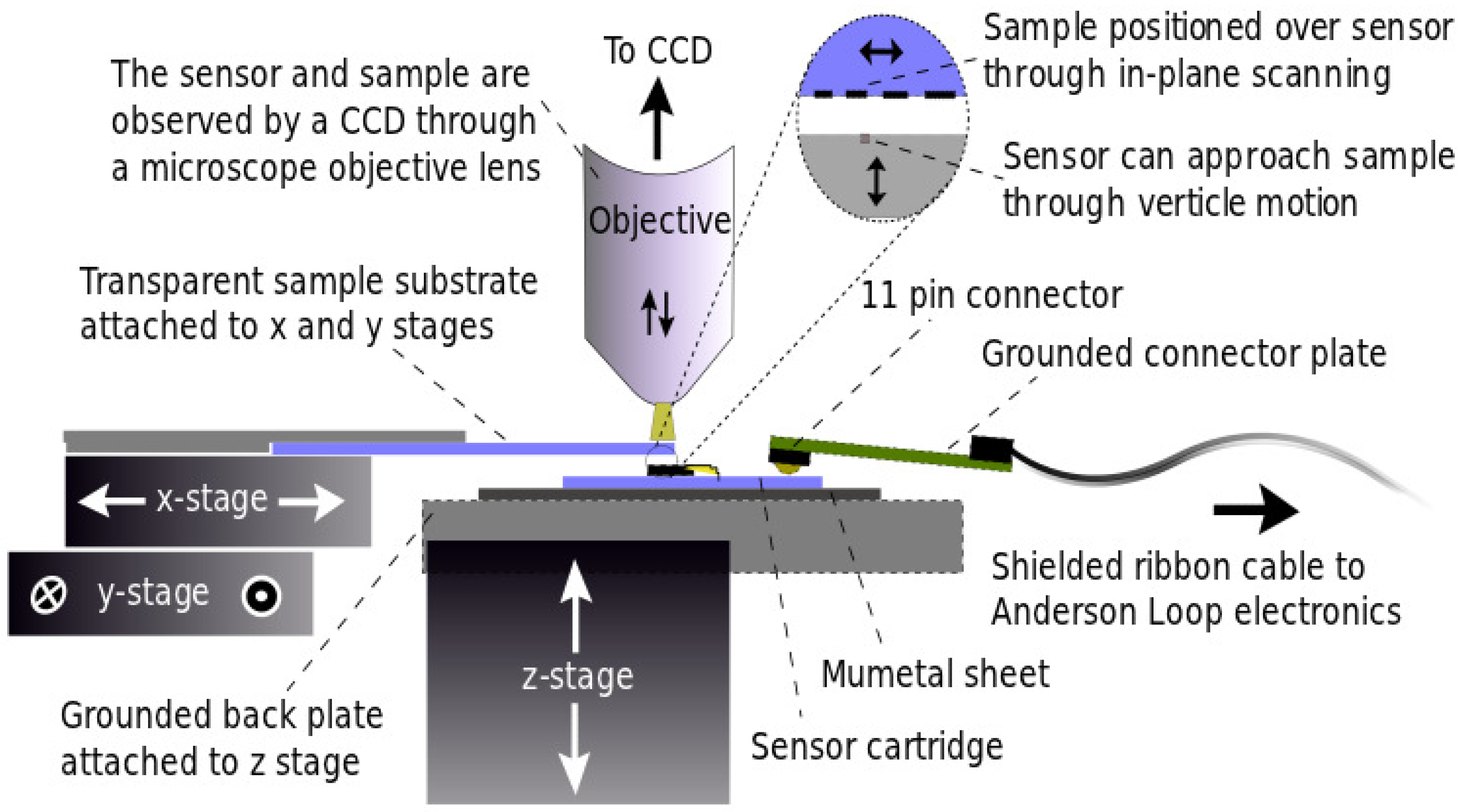
3. Characterisation
3.1. Frequency Response of the Pre-Amplifier
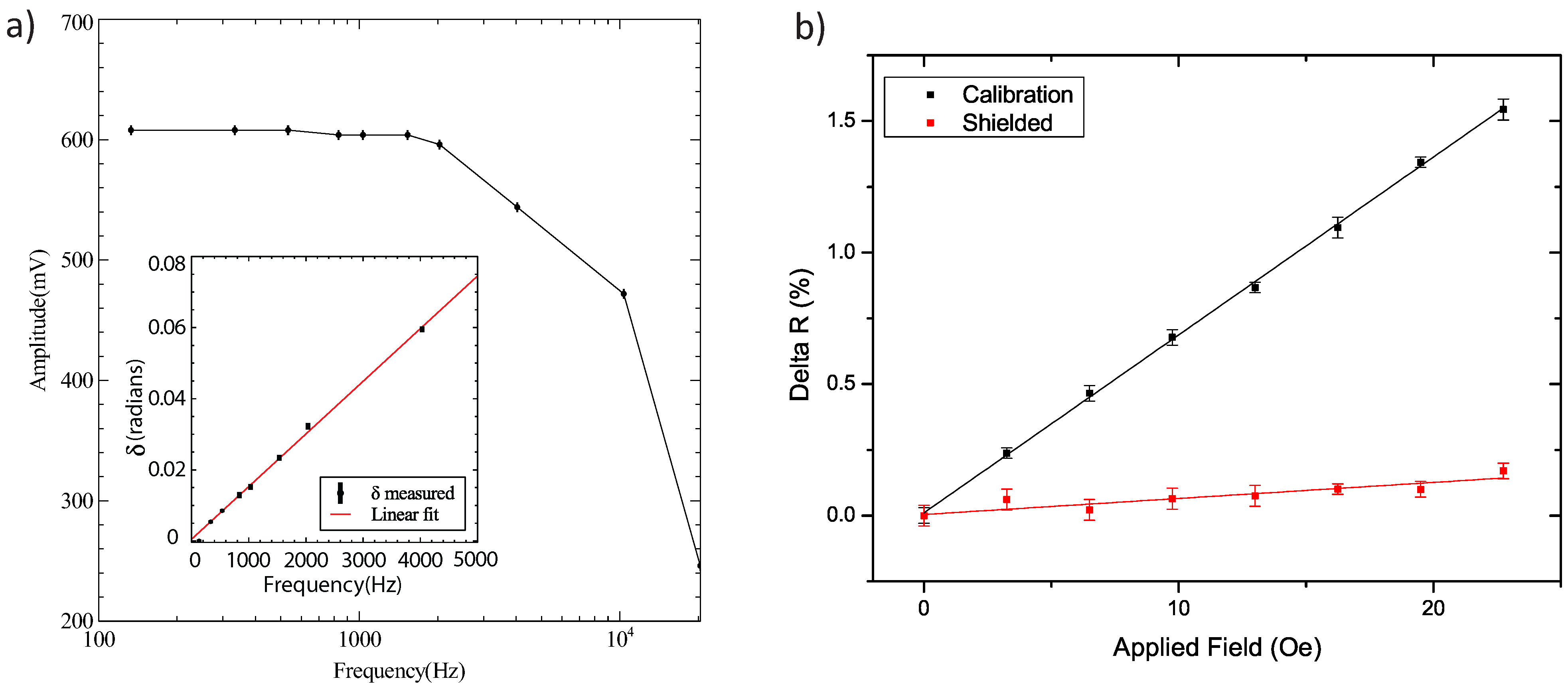
3.2. Sensor Calibration and Mu-Metal Shield
4. Detection of Magnetic Barcodes
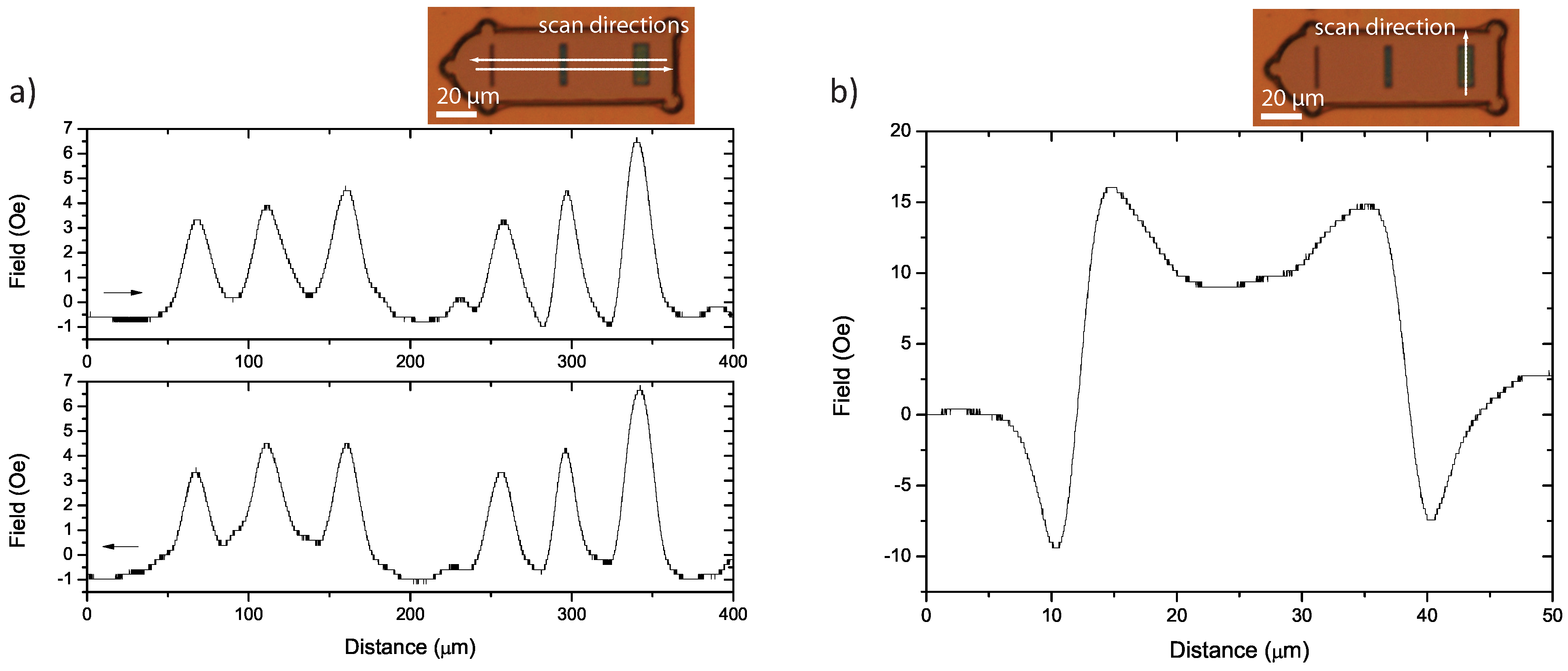
4.1. One-Dimensional Stray Field Scans
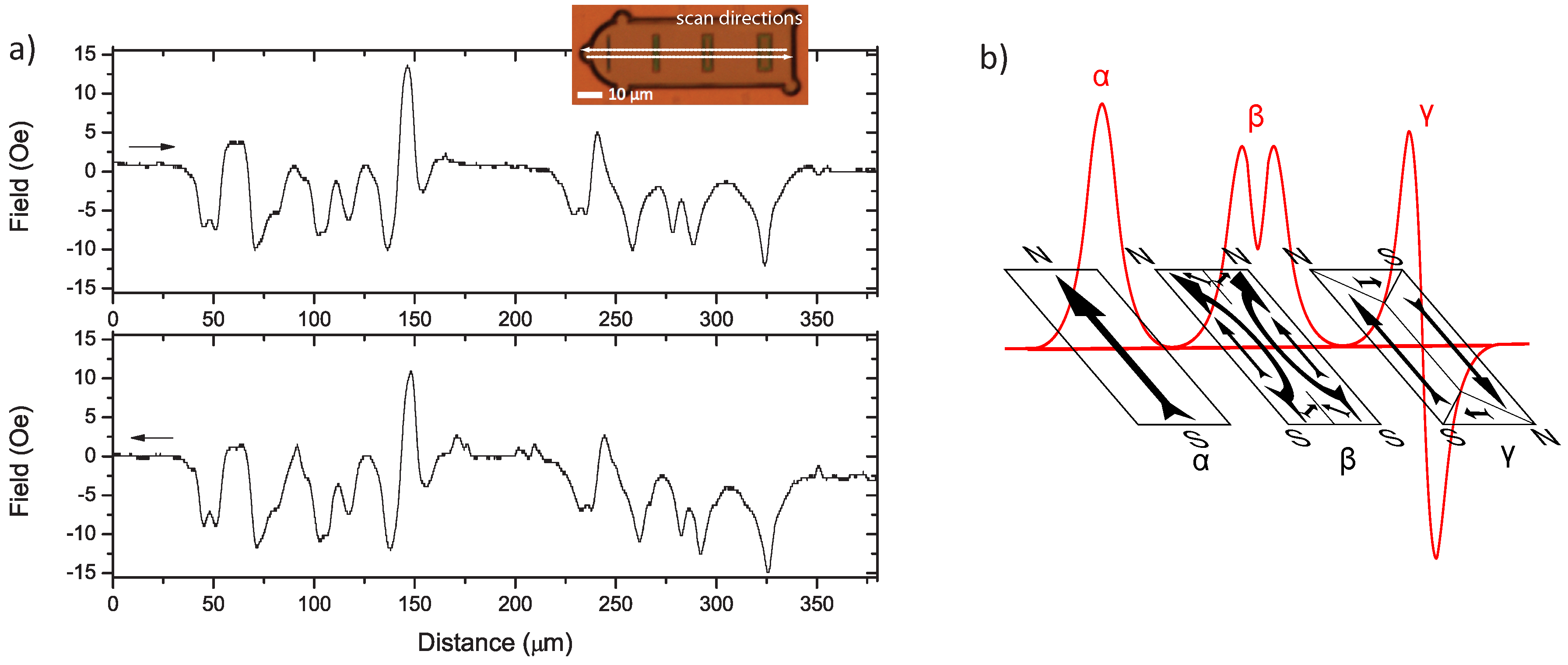
- α
- A single peak resulting from a single north-south (N-S) dipole. This is due to a relatively uniform magnetisation along the easy axis of the magnetic element, when the element’s width is small enough.
- β
- A double peak resulting from two parallel N-S dipoles. This is due to the splitting of the N and S poles, as the magnetisation prefers to point towards/away from the corners rather than the flat edge. In Figure 6b, two “c”-shaped structures are assumed. Two equal abutting “c” shapes are shown, though one may dominate, resulting in a large peak and a smaller sub-peak.
- γ
- Two peaks of opposite polarity resulting from two anti-parallel N-S, S-N dipoles. Once again, one of these dipoles may dominate, indicating the relative size of the domains, as shown in Figure 6b.
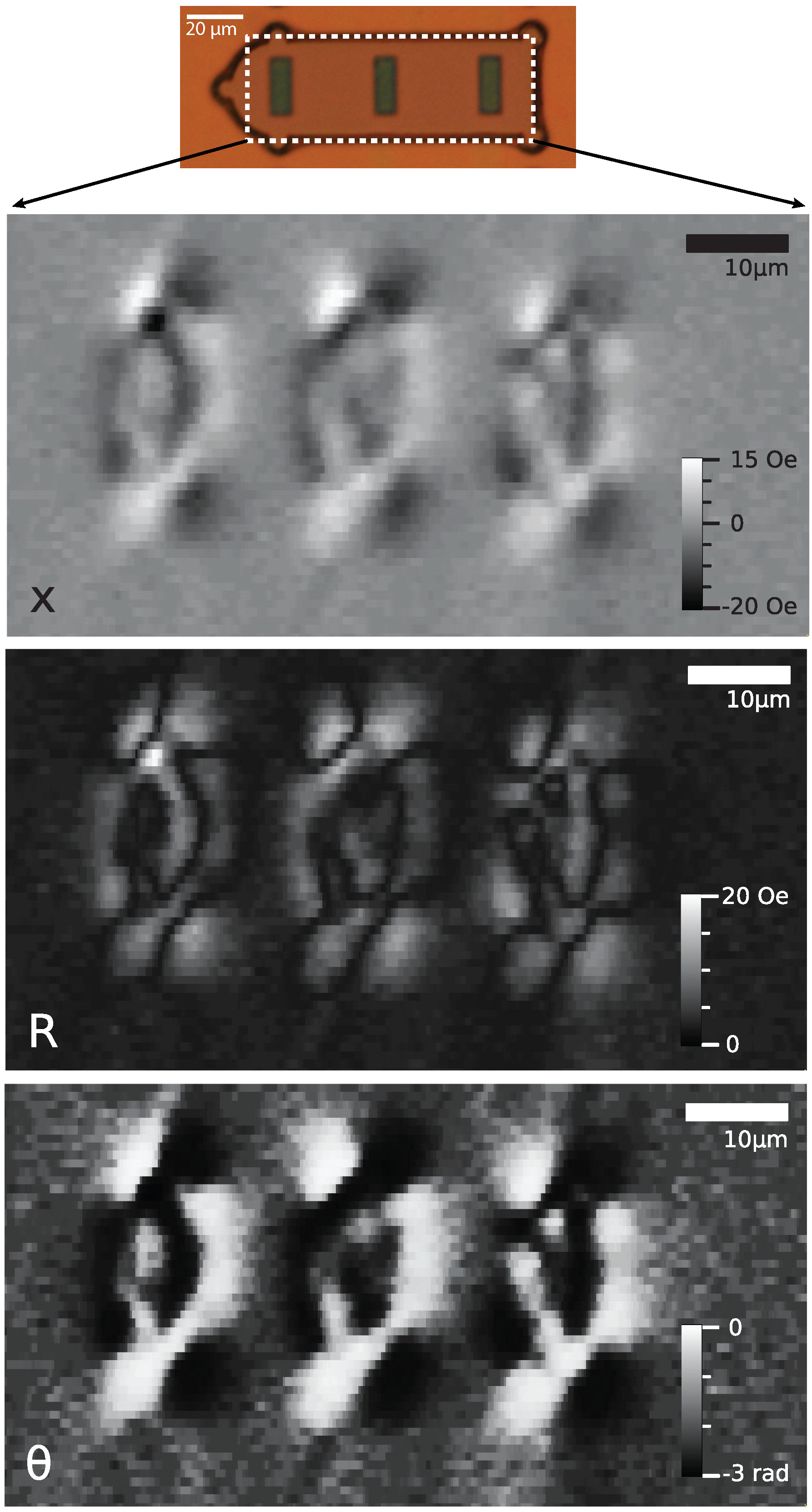
4.2. Multi-Dimensional Stray Field Scans
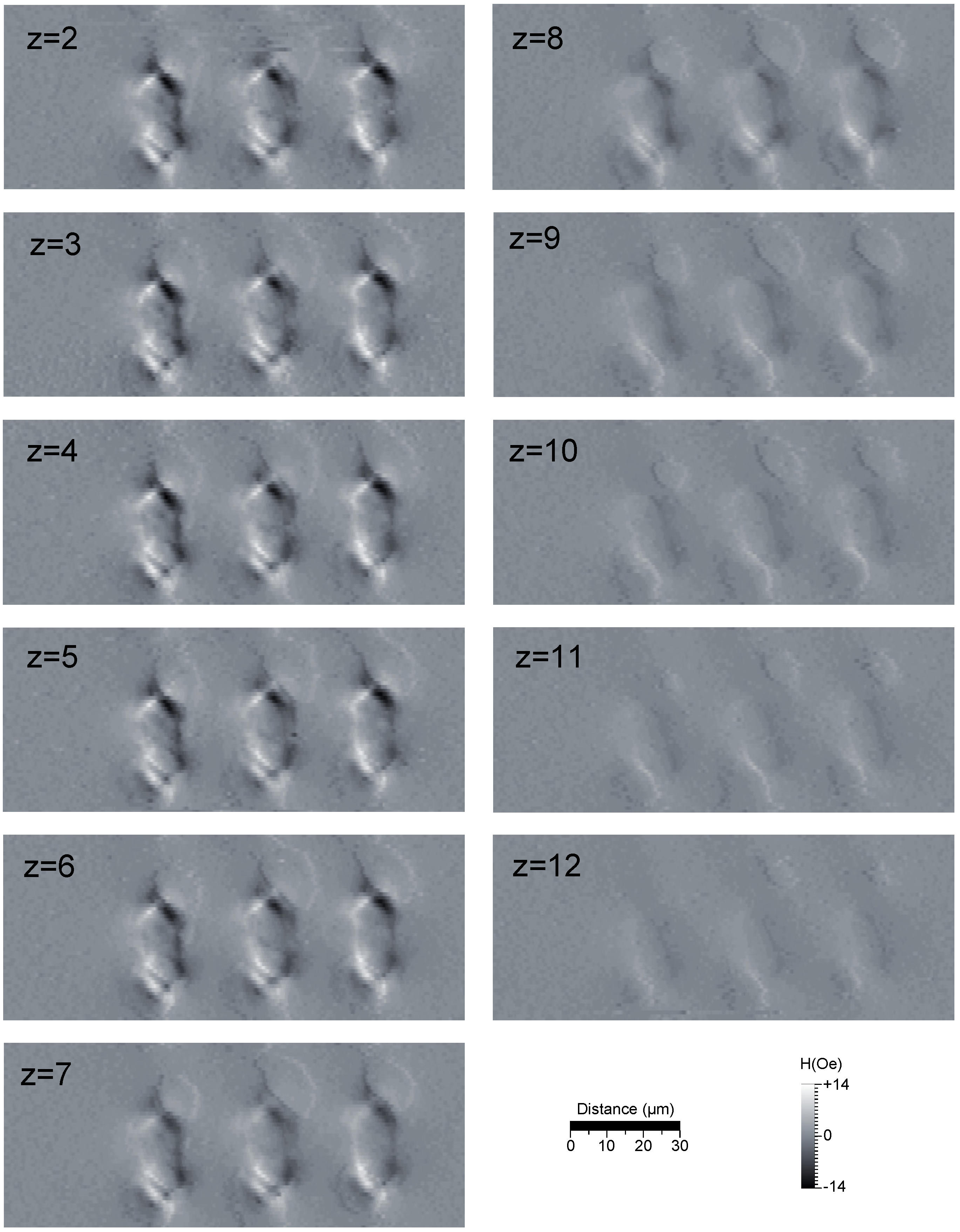
5. Results and Discussion
- Loss of labelling information due to the element being in an ambiguous state.
- Attenuation of the stray field leading to difficulty in detection.
- Highly distributed stray fields due to switching dynamics.
- Broadened coercivity values of bits may result in unintentional switching of neighbouring bits during the encoding process.
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bland, J.; Ionescu, A. Biomagnetism and Magnetic Biosystems Based on Molecular Recognition Processes. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference, New York, NY, USA, 19 June 2008.
- Nolan, J.P.; Sklar, L.A. Suspension array technology: Evolution of the flat-array paradigm. Trends Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pregibon, D.C.; Toner, M.; Doyle, P.S. Multifunctional Encoded Particles for High-Throughput Biomolecule Analysis. Science 2007, 315, 1393–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Kwon, S. Colour-barcoded magnetic microparticles for multiplexed bioassays. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, W.Z.; Collins, J.; Hou, C.J. Apparatus and Method for Barcoded Magnetic Beads Analysis. U.S. Patent 12/832,972, 13 January 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dunbar, S.A. Applications of Luminex® xMAP™ technology for rapid, high-throughput multiplexed nucleic acid detection. Clin. Chim. Acta 2006, 363, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruls, D.M.; Evers, T.H.; Kahlman, J.A.H.; van Lankvelt, P.J.W.; Ovsyanko, M.; Pelssers, E.G.M.; Schleipen, J.J.H.B.; de Theije, F.K.; Verschuren, C.A.; van der Wijk, T.; et al. Rapid integrated biosensor for multiplexed immunoassays based on actuated magnetic nanoparticles. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 3504–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Joshi, V.; White, R.L.; Wang, S.X.; Kemp, J.T.; Webb, C.; Davis, R.W.; Sun, S. Detection of single micron-sized magnetic bead and magnetic nanoparticles using spin valve sensors for biological applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 7557–7559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llandro, J.; Palfreyman, J.J.; Ionescu, A.; Barnes, C.H.W. Magnetic biosensor technologies for medical applications: a review. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2010, 48, 977–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, A.; Scholz, R.; Wust, P.; Fähling, H.; Felix, R. Magnetic fluid hyperthermia (MFH): Cancer treatment with AC magnetic field induced excitation of biocompatible superparamagnetic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 201, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaster, R.S.; Xu, L.; Han, S.J.; Wilson, R.J.; Hall, D.A.; Osterfeld, S.J.; Yu, H.; Wang, S.X. Quantification of protein interactions and solution transport using high-density GMR sensor arrays. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Connolly, J.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R167–R181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Progress in applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T. Magnetic Nanoparticles: From Fabrication to Clinical Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, J.R.; Llandro, J.; Hong, B.; Hayward, T.J.; Mitrelias, T.; Kopper, K.P.; Trypiniotis, T.; Steinmuller, S.J.; Simpson, G.K.; Bland, J.A.C. Rewritable remote encoding and decoding of miniature multi-bit magnetic tags for high-throughput biological analysis. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 1883–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palfreyman, J.; Love, D.; Philpott, A.; Vyas, K.; Cimorra, C.; Mitrelias, T.; Barnes, C.; Muir, L.; Cook, G.; Keynes, R. Hetero-Coated Magnetic Microcarriers for Point-Of-Care Diagnostics. IEEE Trans. Magnet. 2013, 49, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, K.N.; Hong, B.; Cooper, J.F.K.; Palfreyman, J.J.; Barnes, C.H.W. Detection of Magnetically Labelled Microcarriers for Suspension Based Bioassay Technologies. IEEE Trans. Magnet. 2011, 47, 1571–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, K.N.; Palfreyman, J.J.; Love, D.M.; Mitrelias, T.; Barnes, C.H.W. Magnetically labelled gold and epoxy bi-functional microcarriers for suspension based bioassay technologies. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 5272–5278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, K.F. NASA’s Anderson Loop. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 1998, 1, 5–15, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, A.; Darton, N.; Vyas, K.; Llandro, J. Detection of endogenous magnetic nanoparticles with a tunnelling magneto resistance sensor. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2010, 368, 4371–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takezaki, T.; Sueoka, K. Quantitative current measurements using scanning magnetoresistance microscopy. Ultramicroscopy 2008, 108, 970–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, J.M.; Wisniowski, P.; Freitas, P.P. Low-Frequency Noise in MgO Magnetic Tunnel Junctions: Hooge’s Parameter Dependence on Bias Voltage. IEEE Trans. Magnet. 2008, 44, 2569–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooge, F.N. 1/f Noise. Physica B 1976, 83, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, H.; Stroock, A.; Ajdari, A. Engineering flows in small devices: Microfluidics toward a Lab-on-a-Chip. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2004, 36, 381–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyeye, A.O.; Bland, J.A.C.; Daboo, C.; Lee, J.; Ebels, U.; Ahmed, H. Size dependence of the magnetoresistance in submicron FeNi wires. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, D.M.; Vyas, K.N.; Fernandez-Pacheco, A.; Llandro, J.; Palfreyman, J.J.; Mitrelias, T.; Barnes, C.H.W. A composite element bit design for magnetically encoded microcarriers for future combinatorial chemistry applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 10211–10218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vyas, K.N.; Love, D.M.; Ionescu, A.; Llandro, J.; Kollu, P.; Mitrelias, T.; Holmes, S.; Barnes, C.H.W. The Scanning TMR Microscope for Biosensor Applications. Biosensors 2015, 5, 172-186. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios5020172
Vyas KN, Love DM, Ionescu A, Llandro J, Kollu P, Mitrelias T, Holmes S, Barnes CHW. The Scanning TMR Microscope for Biosensor Applications. Biosensors. 2015; 5(2):172-186. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios5020172
Chicago/Turabian StyleVyas, Kunal N., David M. Love, Adrian Ionescu, Justin Llandro, Pratap Kollu, Thanos Mitrelias, Stuart Holmes, and Crispin H. W. Barnes. 2015. "The Scanning TMR Microscope for Biosensor Applications" Biosensors 5, no. 2: 172-186. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios5020172
APA StyleVyas, K. N., Love, D. M., Ionescu, A., Llandro, J., Kollu, P., Mitrelias, T., Holmes, S., & Barnes, C. H. W. (2015). The Scanning TMR Microscope for Biosensor Applications. Biosensors, 5(2), 172-186. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios5020172





