Single Step Nanoplasmonic Immunoassay for the Measurement of Protein Biomarkers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Gold Nanoparticles/Nanoseeds
2.3. Preparation and Characterization of GNRs
2.4. Surface Modification of GNRs
2.5. Anti-Glut-1 Immobilization on the Surface of Modified GNRs
2.6. Optimization of Antibody Immobilization Protocol
2.7. Immunoassay Plate Preparation
2.8. OCT Imaging of Immunoassay Plate
2.9. OCT Image Processing
2.10. Specificity Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Gold Nanorod Fabrication and Characterization
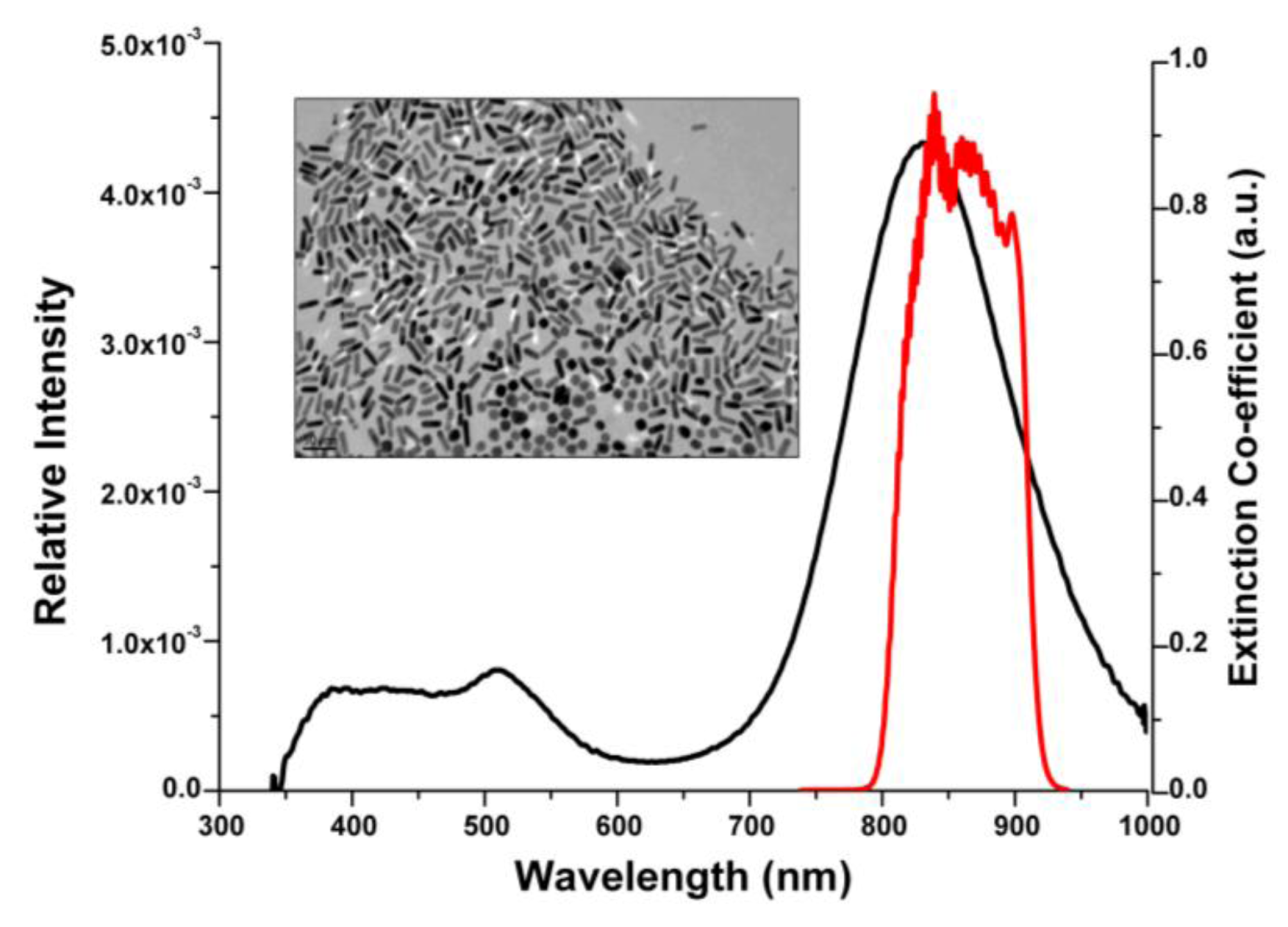
3.2. Gold Nanorod Surface Modification and Antibody Functionalization
| Surface activity of Nanorods | Zeta potential (ζ) mV |
| (suspended in DI water) | |
| CTAB | +38.8 ± 2 |
| Anionic polymer (Poly-acrylic acid) | −64.9 ± 5 |
| Anti-Glut-1 labeled GNRs | −47.36 ± 3 |
| Empty | Glut-1 | Bare | Glut-1 | Glut-1 | Glut-1 | Glut-1 | Glut-1 | Glut-1 | BSA | BSA | BSA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| well | Antibody | GNR | protein | protein | protein | protein | protein | protein | ||||
| Ab | Bare GNR | Ab-GNR | Ab | Ab-GNR | Ab-GNR | Bare GNR | ||||||
| 2'-Ab | 2'-Ab | 2'-Ab | ||||||||||
| Average Absorbance | 0.595 | 0.555 | 0.544 | 0.619 | 0.562 | 0.560 | 0.544 | 0.885 | 0.719 | 0.552 | 0.535 | 0.600 |
3.3. Glut-1 Detection Using OCT
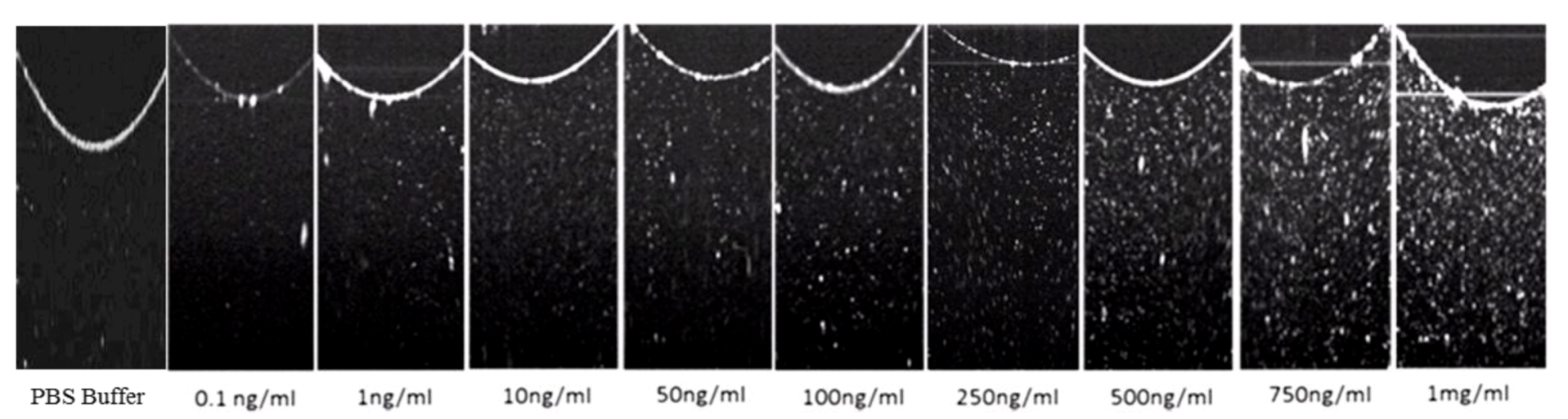
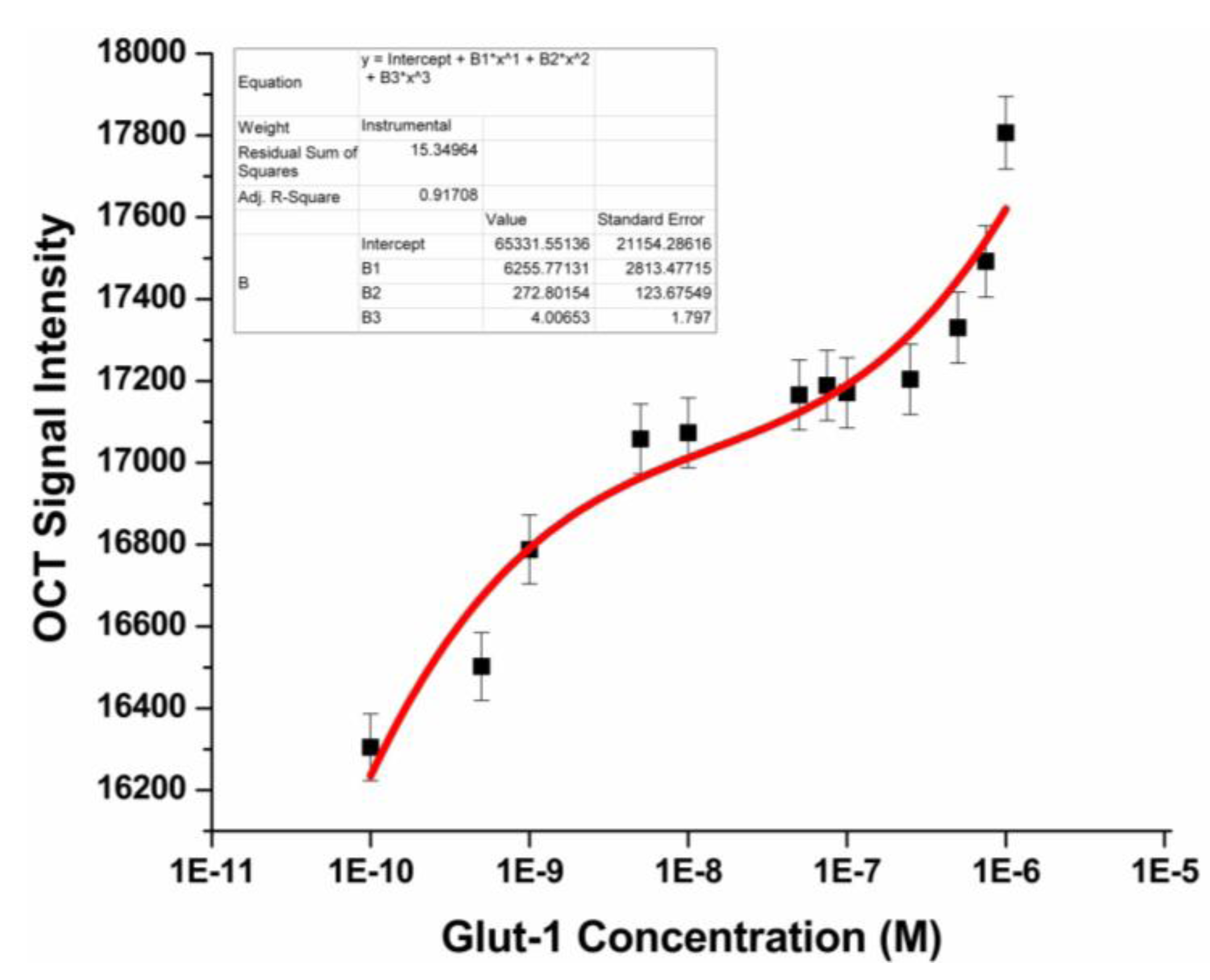
3.4. Specificity Study
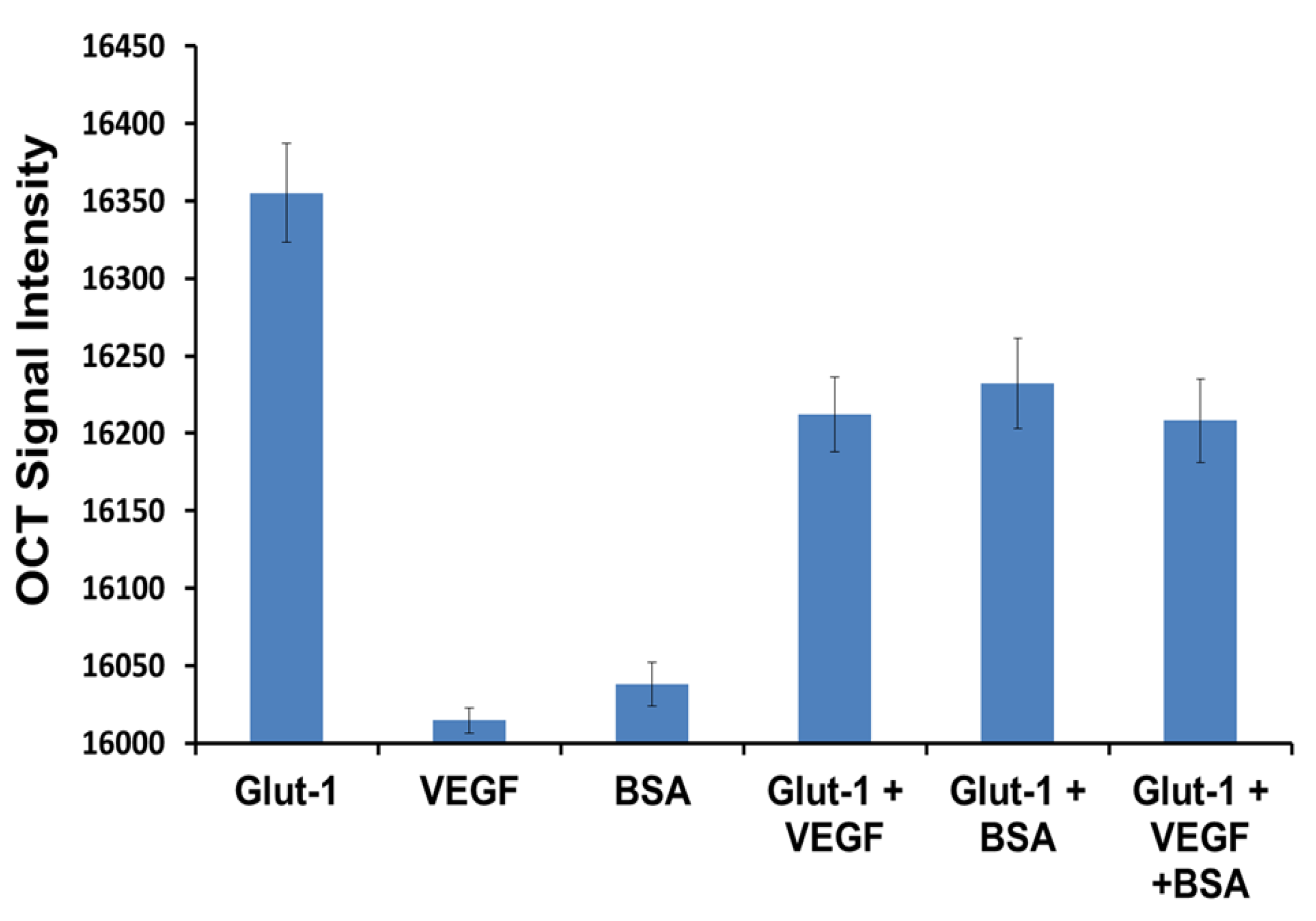
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Bock, J.L. The new era of automated immunoassay. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2000, 113, 628–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hage, D.S. Immunoassays. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 294R–304R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joos, T.O.; Stoll, D.; Templin, M.F. Miniaturised multiplexed immunoassays. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2002, 6, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrebaeck, C.A.K. Antibodies in diagnostics—From immunoassays to protein chips. Immunol. Today 2000, 21, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Neretina, S.; El‐Sayed, M.A. Gold nanorods: From synthesis and properties to biological and biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 4880–4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Wei, Q.; Wei, A.; Cheng, J.X. Gold nanorods as contrast agents for biological imaging: Optical properties, surface conjugation and photothermal effects. Photochem. Photobiol. 2009, 85, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizpurua, J.; Bryant, G.W.; Richter, L.J.; De Abajo, F.J.G.; Kelley, B.K.; Mallouk, T. Optical properties of coupled metallic nanorods for field-enhanced spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 235420:1–235420:13. [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson, E.B.; Dreaden, E.C.; Huang, X.; El-Sayed, I.H.; Chu, H.; Pushpanketh, S.; McDonald, J.F.; El-Sayed, M.A. Gold nanorod assisted near-infrared plasmonic photothermal therapy (PPTT) of squamous cell carcinoma in mice. Cancer Lett. 2008, 269, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, I.; Dawson, K.A. Protein-nanoparticle interactions. Nano Today 2008, 3, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkilany, A.M.; Nagaria, P.K.; Hexel, C.R.; Shaw, T.J.; Murphy, C.J.; Wyatt, M.D. Cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of gold nanorods: molecular origin of cytotoxicity and surface effects. Small 2009, 5, 701–708. [Google Scholar]
- Alekseeva, A.; Bogatyrev, V.; Khlebtsov, B.; Mel’nikov, A.; Dykman, L.; Khlebtsov, N. Gold nanorods: Synthesis and optical properties. Colloid J. 2006, 68, 661–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troutman, T.S.; Barton, J.K.; Romanowski, M. Optical coherence tomography with plasmon resonant nanorods of gold. Optic. Lett. 2007, 32, 1438–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; El-Sayed, I.H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Applications of gold nanorods for cancer imaging and photothermal therapy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 624, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Kou, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J. Tailoring longitudinal surface plasmon wavelengths, scattering and absorption cross sections of gold nanorods. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sönnichsen, C.; Franzl, T.; Wilk, T.; von Plessen, G.; Feldmann, J.; Wilson, O.; Mulvaney, P. Drastic reduction of plasmon damping in gold nanorods. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 77402:1–77402:4. [Google Scholar]
- Thanh, N.T.K.; Rosenzweig, Z. Development of an aggregation-based immunoassay for anti-protein a using gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 1624–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.M.; Jang, K.J.; Groves, J.T. Detection of proteins using a colorimetric bio-barcode assay. Nat. Protocol. 2007, 2, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.C.; De, M.; Rotello, V.M. Monolayer-protected nanoparticle-protein interactions. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2005, 9, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, I.; Morgan, M.R.A.; Lindner, W.; Pittner, F. Optical resonance-enhanced absorption-based near-field immunochip biosensor for allergen detection. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 2694–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Swanson, E.A.; Lin, C.P.; Schuman, J.S.; Stinson, W.G.; Chang, W.; Hee, M.R.; Flotte, T.; Gregory, K.; Puliafito, C.A. Optical coherence tomography. Science 1991, 254, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar]
- Schuman, J.S.; Stinson, W.G.; Chang, W.; Puliafito, C.A.; Fujimoto, J.G. Optical coherence tomography. Science 1995, 254, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, K.C.; Cunha, I.W.; Rocha, R.M.; Ayala, F.R.; Cajaíba, M.M.; Begnami, M.D.; Vilela, R.S.; Paiva, G.R.; Andrade, R.G.; Soares, F.A. GLUT1 expression in malignant tumors and its use as an immunodiagnostic marker. Clinics 2011, 66, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Seino, Y.; Fukumoto, H.; Koh, G.; Yano, H.; Inagaki, N.; Yamada, Y.; Inoue, K.; Manabe, T.; Imura, H. Over-expression of facilitative glucose transporter genes in human cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1990, 170, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, M.; Lechago, L.V.; Somoano, J.R.; Mosharaf, M.; Lechago, J. Wide expression of the human erythrocyte glucose transporter Glut1 in human cancers. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 1164–1167. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, R.; Sarioglu, S.; Sökmen, S.; Füzün, M.; Küpelioglu, A.; Valentine, H.; Görken, I.B.; Airley, R.; West, C. Glucose transporter-1 (GLUT-1): A potential marker of prognosis in rectal carcinoma. Br. J. Canc. 2003, 89, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohma, T.; Okazumi, S.; Makino, H.; Cho, A.; Mochizuki, R.; Shuto, K.; Kudo, H.; Matsubara, K.; Gunji, H.; Matsubara, H. Overexpression of glucose transporter 1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas: A marker for poor prognosis. Dis. Esophagus 2005, 18, 185–189. [Google Scholar]
- Nikoobakht, B.; El-Sayed, M.A. Preparation and growth mechanism of gold nanorods (NRs) using seed-mediated growth method. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 1957–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orendorff, C.J.; Murphy, C.J. Quantitation of metal content in the silver-assisted growth of gold nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 3990–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Guyot-Sionnest, P. Mechanism of silver (I)-assisted growth of gold nanorods and bipyramids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 22192–22200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, L.; Murphy, C.J. Fine-tuning the shape of gold nanorods. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 3668–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Fu, Q.; Peng, J.; Wang, Y.; Du, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhan, L. Gold nanorod-based localized surface plasmon resonance biosensor for sensitive detection of hepatitis B virus in buffer, blood serum and plasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didychuk, C.L.; Ephrat, P.; Belton, M.; Carson, J.J.L. Synthesis and in vitro cytotoxicity of mPEG-SH modified gold nanorods. Proc. SPIE 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirui, D.K.; Krishnan, S.; Strickland, A.D.; Batt, C.A. PAA-derived gold nanorods for cellular targeting and photothermal therapy. Macromol. Biosci. 2011, 11, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.J.; Thompson, L.B.; Chernak, D.J.; Yang, J.A.; Sivapalan, S.T.; Boulos, S.P.; Huang, J.; Alkilany, A.M.; Sisco, P.N. Gold nanorod crystal growth: From seed-mediated synthesis to nanoscale sculpting. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 16, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenburg, A.L.; Hansen, M.N.; Ralston, T.S.; Wei, A.; Boppart, S.A. Imaging gold nanorods in excised human breast carcinoma by spectroscopic optical coherence tomography. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 6407–6411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orendorff, C.J.; Hankins, P.L.; Murphy, C.J. pH-Triggered assembly of gold nanorods. Langmuir 2005, 21, 2022–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Prabhulkar, S.; De la Zerda, A.; Paranjape, A.; Awdeh, R.M. Single Step Nanoplasmonic Immunoassay for the Measurement of Protein Biomarkers. Biosensors 2013, 3, 77-88. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios3010077
Prabhulkar S, De la Zerda A, Paranjape A, Awdeh RM. Single Step Nanoplasmonic Immunoassay for the Measurement of Protein Biomarkers. Biosensors. 2013; 3(1):77-88. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios3010077
Chicago/Turabian StylePrabhulkar, Shradha, Adam De la Zerda, Amit Paranjape, and Richard M. Awdeh. 2013. "Single Step Nanoplasmonic Immunoassay for the Measurement of Protein Biomarkers" Biosensors 3, no. 1: 77-88. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios3010077
APA StylePrabhulkar, S., De la Zerda, A., Paranjape, A., & Awdeh, R. M. (2013). Single Step Nanoplasmonic Immunoassay for the Measurement of Protein Biomarkers. Biosensors, 3(1), 77-88. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios3010077




