Evaluating Inhibition of the Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF)-Induced Response of Mutant MCF10A Cells with an Acoustic Sensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. QCM-D Measurements
2.4. Fluorescence Imaging
2.5. Data Analysis

2.6. Fluorescence Quantitation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Overview
3.2. Inhibition of the EGF-Induced Time-Dependent Cellular Responses: QCM-D Measurements
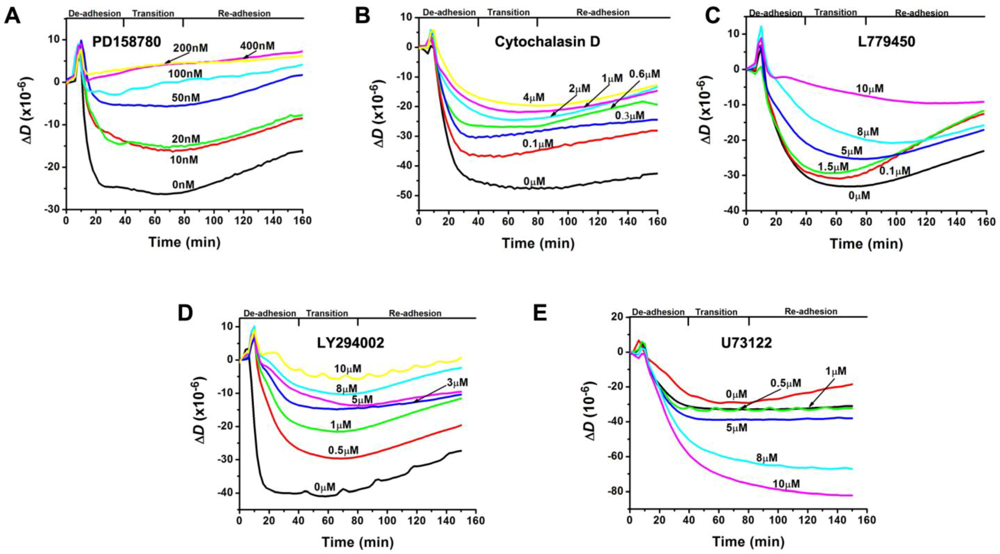
3.3. Inhibition of the EGF-Induced Time-Dependent Cellular Responses: Fluorescence Imaging
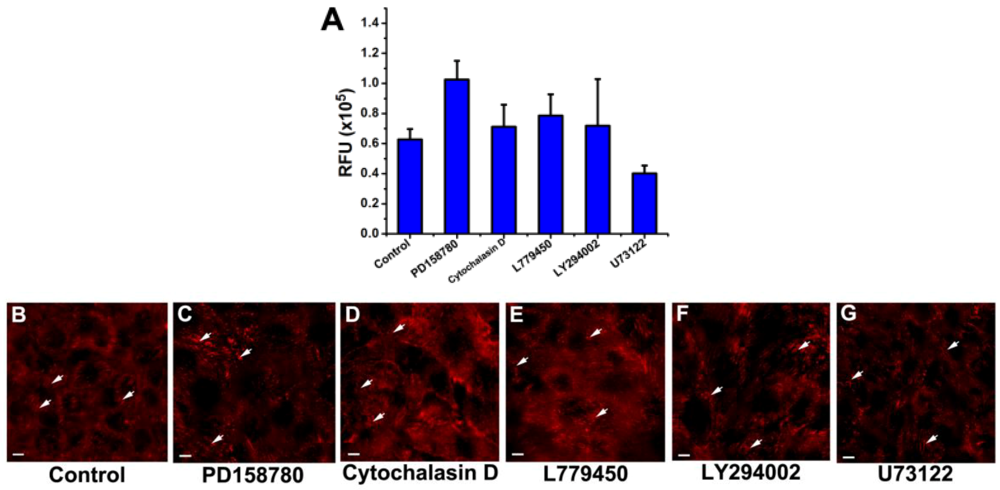
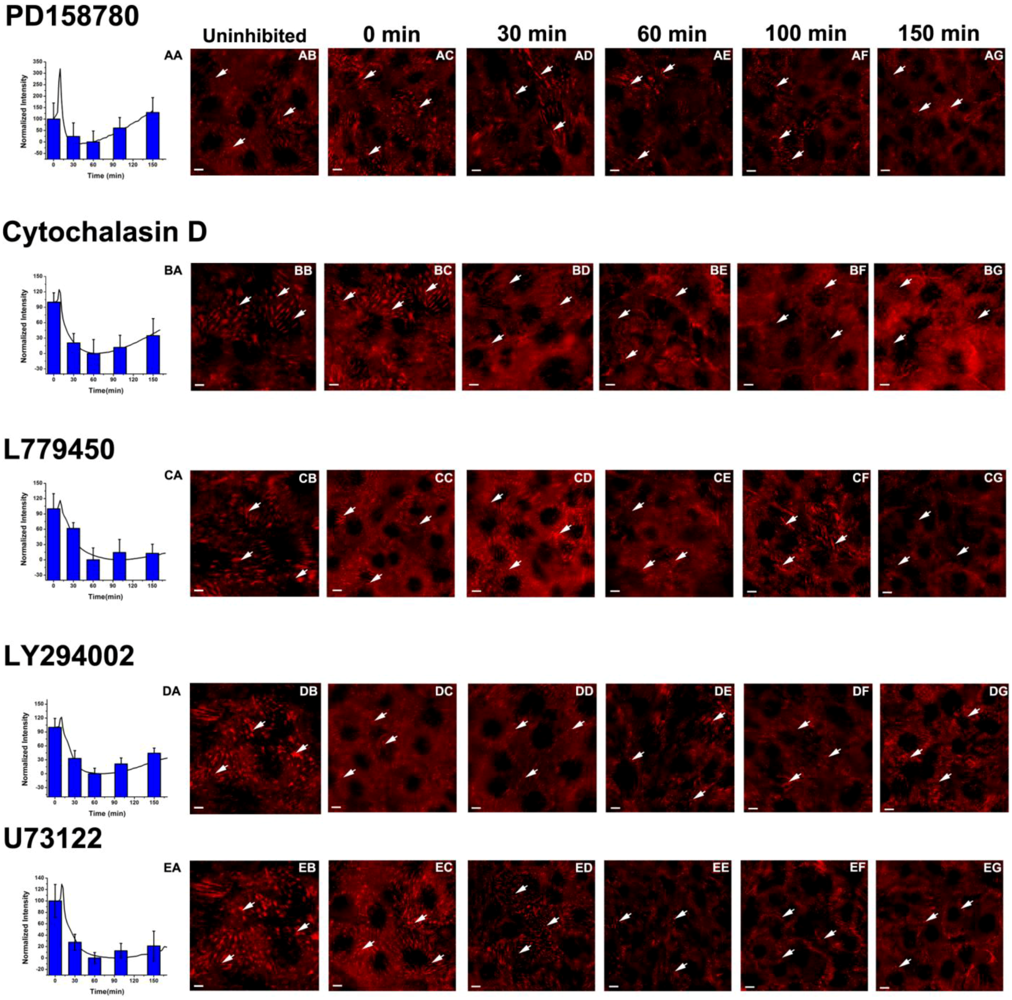
3.4. Inhibition of the EGF-Induced Time-Dependent Cellular Responses: Potencies of the Inhibitors
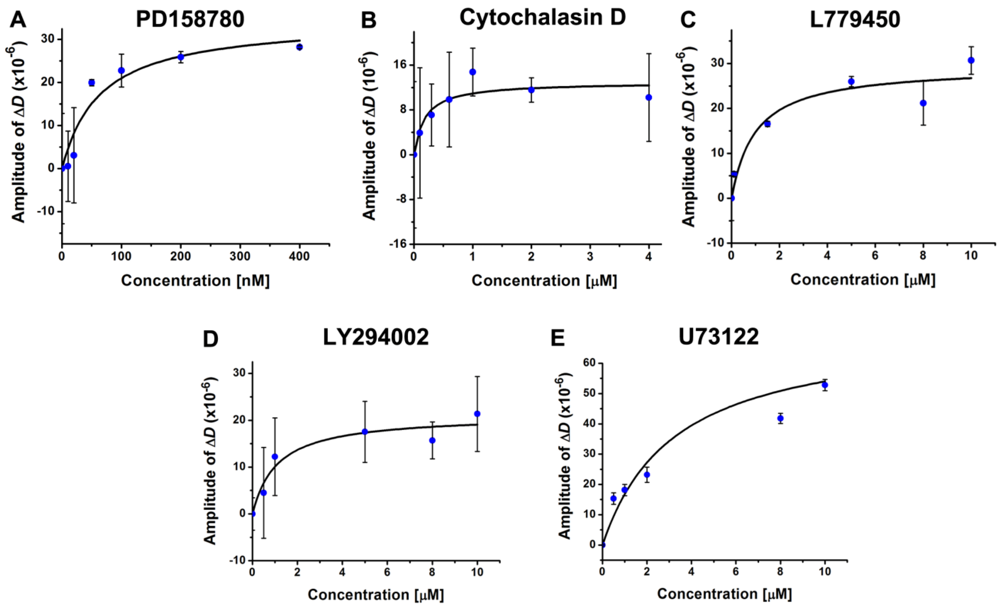
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Carpenter, G. Receptors for epidermal growth factor and other polypeptide mitogens. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1987, 56, 881–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmon, M.A.; Schlessinger, J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 2010, 141, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaltriti, M.; Baselga, J. The epidermal growth factor receptor pathway: A model for targeted therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5268–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaki, M.; Oshimura, M.; Ito, H. PI3K-Akt pathway: Its functions and alterations in human cancer. Apoptosis 2004, 9, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Pallero, M.A.; Gupta, K.; Chang, P.; Ware, M.F.; Witke, W.; Kwiatkowski, D.J.; Lauffenburger, D.A.; Murphy-Ullrich, J.E.; Wells, A. EGF receptor regulation of cell motility: EGF induces disassembly of focal adhesions independently of the motility-associated PLCgamma signaling pathway. J. Cell. Sci. 1998, 111, 615–624. [Google Scholar]
- Zandi, R.; Larsen, A.B.; Andersen, P.; Stockhausen, M.-T.; Poulsen, H.S. Mechanisms for oncogenic activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Cell. Signal. 2007, 19, 2013–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, S.; Settleman, J.; Reshkin, S.J.; Azzariti, A.; Bellizzi, A.; Paradiso, A. The complexity of targeting EGFR signalling in cancer: From expression to turnover. BBA-Rev. Cancer 2006, 1766, 120–139. [Google Scholar]
- Normanno, N.; De Luca, A.; Bianco, C.; Strizzi, L.; Mancino, M.; Maiello, M.R.; Carotenuto, A.; De Feo, G.; Caponigro, F.; Salomon, D.S. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling in cancer. Gene 2006, 366, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, K.; Matsuoka, Y.; Funahashi, A.; Kitano, H. A comprehensive pathway map of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, J.D.; Landau, E.M.; Iyengar, R. Signaling networks: The origins of cellular multitasking. Cell 2000, 103, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholodenko, B.N. Cell-signalling dynamics in time and space. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denholm, E.M.; Gerald, P.S. Differential effects of two fluorescent probes on macrophage migration as assessed by manual and automated methods. Cytometry 1995, 19, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbitt, K.B.; Rainger, G.E.; Nash, G.B. Effects of fluorescent dyes on selectin and integrin-mediated stages of adhesion and migration of flowing leukocytes. J. Immunol. Meth. 2000, 239, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, B.; Naichen, Y.; Xiaobo, W.; Xiao, X.; Yama, A. The application of cell-based label-free technology in drug discovery. Biotechnol. J. 2008, 3, 484–495. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y. Label-free biosensors for cell biology. Int. J. Electrochem. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.A. Non-optical screening platforms: The next wave in label-free screening? Drug Discov. Today 2006, 11, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.A. Optical biosensors: Where next and how soon? Drug Discov. Today 2006, 11, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y. Non-invasive optical biosensor for probing cell signaling. Sensors 2007, 7, 2316–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Ferrie, A.M.; Fontaine, N.H.; Mauro, J.; Balakrishnan, J. Resonant waveguide grating biosensor for living cell sensing. Biophys. J. 2006, 91, 1925–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattnaik, P. Surface plasmon resonance. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2005, 126, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, J.M. Surface plasmon resonance: Towards an understanding of the mechanisms of biological molecular recognition. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2001, 5, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaever, I.; Keese, C.R. A morphological biosensor for mammalian cells. Nature 1993, 366, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Li, M.; Penn, L.S.; Xi, J. Real-time and label-free detection of cellular response to signaling mediated by distinct subclasses of epidermal growth factor receptors. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 3141–3146. [Google Scholar]
- Atienza, J.M.; Yu, N.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Abassi, Y. Label-free and real-time cell-based kinase assay for screening selective and potent receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors using microelectronic sensor array. J. Biomol. Screen. 2006, 11, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Ferrie, A.M.; Fontaine, N.H.; Yuen, P.K. Characteristics of dynamic mass redistribution of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in living cells measured with label-free optical biosensors. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 5720–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, J.; Deng, Y.; Wang, D.; Lu, Y.; Yu, X. Detection of EGFR on living human gastric cancer BGC823 cells using surface plasmon resonance phase sensing. Sens. Actuator. B: Chem. 2011, 153, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson, C.; Kihlman, S.; Rodahl, M.; Kasemo, B. The piezoelectric quartz crystal mass and dissipation sensor: A means of studying cell adhesion. Langmuir 1998, 14, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodahl, M.; Hook, F.; Fredriksson, C.; Keller, C.A.; Krozer, A.; Brzezinski, P.; Voinova, M.; Kasemo, B. Simultaneous frequency and dissipation factor QCM measurements of biomolecular adsorption and cell adhesion. Faraday Discuss. 1997, 107, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, M.C. Quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring: Enabling real-time characterization of biological materials and their interactions. J. Biomol. Tech. 2008, 19, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Marx, K.A. The quartz crystal microbalance and the electrochemical QCM: Applications to studies of thin polymer films, electron transfer systems, biological macromolecules, biosensors, and cells. Piezoelectric Sens. 2007, 5, 371–424. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda, T.; Kishida, A.; Ebato, H.; Okahata, Y. Novel instrumentation monitoring in situ platelet adhesivity with a quartz crystal microbalance. ASAIO J. 1992, 38, M171–M173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redepenning, J.; Schlesinger, T.K.; Mechalke, E.J.; Puleo, D.A.; Bizios, R. Osteoblast attachment monitored with a quartz crystal microbalance. Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 3378–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryte, D.M.; Michael, D.W.; Wei-Shou, H. Real-time measurement of anchorage-dependent cell adhesion using a quartz crystal microbalance. Biotechnol. Progr. 1993, 9, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janshoff, A.; Wegener, J.; Sieber, M.; Galla, H.J. Double-mode impedance analysis of epithelial cell monolayers cultured on shear wave resonators. Eur. Biophys. J. 1996, 25, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegener, J.; Janshoff, A.; Galla, H.J. Cell adhesion monitoring using a quartz crystal microbalance: Comparative analysis of different mammalian cell lines. Eur. Biophys. J. 1998, 28, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitmann, V.; Reiss, B.; Wegener, J. The quartz crystal microbalance in cell biology: Basics and applications. Piezoelectric Sens. 2007, 5, 303–338. [Google Scholar]
- Nimeri, G.; Fredriksson, C.; Elwing, H.; Liu, L.; Rodahl, M.; Kasemo, B. Neutrophil interaction with protein-coated surfaces studied by an extended quartz crystal microbalance technique. Colloid. Surface. B 1998, 11, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitakis, M.; Gizeli, E. Acoustic sensors as a biophysical tool for probing cell attachment and cell/surface interactions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Shahid, A.; Garcia, M.P.; Penn, L.S.; Xi, J. Dissipation monitoring for assessing EGF-induced changes of cell adhesion. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 38, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Chen, J.Y.; Xi, N.; Lai, K.W.C.; Qu, C.; Fung, C.K.M.; enn, L.S.; Xi, J. Characterization of mechanical behavior of an epithelial monolayer in response to epidermal growth factor stimulation. Exp. Cell Res. 2012, 318, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.P.; Shahid, A.; Chen, J.Y.; Xi, J. Effects of the expression level of epidermal growth factor receptor on the ligand-induced restructuring of focal adhesions: A QCM-D study. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Reginato, M.J.; Mills, K.R.; Paulus, J.K.; Lynch, D.K.; Sgroi, D.C.; Debnath, J.; Muthuswamy, S.K.; Brugge, J.S. Integrins and EGFR coordinately regulate the pro-apoptotic protein Bim to prevent anoikis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dei Tos, A.P.; Ellis, I. Assessing epidermal growth factor receptor expression in tumours: What is the value of current test methods. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, R.O. Integrins: Bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 2002, 110, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheelock, M.J.; Johnson, K.R. Cadherins as modulators of cellular phenotype. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2003, 19, 207–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga, C.L. Epidermal growth factor receptor dependence in human tumors: More than just expression. Oncologist 2002, 7, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaban, N.Q.; Schwarz, U.S.; Riveline, D.; Goichberg, P.; Tzur, G.; Sabanay, I.; Mahalu, D.; Safran, S.; Bershadsky, A.; Addadi, L.; Geiger, B. Force and focal adhesion assembly: A close relationship studied using elastic micropatterned substrates. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beningo, K.A.; Dembo, M.; Kaverina, I.; Small, J.V.; Wang, Y.-l. Nascent focal adhesions are responsible for the generation of strong propulsive forces in migrating fibroblasts. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 153, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallant, N.D.; Michael, K.E.; García, A.J. Cell adhesion strengthening: contributions of adhesive area, integrin binding, and focal adhesion assembly. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 4329–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.L.; Tien, J.; Pirone, D.M.; Gray, D.S.; Bhadriraju, K.; Chen, C.S. Cells lying on a bed of microneedles: An approach to isolate mechanical force. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 1484–1489. [Google Scholar]
- Rewcastle, G.W.; Palmer, B.D.; Thompson, A.M.; Bridges, A.J.; Cody, D.R.; Zhou, H.; Fry, D.W.; McMichael, A.; Denny, W.A. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors. 10. isomeric 4-[(3-bromophenyl)amino]pyrido[d]-pyrimidines are potent ATP binding site inhibitors of the tyrosine kinase function of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 1823–1835. [Google Scholar]
- Schliwa, M. Action of cytochalasin D on cytoskeletal networks. J. Cell Biol. 1982, 92, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janmey, P.A. The cytoskeleton and cell signaling: Component localization and mechanical coupling. Physiol. Rev. 1998, 78, 763–781. [Google Scholar]
- Papakonstanti, E.A.; Stournaras, C. Cell responses regulated by early reorganization of actin cytoskeleton. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 2120–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, R.J.; Ridley, A.J. Phosphoinositide 3-kinases in cell migration. Biol. Cell. 2009, 101, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, F.D.; Asnes, C.F.; Chang, P.; Elson, E.L.; Lauffenburger, D.A.; Wells, A. Epidermal growth factor induces acute matrix contraction and subsequent calpain-modulated relaxation. Wound Repair Regen. 2002, 10, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharait, S.; Tran, K.; Yates, C.; Wells, A. Cell motility in prostate tumor invasion and metastasis. In Cell Motility in Cancer Invasion and Metastasis; Wells, A., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 8, pp. 301–338. [Google Scholar]
- Workman, P.; Clarke, P.A.; Raynaud, F.I.; van Montfort, R.L.M. Drugging the PI3 kinome: From chemical tools to drugs in the clinic. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 2146–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, N.; Lyons, J. Recent progress in targeting the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway with inhibitors in cancer drug discovery. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2005, 5, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, M.A.; Biggs, W.H.; Treiber, D.K.; Atteridge, C.E.; Azimioara, M.D.; Benedetti, M.G.; Carter, T.A.; Ciceri, P.; Edeen, P.T.; Floyd, M.; et al. A small molecule-kinase interaction map for clinical kinase inhibitors. Nat. Biotech. 2005, 23, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollob, J.A.; Wilhelm, S.; Carter, C.; Kelley, S.L. Role of Raf kinase in cancer: Therapeutic potential of targeting the Raf/MEK/ERK signal transduction pathway. Semin. Oncol. 2006, 33, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahos, C.J.; Matter, W.F.; Hui, K.Y.; Brown, R.F. A specific inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, 2-(4-morpholinyl)-8-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one (LY294002). J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 5241–5248. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, R.J.; Sam, L.M.; Justen, J.M.; Bundy, G.L.; Bala, G.A.; Bleasdale, J.E. Receptor-coupled signal transduction in human polymorphonuclear neutrophils: Effects of a novel inhibitor of phospholipase C-dependent processes on cell responsiveness. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1990, 253, 688–697. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, A.; Kassis, J.; Solava, J.; Turner, T.; Lauffenburger, D.A. Growth factor-induced cell motility in tumor invasion. Acta Oncol. 2002, 41, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, R.; Janssen, N.; Schmidt, J.; Kebig, A.; Merten, N.; Hennen, S.; Muller, A.; Blattermann, S.; Mohr-Andra, M.; Zahn, S.; et al. Deconvolution of complex G protein-coupled receptor signaling in live cells using dynamic mass redistribution measurements. Nat. Biotech. 2010, 28, 943–949. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y. Label-free cell-based assays with optical biosensors in drug discovery. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2006, 4, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y. Label-free receptor assays. Drug Discovery Today 2010, 7, e5–e11. [Google Scholar]
- Rocheville, M.; Jerman, J.C. 7TM pharmacology measured by label-free: A holistic approach to cell signalling. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakatsuki, T.; Schwab, B.; Thompson, N.C.; Elson, E.L. Effects of cytochalasin D and latrunculin B on mechanical properties of cells. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Fry, D.W.; Nelson, J.M.; Slintak, V.; Keller, P.R.; Rewcastle, G.W.; Denny, W.A.; Zhou, H.; Bridges, A.J. Biochemical and antiproliferative properties of 4-[Ar(alk)ylamino]pyridopyrimidines, a new chemical class of potent and specific epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1997, 54, 877–887. [Google Scholar]
- Shelton, J.G.; Moye, P.W.; Steelman, L.S.; Blalock, W.L.; Lee, J.T.; Franklin, R.A.; McMahon, M.; McCubrey, J.A. Differential effects of kinase cascade inhibitors on neoplastic and cytokine-mediated cell proliferation. Leukemia 2003, 17, 1765–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Peng, H.; Zalkow, L.H.; Li, Y.-H.; Zhu, C.; Powis, G.; Kunkel, M. 3β-Hydroxy-6-aza-cholestane and related analogues as phosphatidylinositol specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) inhibitors with antitumor activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2000, 8, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia, M.P.; Shahid, A.; Chen, J.Y.; Xi, J. Evaluating Inhibition of the Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF)-Induced Response of Mutant MCF10A Cells with an Acoustic Sensor. Biosensors 2012, 2, 448-464. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios2040448
Garcia MP, Shahid A, Chen JY, Xi J. Evaluating Inhibition of the Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF)-Induced Response of Mutant MCF10A Cells with an Acoustic Sensor. Biosensors. 2012; 2(4):448-464. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios2040448
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia, Marcela P., Ammar Shahid, Jennifer Y. Chen, and Jun Xi. 2012. "Evaluating Inhibition of the Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF)-Induced Response of Mutant MCF10A Cells with an Acoustic Sensor" Biosensors 2, no. 4: 448-464. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios2040448
APA StyleGarcia, M. P., Shahid, A., Chen, J. Y., & Xi, J. (2012). Evaluating Inhibition of the Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF)-Induced Response of Mutant MCF10A Cells with an Acoustic Sensor. Biosensors, 2(4), 448-464. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios2040448




