Simulation-Based Performance Assessment of Bulk Junctionless FET with Asymmetric Source/Drain for Ultrasensitive Detection of Biomolecules
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Simulation Methods
2.1. Device Simulation Parameters
2.2. Physics Models
3. Results and Discussion
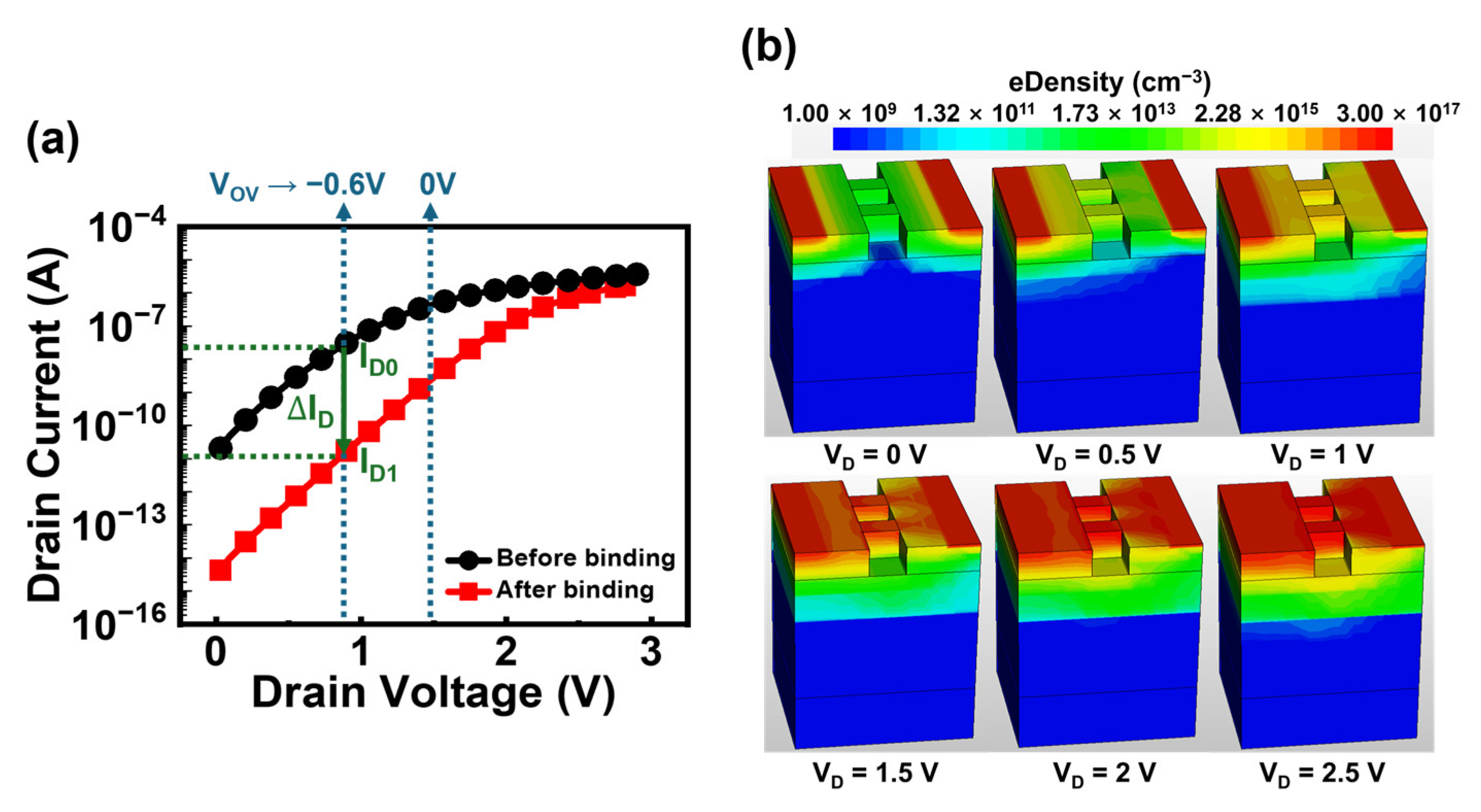
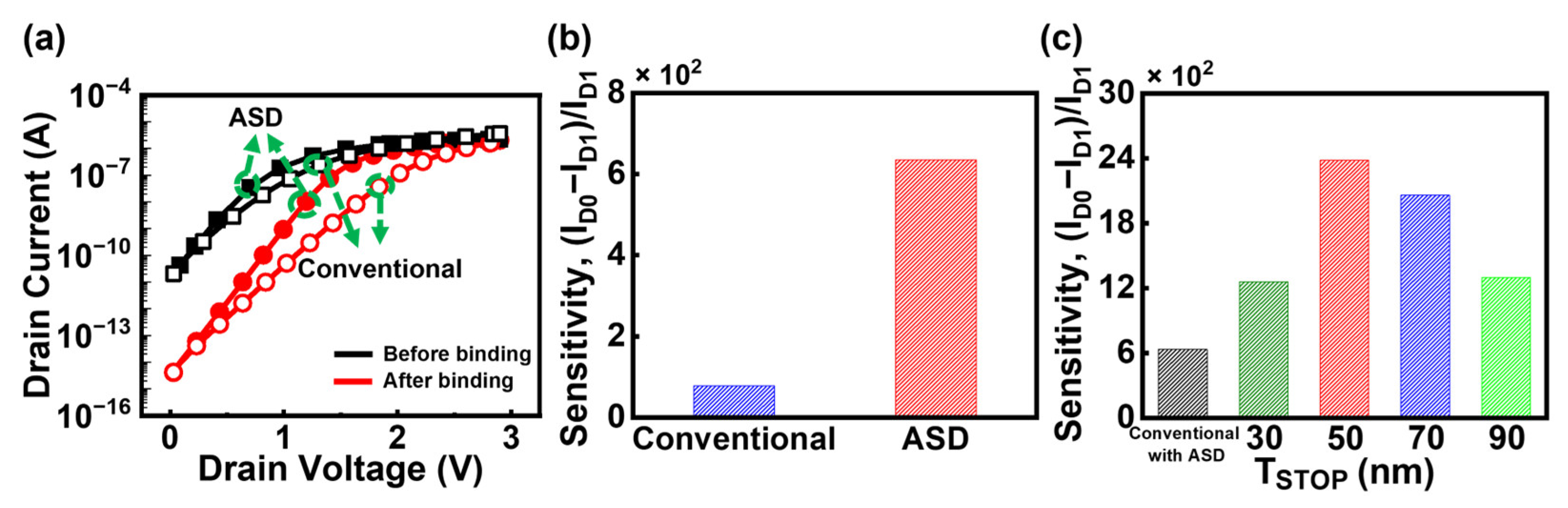
3.1. Operation of JL-BioFET
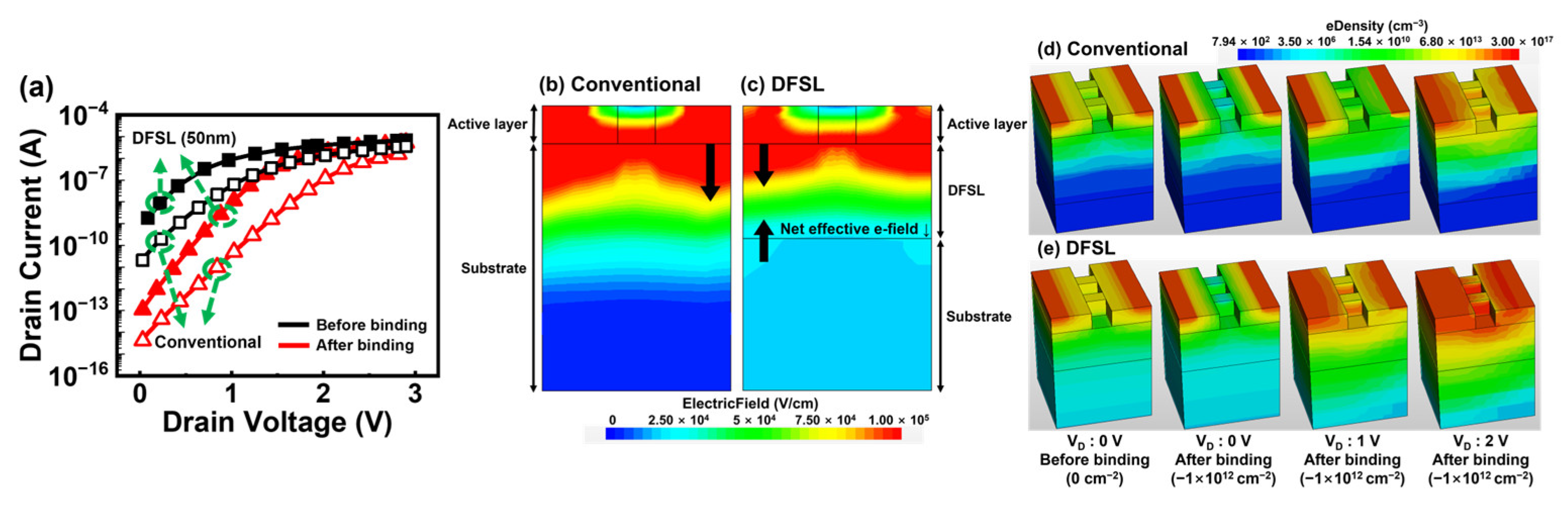
3.2. Bulk JL-BioFET with Doped Field Stop Layer
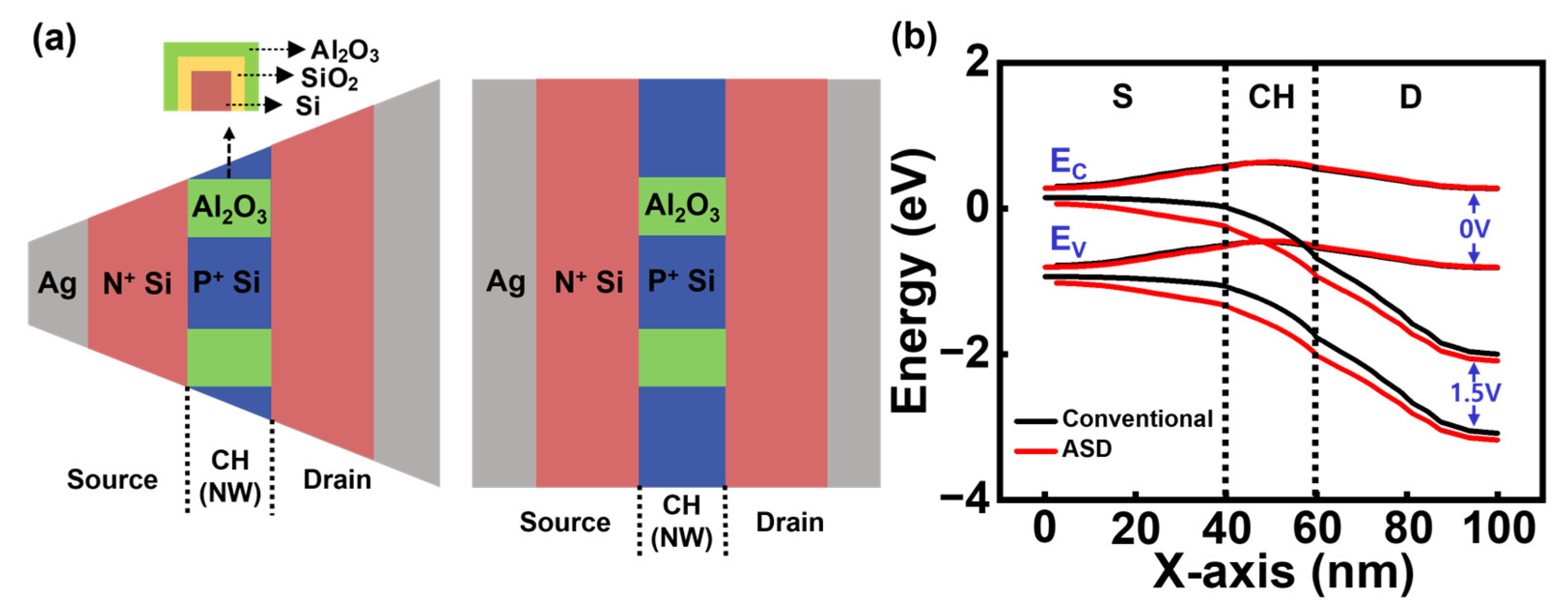
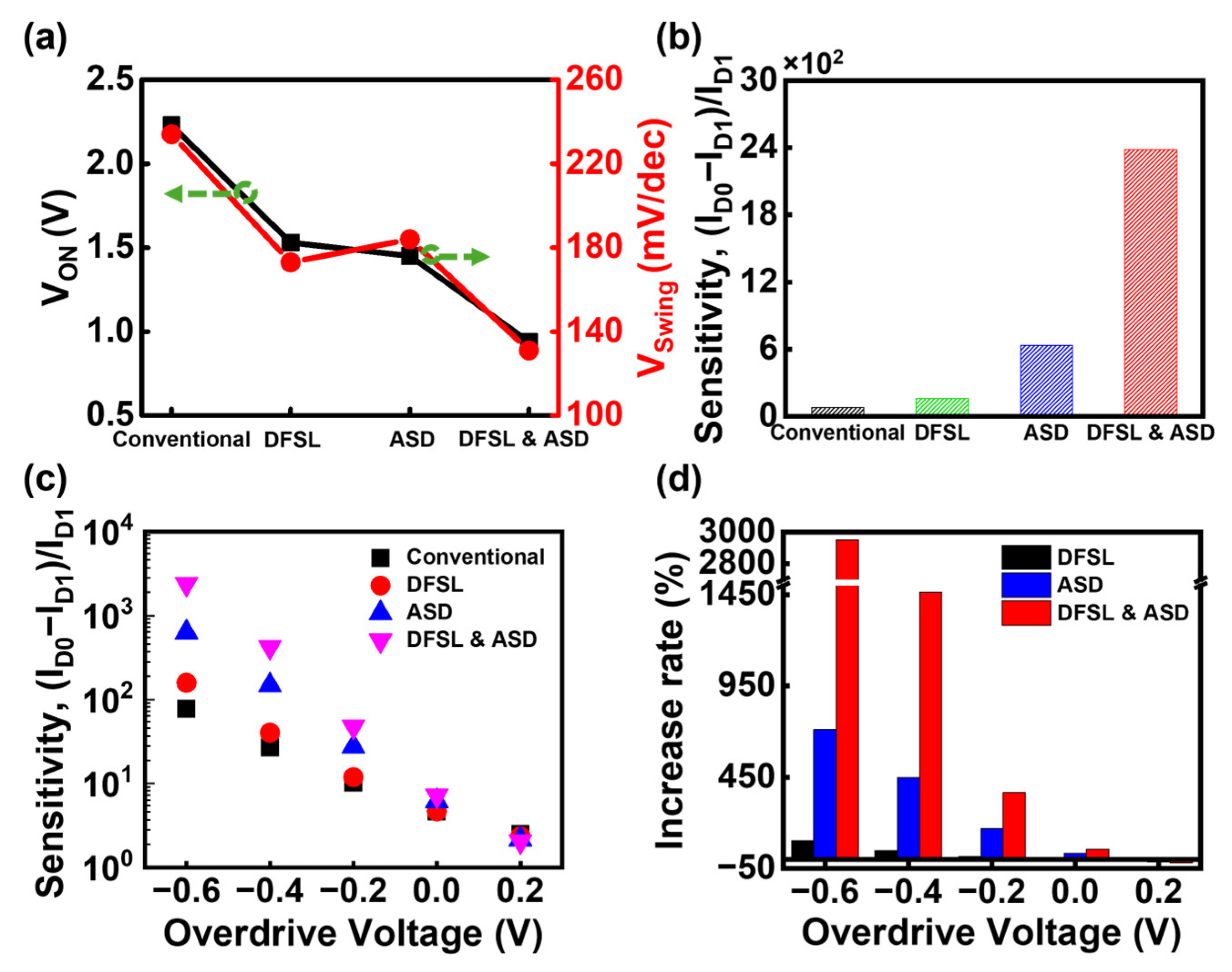
3.3. DFSL Bulk JL-BioFET with Asymmetric Source/Drain Structure
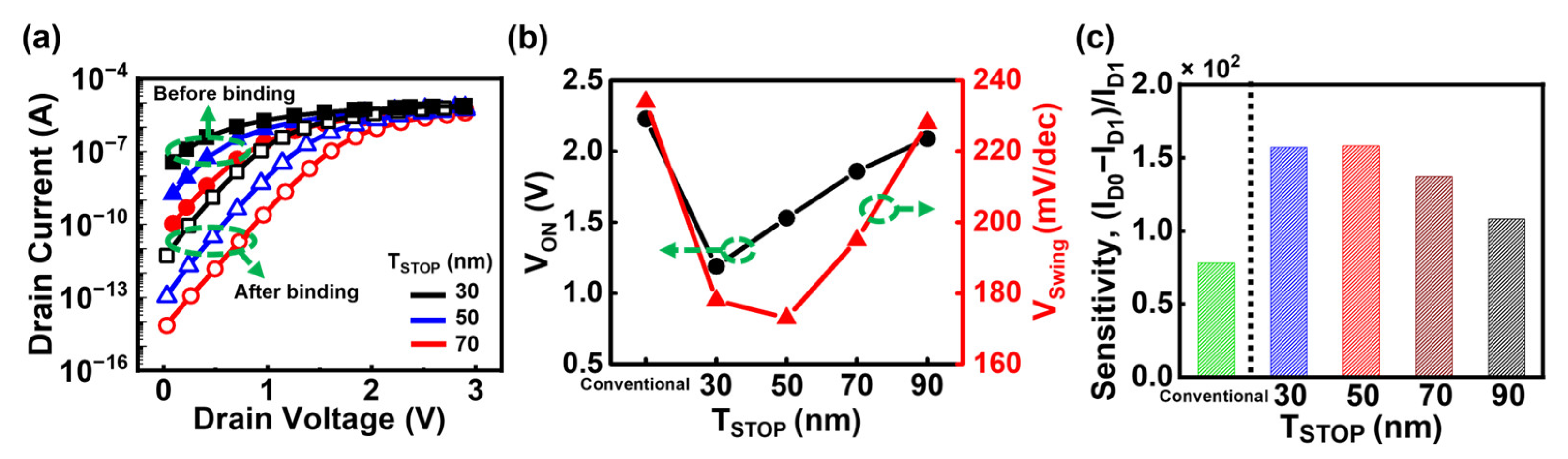
3.4. Comparison of the Sensitivity of Proposed Structures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gubala, V.; Harris, L.F.; Ricco, A.J.; Tan, M.X.; Williams, D.E. Point of care diagnostics: Status and future. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 487–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justino, C.I.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T.A. Recent progress in biosensors for environmental monitoring: A review. Sensors 2017, 17, 2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.H.; Nguyen, C.M.; Huynh, M.A.; Vu, H.H.; Nguyen, T.K.; Nguyen, N.T. Field effect transistor based wearable biosensors for healthcare monitoring. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, T.C. Polymerase chain reaction: Basic protocol plus troubleshooting and optimization strategies. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 63, e3998. [Google Scholar]
- Morad-Farajollahi, M.; Hamzehlou, S. Development of a new indirect ELISA method for detection of anti-tuberculosis antibodies in human serum. J. Med. Bacteriol. 2012, 1, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado-Povedano, M.; Calderón-Santiago, M.; De Castro, M.L.; Priego-Capote, F. Metabolomics analysis of human sweat collected after moderate exercise. Talanta 2018, 177, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-S.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, M. Ion-sensitive field-effect transistor for biological sensing. Sensors 2009, 9, 7111–7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souteyrand, E.; Cloarec, J.P.; Martin, J.R.; Wilson, C.; Lawrence, I.; Mikkelsen, S.; Lawrence, M.F. Direct detection of the hybridization of synthetic homo-oligomer DNA sequences by field effect. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 2980–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, D.; Prazeres, D.; Chu, V.; Conde, J. Detection of DNA and proteins using amorphous silicon ion-sensitive thin-film field effect transistors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, T.; Baek, C.K.; Kim, K.; Jeong, Y.H.; Lee, J.S.; Meyyappan, M. Silicon nanowire biologically sensitive field effect transistors: Electrical characteristics and applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Park, C.; Kwon, D.; Kim, D.; Meyyappan, M.; Jeon, S.; Lee, J.S. Silicon nanowire biosensors for detection of cardiac troponin I (cTnI) with high sensitivity. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, K.Y.; Park, C.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.S.; Yi, H.; Kim, B. A reconfigurable and portable highly sensitive biosensor platform for ISFET and enzyme-based sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 4443–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Periyakaruppan, A.; Meyyappan, M.; Koehne, J.E. Label-free detection of c-reactive protein using a carbon nanofiber based biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 59, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Pandya, R.; Sieffert, T.; Meyyappan, M.; Koehne, J.E. Multiplexed electrochemical immunosensor for label-free detection of cardiac markers using a carbon nanofiber array chip. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 773, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Dai, Z.; Tang, X.; Lin, Z.; Lo, P.K.; Meyyappan, M.; Lai, K.W.C. Graphene field-effect transistors for the sensitive and selective detection of Escherichia coli using pyrene-tagged DNA aptamer. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1700736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mia, A.K.; Meyyappan, M.; Giri, P. Two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenide based biosensors: From fundamentals to healthcare applications. Biosensors 2023, 13, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Dak, P.; Lee, Y.; Park, H.; Choi, W.; Alam, M.A.; Kim, S. Two-dimensional layered MoS2 biosensors enable highly sensitive detection of biomolecules. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Alharbi, A.; You, K.D.; Kisslinger, K.; Stach, E.A.; Shahrjerdi, D. Experimental study of the detection limit in dual-gate biosensors using ultrathin silicon transistors. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 7142–7147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Liu, F.; Han, R.; Zhuang, Y. A vertically stacked nanosheet gate-all-around FET for biosensing application. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 63602–63610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Banerjee, K. Proposal for tunnel-field-effect-transistor as ultra-sensitive and label-free biosensors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 143108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.; Heo, C.; Kim, H.; Meyyappan, M.; Kim, K. A novel bulk planar junctionless field-effect transistor for high-performance biosensing. Biosensors 2025, 15, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, G.C.; Bonge, V.H.; Malode, M.M.; Jain, R.G. Novel δ -doped partially insulated junctionless transistor for mixed signal integrated circuits. Superlattices Microstruct. 2016, 90, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, V.P.; Ilnitskii, M.A.; Zhanaev, E.D.; Myakon’Kich, A.V.; Rudenko, K.V.E.; Glukhov, A.V. Biosensor properties of SOI nanowire transistors with a PEALD Al2O3 dielectric protective layer. Semiconductors 2016, 50, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wei, Q.; Park, H.; Lieber, C.M. Nanowire nanosensors for highly sensitive and selective detection of biological and chemical species. Science 2001, 293, 1289–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, A.; Werner, F.; Cuevas, A.; Schmidt, J.; Glunz, S.W. Improved parameterization of auger recombination in silicon. Energy Procedia 2012, 27, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Overstraeten, R.; De Man, H. Measurement of the ionization rates in diffused silicon PN junctions. Solid-State Electron. 1970, 13, 583–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Ko, E.; Shin, C. Steep slope silicon-on-insulator feedback field-effect transistor: Design and performance analysis. IEEE Tran. Electron Devices 2018, 66, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurkx, G.A.M.; Klaassen, D.; Knuvers, M. A new recombination model for device simulation including tunneling. IEEE Tran. Electron Devices 1992, 39, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, A. A model for the field and temperature dependence of Shockley-read-hall lifetimes in silicon. Solid-State Electron. 1992, 35, 1585–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotboom, J.; De Graaff, H. Measurements of bandgap narrowing in Si bipolar transistors. Solid-State Electron. 1976, 19, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Patil, G.C. Dielectric-modulated bulk-planar junctionless field-effect transistor for biosensing applications. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2021, 68, 3545–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Ko, M.D.; Kim, K.H.; Baek, R.H.; Sohn, C.W.; Baek, C.K.; Park, S.; Deen, M.J.; Jeong, Y.-H.; Lee, J.S. Electrical characteristics of 20-nm junctionless Si nanowire transistors. Solid-State Electron. 2012, 73, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, M.; Van Overstraeten, R. Minority carrier recombination in heavily-doped silicon. Solid-State Electron. 1983, 26, 577–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Description (Parameter) | Values |
|---|---|
| Active layer (TAL) | 20 nm |
| SiO2 thickness (TSiO2) | 2.5 nm |
| Al2O3 thickness (TAl2O3) | 2.5 nm |
| Source region length (LSource) | 40 nm |
| Drain region length (LDrain) | 40 nm |
| Nanowire channel length (LNW) | 20 nm |
| Nanowire channel width (WNW) | 16 nm |
| N+-type Si doping concentration (CN+) | 3 × 1017 cm−3 |
| P+-type Si doping concentration (CP+) | 1.5 × 1017 cm−3 |
| P-type Si doping concentration (CP) | 1 × 1015 cm−3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Son, J.; Meyyappan, M.; Kim, K. Simulation-Based Performance Assessment of Bulk Junctionless FET with Asymmetric Source/Drain for Ultrasensitive Detection of Biomolecules. Biosensors 2025, 15, 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090597
Son J, Meyyappan M, Kim K. Simulation-Based Performance Assessment of Bulk Junctionless FET with Asymmetric Source/Drain for Ultrasensitive Detection of Biomolecules. Biosensors. 2025; 15(9):597. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090597
Chicago/Turabian StyleSon, Jeongmin, M. Meyyappan, and Kihyun Kim. 2025. "Simulation-Based Performance Assessment of Bulk Junctionless FET with Asymmetric Source/Drain for Ultrasensitive Detection of Biomolecules" Biosensors 15, no. 9: 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090597
APA StyleSon, J., Meyyappan, M., & Kim, K. (2025). Simulation-Based Performance Assessment of Bulk Junctionless FET with Asymmetric Source/Drain for Ultrasensitive Detection of Biomolecules. Biosensors, 15(9), 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090597





