Evaluation of Fluorescence Detection Algorithms for Efficient ROI Setting in Low-Cost Real-Time PCR Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
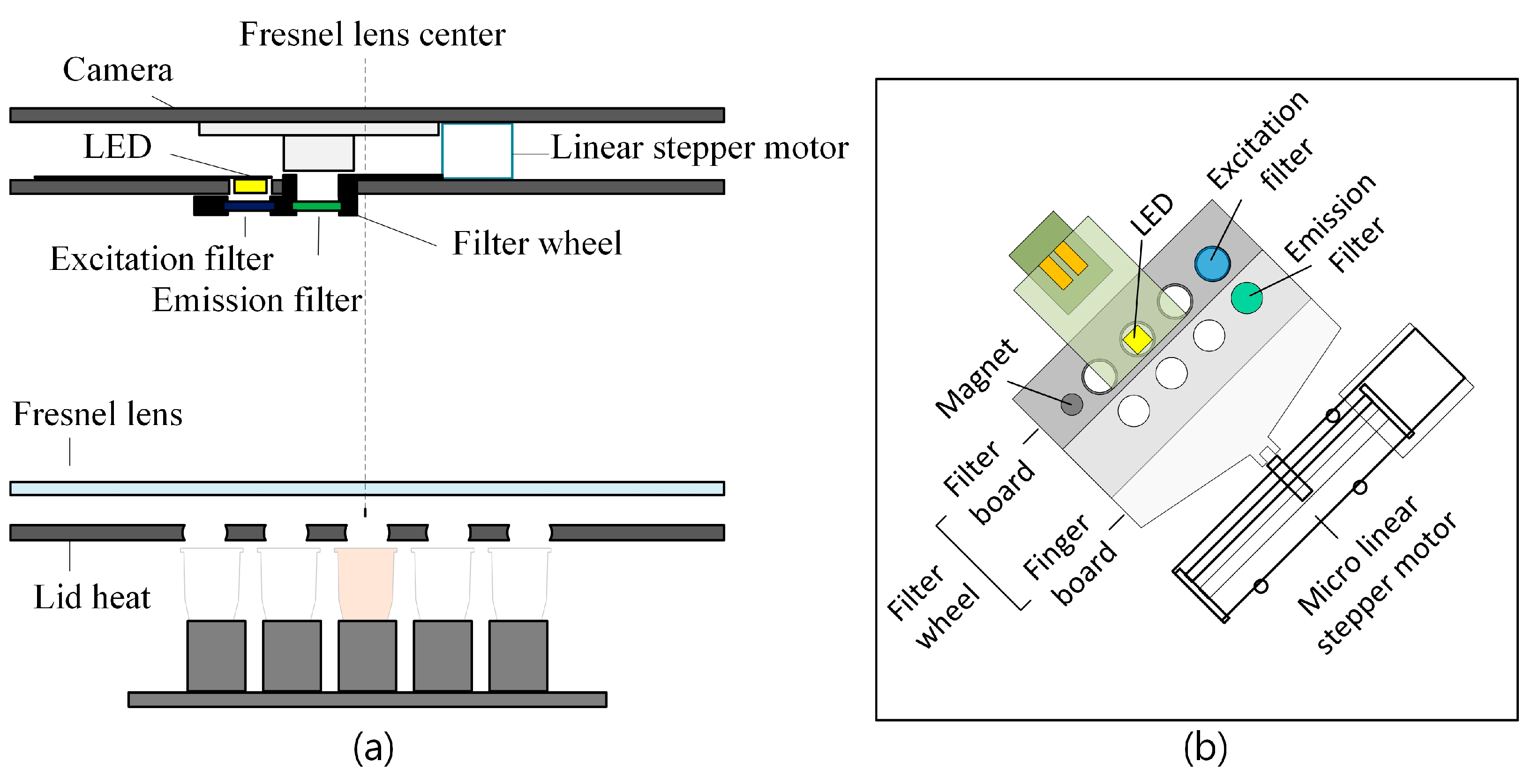
2.1. Equipment Description
2.2. ROI Detection Considerations
2.3. Image Processing for Fluorescence Detection
2.4. Validation and Comparison of Fluorescence Detection Methods
3. Results
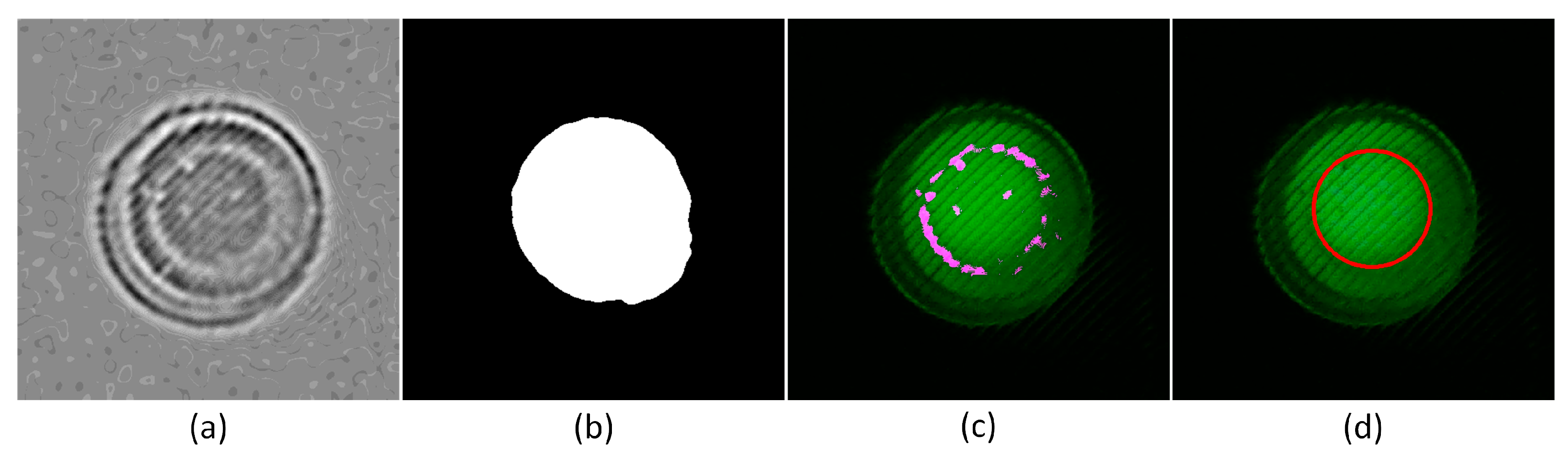
3.1. Image Processing Results
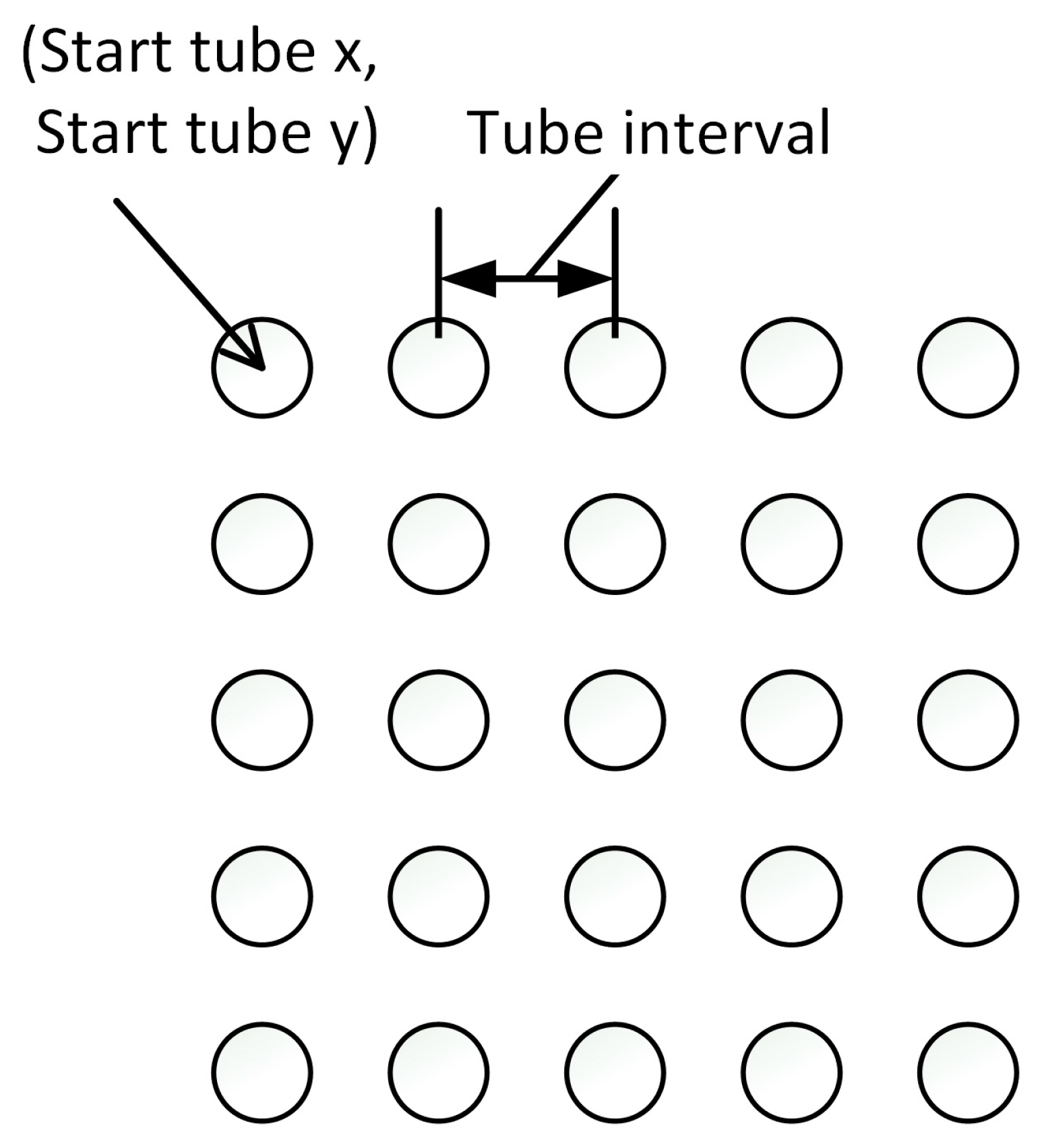
3.1.1. Parameters for Tube Grid
3.1.2. Tube Grid Results Using the Simple Algorithm
3.1.3. Optical Window Detection Results Using the Complex Algorithm
3.2. Comparison of Fluorescence Detection Algorithms
3.2.1. Validation of Manual Detection
3.2.2. Evaluation of the Complex Algorithm
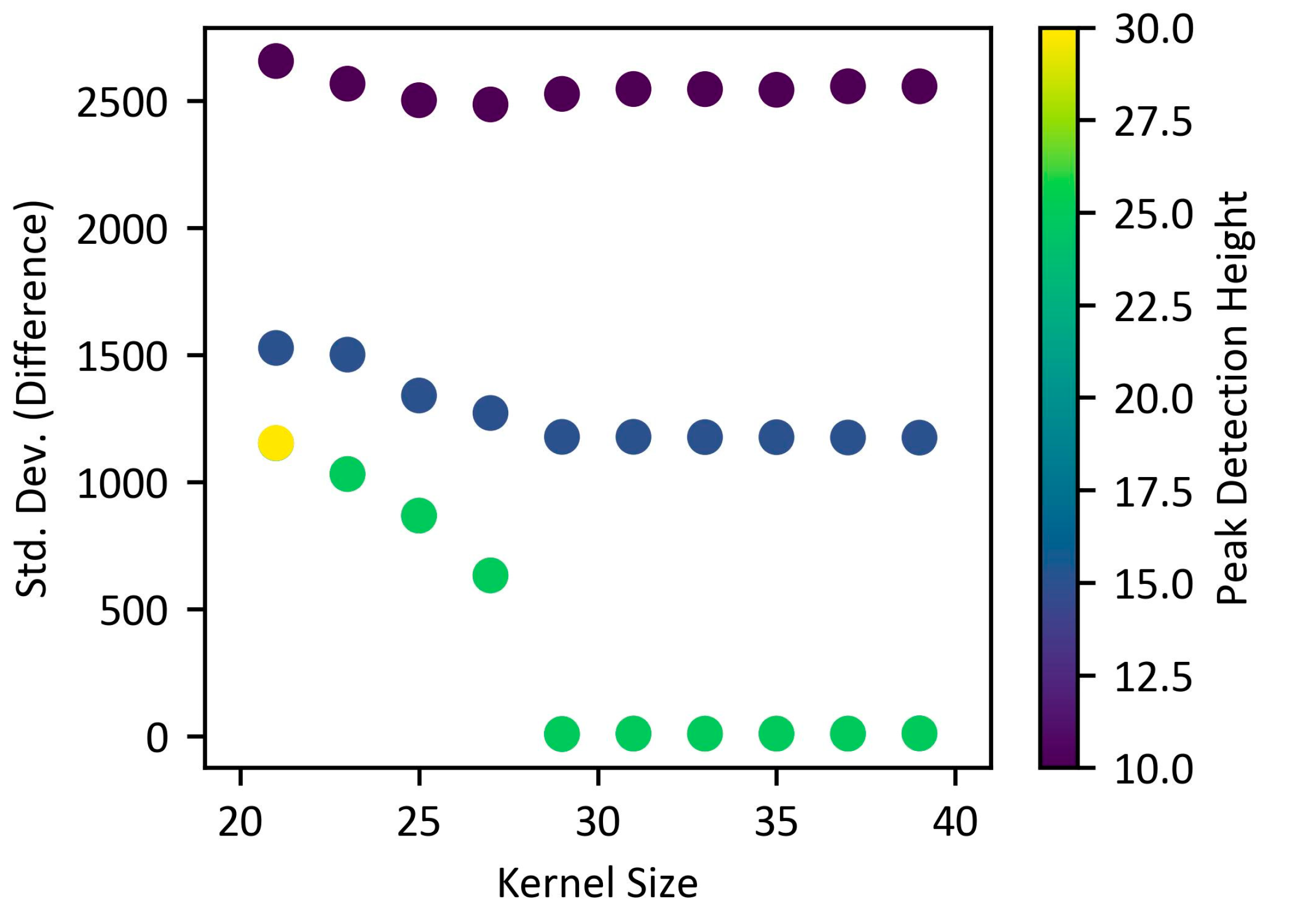
3.2.3. Evaluation of the Efficiency of the Simple Algorithm
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xing, D. Integrated paper-based detection chip with nucleic acid extraction and amplification for automatic and sensitive pathogen detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 261, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.E.; Patel, N.G.; Levy, M.A.; Storeygard, A.; Balk, D.; Gittleman, J.L.; Daszak, P. Global trends in emerging infectious diseases. Nature 2008, 451, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, A.P.; Carper, E.R. Infectious diseases and human population history. Bioscience 1996, 46, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valasek, M.A.; Repa, J.J. The power of real-time PCR. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2005, 29, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Nehra, M.; Kumar, R.; Dilbaghi, N.; Hu, T.; Kumar, S.; Kaushik, A.; Li, C.-z. Internet of medical things (IoMT)-integrated biosensors for point-of-care testing of infectious diseases. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 179, 113074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Laboratory Testing for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Suspected Human Cases: Interim Guidance, 2 March 2020; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, H.; Fan, C.; Chen, M.; Zhang, X.; Yan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gong, Z.; Shi, L.; Li, X. Recent advances of fluorescent biosensors based on cyclic signal amplification technology in biomedical detection. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwe, I.A.; Li, Z.; Huang, J. A dual-cycling fluorescence scheme for ultrasensitive DNA detection through signal amplification and target regeneration. Analyst 2019, 144, 2649–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S. Real-Time Detection of Amplification Products Through Fluorescence Quenching or Energy Transfer. In Advanced Techniques in Diagnostic Microbiology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 413–440. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.-t.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, J.-h. A fluorescence detection optical system for real-time quantitative PCR. In Proceedings of the Optical Design and Testing X, Online, 10 October 2020; pp. 409–417. [Google Scholar]
- Neuzil, P.; Novak, L.; Pipper, J.; Lee, S.; Ng, L.F.; Zhang, C. Rapid detection of viral RNA by a pocket-size real-time PCR system. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 2632–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Shin, J.H. Point-of-care diagnostics for infectious diseases: Present and future. Korean J. Med. 2018, 93, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Petralia, S.; Conoci, S. PCR technologies for point of care testing: Progress and perspectives. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 876–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, K.; Li, Z.; Wang, P. Point of care testing for infectious diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 493, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spata, M.O.; Castagna, M.E.; Conoci, S. Image data analysis in qPCR: A method for smart analysis of DNA amplification. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2015, 6, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wei, W.; Yuan, X.; Zhou, R. Research on Calibration Methods of Long-Wave Infrared Camera and Visible Camera. J. Sens. 2022, 2022, 8667606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Li, Y.; Wu, D.; Wu, W. A handheld continuous-flow real-time fluorescence qPCR system with a PVC microreactor. Analyst 2020, 145, 2767–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehnert, M.; Kipf, E.; Schlenker, F.; Borst, N.; Zengerle, R.; von Stetten, F. Fluorescence signal-to-noise optimisation for real-time PCR using universal reporter oligonucleotides. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 3444–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonnette, L.; Bergeron, M.G. Portable devices and mobile instruments for infectious diseases point-of-care testing. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 17, 471–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767, 02767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929, 11929. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.S.; Shahriar, G.M.; Syeed, M.M.; Uddin, M.F.; Hasan, M.; Shivam, S.; Advani, S. Region of interest (ROI) selection using vision transformer for automatic analysis using whole slide images. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.-E.; Son, C.-H.; Lee, S. ROI-aware multiscale cross-attention vision transformer for pest image identification. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 237, 110732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Gaňová, M.; Lednický, T.; Zhu, H.; Liu, X.; Korabečná, M.; Chang, H.; Neužil, P. An image-to-answer algorithm for fully automated digital PCR image processing. Lab Chip 2022, 22, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, S.-B.-N.; Kim, Y.-S.; Park, C.-Y.; Lee, D.-J. Compact Camera Fluorescence Detector for Parallel-Light Lens-Based Real-Time PCR System. Sensors 2022, 22, 8575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





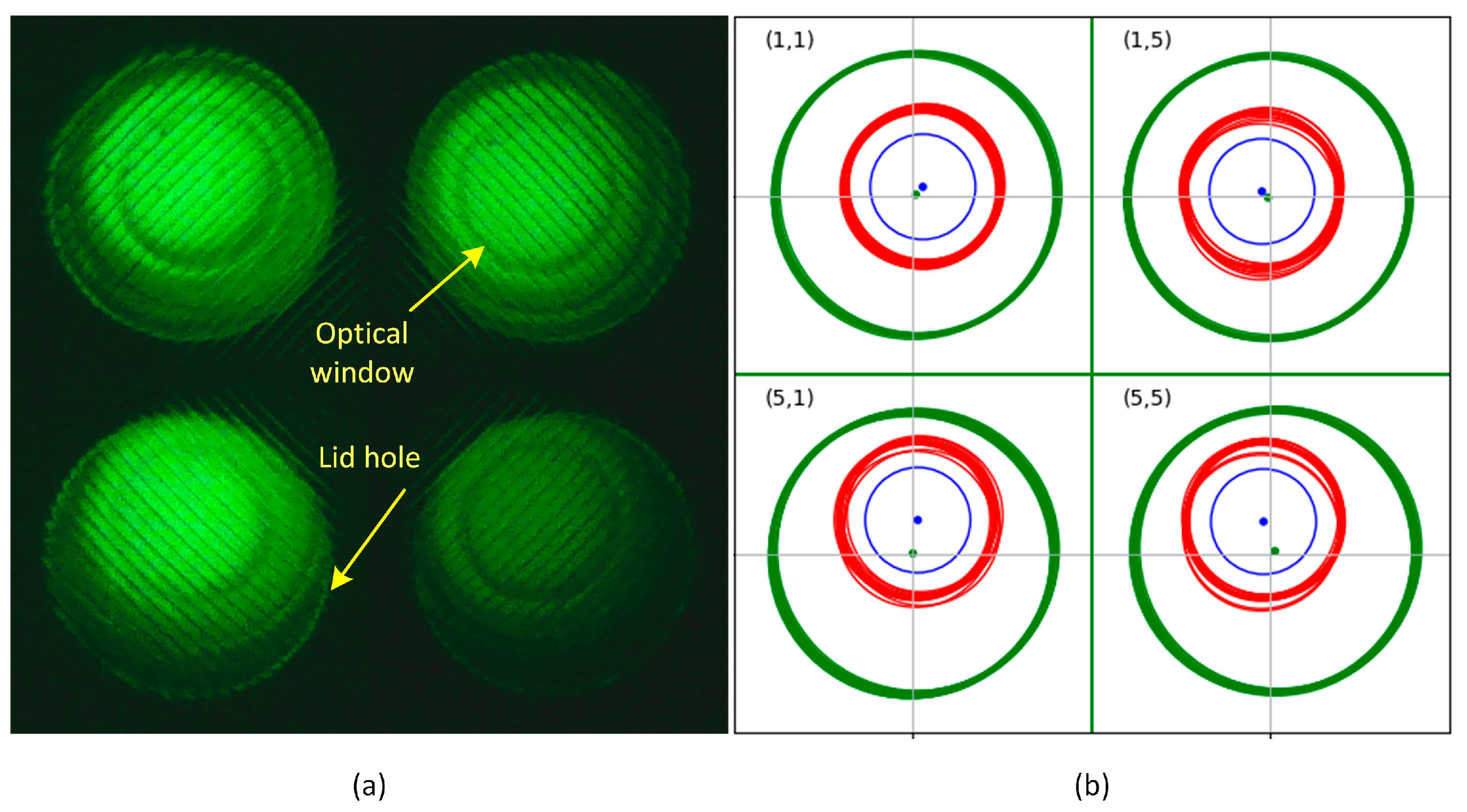


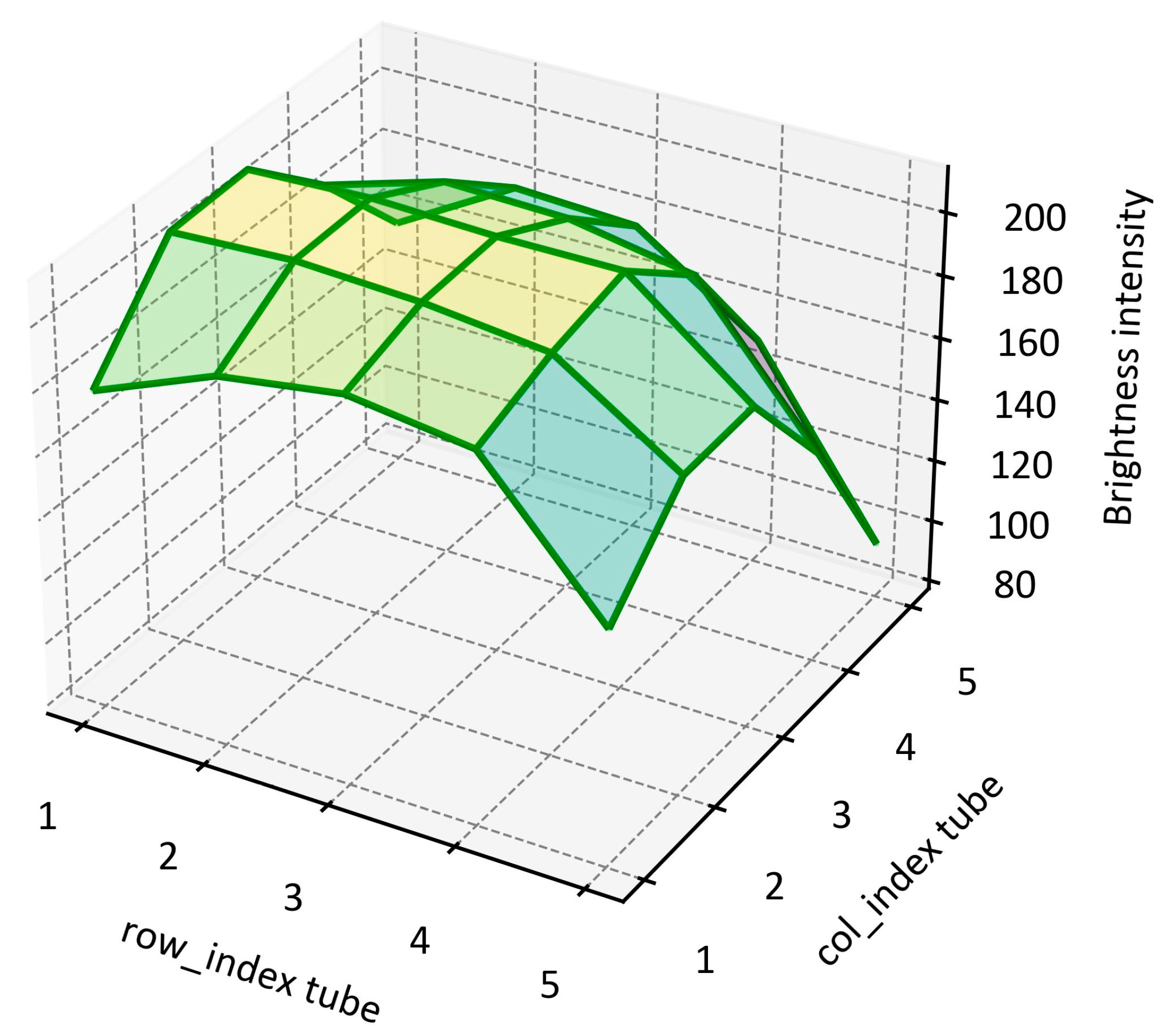
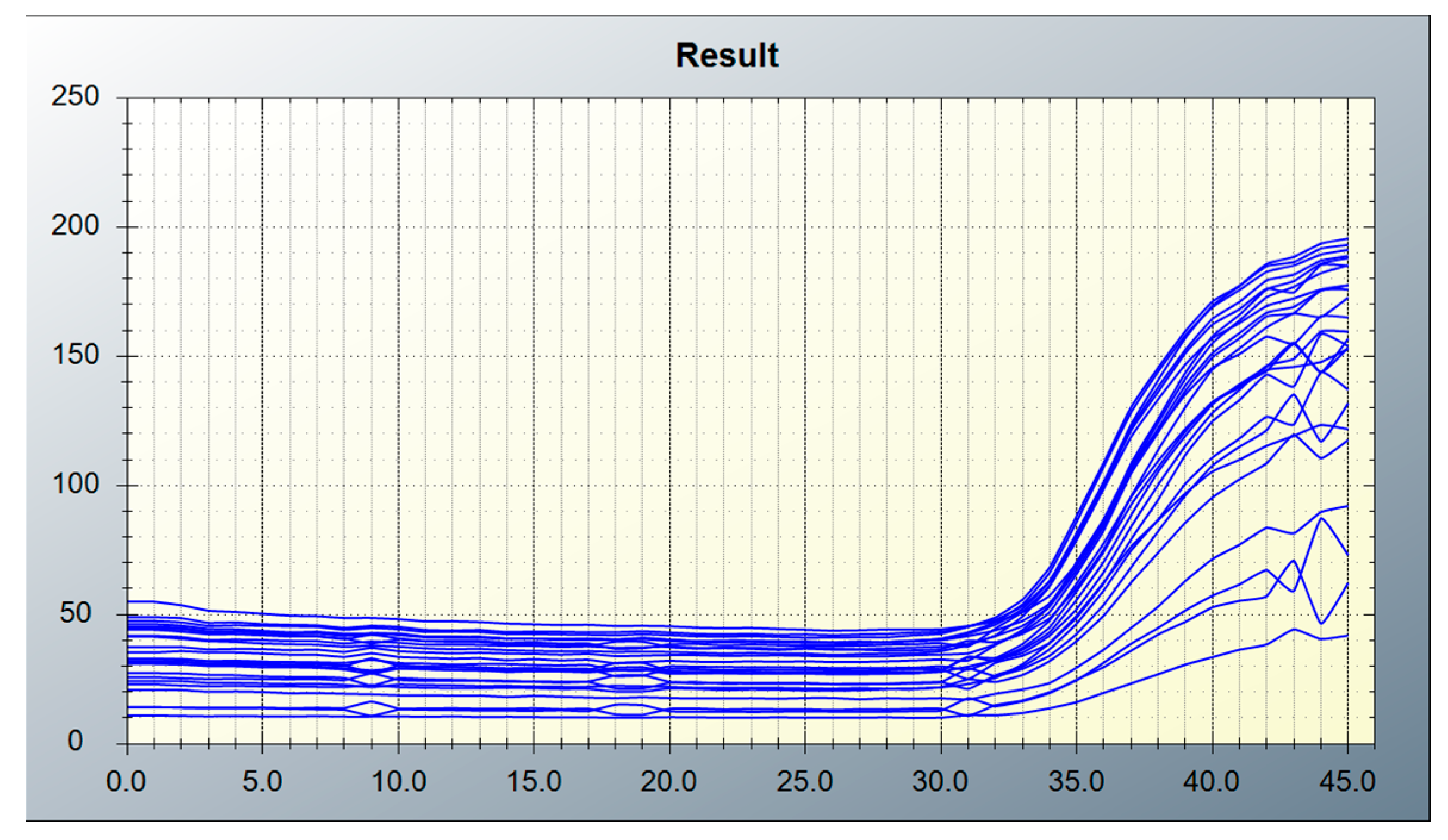
| Area Mean | Area Std/m | Center Std | Center Max Dev | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Led holes | 57,241.45 | 0.024 | 2.08 | 9.0 (0.172 mm) |
| Inner circles | 17,264.93 | 0.039 | 3.24 | 15.5 (0.296 mm) |
| Measurement Method | Maximum Position Deviation | Maximum Displacement | Standard Deviation | Mean Displacement | Variability Ratio (Std/Mean) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual measurement | 15.5 | 15.182 | 3.363 | 5.927 | 0.567 |
| Complex algorithm | 22 | 19.235 | 3.88 | 7.682 | 0.505 |
| Manual measurement–Complex algorithm | 10.607 | 2.27 | 5.47 | 0.415 |
| Analysis Item | Maximum Displacement (Pixel) |
|---|---|
| Maximum Displacement of Tube Position Across All 20 Images | 24.18 |
| Maximum Displacement Comparing Averaged Fluorescence Image Positions with Amplification Image Tube Positions | 16.29 |
| Maximum Displacement Comparing Generalized Tube Position Across All 20 Images | 24.93 |
| Methods | Result (Pixel) |
|---|---|
| 1st center | 3.6 |
| Interval | Mean: 473 Deviation: 0.278 |
| Real interval | 477.93 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koo, S.-B.-N.; Hwang, J.-S.; Park, C.-Y.; Lee, D.-J. Evaluation of Fluorescence Detection Algorithms for Efficient ROI Setting in Low-Cost Real-Time PCR Systems. Biosensors 2025, 15, 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090598
Koo S-B-N, Hwang J-S, Park C-Y, Lee D-J. Evaluation of Fluorescence Detection Algorithms for Efficient ROI Setting in Low-Cost Real-Time PCR Systems. Biosensors. 2025; 15(9):598. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090598
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoo, Seul-Bit-Na, Ji-Soo Hwang, Chan-Young Park, and Deuk-Ju Lee. 2025. "Evaluation of Fluorescence Detection Algorithms for Efficient ROI Setting in Low-Cost Real-Time PCR Systems" Biosensors 15, no. 9: 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090598
APA StyleKoo, S.-B.-N., Hwang, J.-S., Park, C.-Y., & Lee, D.-J. (2025). Evaluation of Fluorescence Detection Algorithms for Efficient ROI Setting in Low-Cost Real-Time PCR Systems. Biosensors, 15(9), 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090598





