An Amperometric Enzyme–Nanozyme Biosensor for Glucose Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Solutions
2.3. Synthesis and Characterization of PtCo Nanoparticles
2.4. Preparation of Working Electrodes
2.5. Electrochemical Measurements
2.6. Interpretation of Experimental Data
3. Results and Discussion
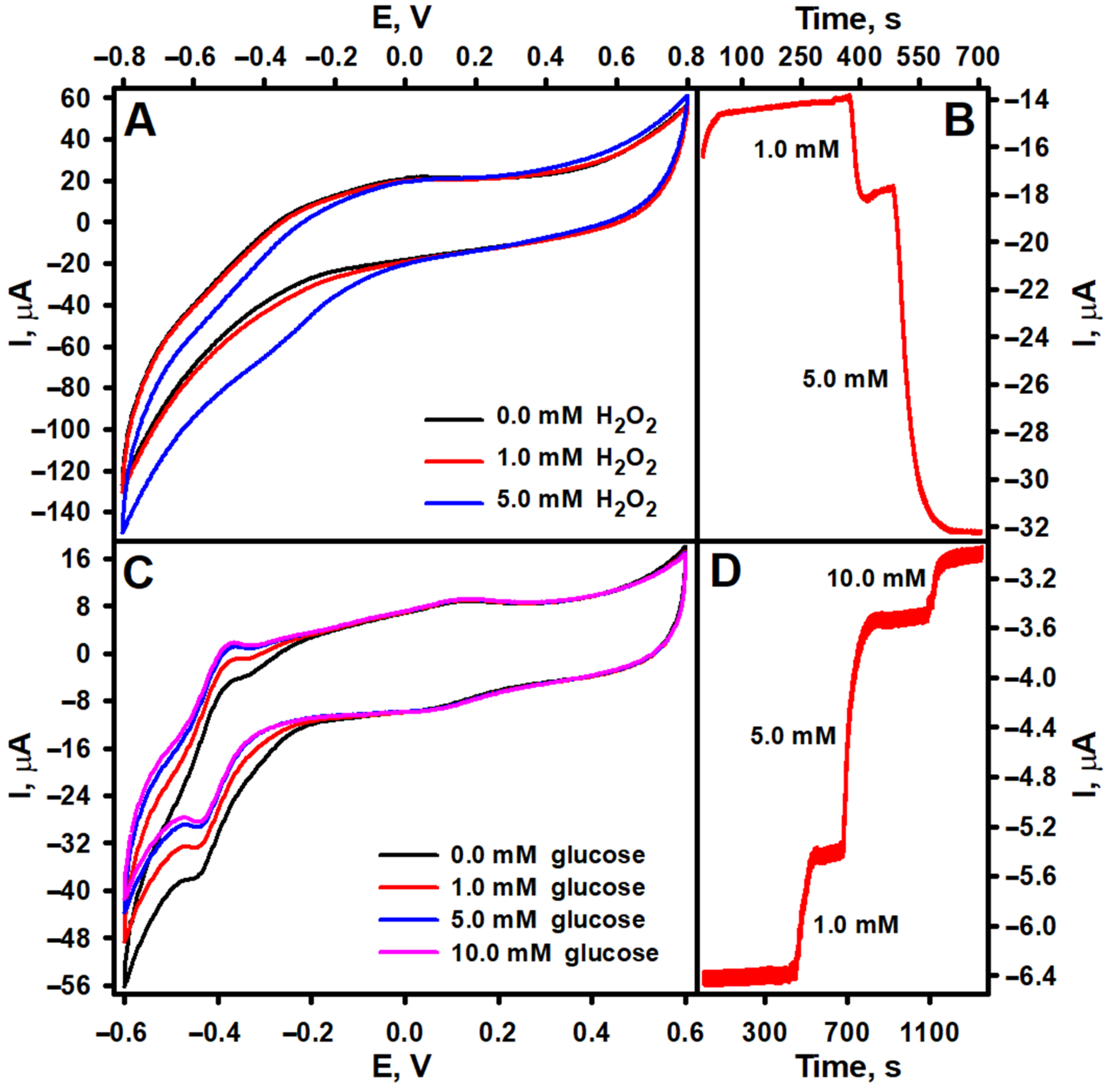
3.1. Characterization of Morphological and PO-like Properties of PtCo Nanoparticles
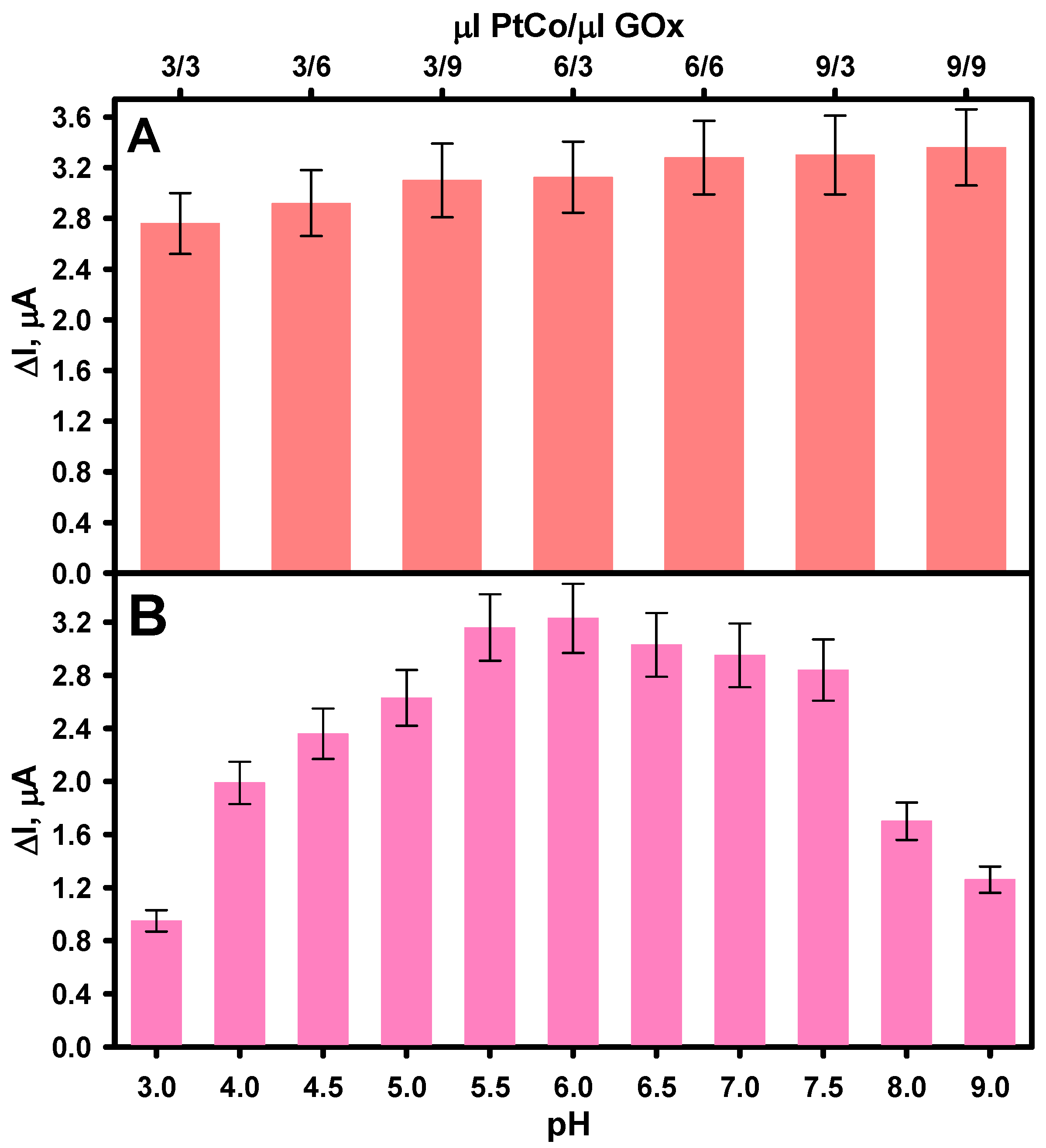
3.2. Optimization of GRE/PtCo/GOx/Nafion Composition and Buffer pH
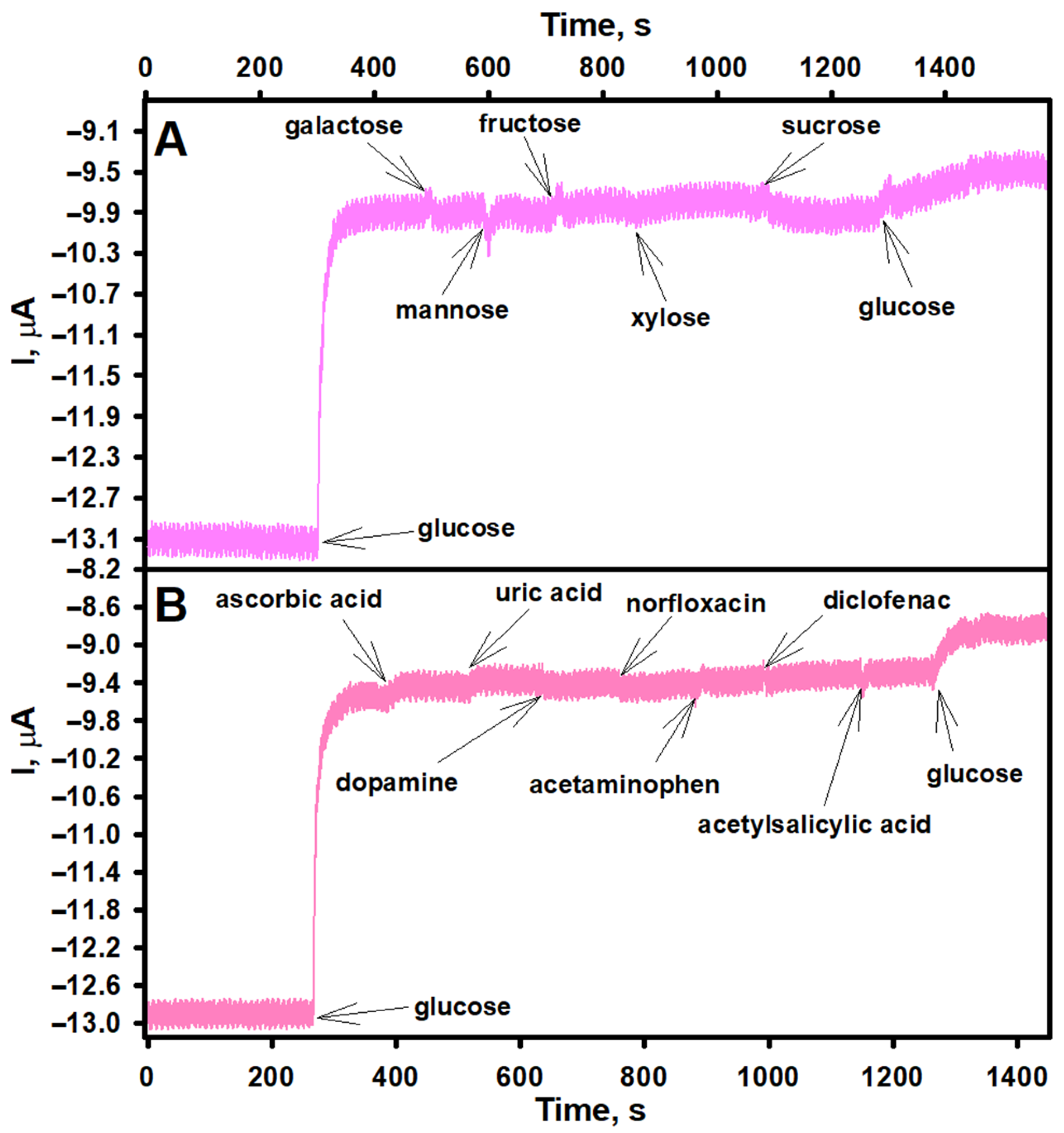
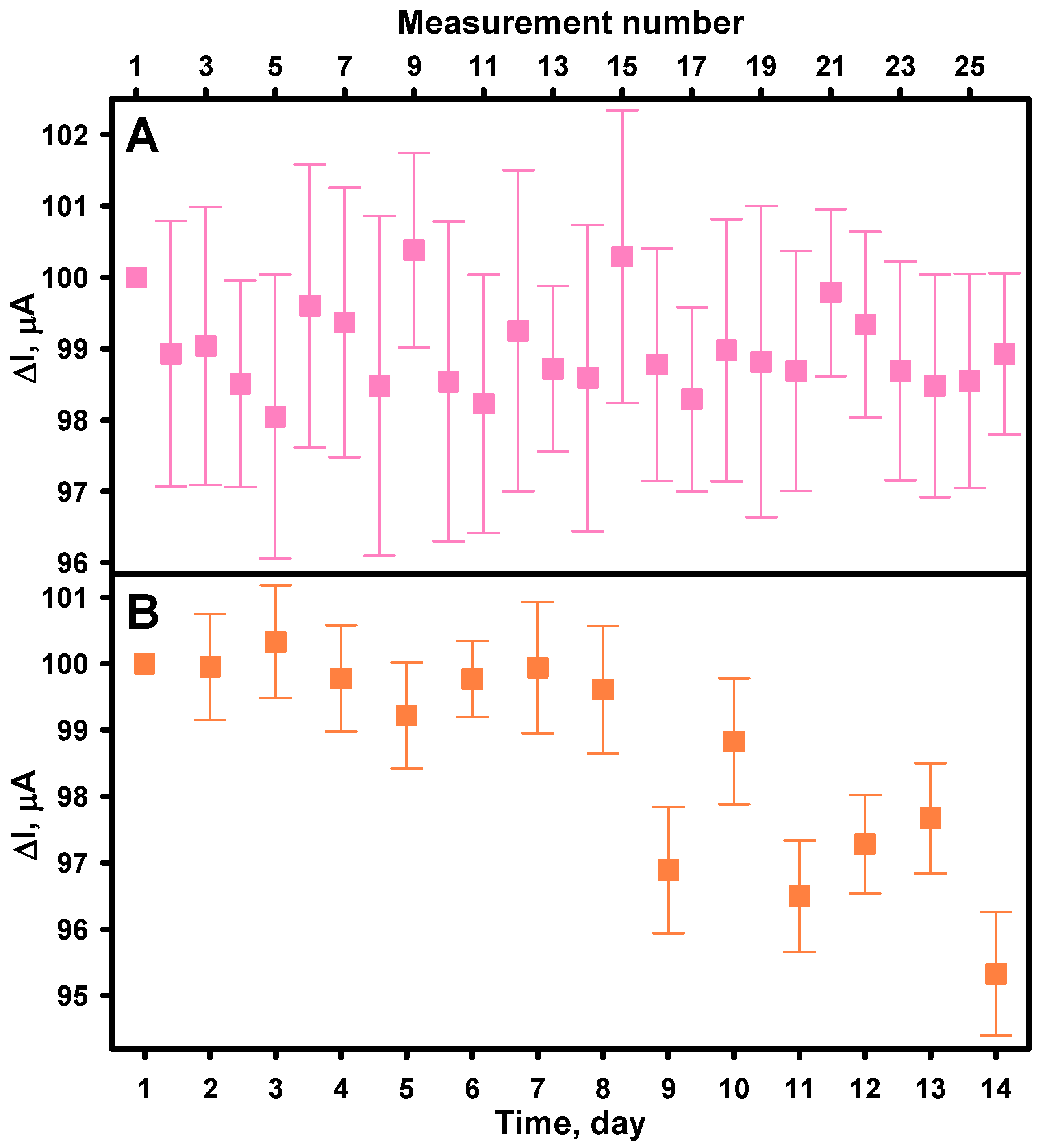
3.3. Evaluation of the Analytical Performance of the Biosensor
3.4. Analysis of Human Serum Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GOx | Glucose oxidase |
| PtCo | platinum cobalt nanoparticles |
| RSD | Relative standard deviation |
| PO | Peroxidase |
| PO-MNZs | Metal nanoparticle-based nanozymes with peroxidase-like properties |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| GCE | Glassy carbon electrode |
| GRE | Graphite rod electrode |
| UHQ | Ultra-high quality |
| ABTS | 2,2′-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid |
| AFBS | Buffer solution prepared by dissolving CH3COONa, Na2HPO4, NaH2PO4 and KCl in ultra-high-quality water |
| FE-SEM | Field-emission scanning electron microscope |
| GRE/PtCo/Nafion | Graphite rod electrode modified with PtCo nanoparticles |
| GRE/PtCo/GOx/Nafion | Graphite rod electrode modified with PtCo nanoparticles and glucose oxidase |
| R2 | Coefficient of determination |
| LOQ | Limit of quantification |
| GOx@ZIF-8(TiO2) | Glucose oxidase and TiO2 nanoparticles encapsulated in a zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 |
| GRE/GOx/Nafion | Graphite rod electrode modified with glucose oxidase |
| Cs | Chitosan |
| LSG | Laser-scribed graphene |
| LOx | Lactate oxidase |
| AuNPs | Gold nanoparticles |
| OMC | Ordered mesoporous carbon |
| RGO | Reduced graphene oxide |
| STDEV | Standard deviation |
References
- Clark, L.C.; Lyons, C. Electrode systems for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1962, 102, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Rayner, A.W.; Gregg, E.W.; Sheffer, K.E.; Carrillo-Larco, R.M.; Bennett, J.E.; Shaw, J.E.; Paciorek, C.J.; Singleton, R.K.; Pires, A.B.; et al. Worldwide trends in diabetes prevalence and treatment from 1990 to 2022: A pooled analysis of 1108 population-representative studies with 141 million participants. Lancet 2024, 404, 2077–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antar, S.A.; Ashour, N.A.; Sharaky, M.; Khattab, M.; Ashour, N.A.; Zaid, R.T.; Roh, E.J.; Elkamhawy, A.; Al-Karmalawy, A.A. Diabetes mellitus: Classification, mediators, and complications; A gate to identify potential targets for the development of new effective treatments. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 168, 115734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Nan, X.; Shi, W.; Liu, X.; He, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ge, D. A glucose biosensor based on the immobilization of glucose oxidase and Au nanocomposites with polynorepinephrine. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 16439–16446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.-Z.; Wang, K.; Xia, X.-H. Elimination of electrochemical interferences in glucose biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naikoo, G.A.; Arshad, F.; Hassan, I.U.; Omar, F.B.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Mustaqeem, M.; Saleh, T.A. Trends in bimetallic nanomaterias and methods for fourth-generation glucose sensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 162, 117042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-S.; Park, B.U.; Jeon, H.-J. Advances in machine learning-enhanced nanozymes. Front. Chem. 2024, 12, 1483986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkomy, H.A.; El-Naggar, S.A.; Elantary, M.A.; Gamea, S.M.; Ragab, M.A.; Basyouni, O.M.; Mouhamed, M.S.; Elnajjar, F.F. Nanozyme as detector and remediator to environmental pollutants: Between current situation and future prospective. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 3435–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demkiv, O.; Nogala, W.; Stasyuk, N.; Grynchyshyn, N.; Vus, B.; Gonchar, M. The peroxidase-like nanocomposites as hydrogen peroxide-sensitive elements in cholesterol oxidase-based biosensors for cholesterol assay. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Ban, H.; Yu, S.; Tao, D.; Hu, Z. An amperometric sensitive hydrogen peroxide sensor based on a silver nanoparticle-doped polyimide-modified glassy carbon electrode. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 10961–10972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, E.; Tran, V.-K.; Son, S.E.; Hur, W.; Choi, H.; Seong, G.H. Characterization of Au@PtNP/GO nanozyme and its application to electrochemical microfluidic devices for quantification of hydrogen peroxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 294, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Xu, F.; Sun, L.; Luo, Y.; Cheng, R.; Zou, Y.; Liao, L.; Cao, Z. Hydrogen peroxide electrochemical sensor based on Ag/Cu bimetallic nanoparticles modified on polypyrrole. Sensors 2023, 23, 8536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kader, M.A.; Azmi, N.S.; Kafi, A.K.M.; Hossain, M.S.; Jose, R.; Goh, K.W. Ultrasensitive nonenzymatic real-time hydrogen peroxide monitoring using gold nanoparticle-decorated titanium dioxide nanotube electrodes. Biosensors 2023, 13, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komkova, M.A.; Andreeva, K.D.; Zarochintsev, A.A.; Karyakin, A.A. Nanozymes “artificial peroxidase”: Enzyme oxidase mixtures for single-step fabrication of advanced electrochemical biosensors. ChemElectroChem 2021, 8, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasyuk, N.; Demkiv, O.; Gayda, G.; Zakalska, O.; Nogala, W.; Gonchar, M. Amperometric biosensors based on alcohol oxidase and peroxidase—Like nanozymes for ethanol determination. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasyuk, N.; Gayda, G.; Demkiv, O.; Darmohray, L.; Gonchar, M.; Nisnevitch, M. Amperometric biosensors for L-arginine determination based on L-arginine oxidase and peroxidase-like nanozymes. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, K.; Guo, Y. Development of Cu nanoflowers modified the flexible needle-type microelectrode and its application in continuous monitoring glucose in vivo. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 110, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.F.; Park, J.Y. Amperometric glucose biosensor based on Pt-Pd nanoparticles supported by reduced graphene oxide and integrated with glucose oxidase. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 940–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Yin, L.; Ma, J.; Guo, E.; Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Liu, K. Amperometric hydrogen peroxide and glucose biosensor based on NiFe2/ordered mesoporous carbon nanocomposites. Analyst 2015, 140, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayda, G.Z.; Demkiv, O.M.; Gurianov, Y.; Serkiz, R.Y.; Klepach, H.M.; Gonchar, M.V.; Nisnevitch, M. “Green” Prussian blue analogues as peroxidase mimetics for amperometric sensing and biosensing. Biosensors 2021, 11, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thao, N.T.M.; Do, H.D.K.; Nam, N.N.; Tran, N.K.S.; Dan, T.T.; Trinh, K.T.L. Antioxidant nanozymes: Mechanisms, activity manipulation, and applications. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Yan, X.; Fan, K. Structure and activity of nanozymes: Inspirations for de novo design of nanozymes. Mater. Today 2020, 41, 81–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Jiang, G.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Liu, S.; Lin, T.; Ye, F.; Zhao, S. Progress and trend on the regulation methods for nanozyme activity and its application. Catalysts 2019, 9, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.F.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, N. Size-dependent peroxidase-like catalytic activity of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2008, 19, 730–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, T.; Wang, B.; Yang, Z. A simple route to CoFe2O4 nanoparticles with shape and size control and their tunable peroxidase-like activity. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 10632–10640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.V.; Le, T.A.; Giang, B.L.; Piro, B.; Tran, L.D. Silver nanoparticles on graphene quantum dots as nanozyme for efficient H2O2 reduction in a glucose biosensor. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 115403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Srivastava, D.N. Amperometric glucose sensing at nanomolar level using MOF-encapsulated TiO2 platform. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 14634–14640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Shi, F.; Li, J.; Hub, X.; Yang, Z. Dual-strategy biosensing of glucose based on multifunctional CuWO4 nanoparticles. Analyst 2022, 147, 4049–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.S.; Choi, D.; Park, H.-Y.; Yoo, S.J. Tuning the surface structure of PtCo nanocatalysts with high activity and stability toward oxygen reduction. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 78, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, Y. Oxygen reduction reaction on PtCo nanocatalyst: (Bi)sulfate anion poisoning. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Fernández, P.; Rojas, S.; Ocón, P.; Gómez de la Fuente, J.L.; Terreros, P.; Peña, M.A.; García-Fierro, J.L. An opening route to the design of cathode materials for fuel cells based on PtCo nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 77, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wei, M.; Qi, R.; Dong, C.-L.; Dang, D.; Yang, C.-C.; Xia, C.; Chen, C.; Zaman, S.; Li, F.-M.; et al. An integrated platinum-nanocarbon electrocatalyst for efficient oxygen reduction. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gara, M.; Compton, R.G. Activity of carbon electrodes towards oxygen reduction in acid: A comparative study. New J. Chem. 2011, 35, 2647–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, L.; Zhu, J.; Xiao, M.; Liu, C.; Xing, W.; Zhang, J. Electrochemical oxygen reduction reaction. In Book Rotating Electrode Methods and Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalysts; Xing, W., Yin, G., Zhang, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 133–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ren, X.; Tang, F.; Zhang, L. A practical glucose biosensor based on Fe3O4 nanoparticles and chitosan/nafion composite film. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, A.; Rijo, P.; Batanero, B.; Nicolai, M. Low platinum-content electrocatalysts for highly sensitive detection of endogenously released H2O2. Biosensors 2022, 12, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausaite-Minkstimiene, A.; Glumbokaite, L.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Dauksaite, E.; Ramanavicius, A. An amperometric glucose biosensor based on poly(pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid)/glucose oxidase biocomposite. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 1642–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor, N.M.; Ridhuan, N.S.; Abdul Razak, K. Progress of enzymatic and non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose biosensor based on nanomaterial-modified electrode. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankar, S.B.; Bule, M.V.; Singhal, R.S.; Ananthanarayan, L. Glucose oxidase—An overview. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.M.; Wong, K.H.; Chen, X.D. Glucose oxidase: Natural occurrence, function, properties and industrial applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 78, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.F.P.; Taqueda, M.E.; Converti, A.; Vitolo, M.; Pessoa, A. Purification of glucose oxidase from Aspergillus niger by liquid-liquid cationic reversed micelles extraction. Biotechnol. Prog. 2005, 21, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, E. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): Next-generation artificial enzymes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6060–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Lou, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, Y.; Qina, L.; Wei, H. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): Next-generation artificial enzymes (II). Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 1004–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wang, C.; You, L.; Fu, F.; Liu, Q. Nanozyme colorimetric sensing of L-cysteine and copper ions based on PtCo nanoparticles@multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Anal. Sci. 2023, 39, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Cui, M.; Luo, Z.; Wang, L. Strain-driven intermetallic PtCo nanozymes for high and specific peroxidase-like activity. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2025, 111227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Li, M.; Chen, L.; Peng, B.; Jiang, H. A wearable nanozyme–enzyme electrochemical biosensor for sweat lactate monitoring. Talanta 2024, 279, 126675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popenda, A.; Wiśniowska, E.; Manuel, C. Biosensors in environmental analysis of microplastics and heavy metal compounds–A review on current status and challenges. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 319, 100456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Sun, F.; Gao, H.; Wang, J. Nanoporous platinum–cobalt alloy for electrochemical sensing for ethanol, hydrogen peroxide, and glucose. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 780, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Q.; Mei, H.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S. A highly sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on PtxCo1−x/C nanostructured composites. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda-Morales, E.; Gómez-Gómez, F.A.; Li, Y.; Manzo-Robledo, A. Insights in Pt-based electrocatalysts on carbon supports for electro-oxidation of carbohydrates: An EIS-DEMS analysis. Front. Chem. 2024, 12, 1383443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bai, X.; Wang, X.; Shiu, K.-K.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, H. Highly sensitive graphene–Pt nanocomposites amperometric biosensor and its application in living cell H2O2 detection. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9459–9465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, G.-J. Electrochemical detection of H2O2 released from prostate cancer cells using Pt nanoparticle-decorated rGO–CNT nanocomposite-modified screen-printed carbon electrodes. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-C.; Yang, C.-Y.; Chen, S.-M.; Zhao, D.-H.; Hou, Y.-S. An interference study with different working potentials for an amperometric glucose sensor. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 2755–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doseděl, M.; Jirkovský, E.; Macáková, K.; Krčmová, L.K.; Javorská, L.; Pourová, J.; Mercolini, L.; Remião, F.; Nováková, L.; Mladěnka, P. On behalf of the oemonom. Vitamin C-sources, physiological role, kinetics, deficiency, use, toxicity, and determination. Nutrients 2021, 13, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Electrochemical glucose biosensors. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Chatterjee, S. Nanomaterials based electrochemical sensors for biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5425–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Working Electrode | Linear Range, mM | LOD, mM | LOQ, mM | Sensitivity, μA mM−1 cm−2 | Response Time, s | Stability, % From Initial | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRE/PtCo/GOx/Nafion | 0.04–2.18 | 0.021 | 0.064 | 19.38 | <10 | 95.33% after 14 days | this work |
| GRE/CuHCF/GOx/Nafion | up to 0.50 | – | – | 32.2 | – | – | [20] |
| Pt/GOx/Fe3O4/Cs/Nafion | 0.006–2.2 | 0.006 | – | 11.54 | – | 84% after 1 month | [35] |
| LSG/CeO2-MoS2/AuNPs/LOx | 0.1–1 1–50 | 0.052 | – | 25.58 2.35 | – | 96.6% after 25 days | [46] |
| GCE/CuWO4/GOx/Nafion | 0.005–1.8 | 0.0015 | – | 28.02 | – | – | [28] |
| GCE/NiFe2/OMC/GOx/Nafion | 0.0486–12.5 | 0.0027 | – | 6.9 | – | 93% after 4 weeks | [19] |
| GCE/GOx@ZIF-8(TiO2) | 0.00008 | – | – | – | <5 | – | [27] |
| Au/RGO/PtPd/GOx | 2–12 | 0.001 | – | 24 | <5 | – | [18] |
| Study | ΔI, µA | Average of ΔI, µA | STDEV | RSD, % (n = 5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Repeatability | 2.61 | 2.81 | 0.14 | 4.90 |
| 2.90 | ||||
| 2.82 | ||||
| 2.96 | ||||
| 2.74 | ||||
| Reproducibility | 3.63 | 3.19 | 0.28 | 8.90 |
| 3.15 | ||||
| 3.27 | ||||
| 2.96 | ||||
| 2.93 |
| Added Glucose, mM | Detected Glucose, mM | Recovery, % | Average, % | RSD, % (n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.70 | 0.66 | 94.29 | 100.95 | 5.89 |
| 0.70 | 0.74 | 105.71 | ||
| 0.70 | 0.72 | 102.86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kausaite-Minkstimiene, A.; Krikstaponyte, A.; Stasyuk, N.; Gayda, G.; Ramanaviciene, A. An Amperometric Enzyme–Nanozyme Biosensor for Glucose Detection. Biosensors 2025, 15, 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080545
Kausaite-Minkstimiene A, Krikstaponyte A, Stasyuk N, Gayda G, Ramanaviciene A. An Amperometric Enzyme–Nanozyme Biosensor for Glucose Detection. Biosensors. 2025; 15(8):545. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080545
Chicago/Turabian StyleKausaite-Minkstimiene, Asta, Aiste Krikstaponyte, Nataliya Stasyuk, Galina Gayda, and Almira Ramanaviciene. 2025. "An Amperometric Enzyme–Nanozyme Biosensor for Glucose Detection" Biosensors 15, no. 8: 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080545
APA StyleKausaite-Minkstimiene, A., Krikstaponyte, A., Stasyuk, N., Gayda, G., & Ramanaviciene, A. (2025). An Amperometric Enzyme–Nanozyme Biosensor for Glucose Detection. Biosensors, 15(8), 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080545







