Aptamer-Conjugated Magnetic Nanoparticles Integrated with SERS for Multiplex Salmonella Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Apparatus
2.2. Preparation of Ag@4MBA@Au NPs
2.3. Synthesis and Optimization of Ag@4-MBA@Au-Fe3O4 Aptamer Probes
2.4. Optimization of Experimental Conditions
2.5. Activation Culture and Enumeration of Salmonella
2.6. SERS Detection
3. Results and Discussion
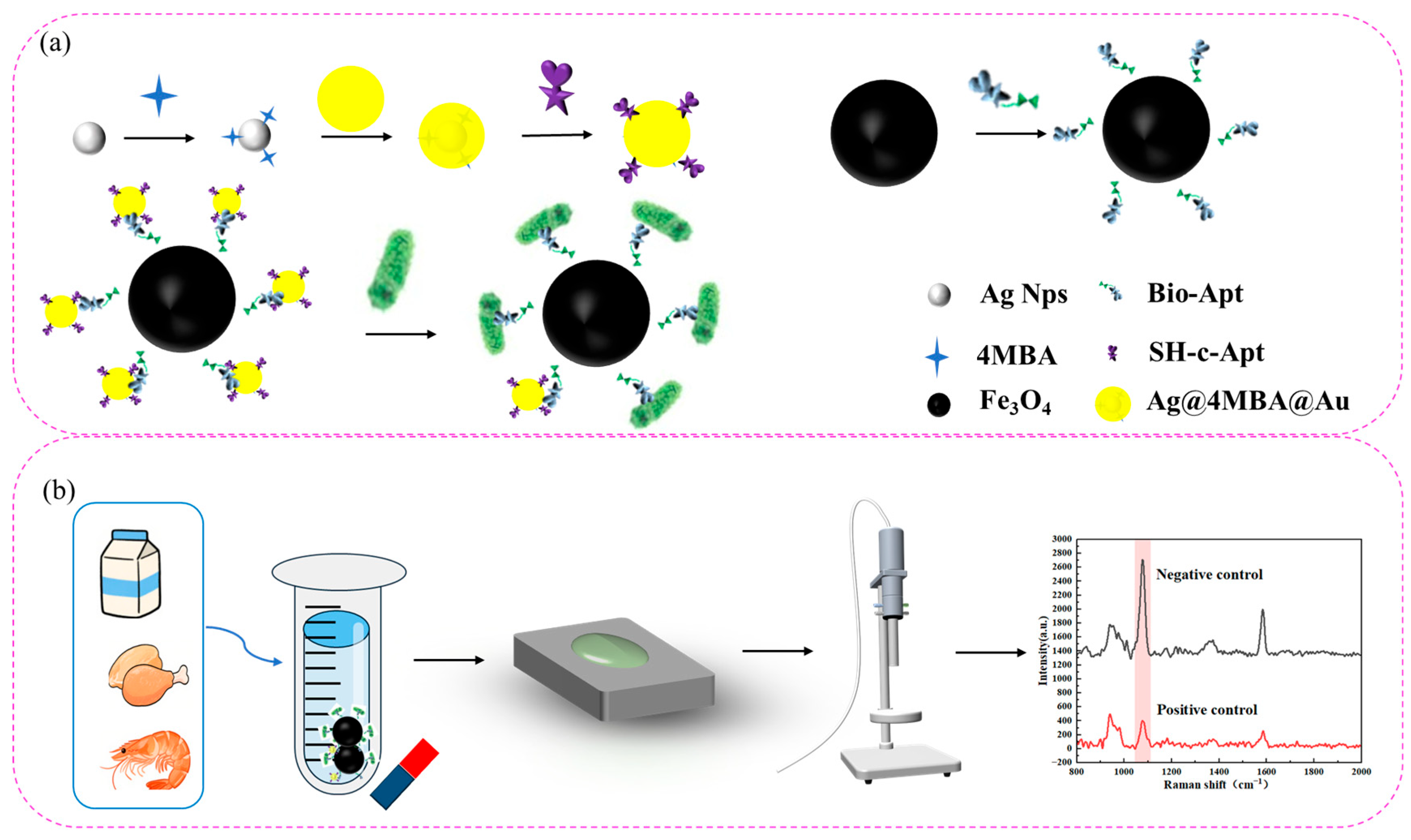
3.1. Detection Principle of the Aptamer Sensor
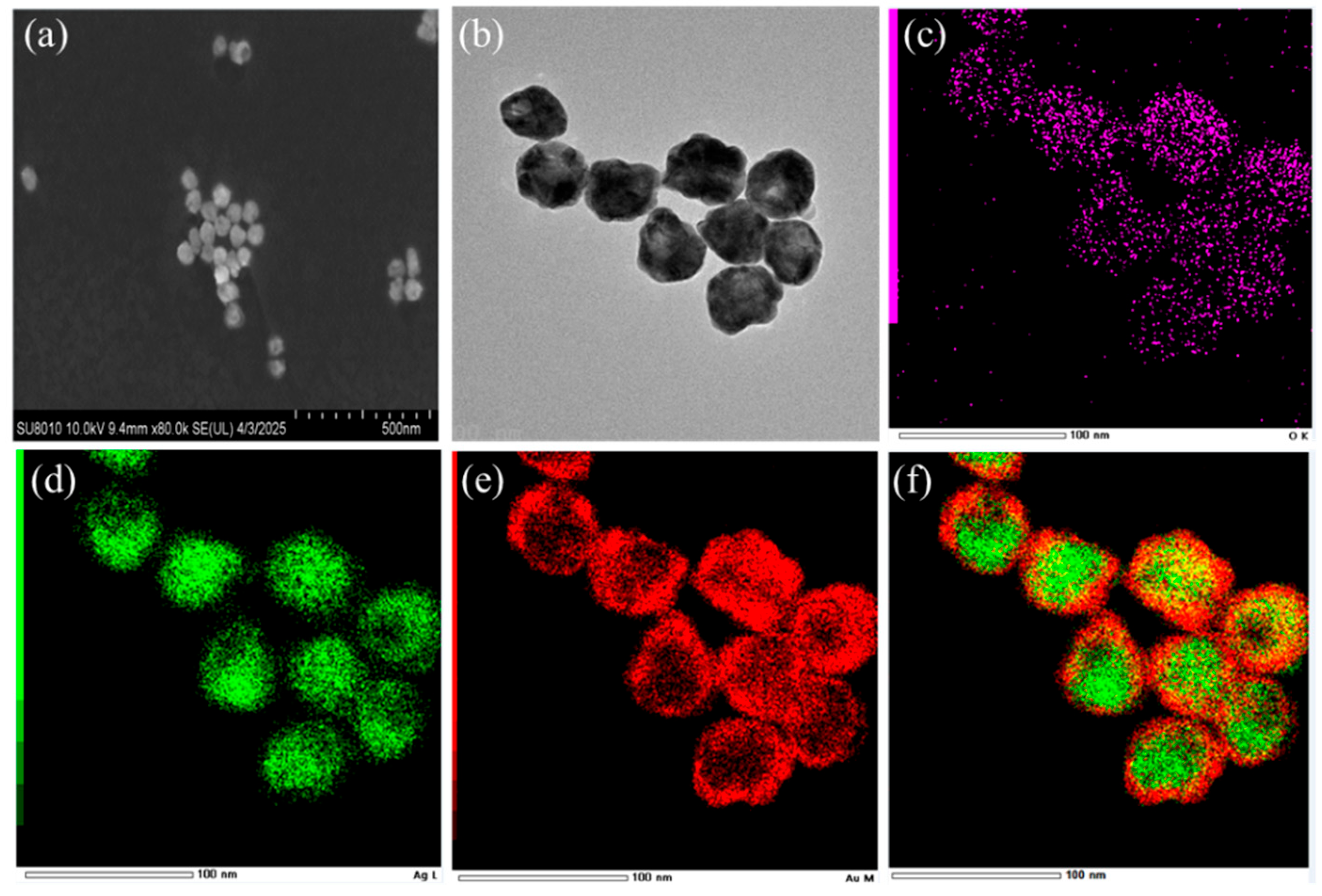
3.2. Characterization of the Ag@4MBA@Au-Fe3O4 Composite Probe
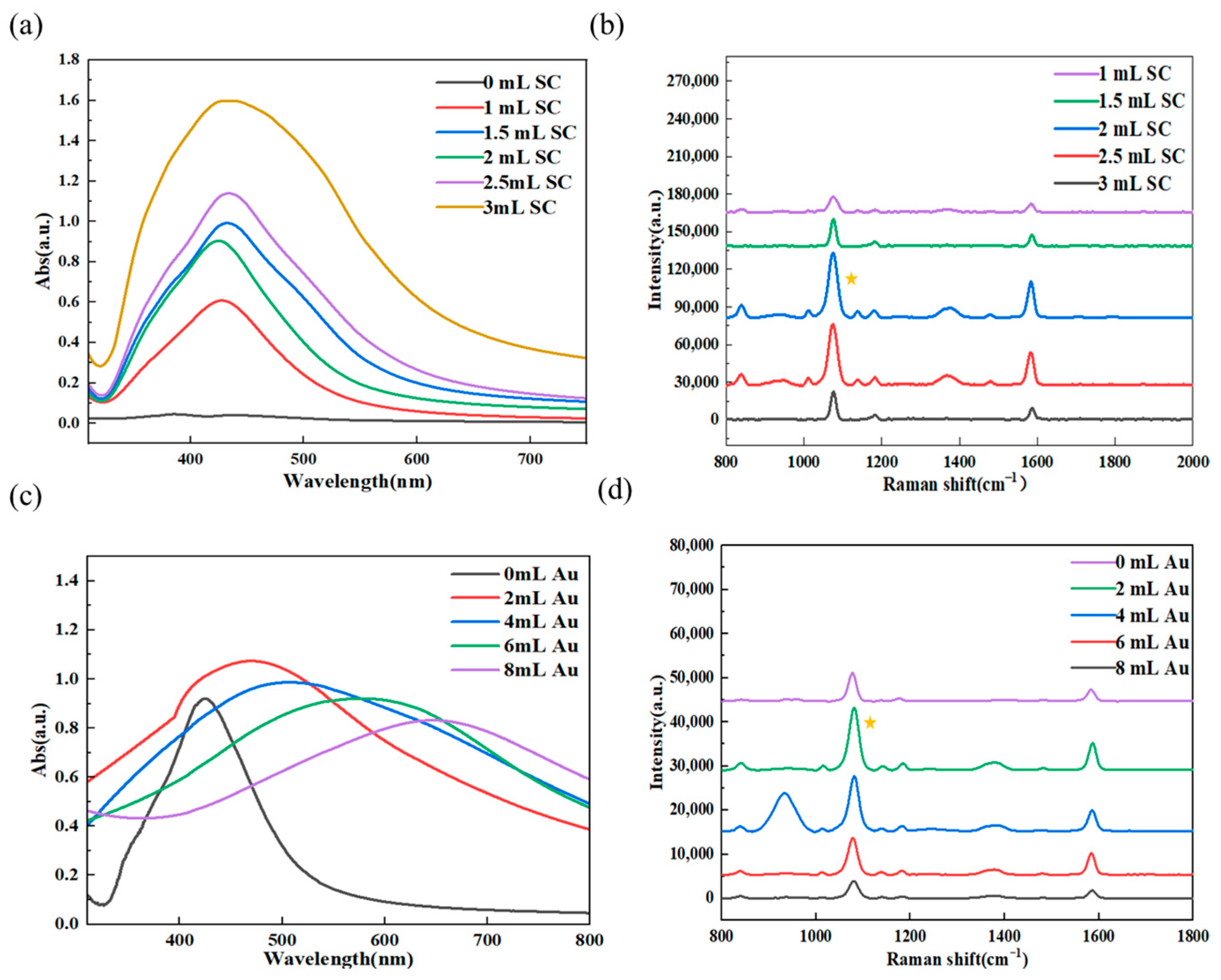
3.3. Results of Experimental Condition Optimization
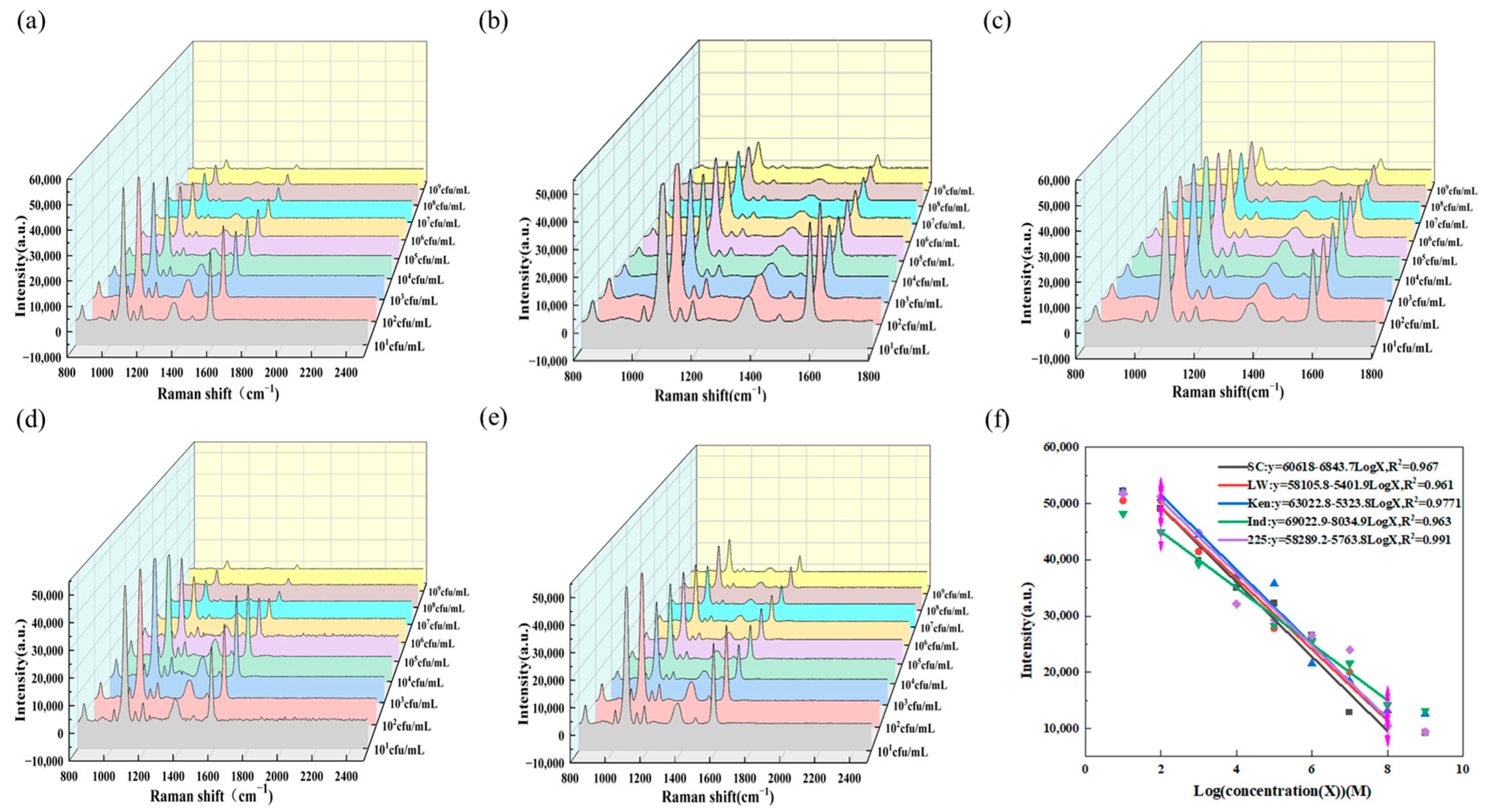
3.4. Detection of Salmonella
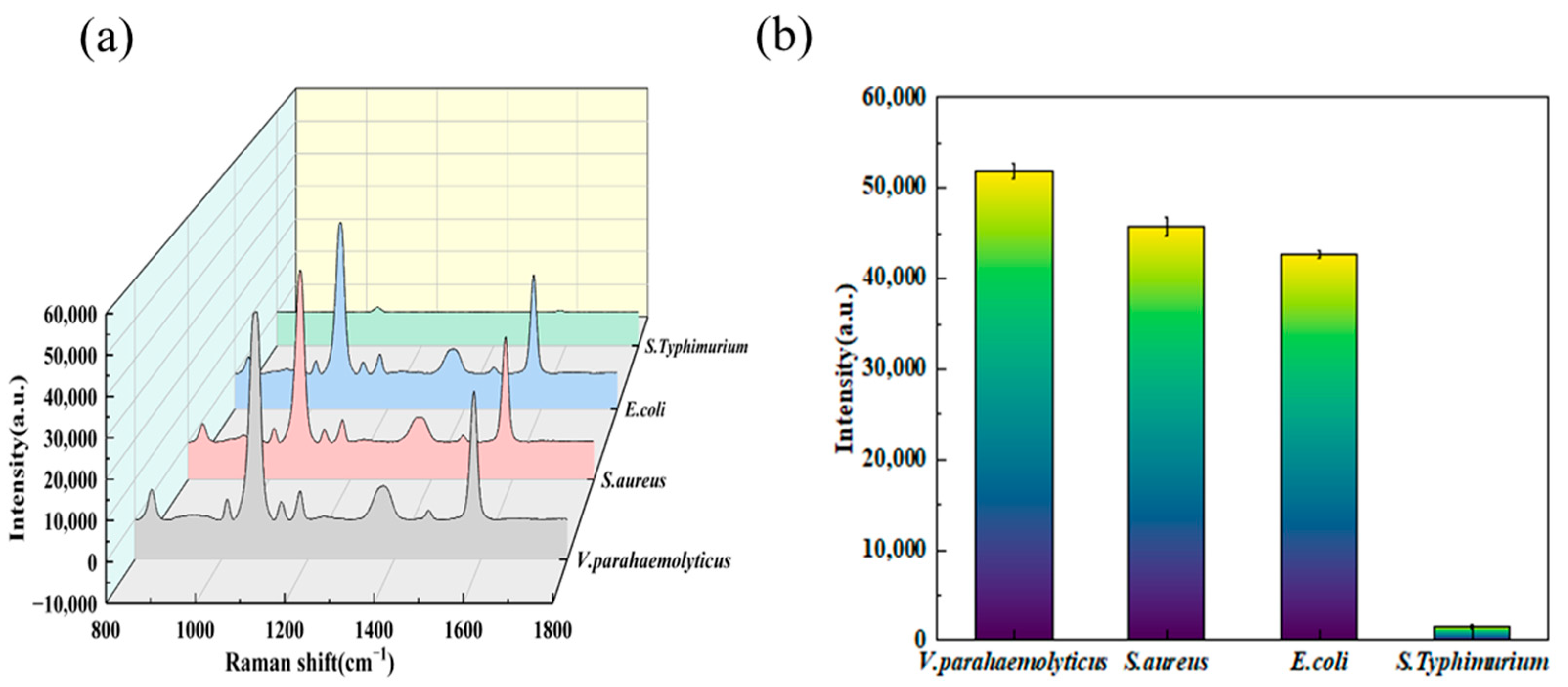
3.5. Specificity Detection
3.6. Detection of Actual Samples
4. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, G.; Moon, J.-H.; Hahm, B.-K.; Morgan, M.; Bhunia, A.; Om, A.-S. Identification of Salmonella Typhimurium-specific DNA aptamers developed using whole-cell SELEX and FACS analysis. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2009, 18, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Andino, A.; Hanning, I. Salmonella enterica: Survival, colonization, and virulence differences among serovars. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 520179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatavarthy, A.; Cannons, A. Real-time PCR detection of Salmonella species using a novel target: The outer membrane porin F gene (ompF). Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 50, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criscuolo, A.; Issenhuth, J.-S.; Didelot, X. The speciation and hybridization history of the genus Salmonella. Microb. Genom. 2019, 5, e000284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yara, S.; Erol, K.; JeanChristophe, L. Genome-scale metabolic reconstructions of multiple Salmonella strains reveal serovar-specific metabolic traits. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3771. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. WHO’s First Ever Global Estimates of Foodborne Diseases Find Children Under 5 Account for Almost One Third of Deaths. 2015. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/03-12-2015-who-s-first-ever-global-estimates-of-foodborne-diseases-find-children-under-5-account-for-almost-one-third-of-deaths (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Sun, Y.-X.; Du, J.-P.; Zhang, C.-Y. Research Progress on Risk Assessment of Salmonella in the Production Chain of Raw Chicken. Bioprocessing 2017, 15, 72–78. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, P.-H. The Hazards of Salmonella and Its Control Strategies for Contamination of Livestock Products. China Anim. Quar. 2007, 10, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.-M.; Runyon, M.; Herrman, T.-J.; Phillips, R.; Hsieh, J. Review of Salmonella detection and identification methods: Aspects of rapid emergency response and food safety. Food Control 2015, 47, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Xue, L.; Cai, G.; Qi, W.; Liu, Y.; Lin, J. Fe-MIL-88NH2 Metal-Organic framework nanocubes decorated with Pt nanoparticles for the detection of Salmonella. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 5115–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velusamy, V.; Arshak, K.; Korostynska, O. An overview of foodborne pathogen detection: In the perspective of biosensors. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 232–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iobal, S.-S.; Mayo, M.-W.; Bruno, J.-G. A review of molecular recognition technologies for detection of biological threat agents. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2000, 15, 549–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malorny, B.; Hoorfar, J.; Bunge, C.; Helmuth, R. Multicenter validation of the analytical accuracy of Salmonella PCR: Towards an international standard. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ye, S.; Luo, X. Sensitive SERS detection of miRNA via enzyme-free DNA machine signal amplification. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 10269–10272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-A.; Wales, D.-J.; Thompson, A.-J.; Yang, G.-Z. Fiber-optic SERS probes fabricated using two-photon polymerization for rapid detection of bacteria. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2020, 8, 1901934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.-M.; Einarsson, G.-G.; Tunney, M.-M.; Bell, S.-E. Characterization of bacteria using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS): Influence of microbiological factors on the SERS spectra. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 9327–9335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Gao, X.; Xu, C. SERS Tags for Biomedical Detection and Bioimaging. Theranostics 2022, 12, 1870–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Feng, L.; Chen, Y.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. A graphene functionalized electrochemical aptasensor for selective label-free detection of cancer cells. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.; Chai, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Bai, L.; Yuan, R. A novel electrochemical aptasensor for highly sensitive detection of thrombin based on the autonomous assembly of hemin/G-quadruplex horseradish peroxidase-mimicking DNAzyme nanowires. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 832, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Tang, L.; Zheng, M. Structure-guided designing pre-organization in bivalent aptamers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 4507–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Gordon, C.-K.; Shin, J.-H. Directed evolution of aptamer discovery technologies. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, N.; Li, C.; Zhu, X. Simultaneous coupled with separate SELEX for heterocyclic biogenic amine-specific aptamers screening and their application in establishment of an effective aptasensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 352, 130985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röthlisberger, P.; Hollenstein, M. Aptamer chemistry. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 134, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iijima, M.; Yamada, Y.; Nakano, H. Bio-nanocapsules for oriented immobilization of DNA aptamers on aptasensors. Analyst 2022, 147, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozokalfa, G.; Akbulut, H.; Demir, B. Polypeptide functional surface for the aptamer immobilization: Electrochemical cocaine biosensing. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 4161–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salam, F.; Tothill, I.-E. Detection of Salmonella typhimurium using an electrochemical immunosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2630–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Tao, Z.; Yu, Y.; Ma, X.; Xia, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z. A visual detection method for Salmonella typhimurium based on aptamer recognition and nanogold labeling. Food Control 2014, 37, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, P.; Li, X.; Dominguez, D.-C.; Ye, B.-C. A PDMS/paper/glass hybrid microfluidic biochipintegrated with aptamer-functionalized graphene oxidenano-biosensors for one-step multiplexed pathogen detection. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 3921–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, W.-R.; Sekhon, S.-S.; Kim, S.-G.; Rhee, S.-J.; Yang, G.-N.; Won, K.; Rhee, S.-K.; Ryu, H.; Kim, K.; Min, J.; et al. Aptamer-Based Pathogen Monitoring for Salmonella enterica ser. Typhimurium. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2018, 14, 1992–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayraç, C.; Eyidoğan, F.; Öktem, H.-A. DNA aptamer-based colorimetric detection platform for Salmonella Enteritidis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.-J.; Yu, Y.-B.; Gao, Z.-Q. A Highly Sensitive Plasmonic DNA Assay Based on Triangular Silver Nanoprism Etching. ACS Nano 2014, 27, 4902–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-Q.; Liu, J.-X.; Luo, D.-L.; Li, P.Y.; Xu, B.C.; Zhong, X.F. Research Progress on Detection Methods of Staphylococcus aureus in Food. Agric. Prod. Process. 2009, 9, 84–86. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, J.; Kwon, D.; Lee, S.; Jeon, S. Detection of Salmonella bacteria in milk using gold-coated magnetic nanoparticle clusters and lateral flow filters. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 48445–48448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.-J. Preliminary Study on the Establishment of a Rapid Detection Method for Staphylococcus aureus Based on Bioimmune Sensors. Master’s Thesis, Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]




| Sample Types | Total | Negative Count | Positive Count | Recovery Rate (%) | Positive Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| milk | 20 | 9 | 11 | 95.6–100.4 | 100 |
| chicken | 15 | 7 | 8 | 94.0–100.1 | 100 |
| shrimp | 15 | 7 | 8 | 94.0–100.0 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, F.; Pang, K.; Yang, K.; Zheng, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Ye, Z.; Liang, P.; Yu, X. Aptamer-Conjugated Magnetic Nanoparticles Integrated with SERS for Multiplex Salmonella Detection. Biosensors 2025, 15, 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070464
Sun F, Pang K, Yang K, Zheng L, Wang M, Wang Y, Chen Q, Ye Z, Liang P, Yu X. Aptamer-Conjugated Magnetic Nanoparticles Integrated with SERS for Multiplex Salmonella Detection. Biosensors. 2025; 15(7):464. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070464
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Fan, Kun Pang, Keke Yang, Li Zheng, Mengmeng Wang, Yufeng Wang, Qiang Chen, Zihong Ye, Pei Liang, and Xiaoping Yu. 2025. "Aptamer-Conjugated Magnetic Nanoparticles Integrated with SERS for Multiplex Salmonella Detection" Biosensors 15, no. 7: 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070464
APA StyleSun, F., Pang, K., Yang, K., Zheng, L., Wang, M., Wang, Y., Chen, Q., Ye, Z., Liang, P., & Yu, X. (2025). Aptamer-Conjugated Magnetic Nanoparticles Integrated with SERS for Multiplex Salmonella Detection. Biosensors, 15(7), 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070464






