Recent Advances in Conductive Hydrogels for Electronic Skin and Healthcare Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of Conductive Hydrogels
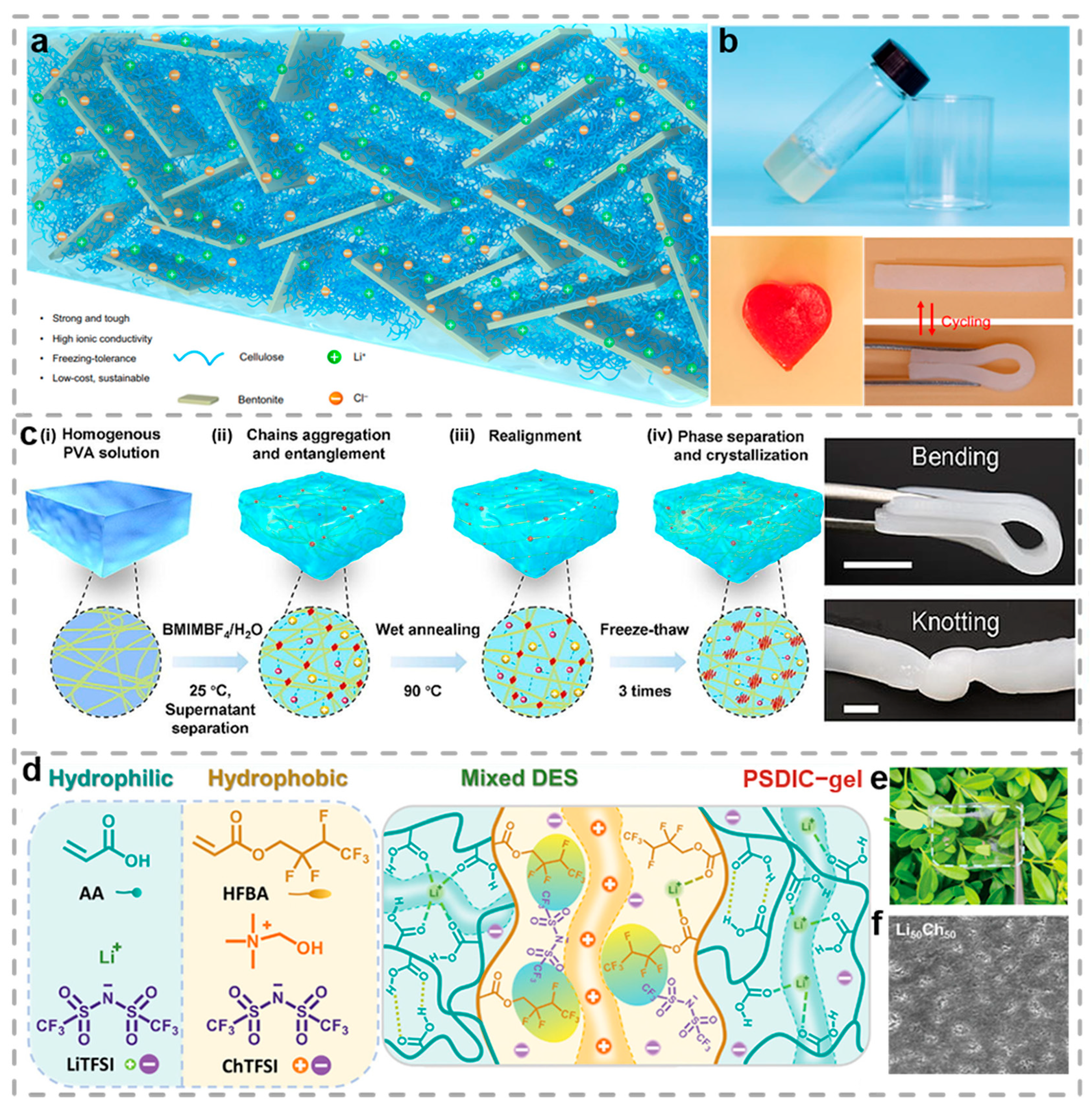
2.1. Ionic Conductive Hydrogels
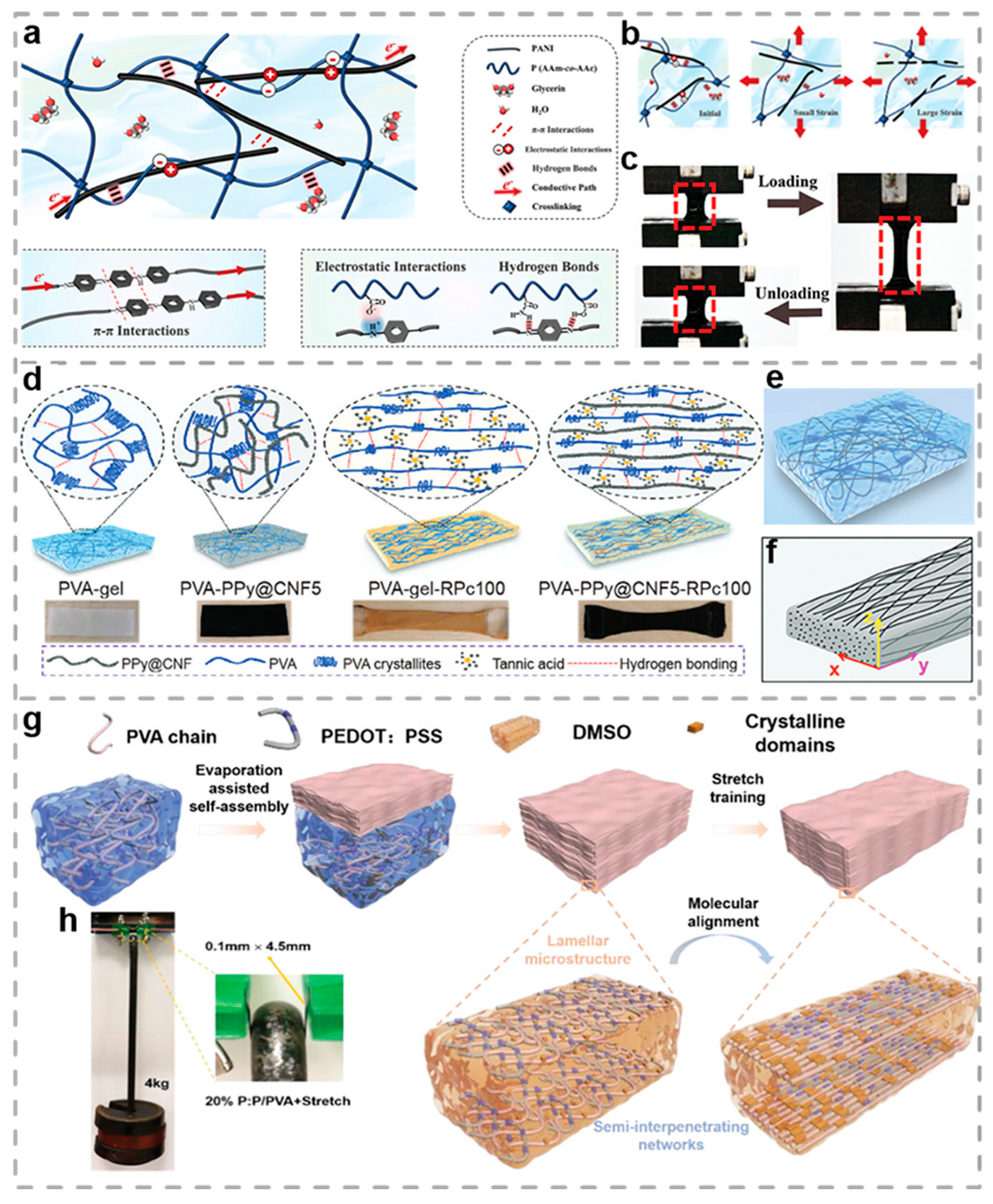
2.2. Conductive Polymer Hydrogels
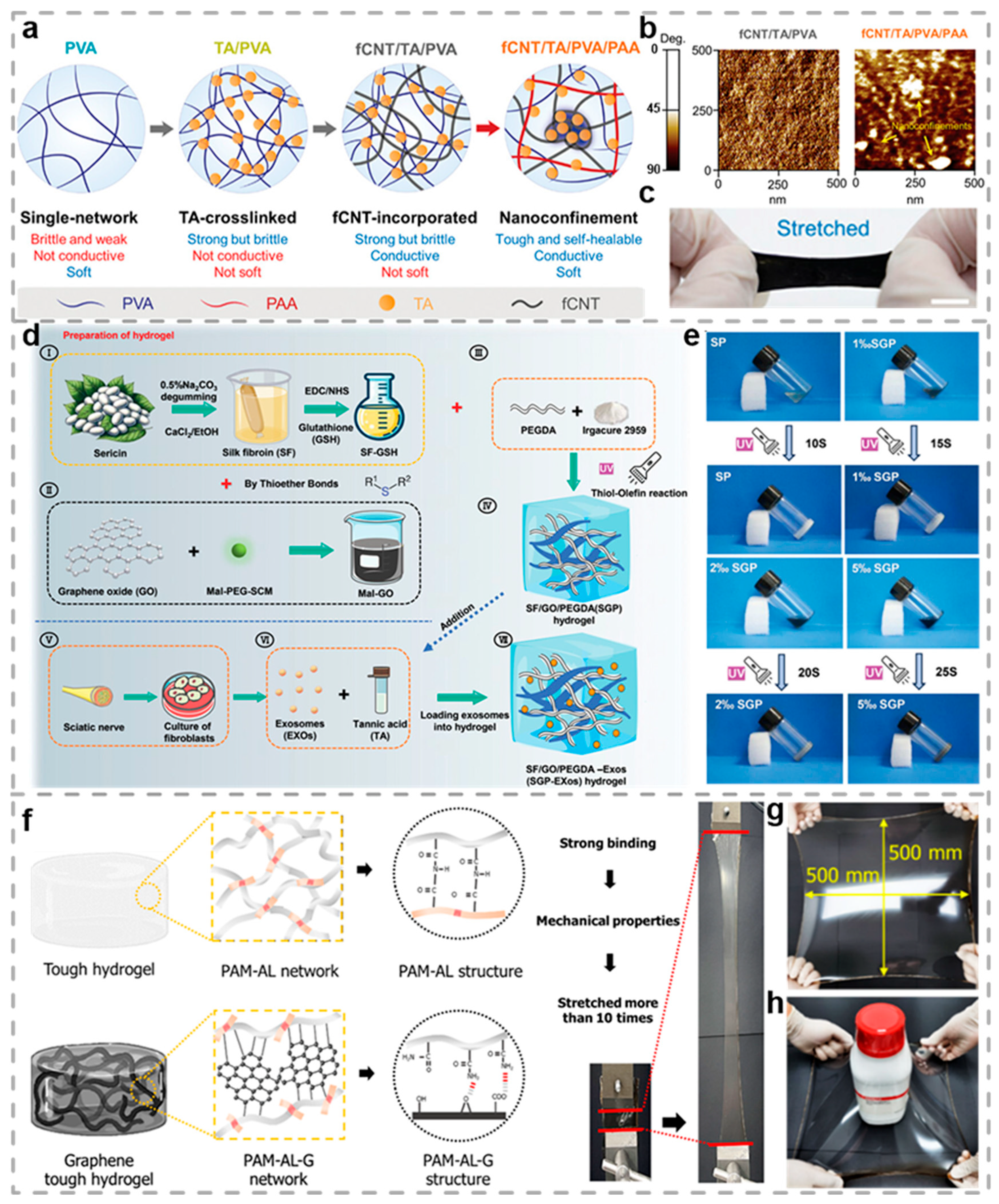
2.3. Carbon-Based Conductive Hydrogels
2.4. Metal-Based Conductive Hydrogels
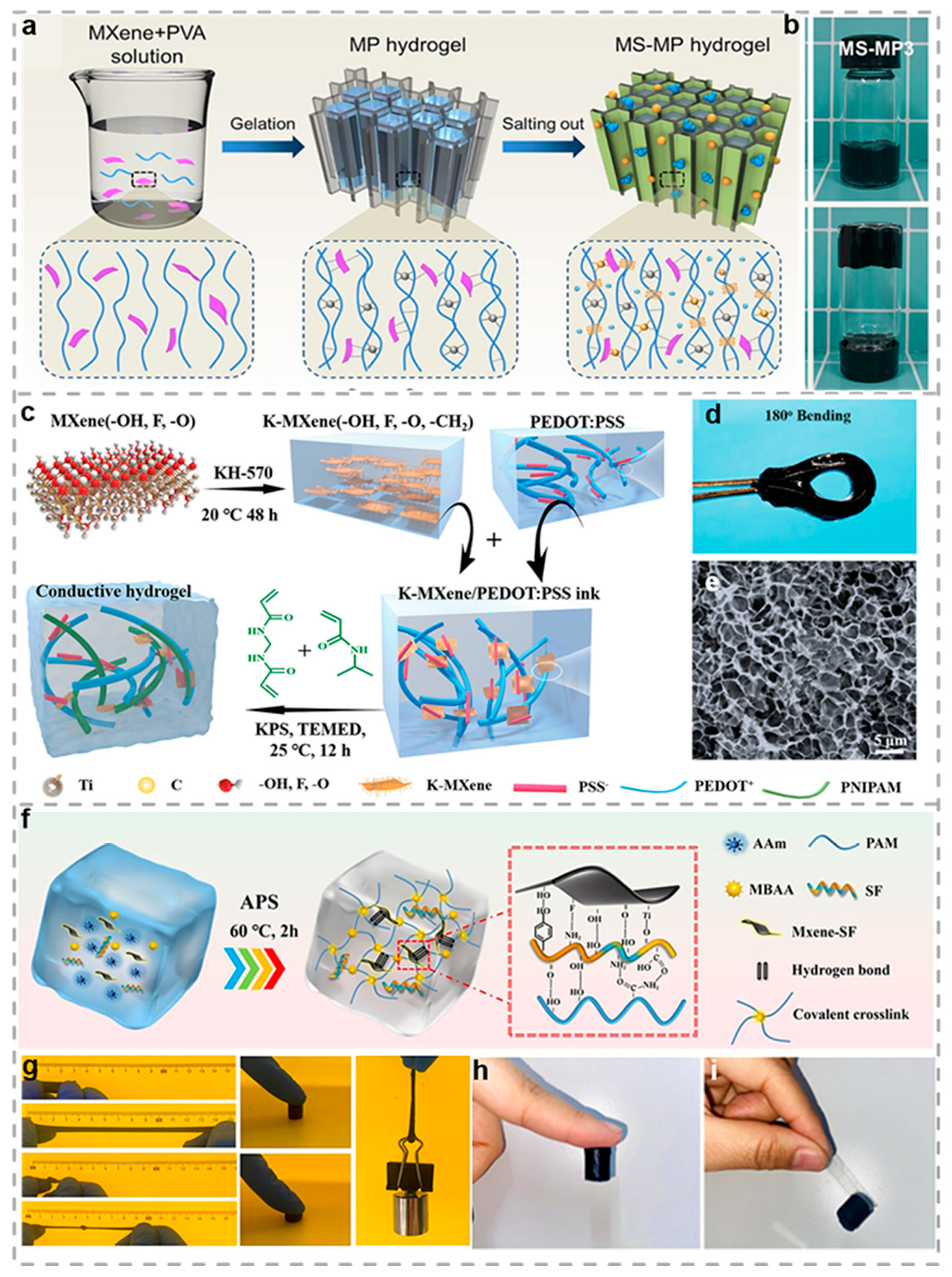
2.5. MXene-Based Conductive Hydrogels
3. Applications of Conductive Hydrogel in Healthcare Monitoring
3.1. Electrophysiological Signal Monitoring
3.1.1. Electroencephalogram
3.1.2. Electrocardiogram
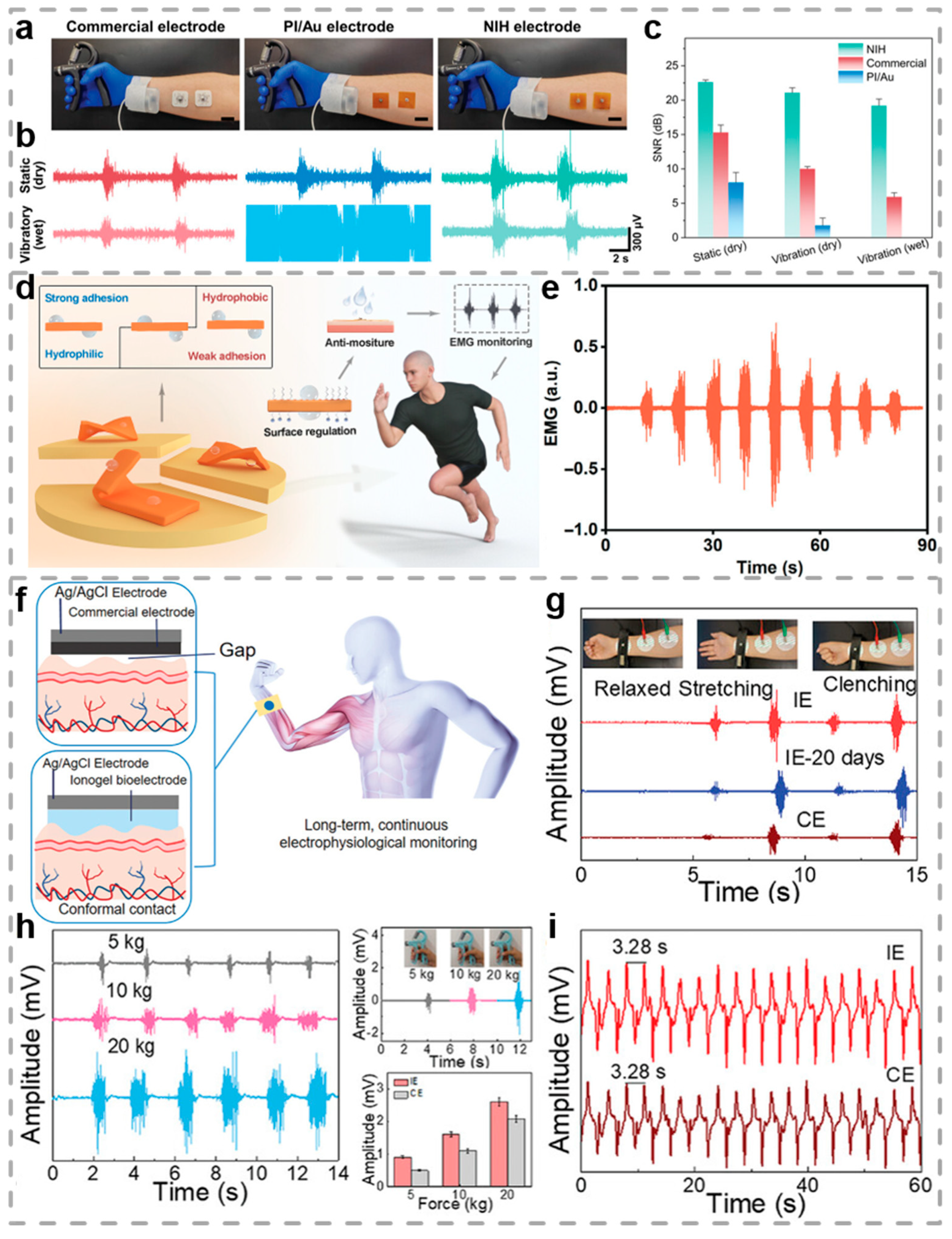
3.1.3. Electromyogram
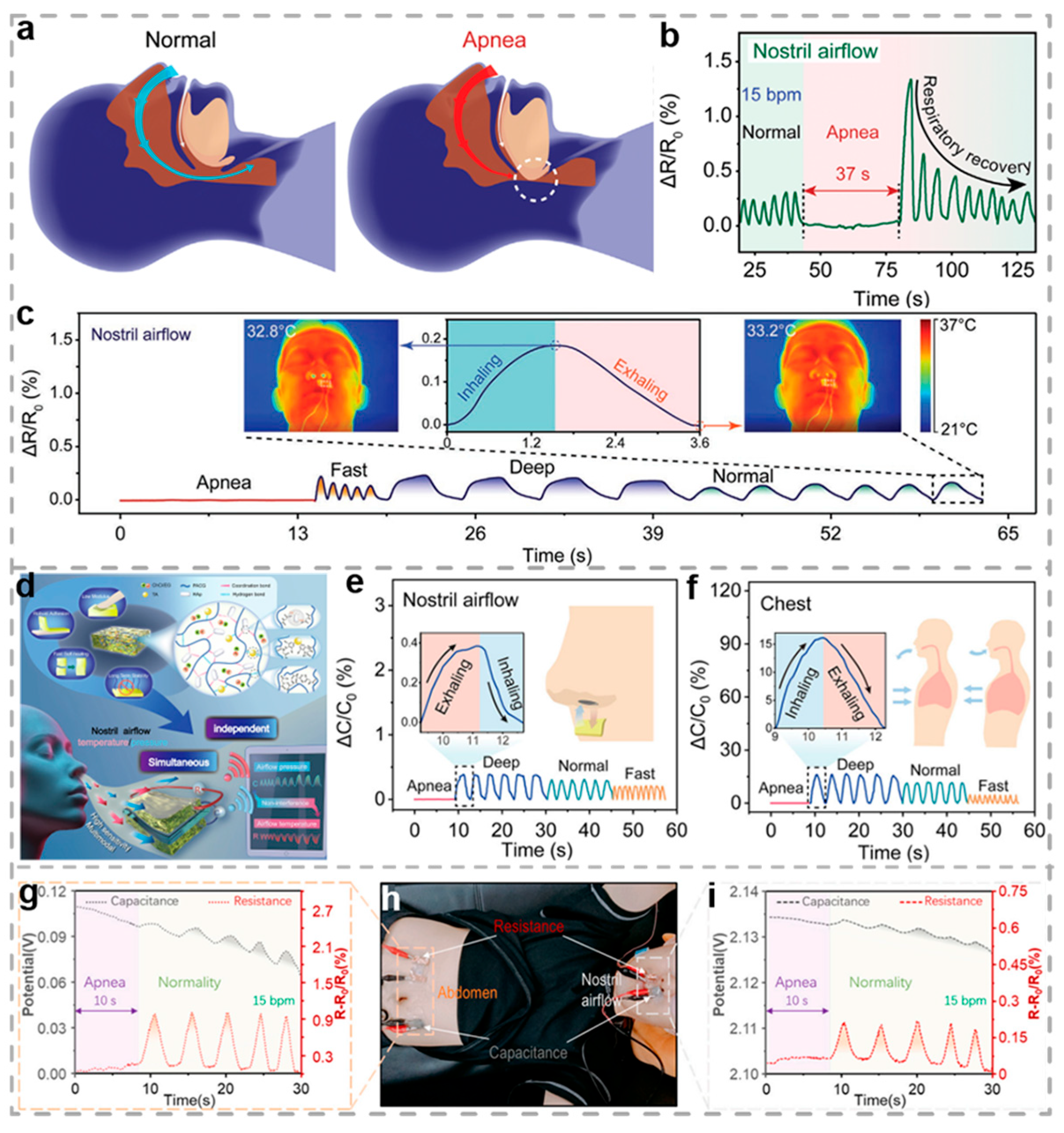
3.2. Respiratory Monitoring
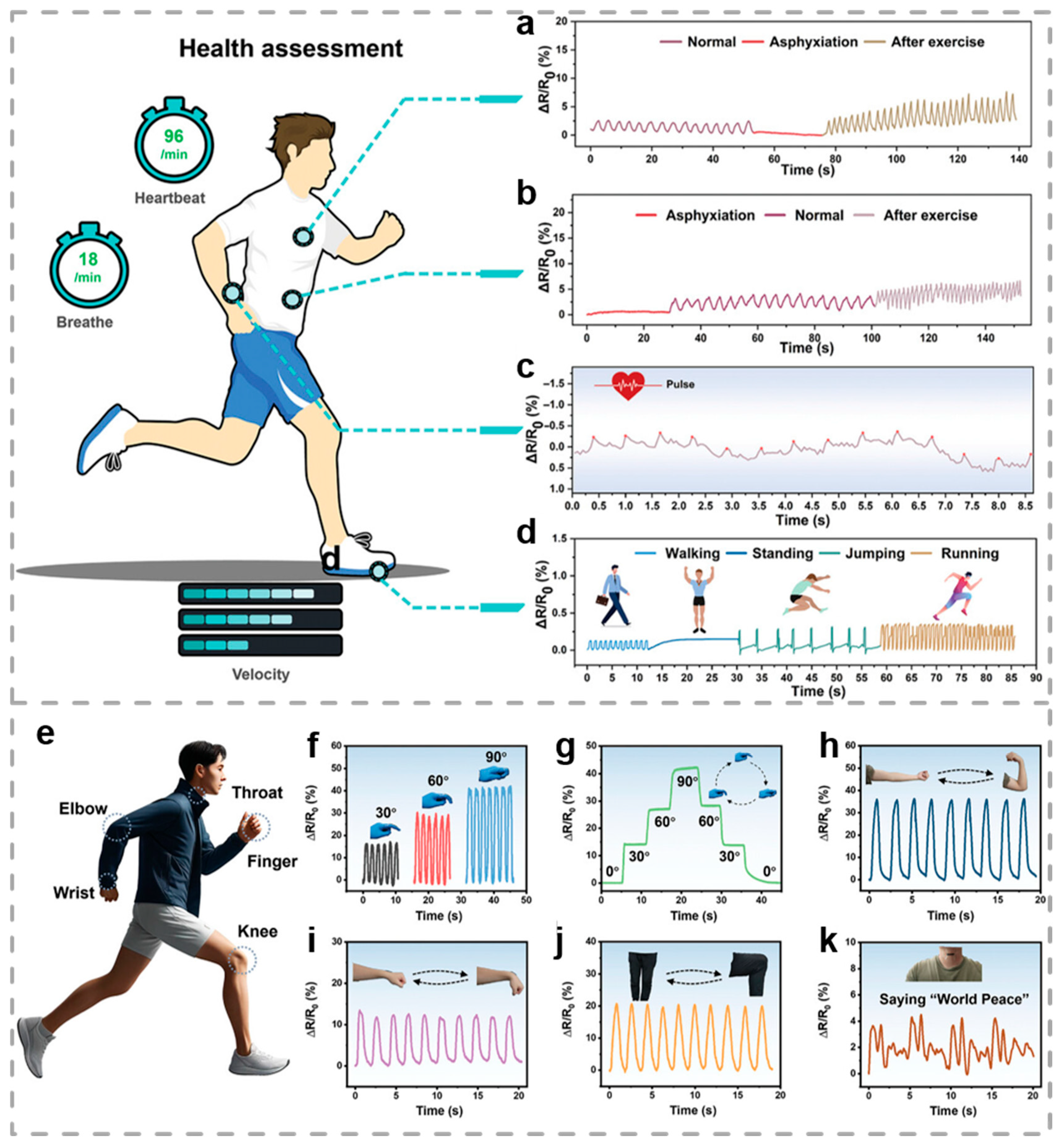
3.3. Motion Monitoring
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Full Name | Abbreviation |
| Conductive hydrogel | CHs |
| Human–machine interfaces | HMI |
| Ionic liquids | ILs |
| Electroencephalogram | EEG |
| Electrocardiogram | ECG |
| Electromyogram | EMG |
| Polypyrrole | PPy |
| Polyaniline | PANI |
| Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene): polystyrene sulfonate | PEDOT: PSS |
| Bentonite | BT |
| Polyvinyl alcohol | PVA |
| 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate | BMIMBF4 |
| Polyacrylic acid | PAA |
| Phase-separated dual ionic channels | PSDIC |
| Scanning electron microscopy | SEM |
| Conductive polymer hydrogels | CPHs |
| Cellulose nanofibrils | PPy@CNF |
| Tannic acid | TA |
| Graphene oxide | GO |
| Functionalized carbon nanotubes | fCNTs |
| Polyethylene glycol diacrylate | PEGDA |
| SF/GO/PEGDA | SGP |
| Graphene composite hydrogel | GTH |
| Electromagnetic interference | EMI |
| PVA-AgNWs-LM | PAL |
| Acrylamide | AAm |
| N-acryloyl-11-aminoundecanoic acid | A-11 |
| Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) | PNIPAM |
| Silk fibroin-functionalized MXene | MXene-SF |
| Polyacrylamide | PAM |
| Brain–computer interface | BCI |
| Elastic conductive composite | ECC |
| Polyvinylpyrrolidone | PVP |
| Polydopamine nanoparticles | PDA NPs |
| Liquid metal@silk fibroin peptide | LM@SF |
| Sodium caseinate | SC |
| Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome | OSAS |
References
- Hu, L.; Chee, P.L.; Sugiarto, S.; Yu, Y.; Shi, C.; Yan, R.; Yao, Z.; Shi, X.; Zhi, J.; Kai, D.; et al. Hydrogel-Based Flexible Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2205326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ren, G.; Sun, G.; Yu, H.-D.; Huang, W. Green Flexible Electronics: Natural Materials, Fabrication, and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2211202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Ye, D.; Duan, Y.; Li, K.; Yin, Z.; Huang, Y. Flexible Metamaterial Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2200070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Almuslem, A.S.; Babatain, W.; Bahabry, R.R.; Das, U.K.; El-Atab, N.; Ghoneim, M.; Hussain, A.M.; Kutbee, A.T.; Nassar, J.; et al. Beyond Flexible: Unveiling the Next Era of Flexible Electronic Systems. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2406424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liu, W.-D.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Z.-G. Multifunctional Wearable Thermoelectrics for Personal Thermal Management. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2200548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.T.; Rahman, M.S.; Kumar, H.; Kim, K.; Kim, S. Metal-Organic Framework Reinforced Highly Stretchable and Durable Conductive Hydrogel-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Biomotion Sensing and Wearable Human-Machine Interfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2303471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xue, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Wang, H.; Shao, A.; Ma, Y. A Hydrogel Electrolyte toward a Flexible Zinc-Ion Battery and Multifunctional Health Monitoring Electronics. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 7596–7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Zhang, Y.; Rajabi, N.; Taleb, F.; Yang, Q.; Kragic, D.; Li, Z. Shaping high-performance wearable robots for human motor and sensory reconstruction and enhancement. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, M.; Lee, G.; Lee, S.G.; Cho, K. Advances in Biodegradable Electronic Skin: Material Progress and Recent Applications in Sensing, Robotics, and Human-Machine Interfaces. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2203193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Wu, J.; Yan, J.; Liu, X. Advanced Fiber Materials for Wearable Electronics. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2023, 5, 12–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, T.; He, A.; Huang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Shi, Z.; Ke, G.; Bai, J.; Zhao, S.; et al. Silk-based flexible electronics and smart wearable Textiles: Progress and beyond. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, S.; Wu, Y.; Bao, X.; Xiang, Z.; Xie, Y.; Pan, L.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.-W. Advances in Flexible Magnetosensitive Materials and Devices for Wearable Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2311996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Lao, J.; Gao, H.; Yu, J. Hydrogels for Flexible Electronics. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 9681–9693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.; Kim, H.S.; Kwon, K.; Kim, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, S.H.; Jeong, J.-W.; Trotti, L.M.; Duarte, A.; Yeo, W.-H. At-home wireless sleep monitoring patches for the clinical assessment of sleep quality and sleep apnea. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg9671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, R.R.; Wang, C.F.; Dong, L.; Shen, C.Y.; Zhao, K.; Pan, C.F. CdS nanorods/organic hybrid LED array and the piezo-phototronic effect of the device for pressure mapping. NANOSCALE 2016, 8, 8078–8082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.L.; Deng, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, L.J.; Shan, C.X.; Dong, L. Continuous synthesis of ultra-fine fiber for wearable mechanoluminescent textile. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 9379–9386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.X.; Yang, X.; Lou, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Lu, Y.C.; Dong, L.; Shan, C.X. Fabry-Perot interference and piezo-phototronic effect enhanced flexible MoS2 photodetector. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 4395–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.X.; Ling, D.; Li, C.Y.; Zheng, W.T.; Zhang, S.C.; Li, C.; Emel’yanov, A.; Pozdnyakov, A.S.; Lu, L.J.; Mao, Y.C. Stretchable on-skin touchless screen sensor enabled by ionic hydrogel. Nano Res. 2024, 17, 4462–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.Y.; Liu, W.J.; Chen, K.; Sun, H.L.; Liu, X.Q.; Xing, H.N.; Wang, H.T.; Zhu, B.P.; Guo, H.Z. Piezoresistive Effect: A New Concept for Hearing Aids. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2501227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Guo, H.Z.; Yu, H.Y. Programmable and Surface-Conformable Origami Design for Thermoelectric Devices. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2309052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Islam, M.R.; Yin, J.; Eichhorn, S.J.; Chen, J.; Karim, N.; Afroj, S. Advances in Smart Photovoltaic Textiles. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 3871–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.; Marvi, P.K.; Ganguly, S.; Tang, X.; Wang, B.; Srinivasan, S.; Rajabzadeh, A.R.; Rosenkranz, A. MXene-Based Elastomer Mimetic Stretchable Sensors: Design, Properties, and Applications. Nano-Micro Lett. 2024, 16, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Yin, F.; Li, Y.; Shen, G.; Lee, J.-C. Incorporating Wireless Strategies to Wearable Devices Enabled by a Photocurable Hydrogel for Monitoring Pressure Information. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2300855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, F.H.; Lin, C.N.; Dong, L.; Mao, X.; Wu, Y.; Dong, F.Y.; Zhang, Z.F.; Sun, J.L.; Li, S.F.; Yang, X.; et al. Silicon Vacancies Diamond/Silk/PVA Hierarchical Physical Unclonable Functions for Multi-Level Encryption. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2308337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Carlos, C.; Zhou, H.; Sui, J.J.; Wang, Y.K.; Silva-Pedraza, Z.; Yang, F.; Dong, Y.T.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Hacker, T.A.; et al. Stretchable piezoelectric biocrystal thin films. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.J.; Zhu, P.C.; Zhang, F.K.; Li, P.S.; Huang, W.H.; Li, C.; Han, N.N.; Mu, S.R.; Zhou, H.; Mao, Y.C. Intrinsically stretchable polymer semiconductor based electronic skin for multiple perceptions of force, temperature, and visible light. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 1196–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Qin, J.X.; Yang, X.G.; Lv, C.F.; Huang, W.T.; Li, F.K.; Zhang, C.; Wu, Y.R.; Dong, L.; Shan, C.X. Highly sensitive humidity sensors based on hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets for contactless sensing. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 10279–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.J.; Hu, G.S.; Liu, J.Q.; Yang, B. 5G NB-IoT System Integrated with High-Performance Fiber Sensor Inspired by Cirrus and Spider Structures. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2309894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.X.; Wu, Y.J.; Dai, S.G.; Lin, P.; Sun, J.L.; Dong, L. A soft-contact hybrid electromagnetic-triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered water splitting towards hydrogen production. Nano Res. 2024, 17, 6567–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, A.; Ferreira, I.; Abbas, G.; Baptista, A.C. Recent Advances and Challenges Toward Application of Fibers and Textiles in Integrated Photovoltaic Energy Storage Devices. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Shen, H.; Zhao, S.; Li, N.; Liu, J. Flexible brain-computer interfaces. Nat. Electron. 2023, 6, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Tao, G.; Zhu, M.; Hou, C. All-Polymer Aqueous Fiber Battery for Sustainable Electronics. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2025, 7, 351–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Li, A.; He, X.; Wang, L.; Qin, X. Liquid metals and electrospun nanofibers: A magical marriage for wearable electronics. Nano Energy 2024, 129, 110078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Zhang, N.; Tang, Y.; Wang, M.; Chao, M.; Liang, E. A paper triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered electronic systems. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 14499–14505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Q.C.; Lou, Q.; Shen, C.L.; Zheng, G.S.; Song, R.W.; Hao, J.N.; Liu, J.L.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zang, J.H.; Dong, L.; et al. Sensitive humidity sensor based on moisture-driven energy generation. Nano Res. 2024, 17, 5578–5586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.G.; Chu, N.N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, T.T.; Li, X.L.; Huang, S.Z.; Li, X.J.; Luo, Y.S.; Yang, H.Y.; et al. 3D Printed Low-Tortuosity and Ultra-Thick Hierarchical Porous Electrodes for High-Performance Wearable Quasi-Solid-State Zn-VOH Batteries. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2401660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Cheng, Y.F.; Yue, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gao, H.; Li, L.; Cai, B.; Liu, W.J.; Wang, Z.Y.; Guo, H.Z.; et al. High-Performance Flexible Pressure Sensor with a Self-Healing Function for Tactile Feedback. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2200507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Qin, C.; Feng, T.X.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.R.; Sun, X.P.; Liang, E.J.; Mao, Y.C.; Wang, X.D. Non-contact cylindrical rotating triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting kinetic energy from hydraulics. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 1903–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, K.; Tan, R.; Zhang, S.; Su, Y.; Hu, J. Continuous Phase Separation Induced Tough Hydrogel Fibers with Ultrahigh Conductivity for Multidimensional Soft Electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2413478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, H.; Tang, M.; Xu, Z.; Xia, H.; Li, K.; Wang, J. Trehalose-enhanced ionic conductive hydrogels with extreme stretchability, self-adhesive and anti-freezing abilities for both flexible strain sensor and all-solid-state supercapacitor. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 472, 144849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Sung, C.; Nam, K.S.; Kang, T.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.; Park, H.; Park, S.; Kang, J. Highly conductive tissue-like hydrogel interface through template-directed assembly. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wen, F.; Lai, Y.; Li, H. Conductive Hydrogel for Flexible Bioelectronic Device: Current Progress and Future Perspective. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2308974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Park, J.M.; Oh, M.S.; Nguyen, T.L.; Shin, H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, D.; Park, H.S.; Kim, J. Superstrong, superstiff, and conductive alginate hydrogels. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, W.; Han, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, X.; Guo, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Jin, L.; Feng, S.; et al. Multifunctional Conductive and Electrogenic Hydrogel Repaired Spinal Cord Injury via Immunoregulation and Enhancement of Neuronal Differentiation. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2313672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Yu, D.; Liu, W. Ultrastretchable, repairable and highly sensitive xanthan collagen nanosilver hydrogel for wide temperature flexible sensing. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 470, 144385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Wang, P.; Lu, Y.; Jia, Z.; Qu, S.; Yang, W. A versatile hydrogel network-repairing strategy achieved by the covalent-like hydrogen bond interaction. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabl5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Mu, L.; Zhao, X.; Han, Y.; Guo, B. Bacterial Growth-Induced Tobramycin Smart Release Self-Healing Hydrogel for Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Infected Burn Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 13022–13036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; He, S.; Yao, M.; Tan, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, M.; Yu, C.; Liang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, Z.; et al. MXene-containing anisotropic hydrogels strain sensors with enhanced sensing performance for human motion monitoring and wireless transmission. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 461, 43833–43843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Y.; Yao, Y.; Qian, Q.; Luo, J.; Chen, H.; Qiao, Z.; Yu, Y.; Tao, L.; Zhou, N. Three-dimensional printing of soft hydrogel electronics. Nat. Electron. 2022, 5, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, M.; Yan, L.; Wang, K.; Han, L.; Lu, X. Infant Skin Friendly Adhesive Hydrogel Patch Activated at Body Temperature for Bioelectronics Securing and Diabetic Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 8662–8676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xu, H.; Weng, J.; Yu, F.; Xiong, A.; Udduttula, A.; Wang, D.; et al. An injectable liposome-anchored teriparatide incorporated gallic acid-grafted gelatin hydrogel for osteoarthritis treatment. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wang, P.; Hong, R.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; Pan, X.; Qiu, X.; Qin, Y. Fully Lignocellulosic Biomass-Based Double-Layered Porous Hydrogel for Efficient Solar Steam Generation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2209262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lou, Q.; Sun, J.L.; Liao, J.; Zheng, G.S.; Jiao, F.H.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Meng, J.J.; Shan, C.X.; et al. Carbon nanodot-based flexible and self-powered white displays. Nano Res. 2025, 18, 107549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.C.; Mu, S.R.; Huang, W.H.; Sun, Z.Y.; Lin, Y.Y.; Chen, K.; Pan, Z.F.; Haghighi, M.G.; Sedghi, R.; Wang, J.L.; et al. Soft multifunctional neurological electronic skin through intrinsically stretchable synaptic transistor. Nano Res. 2024, 17, 6550–6559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.C.; Niu, M.J.; Liang, S.Y.; Yang, W.Q.; Zhang, Y.T.; Chen, K.; Pan, Z.F.; Mao, Y.C. Non-hand-worn, load-free VR hand rehabilitation system assisted by deep learning based on ionic hydrogel. Nano Res. 2025, 18, 94907301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.C.; Zhang, B.S.; Wang, H.Y.; Wu, Y.H.; Cao, H.J.; He, L.B.; Li, C.Y.; Luo, X.P.; Li, X.; Mao, Y.C. 3D printed triboelectric nanogenerator as self-powered human-machine interactive sensor for breathing-based language expression. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 7460–7467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Fan, X.; Shen, J.; Gu, H. Ultra-stable and self-healing coordinated collagen-based multifunctional double-network organohydrogel e-skin for multimodal sensing monitoring of strain-resistance, bioelectrode, and self-powered triboelectric nanogenerator. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, D.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, M.W.; Ahn, J.; Min, K.; Lee, Y.; Hong, S.; Choi, J.; et al. Laser-induced wet stability and adhesion of pure conducting polymer hydrogels. Nat. Electron. 2024, 7, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Jiang, D.; Ge, Y.; Huang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Ren, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y. A PEDOT:PSS conductive hydrogel incorporated with Prussian blue nanoparticles for wearable and noninvasive monitoring of glucose. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 134109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Wan, P. Flexible Antiswelling Photothermal-Therapy MXene Hydrogel-Based Epidermal Sensor for Intelligent Human-Machine Interfacing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2300299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Chen, M.; Sun, Y.; Zuo, B. Self-Healing, Wet-Adhesion silk fibroin conductive hydrogel as a wearable strain sensor for underwater applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 136931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, J.; Ding, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Wu, J. Functionalized Hydrogel-Based Wearable Gas and Humidity Sensors. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhong, L.; Chen, C.; Xu, Z. Tough, antifreezing, and conductive double network zwitterionic-based hydrogel for flexible sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jian, Y.; He, L.; Yu, T.; Luo, H.; Kong, D.; Xianyu, Y.; et al. Stretchable graphene-hydrogel interfaces for wearable and implantable bioelectronics. Nat. Electron. 2023, 7, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Mo, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Fu, Q.; Wang, S.; Nie, S. Stretchable Triboelectric Self-Powered Sweat Sensor Fabricated from Self-Healing Nanocellulose Hydrogels. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2201846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Aladejana, J.T.; Ren, J.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Peng, X.; et al. A Simple and Effective Physical Ball-Milling Strategy to Prepare Super-Tough and Stretchable PVA@MXene@PPy Hydrogel for Flexible Capacitive Electronics. Small 2023, 19, 2303038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Lee, H.S.; Hong, Y.J.; Sunwoo, S.-H.; Park, O.K.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, D.-H.; Lee, S. Low-impedance tissue-device interface using homogeneously conductive hydrogels chemically bonded to stretchable bioelectronics. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadi7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Xu, C.; Zou, X.; Yang, K.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Z. Capacitive-Coupling-Responsive Hydrogel Scaffolds Offering Wireless In Situ Electrical Stimulation Promotes Nerve Regeneration. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2310483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, K.; Huang, J.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Cheng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Shi, Y.; Pan, L. Mechanically Robust, Flexible, Fast Responding Temperature Sensor and High-Resolution Array with Ionically Conductive Double Cross-Linked Hydrogel. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2314433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Li, K.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, T.; Yan, J.; Wang, H. Ultra-High Electrical Conductivity in Filler-Free Polymeric Hydrogels Toward Thermoelectrics and Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2109904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lian, L.; Liu, K.; Lu, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Wan, P. Flexible Accelerated-Wound-Healing Antibacterial MXene-Based Epidermic Sensor for Intelligent Wearable Human-Machine Interaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2208141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Yue, D.; Xiao, W.; Wang, W.; Chen, H.; Bai, L.; Yang, L.; Yang, H.; Wei, D. Anti-freezing and self-healing nanocomposite hydrogels based on poly (vinyl alcohol) for highly sensitive and durable flexible sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 436, 135243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, X.; Xia, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Jia, C.; Guo, W.; Li, Q.; Yan, Z. Stretchable freezing-tolerant triboelectric nanogenerator and strain sensor based on transparent, long-term stable, and highly conductive gelatin-based organohydrogel. Nano Energy 2022, 95, 106967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Dong, Q.; Peng, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, P.; Zhou, Y. Self-Healing Hyaluronic Acid Nanocomposite Hydrogels with Platelet-Rich Plasma Impregnated for Skin Regeneration. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 11346–11359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, M.; Du, Y.; Ding, X.; Xiao, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhuo, Y.; Zheng, K.; Liu, X.; et al. Self-healing liquid metal hydrogel for human-computer interaction and infrared camouflage. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 2945–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lu, J.; Ji, T.; Xue, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, K.; Jia, B.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; et al. Self-Healing Hydrogel Bioelectronics. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2306350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, M.; Yang, R.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; He, B.; Li, K.; Yang, Q.; Wei, L.; Pan, C.; et al. Bioinspired Self-healing Soft Electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2214479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Dong, Z.; Tang, Q.; Ding, R.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, K.; Wu, L.; Hao, L.; He, Y.; Yang, J.; et al. Glycopeptide-Based Multifunctional Hydrogels Promote Diabetic Wound Healing through pH Regulation of Microenvironment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2215116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Kang, X.; Gao, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Fan, C.; Shen, H.; Chen, Y.; Dai, J. Biomimetic Natural Biopolymer-Based Wet-Tissue Adhesive for Tough Adhesion, Seamless Sealed, Emergency/Nonpressing Hemostasis, and Promoted Wound Healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2211340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Fan, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, T. Highly Stretchable, Ultra-Soft, and Fast Self-Healable Conductive Hydrogels Based on Polyaniline Nanoparticles for Sensitive Flexible Sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2204366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, N.; Chu, X.; Sun, F.; Ali, M.U.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, B.; Cai, Y.; Liu, M.; Gasparini, N.; et al. Wide-Humidity Range Applicable, Anti-Freezing, and Healable Zwitterionic Hydrogels for Ion-Leakage-Free Iontronic Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2211617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, R.; Chen, Q.; Yu, A.; Lu, A. Self-Healing, Injectable Hydrogel Dressing for Monitoring and Therapy of Diabetic Wound. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2401209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ohm, Y.; Liao, J.; Luo, Y.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Won, P.; Roberts, P.; Carneiro, M.R.; Islam, M.F.F.; Ahn, J.H.; et al. A self-healing electrically conductive organogel composite. Nat. Electron. 2023, 6, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Hu, Y.; Wei, J.; Li, S.; Yang, P.; Mi, H.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. A Semi-Interpenetrating Poly(Ionic Liquid) Network-Driven Low Hysteresis and Transparent Hydrogel as a Self-Powered Multifunctional Sensor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2401607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Li, H.; Pu, A.; Li, W.; Ban, K.; Xu, L. Hybrid assembly of polymeric nanofiber network for robust and electronically conductive hydrogels. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Han, J.; Shi, Z.; Chen, K.; Xu, N.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, R.; Tao, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Z.L.; et al. Biodegradable, Super-Strong, and Conductive Cellulose Macrofibers for Fabric-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lu, H.; Pi, M.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Yan, B.; Cui, W.; Ran, R. Water-Induced Phase Separation for Anti-Swelling Hydrogel Adhesives in Underwater Soft Electronics. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2304780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, H.; Ju, Z.; Jin, Z.; Ma, J.; Yang, L.; Zhao, X.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y. Ti3C2T x MXene- and Sulfuric Acid-Treated Double-Network Hydrogel with Ultralow Conductive Filler Content for Stretchable Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 2906–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-N.; He, X.-F.; Zeng, Z.-F.; Jiang, B.; Wu, Q.; Gong, L.-X.; Li, Y.; Bae, J.; Wang, S.; Tang, L.-C. Mechanically ductile, ionically conductive and low-temperature tolerant hydrogel enabled by high-concentration saline towards flexible strain sensor. Nano Energy 2022, 103, 107789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, J.; Cao, H.; Liang, D.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xie, J.; Duan, H.; Fu, Y. Thermo-responsive and phase-separated hydrogels for cardiac arrhythmia diagnosis with deep learning algorithms. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 276, 117262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, X.; Fu, Y.; Wang, X. Versatile Biomass-Based Injectable Photothermal Hydrogel for Integrated Regenerative Wound Healing and Skin Bioelectronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2405745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Zhang, C.; Guo, T.; Tian, Y.; Song, W.; Lei, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, A.; Zhang, M.; Bai, S.; et al. Hydrogel Nanoarchitectonics of a Flexible and Self-Adhesive Electrode for Long-Term Wireless Electroencephalogram Recording and High-Accuracy Sustained Attention Evaluation. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2209606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gu, Y.; Qian, S.; Zheng, S.; Pang, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, B.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Q. An injectable, self-healable, and reusable PEDOT:PSS/PVA hydrogel patch electrode for epidermal electronics. Nano Res. 2024, 17, 5479–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Wu, Q.; Ding, Y.; Ou, R.; Guo, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q. Multimodal Hydrogel-Based Respiratory Monitoring System for Diagnosing Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2204686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xian, J.; He, C.; Lin, H.; Li, J.; Li, F. Asymmetric Wettability Hydrogel Surfaces for Enduring Electromyographic Monitoring. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2405372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, H. Bioinspired Super-Robust Conductive Hydrogels for Machine Learning-Assisted Tactile Perception System. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2416275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Zhao, R.; Lin, H.; Zhao, Z.; Song, S.; Wang, Y. Nucleobase-Driven Wearable Ionogel Electronics for Long-Term Human Motion Detection and Electrophysiological Signal Monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2412244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yu, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, N.; Du, J.; Xu, L.; Xu, J. Triboelectric nanogenerator based on well-dispersed and oxide-free liquid metal-doped conductive hydrogel as self-powered wearable sensor for respiratory and thyroid cartilage signal monitoring. Nano Energy 2025, 134, 110530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Wang, B.; Ren, Q.; Nie, J.; Guo, B.; Lu, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, D.; Lv, Y.; et al. Fully Implantable Wireless Cardiac Pacing and Sensing System Integrated with Hydrogel Electrodes. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2401982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yu, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Xu, X.; Song, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, C. Strong, tough, ionic conductive, and freezing-tolerant all-natural hydrogel enabled by cellulose-bentonite coordination interactions. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Mo, F.; Ji, Z.; Yang, J.; Du, H.; Wang, Z.; Haick, H.; Wang, Y. Highly tough and responsible ionic liquid/polyvinyl alcohol-based hydrogels for stretchable electronics. Sci. Bull. 2025, 70, 1410–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Wang, M.; Hou, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, P.; Wang, F. Strong and Tough Water-Tolerant Conductive Eutectogels with Phase-Separated Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Dual Ionic Channels. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2500770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Zheng, J.; Yang, H.; Ren, J.; Zhu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fu, J. Flexible Artificial Tactility with Excellent Robustness and Temperature Tolerance Based on Organohydrogel Sensor Array for Robot Motion Detection and Object Shape Recognition. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2408193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.; Yang, W.; Lu, B.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.; Zheng, X.; Liu, S.; Lin, C.; Zeng, H.; Huang, B. Muscle-Inspired Robust Anisotropic Cellulose Conductive Hydrogel for Multidirectional Strain Sensors and Implantable Bioelectronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2416419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Qi, H.; Dong, X.; Li, G.; Zhai, W. Highly Robust Conductive Organo-Hydrogels with Powerful Sensing Capabilities Under Large Mechanical Stress. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2304145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Heo, J.H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.A.; Park, K.; Lee, Y.; Jin, Y.; Shin, S.R.; Kim, D.W.; et al. Intrinsically Nonswellable Multifunctional Hydrogel with Dynamic Nanoconfinement Networks for Robust Tissue-Adaptable Bioelectronics. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2207237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Dai, C.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Yin, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Biomimetic Silk Fibroin Hydrogel for Enhanced Peripheral Nerve Regeneration: Synergistic Effects of Graphene Oxide and Fibroblast Exosome. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2314610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwon, Y.; Park, S.; Kim, W.; Park, S.; Sharma, H.; Jeong, H.E.; Kong, H.; Kim, J. Graphene Hybrid Tough Hydrogels with Nanostructures for Tissue Regeneration. Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 2188–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, S.; Xiong, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Yan, F. Stretch-Induced Conductivity Enhancement in Highly Conductive and Tough Hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2313845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, L.; Shen, Z.; Ren, J.; Chen, G.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Z. Super-Stretchable and Self-Healing hydrogel with a Three-Dimensional silver nanowires network structure for wearable sensor and electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Valenzuela, C.; Ma, S.; Zhang, X.; Ma, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, L. Highly Conductive MXene/PEDOT:PSS-Integrated Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) Hydrogels for Bioinspired Somatosensory Soft Actuators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2214867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Qin, Z.; Jiao, T. Ultrastretchable, Self-Adhesive and conductive MXene nanocomposite hydrogel for body-surface temperature distinguishing and electrophysiological signal monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 483, 149303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lin, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, D. Jellyfish-Inspired Ultrastretchable, Adhesive, Self-Healing, and Photoswitchable Fluorescent Ionic Skin Enabled by a Supramolecular Zwitterionic Network. Nano Lett. 2025, 25, 6957–6965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, X.; You, X.; Rao, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; Xing, L.; Li, J.; et al. Super stretchable gelatin/poly (ionic liquid) hydrogel enabled by weak hydrogen bonds and microphase separation towards multifunctional and self-powered sensors. Nano Energy 2025, 138, 110875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ji, X.; Zhu, R.; Gu, J.; Liang, J. A Microphase-Separated Design toward an All-Round Ionic Hydrogel with Discriminable and Anti-Disturbance Multisensory Functions. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2309508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, L.; Jing, H.; Xu, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Hao, J. Optically modulated ionic conductivity in a hydrogel for emulating synaptic functions. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadd6950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Dong, F.; Sun, X.; Bu, Y.; Wang, H.; Tang, D.; Li, L. Biphase Ionic Hydrogels with Ultrasoftness and High Conductivity for Bio-Ionotronics. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 16488–16499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Chen, G.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y. Structural Color Ionic Hydrogel Patches for Wound Management. ACS Nano 2022, 17, 1437–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Pan, M.; Qiao, C.; Ma, Y.; Yan, B.; Yang, W.; Peng, Q.; Han, L.; Zeng, H. Ultra stretchable, tough, elastic and transparent hydrogel skins integrated with intelligent sensing functions enabled by machine learning algorithms. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afting, C.; Mainik, P.; Vazquez-Martel, C.; Abele, T.; Kaul, V.; Kale, G.; Goepfrich, K.; Lemke, S.; Blasco, E.; Wittbrodt, J. Minimal-Invasive 3D Laser Printing of Microimplants in Organismo. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2401110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Y.L.; Sun, D.X.; Qi, X.D.; Yang, J.H.; Wang, Y. Recent progress in structural design of graphene/polymer porous composites toward electromagnetic interference shielding application. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 495, 153586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wang, Z.; Zen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ren, Q.; Ding, Z.; Ni, K.; Tang, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; et al. A Flexible, Bioadhesive, and Breathable On-Skin Battery Based on Silk Fibroin Hydrogel for Wearable Electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2410140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, L.; Lu, Z. Multifunctional enhanced energy density of flexible wide-temperature supercapacitors based on MXene/PANI conductive hydrogel. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 485, 149951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhou, J.; Lai, J.; Zheng, X.; Wang, H.; Lu, B.; Huang, R.; Zhang, L.-M. Novel Natural Polymer-Based Hydrogel Patches with Janus Asymmetric-Adhesion for Emergency Hemostasis and Wound Healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2401030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lu, H.; Kang, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Shi, X. Electroconductive and Immunomodulatory Natural Polymer-Based Hydrogel Bandages Designed for Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2310903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhan, X.; Du, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, D. Fluorescent hydrogel with high toughness response based on lanthanide Metals: Material Adhesion, multicolor Modulation, information encryption. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 489, 151303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Huang, W.; Peng, K.; Shi, R.; Tian, W.; Lin, L.; Yuan, J.; Yao, W.; Ma, X.; et al. A natural polymer-based hydrogel with shape controllability and high toughness and its application to efficient osteochondral regeneration. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 3797–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcudi, F.; Dordevic, L. Supramolecular Chemistry of Carbon-Based Dots Offers Widespread Opportunities. Small 2023, 19, 2300906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhuo, F.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dong, S.; Liu, X.; Elmarakbi, A.; Duan, H.; Fu, Y. Advances in graphene-based flexible and wearable strain sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 142576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Liu, F.; Abdiryim, T.; Liu, X. Hydrogels as promising platforms for solar-driven water evaporators. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 479, 147519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, N.; Kumar, V.; Joo, S.W.; Mandal, T.K. Emerging Trends in Nanomedicine: Carbon-Based Nanomaterials for Healthcare. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Ren, X.; Song, G.; Chen, S.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, R.; Pan, L.; et al. A chemically mediated artificial neuron. Nat. Electron. 2022, 5, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Zhang, C.; Bai, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Li, X.; He, J.; Wang, L.; Li, D. Tailoring Stretchable, Biocompatible, and 3D Printable Properties of Carbon-Based Conductive Hydrogel for Bioelectronic Interface Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2418554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Zou, S.; Cao, C.; Hou, J.; Guo, F.; Li, C.; Shi, W. Hydrogel-based 3D evaporator with cross-linked fixation by carbon dots for ultra-high and stable solar steam generation. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 497, 154793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Fan, L.; Wang, X.; Shang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y. Liquid metal hybrid antibacterial hydrogel scaffolds from 3D printing for wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 153805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fu, Z.; Liu, Y. Encapsulation of liquid metal nanoparticles inside metal-organic frameworks for hydrogel-integrated dual functional biotherapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 457, 141302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Qiu, X.; Cai, Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, X.; Zhang, J.; Hu, X.; Bai, H. High internal phase emulsions gel ink for direct-ink-writing 3D printing of liquid metal. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Liu, L.; Du, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, S.; Yang, L. Self-Sustained Water and Electricity Generation from Ambient Humidity by Using Metal-Ion Controlled Hygroscopic Hydrogels. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2420936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Wu, P.; Gao, Q.; Xu, J.; Guo, B.; He, Y. Multifunctionally wearable monitoring with gelatin hydrogel electronics of liquid metals. Mater. Horiz. 2022, 9, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Bai, Z.; Lv, H.; Yan, Z.; Du, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, L.; Deng, J.; Zhang, D.W.; et al. Self-Healing Liquid Metal Magnetic Hydrogels for Smart Feedback Sensors and High-Performance Electromagnetic Shielding. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, A.; Murali, G.; Lee, S.-Y.; Gwak, J.; Kim, S.J.; Jeong, Y.J.; Kang, H.; Park, S.; Lee, A.S.; Koh, D.-Y.; et al. Highly Oxidation-Resistant and Self-Healable MXene-Based Hydrogels for Wearable Strain Sensor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2213382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.-P.; Du, X.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, Q.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Wei, Y.; Yu, Q.; Guo, W. Thermal-Responsive MXene-DNA Hydrogel for Near-Infrared Light Triggered Localized Photothermal-Chemo Synergistic Cancer Therapy. Small 2022, 18, 2200263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.; Li, Y.; Duan, Z.; Shen, X.; Fu, R.; Fan, D. A Mxene@TA/Fe dual-nanozyme composited antifouling hydrogel for burn wound repair. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 476, 146420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, L.; Rostami, J.; Zhang, T.; Matthews, K.; Chen, S.; Fan, W.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, M.; et al. Tough MXene-Cellulose Nanofibril Ionotronic Dual-Network Hydrogel Films for Stable Zinc Anodes. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 13399–13413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; He, Q.; Xu, T.; Zhang, W.; Peng, Z.; Meng, B. Recent Progress in MXene Hydrogel for Wearable. Electronics 2023, 13, 495. [Google Scholar]
- Sikdar, A.; Heraly, F.; Zhang, H.; Hall, S.; Pang, K.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, J. Hierarchically Porous 3D Freestanding Holey-MXene Framework via Mild Oxidation of Self-Assembled MXene Hydrogel for Ultrafast Pseudocapacitive Energy Storage. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 3707–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Li, Z.; Hou, K.; Gao, Q.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, S. Bioinspired multi-crosslinking and solid–liquid composite lubricating MXene/PVA hydrogel based on salting out effect. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 476, 146848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Sun, C.; Chang, B.; Jing, Y.; Li, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Hou, C. MXene-Enabled Self-Adaptive Hydrogel Interface for Active Electroencephalogram Interactions. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 19373–19384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Mao, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, P.; Pu, J.; Mao, Z.; Fujiwara, T.; Ma, Y.; Mao, X.; Li, T. A Complementary Dual-Mode Ion-Electron Conductive Hydrogel Enables Sustained Conductivity for Prolonged Electroencephalogram Recording. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2405273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Miyata, H.; Wang, Y.; Nayeem, M.O.G.; Kim, J.J.; Lee, S.; Yokota, T.; Onodera, H.; et al. On-skin paintable biogel for long-term high-fidelity electroencephalogram recording. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabo1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhu, K.; Guo, W.; Wu, D.; Quan, X.; Huang, X.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Fang, H.; Qiu, Y.; et al. Adhesive and Hydrophobic Bilayer Hydrogel Enabled On-Skin Biosensors for High-Fidelity Classification of Human Emotion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2200457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Guo, T.; Deng, X.; Zhang, H.; Xie, C.; Lu, X. Tuning Water-Resistant Networks in Mussel- Inspired Hydrogels for Robust Wet Tissue and Bioelectronic Adhesion. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 2745–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, T.; Zhang, T.; Chen, L. Multifunctional crystalline hydrogel with a multistage porous structure inspired by biomineralization and Ostwald ripening process: High elasticity, low hysteresis, and excellent sensing properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 500, 156601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Veronica, A.; Yeung, S.Y.; Hsing, I.M. Skin-Adherent Elastomer-Hydrogel Patch for Continuous 12-Lead Cardiac Ambulatory Monitoring during Physical Activities. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2300326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Yu, D.; Wang, W. 3D-printed octopus-inspired PAM/CS hydrogels with excellent adhesion for high-performance ECG sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 508, 161043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Sun, C.; Chang, B.; Zhang, B.; Li, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Hou, C. On-Skin Paintable Water-Resistant Biohydrogel for Wearable Bioelectronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2400884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lu, Y.; Cui, H.; Zhang, J.; Tan, Y. Water-resistant conformal hydrogels toward underwater human-machine interfaces based on synergistic immersion method and supramolecular interactions strategy. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 485, 149925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Liu, Z.; Fu, Y.; Chen, X.; Gan, S.; Yang, W.; Chen, S.; Liu, L. Liquid Metal@Silk Fibroin Peptide Particles Initiated Hydrogels with High Toughness, Adhesion, and Conductivity for Portable and Continuous Electrophysiological Monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2420240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Guo, B.; Yu, J.; Yan, Z.; Liu, R.; Yu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yao, F.; Li, J. A polypyrrole-dopamine/poly(vinyl alcohol) anisotropic hydrogel for strain sensor and bioelectrodes. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 486, 150182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Ye, Y.; Li, S.; Huang, H.; Su, S.; Chen, L.; Li, S.; He, X.; He, Z.; Wan, P.; et al. Skin-Inspired Ultrafast Self-Healing Wearable Patch with Hybrid Cooling for Comfortable and Durable Electromyographic Monitoring. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 9, 2301933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ding, Q.; Luo, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yu, J.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tao, K.; Chen, X.; et al. High-Performance Hydrogel Sensors Enabled Multimodal and Accurate Human-Machine Interaction System for Active Rehabilitation. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2309868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Song, Z.; Liu, H.; Xu, X. Sweat-adaptive adhesive hydrogel electronics enabled by dynamic hydrogen bond networks. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 492, 152290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Su, Y.; Xu, J.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, G.; Xu, J.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, X.; Cao, F.; et al. Self-Adhesive ILn@MXene multifunctional hydrogel with excellent dispersibility for human-machine interaction, capacitor, antibacterial and detecting various physiological electrical signals in humans and animals. Nano Energy 2025, 133, 110484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Lan, Z.; Gong, H.; Wen, J.; Pang, B.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, W.; Bu, T.; Xie, B.; et al. A Nepenthes-Inspired Hydrogel Hybrid System for Sweat-Wicking Electrophysiological Signal Recording during Exercises. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2417841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Ming, X.; Yan, G.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Lai, J.; Li, D.; Xiang, D.; Zhao, C.; et al. Double-network conductive hydrogel for non-contact respiratory monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 502, 157719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Ding, Q.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Tao, K.; Gui, X.; Wu, J. Humidity Sensing of Stretchable and Transparent Hydrogel Films for Wireless Respiration Monitoring. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wang, Y.; Chu, H.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Xia, Z. High-performance gelatin-based hydrogel flexible sensor for respiratory monitoring and human-machine interaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 157975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Zang, X.; Yang, Y.; Gong, Z.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Wu, C.; Huang, J.; Lai, Y. Environmental Stability Stretchable Organic Hydrogel Humidity Sensor for Respiratory Monitoring with Ultrahigh Sensitivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2402853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Su, P.; Jin, M.; Huang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Xu, H.; Liu, W.; Ye, Y. Ultrathin hierarchical hydrogel-carbon nanocomposite for highly stretchable fast-response water-proof wearable humidity sensors. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 5263–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wu, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhao, X.; Yi, X.; Liu, J.; Nong, Z.; Zhou, B.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z. A crosslinked eutectogel for ultrasensitive pressure and temperature monitoring from nostril airflow. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, W.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Xu, S.; Sun, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, H.; Ren, L. Multimodal and flexible hydrogel-based sensors for respiratory monitoring and posture recognition. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 243, 115773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Mi, Y.; Zhao, S.; Yang, W.; Che, S.; Liu, H.; Chen, F.; Xu, C.; et al. Conductive photo-thermal responsive bifunctional hydrogel system with self-actuating and self-monitoring abilities. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 7703–7712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Chen, B.; Wang, X.; Nie, J.; Ma, G. A Heterojunction Piezoelectric Antimicrobial Asymmetric Hydrogel for Dynamic Wound Healing and Monitoring. Small 2025, 21, 2411265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Liu, T.; Jiang, Y.; He, B.; Hao, H. Multifunctional hydrogel sensor with Tough, self-healing capabilities and highly sensitive for motion monitoring and wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 497, 154890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.-C.; Yang, Y.-Q.; Pang, X.-W.; Jiang, B.; Mao, P.-F.; Gong, L.-X.; Wang, B.; Peng, L.; Tang, L.-C.; Li, S.-N. Rapid gelation of mechanical robust, conductive, and self-healing lignocellulosic nanofibrils hydrogel toward flexible sensor over a broad temperature spectrum. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 503, 158243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Sun, Q.; Shi, X.; Sun, Z.; Tan, S.; Tang, B.; Chen, W.; Liang, F.; Yu, H.-D.; Huang, W. Skin-interfaced self-powered pressure and strain sensors based on fish gelatin-based hydrogel for wireless wound strain and human motion detection. Nano Energy 2023, 118, 108932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Sun, F.; Jia, C.; Zhao, T.; Mao, Y. A Stretchable and Self-Healing Hybrid Nano-Generator for Human Motion Monitoring. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Materials | Conductivity (S m−1) | Strain (%) | Stability | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cellulose–BT/LiCl | 8.9 | 100 | −30 °C to 25 °C | [100] |
| BMIMBF4/PVA | 3.185 | 1000 | 0 °C to 317.92 °C | [101] |
| LiTFSI/ChTFSI/PHFBA | 1.6 × 10−3 | 683 | −20 °C to 200 °C | [102] |
| XP(Aam-co-AAc) | 0.3 | 100 | −18 °C to 60 °C | [103] |
| PVA-PPy@CNF-RPc | 0.01 | 451.77 | >14 days (in the mouse body) | [104] |
| PVA/PEDOT: PSS | 220 | 400 | >5 days | [105] |
| fCNT/TA/PVA/PAA | 40 | 1000 | >13 days (under water) | [106] |
| SF/GO/PEGDA | 0.6 | N/A | >7 days | [107] |
| PAM-AL-GO | N/A | 2100 | N/A | [108] |
| PVA/AgNWs/LM | 24 | 5300 | N/A | [109] |
| PAA/AgNWs/A-11 | 83 | 800 | N/A | [110] |
| MXene/PEDOT: PSS/PNIPAM | 11.76 | 560 | N/A | [111] |
| PAM/MXene-SF | 0.25 | 1560 | 22 °C to 100 °C | [112] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Chen, B.; Liu, Y.; Tan, T.; Gao, B.; Lu, L.; Zhu, P.; Mao, Y. Recent Advances in Conductive Hydrogels for Electronic Skin and Healthcare Monitoring. Biosensors 2025, 15, 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070463
Zhu Y, Chen B, Liu Y, Tan T, Gao B, Lu L, Zhu P, Mao Y. Recent Advances in Conductive Hydrogels for Electronic Skin and Healthcare Monitoring. Biosensors. 2025; 15(7):463. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070463
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yan, Baojin Chen, Yiming Liu, Tiantian Tan, Bowen Gao, Lijun Lu, Pengcheng Zhu, and Yanchao Mao. 2025. "Recent Advances in Conductive Hydrogels for Electronic Skin and Healthcare Monitoring" Biosensors 15, no. 7: 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070463
APA StyleZhu, Y., Chen, B., Liu, Y., Tan, T., Gao, B., Lu, L., Zhu, P., & Mao, Y. (2025). Recent Advances in Conductive Hydrogels for Electronic Skin and Healthcare Monitoring. Biosensors, 15(7), 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070463









