Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy-Based Biosensors for Label-Free Detection of Pathogens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Principles of EIS for Biosensing Applications
2.1. Fundamental Theory of EIS
2.2. Data Representation and Interpretation: Nyquist and Bode Plots
2.3. Equivalent Electrical Circuit (EEC) Models
2.4. Mechanism of Signal Generation in Label-Free EIS Biosensors
3. Design and Fabrication Strategies for EIS-Based Label-Free Pathogen Biosensors
3.1. Biorecognition Elements: The Key to Specificity
3.2. Electrode Materials and Nanomaterial Integration: Enhancing the Transduction Interface
3.3. Surface Modification and Bioreceptor Immobilization Techniques: Anchoring Recognition
4. Performance and Applications of EIS-Based Label-Free Pathogen Biosensors
4.1. Detection of Bacterial Pathogens
4.2. Detection of Viral Pathogens
4.3. Detection of Fungal and Parasitic Pathogens
4.4. Integration with Microfluidics and POC Systems
4.5. Multiplexed Pathogen Detection
5. Critical Evaluation, Current Challenges, and Future Perspectives
5.1. Critical Evaluation of EIS Technology for Label-Free Pathogen Detection
5.2. Current Challenges in Practical Implementation
5.3. Recent Breakthroughs and Emerging Trends
5.4. Future Outlook and Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cesewski, E.; Johnson, B.N. Biosensors for the Detection of Bacterial and Viral Clinical Pathogens. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 159, 112214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.-X.; Shaw, P.; Wen, X.; Dou, Q.; Zhang, X. Recent Developments towards Portable Point-of-Care Diagnostic Devices for Pathogen Detection. Sens. Diagn. 2022, 1, 252–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardian, Y.; Kosasih, H.; Karyana, M.; Neal, A.; Lau, C.-Y. Review of Current COVID-19 Diagnostics and Opportunities for Further Development. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 615099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhadra, S.; Riedel, T.E.; Lakhotia, S.; Tran, N.D.; Ellington, A.D. High-Surety Isothermal Amplification and Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Msphere 2021, 6, e00911-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, W.; Feng, L. Are We Prepared for the next Pandemic: Monitor on Increasing Human and Animal H5N1 Avian Influenza Infection. Chin. Med. J. 2024, 137, 2776–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.A.; Jorge, P.A.S. Applications of Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy in Disease Diagnosis—A Review. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2024, 8, 100205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, R.J.; Jovanov, E. Enabling Complex Impedance Spectroscopy for Cardio-Respiratory Monitoring with Wearable Biosensors: A Case Study. Electrochem 2023, 4, 389–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennison, A.; Pasricha, S.; Azzato, F. Direct Sequencing Technologies for Bacterial Sexually Transmitted Infections. Microbiol. Aust. 2024, 45, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Luz, L.; Mendonça, M.; Bernardes Fogaça, M.; Kipnis, A.; Bhunia, A.K.; Bührer-Sékula, S. Listeria monocytogenes: Review of Pathogenesis and Virulence Determinants-Targeted Immunological Assays. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 47, 647–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, F.; Arnold, D.; Bzdek, B.R.; Dodd, J.; Reid, J.; Maskell, N.; White, C.; Murray, J.; Keller, J.; Brown, J.; et al. Aerosol Generating Procedures: Are They of Relevance for Transmission of SARS-CoV-2? Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 687–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, K.T.L.; Lee, N.Y. Recent Methods for the Viability Assessment of Bacterial Pathogens: Advances, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreland, R.B.; Brubaker, L.; Tinawi, L.; Wolfe, A.J. Rapid and Accurate Testing for Urinary Tract Infection: New Clothes for the Emperor. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2025, 38, e00129-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Wahed, A.A.; Patel, P.; Maier, M.; Pietsch, C.; Rüster, D.; Böhlken-Fascher, S.; Kissenkötter, J.; Behrmann, O.; Frimpong, M.; Diagne, M.M.; et al. Suitcase Lab for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Based on Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 2627–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laczka, O.; Baldrich, E.; Muñoz, F.X.; del Campo, F.J. Label-Free Detection of Bacteria by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy: Comparison to Surface Plasmon Resonance. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 7239–7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Huang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Xu, Z.; Yu, H. Microfluidic Biosensors for Rapid Detection of Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Front. Chem. 2024, 12, 1536928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Tian, F.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Pan, J.; Luo, Z.; Yang, M.; Yi, C. Virus Detection: From State-of-the-Art Laboratories to Smartphone-Based Point-of-Care Testing. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2105904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, S.Q.; Wallace, E.L.; Srivatana, V.; Warady, B.A.; Watnick, S.; Hood, J.; White, D.L.; Aggarwal, V.; Wilkie, C.; Naljayan, M.V.; et al. Telehealth for Home Dialysis in COVID-19 and Beyond: A Perspective from the American Society of Nephrology COVID-19 Home Dialysis Subcommittee. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 77, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabay, G.; DeCastro, J.; Altay, A.; Smith, K.; Lu, H.; Capossela, A.M.; Moarefian, M.; Aran, K.; Dincer, C. Emerging Biosensing Technologies for the Diagnostics of Viral Infectious Diseases. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2201085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JoKaurrnal, M.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, D. An Insight into the Multifarious Applications of Biosensors and the Way Forward. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2022, 12, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posner, C.; Mehta, S.; Zhang, J. Fluorescent Biosensor Imaging Meets Deterministic Mathematical Modelling: Quantitative Investigation of Signalling Compartmentalization. J. Physiol. 2023, 601, 4227–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhuang, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, A.; Su, W.; Yu, J.; Lin, C.-T. Enhanced Electrochemical Voltammetric Fingerprints for Plant Taxonomic Sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 120, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Ye, C.; Xiao, X.; Sun, Z.; Li, X.; Fu, L.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Chen, J.; Lin, C.-T. Graphene-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Antibiotics: Sensing Theories, Synthetic Methods, and on-Site Monitoring Applications. Mater. Horiz. 2025, 12, 343–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, R.; Li, Y. A Review on Impedimetric Immunosensors for Pathogen and Biomarker Detection. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.; Juska, V.B.; O’Riordan, A. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) Based Label-Free Immunosensors. Chemrxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, R. Label-Free Biosensor. Biosensors 2023, 13, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, C.-M.; Tseng, C.-C.; Wu, F.-Y.; Chang, H.-P.; Li, L.-J.; Hsieh, Y.-P.; Lin, C.-T.; Chen, J.-C. Flexible Transparent Electrodes Made of Electrochemically Exfoliated Graphene Sheets from Low-Cost Graphite Pieces. Displays 2013, 34, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Spencer, R.H.; Hopkins, A.C.; Pham, J.D.; Mattrey, F.; Mohamed, A.; Melo, M.; Rosenberg, D.J.; Tucker, A.T.; Shen, T.; et al. Label-Free Electrochemical Sensor for Rapid Bacterial Pathogen Detection Using Vancomycin-Modified Highly Branched Polymers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 9543–9553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamied, N.; Abdelrahman, F.; El-Shibiny, A.; Hassan, R.Y.A. Bacteriophage-Based Nano-Biosensors for the Fast Impedimetric Determination of Pathogens in Food Samples. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari Nakhjavani, S.; Tokyay, B.K.; Soylemez, C.; Sarabi, M.R.; Yetisen, A.K.; Tasoglu, S. Biosensors for Prostate Cancer Detection. Trends Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 1248–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Lukas, H.; Tu, J.; Min, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, C.; Rossiter, H.B.; Gao, W. A Label-Free Electrochemical Impedimetric Immunosensor with Gold Nanostructured Screen-Printed Carbon Electrodes for Rapid Determination of SARS-CoV-2 in Saliva Samples. Biosensors 2022, 12, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronkainen, N.J.; Halsall, H.B.; Heineman, W.R. Electrochemical Biosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1747–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, A.; Ahmed, A.; Sundramoorthy, A.K.; Furukawa, H.; Arya, S.; Khosla, A. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Biosensors: Applications, Challenges, and Future Scope. Biosensors 2021, 11, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbhag, D.; Bindu, K.; Rao, V.; Srinivasan, K. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) as a Tool for Pathogen Detection. Biosensors 2022, 12, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvovich, V.F. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy A Tutorial. ACS Meas. Sci. Au 2023, 3, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randviir, E.P.; Banks, C.E. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS): Principles, Construction, and Biosensing Applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, M.A.; Cormier, M.M.E.; Zsoldos, E.; Phattharasupakun, N.; Johnson, M.B.; Metzger, M.; Yang, C.; Dahn, J.R.; Hamam, I.; Zhang, N. AMIDR: A Complete Pulse Method for Measuring Cathode Solid-State Diffusivity. ECS Meet. Abstr. 2023, MA2023-2, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Lee, C.-S.; Kim, T.H. Label-Free Assay of Protein Kinase A Activity and Inhibition Using a Peptide-Based Electrochemical Sensor. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajula, G.R.; Buddiga, L.R.; Dasari, M. Influence of Gd/Nb on Activation Energy, Relaxation Response, Impedance, Nyquist Plots and Dielectric Studies at High Frequency of BaTiO3-Li0.5Fe2.5O4 Solid Compounds. Results Phys. 2020, 18, 103196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, M.; Zabel, J.; Franzreb, M. New Approach for Investigating Diffusion Kinetics Within Capacitive Deionization Electrodes Using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. Front. Mater. 2020, 7, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, R.; Pradhan, S.K.; Majumdar, S.; De, S.K. Dielectric and Impedance Spectroscopy of Nd2 CoIrO6 Double Perovskite. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2020, 32, 495702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Long, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Meng, H.; Jiang, C.; Dong, W.; Lu, N. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Applied to Microbial Fuel Cells: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 973501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, B.; Bonomi, P.; Casalegno, A.; Rinaldi, F.; Baricci, A. Rapid Fault Diagnosis of PEM Fuel Cells through Optimal Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Tests. Energies 2020, 13, 3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P.P.; Kemeny, M.; Hudec, B.; Mikolasek, M.; Mičušík, M.; Siffalovic, P.; Strakova Fedorkova, A.; Frohlich, K. Enhanced Performance of LiFePO4 Cathodes Protected by Atomic Layer Deposited Ultrathin Alumina Films. In Electrochemical Society Meeting Abstracts 242; The Electrochemical Society, Inc.: Pennington, NJ, USA, 2022; Volume MA2022-2, p. 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voropaeva, D.; Golubenko, D.; Merkel, A.; Yaroslavtsev, A. Sulfonylimide-Based Cation Exchange Membranes as Electrolyte for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Synthesis and Characterization. In Electrochemical Society Meeting Abstracts prime2020; The Electrochemical Society, Inc.: Pennington, NJ, USA, 2020; Volume MA2020-2, p. 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EIS Data Plotting | Pine Research Instrumentation. Available online: https://pineresearch.com/support-article/eis-data-plotting/ (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Schalenbach, M.; Durmus, Y.E.; Robinson, S.A.; Tempel, H.; Kungl, H.; Eichel, R.-A. Physicochemical Mechanisms of the Double-Layer Capacitance Dispersion and Dynamics: An Impedance Analysis. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 5870–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, N.L.; Eggebeen, J.J.J.; Koper, M.T.M. Measurement of the Double-Layer Capacitance of Pt(111) in Acidic Conditions near the Potential of Zero Charge. Electrochim. Acta 2024, 494, 144456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewska, M.; Zamlynny, V.; Pieta, I.S.; Nowakowski, R.; Pieta, P. Interaction of LL-37 Human Cathelicidin Peptide with a Model Microbial-like Lipid Membrane. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 141, 107842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchicchio, E.; De Angelis, A.; Santoni, F.; Carbone, P. Uncertainty Characterization of a CNN Method for Lithium-Ion Batteries State of Charge Estimation Using EIS Data. Measurement 2023, 220, 113341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Mishra, S.; Gupta, R.K.; Manjuladevi, V. Synergistic Detection of E. Coli Using Ultrathin Film of Functionalized Graphene with Impedance Spectroscopy and Machine Learning. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 15177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Hamsan, M.H.; Nofal, M.M.; San, S.; Abdulwahid, R.T.; Raza Saeed, S.; Brza, M.A.; Kadir, M.F.Z.; Mohammed, S.J.; Al-Zangana, S. From Cellulose, Shrimp and Crab Shells to Energy Storage EDLC Cells: The Study of Structural and Electrochemical Properties of Proton Conducting Chitosan-Based Biopolymer Blend Electrolytes. Polymers 2020, 12, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukács, Z.; Kristóf, T. A Generalized Model of the Equivalent Circuits in the Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 363, 137199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žic, M.; Fajfar, I.; Subotić, V.; Pereverzyev, S.; Kunaver, M. Investigation of Electrochemical Processes in Solid Oxide Fuel Cells by Modified Levenberg–Marquardt Algorithm: A New Automatic Update Limit Strategy. Processes 2021, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, N.T. A Tutorial on Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy and Nanogap Electrodes for Biosensing Applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 22232–22245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simić, M.; Stavrakis, A.K.; Kojić, T.; Jeoti, V.; Stojanović, G.M. Parameter Estimation of the Randles Equivalent Electrical Circuit Using Only Real Part of the Impedance. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 4922–4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Li, B.; Sun, S.; Zhu, L.-J.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.-L.; Zang, H.-Y. Proton-Conducting Polyoxometalates as Redox Electrolytes Synergistically Boosting the Performance of Self-Healing Solid-State Supercapacitors with Polyaniline. CCS Chem. 2021, 3, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martellone, S.; Molino, D.; Zaccagnini, P.; Pedico, A.; Bocchini, S.; Ferraro, G.; Lamberti, A. (Best Poster Award-2nd Place) Energy Harvesting from CO2 Emission Exploiting an Ionic-Liquid Based Electrochemical Capacitor. ECS Meet. Abstr. 2023, MA2023-2, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, L.; Silcox, R.; Giammalvo, K.; Brower, E.; Isip, E.; Bala Chandran, R. Combined Effects of Concentration, pH, and Polycrystalline Copper Surfaces on Electrocatalytic Nitrate-to-Ammonia Activity and Selectivity. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 4178–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, X.; Deng, S.; Tang, M.; Du, G. Amphoteric Surfactant of Octadecyl Dimethyl Betaine as an Efficient Corrosion Inhibitor for Cold Rolled Steel in Phosphoric Acid Solution. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 7050–7069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, H.; Kant, R. Rms Roughness Determination Using Eis: Gold and Platinum Electrodes in Rtil and Viscous Medium. SSRN Electron. J. 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Lu, Y.-X.; Tsai, M.H.; Lin, C.-T. An Exploration of Graphene-Water Interface Electrochemical Circuit Model. In Electrochemical Society Meeting Abstracts 243; The Electrochemical Society, Inc.: Pennington, NJ, USA, 2023; Volume MA2023-1, p. 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.-F.; Hou, J.-F.; Kong, L.-B. Capacitive Charge Storage Mechanism in Sanmartinite to Be Determined by Qualitative and Quantitative Electrochemical Analysis. SSRN Electron. J. 2022, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbi, O.; Orazem, M.E.; Tran, M.T.T.; Tribollet, B.; Turmine, M.; Vivier, V. On the Graphical Analysis of the Impedance Response of Passive Electrodes. In Electrochemical Society Meeting Abstracts 241; The Electrochemical Society, Inc.: Pennington, NJ, USA, 2022; Volume MA2022-1, p. 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antaloae, C.; Marco, J.; Assadian, F. A Novel Method for the Parameterization of a Li-Ion Cell Model for EV/HEV Control Applications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2012, 61, 3881–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Cao, X.; Tian, M.; Jiang, R.; Gao, C.; Xia, J.; Wang, Z. A Novel Electrochemical Biosensor Based on MIL-101-NH2 (Cr) Combining Target-Responsive Releasing and Self-Catalysis Strategy for P53 Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 214, 114518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churcher, N.; Prasad, S. Non-Invasive Detection of Cytokines in Saliva Towards Asthma Phenotyping Using an Electrochemical Sensor. In Electrochemical Society Meeting Abstracts 245; The Electrochemical Society, Inc.: Pennington, NJ, USA, 2024; Volume MA2024-1, p. 2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, Z.; Halpern, J.M. Polyether-Cyclodextrin Modified Surfaces for Sensing of Hydrophobic Molecules. In Electrochemical Society Meeting Abstracts 239; The Electrochemical Society, Inc.: Pennington, NJ, USA, 2021; Volume MA2021-1, p. 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Lu, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, X. A Label-Free Electrochemical Sensor for the Detection of Two Kinds of Targets Based on CRISPR/Cas12a System. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 406, 135406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, E.G.D.L.; de Oliveira, H.P. β-Cyclodextrin-Silver Nanoparticles Inclusion Complexes: Insights into Applications in Trace Level Detection (Light-Driven and Electrochemical Assays) and Antibacterial Activity. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 23943–23956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.U.H.A.; Zia, S.; Rahman, G.; Bilal, S. Performance Improvement of Gold Electrode towards Methanol Electrooxidation in Akaline Medium: Enhanced Current Density Achieved with Poly(Aniline-Co-2-Hydroxyaniline) Coating at Low Overpotential. Polymers 2022, 14, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieu, M.-V.; Abafogi, A.T.; Hoang, T.X.; Pham, D.-T.; Park, J.; Park, S.; Park, S.; Cho, S. Impedimetric Gram-Positive Bacteria Biosensor Using Vancomycin-Coated Silica Nanoparticles with a Gold Nanocluster-Deposited Electrode. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 16658–16667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, A.; Rice, P.; Lin, K.-C.; Muthukumar, S.; Prasad, S. A Combinatorial Electrochemical Biosensor for Sweat Biomarker Benchmarking. SLAS Technol. 2020, 25, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzinger, M.; Le Goff, A.; Cosnier, S. Nanomaterials for Biosensing Applications: A Review. Front. Chem. 2014, 2, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Zhao, X.; Bao, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, L.; Tang, Y.; Wu, H.; Ye, H.; Yang, Y.; et al. SARS-Cov-2 Spike-S1 Antigen Test Strip with High Sensitivity Endowed by High-Affinity Antibodies and Brightly Fluorescent QDs/Silica Nanospheres. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 27612–27623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.; Guo, X.; Musavi, L.; Lin, C.-S.; Chen, S.-H.; Wu, V.C.H. Detection of Listeria Monocytogenes by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 4120–4131. [Google Scholar]
- Nidzworski, D.; Siuzdak, K.; Niedziałkowski, P.; Bogdanowicz, R.; Sobaszek, M.; Ryl, J.; Weiher, P.; Sawczak, M.; Wnuk, E.; Goddard, W.A.; et al. Universal Biosensor for Detection of Influenza Virus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 59, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelada-Guillén, G.A.; Sebastián-Avila, J.L.; Blondeau, P.; Riu, J.; Rius, F.X. Label-Free Detection of Staphylococcus Aureus in Skin Using Real-Time Potentiometric Biosensors Based on Carbon Nanotubes and Aptamers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 31, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Neuta, I.; Neumann, F.; Brightmeyer, J.; Ba Tis, T.; Madaboosi, N.; Wei, Q.; Ozcan, A.; Nilsson, M. Electrochemical Biosensors for Pathogen Detection. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 14, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Calvo, A.; Criado, A.; Seral-Ascaso, A.; Prato, M.; Vázquez, E.; Muñoz, J. Comparative Analysis of QCM and Electrochemical Aptasensors for SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD Protein Detection. Biosensors 2024, 14, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, P.M.; Anany, H.; Sailor, K.; Griffiths, M.; Didar, T.F. A Bacteriophage Protein-Based Impedimetric Electrochemical Biosensor for the Rapid Detection of Campylobacter Jejuni. Biosensors 2024, 14, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templier, V.; Roux, A.; Roupioz, Y.; Livache, T. Ligands for Label-Free Detection of Whole Bacteria on Biosensors: A Review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropero-Vega, J.L.; Redondo-Ortega, J.F.; Rodríguez-Caicedo, J.P.; Rondón-Villarreal, P.; Flórez-Castillo, J.M. New PEPTIR-2.0 Peptide Designed for Use as Recognition Element in Electrochemical Biosensors with Improved Specificity towards E. coli O157:H7. Molecules 2022, 27, 2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismailova, A.; White, J.H. Vitamin D, Infections and Immunity. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, M.J.; Davis, S.A.; Tumer, N.E.; Li, X.-P. Structural Basis for the Interaction of Shiga Toxin 2a with a C-Terminal Peptide of Ribosomal P Stalk Proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 15588–15596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, T.; Bain, S.C. The Role of Tirzepatide, Dual GIP and GLP-1 Receptor Agonist, in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes: The SURPASS Clinical Trials. Diabetes Ther. 2021, 12, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Linli, F.; Yang, W.; Chen, X. Enhancing the Stability of Natural Anthocyanins against Environmental Stressors through Encapsulation with Synthetic Peptide-Based Gels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Alhassan, M.; Lopez, J.; Albericio, F.; De La Torre, B.G. N-Butylpyrrolidinone for Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis Is Environmentally Friendlier and Synthetically Better than DMF. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 5288–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagar, P.K.; Savargaonkar, D.; Anvikar, A.R. Detection of Dengue Virus-Specific IgM and IgG Antibodies through Peptide Sequences of Envelope and NS1 Proteins for Serological Identification. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 1820325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wu, M.; Shi, M.; Shi, P.; Zhao, N.; Zhu, Y.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Ye, C.; Lin, C.-T.; Fu, L. An Overview to Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensors for the Detection of Bisphenol A. Sensors 2023, 23, 8656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.K.; Pal, S.; Verma, A.; Prajapati, Y.K.; Prakash Saini, J. Highly Sensitive Antimonene-Coated Black Phosphorous-Based Surface Plasmon-Resonance Biosensor for DNA Hybridization: Design and Numerical Analysis. J. Nanophoton. 2020, 14, 46015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Mishra, R.K.; Goud, K.Y.; Mohamed, M.A.; Kummari, S.; Tiwari, S.; Li, Z.; Narayan, R.; Stanciu, L.A.; Marty, J.L. Optical Biosensors for Diagnostics of Infectious Viral Disease: A Recent Update. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, M.; Furst, A.L. Electricity, Chemistry and Biomarkers: An Elegant and Simple Package: The Potential of Electrochemical Biosensors for Developing Novel Point-of-care Diagnostics. EMBO Rep. 2022, 23, e55096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Canoura, J.; Alkhamis, O.; Xiao, Y. Immobilization Strategies for Enhancing Sensitivity of Electrochemical Aptamer-Based Sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 9491–9499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbhag, M.M.; Manasa, G.; Mascarenhas, R.J.; Mondal, K.; Shetti, N.P. Fundamentals of Bio-Electrochemical Sensing. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2023, 16, 100516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Shi, D.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, P.; Zhao, N.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Lv, Y.; Wu, W.; et al. Graphene Electrochemical Biosensors Combining Effervescent Solid-Phase Extraction (ESPE) for Rapid, Ultrasensitive, and Simultaneous Determination of DA, AA, and UA. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 268, 116899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, C.E.; Otieno, B.A.; Latus, A.; Faria, R.C.; Patel, V.; Gutkind, J.S.; Rusling, J.F. Rapid Microfluidic Immunoassays of Cancer Biomarker Proteins Using Disposable Inkjet-Printed Gold Nanoparticle Arrays. ChemistryOpen 2013, 2, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yu, M.; Chen, X.; Nie, S.; Lai, W.; Su, W.; Cui, Z.; Huang, W. Screen-Printed Poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene):Poly(Styrenesulfonate) Grids as ITO-Free Anodes for Flexible Organic Light-Emitting Diodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pander, J.E.; Baruch, M.F.; Bocarsly, A.B. Probing the Mechanism of Aqueous CO2 Reduction on Post-Transition-Metal Electrodes Using ATR-IR Spectroelectrochemistry. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 7824–7833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bappy, M.O.; Jiang, Q.; Atampugre, S.; Zhang, Y. Aerosol Jet Printing of High-Temperature Bimodal Sensors for Simultaneous Strain and Temperature Sensing Using Gold and Indium Tin Oxide Nanoparticle Inks. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 9453–9459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.-H.; Kim, D.H.; Park, S. Electrochemical Biosensors: Perspective on Functional Nanomaterials for on-Site Analysis. Biomater. Res. 2020, 24, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangopadhyay, R.; De, A. Conducting Polymer Nanocomposites: A Brief Overview. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 608–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Rai, N.; Tiwari, H.; Gupta, P.; Verma, A.; Kumar, R.; Kailashiya, V.; Salvi, P.; Gautam, V. Recent Advancements in the Formulation of Nanomaterials-Based Nanozymes, Their Catalytic Activity, and Biomedical Applications. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2023, 6, 3577–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disha; Kumari, P.; Nayak, M.K.; Kumar, P. An Electrochemical Biosensing Platform for Progesterone Hormone Detection Using Magnetic Graphene Oxide. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 5264–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakides, T.R.; Raj, A.; Tseng, T.H.; Xiao, H.; Nguyen, R.; Mohammed, F.S.; Halder, S.; Xu, M.; Wu, M.J.; Bao, S.; et al. Biocompatibility of Nanomaterials and Their Immunological Properties. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 16, 42005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salek Maghsoudi, A.; Hassani, S.; Mirnia, K.; Abdollahi, M. Recent Advances in Nanotechnology-Based Biosensors Development for Detection of Arsenic, Lead, Mercury, and Cadmium. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 803–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Chen, F.; Zhao, S.; Ye, C.; Lin, C.-T.; Zhu, J.; Fu, L. Preparation of Cassava Fiber-Iron Nanoparticles Composite for Electrochemical Determination of Tea Polyphenol. Food Meas. 2021, 15, 4711–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Zhang, S.; Yang, L.; Liu, M.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S. Multifunctional Electrochemical Platforms Based on the Michael Addition/Schiff Base Reaction of Polydopamine Modified Reduced Graphene Oxide: Construction and Application. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 17935–17946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.; Coleman, J.N. Are There Fundamental Limitations on the Sheet Resistance and Transmittance of Thin Graphene Films? ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2713–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, S. Graphene Oxide: A Promising Nanomaterial for Energy and Environmental Applications. Nano Energy 2015, 16, 488–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhiwen, T.; Shijiang, H.; Hao, P.; Dan, D.; Chunhai, F.; Yuehe, L. Graphene-Based Optical Biosensors and Imaging. In Biosensors Based on Nanomaterials and Nanodevices; Jun, L., Nianqiang, W., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 93–110. ISBN 978-1-315-21631-7. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Wen, Z.; Cui, S.; Guo, X.; Chen, J. Constructing 2D Porous Graphitic C3 N4 Nanosheets/Nitrogen-Doped Graphene/Layered MoS2 Ternary Nanojunction with Enhanced Photoelectrochemical Activity. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6291–6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Dever, B.; Li, X.-F.; Le, X.C. DNA-Mediated Homogeneous Binding Assays for Nucleic Acids and Proteins. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 2812–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, A.; Hassan, M.M.; Ouyang, Q.; Li, H.; Chen, Q. A Highly Sensitive Upconversion Nanoparticles-WS2 Nanosheet Sensing Platform for Escherichia Coli Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 320, 128434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Long, C.; Su, L.; Liu, S.; Tang, Z. Applications of Nanomaterials in Asymmetric Photocatalysis: Recent Progress, Challenges, and Opportunities. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2001731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Sain, S.; Wadhwa, S.; Mathur, A.; Dubey, S.; Roy, S.S. Electrochemical Impedimetric Analysis of Different Dimensional (0D–2D) Carbon Nanomaterials for Effective Biosensing of L-Tyrosine. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2022, 33, 14002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, W.; Gong, W.; Liu, N.; Jia, Y.; Ding, D.; Ning, Z. Ultrasensitive Determination of Microcystin-Leucine-Arginine (MCLR) by an Electrochemiluminescence (ECL) Immunosensor with Graphene Nanosheets as a Scaffold for Cadmium-Selenide Quantum Dots (QDs). Anal. Lett. 2021, 54, 2523–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Wei, Q.; Long, H.; Yu, Z.; Deng, Z.; Meng, L.; Wang, J.; Luo, J.; Lin, C.-T.; Ma, L.; et al. Long-Term Stability of Au Nanoparticle-Anchored Porous Boron-Doped Diamond Hybrid Electrode for Enhanced Dopamine Detection. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 271, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narware, J.; Chakma, J.; Singh, S.; Prasad, D.; Meher, J.; Singh, P.; Bhargava, P.; Sawant, S.B.; Singh, J.P.; Manzar, N. Nanomaterial-Based Biosensors for a New Frontier in Plant Pathogen Detection and Plant Disease Management. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2025, 13, 1570318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolba, M.; Ahmed, M.U.; Tlili, C.; Eichenseher, F.; Loessner, M.J.; Zourob, M. Electrochemical Biosensor for Rapid Detection of Listeria Monocytogenes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 34, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Lai, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. Recent Advances in Aptasensors For Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Bioeng.Biotechnol. 2022, 23, 889431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Chai, Y.; Yuan, R. A Review: Metal-Organic Frameworks Electrochemical Biosensors for Biomolecules. Anal. Bioanal. Electrochem. 2020, 12, 100–125. [Google Scholar]
- Gajula, S.P.K.; Reddy, K.A.; Pratap, C.; Reddy, C.N.K.; Reddy, K.C.S.; Madhavi, G. Electrochemical Biosensors for Pathogen Detection: An Updated Review. Biosensors 2022, 12, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, N.; Sharma, R. Recent Advances in Nanomaterials for the Detection of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2024, 53, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.N.P.; Nguyen, S.H.; Tran, M.T. Disposable Impedance Sensors Based on Novel Hybrid MoS2 Nanosheets and Microparticles to Detect Escherichia Coli DNA. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0299272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Chen, G.; Jiang, N.; Yu, J.; Lin, C.-T.; Yu, A. In Situ Growth of Metal Nanoparticles on Boron Nitride Nanosheets as Highly Efficient Catalysts. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 19107–19115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, L.M.; Hengge, E.; Steyskal, E.-M.; Würschum, R.; Nidetzky, B. Interplay of Surface Charge and Pore Characteristics in the Immobilization of Lactate Oxidase on Bulk Nanoporous Gold Electrodes. Langmuir 2025, 41, 5136–5146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candreva, A.; Di Maio, G.; Parisi, F.; Scarpelli, F.; Crispini, A.; Godbert, N.; Ricciardi, L.; Nucera, A.; Rizzuto, C.; Barberi, R.C.; et al. Luminescent Self-Assembled Monolayer on Gold Nanoparticles: Tuning of Emission According to the Surface Curvature. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, A.; Blues, E.; Williamson, P.; Cardona, M.; Gray, L.; Corrigan, D.K. SAM Composition and Electrode Roughness Affect Performance of a DNA Biosensor for Antibiotic Resistance. Biosensors 2019, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Integrated Affinity Biosensing Platforms on Screen-Printed Electrodes Electrografted with Diazonium Salts. Sensors 2018, 18, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y. Toward Highly Sensitive, Selective, and Stable Palladium-based MEMS Gas Sensors for Hydrogen Energy Security. Smartmat 2024, 5, e1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-Y.; Nan, H.; Shen, S.-C.; Chen, M.-X.; Liang, H.-W.; Huang, C.-Q.; Yao, T.; Chu, S.-Q.; Li, W.-X.; Yu, S.-H. Incorporating Sulfur Atoms into Palladium Catalysts by Reactive Metal–Support Interaction for Selective Hydrogenation. CCS Chem. 2022, 4, 3051–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Xu, X.; Yang, J.; Huo, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, X.; Ma, Y. Recent Advances in Surface Modifications of Elemental Two-Dimensional Materials: Structures, Properties, and Applications. Molecules 2022, 28, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, E.; Pankratov, D.; Sotres, J.; Arnebrant, T.; Ruzgas, T. Pathogen Detection via Impedance Spectroscopy-Based Biosensor. Sensors 2024, 24, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juska, V.B.; Pemble, M.E. A Critical Review of Electrochemical Glucose Sensing: Evolution of Biosensor Platforms Based on Advanced Nanosystems. Sensors 2020, 20, 6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinberg, H.; Castelli, R.; Drickamer, K.; Seeberger, P.H.; Weis, W.I. Multiple Modes of Binding Enhance the Affinity of DC-SIGN for High Mannose N-Linked Glycans Found on Viral Glycoproteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 4202–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, S.; Aghakhani, A.; Whalley, R.D.; Ferreira, A.M.; Kotov, N.; Gentile, P. Layer-by-Layer Nanoparticle Assembly for Biomedicine: Mechanisms, Technologies, and Advancement via Acoustofluidics. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 15874–15902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, M.; Srisomwat, C.; Urban, M.; Rosati, G.; Maroli, G.; Yaman Akbay, H.G.; Chailapakul, O.; Merkoçi, A. Unleashing Inkjet-Printed Nanostructured Electrodes and Battery-Free Potentiostat for the DNA-Based Multiplexed Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Genes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 250, 116079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.; Zhang, G.F.; Hu, C.; Yuan, B.; Gao, S.-J.; Panat, R. An Advanced Healthcare Sensing Platform for Direct Detection of Viral Proteins in Seconds at Femtomolar Concentrations via Aerosol Jet 3D-Printed Nano and Biomaterials. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 11, 2400005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Ma, D.; Li, H.; Cui, G.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z. Review of Industrialization Development of Nanoimprint Lithography Technology. Chips 2025, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, D.; Pedrero, M.; Guo, Z.; Pingarrón, J.M.; Campuzano, S.; Zou, X. Advances and Opportunities of Polydopamine Coating in Biosensing: Preparation, Functionality, and Applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 501, 215564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luka, G.S.; Najjaran, H.; Hoorfar, M. On-Chip-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for the Sensitive and Label-Free Detection of Cryptosporidium. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowska, N.; Białobrzeska, W.; Łęga, T.; Pałka, K.; Dziąbowska, K.; Żołędowska, S.; Czaczyk, E.; Pala, K.; Nidzworski, D. Antibody Modified Gold Electrode as an Impedimetric Biosensor for the Detection of Streptococcus Pyogenes. Sensors 2020, 20, 5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Zhi, N.; Yang, L.; Xu, G.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, S. A Highly Sensitive Uric Acid Electrochemical Biosensor Based on a Nano-Cube Cuprous Oxide/Ferrocene/Uricase Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phukon, A.; Bora, U.; Konwar, A. Exploring Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy for Tuberculosis Detection: A Review. Front. Sens. 2024, 5, 1512936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.D.; De, A.; Chaudhuri, C.R.; Bandyopadhyay, K.; Sen, P. An Electrochemical Impedimetric Immunosensor for Label-Free Detection of Campylobacter jejuni in Diarrhea Patients’ Stool Based on O-Carboxymethylchitosan Surface Modified Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 28, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Cui, F.; Guan, W.; Wheatley, W.; Zheng, J.; Yan, X.; Huang, X. Recent Advancements in Electrochemical Biosensors for Monitoring Aquaculture Pathogens. Biosensors 2022, 12, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, T.; Irkham, I.; Pratomo, U.; Gaffar, S.; Zakiyyah, S.; Rahmawati, I.; Topkaya, S.N.; Hartati, Y.W. Label-Free and Label-Based Electrochemical Detection of Disease Biomarker Proteins. ADMET DMPK 2024, 12, 463–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Calvo, A.; Pérez-García, C.; Sánchez-Paniagua, M.; Sánchez-Paniagua López, M.; Abad, M.-M.; Rodríguez-Frade, J.M.; Blázquez, A.-B.; Saiz, J.-C.; Muñoz, J.; Vázquez, E. A Cell-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for the Detection of Infectious Hepatitis A Virus. Biosensors 2024, 14, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Guo, H.; Xia, H.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, F. Metal–Organic Frameworks-Derived Material for Electrochemical Biosensors: Recent Applications and Prospects. Biosensors 2023, 13, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, M.Z.; Kopechek, J.A.; Priddy, M.C.; Hamorsky, K.T.; Palmer, K.E.; Mittal, N.; Valdez, J.; Flynn, J.; Williams, S.J. Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Using Electrochemical Impedance-Based Detector. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, T.; Foo, K.L.; R., H.; Sam, A.J.; Solayappan, M. Gold-Hybridized Zinc Oxide Nanorods as Real-Time Low-Cost NanoBiosensors for Detection of Virulent DNA Signature of HPV-16 in Cervical Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.; Solanki, P.R.; Kaushik, A. Biosensors for Fungal Detection. Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Cao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Dou, W.; Xiao, F.; Zhu, J.; Huang, Q.-A.; Shi, Y. Biosensors for Detection of Airborne Pathogenic Fungal Spores: A Review. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 11603–11622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Chen, D.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Guo, L.; Dai, D.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, P.; Jiang, N.; Lin, C.-T. High Quality Graphene Films with a Clean Surface Prepared by an UV/Ozone Assisted Transfer Process. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 1880–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, J.; Sánchez, J.; Ortega, G.; Prado, M.; Espinoza-Montero, P.; Fernández, L.; Merkoçi, A. Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Genosensors for Species-Specific Diagnosis of Human Malaria. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 214, 114514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; He, J.; Tian, K.; Qu, J.; Hong, L.; Lin, Q.; Yang, K.; Ma, L.; Xu, X. Research Progress on Detection of Pathogens in Medical Wastewater by Electrochemical Biosensor. Molecules 2024, 29, 3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, H.; Wu, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, A.; Su, W.; Chen, F.; Yu, J.; et al. An Electrochemical Method for Plant Species Determination and Classification Based on Fingerprinting Petal Tissue. Bioelectrochemistry 2019, 129, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idil, N.; Mattana, G.; Bouhadda, I.; Guan, B.; Marote, P.; Bendali, A.; Mailley, P.; Livache, T.; Roupioz, Y. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy-Based Microfluidic Biosensor Using Cell-Imprinted Polymers for Bacteria Detection. Biosensors 2024, 14, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, R.; Singh, J.; Chaudhary, U.; Chauhan, N. Development of Nanobiosensors for Human Immunodeficiency Virus Detection. Explor. Med. 2023, 4, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 13485; Medical Devices—Quality Management Systems—Requirements for Regulatory Purposes. CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018.
- ISO 23418; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Whole Genome Sequencing for Typing and Genomic Characterization of Bacteria—General Requirements and Guidance. CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022.
- Jyothi, S.; Sadanandan, S.; Sadanandan, R. A Critical Review on the Identification of Pathogens by Employing Peptide-Based Electrochemical Biosensor. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2024, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshavsky-Graham, S.; Massad-Ivanir, N.; Segal, E.; Weiss, S. A Review of Membrane-Based Biosensors for Pathogen Detection. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 441–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Li, Z.; Wei, X.; Huang, R.; Qi, H.; Gao, Q.; Li, C.; Zhang, C. Detection and Discrimination of Alpha-Fetoprotein with a Label-Free Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Biosensor Array Based on Lectin Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes. Talanta 2013, 111, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-S.; Huang, C.-H.; Pai, P.-C.; Seo, J.; Lei, K.F. A Review on Microfluidics-Based Impedance Biosensors. Biosensors 2023, 13, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Purrà, M.; Carré-Camps, M.; de Puig, H.; Bosch, I.; Gehrke, L.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. Review of Label-Free Monitoring of Bacteria: From Challenging Aspects to Advanced Approaches. Biosensors 2022, 12, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, F.; Liu, X.; Du, S.; Ren, G. Overview of Rapid Detection Methods for Salmonella in Foods: Progress and Challenges. Foods 2021, 10, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhao, N.; Sun, Z.; Sun, K.; Chu, W.; Tsai, H.-S.; Wu, L.; Cai, T.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, N.; et al. Synthesis of Tumbleweed-like MoSe2 Nanostructures for Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Detection of Uric Acid. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busa, L.S.A.; Mohammadi, S.; Maeki, M.; Ishida, A.; Tani, H.; Tokeshi, M. Advances in Paper-Based Electrochemical Immunosensors: Review of Fabrication Strategies and Biomedical Applications. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2023, 10, 230940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, T.-H.; Zhou, W.; Shi, M.; Wu, M.; Shi, P.; Zhao, N.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D.; et al. An “On-Site Transformation” Strategy for Electrochemical Formation of TiO2 Nanoparticles/Ti3C2Tx MXene/Reduced Graphene Oxide Heterojunction Electrode Controllably toward Ultrasensitive Detection of Uric Acid. Small Struct. 2024, 5, 2400034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Ye, C.; Sun, Z.; Sun, K.; Zhao, N.; Pourfakhr, M.; Cai, T.; Nishimura, K.; Jiang, N.; Tsai, H.-S.; et al. Synthesis of Churros-like V2Se9 Nanostructures for Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Detection of Oxalic Acid in Urine with Portable Point-of-Care Diagnostic Devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 285, 117589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-C.; Chiang, Y.-H.; Chiang, H.-Y. A Label-Free Electrochemical Impedimetric Immunosensor with Biotinylated-Antibody for SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein Detection in Saliva. Biosensors 2022, 12, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, L.; Alves, L.N.; Petti, L. Biosensors for Public Health and Environmental Monitoring: The Sustainability Perspective. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 637–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
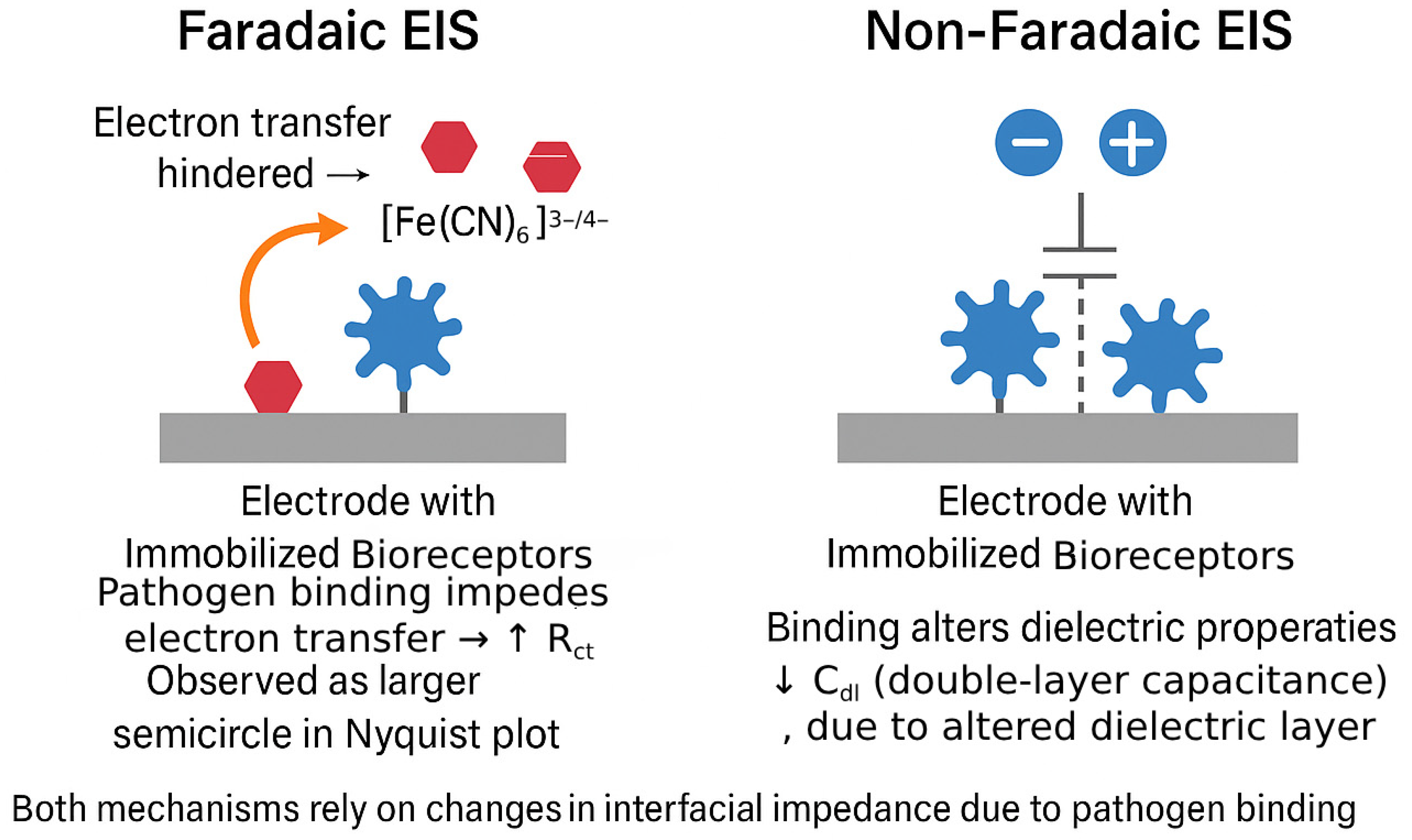
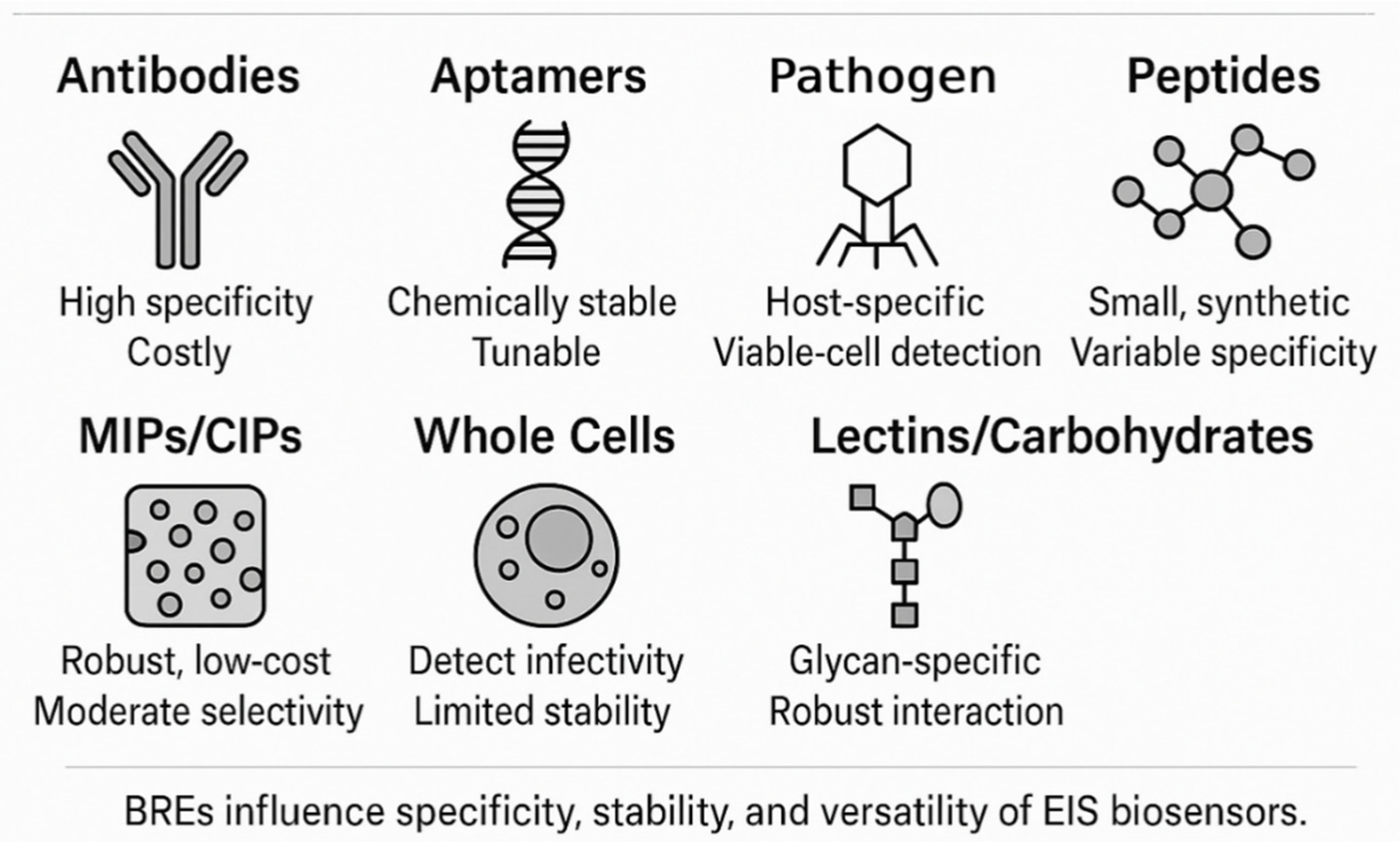
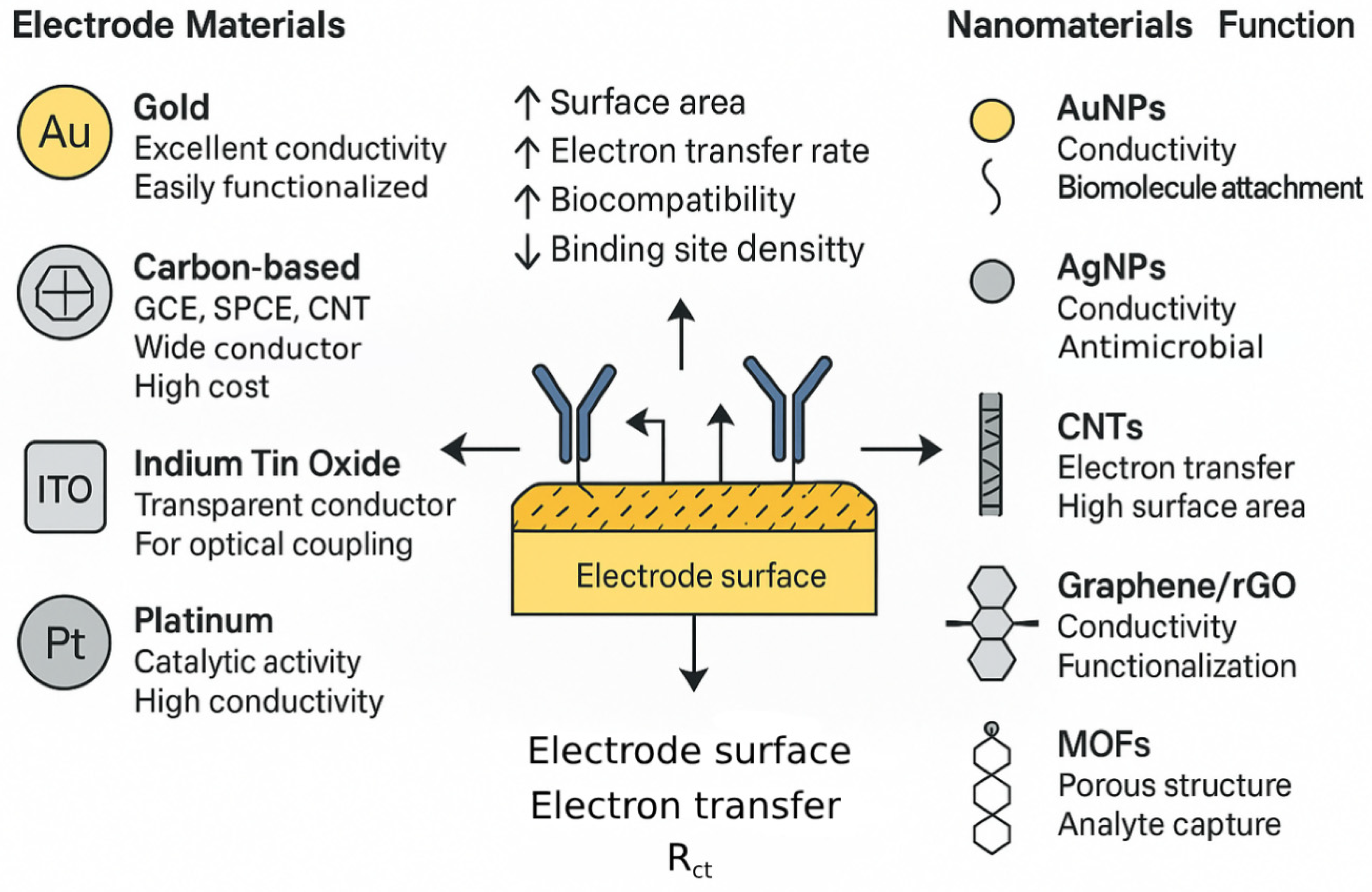





| Attribute | Faradaic EIS | Non-Faradaic (Capacitive) EIS | Implications for Pathogen Biosensors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Signal origin | Change in charge-transfer resistance (ΔRct) caused by hindered electron exchange between electrode and freely diffusing redox probe | Change in double-layer or interfacial capacitance (ΔCdl) caused by dielectric/charge redistribution at the electrode surface | Offers complementary transduction pathways targeting either electron-transfer or dielectric perturbations. |
| Redox probe requirement | Mandatory (e.g., [Fe(CN)6]3−/4−, [Ru(NH3)6]3+/2+) | Not required | Eliminating the probe simplifies reagent handling and avoids probe–matrix interactions. |
| Typical sensitivity (ΔRct or ΔCdl) | Often one to two orders of magnitude larger owing to exponential dependence of Rct on interfacial blockage | Moderate; signal amplitude can be enhanced by nanostructuring or high-κ dielectrics | Faradaic favors ultralow-abundance targets; non-Faradaic can match sensitivity when high-area nanointerfaces are used. |
| Limit of detection (typical) | 100–102 CFU mL−1 or sub-pg mL−1 proteins in optimized systems | 101–103 CFU mL−1 or low-ng mL−1 proteins (can reach fg mL−1 with nano-amplification) | Choice driven by application-specific LOD requirements |
| Matrix tolerance | Probe diffusion can be hampered by viscous or high-ionic-strength samples; colored matrices may foul electrode | Less affected by bulk diffusion; still sensitive to ionic strength via Debye screening | Non-Faradaic often preferred for turbid food or whole-blood samples |
| Electrode configuration | Requires stable reference electrode and three-electrode set-up | Two-electrode layouts feasible; reference optional | Non-Faradaic is more amenable to fully printed or disposable chips. |
| Miniaturization/POC potential | Additional fluidics to refresh redox probe; higher power for stirring/pumping | Simple passive microfluidics; lower power | Non-Faradaic favored in ultra-compact wearables |
| Susceptibility to surface fouling | High—biofouling blocks electron pathways | Moderate—fouling alters capacitance but may still yield measurable ΔCdl | Surface chemistry (e.g., zwitterionic SAMs) critical in both modes |
| Assay time | Rapid (<5 min) once probe equilibrates | Instantaneous; limited only by binding kinetics | Comparable when identical recognition layers are used |
| Operational stability | Redox species can degrade (photo-oxidation of ferricyanide) | Excellent shelf-life (no chemical mediator) | Non-Faradaic offers longer storage stability |
| Bioreceptor Type | Typical Target(s) | Strengths | Limitations | Recommended Immobilization Chemistry |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibodies | Bacteria, viruses, toxins | Picomolar affinity; long clinical track-record | Expensive; cold-chain transport; Fc-orientation critical | Protein A/G capture, EDC/NHS coupling |
| Aptamers | Bacterial cells, viral RNA, toxins | Chemically stable; low cost; PCR-free synthesis | Moderate KD; nuclease attack in serum | Thiol–Au SAM, carboxylate–EDC/NHS |
| Phages | Whole bacteria | Strain-level specificity; self-amplifying | Large biomolecule; limited to bacteria | Cysteine-tag–Au, physical adsorption |
| Peptides | Bacteria, viruses | Fully synthetic; easy sequence tuning | Lower affinity than antibodies; protease cleavage | Maleimide-thiol, strain-promoted click |
| Lectins | Viral/bacterial glycans | Recognize glycosylation motifs; inexpensive | Moderate affinity; cross-reactivity | EDC/NHS, diazonium grafting |
| Bioreceptor Type | Typical Target(s) | Strengths | Limitations | Recommended Immobilization Chemistry |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) | Small molecules, peptides | Solvent/heat-stable, ultra-cheap | Template leakage; size-limited | Electropolymerization on electrode |
| Cell-imprinted polymers (CIPs) | Whole bacteria, spores | Capture shape & epitope ensemble | Surface roughness may trap debris | Electropolymerization, sol-gel casting |
| Whole-cell layers | Bacteria, yeast | Natural ligand display; synergistic signal | Viability and biofouling issues | Poly-L-lysine electrostatic deposition |
| Lectin-functionalized beads | Viral/bacterial glycans | Magnetic separation + recognition | Limited selectivity spectrum | Carbodiimide coupling to beads |
| Material Type | Key Properties | Role in EIS Biosensor | Examples of Pathogens Detected | Impact on Performance (Typical) | Key References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AuNPs | High conductivity, biocompatibility, ease of functionalization, catalytic activity | Enhance electron transfer, increase surface area for BRE loading, signal amplification, direct pathogen interaction | Bacteria (E. coli, S. aureus), Viruses (Hepatitis A, SARS-CoV-2, HIV), Mtb | Significant improvement in LOD and sensitivity (e.g., 10–100 fold), faster response | [30] |
| AgNPs | High conductivity, antimicrobial properties | Enhance conductivity, signal amplification | Bacteria, general pathogen detection | Improved sensitivity, potential for antimicrobial surfaces | [118] |
| MNPs | Magnetic susceptibility, high surface area | Sample pre-concentration (IMS), separation from matrix, bringing target to sensor surface | Bacteria (Salmonella, E. coli), Viruses | Indirectly improves LOD by concentrating analyte and reducing matrix effects, enables analysis of larger sample volumes | [15] |
| CNTs | High surface area, excellent electrical & thermal conductivity, mechanical strength | Enhance electron transfer, increase BRE loading, create 3D electrode architectures | Bacteria (L. monocytogenes, S. aureus, E. coli), Viruses | Lowered Rct, increased capacitive changes, improved LOD and sensitivity | [119] |
| GO, rGO | Exceptional surface area, high conductivity (graphene), tunable surface chemistry | Enhance electron transfer, platform for BRE immobilization, increase active sites | Bacteria (S. aureus), Viruses (Hepatitis A DNA, SARS-CoV-2), Mtb DNA | Dramatically improved sensitivity and LOD (often orders of magnitude), faster kinetics | [120] |
| QDs | Unique electronic properties, photoluminescence (less relevant for direct EIS) | Can modify electrode conductivity, act as redox mediators or labels in hybrid systems | Viruses (HIV) | Can contribute to signal amplification or unique transduction pathways | [1] |
| MOFs & Derivatives | High porosity, tunable pore size, large surface area, catalytic sites (MOF-derived carbons: enhanced conductivity) | BRE encapsulation, analyte pre-concentration, catalytic signal enhancement, conductive support | Viruses (HBV DNA) | Improved stability of BREs, enhanced sensitivity due to pre-concentration or catalysis, better conductivity with derivatives | [121] |
| Conductive Polymers | Intrinsic conductivity, biocompatibility, ease of deposition, porous structure | BRE immobilization matrix, enhance charge transfer, signal amplification, reduce electrode impedance | Bacteria (E. coli), Viruses (Influenza A H1N1) | Lowered impedance, enhanced signal changes, improved sensor stability | [122] |
| MXenes | Large surface area, high electrical conductivity, ease of functionalization | Electrode material, BRE immobilization platform | Mtb (biomarkers) | Potential for high sensitivity and rapid detection | [123] |
| 2D TMDs | Unique electronic properties, layer-dependent bandgap | Sensing layer for DNA hybridization | Bacteria (E. coli DNA) | Ultrasensitive detection, potential for specific electronic interactions | [124] |
| Pathogen Type | Target Pathogen (Specific) | Biorecognition Element (BRE) | Electrode Material/Modification | Key EIS Parameter Monitored | Limit of Detection (LOD) | Linear/Dynamic Range | Response/Assay Time | Sample Matrix Tested | Redox Probe Used (if Any) | Key Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | E. coli O157:H7 | Anti-E. coli Abs | TaSi2 electrodes | Rct | 10 CFU/mL | 101–105 CFU/mL | <1 h | Drinking water | Not specified | [146] |
| E. coli | Cell-Imprinted Polymer (CIP) | Stainless steel microwires | Rct | 2 × 102 CFU/mL | 102–107 CFU/mL | 30 min incubation | Buffer | Not specified | [158] | |
| Salmonella Typhimurium | Anti-Salmonella Abs | PCB IDEs, Magnetic Nanobeads (IMS) | Impedance change | 50 CFU/mL | 1.8 × 103–1.8 × 106 CFU/mL | 60 min | Buffer, Milk | Not specified | [15] | |
| Listeria monocytogenes | Anti-Listeria mAb | Au electrode | Rct | 4 CFU/mL | Not specified | Not specified | Filtered tomato extract | Not specified | [75] | |
| Listeria monocytogenes | P100 Bacteriophage | Quaternized PEI-modified CNTs on electrode | Rct | 8.4 CFU/mL | 10–105 CFU/mL | <1 h | Buffer, Milk | [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− | [119] | |
| Staphylococcus aureus | Aptamer | rGO-ssDNA-AuNPs composite | Impedance | 10 CFU/mL | Not specified | Not specified | Buffer | Not specified | [144] | |
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis (CFP10:ESAT6 protein) | Anti-CFP10 mAb | APTES/ITO electrode | Rct | 4.80 ng/mL | 0.5–50 ng/mL | 4 h | Buffer | None (label-free) | [144] | |
| Campylobacter jejuni NCTC 11168 | FlaGrab phage protein | MWCNT-GCE, PBSE linker | Rct | 102 CFU/mL (ex vivo) | 102 Rct–109 CFU/mL (ex vivo) | ~30 min incubation | Chicken cecal samples | [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− | [80] | |
| Viruses | Influenza A (M1 protein) | Anti-M1 Abs | Au electrode, HDT, GCPs | Rct | 20 pg/mL (~80–100 viruses/µL) | Not specified | 30 min detection | Throat swabs (simulated) | [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− | [76] |
| Influenza A | Antibody | Hydrogel on IDEs | Impedance | 0.5 µg/mL (sensitivity 695 Ω·mL/µg) | 0.5–50 µg/mL | Not specified | Airborne particles (simulated) | Not specified | [133] | |
| HIV-1 DNA | DNA probe | Bi2Se3 tape electrode, AuNPs | Rct/DPV signal | 50 amol/L | 0.1 fmol/L–1 pmol/L | Not specified | Buffer | [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− | [159] | |
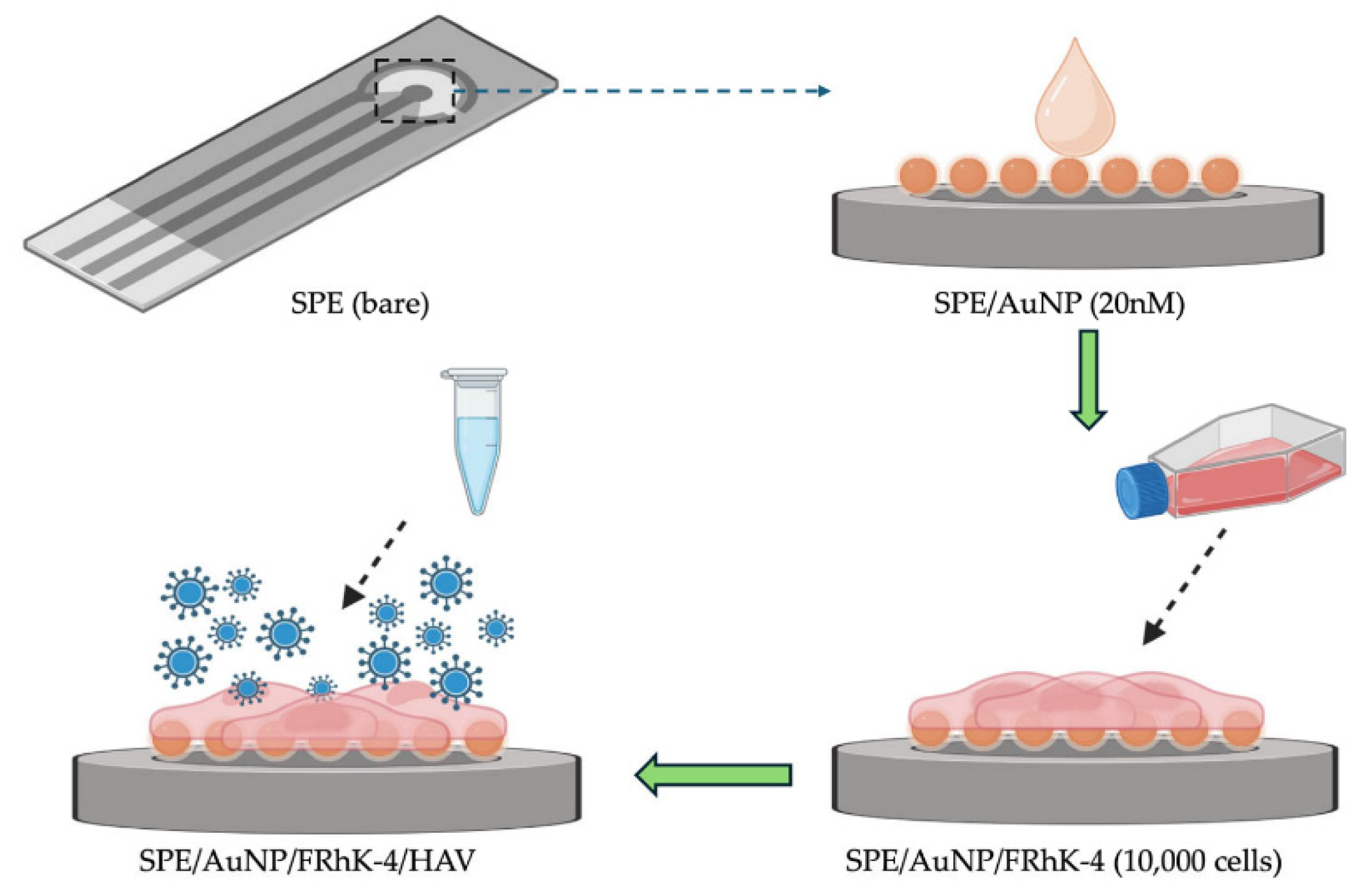
| Hepatitis A Virus (infectious) | FRhK-4 cells | AuNP-modified SPE | Rct | ~5 TCID50mL | 6-log range | 6 h incubation | Cell culture medium | [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− | [148] | |
| SARS-CoV-2 (N-protein) | Biotinylated anti-N-protein Ab | SA-BSA/MPA/AuNS/SPCEs | Rct | 6 pg/mL | 0.01–100 ng/mL | <30 min | Saliva (PBS-diluted) | [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− | [30] | |
| SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD) | Thiol-modified Aptamer | Au electrode | Rct | 132 ng/mL | 175 ng/mL–5 µg/mL | 2 h prep, fast detection | PBS buffer | [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− | [79] | |
| Fungi/Parasites | Sclerotinia sclerotiorum spores | Dielectrophoresis (DEP) capture | Aluminum nanoelectrodes in microfluidic device | Impedance | Single spore detection | Not specified | ~20 s measurement | Air (simulated) | Not specified | [153] |
| Plasmodium falciparum DNA | Thiol-modified DNA probe | Micro-Au electrodes (µAuEs) | Rct | 18.7 aM | Attomolar range | < 30 min | Purified gDNA, whole blood lysates | [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− | [155] | |
| Cryptosporidium oocysts | Anti-Cryptosporidium Abs | Protein G/Thiol SAM on microfabricated Au electrode (on-chip) | Rct | ~20 oocysts/5 µL (4 oocysts/µL) | 10–1000 oocysts/5 µL | 20 min incubation | Water samples | [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− | [141] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Sun, Z.; Sun, K.; Liu, Q.; Chu, W.; Fu, L.; Dai, D.; Liang, Z.; Lin, C.-T. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy-Based Biosensors for Label-Free Detection of Pathogens. Biosensors 2025, 15, 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070443
Zhang H, Sun Z, Sun K, Liu Q, Chu W, Fu L, Dai D, Liang Z, Lin C-T. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy-Based Biosensors for Label-Free Detection of Pathogens. Biosensors. 2025; 15(7):443. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070443
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Huaiwei, Zhuang Sun, Kaiqiang Sun, Quanwang Liu, Wubo Chu, Li Fu, Dan Dai, Zhiqiang Liang, and Cheng-Te Lin. 2025. "Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy-Based Biosensors for Label-Free Detection of Pathogens" Biosensors 15, no. 7: 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070443
APA StyleZhang, H., Sun, Z., Sun, K., Liu, Q., Chu, W., Fu, L., Dai, D., Liang, Z., & Lin, C.-T. (2025). Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy-Based Biosensors for Label-Free Detection of Pathogens. Biosensors, 15(7), 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070443







