Novel Device for Intraoperative Quantitative Measurements of Extraocular Muscle Tensile Strength
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
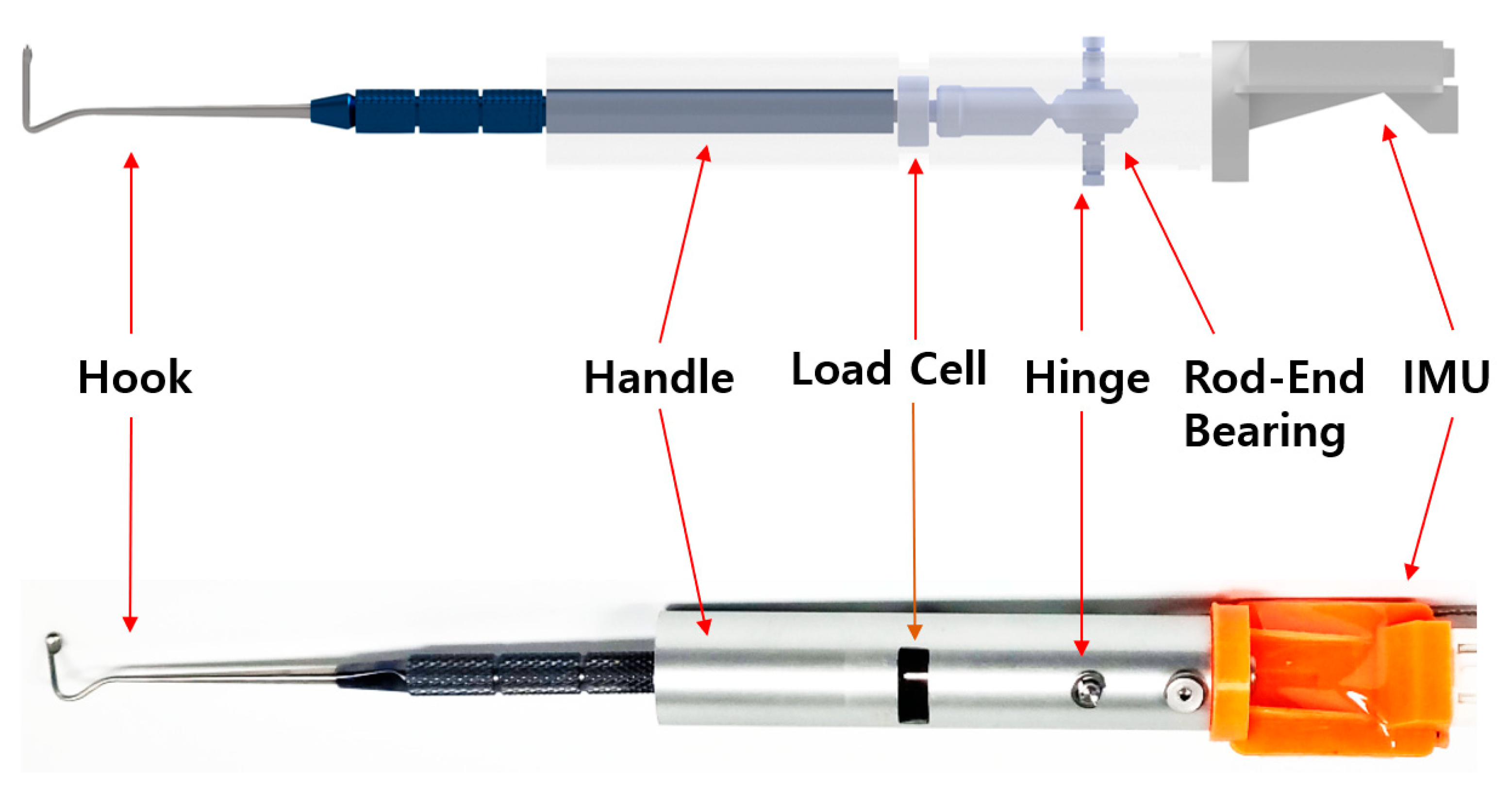
2.1. Design of the EOM Tensile-Strength Measuring Device
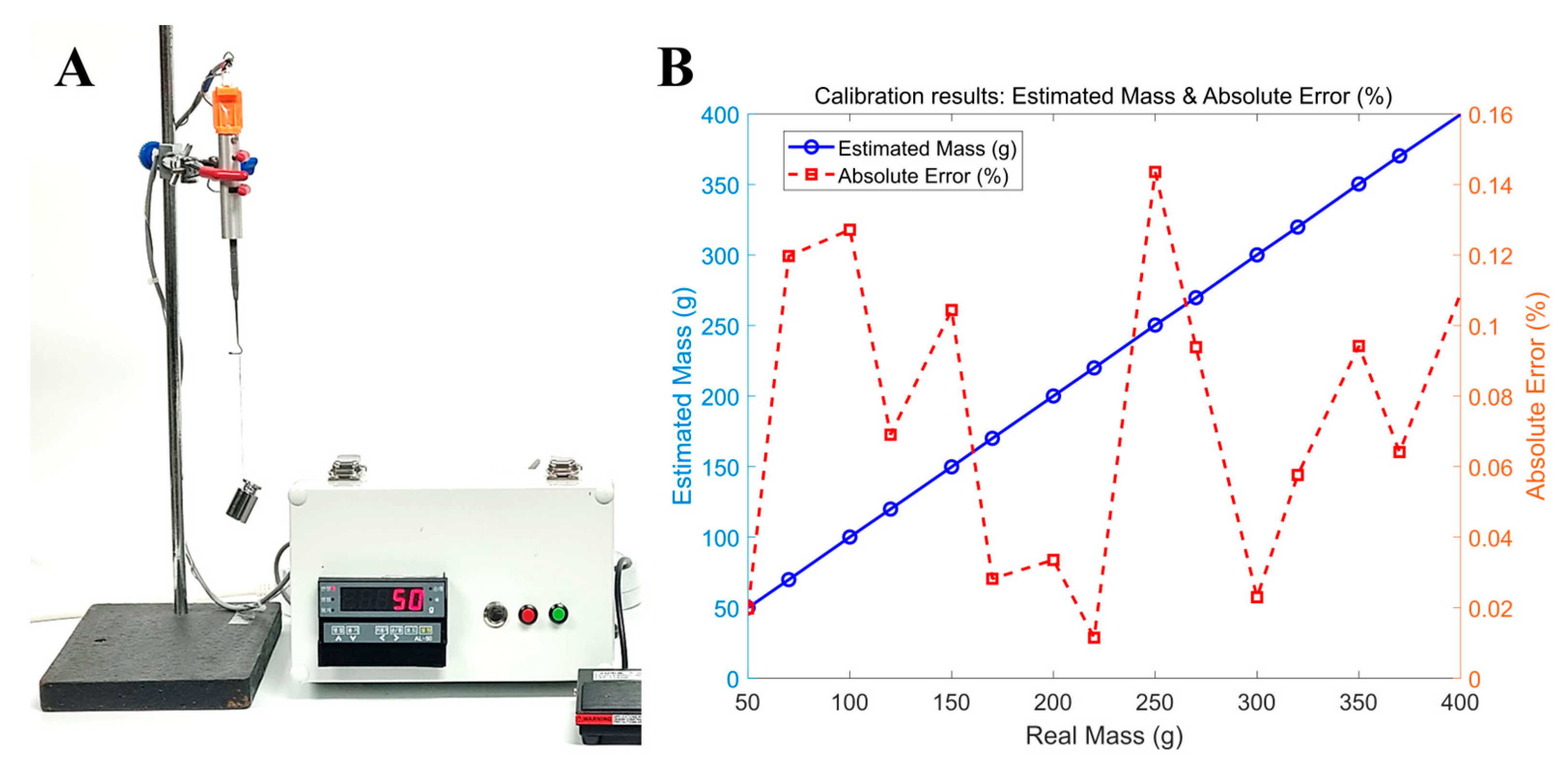
2.2. Calibration of the EOM TSMD
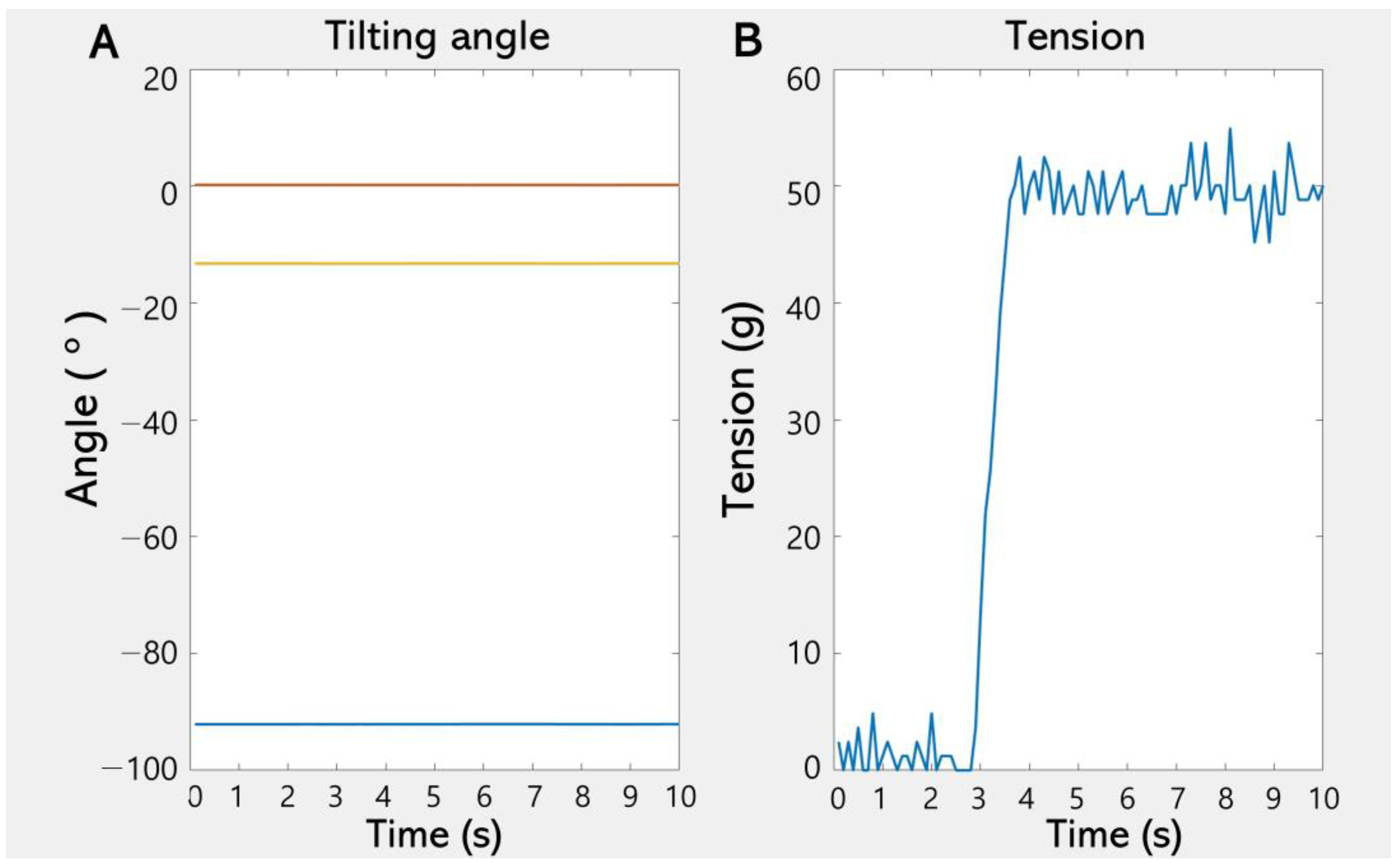
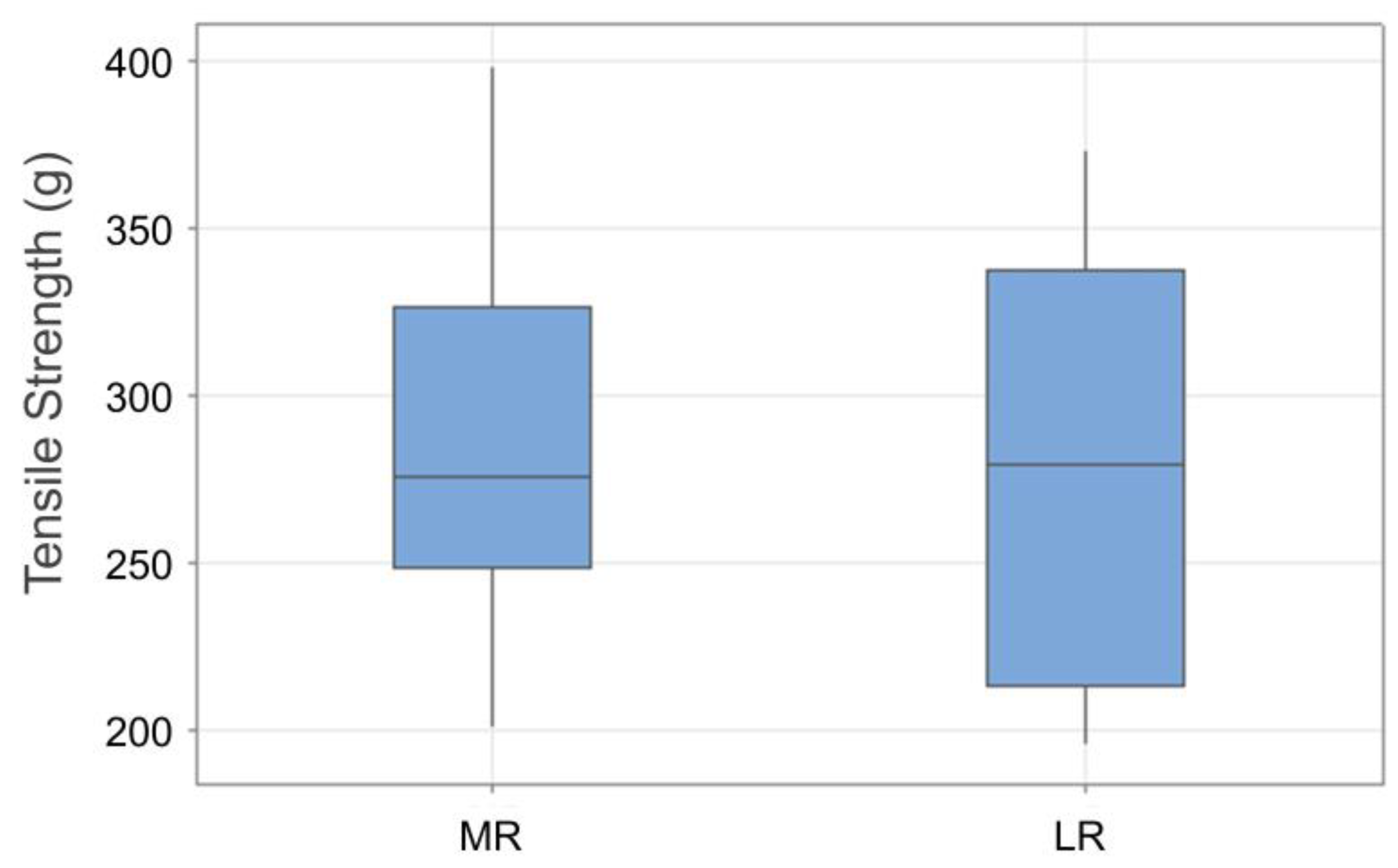
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spiegel, D.P.; Baldwin, A.S.; Hess, R.F. The Relationship Between Fusion, Suppression, and Diplopia in Normal and Amblyopic Vision. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 5810–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, R.F.; Thompson, B. Amblyopia and the binocular approach to its therapy. Vis. Res. 2015, 114, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, S.P.; Antunes-Foschini, R.S.; McLoon, L.K. Effects of recession versus tenotomy surgery without recession in adult rabbit extraocular muscle. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 5646–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Lee, S.H.; Shin, H.J.; Lee, A.G. New instrument for quantitative measurements of passive duction forces and its clinical implications. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2020, 258, 2841–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwashige, H.; Ishida, T.; Koike, N.; Kubota, N. Measurements of active and passive force of horizontal muscles in strabismus. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 1988, 32, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.J.; Lee, S.J.; Oh, C.S.; Kang, H. Novel compact device for clinically measuring extraocular muscle (EOM) tension. J. Biomech. 2020, 109, 109955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hinnawi, M.F.; Barbenel, J.; Al-Qurainy, I.A.; Dutton, G.N. Quantitative mechanical assessment of the extraocular muscles. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 1991, 205, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushner, B.J.; Vrabec, M. Theoretical effects of surgery on length tension relationships in extraocular muscles. J. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus 1987, 24, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szucs-Farkas, Z.; Toth, J.; Balazs, E.; Galuska, L.; Burman, K.D.; Karanyi, Z.; Leovey, A.; Nagy, E.V. Using morphologic parameters of extraocular muscles for diagnosis and follow-up of Graves’ ophthalmopathy: Diameters, areas, or volumes? Am. J. Roentgenol. 2002, 179, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.R.; Mirmohammadsadeghi, A.; Mahmoudzadeh, R.; Veisi, A. Management of Thyroid Eye Disease-Related Strabismus. J. Curr. Ophthalmol. 2020, 23, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.; Park, J.; Lu, Y.; Demer, J. Finite element model of ocular adduction with unconstrained globe translation. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2024, 23, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keene, K.R.; Notting, I.C.; Verschuuren, J.J.G.M.; Voermans, N.C.; de Keizer, R.O.B.; Beenakker, J.-W.M.; Tannemaat, M.R.; Kan, H.E. Eye Muscle MRI in Myasthenia Gravis and Other Neuromuscular Disorders. J. Neuromuscular Dis. 2023, 10, 869–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, G.; Matysik-Woźniak, A.; Pankowska, A.; Pietura, R.; Rejdak, R.; Jonak, K. High Myopia and Thickness of Extraocular and Masticatory Muscles—7T MRI, Preliminary Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettori, S.L.M.; Fasel, L.; Gerig, N.; Rauter, G. Force Feedback Reduces Test Time and Interaction Forces in Telemanipulated Palpation Using a Robotic Endoscope with Series Elastic Actuated Joints. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 10, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Luan, N.; Zhu, X.; Cao, Q. Implementation of 7-DOF External Force/Torque Feedback for Master-Slave Surgical Robot System. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation (ICICTA), Xi’an, China, 24–25 October 2020; pp. 649–655. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, H.J.; Kim, S.; Kang, H.; Lee, A.G. Novel Instrument for Clinical Evaluations of Active Extraocular Muscle Tension. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Shin, H.J.; Lee, A.G. Risk of consecutive esotropia after surgery for intermittent exotropia according to passive duction force. PLoS ONE 2023, 16, e0281392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Lee, S.H.; Oh, C.S.; Shin, H.J.; Lee, A.G. Quantitative measurement of passive duction force tension in intermittent exotropia and its clinical implications. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2021, 259, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.C.; Carlson, M.R.; Scott, A.B.; Jampolsky, A. Extraocular muscle forces in normal human subjects. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1981, 20, 652–664. [Google Scholar]
- Lennerstrand, G.; Schiavi, C.; Tian, S.; Benassi, M.; Campos, E.C. Isometric force measured in human horizontal eye muscles attached to or detached from the globe. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2006, 244, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Yang, H.K.; Hwang, J.M. Surgical outcomes of unilateral recession and resection in intermittent exotropia according to forced duction test results. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasoglu, O.E.; Sener, E.C.; Sanac, A.S. Factors influencing the successful outcome and response in strabismus surgery. Eye 1996, 10, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leffler, C.T.; Woock, A.; Shinbashi, M.; Suggs, M. Variation between surgeons in reoperation rates following vertical strabismus surgery: Associations with patient and surgeon characteristics and adjustable sutures. PLoS ONE 2024, 7, e0310371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, C.C.; O’Meara, D.; Scott, A.B. Muscle tension during unrestrained human eye movements. J. Physiol. 1975, 245, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, T.; Yasumura, K.; Mikami, T.; Maegawa, J. Use of a dial tension gauge to assess quantitatively the intraoperative improvement of ocular movement after endoscopic transantral repair of fracture of the orbital floor. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 51, e135–e136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennerstrand, G.; Bolzani, R.; Benassi, M.; Tian, S.; Schiavi, C. Isometric force development in human horizontal eye muscles and pulleys during saccadic eye movements. Acta Ophthalmol. 2009, 87, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.C.; Jampolsky, A.; Alden, A.B.; Clarke, M.D.; Chung, S.T.; Clark, S.V. Length-tension recording system for strabismus surgery. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1991, 38, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Lin, R.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M.; Luo, Z.; Wang, K.; Tu, J.; Xu, Y.; Fan, Z.; et al. Implantable wireless suture sensor for in situ tendon and ligament strain monitoring. Sci Adv. 2025, 11, eadt3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, S.; Chen, H. Expanding the potential of biosensors: A review on organic field effect transistor (OFET) and organic electrochemical transistor (OECT) biosensors. Mater. Futures 2023, 2, 042401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Yuan, A.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, X.; Qiao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liang, J.; Wang, S.; Duan, Z.; Wu, Y.; et al. Ultrafast Hydrogen Detection System Using Vertical Thermal Conduction Structure and Neural Network Prediction Algorithm Based on Sensor Response Process. ACS Sens. 2025, 10, 2181–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, H.J.; Park, M.; Kang, H.; Lee, A.G. Novel Device for Intraoperative Quantitative Measurements of Extraocular Muscle Tensile Strength. Biosensors 2025, 15, 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15060347
Shin HJ, Park M, Kang H, Lee AG. Novel Device for Intraoperative Quantitative Measurements of Extraocular Muscle Tensile Strength. Biosensors. 2025; 15(6):347. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15060347
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Hyun Jin, Minung Park, Hyunkyoo Kang, and Andrew G. Lee. 2025. "Novel Device for Intraoperative Quantitative Measurements of Extraocular Muscle Tensile Strength" Biosensors 15, no. 6: 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15060347
APA StyleShin, H. J., Park, M., Kang, H., & Lee, A. G. (2025). Novel Device for Intraoperative Quantitative Measurements of Extraocular Muscle Tensile Strength. Biosensors, 15(6), 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15060347






