A Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Immunosensor for Cortisol Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Instruments
2.1. Chemical Materials and Instruments
2.2. G-PANI Ink Synthesis and Fabrication of Anti-Cortisol Antibody-Based Immunosensors
2.3. Immobilization of Antibody upon the Working Electrode’s Surface
2.4. Electrochemical Measurement of Cortisol
3. Results and Discussion
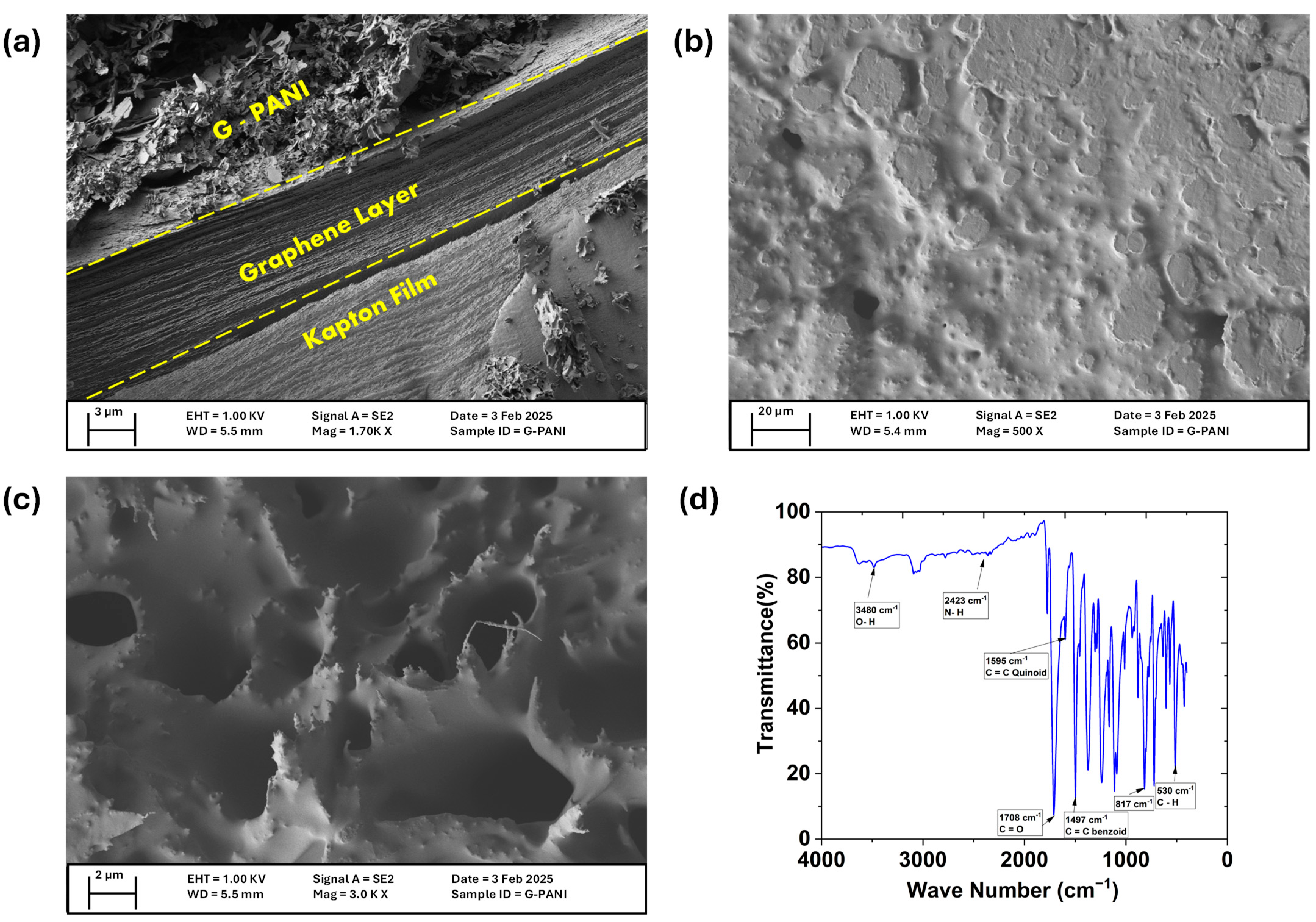
3.1. Characterization of the Prepared LIG/G-PANI Electrode
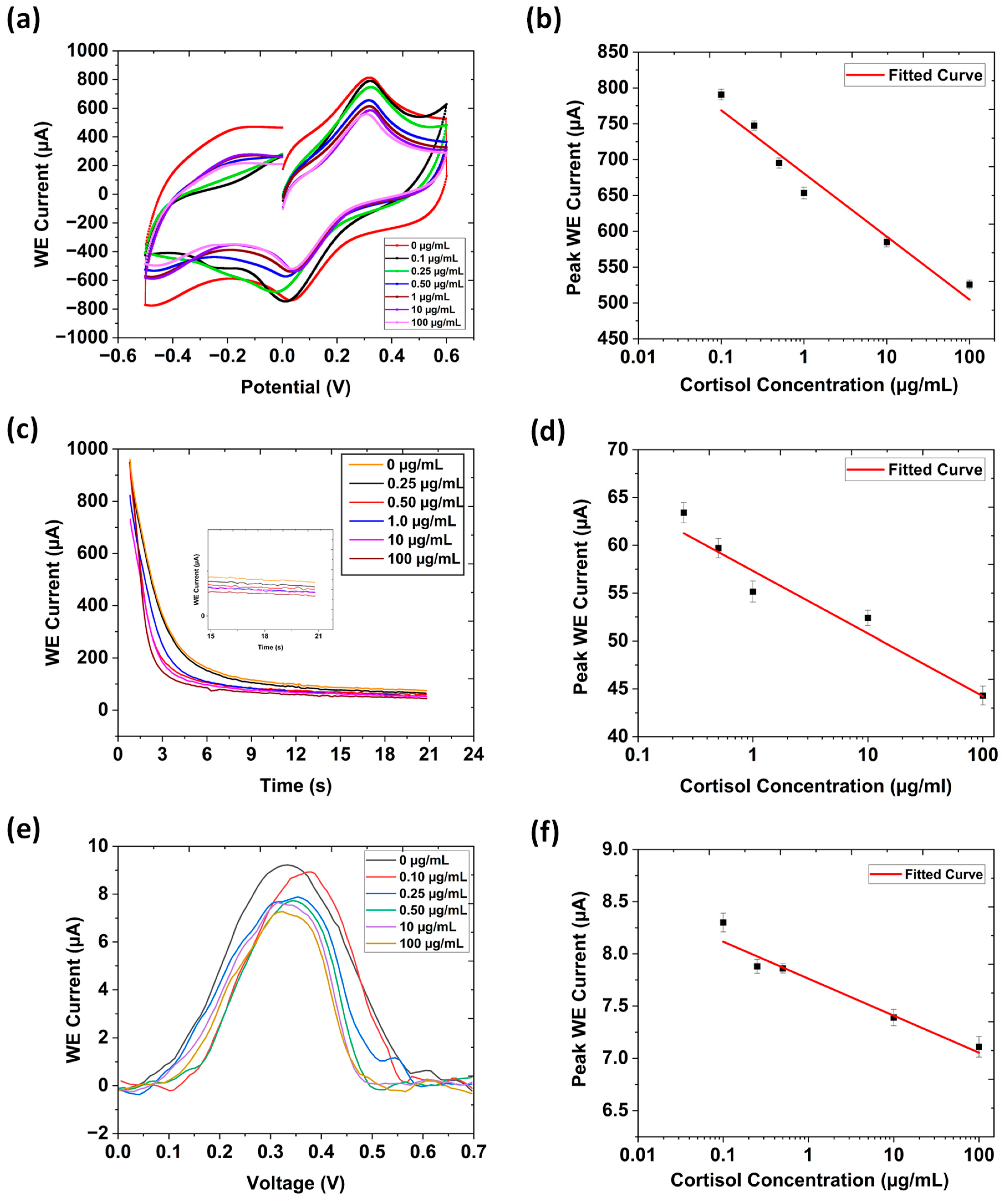
3.2. Cyclic Voltammetry
3.3. Chronoamperometry
3.4. Differential Pulse Voltammetry
3.5. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS)
| Electrode | Technique | Linear Range | Limit of Detection (LOD) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IrOx modified reference electrode/Au | EIS | 1 ng/mL to 1 mg/mL | 11.85 pg/mL | [37] |
| Inject-printed Au | EIS | 5–20 ng/mL | 1.18 ng/mL | [38] |
| Au single-atom nanozymes | Square wave voltammetry (SWV) | 0.15–300 (ng mL−1) | 0.48 pg mL−1 | [39] |
| Sulfur-doped graphene/gold nanoparticles/screen-printed electrode | Linear sweep voltammetry | 35.24–18,123 (ng mL−1) | 15.39 ng mL−1 | [40] |
| Ni-SPE | CV | 0.25−25.0 μM | 74.0 nM | [41] |
| Modified interdigitated gear-shaped working electrode design (LIG/G-PANI) | CV | 0.1–100 μg/mL | 0.0813 μg/mL | Current research |
| Modified interdigitated gear-shaped working electrode design (LIG/G-PANI) | EIS | 0.1–100 μg/mL | 0.0577 μg/mL | Current research |
| Modified interdigitated gear-shaped working electrode design (LIG/G-PANI) | Chrono-amperometry | 0.25–100 μg/mL | 0.105 μg/mL | Current research |
3.6. Cortisol Detection in Human Serum
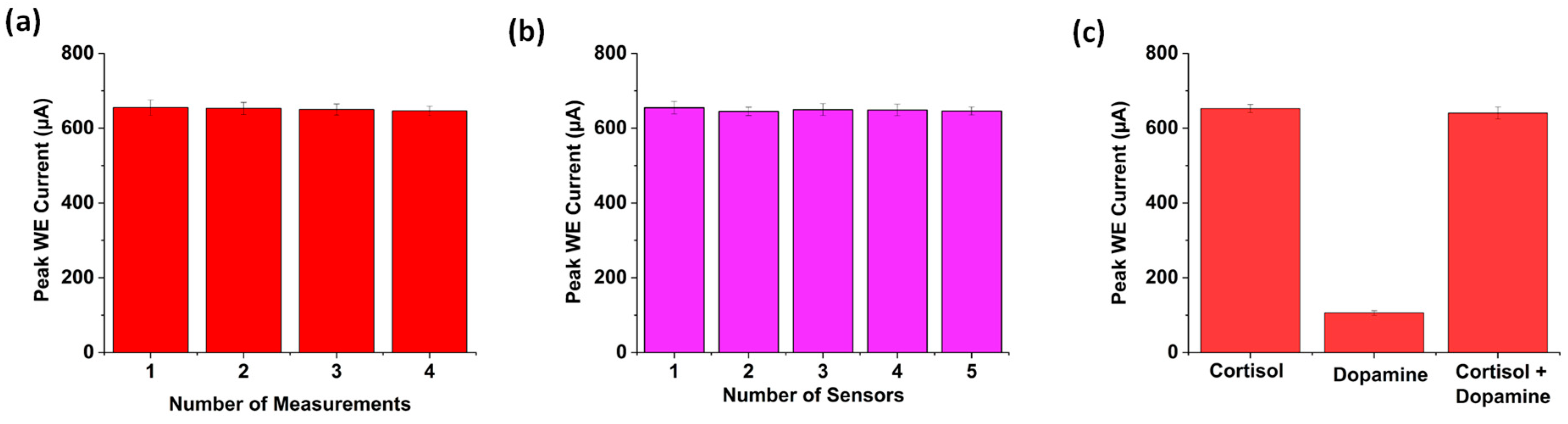
3.7. Repeatability, Reproducibility, and Selectivity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zamkah, A.; Hui, T.; Andrews, S.; Dey, N.; Shi, F.; Sherratt, R.S. Identification of Suitable Biomarkers for Stress and Emotion Detection for Future Personal Affective Wearable Sensors. Biosensors 2020, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, M. The stress of life: A modern complaint? Lancet 2014, 383, 300–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukuda, M.; Nishiyama, Y.; Kawai, S.; Okumura, Y. Identifying stress markers in skin gases by analysing gas collected from subjects undergoing the Trier social stress test and performing statistical analysis. J. Breath Res. 2019, 13, 036003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stress in America 2022: Concerned for the Future, Beset by Inflation. Available online: https://www.apa.org/news/press/releases/stress/2022/concerned-future-inflation (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Team, S. Stress Statistics: How Many People are Affected in the U.S.? Available online: https://www.singlecare.com/blog/news/stress-statistics/ (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- American Adults Express Increasing Anxiousness in Annual Poll; Stress and Sleep are Key Factors Imp. Available online: https://www.psychiatry.org:443/news-room/news-releases/annual-poll-adults-express-increasing-anxiousness (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Steckl, A.J.; Ray, P. Stress Biomarkers in Biological Fluids and Their Point-of-Use Detection. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 2025–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasamy, S.; Atchudan, R.; Arya, S.; Gunasekaran, B.M.; Nesakumar, N.; Sundramoorthy, A.K. Cortisol: Biosensing and detection strategies. Clin. Chim. Acta 2024, 562, 119888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, A.N.; Guldin, S.; Ghoreishizadeh, S.S. Electrochemical Sensors for Cortisol: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 5746–5758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wankhade, U.A.; Thakare, Y.N.; Hardas, B.M.; Pande, R.S. Cortisol Detection Methods for Stress Monitoring: Current Insight and Future Prospect: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 23389–23400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trusso Sfrazzetto, G.; Santonocito, R. Nanomaterials for Cortisol Sensing. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.J.; Clay, O.M.; Lycan, R.E.; Anderson, G.K.; Simoska, O. Advances in electrochemical biosensor design for the detection of the stress biomarker cortisol. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, F.; Zahraee, H.; Izadpanah Kazemi, M.; Habibi, Z.S.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Abnous, K.; Khoshbin, Z.; Chen, C.-H. Recent advances in aptamer-based platforms for cortisol hormone monitoring. Talanta 2024, 266, 125010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, R.C.; Soelberg, S.D.; Near, S.; Furlong, C.E. Detection of Cortisol in Saliva with a Flow-Filtered, Portable Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor System. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 6747–6751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frasconi, M.; Mazzarino, M.; Botrè, F.; Mazzei, F. Surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for cortisol and cortisone determination. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 2151–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Xie, Q.; Jin, J.; Qiao, T.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Lu, Z. HPLC-FLU detection of cortisol distribution in human hair. Clin. Biochem. 2010, 43, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Palo, E.F.; Antonelli, G.; Benetazzo, A.; Prearo, M.; Gatti, R. Human saliva cortisone and cortisol simultaneous analysis using reverse phase HPLC technique. Clin. Chim. Acta 2009, 405, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaneva, M.; Kirilov, G.; Zacharieva, S. Midnight salivary cortisol, measured by highly sensitive electrochemiluminescence immunoassay, for the diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome. Open Med. 2009, 4, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.T.; Jin, E.; Lee, M.-H. Portable Chemiluminescence-Based Lateral Flow Assay Platform for the Detection of Cortisol in Human Serum. Biosensors 2021, 11, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, G.M.M.; Garza, D.; Chavez, E.; Jalal, A.H.; Alam, F.; Hossain, G.M.M.; Garza, D.; Chavez, E.; Jalal, A.H.; Alam, F. ZnO Nanowires for Biosensing Applications. In Carbon Nanotubes—Recent Advances, Perspectives and Applications; IntechOpen: London. UK, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, F.; Ashfaq Ahmed, M.; Jalal, A.; Siddiquee, I.; Adury, R.; Hossain, G.; Pala, N. Recent Progress and Challenges of Implantable Biodegradable Biosensors. Micromachines 2024, 15, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, G.M.M.; Jalal, A.H.; Pala, N.; Alam, F. Advancements in Glucose Monitoring: A Thin Film ZnO-Nanoflakes Based Highly Sensitive Wearable Biosensor for Noninvasive Sweat-Based Point-of-Care Monitoring for Diabetes. ECS Trans. 2024, 113, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Peng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ruiz-Zepeda, F.; Ye, R.; Samuel, E.L.G.; Yacaman, M.J.; Yakobson, B.I.; Tour, J.M. Laser-induced porous graphene films from commercial polymers. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, T.; Silvestre, S.; Coelho, J.; Marques, A.C.; Martins, R.; Sales, M.G.F.; Fortunato, E. Laser-Induced Graphene on Paper toward Efficient Fabrication of Flexible, Planar Electrodes for Electrochemical Sensing. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2101502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D. [PDF] from utrgv.edu Graphene-conductive polymer-based electrochemical sensor for dopamine detection. In Proceedings of the International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Columbus, OH, USA, 30 October–3 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tabassum, R. Label-Free Laser-Induced Graphene-Based Electrochemical Biosensor Modified with Graphene-Conductive Polymer Ink Coating for Detection of Alpha-Fetoprotein and 17β—Estradiol, The University of Texas Rio Grande Valley. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/docview/3115398615?fromopenview=true&pq-origsite=gscholar&sourcetype=Dissertations%20&%20Theses (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Tabassum, R.; Sarkar, P.P.; Jalal, A.H.; Ashraf, A.; Islam, N. An Optimized Laser-Induced Graphene-Based Electrochemical Biosensor Modified with Graphene-Conductive Ink for Alpha-Fetoprotein Detection. In Proceedings of the ASME 2024 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, American Society of Mechanical Engineers Digital Collection, Portland, OR, USA, 17–21 November 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Tabassum, R.; Sarkar, P.P.; Rahman, M.A.; Jalal, A.H.; Islam, N.; Ashraf, A. Graphene Nanocomposite Ink Coated Laser Transformed Flexible Electrodes for Selective Dopamine Detection and Immunosensing. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7, 3143–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, P.P.; Tabassum, R.; Jalal, A.H.; Ashraf, A.; Islam, N. Interdigitated Gear-Shaped Screen-Printed Electrode Using G-PANI Ink for Sensitive Electrochemical Detection of Dopamine. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2024, 13, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, P.P.; Tabassum, R.; Jalal, A.H.; Ashraf, A.; Islam, N. Selective and Sensitive Determination of Dopamine in a Novel Gear-Shaped Screen-Printed Electrode Modified With G-PANI Ink. In Proceedings of the ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Portland, OR, USA, 17–21 November 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Two, Three, Four Electrode System Gamry 4-Probe Potentiostats Gamry Instruments. Available online: https://www.gamry.com/application-notes/instrumentation/two-three-four-electrode-experiments/ (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Collyer, S.D.; Davis, F.; Lucke, A.; Stirling, C.J.M.; Higson, S.P.J. The electrochemistry of the ferri/ferrocyanide couple at a calix [4]resorcinarenetetrathiol-modified gold electrode as a study of novel electrode modifying coatings for use within electro-analytical sensors. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2003, 549, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhu, S.; Zhou, Z.; Yao, Y.; Quan, W.; Liu, B. Enhanced sensitivity of ammonia sensor using graphene/polyaniline nanocomposite. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 178, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Meng, Q. The structure characteristic and electrochemical performance of graphene/polyaniline composites. Synth. Met. 2013, 170, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhull, N.; Kaur, G.; Gupta, V.; Tomar, M. Highly sensitive and non-invasive electrochemical immunosensor for salivary cortisol detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 293, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, S.; Ghosh, D.; Islam, N. Applications of Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) for Various Electrode Pattern in a Microfluidic Channel with Different Electrolyte Solutions. In Proceedings of the SME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Virtual, 1–5 November 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, T.; Ye, W.; Xiao, W.; Dawson, G.; Dong, Q.; Gwenin, C. Iridium oxide-modified reference screen-printed electrodes for point-of-care portable electrochemical cortisol detection. Talanta 2024, 280, 126776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zea, M.; Ben Halima, H.; Villa, R.; Nemeir, I.A.; Zine, N.; Errachid, A.; Gabriel, G. Salivary Cortisol Detection with a Fully Inkjet-Printed Paper-Based Electrochemical Sensor. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Guo, M.; Chen, Y.; Mo, X.; Cao, J.; Hu, F. Ultrasensitive cortisol electrochemical immunosensor amplifying by Au single-atom nanozymes and HRP enzymes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1303, 342462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umuksuz, H.; Uruc, S.; Dokur, E.; Gorduk, O.; Sahin, Y. Flexible Screen-Printed Electrode for Cortisol Detection Based on Sulfur-Doped Graphene/Gold Nanoparticles Conductive Ink. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2025, 14, 027004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaerd, A.; Watanabe, E.Y.; Belli, C.; Marcolino-Junior, L.H.; Bergamini, M.F. A complete lab-made point of care device for non-immunological electrochemical determination of cortisol levels in salivary samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 332, 129532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, R.; Sarkar, P.P.; Jalal, A.H.; Ashraf, A.; Islam, N. Laser-Induced Electrochemical Biosensor Modified with Graphene-Based Ink for Label-Free Detection of Alpha-Fetoprotein and 17β-Estradiol. Polymers 2024, 16, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadurmus, L.; Kaya, S.I.; Ozcelikay, G.; Gumustas, M.; Uslu, B.; Ozkan, S.A. Validation Requirements in Biosensors. In Biosensors; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]




| Cortisol Concentration | Solution Resistance (Rs) | Charge-Transfer Resistance (Rct) | Constant Phase Element (CPE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 µg/mL | 13.2 Ω | 126.41 Ω | Y0 = 2.33 n℧sN N = 1.29 |
| 0.50 µg/mL | 17.2 Ω | 129.60 Ω | Y0 = 2.63 n℧sN N = 1.34 |
| 1 µg/mL | 17.5 Ω | 130.79 Ω | Y0 = 2.64 n℧sN N = 1.33 |
| 10 µg/mL | 18.6 Ω | 138.85 Ω | Y0 = 2.86 n℧sN N = 1.36 |
| 100 µg/mL | 31.8 Ω | 155.30 Ω | Y0 = 1.56 n℧sN N = 1.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarkar, P.P.; Ashraf, A.; Jalal, A.H.; Alam, F.; Islam, N. A Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Immunosensor for Cortisol Detection. Biosensors 2025, 15, 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050321
Sarkar PP, Ashraf A, Jalal AH, Alam F, Islam N. A Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Immunosensor for Cortisol Detection. Biosensors. 2025; 15(5):321. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050321
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarkar, Pritu Parna, Ali Ashraf, Ahmed Hasnain Jalal, Fahmida Alam, and Nazmul Islam. 2025. "A Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Immunosensor for Cortisol Detection" Biosensors 15, no. 5: 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050321
APA StyleSarkar, P. P., Ashraf, A., Jalal, A. H., Alam, F., & Islam, N. (2025). A Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Immunosensor for Cortisol Detection. Biosensors, 15(5), 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050321








