Aptamer-Based Planar Electric Double-Layer Field-Effect Transistor: A Novel Approach for Sensitive Troponin I Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Surface Functionalization
- 5′-CGTGCAGTACGCCAACCTTTCTCATGCGCTGCCCCTCTTA-3′.
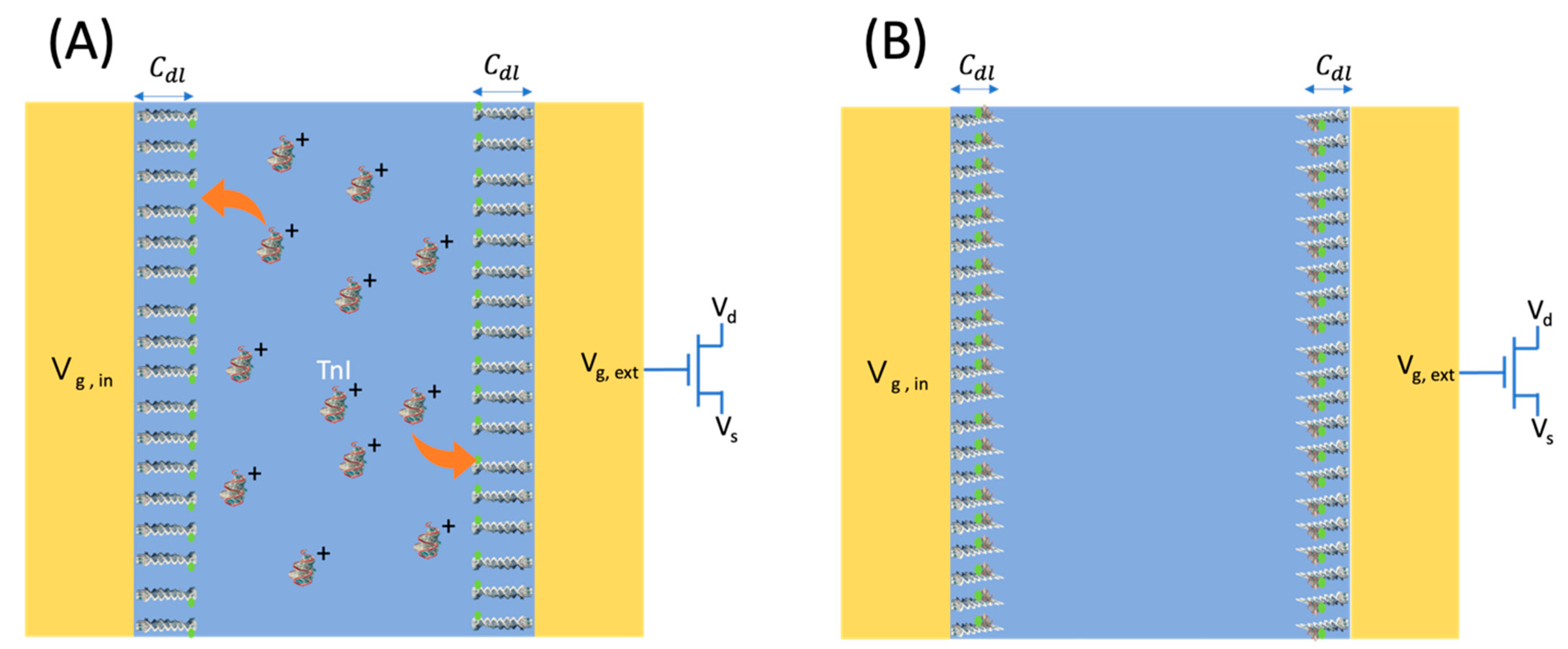
2.3. EDL-Gated BioFET Platform
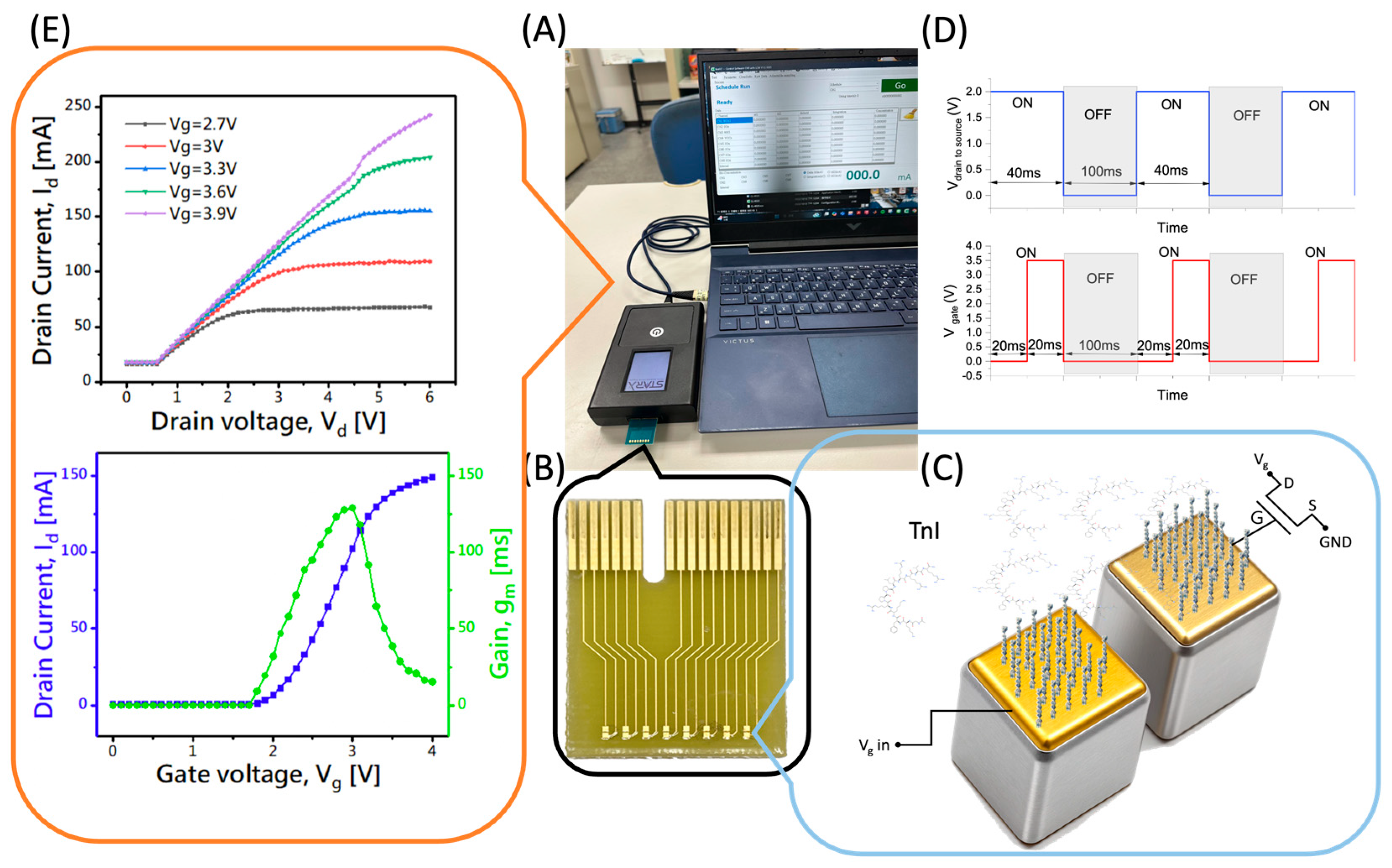
3. Results and Discussion
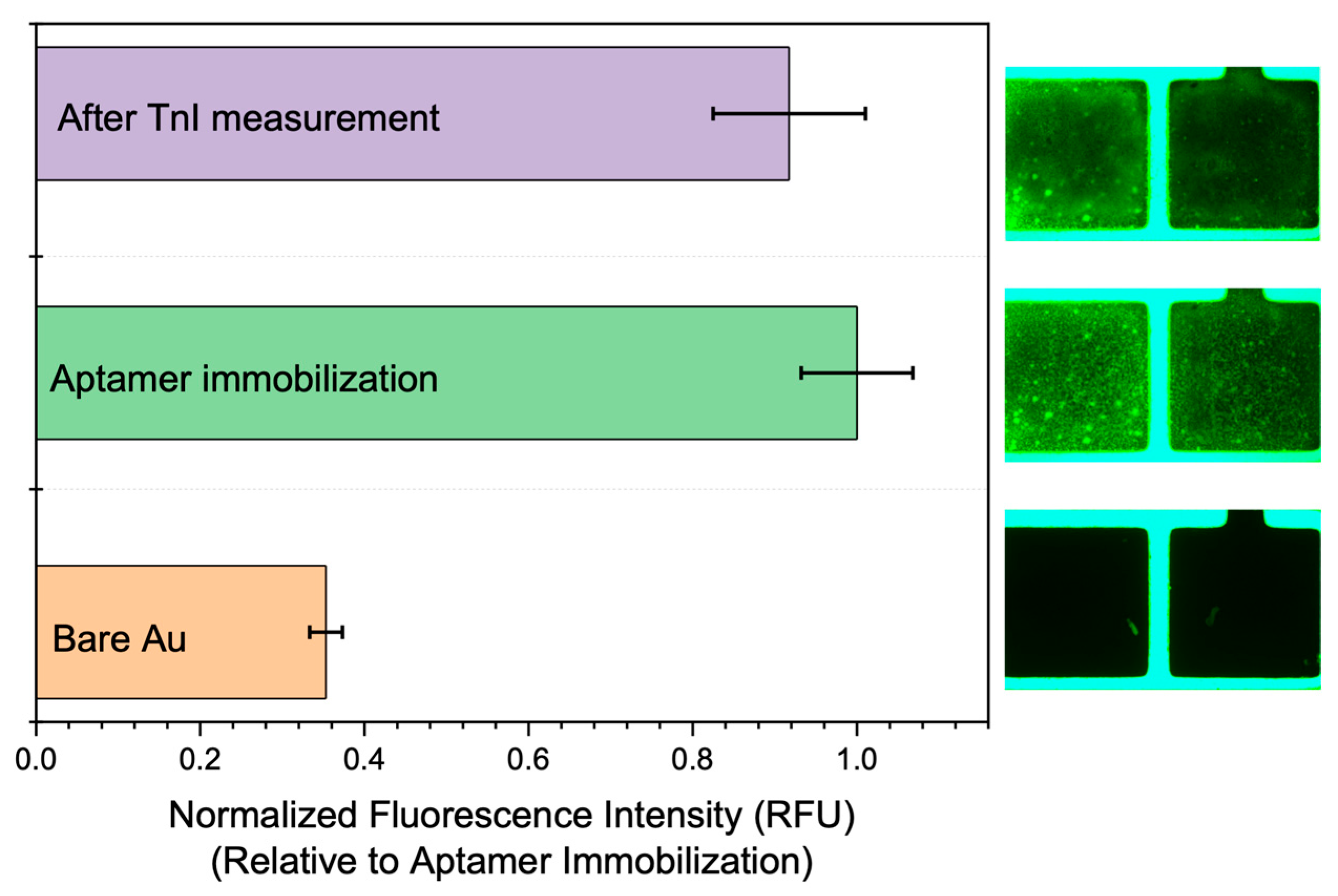
3.1. Immobilization Results
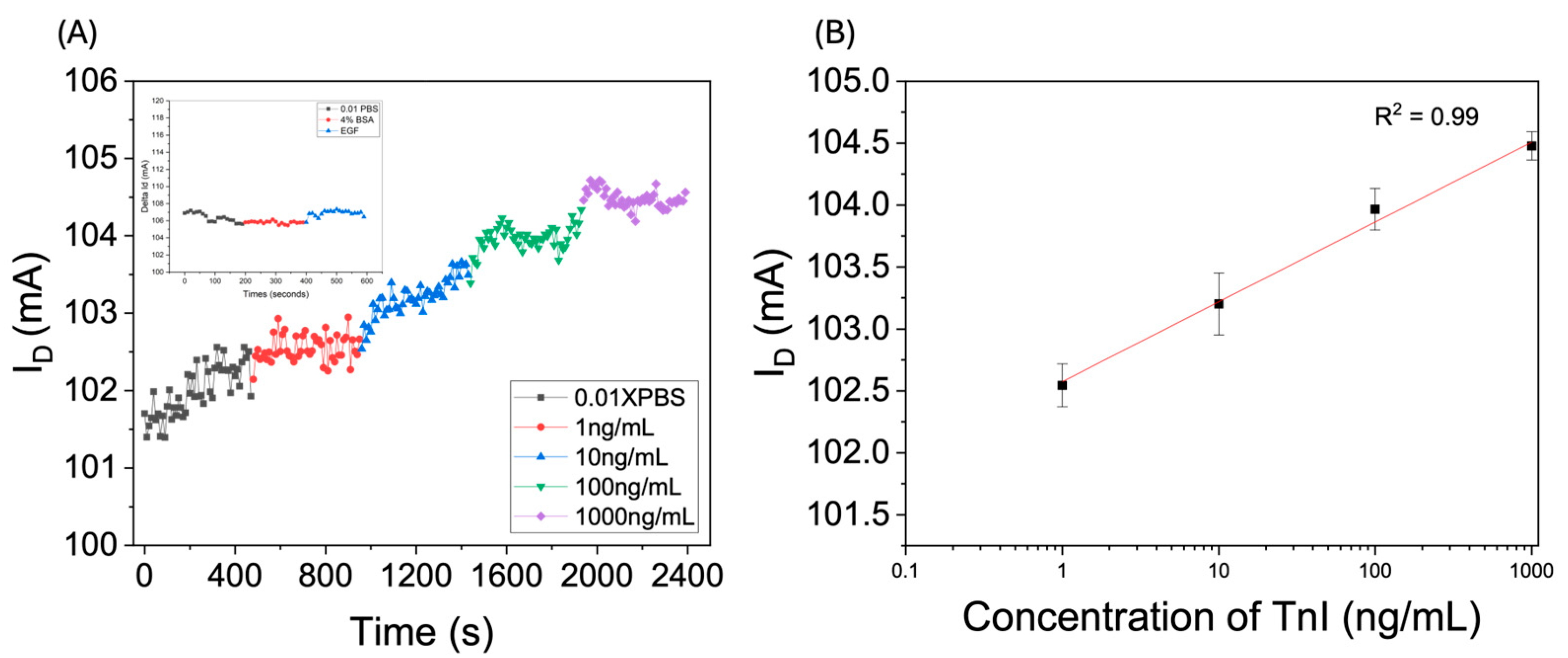
3.2. Measurement
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Severino, P.; D’Amato, A.; Pucci, M.; Infusino, F.; Birtolo, L.I.; Mariani, M.V.; Lavalle, C.; Maestrini, V.; Mancone, M.; Fedele, F. Ischemic Heart Disease and Heart Failure: Role of Coronary Ion Channels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antman, E.M.; Loscalzo, J. Ischemic Heart Disease. In Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine, 20th ed.; Jameson, J.L., Fauci, A.S., Kasper, D.L., Hauser, S.L., Longo, D.L., Loscalzo, J., Eds.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Available online: https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?bookid=2129§ionid=192029847 (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Mendis, S.; Puska, P.; Norrving, B. (Eds.) Global Atlas on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Control; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 3–18. ISBN 978-92-4-156437-3. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10665/44701 (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute. Ischaemic Heart Disease: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment. 2024. Available online: https://www.victorchang.edu.au/heart-disease/ischaemic-heart-disease (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update from the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acute Myocardial Infarction: Symptoms and Treatment. Patient.info. December 2020. Available online: https://patient.info/doctor/acute-myocardial-infarction (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Mechanic, O.J.; Gavin, M.; Grossman, S.A. Acute Myocardial Infarction. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459269/ (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Bruyninckx, R.; Aertgeerts, B.; Bruyninckx, P.; Buntinx, F. Signs and Symptoms in Diagnosing Acute Myocardial Infarction and Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Diagnostic Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2008, 58, e1–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweis, R.N. Acute Myocardial Infarction (MI). MSD Manual Professional Edition. June 2022. Available online: https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/cardiovascular-disorders/coronary-artery-disease/acute-myocardial-infarction-mi (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Sasano, T.; Abraham, M.R.; Chang, K.-C.; Ashikaga, H.; Mills, K.J.; Holt, D.P.; Hilton, J.; Nekolla, S.G.; Dong, J.; Lardo, A.C.; et al. Abnormal Sympathetic Innervation of Viable Myocardium and the Substrate of Ventricular Tachycardia after Myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 2266–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) Test. Better Health Channel. January 2023. Available online: https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/ecg-test (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Aydin, S.; Ugur, K.; Aydin, S.; Sahin, İ.; Yardim, M. Biomarkers in Acute Myocardial Infarction: Current Perspectives. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2019, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.M.O.; Gilbert, R.E. Novel Risk Factors for Heart Failure: When the Whole May Be Greater Than the Sum of Its Parts. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 763–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Pan, N.; An, Y.; Xu, M.; Tan, L.; Zhang, L. Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers for Myocardial Infarction. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 7, 617277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troponin I (Human) ELISA Kit. NET. Available online: https://fnkprddata.blob.core.windows.net/domestic/data/datasheet/ABN/KA0233.pdf (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- Radha, R.; Shahzadi, S.K.; Al-Sayah, M.H. Fluorescent Immunoassays for Detection and Quantification of Cardiac Troponin I: A Short Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Dong, Y.; Meng, H.; Qin, X.; Jiang, Z.; Wei, X. Low-Noise Fluorescent Detection of Cardiac Troponin I in Human Serum Based on Surface Acoustic Wave Separation. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2023, 9, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, S.; Altintas, Z. Development of a Point-of-Care SPR Sensor for the Diagnosis of Acute Myocardial Infarction. Biosensors 2023, 13, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wu, W.; Wang, K.; Han, Z.; Yang, C. Methods for Detecting of Cardiac Troponin I Biomarkers for Myocardial Infarction Using Biosensors: A Narrative Review of Recent Research. J. Thorac. Dis. 2023, 15, 5112–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Lee, J.P.; Shin, W.R.; Oh, I.-H.; Ahn, J.-Y.; Kim, Y.-H. Cardiac Biomarkers and Detection Methods for Myocardial Infarction. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2022, 18, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Fan, C.; Zhao, J. Aptamer-Based Biosensors. Trends Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apple, F.S.; Collinson, P.O. IFCC Task Force on Clinical Applications of Cardiac Biomarkers. Analytical Characteristics of High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin Assays. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowska, I.; Sharma, N.; Vasilescu, A.; Iancu, M.; Badea, G.; Boukherroub, R.; Ogale, S.; Szunerits, S. Electrochemical Aptamer-Based Biosensors for the Detection of Cardiac Biomarkers. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 12010–12018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Chen, L.; Shi, X.; Chen, G.; Sun, D.; Zhang, L. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Aptasensors for Detecting Cardiac Biomarkers: A Review. Microchem. J. 2023, 193, 109063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangadharan, I.; Regmi, A.; Chen, Y.-W.; Hsu, C.-P.; Chen, P.-C.; Chang, W.-H.; Lee, G.-Y.; Chyi, J.-I.; Shiesh, S.-C.; Lee, G.-B.; et al. High Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin I Detection in Physiological Environment Using AlGaN/GaN High Electron Mobility Transistor (HEMT) Biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.-H.; Sarangadharan, I.; Regmi, A.; Chen, Y.-W.; Hsu, C.-P.; Chang, W.-H.; Lee, G.-Y.; Chyi, J.-I.; Chen, C.-C.; Shiesh, S.-C.; et al. Beyond the Debye Length in High Ionic Strength Solution: Direct Protein Detection with Field-Effect Transistors (FETs) in Human Serum. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasamy, M.; Ha, J.W. Single-Particle Spectroelectrochemistry: Promoting the Electrocatalytic Activity of Gold Nanorods via Oxygen Plasma Treatment without Structural Deformation. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejsmont, A.; Kadela, K.; Grzybek, G.; Darvishzad, T.; Slowik, G.; Lofek, M.; Goscianska, J.; Kotarba, A.; Stelmachowski, P. Speciation of Oxygen Functional Groups on the Carbon Support Controls the Electrocatalytic Activity of Cobalt Oxide Nanoparticles in the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 5148–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-T.; Sarangadharan, I.; Sukesan, R.; Hseih, C.-Y.; Lee, G.-Y.; Chyi, J.-I.; Wang, Y.-L. High-Field Modulated Ion-Selective Field-Effect-Transistor (FET) Sensors with Sensitivity Higher than the Ideal Nernst Sensitivity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.; Gu, H.; Jeon, W.; Youn, H.; Her, J.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, J.; Shin, J.H.; Ban, C. Electrochemical Aptasensor of Cardiac Troponin I for the Early Diagnosis of Acute Myocardial Infarction. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9869–9875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komarova, N.; Panova, O.; Titov, A.; Kuznetsov, A. Aptamers Targeting Cardiac Biomarkers as an Analytical Tool for the Diagnostics of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Review. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Li, D.; Su, M.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, F.; Qin, X.; Wang, L.; Gui, Y.; Zhao, J.; Guo, H.; et al. A Label-Free Electrochemical Aptamer Sensor for Sensitive Detection of Cardiac Troponin I Based on AuNPs/PB/PS/GCE. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.H.; Lee, S.K.; Oh, Y.K.; Bae, B.W.; Lee, S.D.; Kim, S.; Shin, Y.B.; Kim, M.-G. A Dual Gold Nanoparticle Conjugate-Based Lateral Flow Assay (LFA) Method for the Analysis of Troponin I. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 1999–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Zou, N.; Zhu, D.; Wang, J.; Jin, Q.; Zhao, J.; Mao, H. Simultaneous Detection of High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin I and Myoglobin by Modified Sandwich Lateral Flow Immunoassay: Proof of Principle. Clin. Chem. 2011, 57, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byzova, N.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Vengerov, Y.Y.; Starovoitova, T.A.; Dzantiev, B.B. A Triple Immunochromatographic Test for Simultaneous Determination of Cardiac Troponin I, Fatty Acid Binding Protein, and C-Reactive Protein Biomarkers. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Lee, S.; Jeon, S. Enhanced Sensitivity of Lateral Flow Immunoassays by Using Water-Soluble Nanofibers and Silver-Enhancement Reactions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 1323–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Tok, A.I.Y.; Lee, C.; Ganapathy, R.; Alagappan, P.; Liedberg, B. Magnetic Field Assisted Preconcentration of Biomolecules for Lateral Flow Assaying. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 285, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byzova, N.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Khlebtsov, N.N.; Burov, A.M.; Khlebtsov, N.G.; Dzantiev, B.B. Advantages of Highly Spherical Gold Nanoparticles as Labels for Lateral Flow Immunoassay. Sensors 2020, 20, 3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, X.; Wu, R.; Wang, G.; Li, J.; Chai, Y.; Shen, H.; Li, L.S. Sensitive and Quantitative Determination of Cardiac Troponin I Based on Silica-Encapsulated CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots and a Fluorescence Lateral Flow Immunoassay. Anal. Lett. 2020, 53, 1757–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.; Jayaraj, J.; Prazeres, D.M.F. A Cellulose Paper-Based Fluorescent Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Quantitative Detection of Cardiac Troponin I. Biosensors 2021, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, T.; Wang, M.; Cao, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, P.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Lu, X. Functionalized Au@Ag-Au Nanoparticles as an Optical and SERS Dual Probe for Lateral Flow Sensing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 2291–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.-R.; Kim, M.-G. Highly Sensitive Chemiluminescence-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Cardiac Troponin I Detection in Human Serum. Sensors 2020, 20, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Xu, H.; Gu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Wei, M. Development of Lateral Flow Immunoassay System Based on Superparamagnetic Nanobeads as Labels for Rapid Quantitative Detection of Cardiac Troponin I. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sensing Method | Material/Nanoparticle | Structure | LOD | Linear Range | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colorimetric | AuNPs | Ab and BSA conjugated Anti-BSA | 0.01 ng/mL | 0.10–1.42 ng/mL | [33] |
| Colorimetric | AuNPs | Antibody/AuNPs-biotin-dsDNA-AuNP as amplifier | 1 ng/mL | 1–1000 ng/mL | [34] |
| Colorimetric | AuNPs | Ab conjugated AuNPs | 10 pg/mL | 30.0–1000 ng/mL | [35] |
| Colorimetric | AuNPs–shell hybrid nanobeads | Ab conjugated | 9.9 pg/mL | N.M. | [36] |
| Colorimetric | L-CGNPs | Ab–CSNPs–Ab–CS-GNPs | 0.129 ng/mL | 0.01–2.0 ng/mL | [37] |
| Fluorescence | CdSe/ZnS QD | Ab conjugated | 0.049 pg/mL | 0.04–50.0 ng/mL | [38] |
| SERS | ZrMOF@AuNPs | Gold nanorods | 5.6 × 10⁻3 ng/mL | 0.08–200 ng/mL | [39] |
| Luminescence | UCNP | Ab conjugated with MB | 0.01 ng/mL | 128.4–190.6 ng/mL | [40] |
| Electrochemical | AuNPs | AuNP-polydopamine conjugated | 0.015 ng/mL | 0.01–500 ng/mL | [41] |
| Electrochemical | Mesoporous silica NP | Ab conjugated with HRP | 5.6 pg/mL | 0.01–6.0 ng/mL | [42] |
| Electrochemical | AuNPs | Magnetic beads (MB) | 0.84 pg/mL | 30–1000 ng/mL | [43] |
| Electrochemical FET (This work) | Extended-gate FET with Tro4 aptamer | FET with aptamer-modified gate | 10–104 pg/mL | This Work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hung, S.-C.; Lee, Y.-H. Aptamer-Based Planar Electric Double-Layer Field-Effect Transistor: A Novel Approach for Sensitive Troponin I Sensing. Biosensors 2025, 15, 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050285
Hung S-C, Lee Y-H. Aptamer-Based Planar Electric Double-Layer Field-Effect Transistor: A Novel Approach for Sensitive Troponin I Sensing. Biosensors. 2025; 15(5):285. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050285
Chicago/Turabian StyleHung, Sheng-Chun, and Yi-Hua Lee. 2025. "Aptamer-Based Planar Electric Double-Layer Field-Effect Transistor: A Novel Approach for Sensitive Troponin I Sensing" Biosensors 15, no. 5: 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050285
APA StyleHung, S.-C., & Lee, Y.-H. (2025). Aptamer-Based Planar Electric Double-Layer Field-Effect Transistor: A Novel Approach for Sensitive Troponin I Sensing. Biosensors, 15(5), 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050285







