A Facile Method for Synthesizing Cobalt Oxide Nanoparticles to Create a Highly Sensitive Non-Enzyme Glucose Sensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
2.4. Characterization Techniques
3. Results
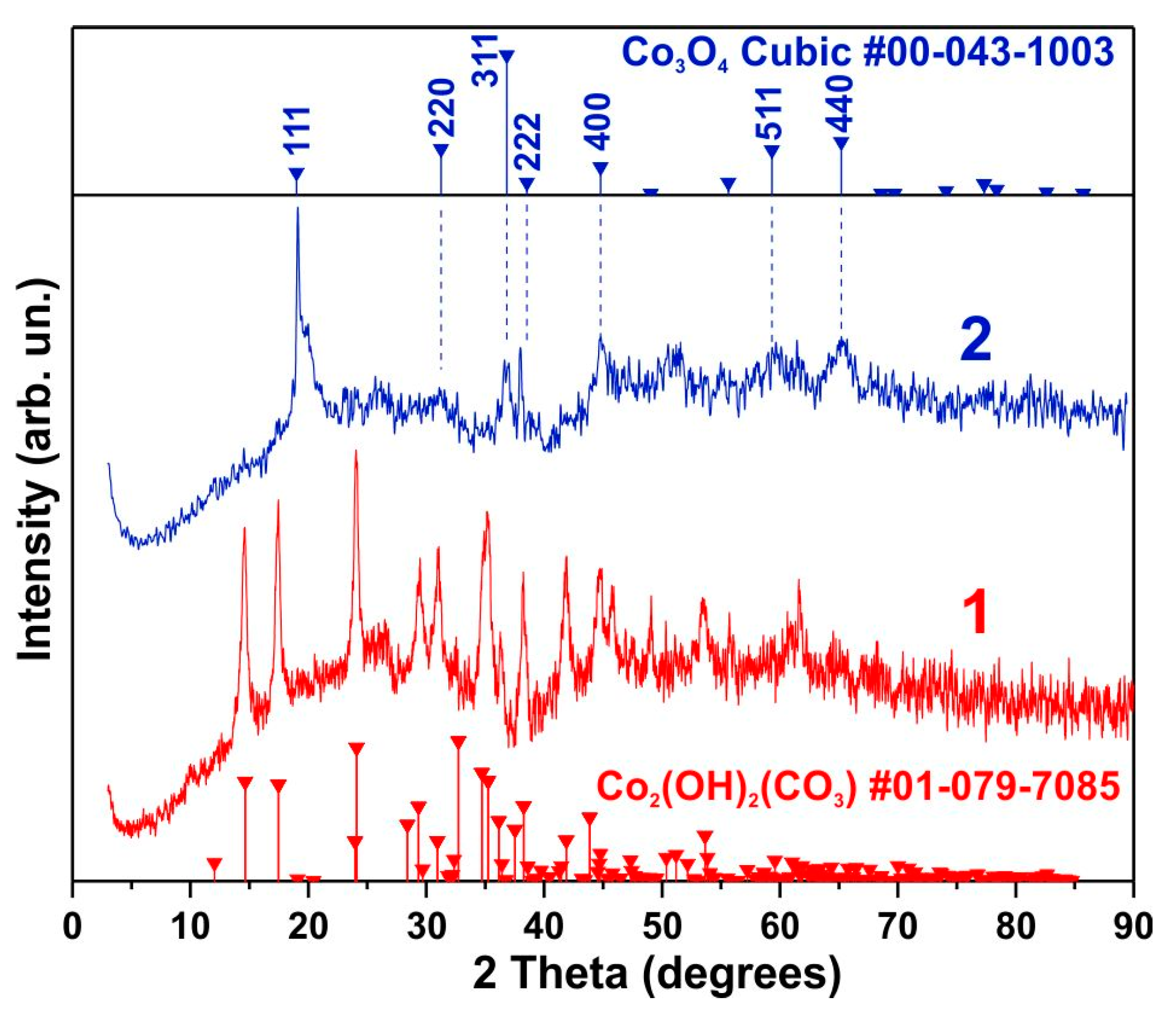
3.1. Morphology and Structure
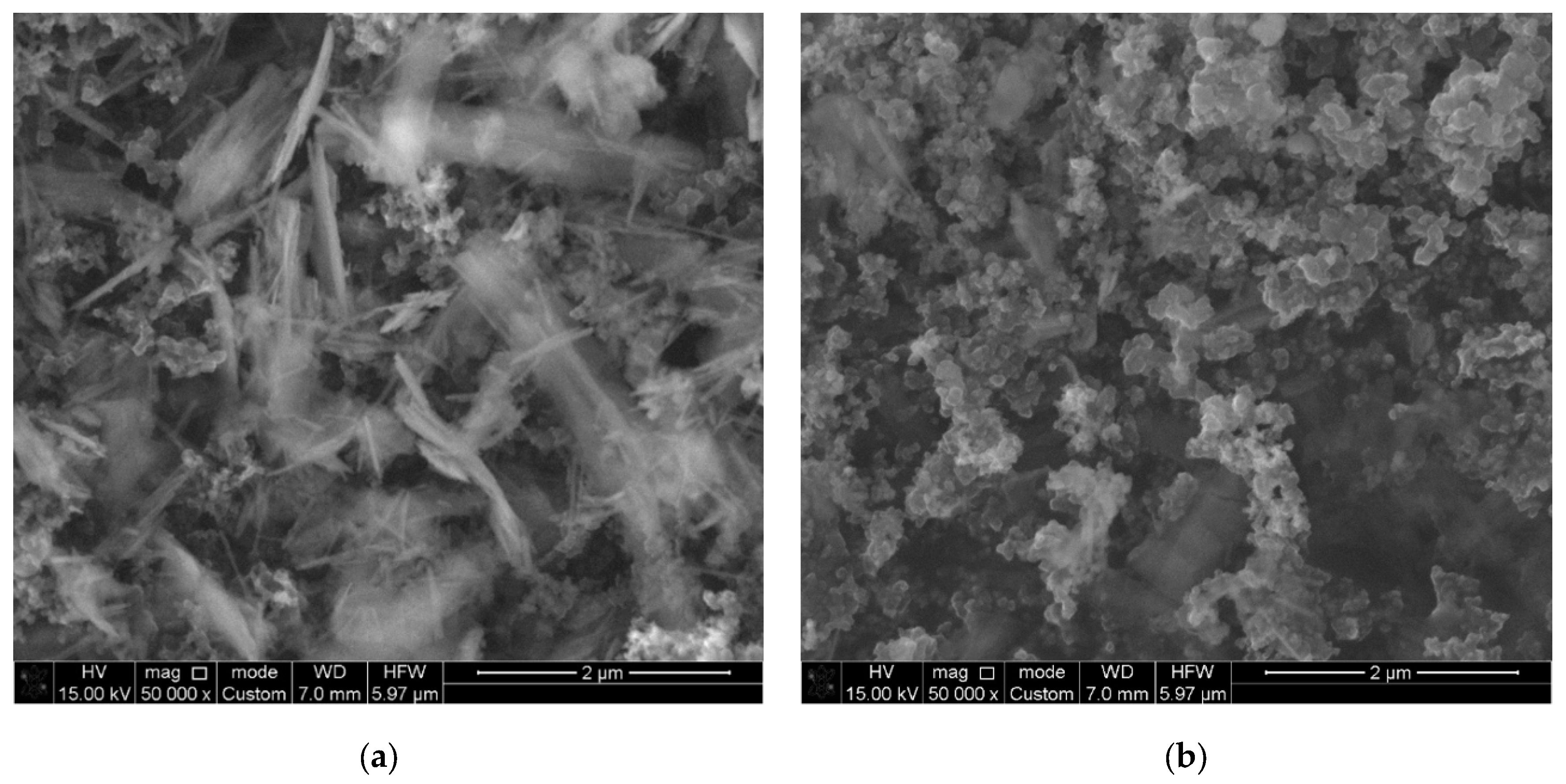
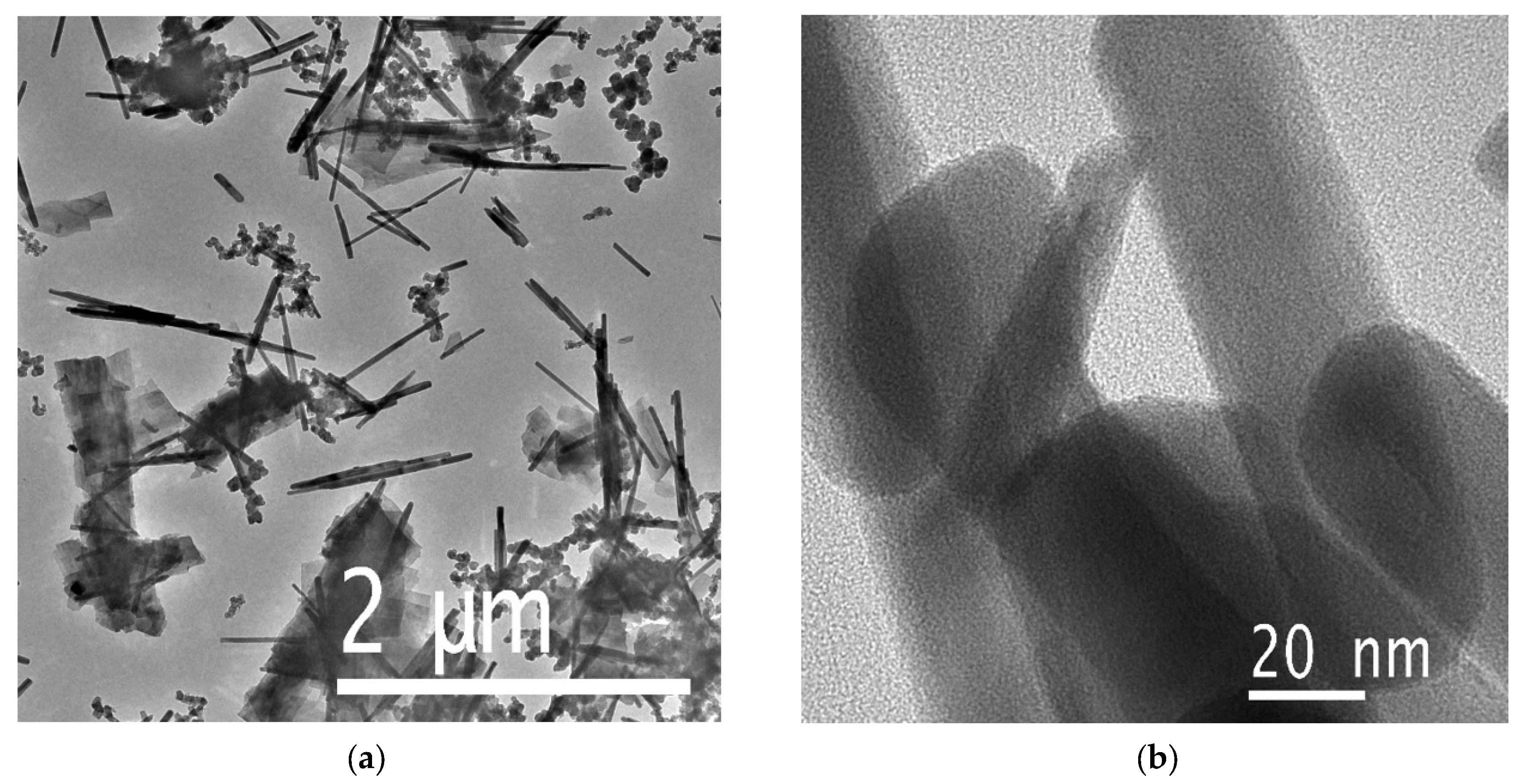
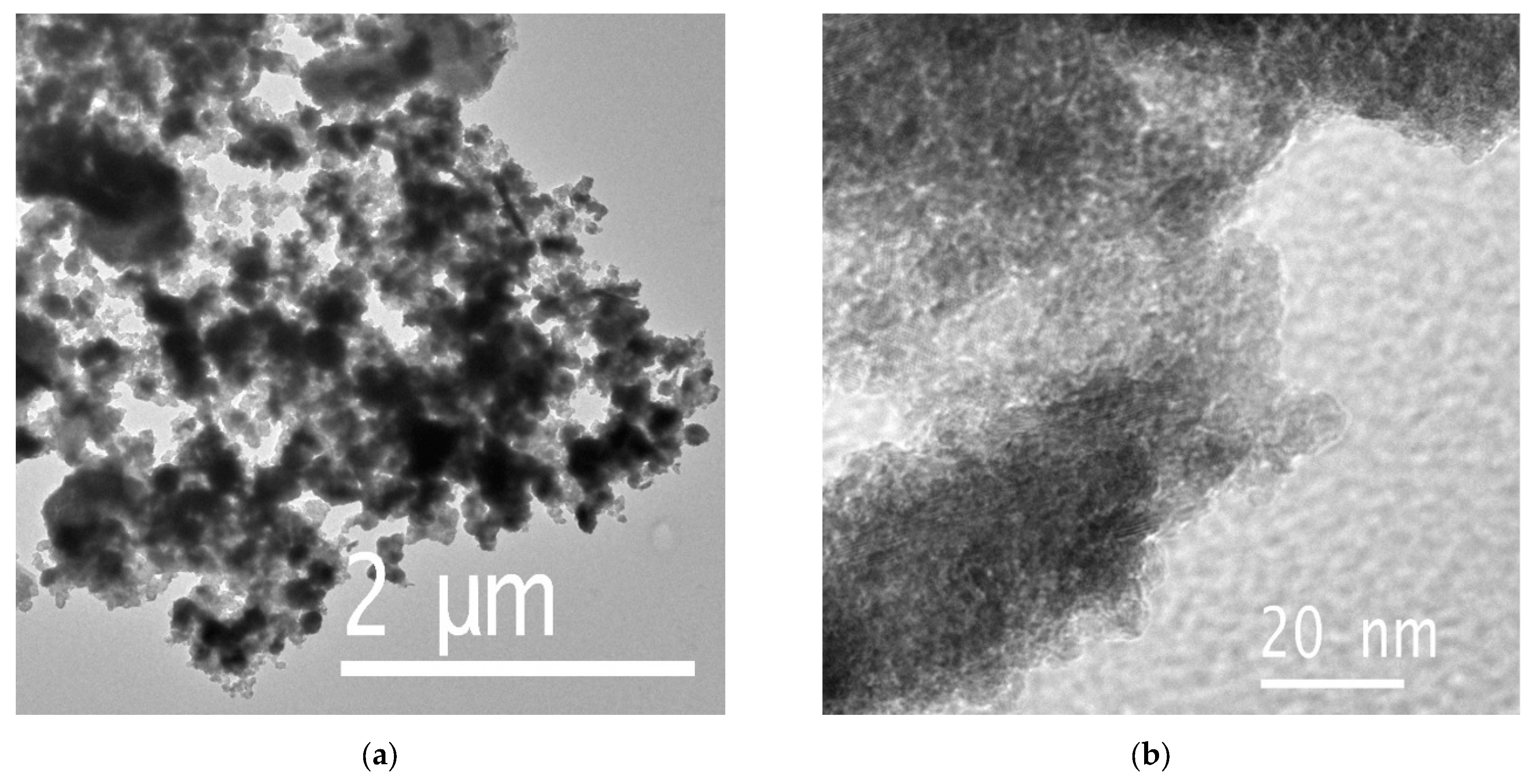
3.2. SEM and TEM Results
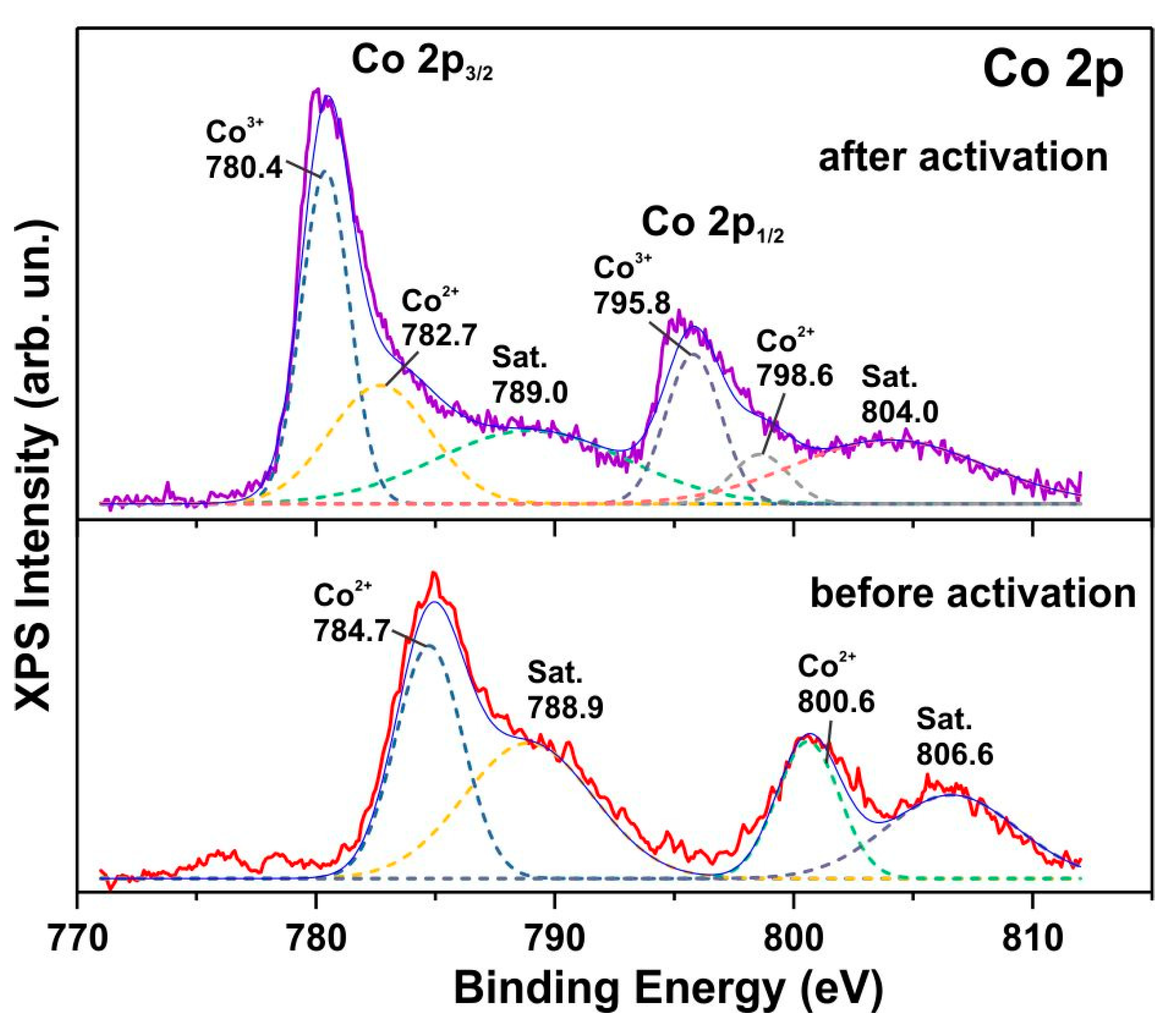
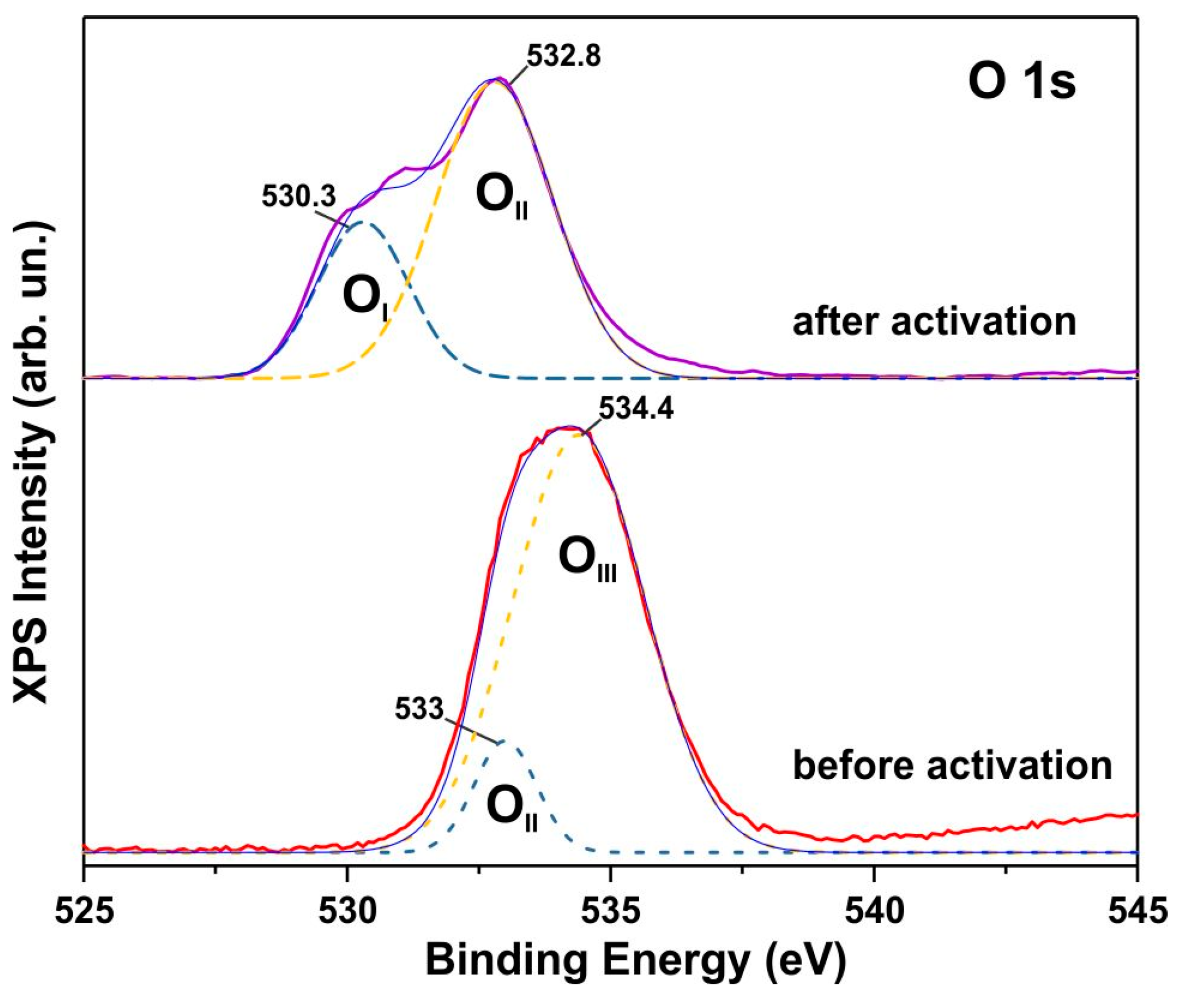
3.3. XPS Spectra
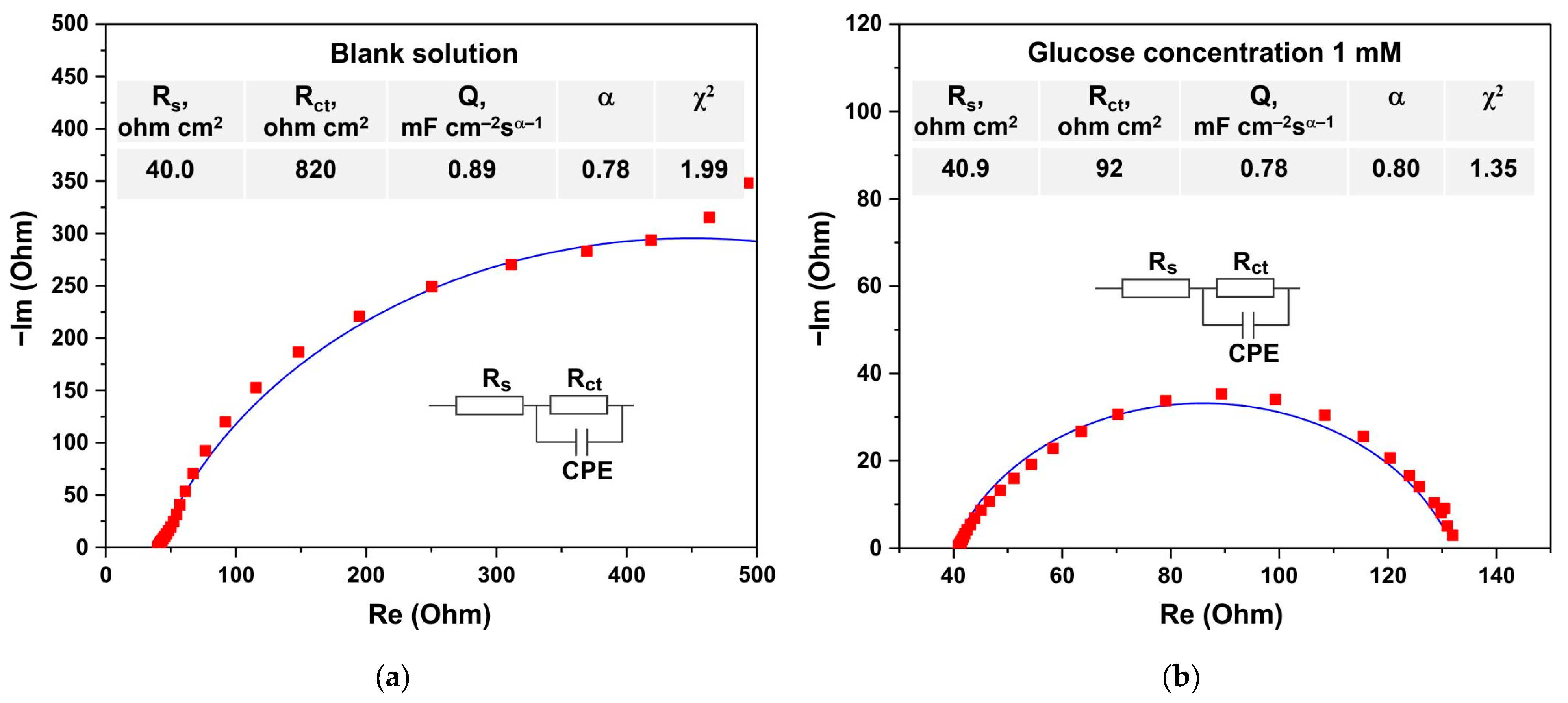
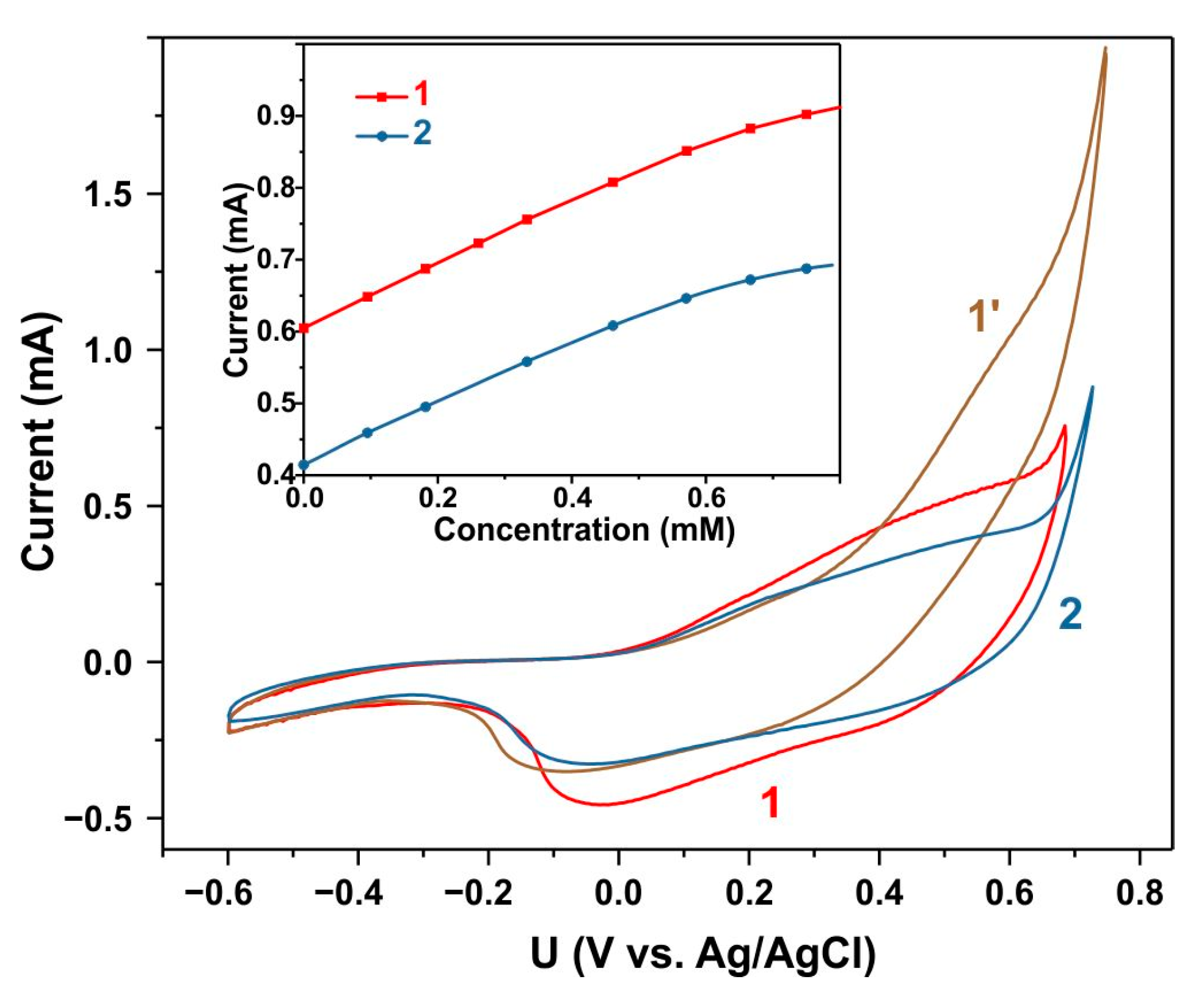
3.4. Electrochemical Glucose Sensing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Osuna, V.; Aparicio Martínez, E.P.; Dominguez, R.B.; Vega Rios, A. A Review on the Advances in Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensors Working in Physiological Conditions. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naikoo, G.A.; Salim, H.; Hassan, I.U.; Awan, T.; Arshad, F.; Pedram, M.Z.; Ahmed, W.; Qurashi, A. Recent Advances in Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensors Based on Metal and Metal Oxide Nanostructures for Diabetes Management—A Review. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 748957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shen, J.; Ji, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, W. Research progress of electrode materials for non-enzymatic glucose electrochemical sensors. Sens. Diagn. 2023, 2, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Tai, N.-H. Carbon nanomaterials and their composites for electrochemical glucose biosensors: A review on fabrication and sensing properties. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2024, 154, 104957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markhabayeva, A.A.; Kalkozova, Z.K.; Nemkayeva, R.; Yerlanuly, Y.; Anarova, A.S.; Tulegenova, M.A.; Tulegenova, A.T.; Abdullin, K.A. Construction of a ZnO Heterogeneous Structure Using Co3O4 as a Co-Catalyst to Enhance Photoelectrochemical Performance. Materials 2024, 17, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdiana, N.A.; Bahti, H.H.; Kurnia, D.; Wyantuti, S. Synthesis, characterization, and electrochemical properties of rare earth element nanoparticles and its application in electrochemical nanosensor for the detection of various biomolecules and hazardous compounds: A review. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2023, 41, 100573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarnda, K.V.; Wang, D.; Qurrat-Ul-Ain; Anaman, R.; Johnson, V.E.; Roberts, G.P.; Johnson, P.S.; Jallawide, B.W.; Kai, T.; Ding, P. Recent advances in electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensor for the detection of glucose in tears and saliva: A Review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2023, 363, 114778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraj, M.; Srivastava, A.; Muthukumaran, M.K.; Tsai, P.-C.; Lin, Y.-C.; Raja, B.K.; Rajendran, J.; Ponnusamy, V.K.; Selvi, J.A. Current advancements and prospects of enzymatic and non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakranova, D.; Seitov, B.; Bakranov, N. Photocatalytic and Glucose Sensing Properties of ZnO-Based Nanocoating. ChemEngineering 2023, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, H.; Ito, Y.; Chien, Y.-A.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chiu, W.-T.; Chakraborty, P.; Nakamoto, T.; Sone, M.; Chang, T.-F.M. Development of polypyrrole/nano-gold composite for non-enzymatic glucose sensors. Micro Nano Eng. 2022, 14, 100109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divyarani, K.; Sreenivasa, S.; Kumar, S.; Vinod, A.; Alharethy, F.; Jeon, B.-H.; Anusuya Devi, V.S.; Martis, P.; Parashuram, L. Fabrication of a novel MOF template-derived ZnCo2O4 composite for the non-enzymatic electrochemical detection of glucose. Results Chem. 2024, 8, 101604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolubayeva, D.B.; Gritsenko, L.V.; Kedruk, Y.Y.; Aitzhanov, M.B.; Nemkayeva, R.R.; Abdullin, K.A. Effect of hydrogen plasma treatment on the sensitivity of ZnO based electrochemical non-enzymatic biosensor. Biosensors 2023, 13, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, I.U.; Naikoo, G.A.; Arshad, F.; Ba Omar, F.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Mishra, V.; Mishra, Y.; EL-Tanani, M.; Charbe, N.B.; Chava, S.R.; et al. Applications of trimetallic nanomaterials as Non-Enzymatic glucose sensors. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2023, 49, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, M.A.; Kang, B.-C.; Ha, T.-J. Non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensors based on polyaniline/reduced-grapheneoxide nanocomposites decorated with silver nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 15, 5112–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileva, A.A.; Mamonova, D.V.; Mikhailovskii, V.; Petrov, Y.V.; Toropova, Y.G.; Kolesnikov, I.E.; Leuchs, G.; Manshina, A.A. 3D Nanocomposite with High Aspect Ratio Based on Polyaniline Decorated with Silver NPs: Synthesis and Application as Electrochemical Glucose Sensor. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitkov, N.; Ryabko, A.; Moshnikov, V.; Aleshin, A.; Kaplun, D.; Zimina, T. Hybrid Impedimetric Biosensors for Express Protein Markers Detection. Micromachines 2024, 15, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fall, B.; Sall, D.D.; Hémadi, M.; Diagne Diaw, A.K.; Fall, M.; Randriamahazaka, H.; Thomas, S. Highly efficient non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor based on carbon nanotubes functionalized by molybdenum disulfide and decorated with nickel nanoparticles (GCE/CNT/MoS2/NiNPs). Sens. Actuators Rep. 2023, 5, 100136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batvani, N.; Tehrani, M.A.; Alimohammadi, S.; Kiani, M.A. Non-enzymatic amperometric glucose sensor based on bimetal-oxide modified carbon fiber ultra-microelectrode. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2022, 38, 100532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghparas, Z.; Kordrostami, Z.; Sorouri, M.; Rajabzadeh, M.; Khalifeh, R. Highly sensitive non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor based on dumbbell-shaped double-shelled hollow nanoporous CuO/ZnO microstructures. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wu, H.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Lv, J.; Kong, C. Wearable Noninvasive Glucose Sensor Based on CuxO NFs/Cu NPs Nanocomposites. Sensors 2023, 23, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guati, C.; Gomez-Coma, L.; Fallanza, M.; Ortiz, I. Non-Enzymatic Amperometric Glucose Screen-Printed Sensors Based on Copper and Copper Oxide Particles. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshi, S.; Rahmanipour, M.; Amirsoleimani, A.R.; Rezazadeh, M.; Siampour, H.; Moshaii, A. Nanopyramid copper structures on screen-printed carbon electrode for high-performance non-enzymatic glucose sensing: A cost-effective and scalable approach. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2024, 46, 100706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosroshahi, Z.; Karimzadeh, F.; Kharaziha, M.; Allafchian, A. A non-enzymatic sensor based on three-dimensional graphene foam decorated with Cu-xCu2O nanoparticles for electrochemical detection of glucose and its application in human serum. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 108, 110216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barui, S.; Percivalle, N.M.; Conte, M.; Dumontel, B.; Racca, L.; Carofiglio, M.; Cauda, V. Development of doped ZnO-based biomimicking and tumor-targeted nanotheranostics to improve pancreatic cancer treatment. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2022, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Ryu, H.; Lei, Y. Metal oxide based non-enzymatic electrochemical sensors for glucose detection. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 370, 137744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Sivakumar, C.; Balraj, B.; Murugesan, G.; Nagarajan, S.K.; Ho, M.-S. Ag-Decorated Vertically Aligned ZnO Nanorods for Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensor Applications. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, B.A.; Tsegaye, A.A.; Shifera, G.; Taddesse, A.M. A sensitive non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor based on a ZnO/Co3O4/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite. Sens. Diagn. 2023, 2, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, T.P.; Butto-Miranda, N.; Neira-Carrillo, A.; Yáñez, C.; Bollo, S.; Ruíz-León, D. Size-controlled synthesis of cobalt phosphide (Co2P) nanoparticles and their application in non-enzymatic glucose sensors via a carbon fiber/Co2P composite. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2024, 8, 100235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Yang, L.; He, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Tang, J.; Huang, K.; Zou, Z.; Xiong, X. Co-Based Transition Metal Hydroxide Nanosheet Arrays on Carbon Cloth for Sensing Glucose and Formaldehyde. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 5076–5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.-J.; Pak, J.J. Synthesis of Laser-Induced Cobalt Oxide for Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Glucose Sensors. ChemElectroChem. 2022, 9, e202200328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://xpsdatabase.net/cobalt-spectra-cooh2/ (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- Available online: https://xpsdatabase.net/cobalt-spectra-coco3/ (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- Biesinger, M.C.; Payne, B.P.; Grosvenor, A.P.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.R.; Smart, R.S.C. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2717–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupin, J.-C.; Gonbeau, D.; Vinatier, P.; Levasseur, A. Systematic XPS studies of metal oxides, hydroxides and peroxides. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 6, 1319–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, Z.; He, Y.; Jiang, H.; Harn, Y.W.; Liu, X.; Su, C.; Jin, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. A Robust Route to Co2(OH)2CO3 Ultrathin Nanosheets with Superior Lithium Storage Capability Templated by Aspartic Acid-Functionalized Graphene Oxide. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1901093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.W.; Yao, J.; Zhang, K.; Zuo, X.; Yang, Q.; Tang, H.; Rehman, K.M.U.; Zhang, H.; Li, G.; Jin, S.; et al. Engineering N-reduced graphene oxide wrapped Co3O4@f-MWCNT hybrid for enhance performance dyesensitized solar cells. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 844, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strakosas, X.; Selberg, J.; Pansodtee, P.; Yonas, N.; Manapongpun, P.; Teodorescu, M.; Rolandi, M. A non-enzymatic glucose sensor enabled by bioelectronic pH control. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, M.; Meng, E.; Gong, F.; Li, F. Non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on three-dimensional hierarchical Co3O4 nanobooks. Micro Nano Lett. 2020, 15, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoj, D.; Aziz, A.; Muhammad, N.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, F.; Asif, M.; Sun, Y. Integrating Co3O4 nanocubes on MXene anchored CFE for improved electrocatalytic activity: Freestanding flexible electrode for glucose sensing. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, T.; Xiao, S.; Huang, P.; Wang, C.; Deng, Q.; Jiang, P.; He, D. Localized photothermal effect of Co3O4 nanowires boosts catalytic performance in glucose electrochemical detection. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2024, 11, 6527–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, E.; Gong, F.; Li, F. Co3O4 Nanoparticles as a Noninvasive Electrochemical Sensor for Glucose Detection in Saliva. Nano 2021, 16, 2150009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.-Y.; Kim, Y.-J.; Seo, W.-C.; Lee, H.-K.; Yang, W.-C.; Xie, W.-F. High-performance non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on Co3O4/rGO nanohybrid. Rare Met. 2023, 42, 3046–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Z. Nonenzymatic Glucose Sensor Based on Porous Co3O4 Nanoneedles. J. Environ. Public Health 2022, 2022, 6442241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Zhu, J.; Chen, J.; Gong, J.; Nie, Q. PEG-templated assembling of Co3O4 nanosheets with nanoparticles for enhanced sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensing performance. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 17305–17313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, X.; Huo, H.; Xu, C.; Han, X. Co3O4 microspheres with free-standing nanofibers for high performance non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Analyst 2013, 138, 6727–6731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; He, G.; Cai, Y.; Wu, S.; Su, Y.; Yan, H.; Yang, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, L. Co3O4 based non-enzymatic glucose sensor with high sensitivity and reliable stability derived from hollow hierarchical architecture. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 075502. Available online: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1361-6528/aaa1d2 (accessed on 15 January 2018).
- Xu, H.; Xia, C.; Wang, S.; Han, F.; Akbari, M.K.; Hai, Z.; Zhuiykov, S. Electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on hierarchical 3D Co3O4/Ni heterostructure electrode for pushing sensitivity boundary to a new limit. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 267, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezhil Vilian, A.T.; Dinesh, B.; Rethinasabapathy, M.; Hwang, S.-K.; Jin, C.-S.; Huh, Y.S.; Han, Y.-K. Hexagonal Co3O4 anchored reduced graphene oxide sheets for high-performance supercapacitors and non-enzymatic glucose sensing. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 14367–14379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilal, M.; Xie, W.; Yang, W. Straw-sheaf–like Co3O4 for preparation of an electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Glucose Sensor | Linear Range (mM) | Sensitivity (µA × mM−1 × cm−2) | Detection Limit (μM) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO/Co3O4/rGO composite | 0.015–10 mM | 1551.38 | 0.043 | [27] |
| Co2P nanoparticles on carbon fiber | 0.04–0.15 mM | 409 | 0.97 | [28] |
| Co(OH)2 nanosheet on carbon cloth | 0.001–5.45 mM | 6759 | 0.32 | [29] |
| Co3O4 nanobooks | 0–6 mM | 1068.85 | 7.94 | [38] |
| Co3O4 nanocubes | 0.05 μM to 7.44 mM | 19.3 | 0.01 | [39] |
| Co3O4 nanowires | 1 μM to 0.73 mM | 26,170 | 0.56 | [40] |
| Co3O4 nanoparticles | up to 3mM | 2495.79 | 0.0093 | [41] |
| Co3O4/rGO nanohybrid | 82 | 50 | [42] | |
| Co3O4 Nanoneedles | 1 μM–0.337 mM | 4570 | 0.91 | [43] |
| Co3O4 nanosheets | 2–3.420 μM | 745.26 | 0.65 | [44] |
| Co3O4 microspheres | 0.005–12 mM | 1449 | 0.91 | [45] |
| hierarchical Co3O4 architecture | 0.53–1900 μM | 839.3 | 0.08 | [46] |
| Co3O4/Ni heterostructure | 0–4 mM | 13,855 | 1 | [47] |
| RGO–Co3O4 | 1 µM–500 µM | 1315 | 0.4 | [48] |
| SS-Co3O4 | 0.04–4.85 mM | 669 | 0.31 | [49] |
| Co3O4 nanoparticles | up to 0.5 mM | 33,245 | 5 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalkozova, Z.K.; Balgimbayeva, U.A.; Gabdullin, M.T.; Gritsenko, L.V.; Suo, G.; Abdullin, K.A. A Facile Method for Synthesizing Cobalt Oxide Nanoparticles to Create a Highly Sensitive Non-Enzyme Glucose Sensor. Biosensors 2025, 15, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15040235
Kalkozova ZK, Balgimbayeva UA, Gabdullin MT, Gritsenko LV, Suo G, Abdullin KA. A Facile Method for Synthesizing Cobalt Oxide Nanoparticles to Create a Highly Sensitive Non-Enzyme Glucose Sensor. Biosensors. 2025; 15(4):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15040235
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalkozova, Zhanar K., Ulpan A. Balgimbayeva, Maratbek T. Gabdullin, Lesya V. Gritsenko, Guoquan Suo, and Khabibulla A. Abdullin. 2025. "A Facile Method for Synthesizing Cobalt Oxide Nanoparticles to Create a Highly Sensitive Non-Enzyme Glucose Sensor" Biosensors 15, no. 4: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15040235
APA StyleKalkozova, Z. K., Balgimbayeva, U. A., Gabdullin, M. T., Gritsenko, L. V., Suo, G., & Abdullin, K. A. (2025). A Facile Method for Synthesizing Cobalt Oxide Nanoparticles to Create a Highly Sensitive Non-Enzyme Glucose Sensor. Biosensors, 15(4), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15040235






