Analysis and Tracking of Intra-Needle Ultrasound Pleural Signals for Improved Anesthetic Procedures in the Thoracic Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
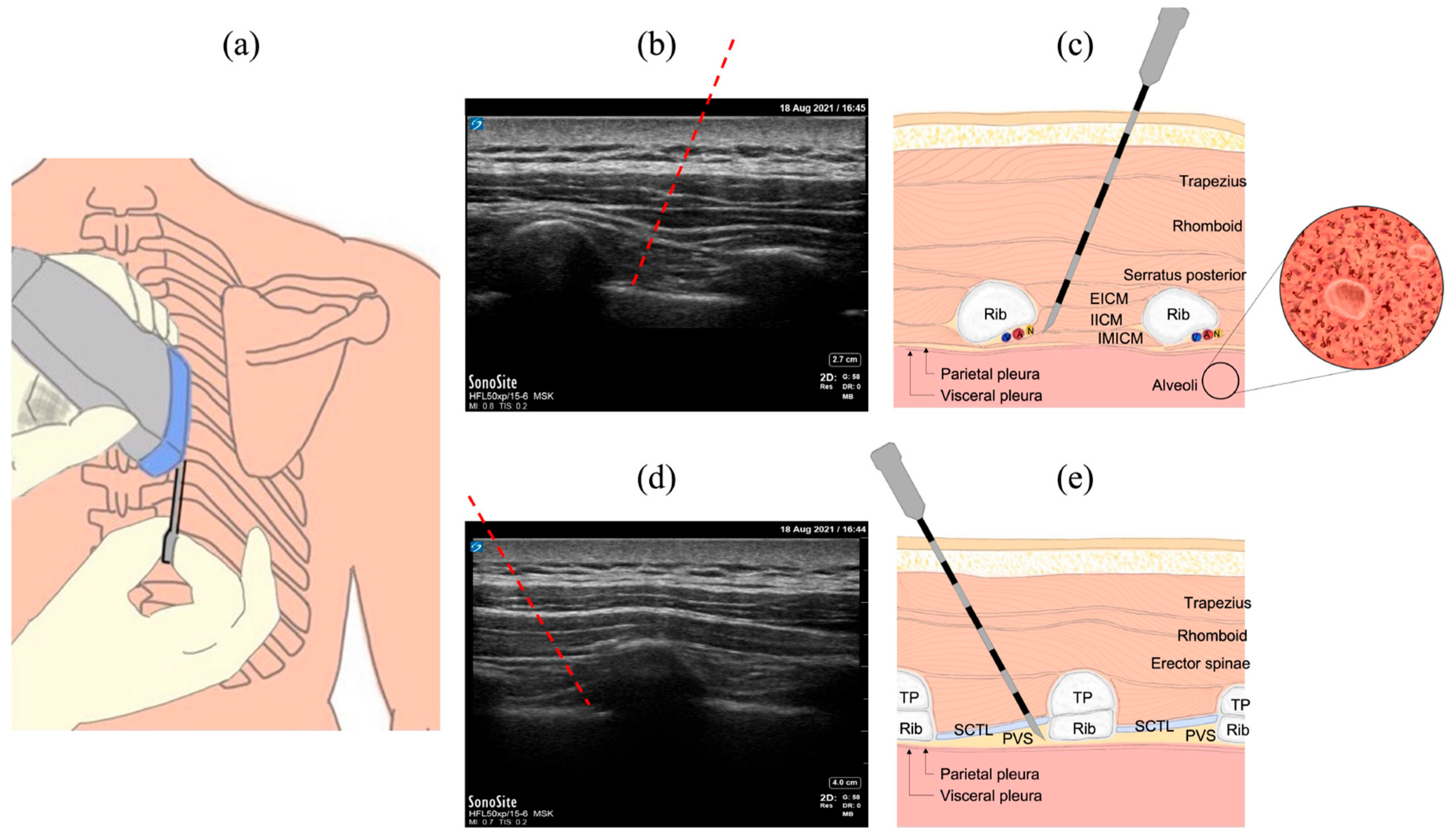
2.1. Common Procedures in the Thoracic Region
2.2. The INUS System
2.3. Ex Vivo Animal Study
2.4. In Vivo Animal Study
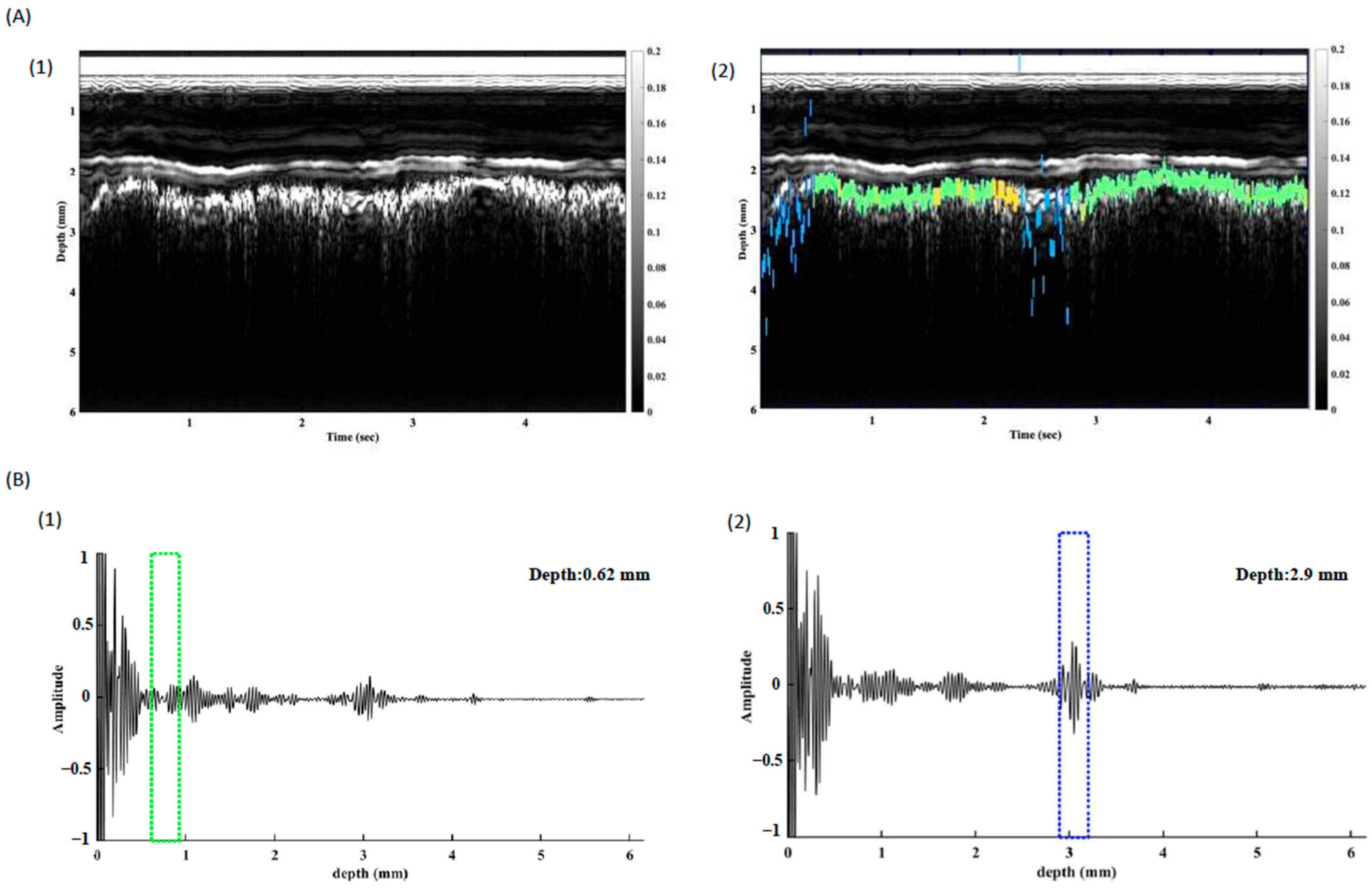
2.5. Time-Frequency Domain Analysis
2.6. In Vivo Study of Pleura Tracking
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Byas-Smith, M.G.; Gulati, A. Ultrasound-guided intercostal nerve cryoablation. Anesth. Analg. 2006, 103, 1033–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matchett, G. Intercostal Nerve Block and Neurolysis for Intractable Cancer Pain. J. Pain Palliat. Care Pharmacother. 2016, 30, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, D.C.; Bridenbaugh, L.D. Intercostal nerve block in 4333 patients: Indications, technique, and complications. Anesth. Analg. 1962, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karmakar, M.K.; Ho, A.M. Acute pain management of patients with multiple fractured ribs. J. Trauma 2003, 54, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, M.K. Thoracic paravertebral block. Anesthesiology 2001, 95, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.W.; Narouze, S. Ultrasound-guided interventional procedures in pain medicine: A review of anatomy, sonoanatomy, and procedures: Part I: Nonaxial structures. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2009, 34, 458–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhashab, Y.; Wang, D. A Review of Techniques of Intercostal Nerve Blocks. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2021, 25, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, T.J.; Rubens, D.J.; Zhao, Y.T.; Weis, J.; O’connor, T.P.; Novak, W.H.; Kaproth-Joslin, K.A. Lung Ultrasound: The Essentials. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2021, 3, e200564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerschug, K.C.; Schmidt, G.A. Intensive care ultrasound: III. Lung and pleural ultrasound for the intensivist. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2013, 10, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oelze, M.L.; Miller, R.J.; Blue, J.P., Jr.; Zachary, J.F.; O’Brien, W.D., Jr. Estimation of the acoustic impedance of lung versus level of inflation for different species and ages of animals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 124, 2340–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Williams, J.; Kang, B.J.; Yoon, C.; Cabrera-Munoz, N.; Jeong, J.S.; Lee, S.G.; Shung, K.K.; Kim, H.H. Angled-focused 45 MHz PMN-PT single element transducer for intravascular ultrasound imaging. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 228, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, T.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Shung, K.K.; Zhou, Q. (100)-Textured KNN-based thick film with enhanced piezoelectric property for intravascular ultrasound imaging. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 173504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Fu, Q.; Su, M.; Zhang, L.; Xia, J.; Dai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, H. Modulated Excitation Imaging System for Intravascular Ultrasound. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Li, Y.; Ma, T.; Shung, K.K.; Zhou, Q. Intravascular Ultrasound Imaging with Virtual Source Synthetic Aperture Focusing and Coherence Factor Weighting. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 2171–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Qiu, Z.; McPhillips, R.; Meggs, C.; Mahboob, S.O.; Wang, H.; Duncan, R.; Rodriguez-Sanmartin, D.; Zhang, Y.; Schiavone, G.; et al. Dual Orientation 16-MHz Single-Element Ultrasound Needle Transducers for Image-Guided Neurosurgical Intervention. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2016, 63, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhillips, R.; Qiu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Mahboob, S.O.; Wang, H.; Meggs, C.; Schiavone, G.; Sanmartin, D.R.; Eljamel, S.; Desmulliez, M.P.; et al. Ex-vivo navigation of neurosurgical biopsy needles using microultrasound transducers with M-mode imaging. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Taipei, Taiwan, 21–24 October 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Meggs, C.; Button, T.; Schiavone, G.; Desmulliez, M.P.; Qiu, Z.; Mahboob, S.; McPhillips, R.; Demore, C.E.; Casey, G.; et al. 15 MHz single element ultrasound needle transducers for neurosurgical applications. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Symposium (IUS) Ultrasonics, Chicago, IL, USA, 3–6 September 2014; pp. 687–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesteie, M.; Lessoway, V.; Abolmaesumi, P.; Rohling, R.N. Automatic Localization of the Needle Target for Ultrasound-Guided Epidural Injections. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, H.K.; Zhou, Q.; Mandell, M.S.; Tsou, M.-Y.; Lin, S.-P.; Shung, K.K.; Ting, C.-K. Eyes in the needle: Novel epidural needle with embedded high-frequency ultrasound transducer—epidural access in porcine model. Anesthesiology 2011, 114, 1320–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.-W.; Su, F.-W.; Ting, C.-K.; Yang, C.-F.; Yang, C.-W.; Tsou, M.-Y.; Chiang, H.K. Intercostal Nerve Block Using an Innovative Intraneedle Ultrasound Transducer: A Proof-of-Concept study. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2021, 47, 1881–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sejdić, E.; Djurović, I.; Jiang, J. Time–frequency feature representation using energy concentration: An overview of recent advances. Digit. Signal Process. 2009, 19, 153–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Qian, S.; Hu, W. Identification of Denatured Biological Tissues Based on Time-Frequency Entropy and Refined Composite Multi-Scale Weighted Permutation Entropy during HIFU Treatment. Entropy 2019, 21, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callejas, A.; Palma, R.; Hernández-Figueirido, D.; Rus, G. Damage Detection Using Ultrasonic Techniques in Concrete-Filled Steel Tubes (CFSTs) Columns. Sensors 2022, 22, 4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, F.W.; Chan, V.W.; Koshkin, A.; Abbas, S.; Brull, R. Ultrasound-guided sciatic nerve block in overweight and obese patients: A randomized comparison of performance time between the infragluteal and subgluteal space techniques. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2013, 38, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlassakov, K.; Vafai, A.; Ende, D.; Patton, M.E.; Kapoor, S.; Chowdhury, A.; Macias, A.; Zeballos, J.; Janfaza, D.R.; Pentakota, S.; et al. A prospective, randomized comparison of ultrasonographic visualization of proximal intercostal block vs paravertebral block. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020, 20, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sviggum, H.P.; Ahn, K.; Dilger, J.A.; Smith, H.M. Needle echogenicity in sonographically guided regional anesthesia: Blinded comparison of 4 enhanced needles and validation of visual criteria for evaluation. J. Ultrasound Med. 2013, 32, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derasse, M.; Lefebvre, S.; Liistro, G.; Reychler, G. Chest Expansion and Lung Function for Healthy Subjects and Individuals With Pulmonary Disease. Respir. Care 2021, 66, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltheart, M. The persistences of vision. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 1980, 290, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Type | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Transducer | Type | Pulse-echo |
| Number of elements | Single element | |
| Natural Focus | 1.5 mm | |
| Pulser | Frequency | 20 MHz |
| Pulse-repetition frequency | 30 Hz | |
| Analog-to-Digital Converter | 12 bits | |
| Sampling rate | 125 MHz | |
| Pulse-type | Sine wave | |
| Excitation voltage | 125 V | |
| Dimensions | 163 mm × 90 mm × 42 mm | |
| Weight | 670 g | |
| Display | Pixel 4 XL |
| Endothoracic Fascia | Parietal Pleura | Visceral Pleura + Alveoli | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation coefficient of RF-mode signals | 0.87 ± 0.13 | 0.80 ± 0.16 | 0.16 ± 0.33 |
| Correlation coefficient of M-mode signals | 0.94 ± 0.04 | 0.80 ± 0.15 | 0.53 ± 0.25 |
| Correlation coefficient (STFT Spectra) | 0.93 ± 0.07 | 0.85 ± 0.14 | 0.39 ± 0.25 |
| Average number per second of STFT bands (m ± σ) | 2.7 ± 0.84 | 2.7 ± 0.81 | 5.5 ± 2.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, F.-W.; Yang, C.-W.; Yang, C.-F.; Tsai, Y.-E.; Teng, W.-N.; Chiang, H.K. Analysis and Tracking of Intra-Needle Ultrasound Pleural Signals for Improved Anesthetic Procedures in the Thoracic Region. Biosensors 2025, 15, 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15040201
Su F-W, Yang C-W, Yang C-F, Tsai Y-E, Teng W-N, Chiang HK. Analysis and Tracking of Intra-Needle Ultrasound Pleural Signals for Improved Anesthetic Procedures in the Thoracic Region. Biosensors. 2025; 15(4):201. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15040201
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Fu-Wei, Chia-Wei Yang, Ching-Fang Yang, Yi-En Tsai, Wei-Nung Teng, and Huihua Kenny Chiang. 2025. "Analysis and Tracking of Intra-Needle Ultrasound Pleural Signals for Improved Anesthetic Procedures in the Thoracic Region" Biosensors 15, no. 4: 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15040201
APA StyleSu, F.-W., Yang, C.-W., Yang, C.-F., Tsai, Y.-E., Teng, W.-N., & Chiang, H. K. (2025). Analysis and Tracking of Intra-Needle Ultrasound Pleural Signals for Improved Anesthetic Procedures in the Thoracic Region. Biosensors, 15(4), 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15040201






