Regulatory Effects of RNA–Protein Interactions Revealed by Reporter Assays of Bacteria Grown on Solid Media
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
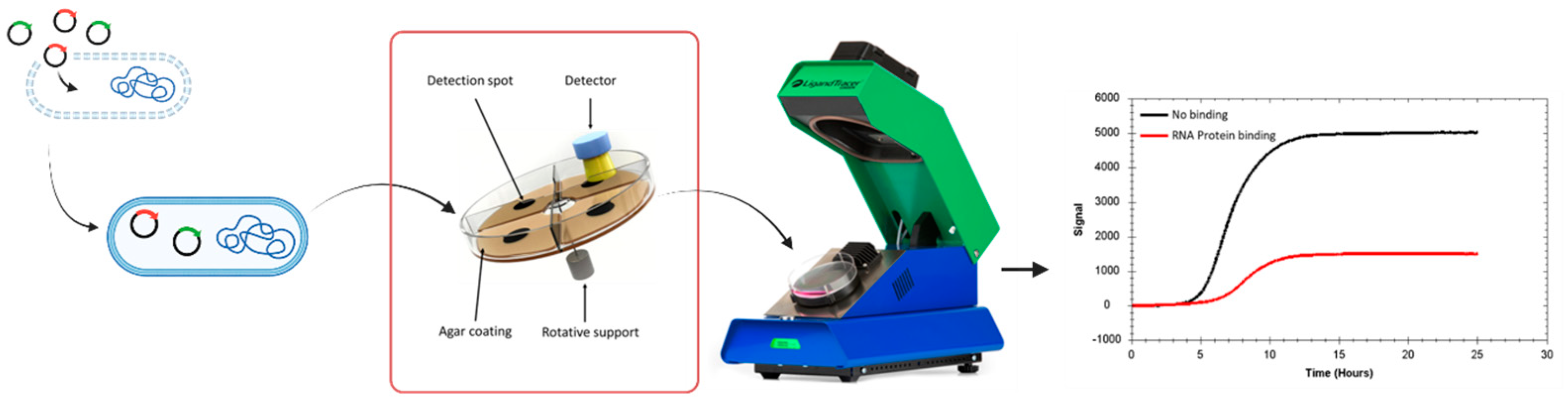
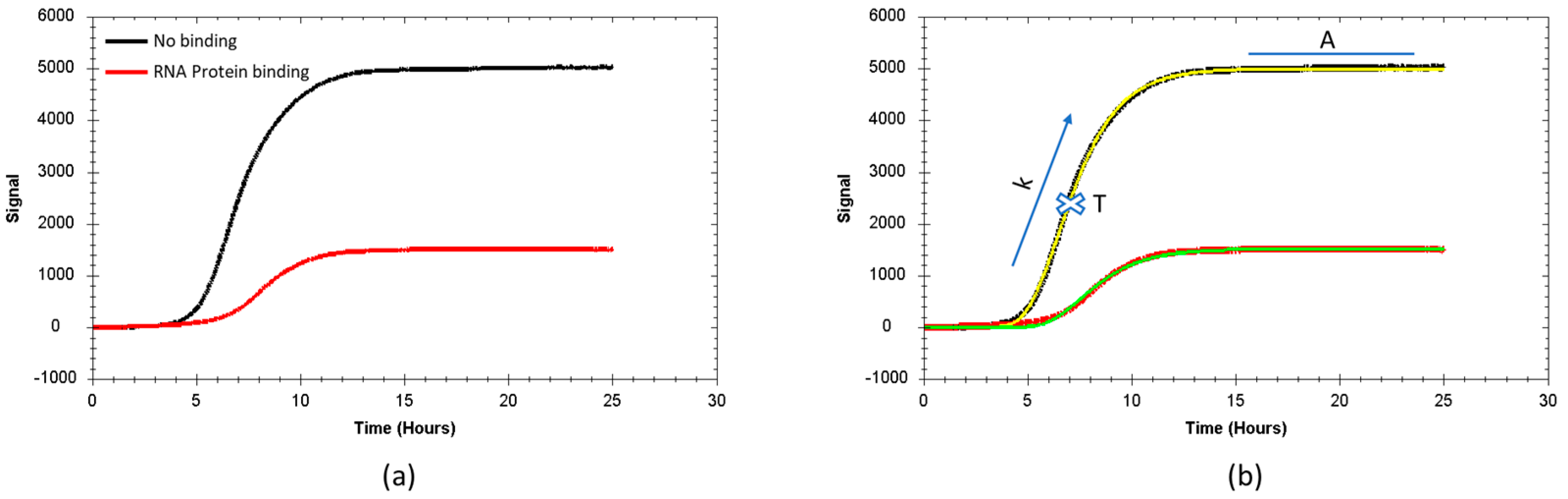
3.1. Real Time Protein Expression Assay (RT-PEA) in Living Bacteria
3.2. Characterization of MSI1 Binding to RNA
3.3. Correlation Between Fluorescence Reduction and Affinity
3.4. Oleic Acid Allosteric Modulation of MSI1 Binding to RNA
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CLIP | Crosslinking and immunoprecipitation |
| EMSA | Electrophoretic mobility shift assay |
| IPTG | Isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranosi |
| LB | Lysogeny broth |
| MSI1 | Musashi-1 |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| RBP | RNA-binding protein |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| RRM | RNA recognition motif |
| RT-CBA | Real-Time Cell Binding Assay |
| RT-PEA | Real-Time Protein Expression Assay |
| sfGFP | Superfolder GFP |
| SPR | Surface plasmon resonance |
References
- Chen, J.; Martindale, J.L.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Kumar, G.; Fortina, P.M.; Gorospe, M.; Rostami, A.; Yu, S. RNA-Binding Protein HuR Promotes Th17 Cell Differentiation and Can Be Targeted to Reduce Autoimmune Neuroinflammation. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 2076–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.J.; Jung, Y.S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X. The RNA-Binding Protein RNPC1 Stabilizes the MRNA Encoding the RNA-Binding Protein HuR and Cooperates with HuR to Suppress Cell Proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 14535–14544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyati, K.K.; Zaman, M.M.U.; Sharma, P.; Kishimoto, T. Arid5a, an RNA-Binding Protein in Immune Regulation: RNA Stability, Inflammation, and Autoimmunity. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Li, B.; Liang, Q.; Liu, A.; Qu, L.; Yang, J. Classification and Function of RNA–Protein Interactions. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2020, 11, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meneses, A.; Koga, S.; Leary, J.O.; Dickson, D.W.; Bu, G.; Zhao, N. TDP-43 Pathology in Alzheimer’ s Disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Cava, C.; Armaos, A.; Lang, B.; Tartaglia, G.G.; Castiglioni, I. Identification of Long Non-Coding RNAs and RNA Binding Proteins in Breast Cancer Subtypes. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, e1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.-C.; Ho, U.Y.; James, A.; De Souza, P.; Roberts, T.L. RNA Metabolism and Links to Inflammatory Regulation and Disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, A.L.; Stoffers, D.A. Stress-Induced Translational Regulation Mediated by RNA Binding Proteins: Key Links to β-Cell Failure in Diabetes. Diabetes 2020, 69, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, D.; de Groot, N.S.; Lorenzo Gotor, N.; Livi, C.M.; Tartaglia, G.G. Advances in the Characterization of RNA-Binding Proteins. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2016, 7, 793–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julio, A.R.; Backus, K.M. New Approaches to Target RNA Binding Proteins. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2021, 62, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, H. Protein-Based Systems for Translational Regulation of Synthetic Mrnas in Mammalian Cells. Life 2021, 11, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, M.; Porter, D.F.; Khavari, P.A. Methods to Study RNA–Protein Interactions. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennig, J.; Warner, L.R.; Simon, B.; Geerlof, A.; Mackereth, C.D.; Sattler, M. Structural Analysis of Protein–RNA Complexes in Solution Using NMR Paramagnetic Relaxation Enhancements. Methods Enzym. Enzymol. 2015, 558, 333–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, S.P.; Recht, M.I.; Williamson, J.R. Quantitative Analysis of Protein-RNA Interactions by Gel Mobility Shift. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 488, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, J.M.; Clingman, C.C.; Ryder, S.P. Quantitative Approaches to Monitor Protein-Nucleic Acid Interactions Using Fluorescent Probes. RNA 2011, 17, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsamba, P.S.; Park, S.; Laird-offringa, I.A. Kinetic Studies of RNA—Protein Interactions Using Surface Plasmon Resonance. Methods 2002, 26, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ropero, G.; Pérez-Ràfols, A.; Martelli, T.; Danielson, U.H.; Buijs, J. Unraveling the Bivalent and Rapid Interactions Between a Multivalent RNA Recognition Motif and RNA: A Kinetic Approach. Biochemistry 2024, 63, 2816–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ule, J.; Jensen, K.; Mele, A.; Darnell, R.B. CLIP: A Method for Identifying Protein-RNA Interaction Sites in Living Cells. Methods 2005, 37, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nostrand, E.L.; Freese, P.; Pratt, G.A.; Wang, X.; Wei, X.; Xiao, R.; Blue, S.M.; Chen, J.Y.; Cody, N.A.L.; Dominguez, D.; et al. A Large-Scale Binding and Functional Map of Human RNA-Binding Proteins. Nature 2020, 583, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauer, C.; Curk, T.; Anders, S.; Schwarzl, T.; Alleaume, A.M.; Sieber, J.; Hollerer, I.; Bhuvanagiri, M.; Huber, W.; Hentze, M.W.; et al. Improved Binding Site Assignment by High-Resolution Mapping of RNA-Protein Interactions Using ICLIP. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, Y.; Vigilante, A.; Darbo, E.; Zirra, A.; Militti, C.; D’Ambrogio, A.; Luscombe, N.M.; Ule, J. HiCLIP Reveals the in vivo Atlas of MRNA Secondary Structures Recognized by Staufen 1. Nature 2015, 519, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Zagore, L.L.; Brister, M.M.; Ye, X.; Crespo-Hernández, C.E.; Licatalosi, D.D.; Jankowsky, E. The Kinetic Landscape of an RNA-Binding Protein in Cells. Nature 2021, 591, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, N.; Cohen, R.; Solomon, O.; Kaufmann, B.; Atar, O.; Yakhini, Z.; Goldberg, S.; Amit, R. An in vivo Binding Assay for RNA-Binding Proteins Based on Repression of a Reporter Gene. ACS Synth. Biol. 2018, 7, 2765–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskeva, E.; Atzberger, A.; Hentze, M.W. A Translational Repression Assay Procedure (TRAP) for RNA-Protein Interactions in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, G.S.; Foglia, M.L.; Copello, G.J.; Desimone, M.F.; Diaz, L.E. Effect of Various Parameters on Viability and Growth of Bacteria Immobilized in Sol-Gel-Derived Silica Matrices. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 82, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premkumar, J.R.; Sagi, E.; Rozen, R.; Belkin, S.; Modestov, A.D.; Lev, O. Fluorescent Bacteria Encapsulated in Sol-Gel Derived Silicate Films. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 2676–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, T.; Noller, H.F. Dominant Lethal Mutations in a Conserved Loop in 16S RRNA (Site-Directed Mutageliesis/RRNA Mutations/A PL Promoter/Ribosomal A Site). Biochemistry 1990, 87, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Usui, M.; Yoshii, Y.; Thiriet-Rupert, S.; Ghigo, J.M.; Beloin, C. Intermittent Antibiotic Treatment of Bacterial Biofilms Favors the Rapid Evolution of Resistance. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malicki, S.; Pucelik, B.; Żyła, E.; Benedyk-Machaczka, M.; Gałan, W.; Golda, A.; Sochaj-Gregorczyk, A.; Kamińska, M.; Encarnação, J.C.; Chruścicka, B.; et al. Imaging of Clear Cell Renal Carcinoma with Immune Checkpoint Targeting Aptamer-Based Probe. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encarnação, J.C.; Napolitano, V.; Opassi, G.; Danielson, U.H.; Dubin, G.; Popowicz, G.M.; Munier-Lehmann, H.; Buijs, J.; Andersson, K.; Björkelund, H. A Real-Time Cell-Binding Assay Reveals Dynamic Features of STxB–Gb3 Cointernalization and STxB-Mediated Cargo Delivery into Cancer Cells. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 2406–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encarnação, J.C.; Schulte, T.; Achour, A.; Björkelund, H.; Andersson, K. Detecting Ligand Interactions in Real Time on Living Bacterial Cells. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 4193–4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruth Zearfoss, N.; Deveau, L.M.; Clingman, C.C.; Schmidt, E.; Johnson, E.S.; Massi, F.; Ryder, S.P. A Conserved Three-Nucleotide Core Motif Defines Musashi RNA Binding Specificity. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 35530–35541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okano, H.; Imai, T.; Okabe, M. Musashi: A Translational Regulator of Cell Fate. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 1355–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.C.; Tsai, J.T.; Chao, T.Y.; Ma, H.I.; Liu, W.H. Musashi-1 Enhances Glioblastoma Migration by Promoting ICAM1 Translation. Neoplasia 2019, 21, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troschel, F.M.; Minte, A.; Ismail, Y.M.; Kamal, A.; Abdullah, M.S.; Ahmed, S.H.; Deffner, M.; Kemper, B.; Kiesel, L.; Eich, H.T.; et al. Knockdown of Musashi RNA Binding Proteins Decreases Radioresistance but Enhances Cell Motility and Invasion in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikpour, P.; Baygi, M.E.; Steinhoff, C.; Hader, C.; Luca, A.C.; Mowla, S.J.; Schulz, W.A. The RNA Binding Protein Musashi1 Regulates Apoptosis, Gene Expression and Stress Granule Formation in Urothelial Carcinoma Cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 1210–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalbano, M.; McAllen, S.; Puangmalai, N.; Sengupta, U.; Bhatt, N.; Johnson, O.D.; Kharas, M.G.; Kayed, R. RNA-Binding Proteins Musashi and Tau Soluble Aggregates Initiate Nuclear Dysfunction. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurihara, Y.; Nagata, T.; Imai, T.; Hiwatashi, A.; Horiuchi, M.; Sakakibara, S.-I.; Katahira, M.; Okano, H.; Uesugi, S. Structural Properties and RNA-Binding Activities of Two RNA Recognition Motifs of a Mouse Neural RNA-Binding Protein, Mouse-Musashi-1. Gene 1997, 186, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maris, C.; Dominguez, C.; Allain, F.H.T. The RNA Recognition Motif, a Plastic RNA-Binding Platform to Regulate Post-Transcriptional Gene Expression. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 2118–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clingman, C.C.; Deveau, L.M.; Hay, S.A.; Genga, R.M.; Shandilya, S.M.D.; Massi, F.; Ryder, S.P. Allosteric Inhibition of a Stem Cell RNA-Binding Protein by an Intermediary Metabolite. Elife 2014, 3, e02848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragle, C.E.; MacNicol, M.C.; Byrum, S.D.; Hardy, L.L.; Mackintosh, S.G.; Richardson, W.A.; Gray, N.K.; Childs, G.V.; Tackett, A.J.; MacNicol, A.M. Musashi Interaction with Poly(A)-Binding Protein Is Required for Activation of Target MRNA Translation. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 10969–10986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolcemascolo, R.; Heras-Hernández, M.; Goiriz, L.; Montagud-Martínez, R.; Requena-Menéndez, A.; Ruiz, R.; Pérez-Ràfols, A.; Higuera-Rodríguez, R.A.; Pérez-Ropero, G.; Vranken, W.F.; et al. Repurposing the Mammalian RNA-Binding Protein Musashi-1 as an Allosteric Translation Repressor in Bacteria. Elife 2024, 12, RP91777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjørve, K.M.C.; Tjørve, E. The Use of Gompertz Models in Growth Analyses, and New Gompertz-Model Approach: An Addition to the Unified-Richards Family. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, T.; Tokunaga, A.; Yoshida, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Mikoshiba, K.; Weinmaster, G.; Nakafuku, M.; Okano, H. The Neural RNA-Binding Protein Musashi1 Translationally Regulates Mammalian Numb Gene Expression by Interacting with Its MRNA. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 21, 3888–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca-Martínez, J.; Dhondge, H.; Sattler, M.; Vranken, W.F. Deciphering the RRM-RNA Recognition Code: A Computational Analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2023, 19, e1010859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madisen, L.; Zwingman, T.A.; Sunkin, S.M.; Oh, S.W.; Zariwala, H.A.; Gu, H.; Ng, L.L.; Palmiter, R.D.; Hawrylycz, M.J.; Jones, A.R.; et al. A Robust and High-Throughput Cre Reporting and Characterization System for the Whole Mouse Brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Yan, Q.; Jones, J.A.; Tang, Y.J.; Fong, S.S.; Koffas, M.A.G. Metabolic Burden: Cornerstones in Synthetic Biology and Metabolic Engineering Applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi, M.T.T.; Wibowo, D.; Rehm, B.H.A. Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressuire-Isoard, C.; Broussolle, V.; Carlin, F. Sporulation Environment Influences Spore Properties in Bacillus: Evidence and Insights on Underlying Molecular and Physiological Mechanisms. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 614–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojanowski, D.; Hołówka, J.; Ginda, K.; Jakimowicz, D.; Zakrzewska-Czerwińska, J. Multifork Chromosome Replication in Slow-Growing Bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Curran, J.M.; Patterson, E.A. Real-Time Monitoring of the Dynamics and Interactions of Bacteria and the Early-Stage Formation of Biofilms. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zutz, A.; Hamborg, L.; Pedersen, L.E.; Kassem, M.M.; Papaleo, E.; Koza, A.; Herrgård, M.J.; Jensen, S.I.; Teilum, K.; Lindorff-Larsen, K.; et al. A Dual-Reporter System for Investigating and Optimizing Protein Translation and Folding in E. coli. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwaoka, R.; Nagata, T.; Tsuda, K.; Imai, T.; Okano, H.; Kobayashi, N.; Katahira, M. Structural Insight into the Recognition of r(UAG) by Musashi-1 RBD2, and Construction of a Model of Musashi-1 RBD1-2 Bound to the Minimum Target RNA. Molecules 2017, 22, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoboda, P.; Di Cara, A. Hairpin RNA: A secondary structure of primary importance. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 901–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Ropero, G.; Dolcemascolo, R.; Pérez-Ràfols, A.; Andersson, K.; Danielson, U.H.; Rodrigo, G.; Buijs, J. Regulatory Effects of RNA–Protein Interactions Revealed by Reporter Assays of Bacteria Grown on Solid Media. Biosensors 2025, 15, 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15030175
Pérez-Ropero G, Dolcemascolo R, Pérez-Ràfols A, Andersson K, Danielson UH, Rodrigo G, Buijs J. Regulatory Effects of RNA–Protein Interactions Revealed by Reporter Assays of Bacteria Grown on Solid Media. Biosensors. 2025; 15(3):175. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15030175
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Ropero, Guillermo, Roswitha Dolcemascolo, Anna Pérez-Ràfols, Karl Andersson, U. Helena Danielson, Guillermo Rodrigo, and Jos Buijs. 2025. "Regulatory Effects of RNA–Protein Interactions Revealed by Reporter Assays of Bacteria Grown on Solid Media" Biosensors 15, no. 3: 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15030175
APA StylePérez-Ropero, G., Dolcemascolo, R., Pérez-Ràfols, A., Andersson, K., Danielson, U. H., Rodrigo, G., & Buijs, J. (2025). Regulatory Effects of RNA–Protein Interactions Revealed by Reporter Assays of Bacteria Grown on Solid Media. Biosensors, 15(3), 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15030175




