Multi-Channel Cellytics for Rapid and Cost-Effective Monitoring of Leukocyte Activation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Preparation and Activation
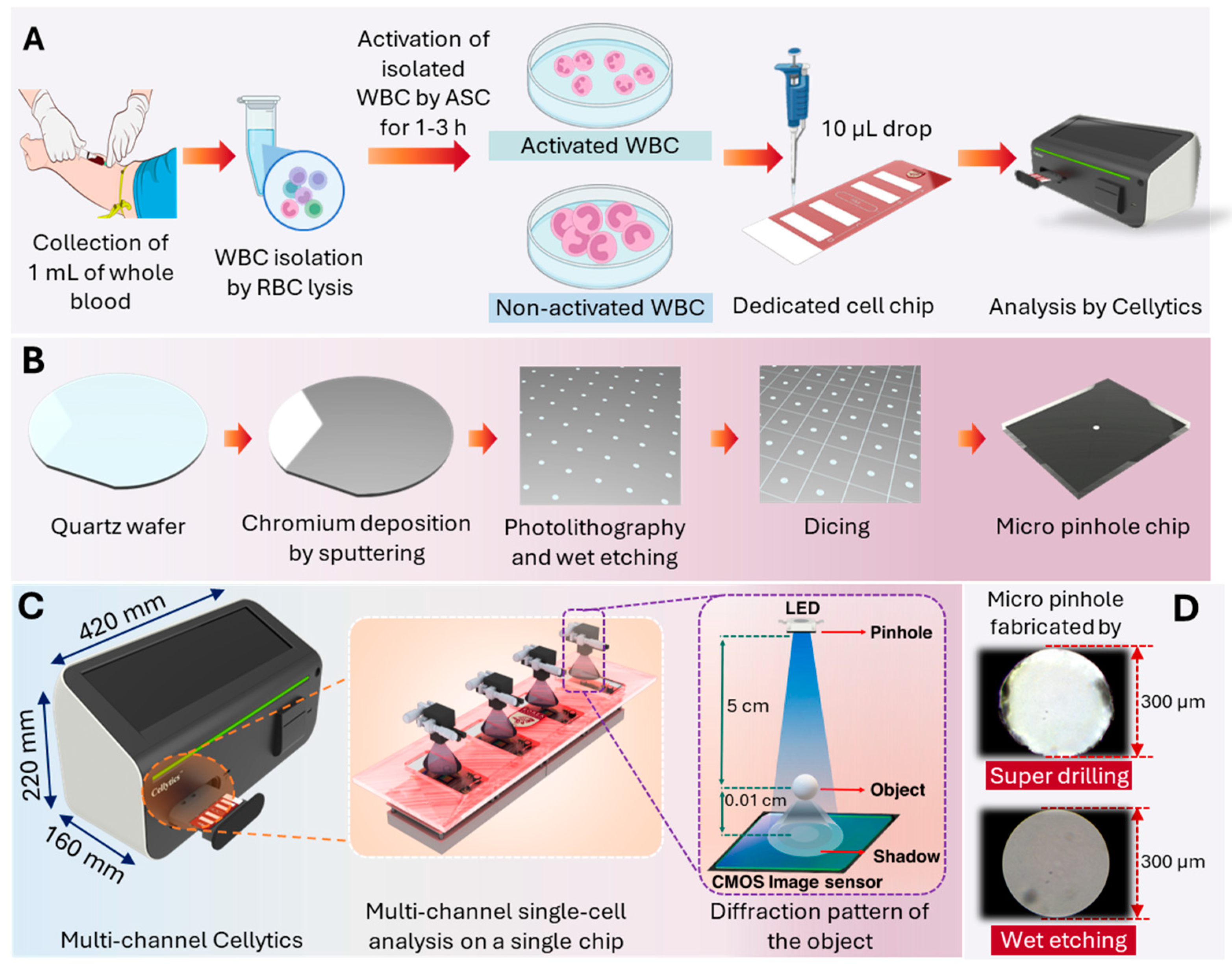
2.1.1. Blood Sample Collection and Leukocyte Isolation
2.1.2. Activation Stimulator Cocktail (ASC) Preparation
2.1.3. Leukocyte Activation Procedure
2.1.4. Shadow Parameter Selection and Comparative Analysis
2.1.5. Statistical Analysis
2.2. Multi-Channel Cellytics Enhancement
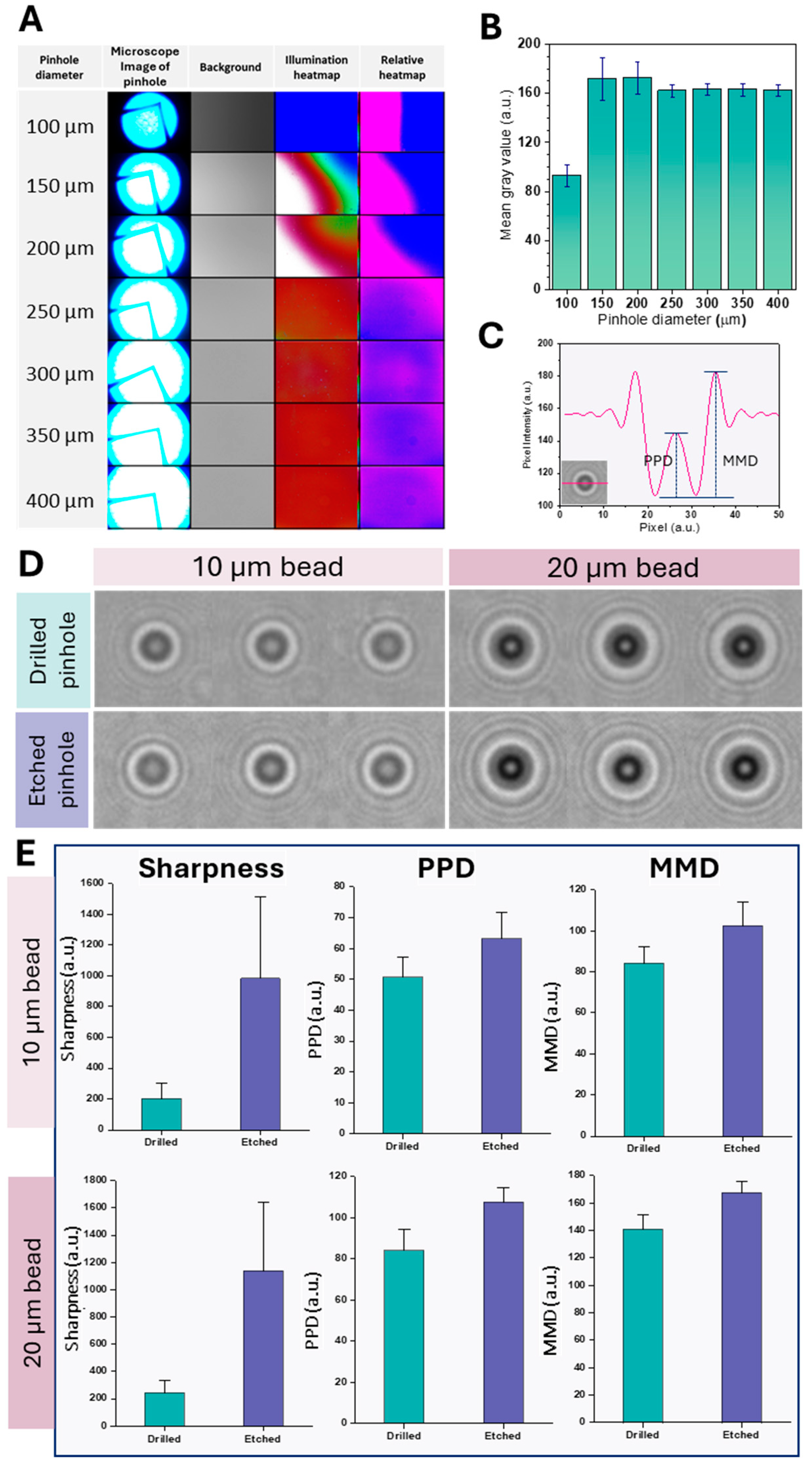
2.2.1. Micro-Pinhole Chip Fabrication
2.2.2. Pinhole Diameter Optimization
2.2.3. Comparison with Conventional Pinhole Design
2.2.4. Multi-Channel Cellytics System Description
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Pinhole Diameter Optimization
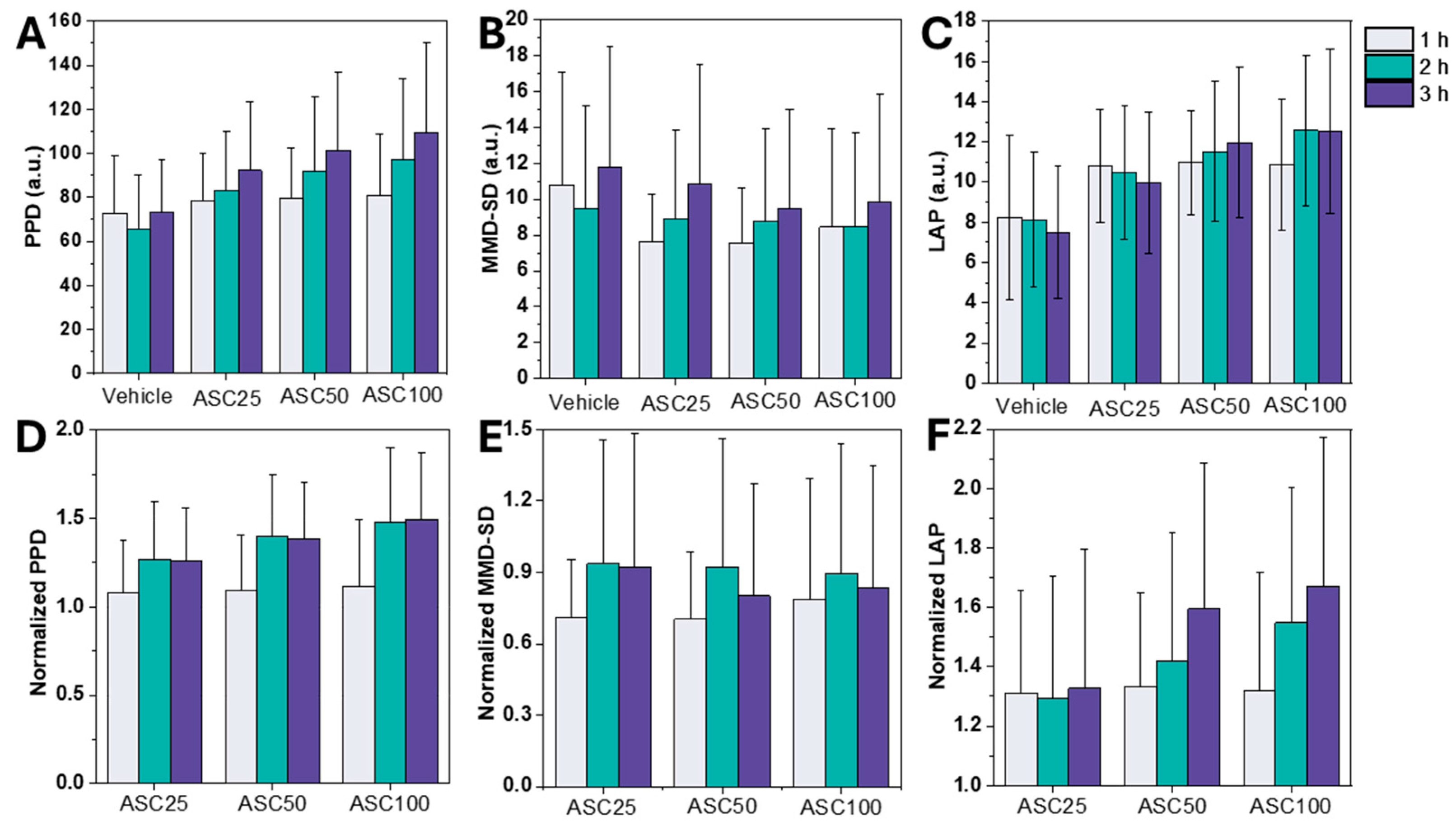
3.2. Leukocyte Activation Assessment Using LSIT-Derived Shadow Parameters
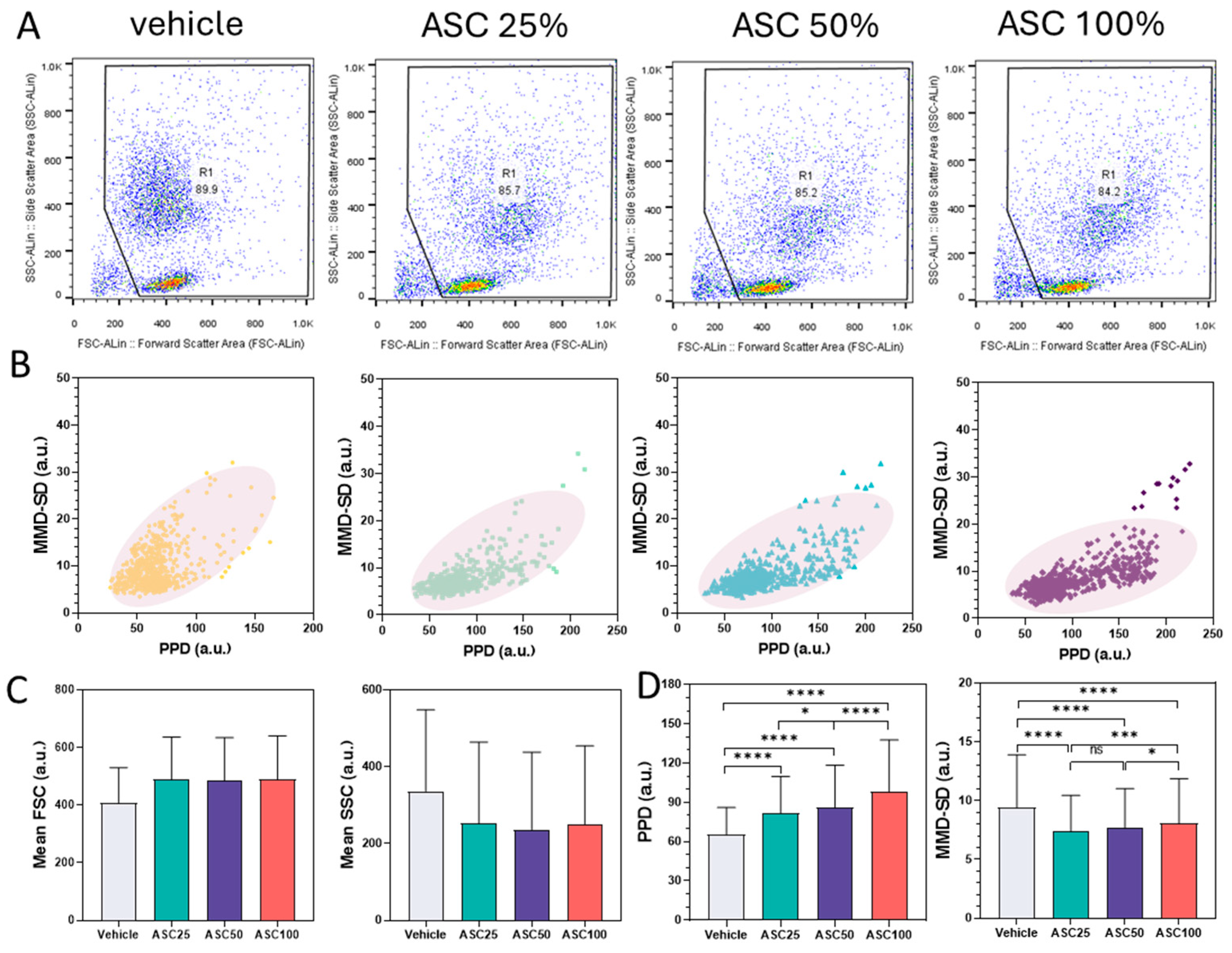
3.3. Comparison Between Flow Cytometry and PPD vs. MMD-SD Density Plots
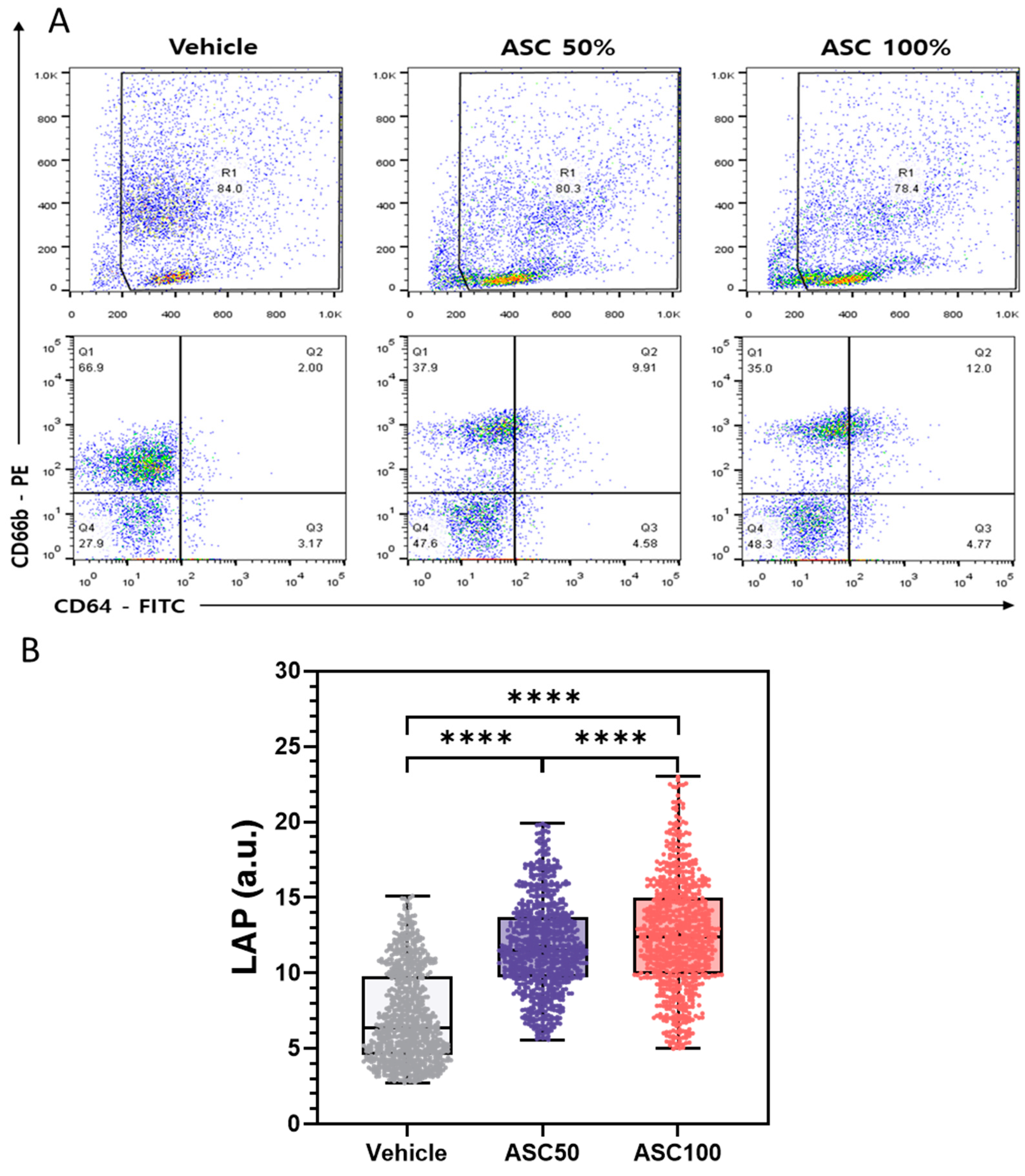
3.4. Flow Cytometry Analysis of CD64 and CD66b Expression and Correlation with LAP
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leach, M. The Diagnostic Utility of Eosinophil Morphology. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 191, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-H.; Gilkes, D.M.; Phillip, J.M.; Narkar, A.; Cheng, T.W.-T.; Marchand, J.; Lee, M.-H.; Li, R.; Wirtz, D. Single-Cell Morphology Encodes Metastatic Potential. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaw6938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, E.; Castle, J.; Quirk, A.; Taylor, C.D.L.; Xu, W.; Prasad, A. Cellular Morphological Features Are Predictive Markers of Cancer Cell State. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 126, 104044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovic, A.; Saini, K.; Carelli, R.; Pham, T.; Corona, C.; Mei, J.; Phelan, M.; Boutet, S.C.; Jacobs, K.; Kim, J.; et al. Abstract 2392: Multi-Dimensional Morphology Analysis Enables Identification and Label-Free Enrichment of Heterogeneous Tumor Cell Populations. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aw Yong, K.M.; Zeng, Y.; Vindivich, D.; Phillip, J.M.; Wu, P.-H.; Wirtz, D.; Getzenberg, R.H. Morphological Effects on Expression of Growth Differentiation Factor 15 (GDF15), a Marker of Metastasis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, H.; Roy, H.K.; Pradhan, P.; Goldberg, M.J.; Muldoon, J.; Brand, R.E.; Sturgis, C.; Hensing, T.; Ray, D.; Bogojevic, A.; et al. Nanoscale Cellular Changes in Field Carcinogenesis Detected by Partial Wave Spectroscopy. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 5357–5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretorius, E.; Bester, J.; Vermeulen, N.; Alummoottil, S.; Soma, P.; Buys, A.V.; Kell, D.B. Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Is Accompanied by Significant Morphological and Ultrastructural Changes in Both Erythrocytes and in Thrombin-Generated Fibrin: Implications for Diagnostics. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2015, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Liao, R.; Zeng, N.; Li, P.; Chen, Z.; Liu, X.; Ma, H. Mueller Matrix Polarimetry—An Emerging New Tool for Characterizing the Microstructural Feature of Complex Biological Specimen. J. Light. Technol. 2019, 37, 2534–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, M.; Selig, M.; Azizi, S.; Walz, K.; Lauer, J.; Rolauffs, B. Cell Morphology as a Biological Fingerprint for Describing Chondrocyte Phenotype under Inflammatory Attack. Bone Jt. J. 2023, 105-B, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapetyan, A.; Niazyan, L.; Shushanyan, R.; Abgaryan, T.; Iritsyan, S.; Galechyan, T.; Sargsyan, K.; Grigoryan, A. Morphological Abnormalities of Peripheral Blood Cells among Patients with COVID-19 Disease. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabr, H.; Bastawy, S.; Abdel Aal, A.A.; Khalil, N.M.; Fateen, M. Changes in Peripheral Blood Cellular Morphology as Diagnostic Markers for COVID-19 Infection. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2022, 44, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Sandeep, F.; Olayinka, O.; Gupta, G. Morphologic Changes in Circulating Blood Cells of COVID-19 Patients. Cureus 2021, 13, e13416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, N.A.; Almugadam, B.S.; Elkhider, A. Relationship between the Hematological Indices and COVID-19. Biomed. Biotechnol. Res. J. (BBRJ) 2022, 6, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüke, F.; Orsó, E.; Kirsten, J.; Poeck, H.; Grube, M.; Wolff, D.; Burkhardt, R.; Lunz, D.; Lubnow, M.; Schmidt, B.; et al. Coronavirus Disease 2019 Induces Multi-Lineage, Morphologic Changes in Peripheral Blood Cells. EJHaem 2020, 1, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Meena, R.; Kumar, V.; Kaur, R.; Tiwari, U. Comparison of Hematologic Abnormalities between Hospitalized Coronavirus Disease 2019 Positive and Negative Patients with Correlation to Disease Severity and Outcome. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 3757–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozdnyakova, O.; Connell, N.T.; Battinelli, E.M.; Connors, J.M.; Fell, G.; Kim, A.S. Clinical Significance of CBC and WBC Morphology in the Diagnosis and Clinical Course of COVID-19 Infection. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 155, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Li, S.; Sun, Q.; Zhu, J.; Chen, B.; Xiong, M.; Cao, G. Immune-Inflammatory Parameters in COVID-19 Cases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 2020, 7, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Agarwal, S.; Patni, P.; Pathak, S.; Kaur, M.; Rehman, N. Peripheral Blood Morphology and Hemogram in COVID-19 Patients Correlates with Disease Severity. Med. J. Dr. DY Patil Vidyapeeth 2022, 15, S278–S285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zini, G.; Bellesi, S.; Ramundo, F.; d’Onofrio, G. Morphological Anomalies of Circulating Blood Cells in COVID-19. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 870–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stouten, K.; Riedl, J.A.; Levin, M.-D.; van Gelder, W. Examination of Peripheral Blood Smears: Performance Evaluation of a Digital Microscope System Using a Large-Scale Leukocyte Database. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2015, 37, e137-40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Chen, W.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z. Improved U-Net-Based Leukocyte Segmentation Method. J. Biomed. Opt. 2023, 28, 045002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, J.; Alford, S.; Allan, B.; Anand, V.; Arnon, S.; Arockiaraj, F.G.; Art, J.; Bai, B.; Balasubramaniam, G.M.; Birnbaum, T.; et al. Roadmap on Computational Methods in Optical Imaging and Holography [Invited]. Appl. Phys. B 2024, 130, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchet, A.; Montes, S.; Ballarin, V.; Díaz, I. Intuitionistic Fuzzy Set and Fuzzy Mathematical Morphology Applied to Color Leukocytes Segmentation. Signal Image Video Process. 2020, 14, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goda, K.; Ayazi, A.; Gossett, D.R.; Sadasivam, J.; Lonappan, C.K.; Sollier, E.; Fard, A.M.; Hur, S.C.; Adam, J.; Murray, C.; et al. High-Throughput Single-Microparticle Imaging Flow Analyzer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11630–11635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, K.; Xue, L.; Wang, S. Field of View Scanning Based Quantitative Interferometric Microscopic Cytometers for Cellular Imaging and Analysis. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2018, 81, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Fang, L.; Chen, Y.; Tong, J.; Ning, X.; Feng, L.; Xu, Y.; Yang, D. Performance Comparison of Two Automated Digital Morphology Analyzers for Leukocyte Differential in Patients with Malignant Hematological Diseases: Mindray MC-80 and Sysmex DI-60. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2024, 46, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Diao, Y.; Zheng, J.; Li, X.; Luan, H. Performance Evaluation of the Digital Morphology Analyser Sysmex DI-60 for White Blood Cell Differentials in Abnormal Samples. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, M.; Yoon, S.; Hur, M.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, H.; Park, M.; Kim, H.N. Digital Morphology Analyzer Sysmex DI-60 vs. Manual Counting for White Blood Cell Differentials in Leukopenic Samples: A Comparative Assessment of Risk and Turnaround Time. Ann. Lab. Med. 2022, 42, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Yang, C.; Peng, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yan, F.; Xing, B.; Ji, R. Lensless Shadow Microscopy-Based Shortcut Analysis Strategy for Fast Quantification of Microplastic Fibers Released to Water. Water Res. 2024, 258, 121758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, S.; Su, T.-W.; Tseng, D.K.; Erlinger, A.; Ozcan, A. Lensfree holographic imaging for on-chip cytometry and diagnostics. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudanyali, O.; Tseng, D.; Oh, C.; Isikman, S.O.; Sencan, I.; Bishara, W.; Oztoprak, C.; Seo, S.; Khademhosseini, B.; Ozcan, A. Compact, light-weight and cost-effective microscope based on lensless incoherent holography for telemedicine applications. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 1417–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, M.; Gollier, F.; Melzer, J.E.; McLeod, E. Lensfree Air-Quality Monitoring of Fine and Ultrafine Particulate Matter Using Vapor-Condensed Nanolenses. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 11166–11174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.; Oh, S.; Seo, D.; Kumar, S.; Lee, A.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.-R.; Lee, M.; Seo, S. Field-Portable Seawater Toxicity Monitoring Platform Using Lens-Free Shadow Imaging Technology. Water Res. 2023, 230, 119585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, H.; Castro, C.M.; Shao, H.; Liong, M.; Song, J.; Pathania, D.; Fexon, L.; Min, C.; Avila-Wallace, M.; Zurkiya, O.; et al. Digital Diffraction Analysis Enables Low-Cost Molecular Diagnostics on a Smartphone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5613–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, G.; Yoo, I.-H.; Pack, S.P.; Yang, J.-W.; Ha, U.-H.; Paek, S.-H.; Seo, S. Lens-free shadow image based high-throughput continuous cell monitoring technique. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 38, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Seo, D.; Oh, C.-H.; Nam, M.-H.; Kim, Y.J.; Seo, S. Low-cost telemedicine device performing cell and particle size measurement based on lens-free shadow imaging technology. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.; Oh, S.; Lee, M.; Hwang, Y.; Seo, S. A Field-Portable Cell Analyzer without a Microscope and Reagents. Sensors 2017, 18, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, M.; Shin, S.; Kumar, S.; Seo, D.; Lee, I.; Jun, H.S.; Kang, K.-W.; Kim, B.S.; Nam, M.-H.; Seo, S. Label-Free CD34+ Cell Identification Using Deep Learning and Lens-Free Shadow Imaging Technology. Biosensors 2023, 13, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaghashiya, R.; Shin, S.; Chauhan, V.; Kapadiya, K.; Sanghavi, S.; Seo, S.; Roy, M. Machine Learning Based Lens-Free Shadow Imaging Technique for Field-Portable Cytometry. Biosensors 2022, 12, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, D.; Han, E.; Kumar, S.; Jeon, E.; Nam, M.-H.; Jun, H.S.; Seo, S. Field-Portable Leukocyte Classification Device Based on Lens-Free Shadow Imaging Technique. Biosensors 2022, 12, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostykus, M.; Soulez, F.; Unser, M.; Moser, C. Compact In-Line Lensfree Digital Holographic Microscope. Methods 2018, 136, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, M.; Seo, D.; Oh, S.; Yang, J.-W.; Seo, S. A review of recent progress in lens-free imaging and sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 88, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Ozcan, A. Lensless Digital Holographic Microscopy and Its Applications in Biomedicine and Environmental Monitoring. Methods 2018, 136, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Lee, A.; Shin, S.; Kumar, S.; Nam, M.-H.; Kang, K.-W.; Kim, B.S.; Cho, S.-D.; Kim, H.; Han, S.; et al. Use of a Platform with Lens-Free Shadow Imaging Technology to Monitor Natural Killer Cell Activity. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 261, 116512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, M.; Jin, G.; Seo, D.; Nam, M.-H.; Seo, S. A Simple and Low-Cost Device Performing Blood Cell Counting Based on Lens-Free Shadow Imaging Technique. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 201, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, V.; Dewangan, P.; Vardhan, R.V.; Rinfela, V.; Menon, P.K.; Pal, P. A Study on Chromium Thin Film with Positive Photoresist as a Masking Layer towards the Wet Bulk Micromachining of Borofloat Glass. Micro Nano Syst. Lett. 2024, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeesters, L.; Magnus, I.; Thienpont, H.; Sorgato, S. Broadband Uniform Illumination Optics for Industrial Applications. In Illumination Optics VII, Proceedings of the PIE Optical Systems Design, Strasbourg, France, 7–12 April 2024; Kidger, T.E., David, S., Schupp, T., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, M.; Jin, G.; Pan, J.-H.; Seo, D.; Hwang, Y.; Oh, S.; Lee, M.; Kim, Y.J.; Seo, S. Staining-Free Cell Viability Measurement Technique Using Lens-Free Shadow Imaging Platform. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 224, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.V. Light Scatter Applications. In Introduction to Flow Cytometry; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991; pp. 186–200. ISBN 9780521380614. [Google Scholar]
- Mourant, J.R.; Marina, O.C.; Sanders, C.K. The Contribution of Specific Organelles to Side Scatter. In Biomedical Applications of Light Scattering VII, Proceedings of the SPIE BiOS, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2–7 February 2013; Wax, A.P., Backman, V., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sack, U. CD64 Expression by Neutrophil Granulocytes. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2017, 92, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Terada, A.; Kita, H. CD66b Regulates Adhesion and Activation of Human Eosinophils. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 8454–8462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheon, H.; Kumar, S.; Lee, I.; Shin, S.; Jang, H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Nam, M.-H.; Jun, H.S.; Seo, S. Multi-Channel Cellytics for Rapid and Cost-Effective Monitoring of Leukocyte Activation. Biosensors 2025, 15, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15030143
Cheon H, Kumar S, Lee I, Shin S, Jang H, Lee Y-S, Nam M-H, Jun HS, Seo S. Multi-Channel Cellytics for Rapid and Cost-Effective Monitoring of Leukocyte Activation. Biosensors. 2025; 15(3):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15030143
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheon, Hojin, Samir Kumar, Inha Lee, Sanghoon Shin, Hyeji Jang, Young-Sun Lee, Myung-Hyun Nam, Hyun Sik Jun, and Sungkyu Seo. 2025. "Multi-Channel Cellytics for Rapid and Cost-Effective Monitoring of Leukocyte Activation" Biosensors 15, no. 3: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15030143
APA StyleCheon, H., Kumar, S., Lee, I., Shin, S., Jang, H., Lee, Y.-S., Nam, M.-H., Jun, H. S., & Seo, S. (2025). Multi-Channel Cellytics for Rapid and Cost-Effective Monitoring of Leukocyte Activation. Biosensors, 15(3), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15030143




