Urinary Metabolomic Changes and Potential Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage Biomarkers Identification in Trained Young Males Following Acute Intermittent Rowing Training
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Exercise Protocol
2.3. Post-Exercise Muscle Function Assessment
2.4. Blood Biochemical Analysis
2.5. Urinary Metabolomics Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Blood Indicators and EIMD
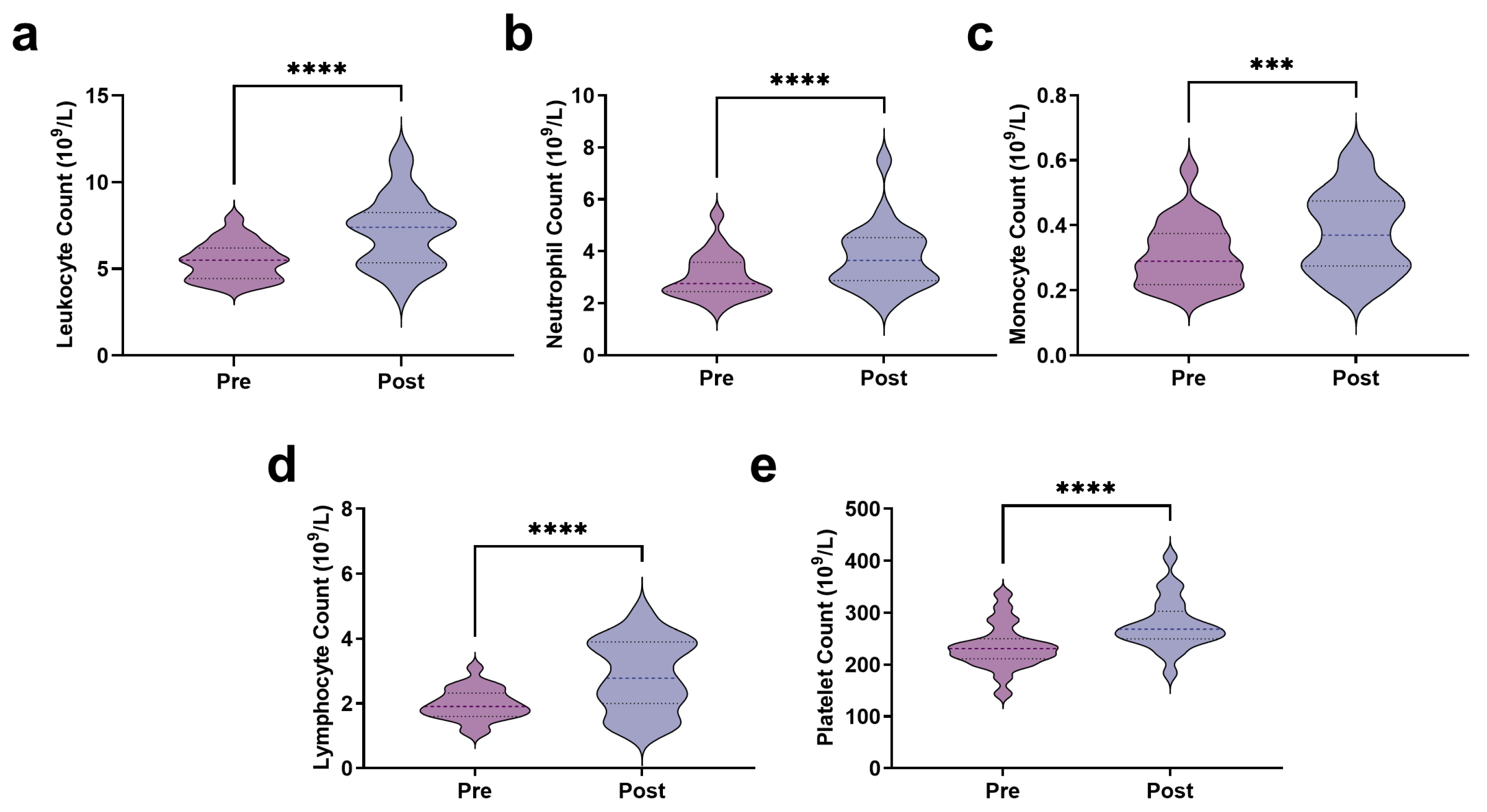
3.2. Immune Stress Response Following AIRT
3.3. Metabolomics Analysis Results
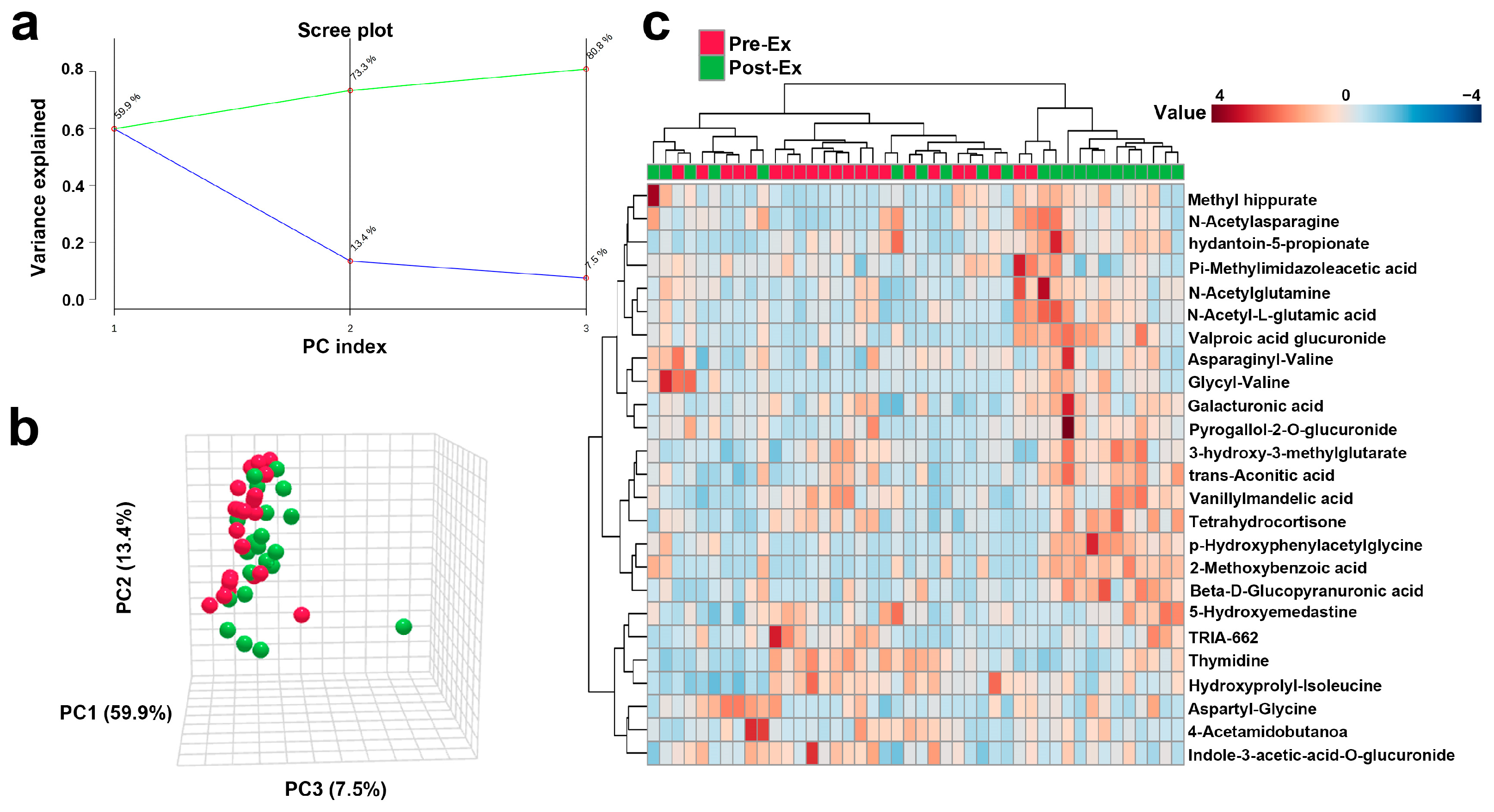
3.3.1. Overall Trend of Urinary Metabolites Following AIRT
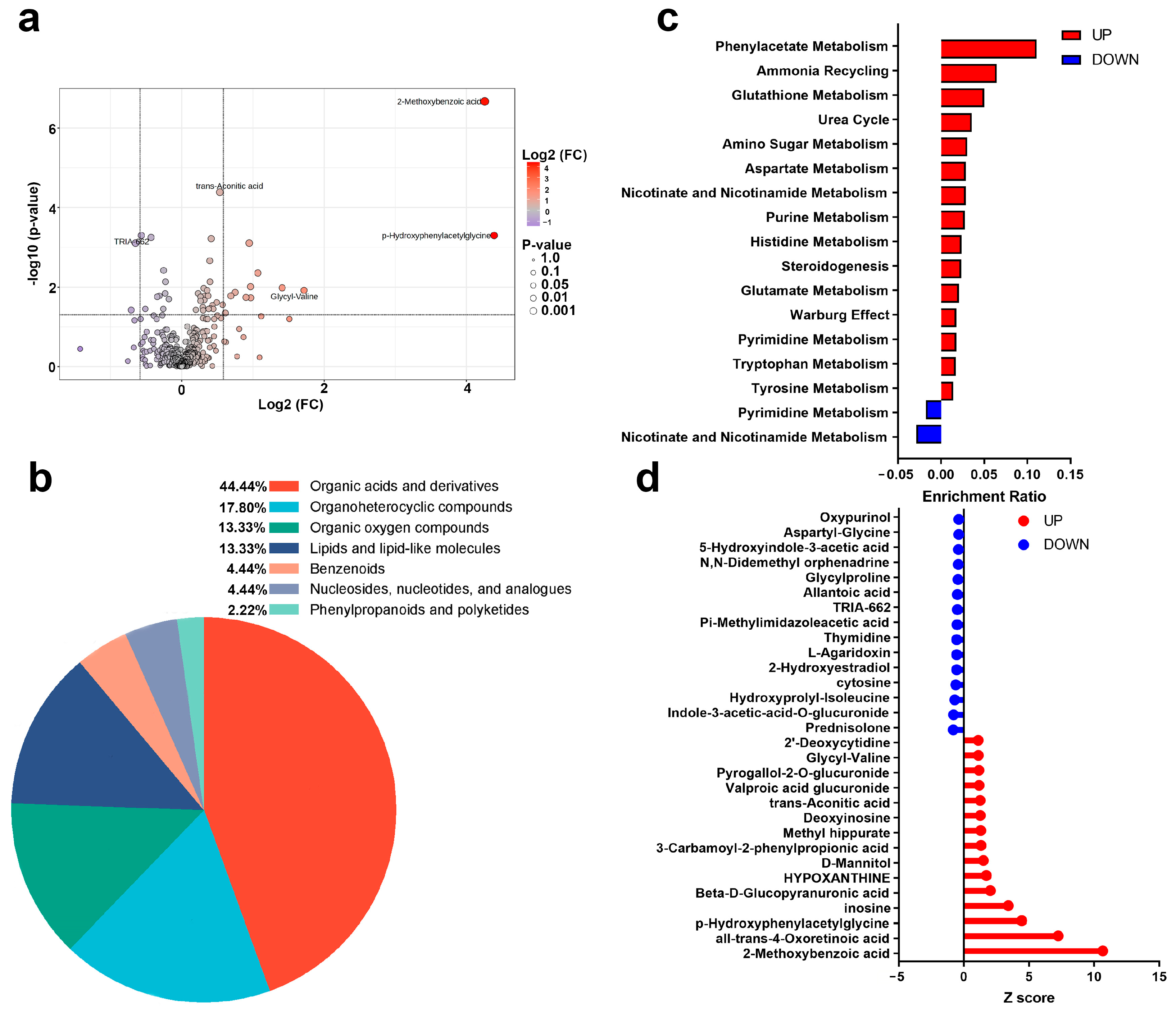
3.3.2. Changes in Urinary Metabolites and Metabolic Pathways After AIRT
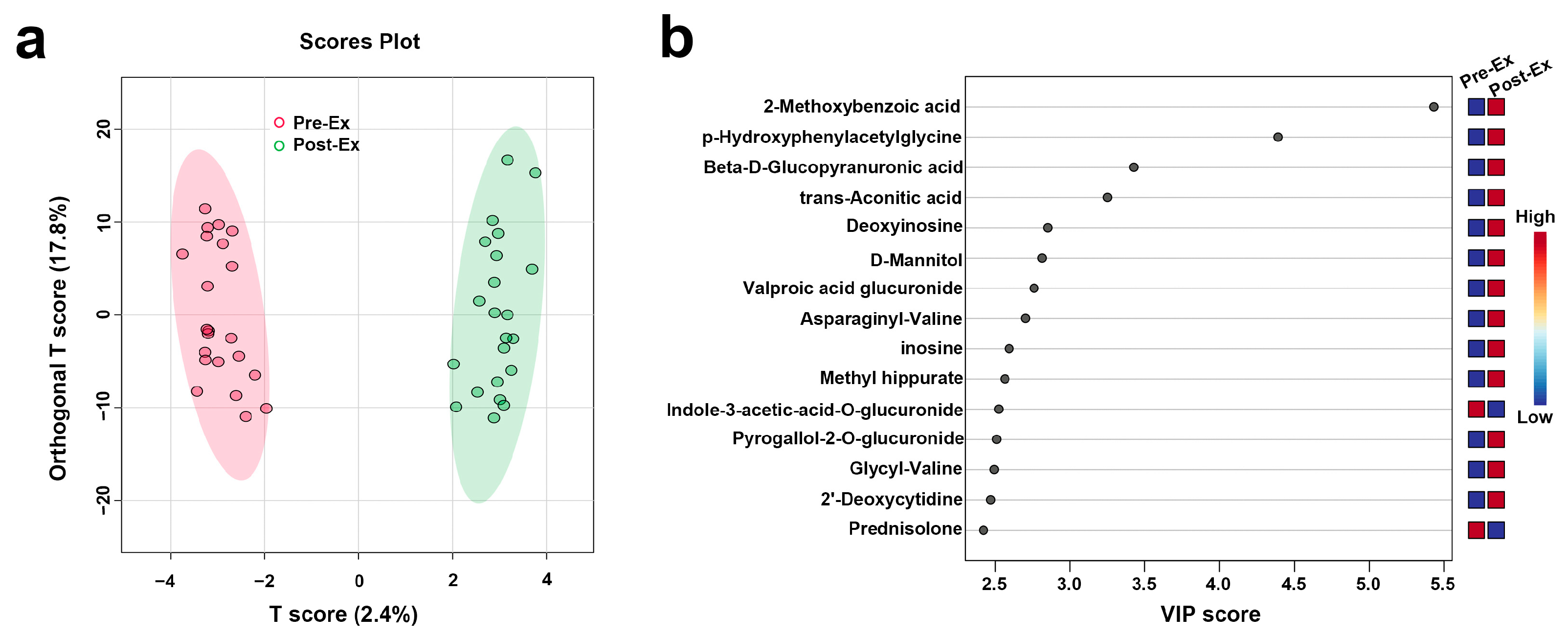
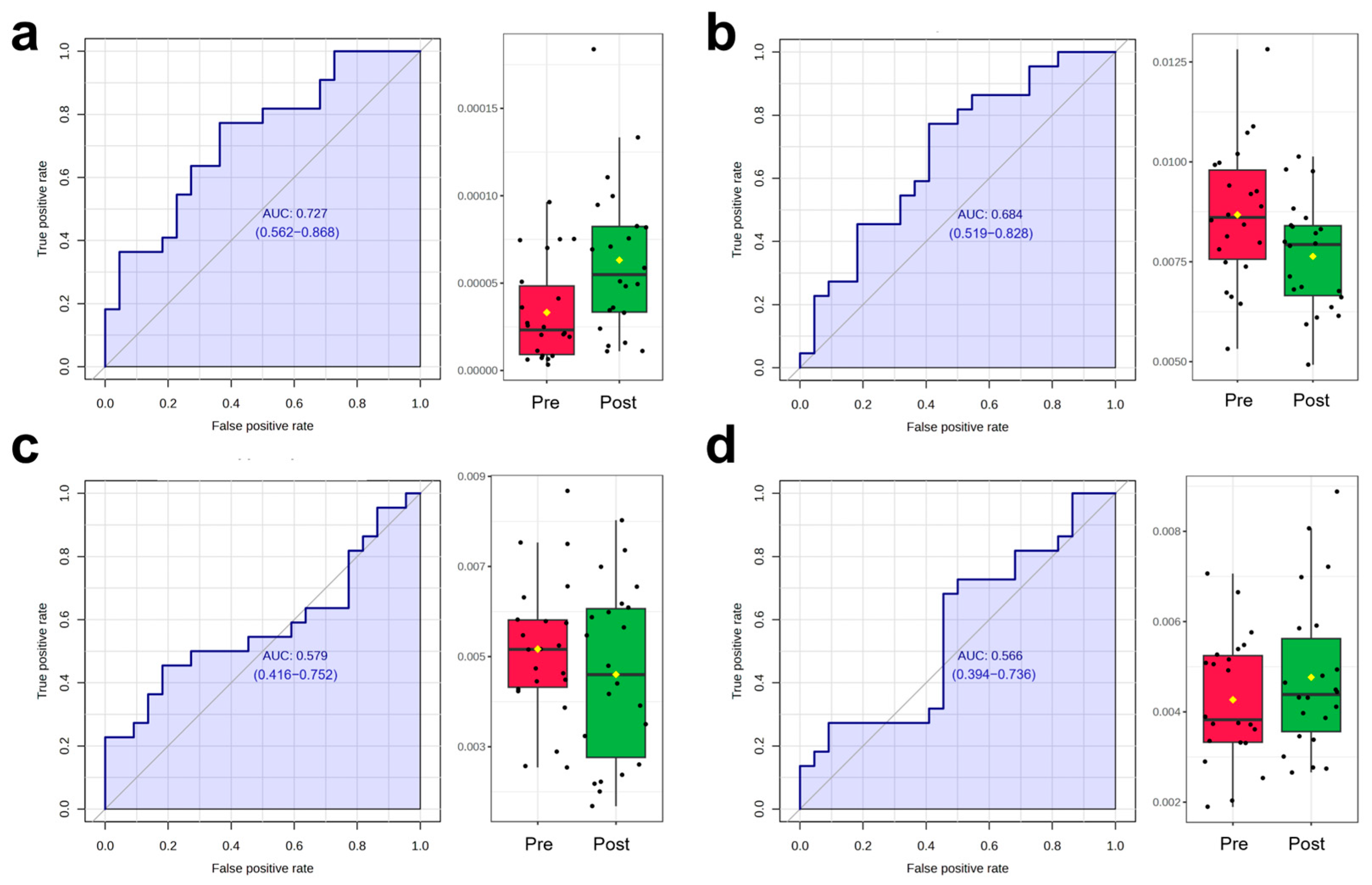
3.3.3. OPLS-DA and ROC Analysis Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIRT | Acute Intermittent Rowing Training |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| CK | Creatine Kinase |
| CK-MB | Creatine Kinase-MB Isoenzyme |
| CMJ | Countermovement Jump |
| DOMS | Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness |
| EIMD | Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage |
| HBDH | Hydroxybutyrate Dehydrogenase |
| HIIT | High-Intensity Interval Training |
| LDH | Lactate Dehydrogenase |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| PC | Principal Component |
| OPLS-DA | Orthogonal Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis |
| R | Correlation Coefficients |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| VIP | Variable Importance in Projection |
References
- Bessa, A.L.; Oliveira, V.N.; Agostini, G.G.; Oliveira, R.J.; Oliveira, A.C.; White, G.E.; Wells, G.D.; Teixeira, D.N.S.; Espindola, F.S. Exercise Intensity and Recovery: Biomarkers of Injury, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarkson, P.M.; Hubal, M.J. Exercise-induced muscle damage in humans. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002, 81, S52–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, J.C.; Bosch, A.N.; Lambert, M.I. Metabolic consequences of exercise-induced muscle damage. Sports Med. 2007, 37, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, H.; Li, Y.L. Inflammation balance in skeletal muscle damage and repair. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1133355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoi, W.; Naito, Y.; Takanami, Y.; Kawai, Y.; Sakuma, K.; Ichikawa, H.; Yoshida, N.; Yoshikawa, T. Oxidative stress and delayed-onset muscle damage after exercise. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 37, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, G.; Crameri, R.; Benestad, H.B.; Fjeld, J.G.; Mørkrid, L.; Hallén, J.; Raastad, T. Time course of leukocyte accumulation in human muscle after eccentric exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2010, 42, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stožer, A.; Vodopivc, P.; Križančić Bombek, L. Pathophysiology of exercise-induced muscle damage and its structural, functional, metabolic, and clinical consequences. Physiol. Res. 2020, 69, 565–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, E.N.; Yardley, H.; Harrison, A.; Eglit, G.M.L.; Antonio, J.; Turcotte, C.; Bonn-Miller, M.O. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, repeated-dose pilot study of the safety, tolerability, and preliminary effects of a cannabidiol (CBD)- and cannabigerol (CBG)-based beverage powder to support recovery from delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS). J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2023, 20, 2280113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preisner, F.; Friedmann-Bette, B.; Wehrstein, M.; Vollherbst, D.F.; Heiland, S.; Bendszus, M.; Hilgenfeld, T. In Vivo Visualization of Tissue Damage Induced by Percutaneous Muscle Biopsy via Novel High-Resolution MR Imaging. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2021, 53, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, H.J.; Caballero-García, A.; Pérez-Valdecantos, D.; Roche, E.; Noriega, D.C.; Córdova-Martínez, A. Effects of Vitamin D in Post-Exercise Muscle Recovery. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Manville, R.W.; Abbott, G.W. The plant-derived alkaloid aloperine prevents ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced sudden cardiac death. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e22999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Campo, D.J.; Ávila-Gandía, V.; Alacid, F.; Soto-Méndez, F.; Alcaraz, P.E.; López-Román, F.J.; Rubio-Arias, J.Á. Muscle damage, physiological changes, and energy balance in ultra-endurance mountain-event athletes. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, N.; Behringer, M.; Reichel, T.; Wahl, P.; Simon, P.; Krüger, K.; Zimmer, P.; Stöggl, T. Blood-Based Biomarkers for Managing Workload in Athletes: Considerations and Recommendations for Evidence-Based Use of Established Biomarkers. Sports Med. 2023, 53, 1315–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markus, I.; Constantini, K.; Goldstein, N.; Amedi, R.; Bornstein, Y.; Stolkovsky, Y.; Vidal, M.; Lev-Ari, S.; Balaban, R.; Leibou, S.; et al. Age Differences in Recovery Rate Following an Aerobic-Based Exercise Protocol Inducing Muscle Damage Among Amateur, Male Athletes. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 916924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Kunugi, H. Skeletal Muscle Damage in COVID-19: A Call for Action. Medicina 2021, 57, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavouras, S.A. Assessing hydration status. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2002, 5, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribarri, J.; El Shamy, O.; Sharma, S.; Winston, J. COVID-19-Associated Acute Kidney Injury and Quantified Protein Catabolic Rate: A Likely Effect of Cytokine Storm on Muscle Protein Breakdown. Kidney Med. 2021, 3, 60–63.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Sanchis-Gomar, F. Exertional hematuria: Definition, epidemiology, diagnostic and clinical considerations. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2019, 57, 1818–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, K.E.; Balanos, G.M.; Bradley, C.; Fountain, A.; Bradwell, A.R.; Lucas, S.J.E. Postexercise urinary alpha-1 acid glycoprotein is not dependent on hypoxia. J. Appl. Physiol. 2022, 132, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Chen, A.P.; Li, J.Y.; Sun, Z.; Yan, S.L.; Xu, K.Y. Mechanism of the Effect of High-Intensity Training on Urinary Metabolism in Female Water Polo Players Based on UHPLC-MS Non-Targeted Metabolomics Technique. Healthcare 2021, 9, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, L.; Chen, P.; Xu, X. Integration of metabolomics and proteomics to reveal the metabolic characteristics of high-intensity interval training. Analyst 2020, 145, 6500–6510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schranner, D.; Kastenmüller, G.; Schönfelder, M.; Römisch-Margl, W.; Wackerhage, H. Metabolite Concentration Changes in Humans After a Bout of Exercise: A Systematic Review of Exercise Metabolomics Studies. Sports Med. Open 2020, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistner, S.; Mack, C.I.; Rist, M.J.; Krüger, R.; Egert, B.; Biniaminov, N.; Engelbert, A.K.; Seifert, S.; Dörr, C.; Ferrario, P.G.; et al. Acute effects of moderate vs. vigorous endurance exercise on urinary metabolites in healthy, young, physically active men-A multi-platform metabolomics approach. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1028643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.J.; Lee, J.D.; Jeon, H.S.; Kim, A.R.; Kim, S.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, K.B. Metabolic Profiling of Eccentric Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage in Human Urine. Toxicol. Res. 2018, 34, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawker, G.A.; Mian, S.; Kendzerska, T.; French, M. Measures of adult pain: Visual Analog Scale for Pain (VAS Pain), Numeric Rating Scale for Pain (NRS Pain), McGill Pain Questionnaire (MPQ), Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ), Chronic Pain Grade Scale (CPGS), Short Form-36 Bodily Pain Scale (SF-36 BPS), and Measure of Intermittent and Constant Osteoarthritis Pain (ICOAP). Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63 (Suppl. 11), S240–S252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.H.; Mendes, R.R.; Franca, C.S.; Da Silva-Grigoletto, M.E.; Pereira da Silva, D.R.; Antoniolli, A.R.; de Oliveira e Silva, A.M.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J. Acute leucocyte, muscle damage, and stress marker responses to high-intensity functional training. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernat-Adell, M.D.; Collado-Boira, E.J.; Moles-Julio, P.; Panizo-González, N.; Martínez-Navarro, I.; Hernando-Fuster, B.; Hernando-Domingo, C. Recovery of Inflammation, Cardiac, and Muscle Damage Biomarkers After Running a Marathon. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2021, 35, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilar, E.; Collado-Boira, E.; Guerrero, C.; Folch-Ayora, A.; Salas-Medina, P.; Hernando, C.; Baliño, P.; Muriach, M. Is There a Role of Beetroot Consumption on the Recovery of Oxidative Status and Muscle Damage in Ultra-Endurance Runners? Nutrients 2024, 16, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokora, I.; Kempa, K.; Chrapusta, S.J.; Langfort, J. Effects of downhill and uphill exercises of equivalent submaximal intensities on selected blood cytokine levels and blood creatine kinase activity. Biol. Sport 2014, 31, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammouda, O.; Chtourou, H.; Chahed, H.; Ferchichi, S.; Kallel, C.; Miled, A.; Chamari, K.; Souissi, N. Diurnal variations of plasma homocysteine, total antioxidant status, and biological markers of muscle injury during repeated sprint: Effect on performance and muscle fatigue—A pilot study. Chronobiol. Int. 2011, 28, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alleva, M.; Sanz, J.M.; Giovanelli, N.; Graniero, F.; Mari, L.; Spaggiari, R.; Sergi, D.; Ghisellini, S.; Passaro, A.; Lazzer, S. The influence of prolonged aerobic exercise on cardiac, muscular, and renal biomarkers in trained individuals with obesity. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2025, 125, 1485–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.; Sullivan, K.; Kim, C.; Winchester, L.J.; Fedewa, M.V. Using Force Plates to Monitor the Recovery of Vertical Jump Performance After Strenuous Exercise: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2025, 10, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosvoglou, A.; Fatouros, I.G.; Poulios, A.; Tsatalas, T.; Papanikolaou, K.; Karampina, E.; Liakoua, C.A.; Tsimeas, P.; Karanika, P.; Tsoukas, D.; et al. Recovery kinetics following eccentric exercise is volume-dependent. J. Sports Sci. 2023, 41, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heileson, J.L.; Harris, D.R.; Tomek, S.; Ritz, P.P.; Rockwell, M.S.; Barringer, N.D.; Forsse, J.S.; Funderburk, L.K. Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation and Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage: EPA or DHA? Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2024, 56, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, C. Effects of ischaemic post-conditioning on eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage. Biol. Sport 2024, 41, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tossige-Gomes, R.; Ottone, V.O.; Oliveira, P.N.; Viana, D.J.S.; Araújo, T.L.; Gripp, F.J.; Rocha-Vieira, E. Leukocytosis, muscle damage and increased lymphocyte proliferative response after an adventure sprint race. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2014, 47, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Nakaji, S.; Yamada, M.; Liu, Q.; Kurakake, S.; Okamura, N.; Kumae, T.; Umeda, T.; Sugawara, K. Impact of a competitive marathon race on systemic cytokine and neutrophil responses. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Ruiz, J.; Alcalá-Carmona, B.; Alejandre-Aguilar, R.; Gómez-Martín, D. Inflammatory myopathies and beyond: The dual role of neutrophils in muscle damage and regeneration. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1113214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, B.V.; Bigley, A.B.; LaVoy, E.C.; Laughlin, M.; Pedlar, C.; Simpson, R.J. Lymphocytes and monocytes egress peripheral blood within minutes after cessation of steady state exercise: A detailed temporal analysis of leukocyte extravasation. Physiol. Behav. 2018, 194, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurowski, M.; Seys, S.; Bonini, M.; Del Giacco, S.; Delgado, L.; Diamant, Z.; Kowalski, M.L.; Moreira, A.; Rukhadze, M.; Couto, M. Physical exercise, immune response, and susceptibility to infections-current knowledge and growing research areas. Allergy 2022, 77, 2653–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistner, S.; Rist, M.J.; Döring, M.; Dörr, C.; Neumann, R.; Härtel, S.; Bub, A. An NMR-Based Approach to Identify Urinary Metabolites Associated with Acute Physical Exercise and Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Healthy Humans-Results of the KarMeN Study. Metabolites 2020, 10, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G.D.; Farrell, L.; Wood, M.J.; Martinovic, M.; Arany, Z.; Rowe, G.C.; Souza, A.; Cheng, S.; McCabe, E.L.; Yang, E.; et al. Metabolic signatures of exercise in human plasma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 33ra37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, D.; Vuckovic, I.; Kunz, H.E.; Lanza, I.R. Metabolomic response to acute resistance exercise in healthy older adults by 1H-NMR. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0301037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, I.; Alberghina, L.; Vai, M. Nicotinamide, Nicotinamide Riboside and Nicotinic Acid-Emerging Roles in Replicative and Chronological Aging in Yeast. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holeček, M. Roles of malate and aspartate in gluconeogenesis in various physiological and pathological states. Metabolism 2023, 145, 155614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, A.F.G.; Fogacci, F.; Di Micoli, V.; Angeloni, C.; Giovannini, M.; Borghi, C. Purine Metabolism Dysfunctions: Experimental Methods of Detection and Diagnostic Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Shao, X.; Mao, X.; Fu, Y.; Yang, Q. Triple-helix β-glucan-based self-assemblies, synthesis, characterization and anticarcinogenic effect. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 286, 138427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saidi, K.; Zouhal, H.; Boullosa, D.; Dupont, G.; Hackney, A.C.; Bideau, B.; Granacher, U.; Ben Abderrahman, A. Biochemical Markers and Wellness Status During a Congested Match Play Period in Elite Soccer Players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2022, 17, 605–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | Mean | Standard Deviation (SD) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 22 | 1.72 |
| Resting Heart Rate | 68.64 | 5.73 |
| Height (cm) | 178.64 | 4.98 |
| Weight (kg) | 76.24 | 10.47 |
| Body Fat Percentage (%) | 22.03 | 4.77 |
| Body Mass Index | 23.83 | 2.46 |
| Muscle Mass (kg) | 55.86 | 6.06 |
| Metabolite Name | VIP | R | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | Pyridoxamine | 1.054 | −0.407 |
| cytosine | 2.122 | −0.403 | |
| LDH | cytosine | 2.122 | −0.709 |
| Pyridoxamine | 1.054 | −0.600 | |
| Phenylacetaldehyde | 1.077 | −0.573 | |
| 2′-Deoxycytidine | 2.470 | 0.303 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, Y.; Yi, Y.; Shi, X.; Bo, S. Urinary Metabolomic Changes and Potential Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage Biomarkers Identification in Trained Young Males Following Acute Intermittent Rowing Training. Biosensors 2025, 15, 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15120803
Cheng Y, Yi Y, Shi X, Bo S. Urinary Metabolomic Changes and Potential Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage Biomarkers Identification in Trained Young Males Following Acute Intermittent Rowing Training. Biosensors. 2025; 15(12):803. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15120803
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Yang, Yue Yi, Xuefeng Shi, and Shumin Bo. 2025. "Urinary Metabolomic Changes and Potential Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage Biomarkers Identification in Trained Young Males Following Acute Intermittent Rowing Training" Biosensors 15, no. 12: 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15120803
APA StyleCheng, Y., Yi, Y., Shi, X., & Bo, S. (2025). Urinary Metabolomic Changes and Potential Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage Biomarkers Identification in Trained Young Males Following Acute Intermittent Rowing Training. Biosensors, 15(12), 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15120803






