MFF-ClassificationNet: CNN-Transformer Hybrid with Multi-Feature Fusion for Breast Cancer Histopathology Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- To address the problem that traditional methods in breast histopathological image classification struggle to simultaneously capture local details and global semantic information, resulting in insufficient feature representation, a novel Multi-Feature Fusion Classification Network (MFF-ClassificationNet) was designed, which uses a parallel dual-branch architecture to enhance local details while modeling global features.
- (2)
- To address the limitation of existing methods in multi-scale feature fusion, which restricts the model’s ability to comprehensively utilize information at different levels, a CBAM-SE Fusion (CSF) block was introduced, integrating SE, CBAM, and IRMLP modules to achieve adaptive multi-scale feature fusion.
- (3)
- Extensive experiments conducted on BreakHis and BACH datasets demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed method in terms of classification accuracy and generalization capability.
2. Dataset Used
2.1. BreakHis Dataset
2.2. BACH Dataset
3. Proposed Method
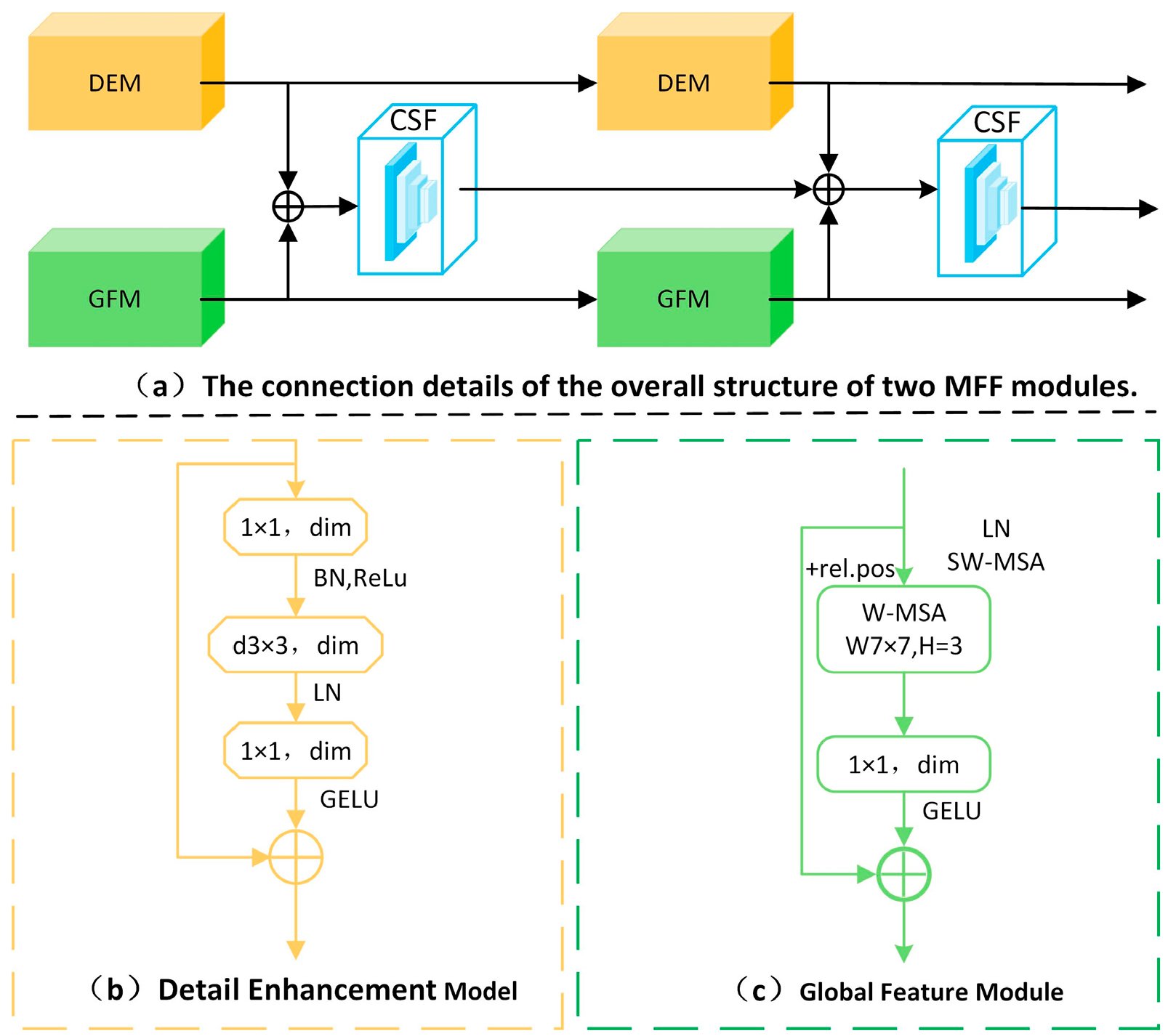
3.1. Multi-Feature Fusion Network
3.2. Multi-Feature Fusion Module
3.2.1. Detail Enhancement Module
3.2.2. Global Feature Module
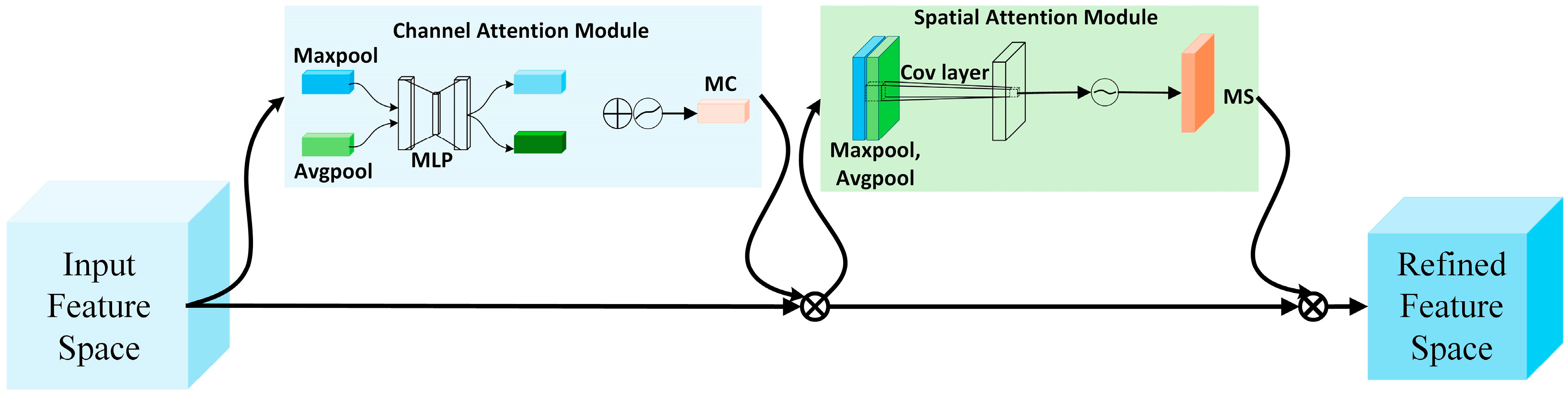
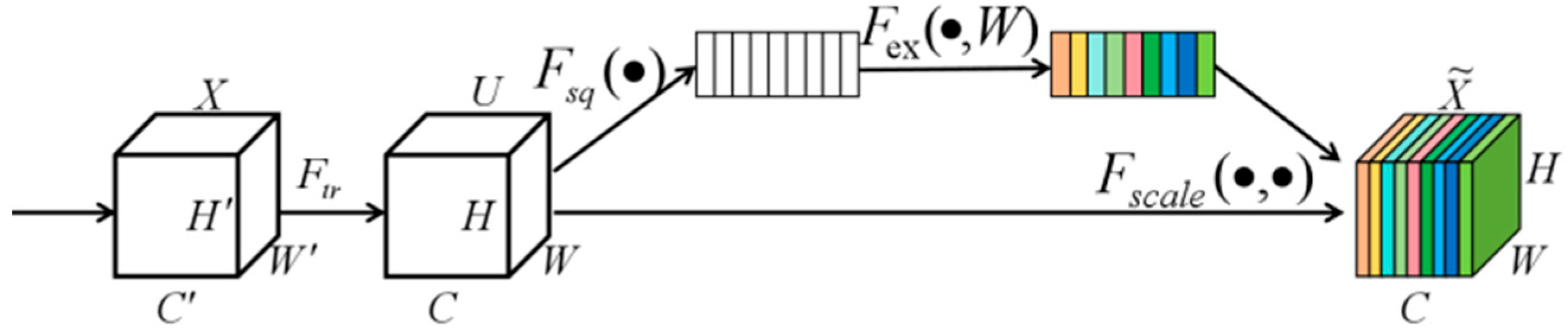
3.3. CSF Module
3.3.1. CBAM Attention Module
3.3.2. SE Attention Module
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Experimental System Setup
4.2. Evaluation Indicators
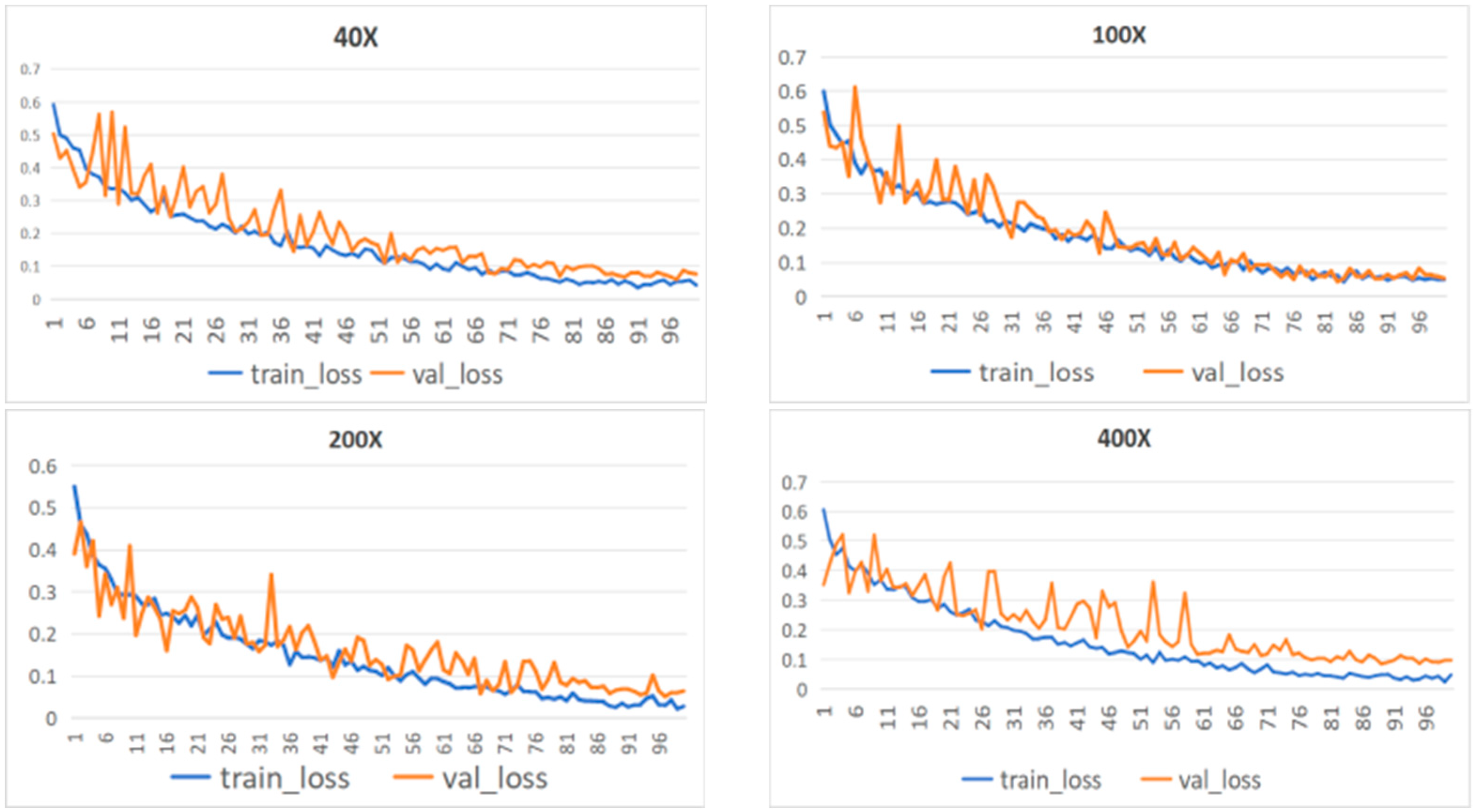
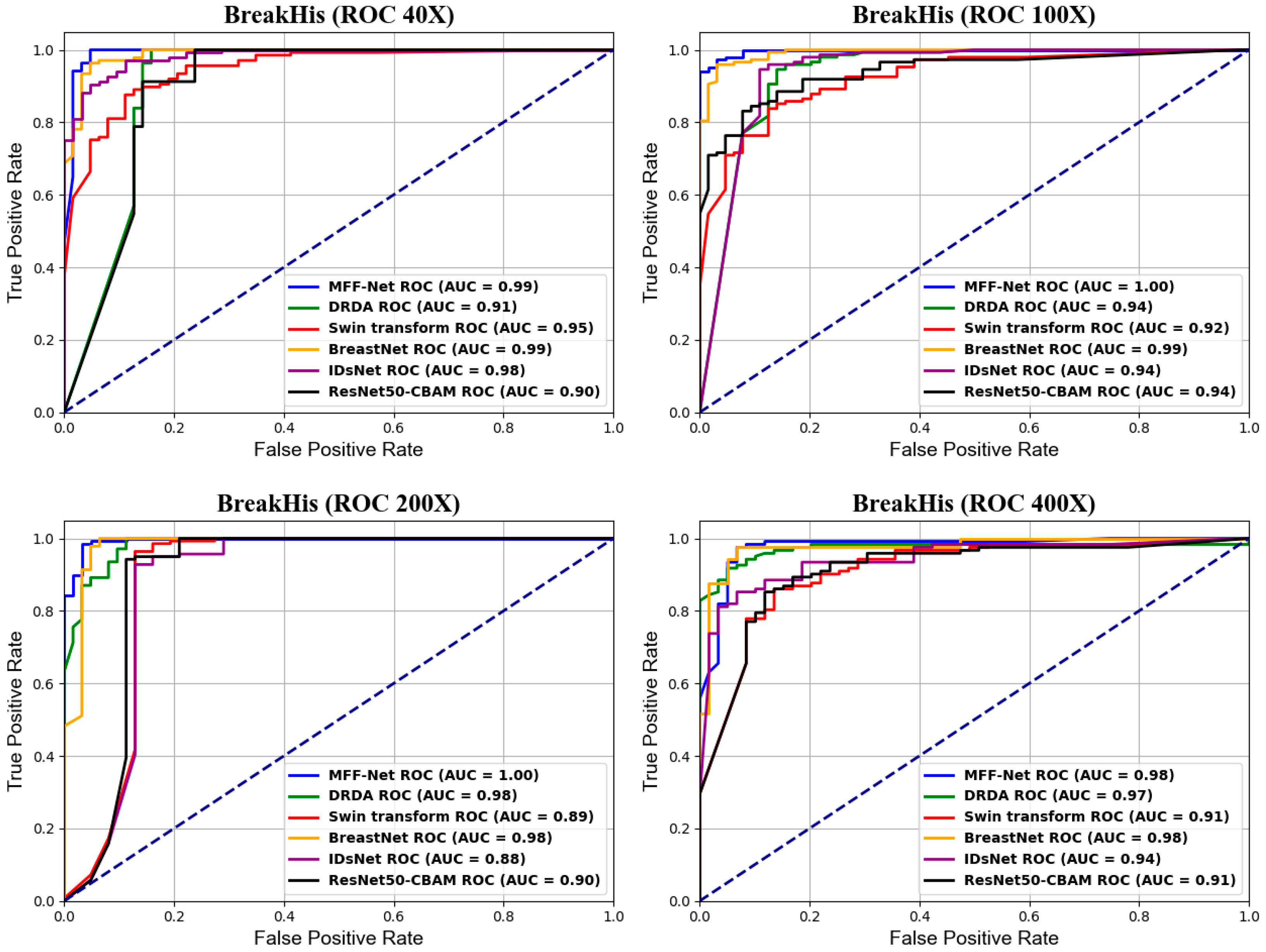
4.3. MFF-ClassificationNet Model Evaluation
4.4. Comparison Experiments
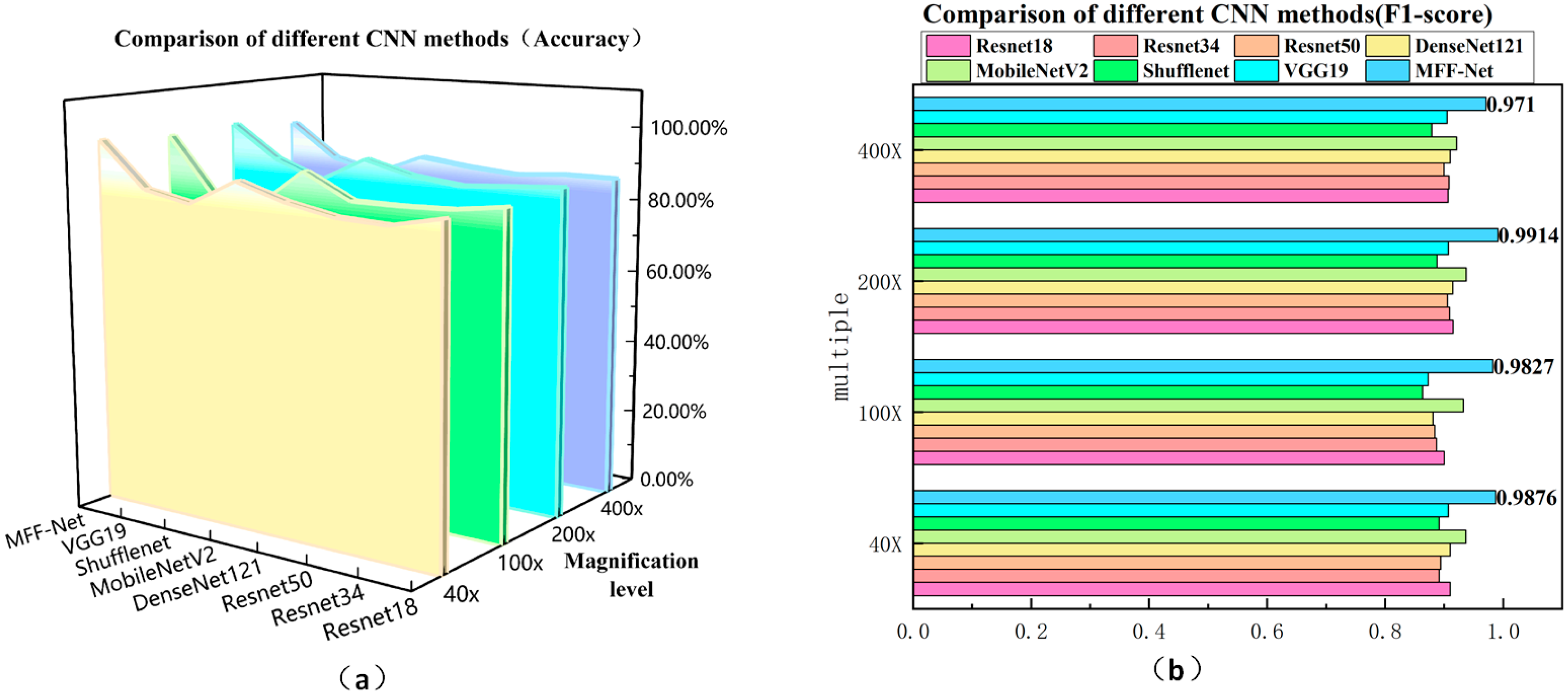
4.4.1. Comparison of Classification Performance of Different CNNs
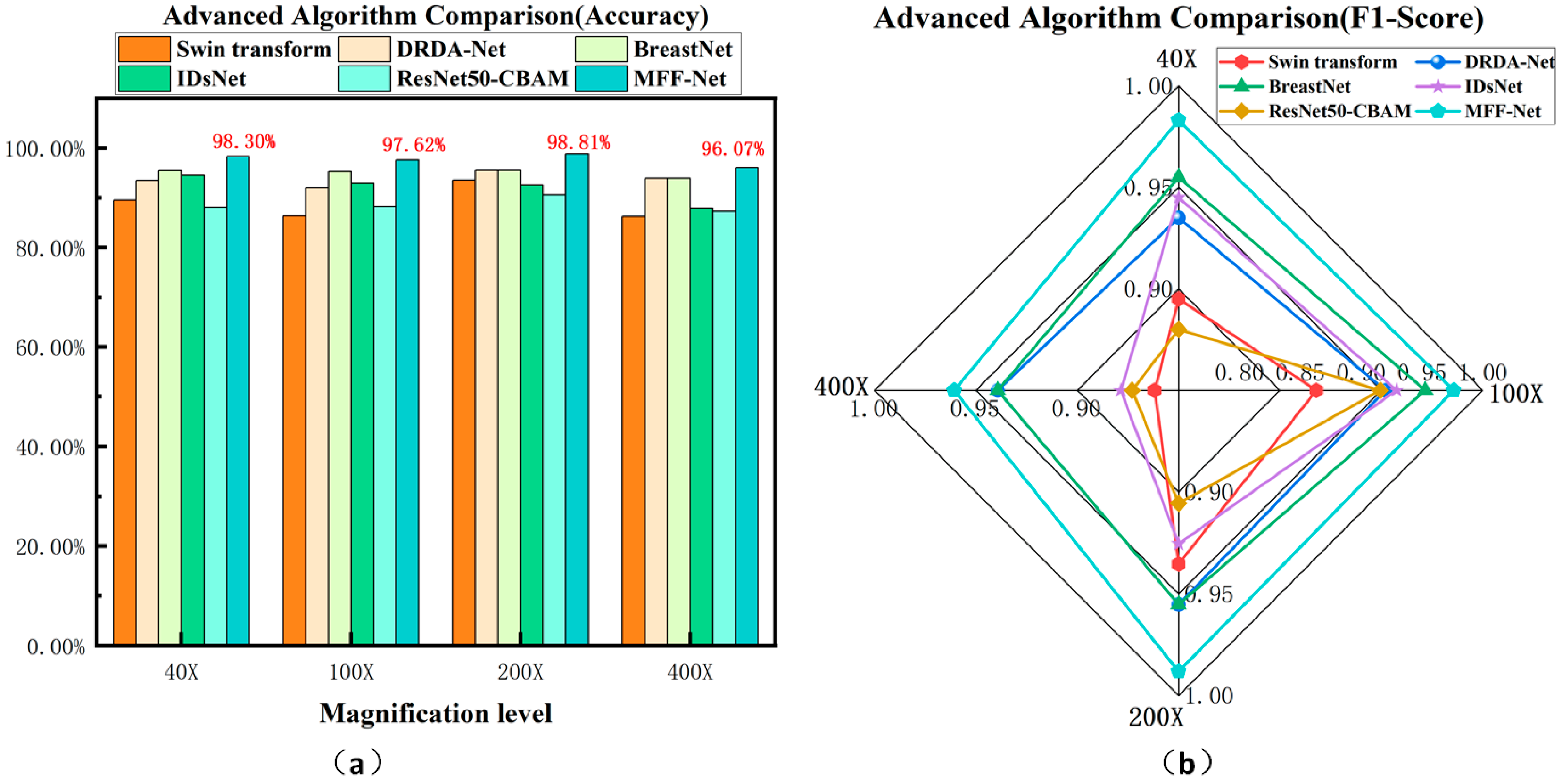
4.4.2. Advanced Comparison of MFF-ClassificationNet Models
4.5. Generalization Experiments
4.6. Visualization
4.7. Ablation Experiments
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, K.D.; Nogueira, L.; Devasia, T.; Mariotto, A.B.; Yabroff, K.R.; Jemal, A.; Kramer, J.; Siegel, R.L. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 409–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M.P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J.-P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R.; et al. World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, D.A.; Sharkas, M.; Attallah, O. Breast Cancer Diagnosis Using an Efficient CAD System Based on Multiple Classifiers. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eluri, E.P.; Kancharla, J.; Gupta, V.K.; Prasad, K.; Sung, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Tej, M.B.; Choi, R.; Lee, J.-H.; Han, Y.-K.; et al. The role of NF-κB in breast cancer initiation, growth, metastasis, and resistance to chemotherapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 163, 114822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, G.S.; Eluri, E.P.; Bandaru, S.S.; Varaprasad, G.L.; Nagaraju, G.P.; Malla, R.R.; Huh, Y.S.; Han, Y.-K. HOTAIR: A potential metastatic, drug-resistant and prognostic regulator of breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Chen, Z.; Tan, M.; Elingarami, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Deng, Y.; He, N.; Li, S.; Fu, J.; et al. A review on methods for diagnosis of breast cancer cells and tissues. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petay, M.; Cherfan, M.; Bouderlique, E.; Reguer, S.; Mathurin, J.; Dazzi, A.; L’Heronde, M.; Daudon, M.; Letavernier, E.; Deniset-Besseau, A. Multiscale approach to provide a better physicochemical description of women breast microcalcifications. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2022, 25, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanhol, F.A.; Oliveira, L.S.; Petitjean, C.; Heutte, L. A dataset for breast cancer histopathological image classification. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 63, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavanhally, A.N.; Ganesan, S.; Agner, S.; Monaco, J.P.; Feldman, M.D.; Tomaszewski, J.E.; Bhanot, G.; Madabhushi, A. Computerized image-based detection and grading of lymphocytic infiltration in HER2+ breast cancer histopathology. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 57, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, S.; Gazinska, P.; Hipwell, J.H.; Mertzanidou, T.; Naidoo, K.; Williams, N.; Pinder, S.; Hawkes, D.J. Automated Classification of Breast Cancer Stroma Maturity From Histological Images. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 2344–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veta, M.; Pluim, J.P.W.; van Diest, P.J.; Viergever, M.A. Breast cancer histopathology image analysis: A review. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 1400–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaviani, S.; Han, K.J.; Sohn, I. Adversarial attacks and defenses on AI in medical imaging informatics: A survey. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 198, 116815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardou, D.; Zhang, K.; Ahmad, S.M. Classification of breast cancer based on histology images using convolutional neural networks. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 24680–24693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhong, S.; Liu, Y. Deep residual learning for image steganalysis. Multimed Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 10437–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; van der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, N.; Gupta, R. Dual Multi-Scale CNN for Multi-layer Breast Cancer Classification at Multi-Resolution. In Proceedings of the 2022 4th International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication Control and Networking (ICAC3N), Greater Noida, India, 16–17 December 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanhol, F.A.; Oliveira, L.S.; Petitjean, C.; Heutte, L. Breast cancer histopathological image classification using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 2560–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Li, L.; Jiang, M. Automatic classification of breast cancer histopathological images based on deep feature fusion and enhanced routing. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 65, 102341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Dey, A.; Singh, P.K.; Sarkar, R. DRDA-Net: Dense residual dual-shuffle attention network for breast cancer classification using histopathological images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 145, 105437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All You Need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (NeurIPS 2017); Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16×16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Yu, W.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Tay, F.E.H.; Feng, J.; Yan, S. Tokens-to-token ViT: Training vision transformers from scratch on ImageNet. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aresta, G.; Araújo, T.; Kwok, S.; Chennamsetty, S.S.; Safwan, M.; Alex, V.; Marami, B.; Prastawa, M.; Chan, M.; Donovan, M.; et al. BACH: Grand challenge on breast cancer histology images. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 56, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 9992–10002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2018), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.-C. MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6848–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abimouloud, M.L.; Bensid, K.; Elleuch, M.; Ben Ammar, M.; Kherallah, M. Vision transformer based convolutional neural network for breast cancer histopathological images classification. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 86833–86868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, T.-Q. Classification of breast cancer histopathological images using interleaved DenseNet with SENet (IDSNet). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulaal, A.H.; Valizadeh, M.; Albaker, B.M.; Yassin, R.A.; Amirani, M.C.; Shah, A.F.M.S. Enhancing breast cancer classification using a modified GoogLeNet architecture with attention mechanism. Al-Iraqia J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2024, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, R.; Pandey, N.N.; Mahapatra, S. BMEA-ViT: Breast cancer classification using lightweight customized vision transformer architecture with multi-head external attention. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 44317–44329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroni, G.L.; Rasotto, L.; Roitero, K.; Tulisso, A.; Di Loreto, C.; Della Mea, V. Optimizing Vision Transformers for Histopathology: Pretraining and Normalization in Breast Cancer Classification. J. Imaging 2024, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhipa, P.C.; Upadhyay, R.; Pihlgren, G.G.; Saini, R.; Uchida, S.; Liwicki, M. Magnification Prior: A Self-Supervised Method for Learning Representations on Breast Cancer Histopathological Images. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2–7 January 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, Y.; Abdullakutty, F.; Al Maadeed, S.; Bouridane, A.; Hamoudi, R. Breast cancer detection based on histological images using fusion of diffusion model outputs. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 21463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Lu, R.; Sun, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q. Breast cancer histopathology image classification using transformer with discrete wavelet transform. Med. Eng. Phys. 2025, 138, 104317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 336–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
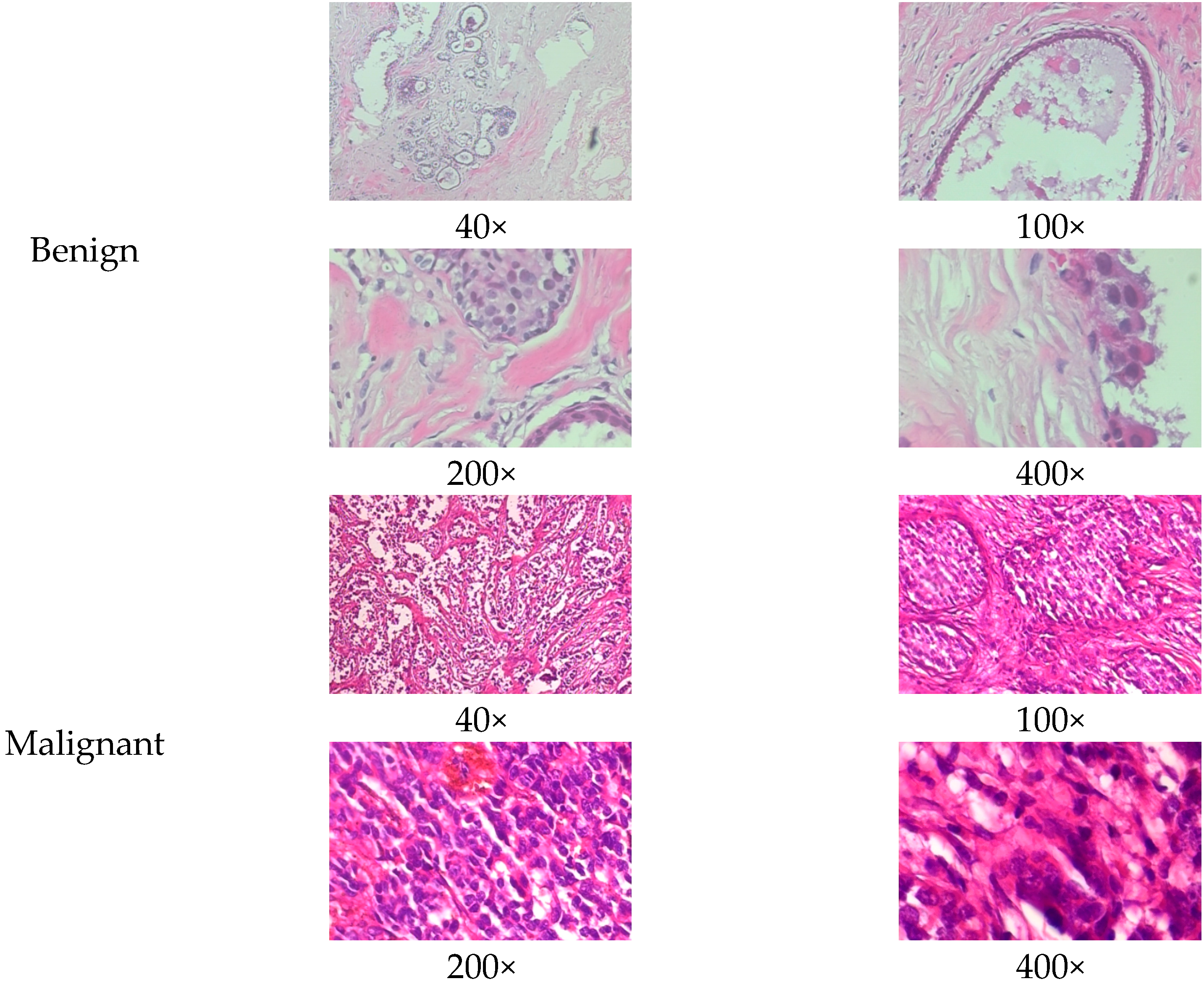
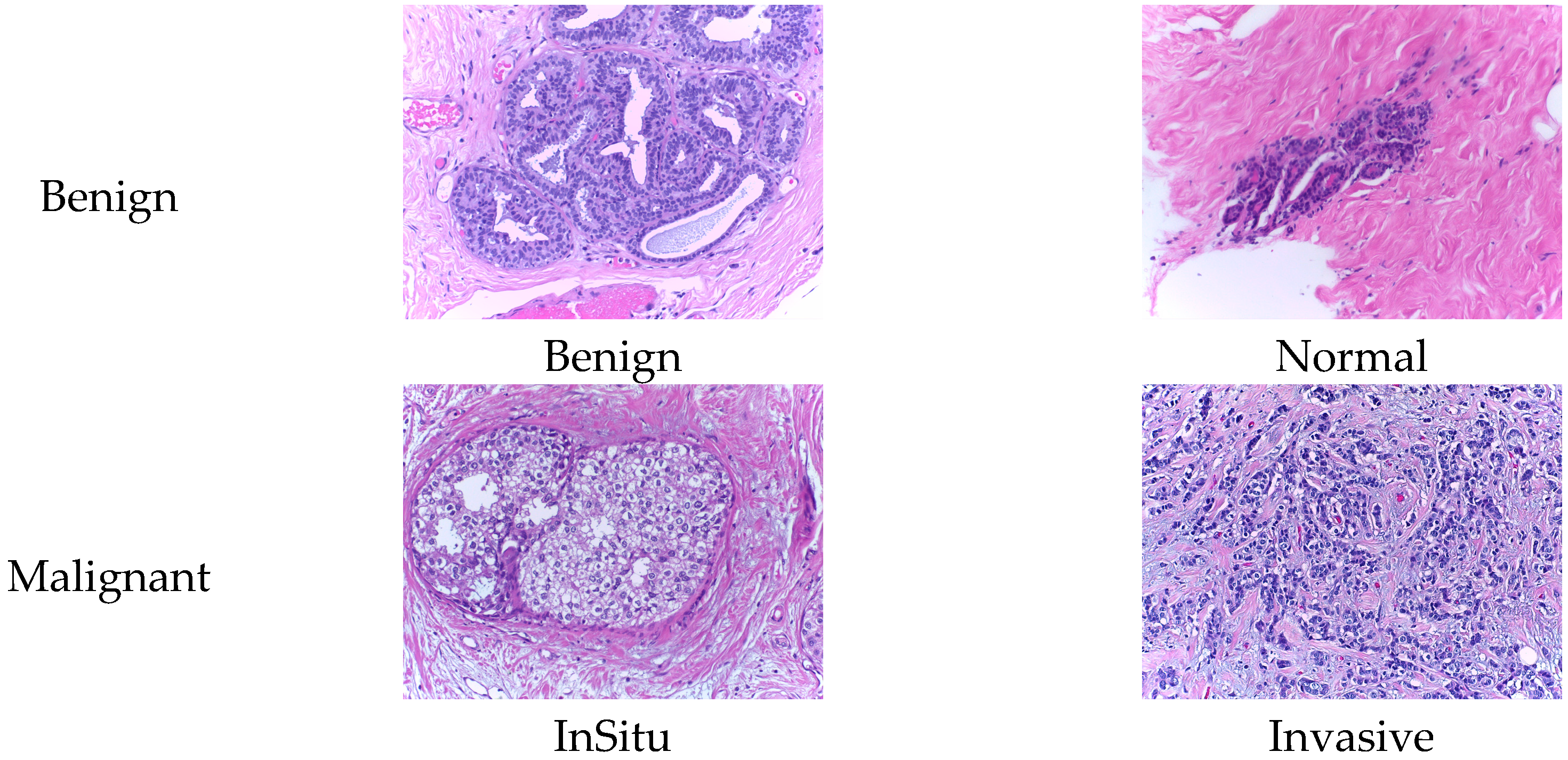





| Magnification Level | Benign | Malignant | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40× | 625 | 1370 | 1995 |
| 100× | 644 | 1437 | 2081 |
| 200× | 623 | 1390 | 2013 |
| 400× | 588 | 1232 | 1820 |
| Total | 2480 | 5429 | 7909 |
| Category | Subtype | Subtype Count | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benign | Normal | 100 | 200 |
| Benign | 100 | ||
| Malignant | InSitu Carcinoma | 100 | 200 |
| InvasiveCarcinoma | 100 |
| Magnification Level | Train Set | Validation Set | Test Set |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40× | 1596 | 199 | 200 |
| 100× | 1654 | 204 | 211 |
| 200× | 1611 | 201 | 201 |
| 400× | 1458 | 181 | 181 |
| Input Shape | Train Set | Validation Set | Test Set |
|---|---|---|---|
| (224, 224, 3) | 320 | 40 | 40 |
| Predicted Label Positive | Predicted Label Negative | |
|---|---|---|
| Actual Label Positive | True Positive (TP) | False Negative (FN) |
| Actual Label Negative | False Positive (FP) | True Negative (TN) |
| Magnification Level | Class | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Support | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40× | Benign | 96.83 ± 1.42% | 97.80 ± 1.56% | 96.83 ± 1.42% | 97.29 ± 0.38% | 63 ± 1 | |
| Malignant | 98.98 ± 0.74% | 98.55 ± 0.63% | 98.98 ± 0.74% | 98.76 ± 0.18% | 137 ± 1 | ||
| Overall (Mean ± SD) | 98.30 ± 0.24% | 98.55 ± 0.63% | 98.98 ± 0.74% | 98.76 ± 0.18% | [98.13%, 98.47%] | ||
| 100× | Benign | 97.22 ± 0.62% | 95.19 ± 1.68% | 97.22 ± 0.62% | 96.19 ± 0.94% | 64 ± 1 | |
| Malignant | 97.80 ± 0.80% | 98.75 ± 0.27% | 97.80 ± 0.80% | 98.27 ± 0.44% | 148 ± 3 | ||
| Overall (Mean ± SD) | 97.62 ± 0.60% | 98.75 ± 0.27% | 97.80 ± 0.80% | 98.27 ± 0.44% | [97.26%, 97.96%] | ||
| 200× | Benign | 98.08 ± 1.86% | 98.09 ± 1.18% | 98.08 ± 1.86% | 98.08 ± 1.21% | 62 ± 1 | |
| Malignant | 99.14 ± 0.54% | 99.14 ± 0.83% | 99.14 ± 0.54% | 99.14 ± 0.54% | 139 ± 1 | ||
| Overall (Mean ± SD) | 98.81 ± 0.74% | 99.14 ± 0.83% | 99.14 ± 0.54% | 99.14 ± 0.54% | [98.25%, 99.38%] | ||
| 400× | Benign | 93.30 ± 1.80% | 94.57 ± 0.0122 | 93.30 ± 0.0180 | 93.91 ± 0.0101 | 59 ± 1 | |
| Malignant | 97.41 ± 0.61% | 96.80 ± 0.83% | 97.41 ± 0.61% | 97.10 ± 0.46% | 122 ± 2 | ||
| Overall (Mean ± SD) | 96.07 ± 0.63% | 96.80 ± 0.83% | 97.41 ± 0.61% | 97.10 ± 0.46% | [95.42%, 96.73%] |
| Model | Metric | Results on Different Scales of the BrakHis Dataset | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40× | 100× | 200× | 400× | ||
| Resnet18 | Accuracy | 87.00% | 86.32% | 88.06% | 87.29% |
| Precision | 86.27% | 91.61% | 89.66% | 89.60% | |
| Recall | 96.35% | 88.51% | 93.53% | 91.80% | |
| F1-Score | 91.03 | 90.03% | 91.55% | 90.69% | |
| Resnet34 | Accuracy | 84.00% | 84.43% | 87.06% | 87.29% |
| Precision | 83.02% | 89.66% | 88.44% | 88.37% | |
| Recall | 96.35% | 87.84% | 93.53% | 93.44% | |
| F1-Score | 89.19% | 88.74% | 90.91% | 90.84% | |
| Resnet50 | Accuracy | 84.50% | 83.96% | 86.07% | 86.19% |
| Precision | 83.97% | 89.04% | 84.91% | 88.19% | |
| Recall | 95.62% | 87.84% | 97.12% | 91.80% | |
| F1-Score | 89.42% | 88.44% | 90.60% | 89.96% | |
| DenseNet121 | Accuracy | 87.00% | 83.96% | 87.56% | 87.29% |
| Precision | 86.27% | 91.30% | 87.01% | 86.67% | |
| Recall | 96.35% | 85.14% | 96.40% | 95.90% | |
| F1-Score | 91.03% | 88.11% | 91.47% | 91.05% | |
| MobileNetV2 | Accuracy | 91.00% | 90.57% | 91.04% | 88.95% |
| Precision | 89.93% | 92.67% | 90.60% | 88.64% | |
| Recall | 97.81% | 93.92% | 97.12% | 95.90% | |
| F1-Score | 93.71% | 93.29% | 93.75% | 92.13% | |
| Shufflenet | Accuracy | 84.00% | 80.19% | 84.08% | 83.43% |
| Precision | 83.02% | 83.13% | 86.39% | 86.51% | |
| Recall | 96.35% | 89.86% | 91.37% | 89.34% | |
| F1-Score | 89.19% | 86.36% | 88.81% | 87.90% | |
| VGG19 | Accuracy | 86.50% | 81.60% | 89.05% | 86.74% |
| Precision | 96.35% | 90.54% | 97.12% | 94.26% | |
| Recall | 96.35% | 90.54% | 97.12% | 94.26% | |
| F1-Score | 90.72% | 87.30% | 90.72% | 90.55% | |
| MFF-ClassificationNet | Accuracy | 98.30% | 97.62% | 98.81% | 96.07% |
| Precision | 98.55% | 98.75% | 99.14% | 96.80% | |
| Recall | 98.98% | 97.80% | 99.14% | 97.41% | |
| F1-Score | 98.76% | 98.27% | 99.14% | 97.10% | |
| Factor | Metric Model | IDsNet (2021) | Swin Transform (2021) | DRDA-Net (2022) | MOBILE VIT (2024) | VIT (2024) | Modified GoogLeNet (2024) | BMEA-ViT (2025) | MFF-ClassificationNet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40× | Accuracy | 94.50% | 89.50% | 93.50% | 94.33% | 96.50% | 97.24% | 95.74% | 98.30% |
| Precision | 95.00% | 89.73% | 93.06% | 93.34% | 95.88% | 96.89% | 94.50% | 98.55% | |
| 5 | Recall | 97.08% | 95.62% | 97.81% | 93.34% | 95.88% | 96.69% | 94.50% | 98.98% |
| F1-Score | 96.03% | 92.58% | 95.37% | 93.34% | 96.50% | 96.79% | 95.00% | 98.76% | |
| 100× | Accuracy | 92.92% | 86.32% | 91.98% | 92.00% | 94.66% | 96.88% | 96.96% | 97.62% |
| Precision | 94.63% | 88.39% | 93.38% | 92.49% | 95.18% | 96.09% | 96.00% | 98.75% | |
| Recall | 95.27% | 92.57% | 95.27% | 92.49% | 95.18% | 96.67% | 95.00% | 97.80% | |
| F1-Score | 94.95% | 90.43% | 94.31% | 92.49% | 94.66% | 96.37% | 95.50% | 98.27% | |
| 200× | Accuracy | 92.54% | 93.53% | 95.52% | 96.91% | 97.87% | 97.77% | 98.18% | 98.81% |
| Precision | 94.93% | 92.57% | 95.14% | 97.32% | 98.70% | 97.29% | 97.50% | 99.14% | |
| Recall | 94.24% | 98.56% | 98.56% | 97.32% | 98.70% | 97.50% | 98.00% | 99.14% | |
| F1-Score | 94.58% | 95.47% | 96.82% | 97.31% | 97.87% | 97.40% | 98.00% | 99.14% | |
| 400× | Accuracy | 87.85% | 86.19% | 93.92% | 92.03% | 98.56% | 98.08% | 97.25% | 96.07% |
| Precision | 93.10% | 86.47% | 95.87% | 89.91% | 98.35% | 97.71% | 96.50% | 96.80% | |
| Recall | 88.52% | 94.26% | 95.08% | 89.91% | 98.35% | 97.92% | 97.00% | 97.41% | |
| F1-Score | 90.76% | 90.20% | 95.47% | 89.91% | 98.56% | 97.81% | 97.00% | 97.10% |
| Model | Accuracy Results on the BACH Dataset |
|---|---|
| CNN + SVM | 83.30% |
| Inception V4 | 93.70% |
| VGG16 | 93.80% |
| Inception-ResNet V2 | 93.75% |
| EfficientNet-B0 (transformer decoder-based fusion) | 96.66 |
| DWNAT-Net | 93.75% |
| MFF-ClassificationNet | 97.50% |
| Image Class | BreakHis Dataset(40×) | |||
| Benign | Malignant | |||
| Original images | 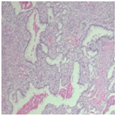 | 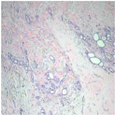 |  |  |
| MFF-ClassificationNet heatmaps | 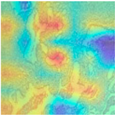 | 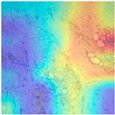 | 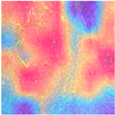 |  |
| Image Class | BreakHis dataset (100×) | |||
| benign | malignant | |||
| Original images | 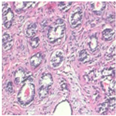 | 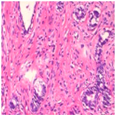 | 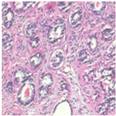 | 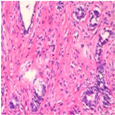 |
| MFF-ClassificationNet heatmaps | 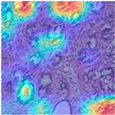 |  |  |  |
| Image Class | BreakHis dataset (200×) | |||
| benign | malignant | |||
| Original images | 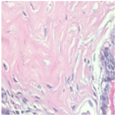 | 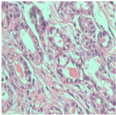 |  |  |
| MFF-ClassificationNet heatmaps | 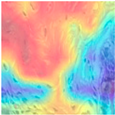 |  |  | 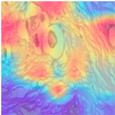 |
| Image Class | BreakHis dataset (400×) | |||
| benign | malignant | |||
| Original images | 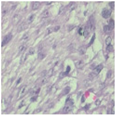 | 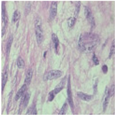 | 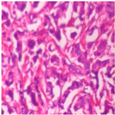 | 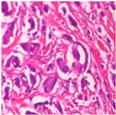 |
| MFF-ClassificationNet heatmaps | 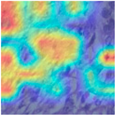 | 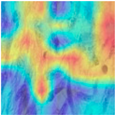 | 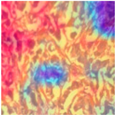 |  |
| Image Class | BACH Dataset | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benign | Malignant | |||
| Original images | 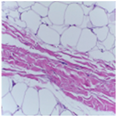 | 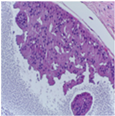 | 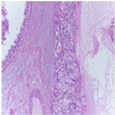 | 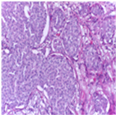 |
| MFF-ClassificationNet heatmaps | 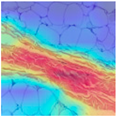 | 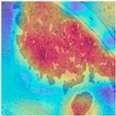 | 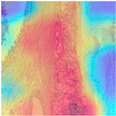 | 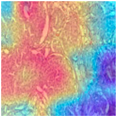 |
| Method | DEM | GFM | SE | CBAM | 40× | 100× | 200× | 400× |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEM | √ | 95.00% | 92.92% | 95.50% | 93.37% | |||
| GFM | √ | 95.50% | 93.80% | 94.02% | 92.81% | |||
| DGF | √ | √ | 96.00% | 94.33% | 95.50% | 94.47% | ||
| DGSF | √ | √ | √ | 96.50% | 96.00% | 96.02% | 95.58% | |
| DGCF | √ | √ | √ | 96.50% | 95.75% | 96.02% | 95.10% | |
| MFF-ClassificationNet | √ | √ | √ | √ | 98.30% | 97.62% | 98.81% | 96.07% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Li, L.; Zou, H.; Cui, J. MFF-ClassificationNet: CNN-Transformer Hybrid with Multi-Feature Fusion for Breast Cancer Histopathology Classification. Biosensors 2025, 15, 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15110718
Wang X, Wang G, Li L, Zou H, Cui J. MFF-ClassificationNet: CNN-Transformer Hybrid with Multi-Feature Fusion for Breast Cancer Histopathology Classification. Biosensors. 2025; 15(11):718. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15110718
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaoli, Guowei Wang, Luhan Li, Hua Zou, and Junpeng Cui. 2025. "MFF-ClassificationNet: CNN-Transformer Hybrid with Multi-Feature Fusion for Breast Cancer Histopathology Classification" Biosensors 15, no. 11: 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15110718
APA StyleWang, X., Wang, G., Li, L., Zou, H., & Cui, J. (2025). MFF-ClassificationNet: CNN-Transformer Hybrid with Multi-Feature Fusion for Breast Cancer Histopathology Classification. Biosensors, 15(11), 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15110718





