Tear-Based Ocular Wearable Biosensors for Human Health Monitoring
Abstract
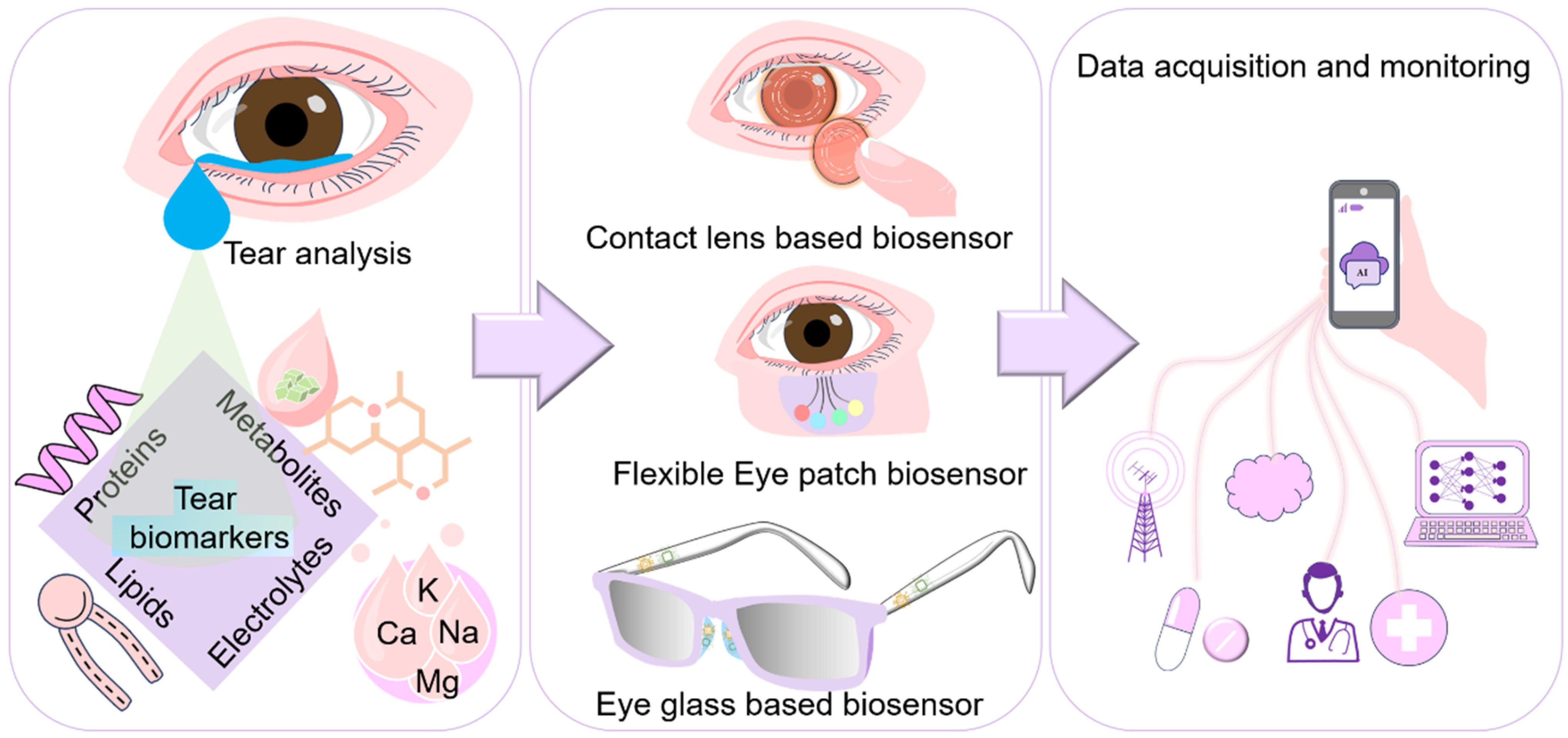
1. Introduction
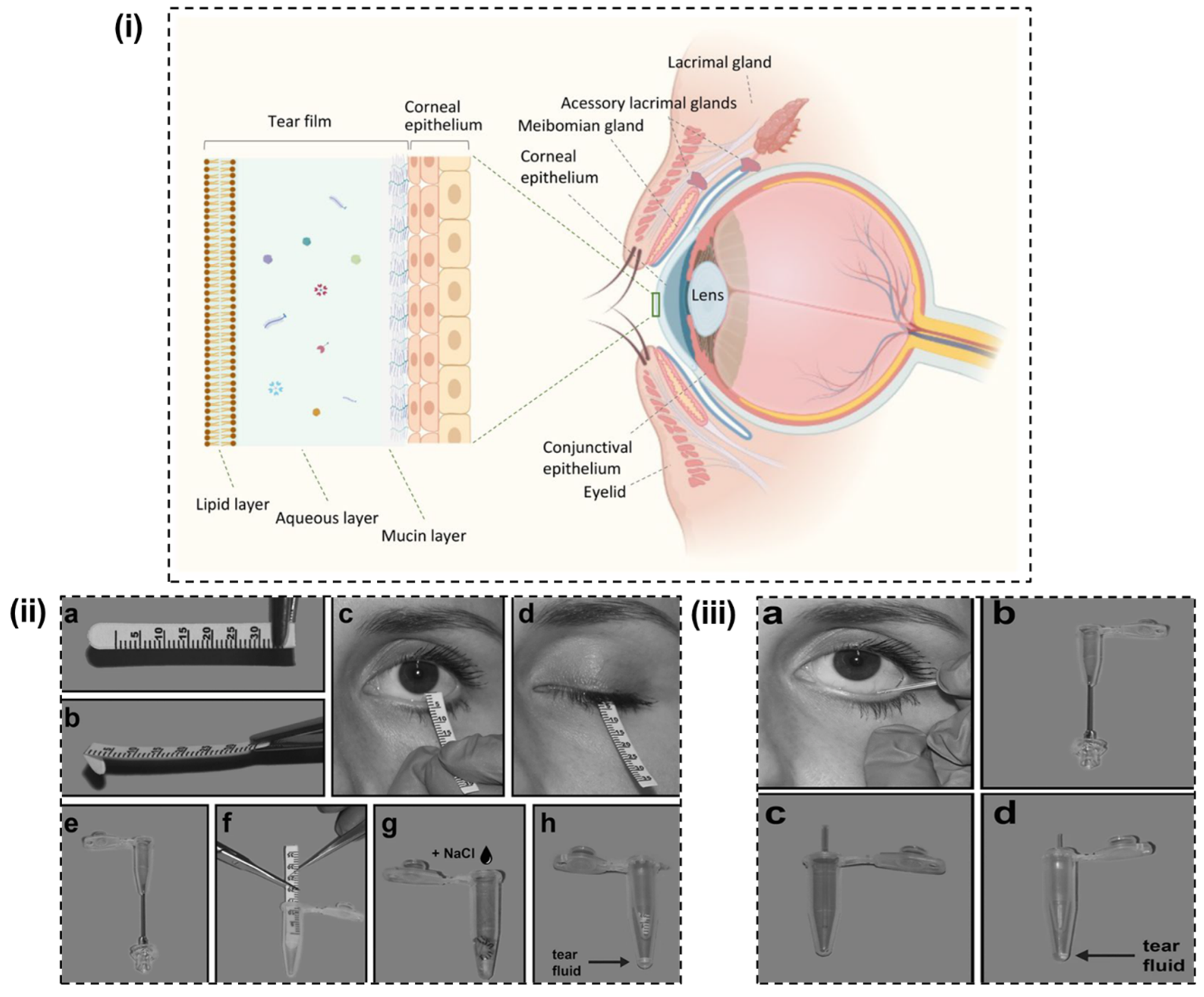
2. Insights into Tear
3. Biomarkers in Tear
3.1. Proteins
3.2. Lipids
3.3. Electrolytes
3.4. Metabolites
4. Tear-Based Wearable Bio-Sensing Technologies
4.1. Glucose Monitoring

4.2. pH Level Monitoring
4.3. Lactate Monitoring
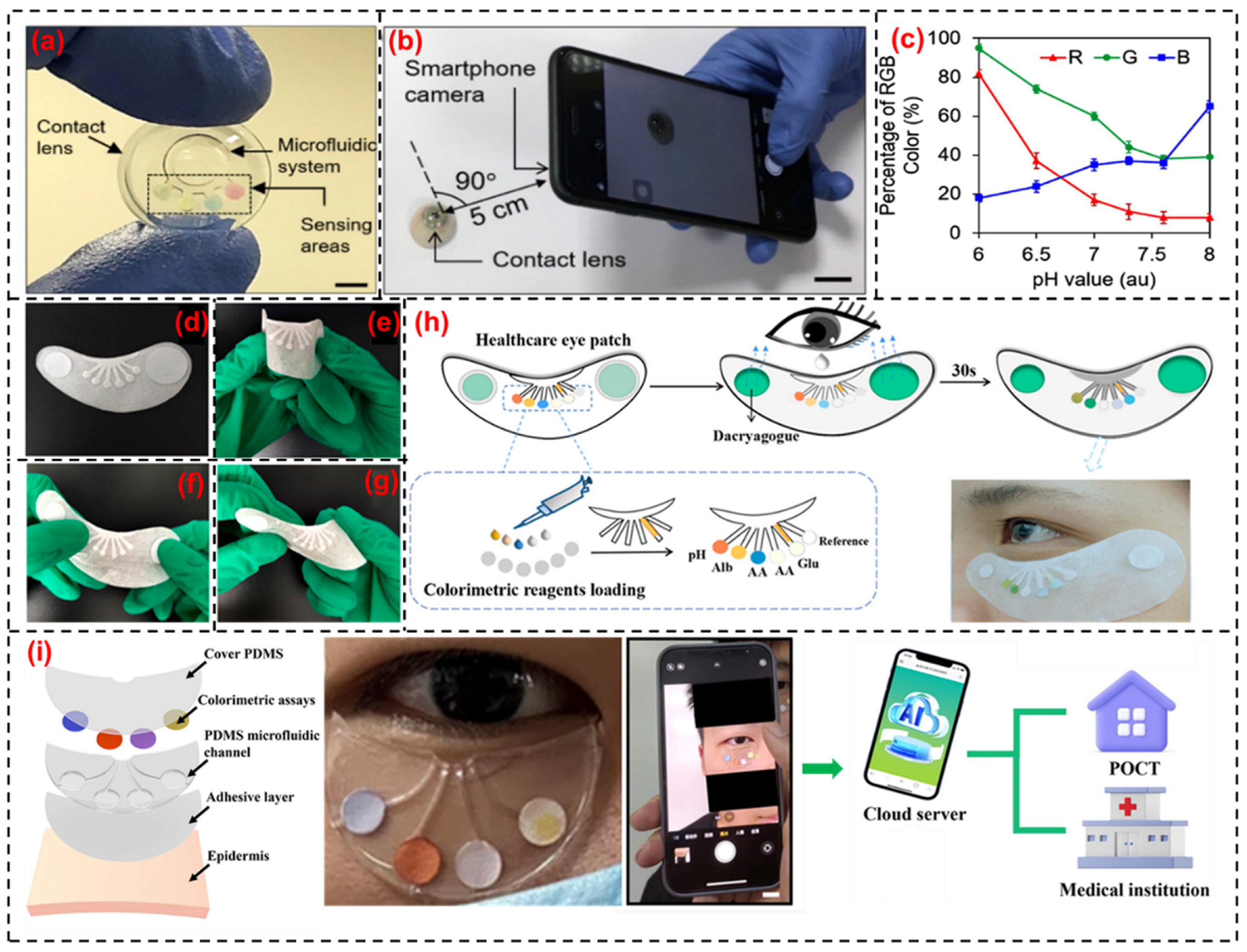
4.4. Proteins, Lipids and Electrolyte Monitoring
5. Outlook and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, P.; Peng, H.; Rwei, A.Y. Flexible, wearable biosensors for digital health. Med. Nov. Technol. Devices 2022, 14, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetisen, A.K.; Martinez-Hurtado, J.L.; Ünal, B.; Khademhosseini, A.; Butt, H. Wearables in Medicine. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, K.; Ghosh, S.K.; Sultana, A.; Garain, S.; Xie, M.; Bowen, C.R.; Henkel, K.; Schmeiβer, D.; Mandal, D. A Self-Powered Wearable Pressure Sensor and Pyroelectric Breathing Sensor Based on GO Interfaced PVDF Nanofibers. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 2013–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.-L.; Dong, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhou, J.; Ma, Z.; Li, J. Battery-free, tuning circuit–inspired wireless sensor systems for detection of multiple biomarkers in bodily fluids. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabo7049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Promphet, N.; Hinestroza, J.P.; Rattanawaleedirojn, P.; Soatthiyanon, N.; Siralertmukul, K.; Potiyaraj, P.; Rodthongkum, N. Cotton thread-based wearable sensor for non-invasive simultaneous diagnosis of diabetes and kidney failure. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 321, 128549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Campbell, A.S.; de Ávila, B.E.-F.; Wang, J. Wearable biosensors for healthcare monitoring. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backiyalakshmi, G.; Snekhalatha, U.; Salvador, A.L. Recent advancements in non-invasive wearable electrochemical biosensors for biomarker analysis—A review. Anal. Biochem. 2024, 692, 115578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z.; Song, Z.; Cai, H.; Fang, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Wearable and flexible electrochemical sensors for sweat analysis: A review. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2023, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shajari, S.; Kuruvinashetti, K.; Komeili, A.; Sundararaj, U. The Emergence of AI-Based Wearable Sensors for Digital Health Technology: A Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 9498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Singh, A.; Gupta, V.; Arya, S. Advancements and future prospects of wearable sensing technology for healthcare applications. Sens. Diagn. 2022, 1, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.; Singh, K.R.B.; Yadav, A.K.; Nayak, V.; Singh, J.; Solanki, P.R.; Singh, R.P. Internet of things (IoT) in nano-integrated wearable biosensor devices for healthcare applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2022, 11, 100153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, B.W.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, J.; Ji, S.; Park, J.; Lee, Y.; Jang, J.; Park, Y.-G.; Cho, E.; et al. Smart Sensor Systems for Wearable Electronic Devices. Polymers 2017, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazanskiy, N.L.; Khonina, S.N.; Butt, M.A. Smart Contact Lenses—A Step towards Non-Invasive Continuous Eye Health Monitoring. Biosensors 2023, 13, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sempionatto, J.R.; Brazaca, L.C.; García-Carmona, L.; Bolat, G.; Campbell, A.S.; Martin, A.; Tang, G.; Shah, R.; Mishra, R.K.; Kim, J.; et al. Eyeglasses-based tear biosensing system: Non-invasive detection of alcohol, vitamins and glucose. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 137, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, H.; Chung, W.G.; Kwon, Y.W.; Kim, S.; Hong, Y.-M.; Park, W.; Kim, E.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, M.; et al. Smart Contact Lenses as Wearable Ophthalmic Devices for Disease Monitoring and Health Management. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 11488–11558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Seo, H.; Chung, W.G.; Joo, B.J.; Jang, J.; Park, J.-U. Recent progress on wearable point-of-care devices for ocular systems. Lab A Chip 2021, 21, 1269–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dong, Y.; Sui, X.; Shao, X.; Li, K.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, D. An artificial intelligence-assisted microfluidic colorimetric wearable sensor system for monitoring of key tear biomarkers. npj Flex. Electron. 2024, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, Y.R.; Cho, M.; Ju, H.J.; Bae, J.M.; Cho, S.H.; Lee, J.D.; Kim, H.S. Ocular Comorbidities in Rosacea: A Case-Control Study Based on Seven Institutions. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesilirmak, N.; Bukan, N.; Kurt, B.; Yuzbasioglu, S.; Zhao, M.; Rodrigues-Braz, D.; Aktas, A.; Behar-Cohen, F.; Bourges, J.-L. Evaluation of Ocular and Systemic Oxidative Stress Markers in Ocular Rosacea Patients. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2023, 64, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammak, A.; Pastrana, C.; Martin-Gil, A.; Carpena-Torres, C.; Peral Cerda, A.; Simovart, M.; Alarma, P.; Huete-Toral, F.; Carracedo, G. Oxidative Stress in the Anterior Ocular Diseases: Diagnostic and Treatment. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolewska, B.; Schaller, M.; Zierhut, M. Rosacea and Dry Eye Disease. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2022, 30, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehm, N.; Riechardt, A.I.; Wiegand, M.; Pfeiffer, N.; Grus, F.H. Proinflammatory Cytokine Profiling of Tears from Dry Eye Patients by Means of Antibody Microarrays. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 7725–7730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versura, P.; Bavelloni, A.; Grillini, M.; Fresina, M.; Campos, E.C. Diagnostic performance of a tear protein panel in early dry eye. Mol. Vis. 2013, 19, 1247. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tamhane, M.; Cabrera-Ghayouri, S.; Abelian, G.; Viswanath, V. Review of Biomarkers in Ocular Matrices: Challenges and Opportunities. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.U.; Chatterjee, S.; Lone, S.A.; Ho, H.-H.; Kaswan, K.; Peringeth, K.; Khan, A.; Chiang, Y.-W.; Lee, S.; Lin, Z.-H. Advanced wearable biosensors for the detection of body fluids and exhaled breath by graphene. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubala, V.; Harris, L.F.; Ricco, A.J.; Tan, M.X.; Williams, D.E. Point of Care Diagnostics: Status and Future. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 487–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, M.; Lee, M.-S.; Kim, K.; Ji, S.; Kim, Y.-T.; Park, J.; Na, K.; Bae, K.-H.; Kyun Kim, H.; et al. Wearable smart sensor systems integrated on soft contact lenses for wireless ocular diagnostics. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.-Y.; Cheong, W.H.; Jang, J.; Park, Y.-G.; Na, K.; Kim, Y.-T.; Heo, J.H.; Lee, C.Y.; et al. Soft, smart contact lenses with integrations of wireless circuits, glucose sensors, and displays. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaap9841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binotti, W.W.; Bayraktutar, B.; Ozmen, M.C.; Cox, S.M.; Hamrah, P. A Review of Imaging Biomarkers of the Ocular Surface. Eye Contact Lens 2020, 46, S84–S105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, S.; Martin, E.; Enríquez-de-Salamanca, A. Tear fluid biomarkers in ocular and systemic disease: Potential use for predictive, preventive and personalised medicine. EPMA J. 2016, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Zhou, S.; Qin, Y.; Xia, X.; Sun, Y.; Han, G.; Shu, T.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Q. Flexible and Wearable Biosensors for Monitoring Health Conditions. Biosensors 2023, 13, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdem, A.; Eksin, E.; Senturk, H.; Yildiz, E.; Maral, M. Recent developments in wearable biosensors for healthcare and biomedical applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 171, 117510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohankumar, P.; Ajayan, J.; Mohanraj, T.; Yasodharan, R. Recent developments in biosensors for healthcare and biomedical applications: A review. Measurement 2021, 167, 108293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazanskiy, N.L.; Khonina, S.N.; Butt, M.A. A review on flexible wearables—Recent developments in non-invasive continuous health monitoring. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2024, 366, 114993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalasin, S.; Surareungchai, W. Challenges of Emerging Wearable Sensors for Remote Monitoring toward Telemedicine Healthcare. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 1773–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Yang, Z.; An, M. Lab on the eye: A review of tear-based wearable devices for medical use and health management. BioScience Trends 2019, 13, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.S.; Wong, H.L.; Ip, Y.L.; Peng, Z.; Yiu, R.; Yuan, H.; Wai Wong, J.K.; Chan, Y.K. Current and Future Perspectives on Microfluidic Tear Analytic Devices. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 1300–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, J.P.; Nichols, K.K.; Akpek, E.K.; Caffery, B.; Dua, H.S.; Joo, C.-K.; Liu, Z.; Nelson, J.D.; Nichols, J.J.; Tsubota, K.; et al. TFOS DEWS II Definition and Classification Report. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, A.M. Antimicrobial compounds in tears. Exp. Eye Res. 2013, 117, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, J.V.; Dick, A.D.; McMenamin, P.G.; Roberts, F.; Pearlman, E. Chapter 4—Biochemistry and cell biology. In The Eye, 4th ed.; Forrester, J.V., Dick, A.D., McMenamin, P.G., Roberts, F., Pearlman, E., Eds.; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 157–268.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavilina, I.S.; Shpak, A.A.; Druzhkova, T.A.; Guekht, A.B.; Gulyaeva, N.V. Shedding Valuable Tears: Tear Fluid as a Promising Source of Disease Biomarkers. Neurochem. J. 2023, 17, 702–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, A.M. Defense Mechanisms of Tears and Ocular Surface. In Encyclopedia of the Eye; Dartt, D.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murube, J. Basal, Reflex, and Psycho-emotional Tears. Ocul. Surf. 2009, 7, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Haeringen, N.J. Clinical biochemistry of tears. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1981, 26, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, R.; Klinngam, W.; Heur, M.; Edman, M.C.; Hamm-Alvarez, S.F. Tear Proteases and Protease Inhibitors: Potential Biomarkers and Disease Drivers in Ocular Surface Disease. Eye Contact Lens 2020, 46, S70–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dartt, D.A.; Willcox, M.D.P. Complexity of the tear film: Importance in homeostasis and dysfunction during disease. Exp. Eye Res. 2013, 117, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrent-Burgués, J. Tear Film Constituents and Medicines for Eyes Investigated as Langmuir Films. BioNanoScience 2023, 13, 1324–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, H.J.; Kuonen, V.J. The tear film and ocular mucins. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2004, 7, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bron, A.J.; Tomlinson, A.; Foulks, G.N.; Pepose, J.S.; Baudouin, C.; Geerling, G.; Nichols, K.K.; Lemp, M.A. Rethinking Dry Eye Disease: A Perspective on Clinical Implications. Ocul. Surf. 2014, 12, S1–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwiklik, L. Tear film lipid layer: A molecular level view. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Biomembr. 2016, 1858, 2421–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, L.; Shang-Kun, O.; Wei, L.; Zu-Guo, L.; Qing-Hua, P. Physical Therapy Modalities of Western Medicine and Traditional Chinese Medicine for Meibomian Gland Dysfunction. Digit. Chin. Med. 2020, 3, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, M.; Martins, B.; Fernandes, R. Immune Fingerprint in Diabetes: Ocular Surface and Retinal Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachhuber, F.; Huss, A.; Senel, M.; Tumani, H. Diagnostic biomarkers in tear fluid: From sampling to preanalytical processing. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dor, M.; Eperon, S.; Lalive, P.H.; Guex-Crosier, Y.; Hamedani, M.; Salvisberg, C.; Turck, N. Investigation of the global protein content from healthy human tears. Exp. Eye Res. 2019, 179, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, K.W.; Myung, D.J.; Fuller, G.G. Tear Film Stability as a Function of Tunable Mucin Concentration Attached to Supported Lipid Bilayers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 6338–6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posa, A.; Bräuer, L.; Schicht, M.; Garreis, F.; Beileke, S.; Paulsen, F. Schirmer strip vs. capillary tube method: Non-invasive methods of obtaining proteins from tear fluid. Ann. Anat.-Anat. Anz. 2013, 195, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tham, M.L.; Mahmud, A.; Abdullah, M.; Md Saleh, R.; Mohammad Razali, A.; Cheah, Y.K.; Mohd Taib, N.; Ho, K.L.; Mahmud, M.; Mohd Isa, M. Tear Samples for Protein Extraction: Comparative Analysis of Schirmer’s Test Strip and Microcapillary Tube Methods. Cureus 2023, 15, e50972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nättinen, J.; Aapola, U.; Jylhä, A.; Vaajanen, A.; Uusitalo, H. Comparison of Capillary and Schirmer Strip Tear Fluid Sampling Methods Using SWATH-MS Proteomics Approach. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Thun und Hohenstein-Blaul, N.; Funke, S.; Grus, F.H. Tears as a source of biomarkers for ocular and systemic diseases. Exp. Eye Res. 2013, 117, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, R.; Das, S.; Shetty, R.; Zhou, L.; Ghosh, A.; Deshpande, V. Tear proteomics in dry eye disease. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 71, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Y.W.; Sze, Y.H.; Bian, J.F.; Lam, T.C. Critical role of mass spectrometry proteomics in tear biomarker discovery for multifactorial ocular diseases (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 47, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhao, S.Z.; Koh, S.K.; Chen, L.; Vaz, C.; Tanavde, V.; Li, X.R.; Beuerman, R.W. In-depth analysis of the human tear proteome. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 3877–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Golubnitschaja, O. Mass spectrometry analysis of human tear fluid biomarkers specific for ocular and systemic diseases in the context of 3P medicine. EPMA J. 2021, 12, 449–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Beuerman, R.W. The power of tears: How tear proteomics research could revolutionize the clinic. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2017, 14, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaštelan, S.; Braš, M.; Pjevač, N.; Bakija, I.; Tomić, Z.; Pjevač Keleminić, N.; Gverović Antunica, A. Tear Biomarkers and Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versura, P.; Nanni, P.; Bavelloni, A.; Blalock, W.L.; Piazzi, M.; Roda, A.; Campos, E.C. Tear proteomics in evaporative dry eye disease. Eye 2010, 24, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.J.F.; Thomas, R.K.; Penfold, J. Polymer/surfactant interactions at the air/water interface. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 132, 69–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, Z.; Bazargan, S.; Jung, D.; Sathianathan, S.; Clemens, A.; Shir, D.; Al-Hashimi, S.; Ozcan, A. Contact lens-based lysozyme detection in tear using a mobile sensor. Lab A Chip 2020, 20, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dartt, D.A. Tear Lipocalin: Structure and Function. Ocul. Surf. 2011, 9, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-C.; Ku, H.-Y.; Chen, T.-S.; Chuang, H.-S. Detection of low-abundance biomarker lipocalin 1 for diabetic retinopathy using optoelectrokinetic bead-based immunosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, M.; Jafari, S.; Hasan, A.; Paray, B.A.; Gong, G.; Zheng, Y.; Falahati, M. Antimetastatic Activity of Lactoferrin-Coated Mesoporous Maghemite Nanoparticles in Breast Cancer Enabled by Combination Therapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 3574–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagge, A.; Senni, C.; Bernabei, F.; Pellegrini, M.; Scorcia, V.; Traverso, C.E.; Giannaccare, G. Therapeutic Effects of Lactoferrin in Ocular Diseases: From Dry Eye Disease to Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzini, E.; Scotti, L.; Grandori, R.; Tavazzi, S.; Zambon, A. Lactoferrin Concentration in Human Tears and Ocular Diseases: A Meta-Analysis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiva, A.J.E.O.R. Tear biomarkers in dry eye disease. Eur. Ophthalmic Rev. 2019, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Dalt, S.; Moncada, A.; Priori, R.; Valesini, G.; Pivetti-Pezzi, P. The Lactoferrin Tear Test in the Diagnosis of Sjögren’s Syndrome. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 1996, 6, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebrecht, A.; Boehm, D.; Schmidt, M.; Koelbl, H.; Schwirz, R.L.; Grus, F.H. Diagnosis of Breast Cancer by Tear Proteomic Pattern. Cancer Genom.-Proteom. 2009, 6, 177. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Yetisen, A.K. Fluorescence Sensing Technologies for Ophthalmic Diagnosis. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 1615–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Moreddu, R.; Fan, Z.; Jiang, N.; Yetisen, A.K. Smartphone-based fluorescent sensing platforms for point-of-care ocular lactoferrin detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 378, 133128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieragostino, D.; D’Alessandro, M.; di Ioia, M.; Di Ilio, C.; Sacchetta, P.; Del Boccio, P. Unraveling the molecular repertoire of tears as a source of biomarkers: Beyond ocular diseases. Proteom.–Clin. Appl. 2015, 9, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, M.J.; González-García, M.J.; Tesón, M.; García, N.; Fernández, I.; Calonge, M.; Enríquez-de-Salamanca, A. Intra- and inter-day variation of cytokines and chemokines in tears of healthy subjects. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 120, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.R.; Praveen, M.; Narasimhan, R.; Khamar, P.; D’Souza, S.; Sinha-Roy, A.; Sethu, S.; Shetty*, R.; Ghosh, A. Tear biomarkers in dry eye disease: Progress in the last decade. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 71, 1190–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gálvez, B.G.; Martinez-Perez, C.; Villa-Collar, C.; Alvarez-Peregrina, C.; Sánchez-Tena, M.Á. Influence of Cytokines on Inflammatory Eye Diseases: A Citation Network Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Guttenplan, K.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Bennett, F.C.; Bohlen, C.J.; Schirmer, L.; Bennett, M.L.; Münch, A.E.; Chung, W.-S.; Peterson, T.C.; et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 2017, 541, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hueber, W.; Patel, D.D.; Dryja, T.; Wright, A.M.; Koroleva, I.; Bruin, G.; Antoni, C.; Draelos, Z.; Gold, M.H.; the Psoriasis Study, G.; et al. Effects of AIN457, a Fully Human Antibody to Interleukin-17A, on Psoriasis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Uveitis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 52ra72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.-X.; Yu, C.-R.; Dambuza, I.M.; Mahdi, R.M.; Dolinska, M.B.; Sergeev, Y.V.; Wingfield, P.T.; Kim, S.-H.; Egwuagu, C.E. Interleukin-35 induces regulatory B cells that suppress autoimmune disease. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akdis, M.; Aab, A.; Altunbulakli, C.; Azkur, K.; Costa, R.A.; Crameri, R.; Duan, S.; Eiwegger, T.; Eljaszewicz, A.; Ferstl, R.; et al. Interleukins (from IL-1 to IL-38), interferons, transforming growth factor β, and TNF-α: Receptors, functions, and roles in diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 984–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abidi, A.; Shukla, P.; Ahmad, A. Lifitegrast: A novel drug for treatment of dry eye disease. J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2016, 7, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, C.E.; Nibbs, R.J.B. A guide to chemokines and their receptors. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 2944–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacalle, R.A.; Blanco, R.; Carmona-Rodríguez, L.; Martín-Leal, A.; Mira, E.; Mañes, S. Chapter Five-Chemokine Receptor Signaling and the Hallmarks of Cancer. In International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology; Galluzzi, L., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 331, pp. 181–244. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Molina, G.; Ruiz-Quintero, N.; Lima, G.; Hernández-Ramírez, D.; Llorente-Chávez, A.; Saavedra-González, V.; Jiménez-Soto, R.; Llorente, L. Chemokine tear levels in primary Sjögren’s syndrome and their relationship with symptoms. Int. Ophthalmol. 2022, 42, 2355–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Shaw, J.L.; Haigis, M.C.; Greka, A. Lipid metabolism in sickness and in health: Emerging regulators of lipotoxicity. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 3708–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, C.J.; Papac-Milicevic, N.; Witztum, J.L. Innate sensing of oxidation-specific epitopes in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, J.D.; Nichols, K.K. Dry Eye Disease Associated with Meibomian Gland Dysfunction: Focus on Tear Film Characteristics and the Therapeutic Landscape. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2023, 12, 1397–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, A.M.; Senchyna, M.; Argüeso, P. Differential contribution of hypertonic electrolytes to corneal epithelial dysfunction. Exp. Eye Res. 2012, 100, 98–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pflugfelder, S.C. Tear Dysfunction and the Cornea: LXVIII Edward Jackson Memorial Lecture. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 152, 900–909.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argüeso, P.; Tisdale, A.; Spurr-Michaud, S.; Sumiyoshi, M.; Gipson, I.K. Mucin Characteristics of Human Corneal-Limbal Epithelial Cells that Exclude the Rose Bengal Anionic Dye. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, D.; Hayes, N.W.; Tighe, B. Fibre optics sensors in tear electrolyte analysis: Towards a novel point of care potassium sensor. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2012, 35, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, J.D.; Krumholz, D.M.; Sack, R.A.; Morris, C. Tear Glucose Dynamics in Diabetes Mellitus. Curr. Eye Res. 2006, 31, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Liao, Y.; Lingley, A.R.; Afanasiev, A.; Lähdesmäki, I.; Otis, B.P.; Parviz, B.A. A contact lens with integrated telecommunication circuit and sensors for wireless and continuous tear glucose monitoring. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2012, 22, 075007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, N.; Lähdesmäki, I.; Parviz, B.A. A contact lens with an integrated lactate sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 162, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Nichols, K.K.; Wilson, L.; Barnes, S.; Nichols, J.J. Untargeted lipidomic analysis of human tears: A new approach for quantification of O-acyl-omega hydroxy fatty acids. Ocul. Surf. 2019, 17, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, R.K.; Catanese, S.; Emond, P.; Corcia, P.; Blasco, H.; Pisella, P.-J. Metabolomics and lipidomics approaches in human tears: A systematic review. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2022, 67, 1229–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, M.; Elgstøen, K.B.; Rootwelt, H.; Shahdadfar, A.; Utheim, Ø.A.; Utheim, T.P. Tear Metabolomics in Dry Eye Disease: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamichos, D.; Zieske, J.D.; Sejersen, H.; Sarker-Nag, A.; Asara, J.M.; Hjortdal, J. Tear metabolite changes in keratoconus. Exp. Eye Res. 2015, 132, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Shen, Z.; Peng, R.; Li, C.; Hu, B.; Hong, J. Tear Lipid Metabolites As Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Ocular Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2021, 27, 232.e1–232.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Mauro, F.M.; Schoeffler, G.L. Point of Care Measurement of Lactate. Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2016, 31, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Kim, E.; Ogando, D.G.; Bonanno, J.A. Corneal Endothelial Pump Coupling to Lactic Acid Efflux in the Rabbit and Mouse. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.A.; Li, R.; Tse, Z.T.H. Reshaping healthcare with wearable biosensors. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Lee, D.H.; Youn, J.; Lee, H.; Jeong, J. Simple and cost-effective microfabrication of flexible and stretchable electronics for wearable multi-functional electrophysiological monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh Fakhr, M.; Lopez Carrasco, I.; Belyaev, D.; Kang, J.; Shin, Y.; Yeo, J.-S.; Koh, W.-G.; Ham, J.; Michaelis, A.; Opitz, J.; et al. Recent advances in wearable electrochemical biosensors towards technological and material aspects. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2024, 19, 100503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdalgic, B.; Gul, M.; Uygun, Z.O.; Atçeken, N.; Tasoglu, S. Emerging Applications of Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy in Tear Film Analysis. Biosensors 2022, 12, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennyson Savariraj, A.; Salih, A.; Alam, F.; Elsherif, M.; AlQattan, B.; Khan, A.A.; Yetisen, A.K.; Butt, H. Ophthalmic Sensors and Drug Delivery. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 2046–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, K.H.; Desai, D.T.; Patel, H.P.; Shah, D.O.; Willcox, M.D.P.; Maulvi, F.A. Contact lens as an emerging platform for non-invasive bio-sensing: A review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2024, 376, 115617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, R.C.; Chen, C.-C.; Hsu, S.-M.; Chuang, H.-S. Contact-Lens Biosensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Badea, M.; Tiwari, S.; Marty, J.L. Wearable Biosensors: An Alternative and Practical Approach in Healthcare and Disease Monitoring. Molecules 2021, 26, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.A. Wearable miniaturized electrochemical sensors: Benefits and challenges. In Electrochemistry; Banks, C., McIntosh, S., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2018; Volume 15, pp. 147–185. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.J.; Al-Mamun, M.; Islam, M.R. Diabetes mellitus, the fastest growing global public health concern: Early detection should be focused. Health Sci. Rep. 2024, 7, e2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reda, A.; El-Safty, S.A.; Selim, M.M.; Shenashen, M.A. Optical glucose biosensor built-in disposable strips and wearable electronic devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 185, 113237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kownacka, A.E.; Vegelyte, D.; Joosse, M.; Anton, N.; Toebes, B.J.; Lauko, J.; Buzzacchera, I.; Lipinska, K.; Wilson, D.A.; Geelhoed-Duijvestijn, N.; et al. Clinical Evidence for Use of a Noninvasive Biosensor for Tear Glucose as an Alternative to Painful Finger-Prick for Diabetes Management Utilizing a Biopolymer Coating. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 4504–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senior, M. Novartis signs up for Google smart lens. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, D.K.; Sarin, G.S. Tear glucose levels in normal people and in diabetic patients. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1980, 64, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Du, W.; Ji, W.; Fang, Z.; Hou, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, C.; Li, L. Optical flexible biosensors: From detection principles to biomedical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 210, 114328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badugu, R.; Lakowicz, J.R.; Geddes, C.D. A Glucose Sensing Contact Lens: A Non-Invasive Technique for Continuous Physiological Glucose Monitoring. J. Fluoresc. 2003, 13, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.-L.; Chen, C.; Shen, J.-H.; Zhao, X.-L.; Qian, S.-H.; Zhu, Z.-G. A Gelated Colloidal Crystal Attached Lens for Noninvasive Continuous Monitoring of Tear Glucose. Polymers 2017, 9, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wu, K.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Sun, Z.; Xi, D.; Zhang, S.; Ding, W.; Zaghloul, M.E.; Wang, C.; et al. Integrated contact lens sensor system based on multifunctional ultrathin MoS2 transistors. Matter 2021, 4, 969–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yan, X.; Gu, Z.; Xiu, G.; Xiao, X. Electrochemical Sensing in Contact Lenses. Electroanalysis 2022, 34, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, W.; Ma, B.; Ju, H. Device integration of electrochemical biosensors. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2023, 1, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Tong, J.; Chen, X.; Deng, W.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, X.; Yin, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Gao, Y.; et al. Advanced nanomaterials for electrochemical sensors: Application in wearable tear glucose sensing technology. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 6774–6804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, H.; Sawada, T.; Kazawa, E.; Yoshida, H.; Iwasaki, Y.; Mitsubayashi, K. A flexible and wearable glucose sensor based on functional polymers with Soft-MEMS techniques. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 22, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajisa, T.; Sakata, T. Glucose-responsive hydrogel electrode for biocompatible glucose transistor. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2017, 18, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsubayashi, K.; Wakabayashi, Y.; Tanimoto, S.; Murotomi, D.; Endo, T. Optical-transparent and flexible glucose sensor with ITO electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 19, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, A.; Benny, L.; Cherian, A.R.; Narahari, S.Y.; Varghese, A.; Hegde, G. Electrochemical sensors using conducting polymer/noble metal nanoparticle nanocomposites for the detection of various analytes: A review. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2021, 11, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajik, S.; Dourandish, Z.; Garkani Nejad, F.; Beitollahi, H.; Jahani, P.M.; Di Bartolomeo, A. Transition metal dichalcogenides: Synthesis and use in the development of electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 216, 114674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachholz Junior, D.; Hryniewicz, B.M.; Tatsuo Kubota, L. Advanced Hybrid materials in electrochemical sensors: Combining MOFs and conducting polymers for environmental monitoring. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Lee, G.-H.; Jeon, C.; Han, H.H.; Kim, S.-J.; Mok, J.W.; Joo, C.-K.; Shin, S.; Sim, J.-Y.; Myung, D.; et al. Bimetallic Nanocatalysts Immobilized in Nanoporous Hydrogels for Long-Term Robust Continuous Glucose Monitoring of Smart Contact Lens. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2110536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, M.X.; Miyajima, K.; Takahashi, D.; Arakawa, T.; Sano, K.; Sawada, S.-i.; Kudo, H.; Iwasaki, Y.; Akiyoshi, K.; Mochizuki, M.; et al. Soft contact lens biosensor for in situ monitoring of tear glucose as non-invasive blood sugar assessment. Talanta 2011, 83, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, G.; Long, F.; Zeng, Z.; Kong, L.; Zhao, B.; Yan, J.; Yang, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.-Y.; Yan, Z.; et al. Silk fibroin based wearable electrochemical sensors with biomimetic enzyme-like activity constructed for durable and on-site health monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 228, 115198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olvera, D.; Monaghan, M.G. Electroactive material-based biosensors for detection and drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 170, 396–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Jia, W.; Hou, C.; Wang, H. NiCo–NiCoO2/carbon hollow nanocages for non-enzyme glucose detection. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 381, 138259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Truong, P.L.; Lee, D.; Ko, S.H. Metal-Oxide Nanomaterials Synthesis and Applications in Flexible and Wearable Sensors. ACS Nanosci. Au 2022, 2, 64–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Yao, G.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Q.; Mo, X.; Dong, Q.; Lou, W.; Lu, F.; Pan, T.; Gao, M.; et al. Multifunctional flexible contact lens for eye health monitoring using inorganic magnetic oxide nanosheets. J. Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Denno, M.E.; Pyakurel, P.; Venton, B.J. Recent trends in carbon nanomaterial-based electrochemical sensors for biomolecules: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 887, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dai, Z. Carbon nanomaterial-based electrochemical biosensors: An overview. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 6420–6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norn, M. Tear pH after instillation of buffer in vivo. Acta Ophthalmol. 1985, 63, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelson, M.B.; Sadun, A.A.; Udell, I.J.; Weston, J.H. Alkaline Tear pH in Ocular Rosacea. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1980, 90, 866–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badugu, R.; Jeng, B.H.; Reece, E.A.; Lakowicz, J.R. Contact lens to measure individual ion concentrations in tears and applications to dry eye disease. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 542, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreddu, R.; Wolffsohn, J.S.; Vigolo, D.; Yetisen, A.K. Laser-inscribed contact lens sensors for the detection of analytes in the tear fluid. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 317, 128183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, R.S.; Elsherif, M.; Moreddu, R.; Rashid, I.; Hassan, M.U.; Yetisen, A.K.; Butt, H. Anthocyanin-Functionalized Contact Lens Sensors for Ocular pH Monitoring. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 21792–21798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Kim, S.-M.; Park, H.J.; Kim, Y.K.; Oh, D.X.; Cho, H.-W.; Lee, K.G.; Hwang, S.Y.; Park, J.; Choi, B.G. Highly self-healable and flexible cable-type pH sensors for real-time monitoring of human fluids. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 150, 111946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, A.; Salih, A.; Hisham, M.; Elsherif, M.; Schiffer, A.; Butt, H. Multifunctional and multimaterial contact lenses: Tailored solutions for tunable color filtering and tear pH sensing. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2024, 19, e2298411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tao, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, L. Wearable Eye Patch Biosensor for Noninvasive and Simultaneous Detection of Multiple Biomarkers in Human Tears. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 8659–8667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjakkal, L.; Dervin, S.; Dahiya, R. Flexible potentiometric pH sensors for wearable systems. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 8594–8617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Lin, X.; Fu, X.; An, Y.; Zou, Y.; Wang, J.-X.; Wang, Z.; Yu, T. Lactate metabolism in human health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, F.; RoyChoudhury, S.; Jalal, A.H.; Umasankar, Y.; Forouzanfar, S.; Akter, N.; Bhansali, S.; Pala, N. Lactate biosensing: The emerging point-of-care and personal health monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushimoto, S.; Akaishi, S.; Sato, T.; Nomura, R.; Fujita, M.; Kudo, D.; Kawazoe, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Miyagawa, N. Lactate, a useful marker for disease mortality and severity but an unreliable marker of tissue hypoxia/hypoperfusion in critically ill patients. Acute Med. Surg. 2016, 3, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathee, K.; Dhull, V.; Dhull, R.; Singh, S. Biosensors based on electrochemical lactate detection: A comprehensive review. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2016, 5, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengarda, P.; Dias, F.A.; Peixoto, J.V.; Osiecki, R.; Bergamini, M.F.; Marcolino-Junior, L.H. Determination of lactate levels in biological fluids using a disposable ion-selective potentiometric sensor based on polypyrrole films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 296, 126663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-E.; Hiraka, K.; Matloff, D.; Johns, J.; Deng, A.; Sode, K.; La Belle, J. Development toward a novel integrated tear lactate sensor using Schirmer test strip and engineered lactate oxidase. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 270, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, S.K.; Singh, D.; Upadhay, J.; Gupta, N.; Dhiman, N.; Mittal, S.K.; Mahindroo, N. Identification of tear-based protein and non-protein biomarkers: Its application in diagnosis of human diseases using biosensors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Shin, H.; Seo, H.; Park, W.; Joo, B.J.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, J.; Park, J.-U. Wireless Non-Invasive Monitoring of Cholesterol Using a Smart Contact Lens. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2203597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badugu, R.; Szmacinski, H.; Reece, E.A.; Jeng, B.H.; Lakowicz, J.R. Fluorescent contact lens for continuous non-invasive measurements of sodium and chloride ion concentrations in tears. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 608, 113902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetisen, A.K.; Jiang, N.; Tamayol, A.; Ruiz-Esparza, G.U.; Zhang, Y.S.; Medina-Pando, S.; Gupta, A.; Wolffsohn, J.S.; Butt, H.; Khademhosseini, A.; et al. Paper-based microfluidic system for tear electrolyte analysis. Lab A Chip 2017, 17, 1137–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlQattan, B.; Yetisen, A.K.; Butt, H. Direct Laser Writing of Nanophotonic Structures on Contact Lenses. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5130–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.; Seo, H.; Kim, J.; Hong, Y.-M.; Song, H.; Joo, B.J.; Kim, S.; Kim, E.; Yae, C.-G.; Kim, J.; et al. In-depth correlation analysis between tear glucose and blood glucose using a wireless smart contact lens. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.; Shan, S.; Huang, L.; Chen, Z.; Lawson, T.; Lin, M.; Yan, L.; Liu, Y. High-Performance Intraocular Biosensors from Chitosan-Functionalized Nitrogen-Containing Graphene for the Detection of Glucose. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, E.F.; Garcia, P.T.; Lopes, F.M.; Coltro, W.K. Paper-Based Colorimetric Biosensor for Tear Glucose Measurements. Micromachines 2017, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Kim, J.; Shin, H.; Park, Y.-G.; Joo, B.J.; Seo, H.; Won, J.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, C.Y.; Kim, H.K.; et al. Smart contact lens and transparent heat patch for remote monitoring and therapy of chronic ocular surface inflammation using mobiles. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf7194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, S.; Sharma, A.; Singh, A.; Ahmed, A.; Dubey, A.; Padha, B.; Khan, S.; Mahadeva, R.; Khosla, A.; Gupta, V. Review—Energy and Power Requirements for Wearable Sensors. ECS Sens. Plus 2024, 3, 022601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, Y.-Z.; Yuan, M. Requirements, challenges, and novel ideas for wearables on power supply and energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2023, 115, 108715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenani, H.; Saeidi, M.; Rastkhiz, M.A.; Bolghanabadi, N.; Aghaii, A.H.; Orouji, M.; Hatamie, A.; Simchi, A. Challenges and Advances of Hydrogel-Based Wearable Electrochemical Biosensors for Real-Time Monitoring of Biofluids: From Lab to Market. A Review. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 8160–8183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sempionatto, J.R.; Lasalde-Ramírez, J.A.; Mahato, K.; Wang, J.; Gao, W. Wearable chemical sensors for biomarker discovery in the omics era. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2022, 6, 899–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TearExo®: New Breast Cancer Detection Method Uses Tears. 2020. Available online: https://www.kobe-u.ac.jp/en/news/article/2020_06_17_03/#:~:text=TearExo%C2%AE%20enables%20non%2Dinvasive,self%2Dcollected%20by%20the%20patient (accessed on 30 August 2024).
- Corrie, S.R.; Coffey, J.W.; Islam, J.; Markey, K.A.; Kendall, M.A.F. Blood, sweat, and tears: Developing clinically relevant protein biosensors for integrated body fluid analysis. Analyst 2015, 140, 4350–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Belle, J.T.; Adams, A.; Lin, C.-E.; Engelschall, E.; Pratt, B.; Cook, C.B. Self-monitoring of tear glucose: The development of a tear based glucose sensor as an alternative to self-monitoring of blood glucose. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 9197–9204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercan, Ö.B.; Kılıç, V.; Şen, M. Machine learning-based colorimetric determination of glucose in artificial saliva with different reagents using a smartphone coupled μPAD. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 329, 129037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarnda, K.V.; Wang, D.; Qurrat Ul, A.; Anaman, R.; Johnson, V.E.; Roberts, G.P.; Johnson, P.S.; Jallawide, B.W.; Kai, T.; Ding, P. Recent advances in electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensor for the detection of glucose in tears and saliva: A Review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2023, 363, 114778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravizza, A.; De Maria, C.; Di Pietro, L.; Sternini, F.; Audenino, A.L.; Bignardi, C. Comprehensive Review on Current and Future Regulatory Requirements on Wearable Sensors in Preclinical and Clinical Testing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wearables for Medical and Wellness Uses: Standards and FDA Guidance Documents. 2017. Available online: https://incompliancemag.com/wearables-for-medical-and-wellness-uses-standards-and-fda-guidance-documents/ (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Flynn, C.D.; Chang, D.; Mahmud, A.; Yousefi, H.; Das, J.; Riordan, K.T.; Sargent, E.H.; Kelley, S.O. Biomolecular sensors for advanced physiological monitoring. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2023, 1, 560–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, J.; Gao, W. Ethical Considerations of Wearable Technologies in Human Research. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2100127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Biomarker | Biorecognition Molecule | Sensing Mode | Type of Biosensors | Working Range | Sensitivity | Limit of Detection (LOD) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein (Lactoferrin) | Terbium chloride | Fluorescence | Contact lens | 0–5 mg/mL | - | 0.44 mg/mL | [78] |
| Glucose | Glucose oxidase | Electrochemical | Contact lens | 0.18–0.7 mM | 1% current change per 0.047 mM | 0.02 mM | [164] |
| Electrolyte (Na+) | Fluorescent diaza-15-crown-5 | Fluorescence | Strip-based | 130–150 mmol/L | 2.7 mmol/L | 1 mM/L (avg detection error) | [162] |
| Electrolyte (K+) | Fluorescent diaza-15-crown-6 | Fluorescence | Strip-based | 24–26 mmol/L | 1.4 mmol/L | 1.3 mM/L (avg detection error) | [162] |
| Glucose | Boronic acid-PVA hydrogel | Colorimetric | Contact lens | 0–50 mM | - | 0.05 mM | [124] |
| Protein | 3′,3′,5′,5′-tetrachlorophenol-3,4,5,6-tetrabromosulfophthalein | Colorimetric | Contact lens | 0.5–5 g/L | 0.49 nm/gL−1 | 0.63 g/L | [147] |
| Glucose | Glucose oxidase | Electrochemical | Contact lens | 0–12 mM | 9.7 μA mM–1 cm–2. | 9.5 μM | [165] |
| Cholesterol | Cholesterol oxidase | Electrochemical | Contact lens | 0.4–46.4 mg/dL | 1% current change per 0.0043 mM | 0.38 mg/dL | [160] |
| Electrolyte (Na+) | sodium green-poly-l-lysine | Fluorescence | Contact lens | 0–120 mM | - | 0.2 mM | [161] |
| Electrolyte (Cl−) | OD-MQB fluorophore of 6-methoxyquinoline and 1-bromooctadecane | Fluorescence | Contact lens | 0–120 mM | - | 10 mM | [161] |
| Glucose | γ-Fe2O3@NiO magnetic oxide nanosheets | Electrochemical | Contact lens | 0.005–6.0 mM | 0.17 MHz mmHg−1 | 0.43 μmol | [141] |
| Glucose | Glucose oxidase/peroxidase/3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine | Colorimetric | Contact lens | 0–20 mM/L | 1.4 nm/mmol L−1 | 1.84 mmol/L | [147] |
| l-Lactate | lactase oxidase | Electrochemical | Contact lens | 1–5 mM | 53 μA mM−1 cm−2 | 1.75 mM | [100] |
| Glucose | 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzydine | Colorimetric | Microcapillary tube | 0.1–1 mM | 84 AU/mM | 50 µM | [166] |
| Protein | Matrix metalloproteinase-9 | Electrochemical | contact lens | 1–500 ng/mL | 11.1 ng/mL per 1% of change in drain current | 0.74 ng/mL | [167] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajan, A.; Vishnu, J.; Shankar, B. Tear-Based Ocular Wearable Biosensors for Human Health Monitoring. Biosensors 2024, 14, 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14100483
Rajan A, Vishnu J, Shankar B. Tear-Based Ocular Wearable Biosensors for Human Health Monitoring. Biosensors. 2024; 14(10):483. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14100483
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajan, Arunima, Jithin Vishnu, and Balakrishnan Shankar. 2024. "Tear-Based Ocular Wearable Biosensors for Human Health Monitoring" Biosensors 14, no. 10: 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14100483
APA StyleRajan, A., Vishnu, J., & Shankar, B. (2024). Tear-Based Ocular Wearable Biosensors for Human Health Monitoring. Biosensors, 14(10), 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14100483






