Multiplex Detection of Biogenic Amines for Meat Freshness Monitoring Using Nanoplasmonic Colorimetric Sensor Array
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Synthesis of Plasmonic NPs
2.3.1. Synthesis of AuNPs
2.3.2. Synthesis of AgNPs
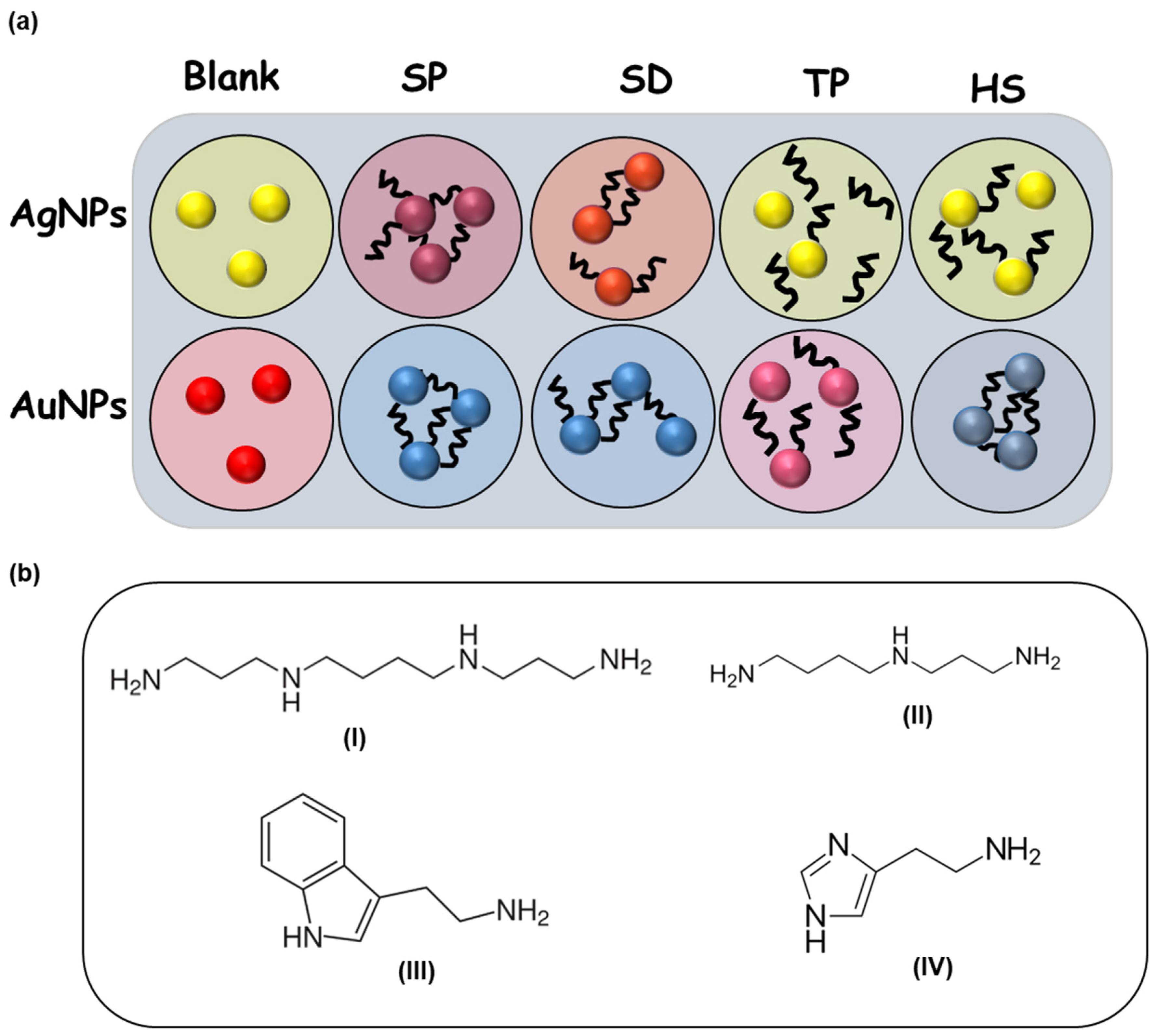
2.4. Design of Sensing Elements
2.5. Real Sample Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Sensing Mechanism of Colorimetric Detection of BAs
3.2. Optimizing of Experimental Conditions
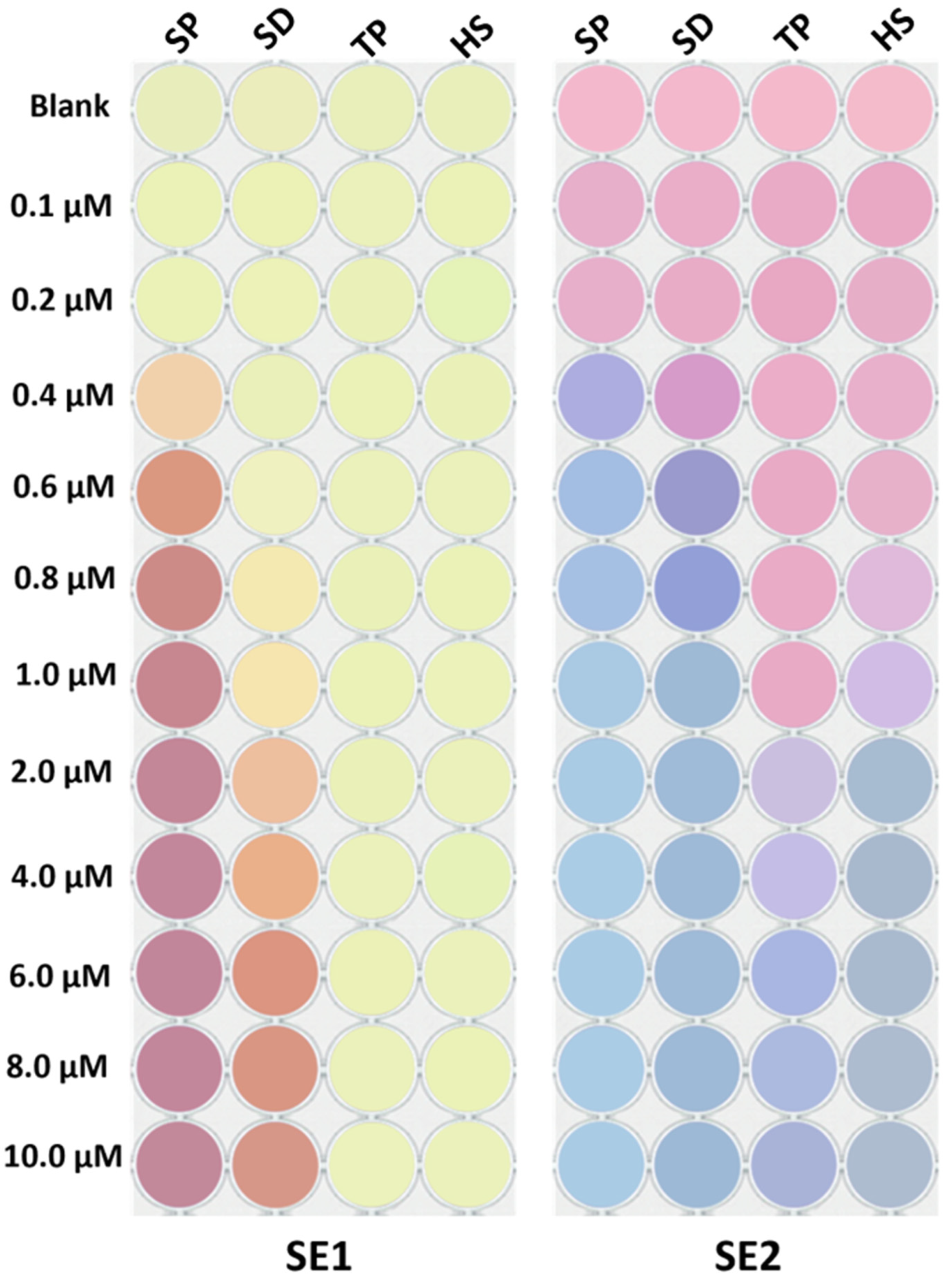
3.3. Sensor Array Responses
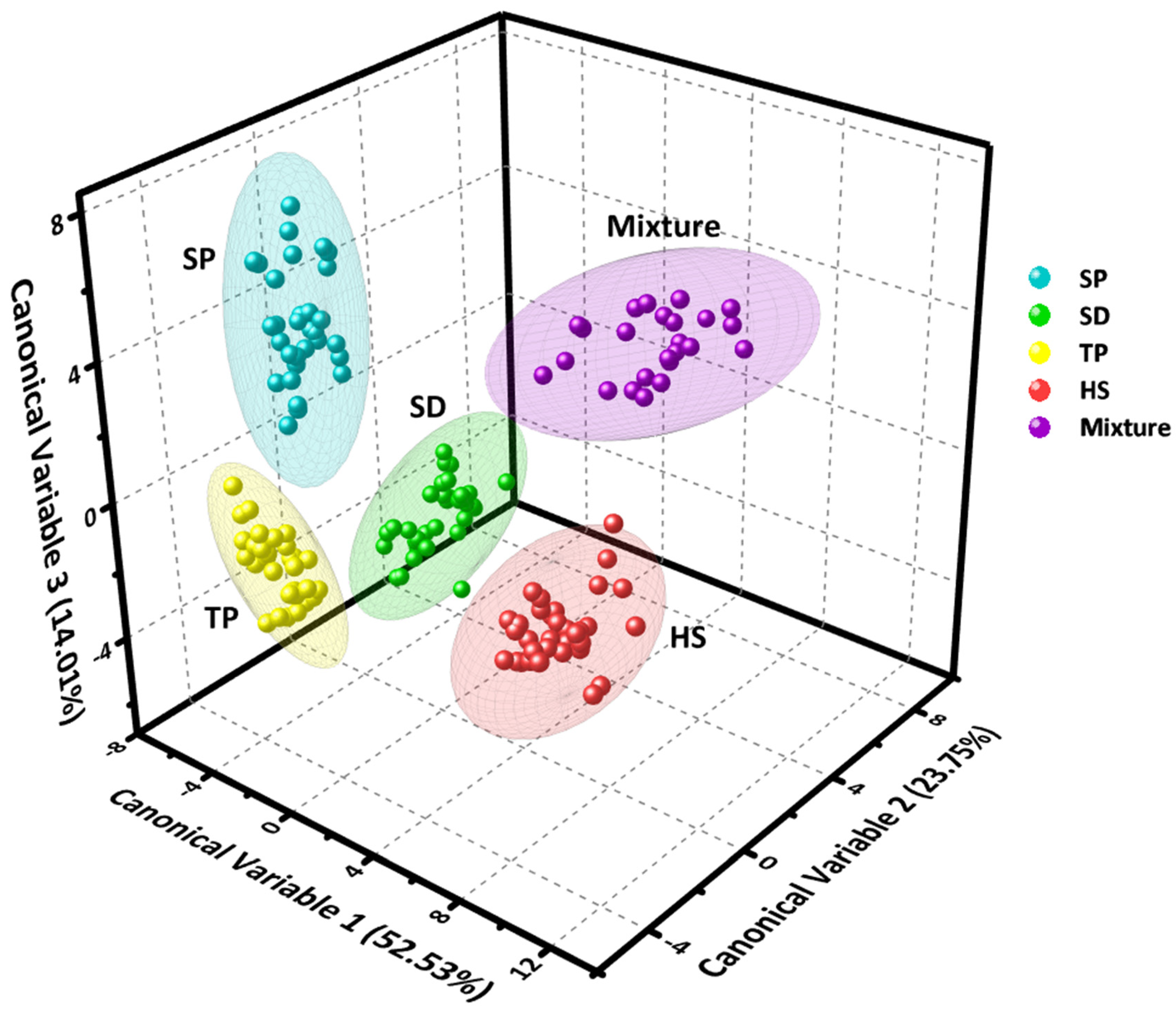
3.4. Detection and Discrimination Ability of Plasmonic Sensor Array
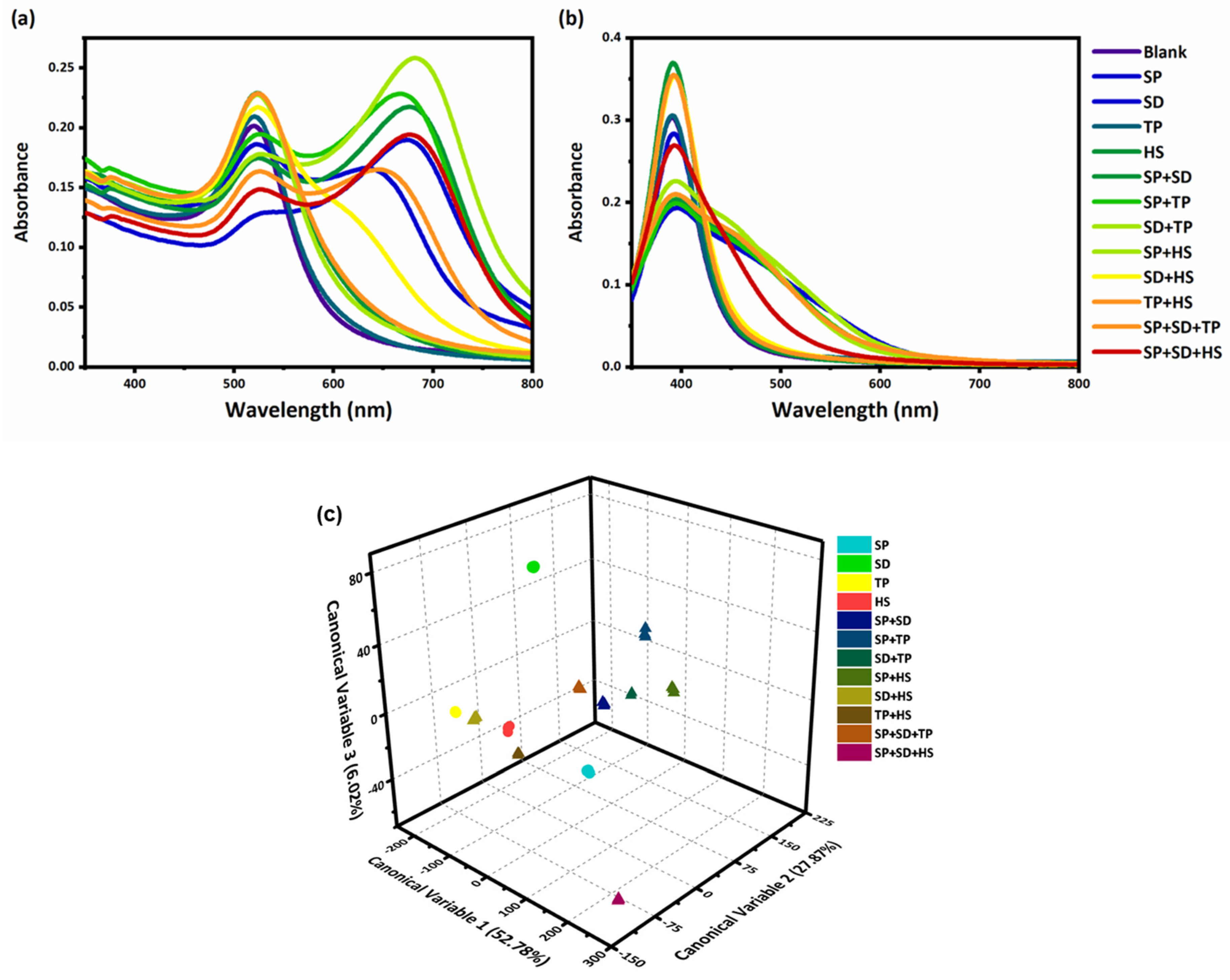
3.5. Mixture Analysis
3.6. Real Sample Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Herrero, A.M. Impact of biogenic amines on food quality and safety. Foods 2019, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothakos, V.; Devlieghere, F.; Villani, F.; Björkroth, J.; Ercolini, D. Lactic acid bacteria and their controversial role in fresh meat spoilage. Meat Sci. 2015, 109, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, K.M.; Aru, V.; Khakimov, B.; Aunskjær, U.; Engelsen, S.B. Biogenic amines: A key freshness parameter of animal protein products in the coming circular economy. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018, 22, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.S.; Sohaib, M.; Ahmad, R.S.; Nadeem, M.T.; Imran, A.; Arshad, M.U.; Kwon, J.H.; Amjad, Z. Ruminant meat flavor influenced by different factors with special reference to fatty acids. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Warner, R.D.; Johnson, S.K. Active and intelligent packaging in meat industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 61, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, A.R. Significance of biogenic amines to food safety and human health. Food Res. Int. 1996, 29, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, H.; de Almeida, J.M.M.; Matias, A.; Saraiva, C.; Jorge, P.A.; Coelho, L.C. Detection of biogenic amines in several foods with different sample treatments: An overview. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 113, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchis, Y.; Yusà, V.; Coscollà, C. Analytical strategies for organic food packaging contaminants. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1490, 22–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucco, E.; Gosetti, F.; Bobba, M.; Marengo, E.; Robotti, E.; Gennaro, M.C. High-performance liquid chromatography− ultraviolet detection method for the simultaneous determination of typical biogenic amines and precursor amino acids. Applications in food chemistry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triki, M.; Herrero, A.M.; Jiménez-Colmenero, F.; Ruiz-Capillas, C. Quality assessment of fresh meat from several species based on free amino acid and biogenic amine contents during chilled storage. Foods 2018, 7, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beneduce, L.; Romano, A.; Capozzi, V.; Lucas, P.; Barnavon, L.; Bach, B.; Vuchot, P.; Grieco, F.; Spano, G. Biogenic amine in wines. Ann. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 573–578. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, N.; Chopra, S.; Singh, G.; Raj, P.; Bhasin, A.; Sahoo, S.K.; Kuwar, A.; Singh, N. Chemosensors for biogenic amines and biothiols. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 4872–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, P.-Q.; Zhao, F.-L.; Yin, B.-C.; Ye, B.-C. A novel, colorimetric method for biogenic amine detection based on arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 8712–8714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, M.-S.; Meier, R.J.; Duerkop, A.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Chromogenic sensing of biogenic amines using a chameleon probe and the red− green− blue readout of digital camera images. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 8402–8405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papageorgiou, M.; Lambropoulou, D.; Morrison, C.; Namieśnik, J.; Płotka-Wasylka, J. Direct solid phase microextraction combined with gas chromatography–Mass spectrometry for the determination of biogenic amines in wine. Talanta 2018, 183, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palermo, C.; Muscarella, M.; Nardiello, D.; Iammarino, M.; Centonze, D. A multiresidual method based on ion-exchange chromatography with conductivity detection for the determination of biogenic amines in food and beverages. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sentellas, S.; Núñez, Ó.; Saurina, J. Recent advances in the determination of biogenic amines in food samples by (U) HPLC. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7667–7678. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ishimaru, M.; Muto, Y.; Nakayama, A.; Hatate, H.; Tanaka, R. Determination of biogenic amines in fish meat and fermented foods using column-switching high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Food Anal. Methods 2019, 12, 166–175. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Johansson, M.; Vidanarachchi, J.K.; Pickova, J.; Zamaratskaia, G. Determination of biogenic amines in aerobically stored beef using high-performance thin-layer chromatography densitometry. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. A—Anim. Sci. 2016, 66, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nour, K.; Salam, E.T.A.; Soliman, H.M.; Orabi, A.S. Gold nanoparticles as a direct and rapid sensor for sensitive analytical detection of biogenic amines. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 231. [Google Scholar]
- García-Acosta, B.; Comes, M.; Bricks, J.L.; Kudinova, M.A.; Kurdyukov, V.V.; Tolmachev, A.I.; Descalzo, A.B.; Marcos, M.D.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Moreno, A.; et al. Sensory hybrid host materials for the selective chromo-fluorogenic detection of biogenic amines. Chem. Commun. 2006, 21, 2239–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Scopelliti, R.; Severin, K. A molecular probe for the optical detection of biogenic amines. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 9639–9641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, P.-C.; Lien, C.-W.; Mao, J.-Y.; Unnikrishnan, B.; Chang, H.-T.; Lin, H.-J.; Huang, C.-C. Detection of urinary spermine by using silver-gold/silver chloride nanozymes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1009, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, Z.; He, H.; Zhou, H.; Liang, Y.; Wang, L.; Tian, S.; Zhu, H.; Wang, S. Designing an intelligent nanofiber ratiometric fluorescent sensor sensitive to biogenic amines for detecting the freshness of shrimp and pork. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 333, 129535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.D.; Zhu, H.Y.; Zhao, H.X.; Huang, C.Z. Highly selective colorimetric detection of spermine in biosamples on basis of the non-crosslinking aggregation of ssDNA-capped gold nanoparticles. Talanta 2013, 106, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Z.L.; Zhang, H.Z.; Li, Y.F.; Huang, C.Z. Selective colorimetric analysis of spermine based on the cross-linking aggregation of gold nanoparticles chain assembly. Talanta 2017, 167, 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Du, L.; Lao, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Lyu, X.; Gao, P.; Wu, S.; Minami, T.; Liu, Y. Freshness monitoring of raw fish by detecting biogenic amines using a gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric sensor array. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 6803–6810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Huo, D.; Fa, H.; Luo, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hou, C. Rapid and ultrasensitive detection of biogenic amines with colorimetric sensor array. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 274, 464–471. [Google Scholar]
- Orouji, A.; Ghasemi, F.; Bigdeli, A.; Hormozi-Nezhad, M.R. Providing multicolor plasmonic patterns with Au@ Ag core–shell nanostructures for visual discrimination of biogenic amines. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 20865–20874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigdeli, A.; Ghasemi, F.; Golmohammadi, H.; Abbasi-Moayed, S.; Nejad, M.A.F.; Fahimi-Kashani, N.; Jafarinejad, S.; Shahrajabian, M.; Hormozi-Nezhad, M.R. Nanoparticle-based optical sensor arrays. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 16546–16563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lu, Y.; He, L.; Pang, J.; Yang, F.; Liu, Y. Colorimetric sensor array based on gold nanoparticles: Design principles and recent advances. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 122, 115754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimi-Kashani, N.; Hormozi-Nezhad, M.R. Gold-nanoparticle-based colorimetric sensor array for discrimination of organophosphate pesticides. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 8099–8106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orouji, A.; Abbasi-Moayed, S.; Hormozi-Nezhad, M.R. ThThnated Development of a pH assisted AgNP-based colorimetric sensor array for simultaneous identification of phosalone and azinphosmethyl pesticides. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 219, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koushkestani, M.; Abbasi-Moayed, S.; Ghasemi, F.; Mahdavi, V.; Hormozi-Nezhad, M.R. Simultaneous detection and identification of thiometon, phosalone, and prothioconazole pesticides using a nanoplasmonic sensor array. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 151, 112109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantari, K.; Fahimi-Kashani, N.; Hormozi-Nezhada, M.R. Development of a colorimetric sensor array based on monometallic and bimetallic nanoparticles for discrimination of triazole fungicides. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 414, 5297–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirghafouri, M.R.; Abbasi-Moayed, S.; Ghasemi, F.; Hormozi-Nezhad, M.R. Nanoplasmonic sensor array for the detection and discrimination of pesticide residues in citrus fruits. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 5877–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, F.; Hormozi-Nezhad, M.R.; Mahmoudi, M. A colorimetric sensor array for detection and discrimination of biothiols based on aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 882, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Lu, Y.; Chang, N.; Yang, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y. Multidimensional colorimetric sensor array for discrimination of proteins. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarinejad, S.; Ghazi-Khansari, M.; Ghasemi, F.; Sasanpour, P.; Hormozi-Nezhad, M.R. Colorimetric fingerprints of gold nanorods for discriminating catecholamine neurotransmitters in urine samples. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivrigh, Z.J.-N.; Bigdeli, A.; Jafarinejad, S.; Hormozi-Nezhad, M.R. Multiplex detection of antidepressants with a single component condition-based colorimetric sensor array. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 363, 131855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, F.; Hormozi-Nezhad, M.R.; Mahmoudi, M. Label-free detection of β-amyloid peptides (Aβ40 and Aβ42): A colorimetric sensor array for plasma monitoring of Alzheimer’s disease. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 6361–6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Dong, Y.; Li, B.; Wu, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, S. Colorimetric sensor array with unmodified noble metal nanoparticles for naked-eye detection of proteins and bacteria. Analyst 2015, 140, 7672–7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Long, D.; Huang, W. Organic antifreeze discrimination by pattern recognition using nanoparticle array. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 264, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordbar, M.M.; Hemmateenejad, B.; Tashkhourian, J.; Nami-Ana, S.F. An optoelectronic tongue based on an array of gold and silver nanoparticles for analysis of natural, synthetic and biological antioxidants. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jornet-Martínez, N.; González-Béjar, M.; Moliner-Martínez, Y.; Campíns-Falcó, P.; Pérez-Prieto, J. Sensitive and selective plasmonic assay for spermine as biomarker in human urine. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kailasa, S.K.; Desai, M.L.; Baek, S.H.; Phan, L.M.T.; Nguyen, T.P.; Rafique, R.; Park, T.J. Independent spectral characteristics of functionalized silver nanoparticles for colorimetric assay of arginine and spermine in biofluids. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 17069–17077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapenna, A.; Dell’Aglio, M.; Palazzo, G.; Mallardi, A. “Naked” gold nanoparticles as colorimetric reporters for biogenic amine detection. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 600, 124903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gan, J.; Yang, Q.; Fu, L.; Wang, Y. Colorimetric detection of food freshness based on amine-responsive dopamine polymerization on gold nanoparticles. Talanta 2021, 234, 122706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Liu, X.; Zeng, W.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, T.; Yu, L.; Zhao, G. Colorimetric sensing towards spermine based on supramolecular pillar [5] arene reduced and stabilized gold nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 221, 117176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, K.A.; Bhamore, J.R.; Singhal, R.K.; Kailasa, S.K. Microwave assisted synthesis of tyrosine protected gold nanoparticles for dual (colorimetric and fluorimetric) detection of spermine and spermidine in biological samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 88, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neethirajan, S.; Ragavan, V.; Weng, X.; Chand, R. Biosensors for sustainable food engineering: Challenges and perspectives. Biosensors 2018, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimling, J.; Maier, M.; Okenve, B.; Kotaidis, V.; Ballot, H.; Plech, A. Turkevich method for gold nanoparticle synthesis revisited. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 15700–15707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Grant, E.; Lu, X. Determination of histamine in canned tuna by molecularly imprinted polymers-surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 901, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Nair, S.S.; Sai, V.; Satija, J. Nanomaterials based optical and electrochemical sensing of histamine: Progress and perspectives. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, R.N.; Kishore, N.; Lennen, R.M. Thermodynamic quantities for the ionization reactions of buffers. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 2002, 31, 231–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brereton, R.G.; Lloyd, G.R. Re-evaluating the role of the Mahalanobis distance measure. J. Chemom. 2016, 30, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

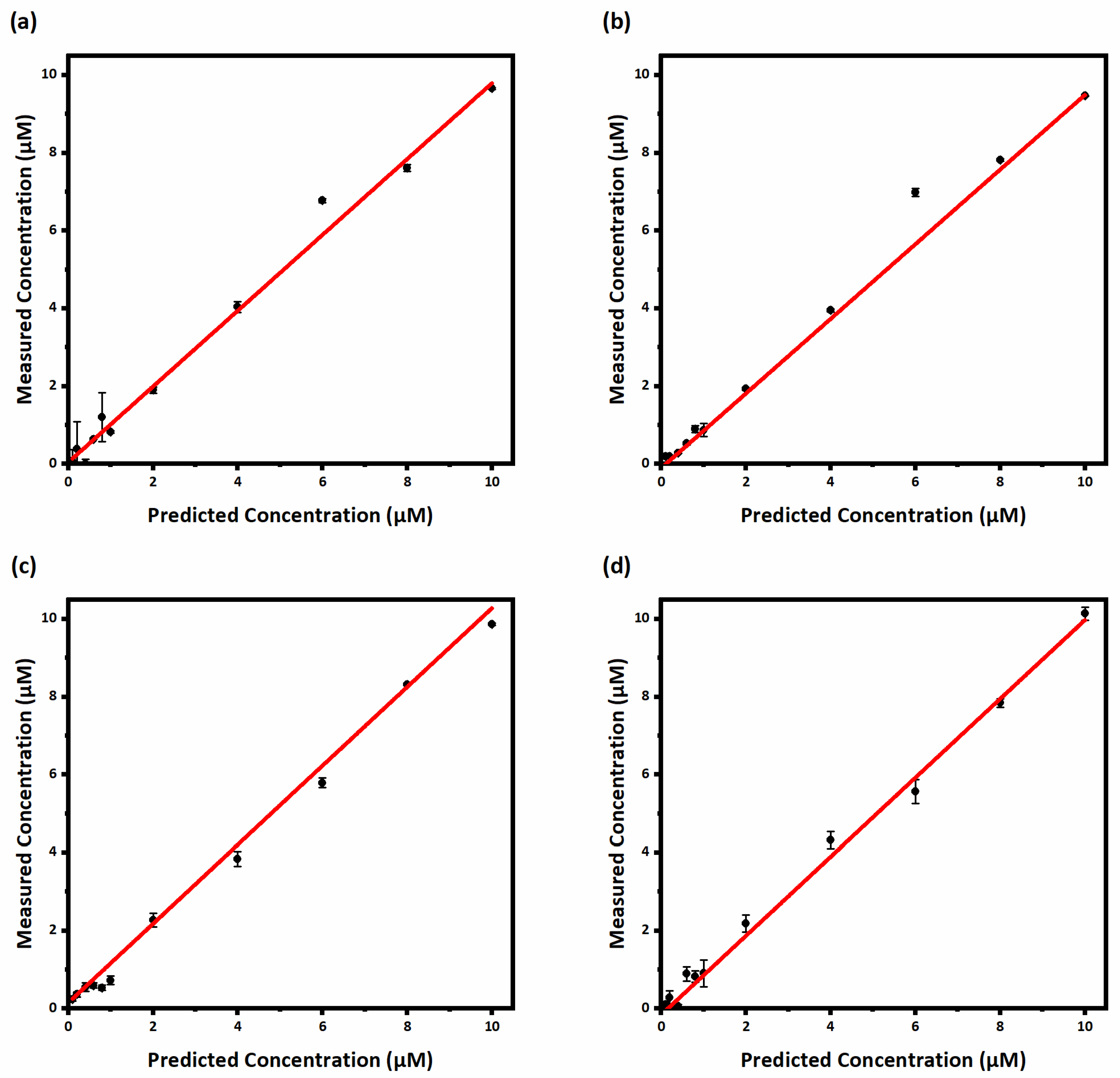

| BAs | LVs | RMSEP | R2 | SEN | Anal. SEN | LOD min | LOQ min | Linear Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SP | 5 | 0.4200 | 0.9921 | 0.0473 | 16.6448 | 0.3 | 0.9 | 0.1–10.0 |
| SD | 4 | 0.3540 | 0.9944 | 0.1373 | 43.1621 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.1–10.0 |
| TP | 5 | 0.2244 | 0.9977 | 0.0822 | 102.751 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.1–10.0 |
| HS | 8 | 0.2836 | 0.9964 | 0.0140 | 22.9916 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.1–10.0 |
| Sample | Spiked (µmol·L−1) | Found (µmol·L−1) | Recovery (%) | RSD (n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SP | 0.60 | 0.683 | 113.9 | 0.026 |
| SD | 0.60 | 0.605 | 100.8 | 0.044 |
| TP | 0.60 | 0.533 | 88.8 | 0.006 |
| HS | 0.60 | 0.661 | 110.1 | 0.117 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbasi-Moayed, S.; Orouji, A.; Hormozi-Nezhad, M.R. Multiplex Detection of Biogenic Amines for Meat Freshness Monitoring Using Nanoplasmonic Colorimetric Sensor Array. Biosensors 2023, 13, 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13080803
Abbasi-Moayed S, Orouji A, Hormozi-Nezhad MR. Multiplex Detection of Biogenic Amines for Meat Freshness Monitoring Using Nanoplasmonic Colorimetric Sensor Array. Biosensors. 2023; 13(8):803. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13080803
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbasi-Moayed, Samira, Afsaneh Orouji, and Mohammad Reza Hormozi-Nezhad. 2023. "Multiplex Detection of Biogenic Amines for Meat Freshness Monitoring Using Nanoplasmonic Colorimetric Sensor Array" Biosensors 13, no. 8: 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13080803
APA StyleAbbasi-Moayed, S., Orouji, A., & Hormozi-Nezhad, M. R. (2023). Multiplex Detection of Biogenic Amines for Meat Freshness Monitoring Using Nanoplasmonic Colorimetric Sensor Array. Biosensors, 13(8), 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13080803





