Mechanistic Elucidation of Nanomaterial-Enhanced First-Generation Biosensors Using Probe Voltammetry of an Enzymatic Reaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Instrumentation
2.2. Preparation of Biosensor Systems
2.3. MPC-Doped Xerogel-Biosensing Schemes
2.4. Xerogel-Biosensing Schemes with CNTs
3. Results and Discussion
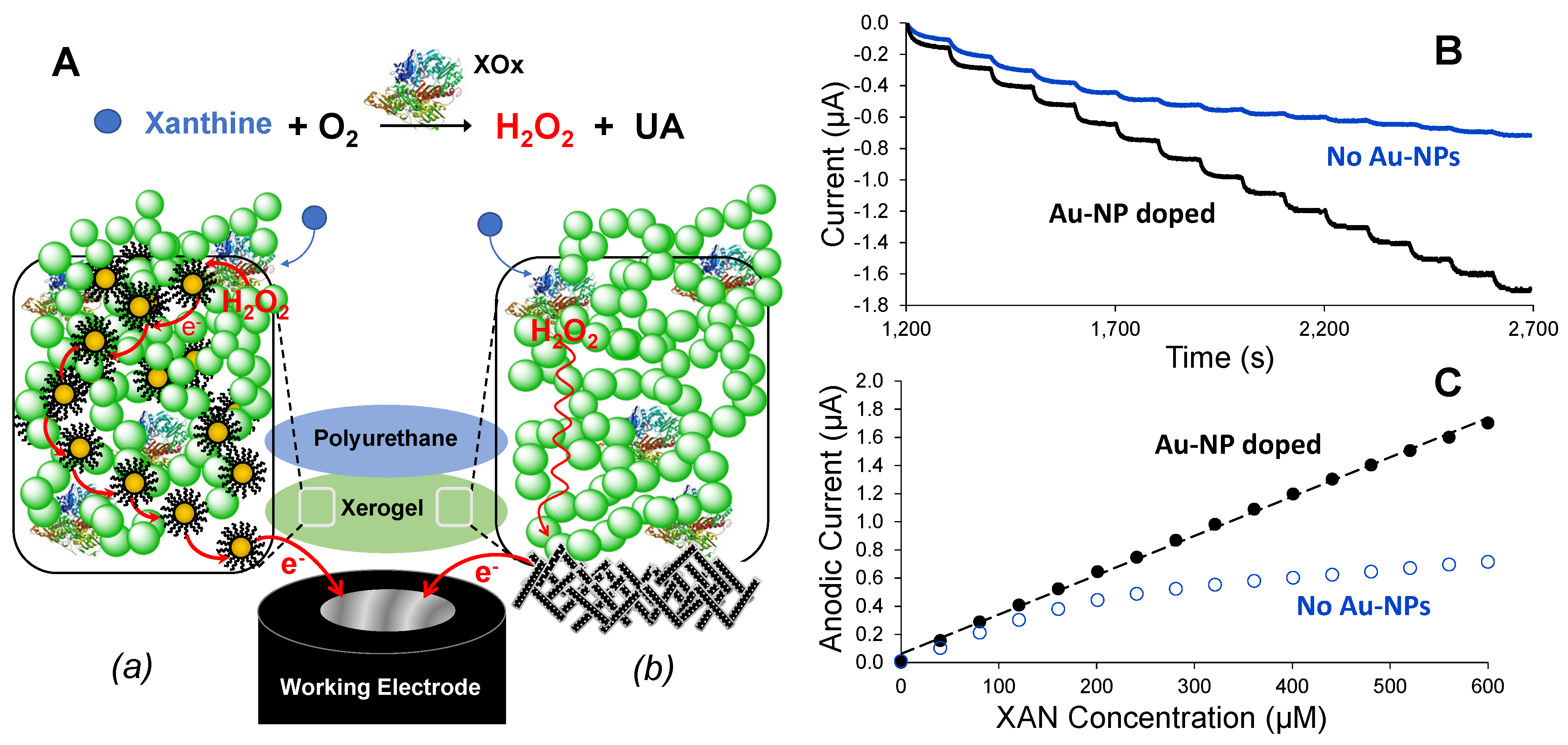
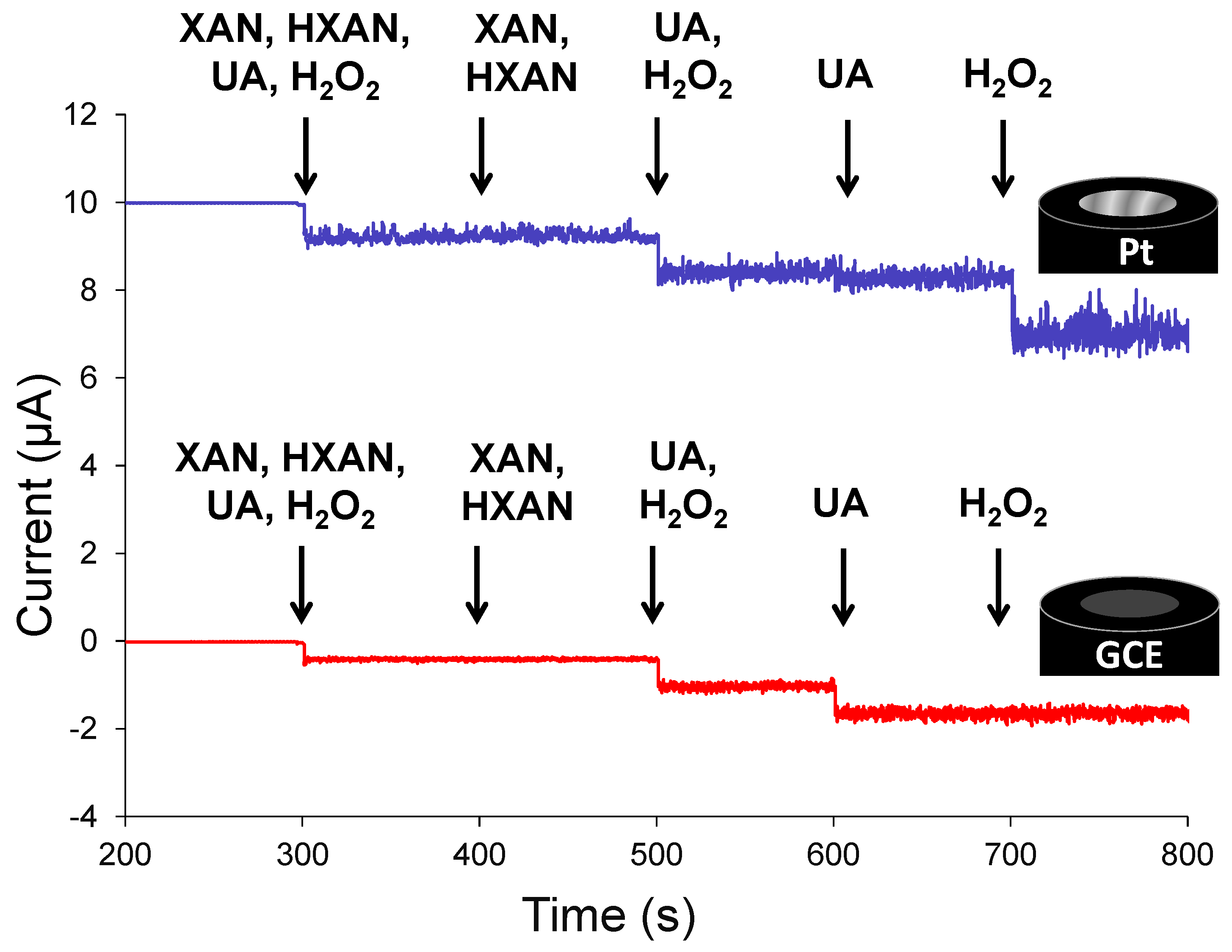
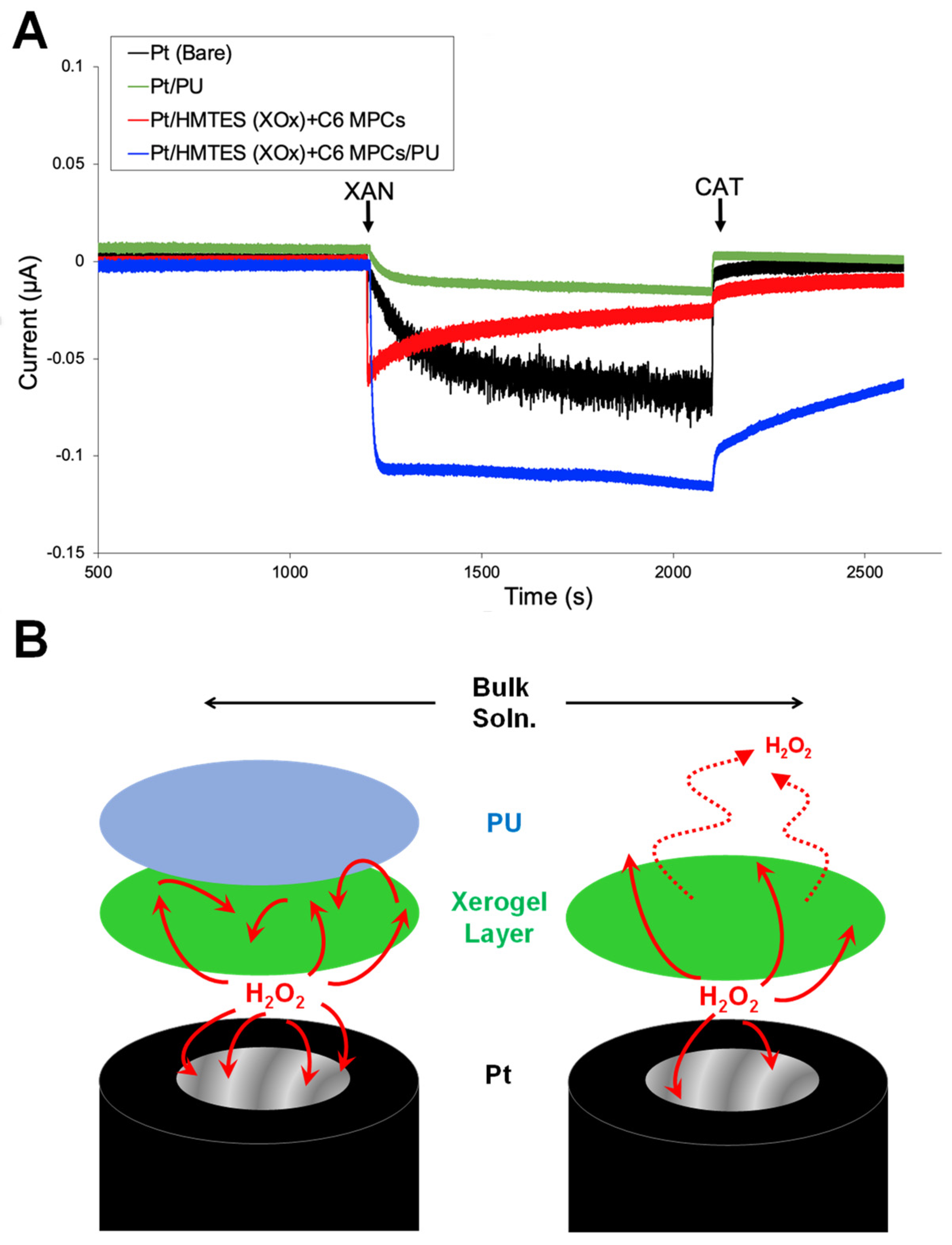
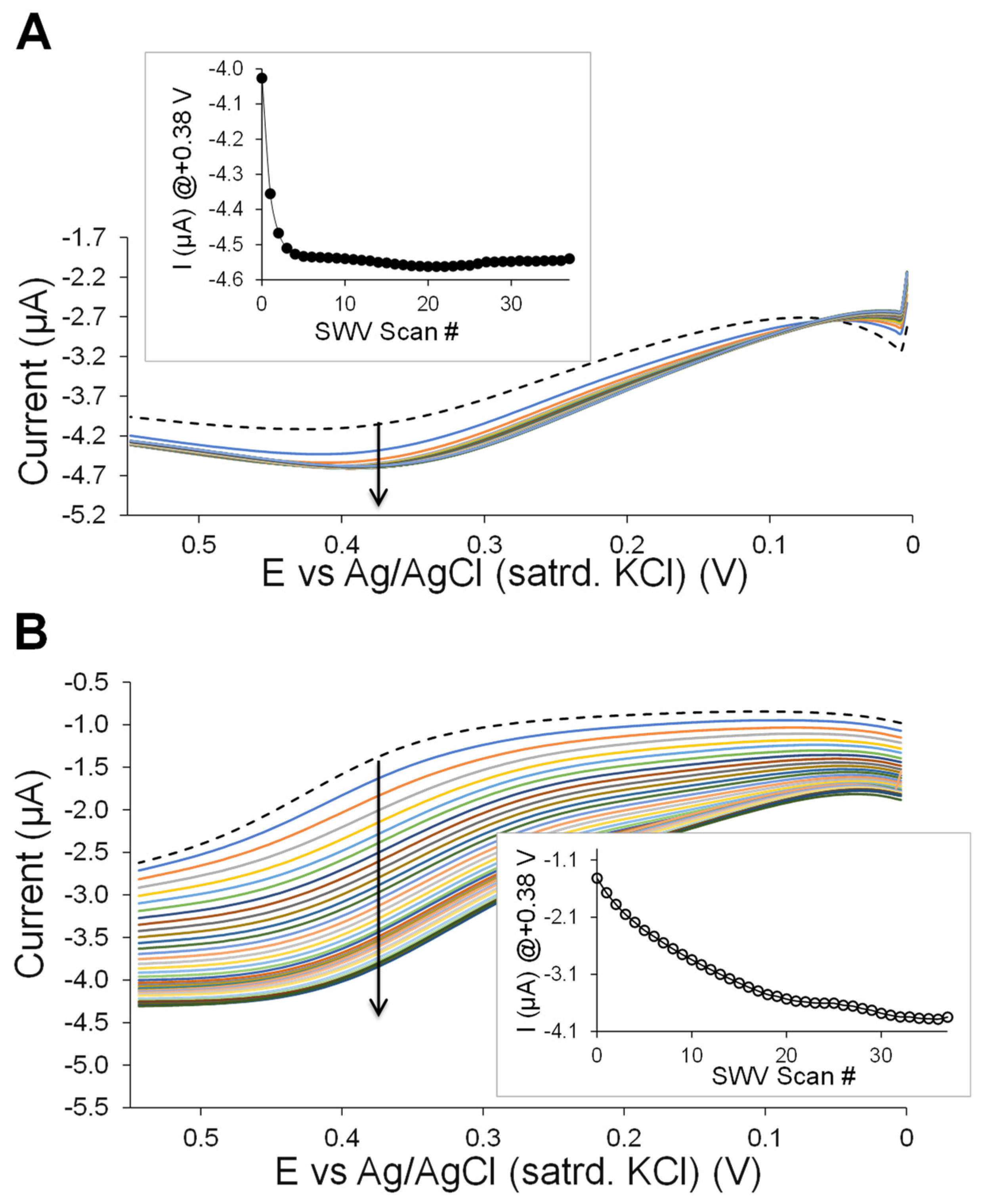
3.1. Nanoparticle Network-Enhanced Xerogel Biosensing Schemes
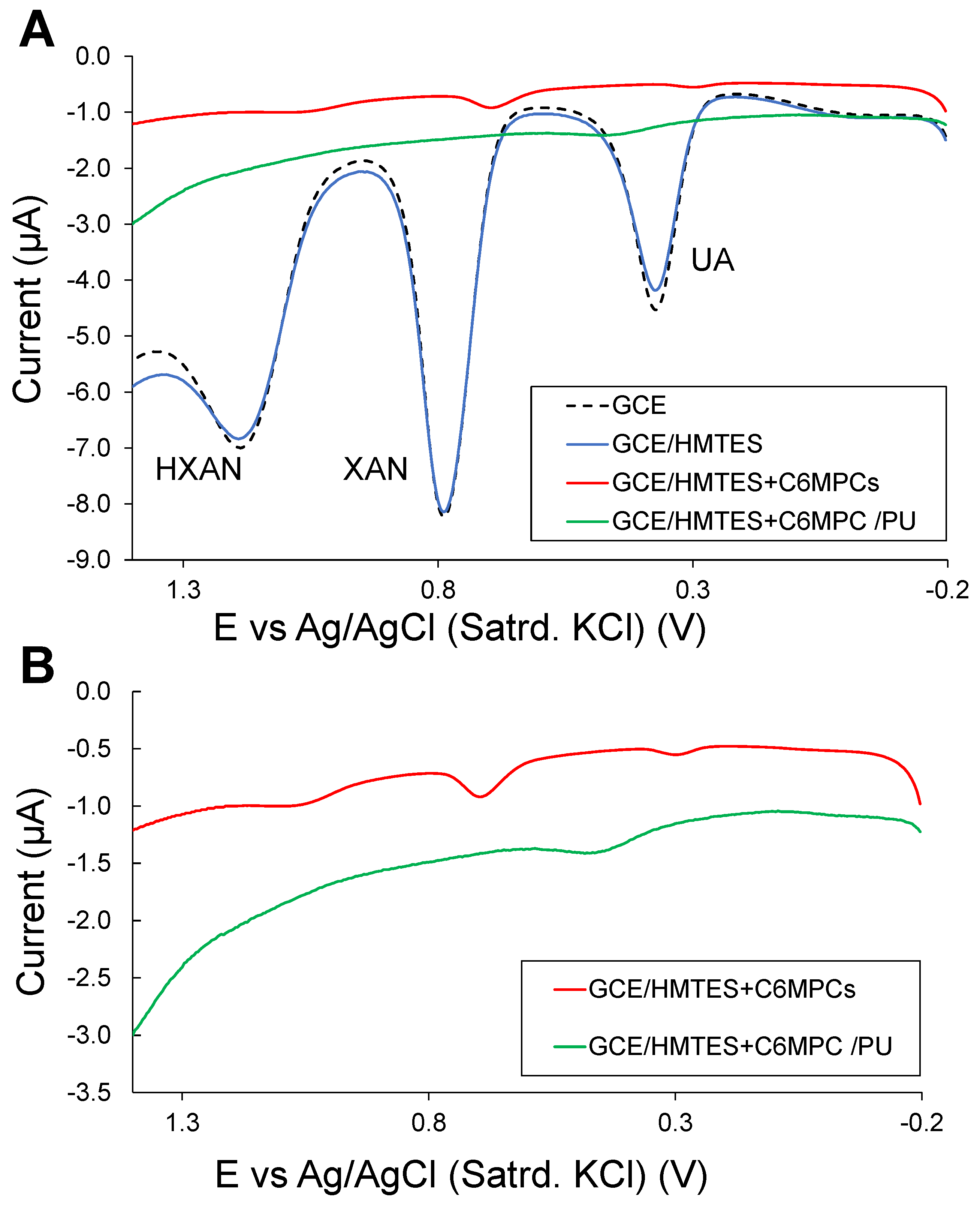
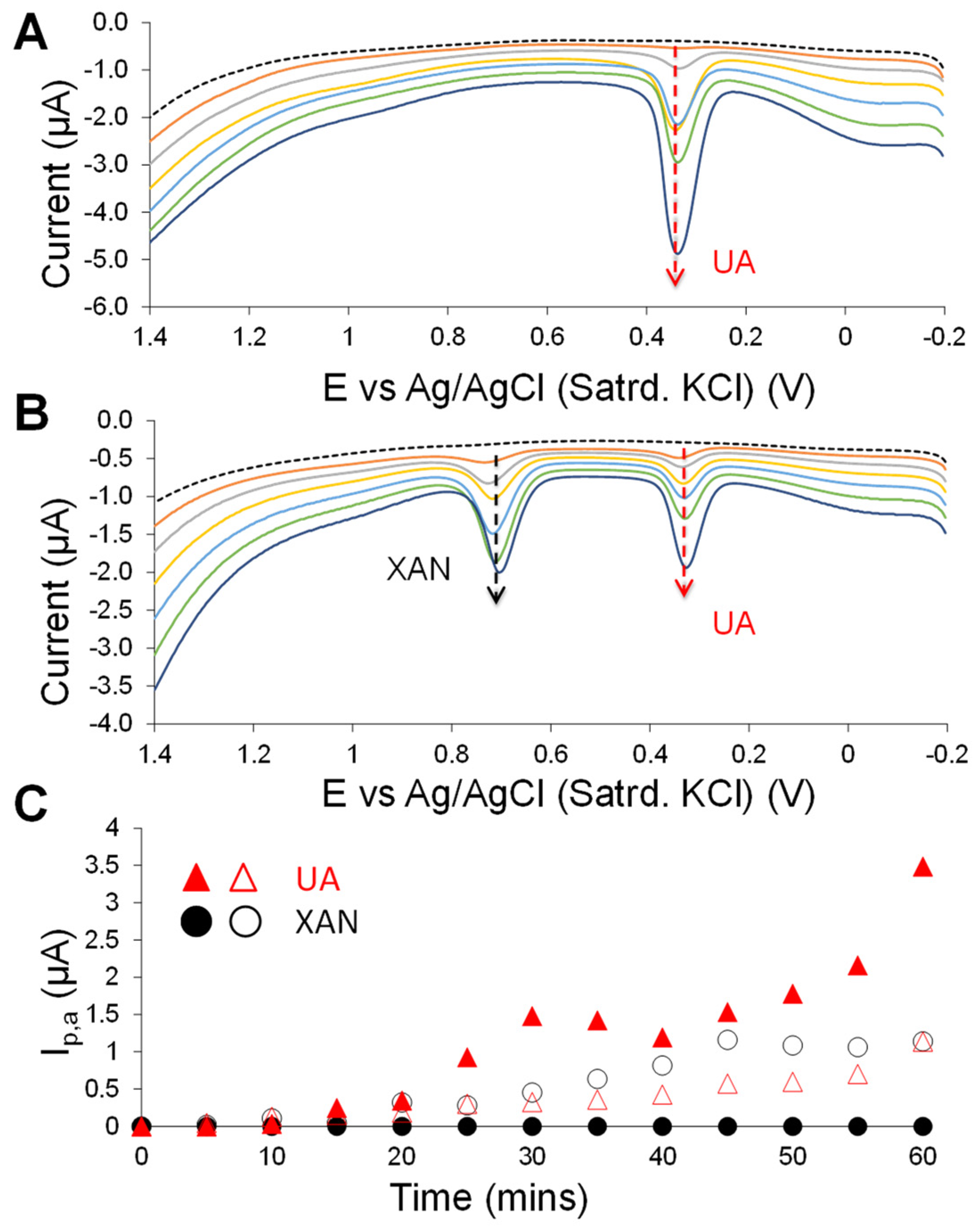
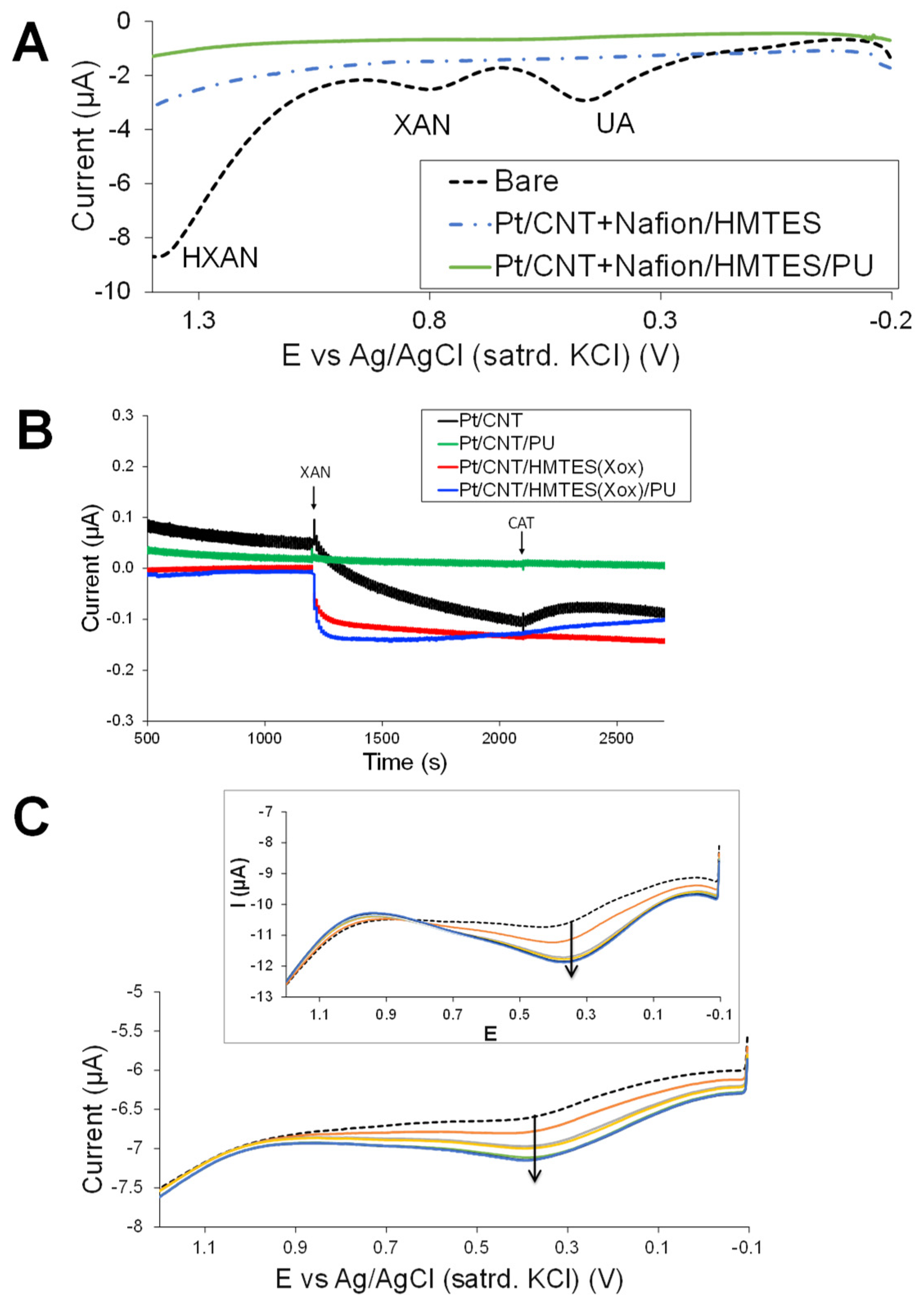
3.2. Carbon Nanotube-Enhanced Xerogel Biosensing Schemes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Theyagarajan, K.; Kim, Y.-J. Recent Developments in the Design and Fabrication of Electrochemical Biosensors Using Functional Materials and Molecules. Biosensors 2023, 13, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, M.; Kuang, Z.; Li, X.; Xu, F.; Miao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Lou, X.; Li, H.; et al. Electrochemical Biosensors for Whole Blood Analysis: Recent Progress, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 7953–8039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.O.; Singh, B. Electrochemical Biosensors for Detection of Pesticides and Heavy Metal Toxicants in Water: Recent Trends and Progress. ACS Est Water 2021, 1, 462–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, A.; Ahmed, A.; Sundramoorthy, A.K.; Furukawa, H.; Arya, S.; Khosla, A. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Biosensors: Applications, Challenges, and Future Scope. Biosensors 2021, 11, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.; Vaughan, D.H.; Cardosi, M.F. Elements of Biosensor Construction. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1995, 17, 1030–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, U.; Gupta, V.; Arun, R.K.; Chanda, N. Recent advances in enzymatic biosensors for point-of-care detection of biomolecules. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2022, 119, 3393–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollella, P.; Katz, E. Enzyme-Based Biosensors: Tackling Electron Transfer Issues. Sensors 2020, 20, 3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollella, P.; Gorton, L. Enzyme based amperometric biosensors. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2018, 10, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinyou, P.; Blay, V.; Muresan, L.M.; Noguer, T. Enzyme-modified electrodes for biosensors and biofuel cells. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 1336–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, U.J.; Fermin, C.D.; Kim, M. Immobilized Enzymes in Biosensor Applications. Materials 2019, 12, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-De-Corcuera, J.I.; Olstad, H.E.; García-Torres, R. Stability and Stabilization of Enzyme Biosensors: The Key to Successful Application and Commercialization. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 293–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramya, M.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Rangasamy, G.; Uma shankar, V.; Rajesh, G.; Nirmala, K.; Saravanan, A.; Krishnapandi, A. A recent advancement on the applications of nanomaterials in electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabulut, G.; Beköz Üllen, N.; Karakuş, S. Nanostructures in Biosensors: Development and Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Kumari, N.; Sharma, R. Nanocomposites (conducting polymer and nanoparticles) based electrochemical biosensor for the detection of environment pollutant: Its issues and challenges. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2020, 85, 106438. [Google Scholar]
- Heydari-Bafrooei, E.; Ensafi, A.A. Nanomaterials-based biosensing strategies for biomarkers diagnosis, a review. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2023, 13, 100245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Li, N. Noble Metal Nanoparticles-Based Colorimetric Biosensor for Visual Quantification: A Mini Review. Chemosensors 2019, 7, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, T.M.; Morais, S. New generation of Electrochemical Sensors Based on Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Bonilla-Cruz, J. Review on Healthcare Biosensing Nanomaterials. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 5042–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, K.; Wang, J.S. Electrochemical sensors: From the bench to the skin. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2021, 344, 130178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Deng, Y.; He, N. Point-of-care diagnostics for infectious diseases: From methods to devices. Nano Today 2021, 37, 101092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrahari, S.; Gautam, R.K.; Singh, A.K.; Tiwari, I. Nanoscale materials-based hybrid frameworks modified electrochemical biosensors for early cancer diagnostics: An overview of current trends and challenges. Microchem. J. 2022, 172, 106980. [Google Scholar]
- Sempionatto, J.R.; Jeerapan, I.; Krishnan, S.; Wang, J. Wearable Chemical Sensors: Emerging Systems for On-Body Analytical Chemistry. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 378–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, S.; Trung, T.Q.; Lee, N.-E. Recent progress, challenges, and prospects of fully integrated mobile and wearable point-of-care testing systems for self-testing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 1812–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.; Cho, H.Y.; Shin, M.; Choi, H.K.; Lee, T.; Choi, J.W. Flexible electrochemical biosensors for healthcare monitoring. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 7303–7318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Lv, L.; Wang, X.; Wei, M. A pattern-free paper enzyme biosensor for one-step detection of fish freshness indicator hypoxanthine with a microfluidic aggregation effect. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hondred, J.A.; Johnson, Z.T.; Claussen, J.C. Nanoporous gold peel-and-stick biosensors created with etching inkjet maskless lithography for electrochemical pesticide monitoring with microfluidics. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 11376–11388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, L.B.; Labban, N.; Conway, G.E.; Pollock, J.A.; Leopold, M.C. Adaptable Xerogel-Layered Amperometric Biosensor Platforms on Wire Electrodes for Clinically Relevant Measurements. Sensors 2019, 19, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasca, F.; Tortolini, C.; Bollella, P.; Antiochia, R. Microneedle-based electrochemical devices for transdermal biosensing: A review. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 16, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yao, C.; Li, Z. Microarray-based chemical sensors and biosensors: Fundamentals and food safety applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 158, 116785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, U.; Saxena, K.; Hooda, V.; Balayan, S.; Singh, A.P.; Tikadar, M.; Chauhan, N. Emerging vistas on pesticides detection based on electrochemical biosensors—An update. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kumar, P.; Pournara, A.; Vellingiri, K.; Kim, K.-H. Nanomaterials for the sensing of narcotics: Challenges and opportunities. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 106, 84–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, A.; Lu, Y.; Schoenfisch, M.H. Fabrication of Nitric Oxide-Releasing Porous Polyurethane Membranes-Coated Needle-type Implantable Glucose Biosensors. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 10488–10494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, G.E.; Lambertson, R.H.; Schwarzmann, M.A.; Pannell, M.J.; Kerins, H.W.; Rubenstein, K.J.; Dattelbaum, J.D.; Leopold, M.C. Layer-by-layer design and optimization of xerogel-based amperometric first generation biosensors for uric acid. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 775, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.H.; Hall, J.R.; Leopold, M.C. Monolayer-Protected Nanoparticle Doped Xerogels as Functional Components of Amperometric Glucose Biosensors. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 4057–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannell, M.J.; Doll, E.E.; Labban, N.; Wayu, M.B.; Pollock, J.A.; Leopold, M.C. Versatile sarcosine and creatinine biosensing schemes utilizing layer-by-layer construction of carbon nanotube-chitosan composite films. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 814, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labban, N.; Wayu, M.B.; Steele, C.M.; Munoz, T.S.; Pollock, J.A.; Case, W.S.; Leopold, M.C. First Generation Amperometric Biosensing of Galactose with Xerogel-Carbon Nanotube Layer-By-Layer Assemblies. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Q.M.; Wemple, A.H.; Leopold, M.C. Nanomaterial-Doped Xerogels for Biosensing Measurements of Xanthine in Clinical and Industrial Applications. Gels 2023, 9, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, A.E.F.; Bettio, G.B.; Pereira, A.C. An Electrochemical Sensor Based on Electropolymerization of ss-Cyclodextrin and Reduced Graphene Oxide on a Glassy Carbon Electrode for Determination of Neonicotinoids. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayu, M.B.; Pannell, M.J.; Leopold, M.C. Layered Xerogel Films Incorporating Monolayer-Protected Cluster Networks on Platinum-Black-Modified Electrodes for Enhanced Sensitivity in First-Generation Uric Acid Biosensing. ChemElectroChem 2016, 3, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiPasquale, L.T.; Poulos, N.G.; Hall, J.R.; Minocha, A.; Bui, T.A.; Leopold, M.C. Structure-function relationships affecting the sensing mechanism of monolayer-protected cluster doped xerogel amperometric glucose biosensors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 450, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finklea, H.O. Electrochemistry of organized monolayers of thiols and related molecules on electrodes. In Electroanalytical Chemistry: A Series of Advances; Bard, A.J., Rubenstein, I., Eds.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Volume 19, pp. 109–335. [Google Scholar]
- Dervisevic, M.; Dervisevic, E.; Senel, M. Recent progress in nanomaterial-based electrochemical and optical sensors for hypoxanthine and xanthine. A review. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.; Fooladi, E.; Malekaneh, M. A nanocomposite/crude extract enzyme-based xanthine biosensor. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 464, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Won, M.S.; Shim, Y.B. Xanthine sensors based on anodic and cathodic detection of enzymatically generated hydrogen peroxide. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.H.; Ahommed, M.S.; Daizy, M. Detection of xanthine in food samples with an electrochemical biosensor based on PEDOT:PSS and functionalized gold nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 36147–36154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierini, G.D.; Robledo, S.N.; Zon, M.A.; Di Nezio, M.S.; Granero, A.M.; Fernández, H. Development of an electroanalytical method to control quality in fish samples based on an edge plane pyrolytic graphite electrode. Simultaneous determination of hypoxanthine, xanthine and uric acid. Microchem. J. 2018, 138, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.G.; Voinov, M.A.; Schmidt, A.C.; Smirnova, T.I.; Sombers, L.A. The Hydroxyl Radical is a Critical Intermediate in the Voltammetric Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2516–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlache, M.; Senturk, Z.; Quarin, G.; Kauffmann, J.-M. Electrochemical behavior of H2O2 on gold. Electroanalysis 1997, 9, 1088–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wilson, G.S. Electrochemical oxidation of H2O2 on Pt and Pt + Ir electrodes in physiological buffer and its applicability to H2O2-based biosensors. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1993, 345, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, V.G.; Zarapkar, L.R.; Dhaneshwar, R.G. Electrochemical studies of hydrogen peroxide at a platinum disc electrode. Electrochim. Acta 1981, 26, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardar, R.; Funston, A.M.; Mulvaney, P.; Murray, R.W. Gold Nanoparticles: Past, Present, and Future. Langmuir 2009, 25, 13840–13851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, C.; Brett, A.M.O. Electrochemistry Principles, Methods, and Applications; Oxford Univeristy Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Miles, D.T.; Leopold, M.C.; Hicks, J.F.; Murray, R.W. Simulations of quantized double layer charging voltammetry of poly-disperse and mono-disperse monolayer-protected clusters. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2003, 554, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wemple, A.H.; Kaplan, J.S.; Leopold, M.C. Mechanistic Elucidation of Nanomaterial-Enhanced First-Generation Biosensors Using Probe Voltammetry of an Enzymatic Reaction. Biosensors 2023, 13, 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13080798
Wemple AH, Kaplan JS, Leopold MC. Mechanistic Elucidation of Nanomaterial-Enhanced First-Generation Biosensors Using Probe Voltammetry of an Enzymatic Reaction. Biosensors. 2023; 13(8):798. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13080798
Chicago/Turabian StyleWemple, Ann H., Jamie S. Kaplan, and Michael C. Leopold. 2023. "Mechanistic Elucidation of Nanomaterial-Enhanced First-Generation Biosensors Using Probe Voltammetry of an Enzymatic Reaction" Biosensors 13, no. 8: 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13080798
APA StyleWemple, A. H., Kaplan, J. S., & Leopold, M. C. (2023). Mechanistic Elucidation of Nanomaterial-Enhanced First-Generation Biosensors Using Probe Voltammetry of an Enzymatic Reaction. Biosensors, 13(8), 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13080798




