Wearable Insulin Biosensors for Diabetes Management: Advances and Challenges
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Insulin Structure and Function and Its Detection in Biological Fluids
3. Difficulties and Limitations of Current Insulin Management Techniques
4. Conventional Insulin Detection Methods
5. Biosensor Technology
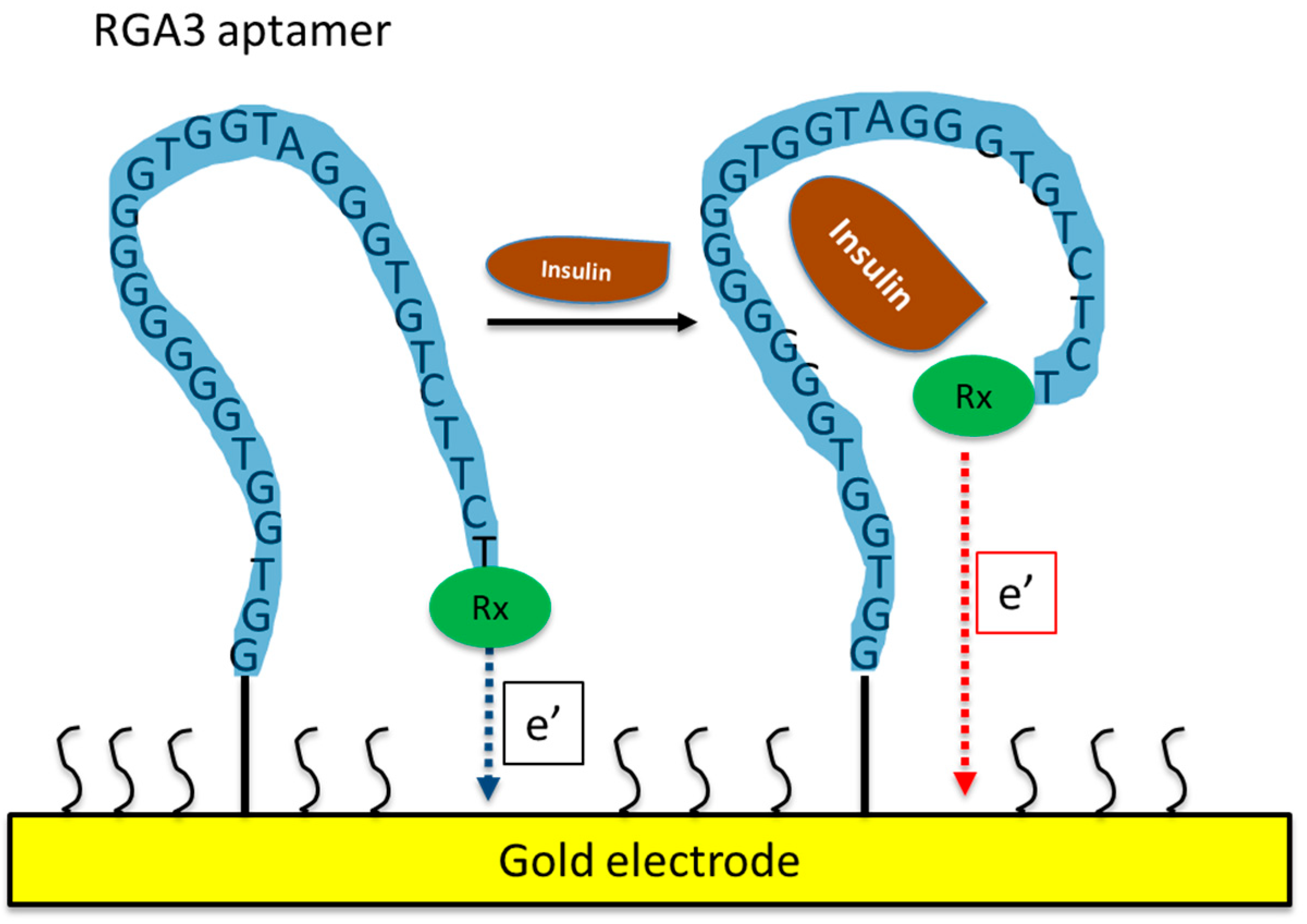
5.1. Aptamer-Based Insulin Biosensors
5.2. MIP-Based Insulin Biosensors
5.3. Label-Free Insulin Biosensors
5.4. Other Types of Insulin Biosensors
6. Challenges Associated with Insulin Detection Methods for Point-of-Care Biosensors
7. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, A. Rethinking the “discovery” of insulin. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2021, 25, E1636–E1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogurtsova, K.; Guariguata, L.; Barengo, N.C.; Lopez-Doriga Ruiz, P.; Sacre, J.W.; Karuranga, S.; Sun, H.; Boyko, E.J.; Magliano, D.J. IDF diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of undiagnosed diabetes in adults for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 183, 109118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Gilbert, E.R.; Liu, D. Regulation of insulin synthesis and secretion and pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction in diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2013, 9, 25–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiedorova, K.; Augustynek, M.; Kubicek, J.; Kudrna, P.; Bibbo, D. Review of present method of glucose from human blood and body fluids assessment. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 211, 114348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadian, N.; Manickavasagan, A.; Ali, A. Comparative assessment of blood glucose monitoring techniques: A review. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2023, 47, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholten, K.; Meng, E. A review of implantable biosensors for closed-loop glucose control and other drug delivery applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 544, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggidis, A.G.A.; Newman, J.D.; Aggidis, G.A. Investigating pipeline and state of the art blood glucose biosensors to formulate next steps. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanghera, N.; Anderson, A.; Nuar, N.; Xie, C.; Mitchell, D.; Klein-Seetharaman, J. Insulin biosensor development: A case study. Int. J. Parallel Emergent Distrib. Syst. 2017, 32, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soffe, R.; Nock, V.; Chase, J.G. Towards point-of-care insulin detection. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabu, C.; Henna, T.K.; Raphey, V.R.; Nivitha, K.P.; Pramod, K. Advanced biosensors for glucose and insulin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, K.; Feng, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, K.; Liu, Q.; Deng, L.; Wang, G.; Chen, Y.; Liu, G. Insulin quantification towards early diagnosis of prediabetes/diabetes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 203, 114029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahoor, I.; Singh, S.; Behl, T.; Sharma, N.; Naved, T.; Subramaniyan, V.; Fuloria, S.; Kumar Fuloria, N.; Bhatia, S.; Al-Harrasi, A.; et al. Emergence of microneedles as a potential therapeutics in diabetes mellitus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 3302–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafiee, B.; Fakhari, A.R. Electrocatalytic oxidation and determination of insulin at nickel oxide nanoparticles-multiwalled carbon nanotube modified screen printed electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 46, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffcoate, W. Growth hormone therapy and its relationship to insulin resistance, glucose intolerance and diabetes mellitus. Drug Saf. 2002, 25, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, G. Insulin and insulin resistance. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2005, 26, 19–39. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G. Optimal homeostasis necessitates bistable control. J. R. Soc. Interface 2012, 9, 2723–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaven, G.M. Banting Lecture 1988: Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 1988, 37, 1595–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groschl, M. The physiological role of hormones in saliva. BioEssays 2009, 31, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, B.; Maccallini, G.; Oneto, A.; Gonzalez, D.; Hirschler, V.; Aranda, C.; Berg, G. Measurement of fasting salivary insulin and its relationship with serum insulin in children. Endocr. Connect. 2012, 1, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, H.; Channa, A.; Jeoti, V.; Stojanovi, G.M. Comprehensive review on wearable sweat-glucose sensors for continuous glucose monitoring. Sensors 2022, 22, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyer, C.; Hanson, R.L.; Tataranni, P.A.; Bogardus, C.; Pratley, R.E. A high fasting plasma insulin concentration predicts type 2 diabetes independent of insulin resistance: Evidence for a pathogenic role of relative hyperinsulinemia. Diabetes 2000, 49, 2094–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muoio, D.M.; Newgard, C.B. Mechanisms of disease: Molecular and metabolic mech- anisms of insulin resistance and beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjostrand, M.; Holmang, A.; Lonnroth, P. Measurement of interstitial insulin in human muscle. Am. Physiol. Soc. 1999, 276, E151–E154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, P.-A.E.; Fowelin, J.P.; von Schenck, H.P.; Smith, U.P.; Lonnroth, P.N. Measurement by microdialysis of the insulin concentration in subcutaneous interstitial fluid-Importance of the endothelial barrier for insulin. Diabetes 1993, 42, 1469–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodenlenz, M.; Schaupp, L.A.; Druml, T.; Sommer, R.; Wutte, A.; Schaller, H.C.; Sinner, F.; Wach, P.; Pieber, T.R. Measurement of interstitial insulin in human adipose and muscle tissue under moderate hyperinsulinemia by means of direct interstitial access. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 289, E296–E300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myette-Côté, É.; Baba, K.; Brar, R.; Little, J.P. Detection of salivary insulin following low versus high carbohydrate meals in humans. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messenger, B.; Clifford, M.N.; Morgan, L.M. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and insulin-like immunoreactivity in saliva following sham-fed and swallowed meals. J. Endocrinol. 2003, 177, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmina, E.; Stanczyk, F.Z.; Lobo, R.A. Evaluation of hormonal status. In Yen and Jaffe’s Reproductive Endocrinology, 8th ed.; Strauss, F., Barbieri, R.L., Gargiulo, A.R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 887–915. [Google Scholar]
- Melmed, S.; Auchus, R.J.; Goldfine, A.B.; Koenig, R.J.; Rosen, C.J. (Eds.) Williams Textbook of Endocrinology, 14th ed.; Elsevier-Health Sciences Division: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Aun, F.; Meguid, M.M.; Soeldner, J.S.; Stolf, N.A. Urinary insulin levels in health and disease-a concise review. Postgrad. Med. J. 1975, 51, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.; Lema, C.; Redfern, R.; Richdale, K. Changes in tear glucose and insulin concentrations following an oral glucose tolerance test. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2022, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, A.D.; Harris-Hayes, M.; Schootman, M. Epidemiology of diabetes and diabetes-related complications. Phys. Ther. 2008, 88, 1254–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhleh, A.; Shehadeh, N. Hypoglycemia in diabetes: An update on pathophysiology, treatment, and prevention. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 2036–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarosinski, M.A.; Chen, Y.-S.; Varas, N.; Dhayalan, B.; Chatterjee, D.; Weiss, M.A. New horizons: Next-generation insulin analogues: Structural principles and clinical goals. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 909–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morello, C.M. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of insulin analogs in special populations with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2011, 4, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olczuk, D.; Priefer, R. A history of continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) in self-monitoring of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2018, 12, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Probst, D.; Klonoff, D.; Sode, K. Continuous glucose monitoring systems—Current status and future perspectives of the flagship technologies in biosensor research. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 181, 113054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajizadeh, I.; Rashid, M.; Turksoy, K.; Samadi, S.; Feng, J.; Frantz, N.; Sevil, M.; Cengiz, E.; Cinar, A. Plasma insulin estimation in people with Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 9846–9857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegmund, T.; Heinemann, L.; Kolassa, R.; Thomas, A. Discrepancies between blood glucose and interstitial glucose—Technological artifacts or physiology: Implications for selection of the appropriate therapeutic target. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2017, 11, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosinski, M.A.; Dhayalan, B.; Rege, N.; Chatterjee, D.; Weiss, M.A. ‘Smart’ insulin-delivery technologies and intrinsic glucose-responsive insulin analogues. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 1016–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, L.M.; Jacobs, P.G.; Riddell, M.C.; Zaharieva, D.P.; Castle, J.R. Opportunities and challenges in closed-loop systems in Type 1 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Prinyawiwatkul, W.; Xu, Z. Insulin: A review of analytical methods. Analyst 2019, 144, 4139–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, M.J.; Gapinski, J.P. A rapid Elisa for measuring insulin in a large number of research samples. Metab. Clin. Exp. 1989, 38, 450–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Matsunaga, T. Fully Automated Chemiluminescence Immunoassay of Insulin Using Antibody-Protein a-Bacterial Magnetic Particle Complexes. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 3518–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosli, N.; Kwon, H.-J.; Lim, J.; Yoon, Y.A.; Jeong, J.-S. Measurement comparability of insulin assays using conventional immunoassay kits. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Caulfield, M.P.; McPhaul, M.J.; Reitz, R.E.; Taylor, S.W.; Clarke, N.J. Quantitative insulin analysis using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in a high-throughput clinical laboratory. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TermehYousef, A.; Bagheri, S.; Adib, N. Integration of biosensors based on microfluidic: A review. Sens. Rev. 2015, 35, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, L.; Mandal, K.; Mecwan, M.M.; Hernandez, A.L.; Maity, S.; Sharma, S.; Herculano, R.D.; Kawakita, S.; Jucaud, V.; Dokmeci, M.R.; et al. Integrated biosensors for monitoring microphysiological systems. Lab A Chip 2022, 22, 3801–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remaggi, G.; Zaccarelli, A.; Elviri, L. 3D printing technologies in biosensors production: Recent developments. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrier, R.; Pirog, A.; Jaffredo, M.; Gaitan, J.; Catargi, B.; Renaud, S.; Raoux, M.; Lang, J. Bioelectronic organ-based sensor for microfluidic real-time analysis of the demand in insulin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalonga, A.; Pérez-Calabuig, A.M.; Villalonga, R. Electrochemical biosensors based on nucleic acid aptamers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, C.K.; Bhakta, S.; Reza, K.K.; Kaushik, A. Exploring molecularly imprinted polymers as artificial antibodies for efficient diagnostics and commercialization: A critical overview. Hybrid Adv. 2022, 1, 100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, Z.; Guerreiro, A.; Piletsky, S.A.; Tothill, I.E. NanoMIP based optical sensor for pharmaceuticals monitoring. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 213, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, G.; Zanoni, C.; Spina, S.; Magnaghi, L.R.; Biesuz, R. Trends in molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs)-based plasmonic sensors. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilvenyte, G.; Ratautaite, V.; Boguzaite, R.; Ramanavicius, A.; Viter, R.; Ramanavicius, S. Molecularly imprinted polymers for the determination of cancer biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futane, A.; Narayanamurthy, V.; Jadhav, P.; Srinivasan, A. Aptamer-based rapid diagnosis for point-of-care application. Microfuidics Nanofuidics 2023, 27, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouha, J.; Li, F.; Xiong, H. A fluorescence biosensor based on DNA aptamers-COF for highly selective detection of ATP and thrombin. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 295, 122615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Fan, C. Aptamer-based biosensors. Trends Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairal, T.; Özalp, V.C.; Sánchez, P.L.; Mir, M.; Katakis, I.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Aptamers: Molecular tools for analytical applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 390, 989–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, A.-D.; Roy, I.; Malhotra, B.D.; Luong, J.H.T. Analytical and biosensing platforms for insulin: A review. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2021, 3, 100028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshbin, Z.; Shakour, N.; Iranshahi, M.; Butler, A.E.; Sahebkar, A. Aptamer-based biosensors: Promising sensing technology for diabetes diagnosis in biological fluids. Curr. Med. Chem. 2023, 30, 3441–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, W.; Mochizuki, E.; Takase, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Morita, Y.; Yamazaki, H.; Sode, K.; Ikebukuro, K. Selection of DNA aptamers against insulin and construction of an aptameric enzyme subunit for insulin sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Huang, P.-J.J.; Ding, J.; Liu, J. Aptamer-based biosensors for biomedical diagnostics. Analyst 2014, 139, 2627–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghdisi, S.M.; Danesh, N.M.; Lavaee, P.; Emrani, A.S.; Ramezani, M.; Abnous, K. Aptamer biosensor for selective and rapid determination of insulin. Anal. Lett. 2015, 48, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimov, J.Y.; Schaefer, C.S.; Yang, W.; Grout, R.L.; Lai, R.Y. Development of an electrochemical insulin sensor based on the insulin-linked polymorphic region. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lin, Y.; Sun, W.; Han, R.; Luo, C.; Wang, X.; Wei, Q. A highly selective and sensitive detection of insulin with chemiluminescence biosensor based on aptamer and oligonucleotide-AuNPs functionalized nanosilica @ graphene oxide aerogel. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1089, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Midinov, B.; White, R.J. Electrochemical aptamer-based sensor for real-time monitoring of insulin. Am. Chem. Soc. Sens. 2019, 4, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Zandieh, M.; Yang, T.; Liu, J. Cytosine-rich DNA binding insulin stronger than guanine-rich aptamers: Effect of aggregation of insulin for its detection. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 8948–8955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdian-Doghaei, A.; Housaindokht, M.R. Spectroscopic study of the interaction of insulin and its aptamer—Sensitive optical detection of insulin. J. Lumin. 2015, 159, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, D.; Zhang, P.; Gong, P.; Chen, C.; Gao, G.; Cai, L. A near infrared fluorescence resonance energy transfer based aptamer biosensor for insulin detection in human plasma. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 811–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertürk, G.; Mattiasson, B. Molecular imprinting techniques used for the preparation of biosensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirhagl, R.; Latif, U.; Podlipna, D.; Blumenstock, H.; Dickert, F.L. Natural and biomimetic materials for the detection of insulin. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 3908–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartal, F.; Çimen, D.; Bereli, N.; Denizli, A. Molecularly imprinted polymer based quartz crystal microbalance sensor for the clinical detection of insulin. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 97, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, A.G.; Haq, I.; Cowen, T.; Di Masi, S.; Trivedi, S.; Alanazi, K.; Piletska, E.; Mujahid, A.; Piletsky, S.A. Design and fabrication of a smart sensor using in silico epitope mapping and electro-responsive imprinted polymer nanoparticles for determination of insulin levels in human plasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidarič, T.; Majer, D.; Maver, T.; Finšgar, M.; Maver, U. The development of an electropolymerized, molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) sensor for insulin determination using single-drop analysis. Analyst 2023, 148, 1102–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardani, N.I.; Kangkamano, T.; Wannapob, R.; Kanatharana, P.; Thavarungkul, P.; Limbut, W. Electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer cryogel and multiwalled carbon nanotubes for direct insulin detection. Talanta 2023, 254, 124137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, E.; Vacic, A.; Rajan, N.K.; Criscione, J.M.; Park, J.; Ilic, B.R.; Mooney, D.J.; Reed, M.A.; Fahmy, T.M. Label-free biomarker detection from whole blood. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhasatia, R.; Sweetman, M.J.; Harding, F.J.; Waibel, M.; Kay, T.; Thomas, H.; Loudovaris, T.; Voelcker, N.H. Non-invasive, in vitro analysis of islet insulin production enabled by an optical porous silicon biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servarayan, K.L.; Sundaram, E.; Manna, A.; Vairathevar Sivasamy, V. Label free optical biosensor for insulin using naturally existing chromene mimic synthesized receptors: A greener approach. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1239, 340692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Yang, R.; Liu, M.; Feng, H.; Li, N.; Jin, M.; Zhang, M.; Shui, L. A liquid crystal-based biosensor for detection of insulin driven by conformational change of an aptamer at aqueous-liquid crystal interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 628, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Luo, X.; Davis, J.J. The label free picomolar detection of insulin in blood serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 39, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkoc, A.; Probst, D.; Lin, C.; Khanwalker, M.; Beck, C.; Cook, C.B.; La Belle, J.T. Enhancing glycemic control via detection of insulin using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2017, 11, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobi, K.V.; Iwasaka, H.; Miura, N. Self-assembled PEG monolayer based SPR immunosensor for label-free detection of insulin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1382–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Rotti, P.G.; DiMarco, C.; Tyler, S.R.; Zhao, X.; Engelhardt, J.F.; Hone, J.; Lin, Q. Real-time monitoring of insulin using a graphene field-effect transistor aptameric nanosensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 27504–27511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, E.; Omidinia, E.; Heidari, H.; Fazli, M. Flow injection amperometric detection of insulin at cobalt hydroxide nanoparticles modified carbon ceramic electrode. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 495, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, F.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xie, X.; Hua, X.; Yang, X.; Huang, H. Facile preparation of peroxidase-like core-shell nanorods and application as platform for colorimetric determination of glucose, insulin and glucose/insulin ratio. Talanta 2019, 204, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhanga, H.; Zuoa, F.; Tanb, X.; Xuc, S.; Yuana, R.; Chen, S. A novel electrochemiluminescent biosensor based on resonance energy transfer between poly(9,9-di-n-octylfluorenyl-2,7-diyl) and 3,4,9,10-perylenetetracar-boxylic acid for insulin detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 104, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regonda, S.; Tian, R.; Gao, J.; Greene, S.; Ding, J.; Hu, W. Silicon multi-nanochannel FETs to improve device uniformity/stability and femtomolar detection of insulin in serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 45, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, E.M.; Cunha, D.A.; Carneiro, E.M.; Boschero, A.C.; Saad, M.J.A.; Velloso, L.A. Identification of insulin in the tear film and insulin receptor and IGF-I receptor on the human ocular surface. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 963–967. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Min, J.; Song, Y.; Tu, J.; Mukasa, D.; Ye, C.; Xu, C.; Heflin, N.; McCune, J.S.; et al. A wearable electrochemical biosensor for the monitoring of metabolites and nutrients. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 6, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, E.; Teymourian, H.; Tehrani, F.; Eksin, E.; Sanchez-Tirado, E.; Warren, P.; Erdem, A.; Dassau, E.; Wang, J. Enzymatic/immunoassay dual-biomarker sensing chip: Towards decentralized insulin/glucose detection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 6376–6379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.; Fortunato, G.; Radacsi, N. Wearable flexible sweat sensors for healthcare monitoring: A review. J. R. Soc. Interface 2019, 16, 20190217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Lee, H. Anti-biofouling strategies for long-term continuous use of implantable biosensors. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiei, H.; Omidian, K.; Chang, C.R.; Little, J.P. Saliva insulin tracks plasma insulin across the day following high-carbohydrate and low-carbohydrate meals. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2023, 48, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues Oliveira, S.M.; Rebocho, A.; Ahmadpour, E.; Nissapatorn, V.; de Lourdes Pereira, M. Type 1 diabetes mellitus: A review on advances and challenges in creating insulin producing devices. Micromachines 2023, 14, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.R.; Joe, C.; Mitchell, R.J.; Gu, M.B. Biosensors for healthcare: Current and future perspectives. Trends Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 374–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Cai, A.; Xu, T.; Zhang, X. Artificial intelligence biosensors for continuous glucose monitoring. Interdiscip. Mater. 2023, 2, 290–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.A.; Li, R.; Tse, Z.T.H. Reshaping healthcare with wearable biosensors. Nat. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, E.; Nandhakumar, P.; Ding, S.; Saha, T.; Wang, J. Insulin detection in diabetes mellitus: Challenges and new prospects. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Biofluids | Insulin Normal Levels | References |
|---|---|---|
| Serum | 30–70 pmol/L | [29] |
| Plasma | <175 pmol/L | [22,30] |
| Urine | 24–136 pmol/L | [12,31] |
| Tears | ~90 pmol/L | [32] |
| Saliva | 7–28 pmol/L | [20,27,28] |
| Aptamer Sequences | References |
|---|---|
| ILPR: 5′-CAGGGGTGTGGGGACAGGGGTGTGGGG-3′ | [63,66] |
| IGA1: 5′-GGAGGTGGATGGGGAGGGGGAGGTGTGTTT-3′ | [9,63] |
| IGA2: 5′-GGAGGGGGTGGGGAGGGGGCTGGTTGTCC-3′ | [63] |
| IGA3: 5′-GGTGGTGGGGGGGGTGGTAGGGTGTCTTCT-3′ | [63,66,67,68,69,70,71] |
| clGA3: 5′-CCCCACACCCCTGTCCCCACACCCCTG-3′ | [69] |
| IBA2: 5′-CTCTCTCGGTGGTGGGGGGGGTTAGGGTGTCTTCCTCTCTC-3′ | [65] |
| Transducer | Sample | Detection Limit | Linear Range | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluorescence | Rat serum and human urine | 9.97 nmol/L | 0–50 nmol/L | [65] |
| Fluorescence | Human serum | 2 nmol/L | 2–70 nmol/L | [70] |
| Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) | Human plasma | 0.6 pmol/L | 1 pmol/L–2.0 nmol/L | [71] |
| Electrochemical | Buffer solution | 10 nmol/L | 10–200 nmol/L | [66] |
| Electrochemical | Buffer solution | 20 nmol/L | 0.02–5 μmol/L | [68] |
| Flow injection chemiluminescence | Buffer solution | 1.6 pmol/L | 7.5 pmol/L–5.0 nmol/L | [67] |
| Transducer | Sample | Detection Limit | Linear Range | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dual-electrode QCM | Buffer solution | 2.247 nmol/L | 2.247–224.7 nmol/L | [73] |
| QCM chips | Aqueous solution and artificial plasma | 18 fmol/L | 18 fmol/L–2.247 pmol/L | [74] |
| Electrochemical | Buffer solution and human plasma | 26 fmol/L (buffer) and 81 fmol/L plasma) | 50–2000 pmol/L | [75] |
| Electrochemical | Buffer solution | 1.9 pmol/L | 20–70 pmol/L | [76] |
| Electrochemical | Buffer solution | 33 fmol/L | 0.050–1.40 pmol/L | [77] |
| Transducer | Sample | Detection Limit | Linear Range | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRS | Buffer solution and human islets | 4.299 nmol/L | 11.235–112.35 nmol/L | [79] |
| Fluorescence | Buffer solution and human serum | 7.07 fmol/L | 10 fmol/L–600 pmol/L | [80] |
| Fluorescence | Buffer solution, human urine and serum | 0.1 nmol/L | 0.1–1.0 nmol/L | [81] |
| Electrochemical | Buffer solution and human serum | 1.2 pmol/L | 5 pmol/L–50 nmol/L | [82] |
| Electrochemical | Buffer solution | 2.26 pmol/L | 50–1500 pmol/L | [83] |
| SPR | Buffer solution and human serum | 2.247 pmol/L | 2.247–674.1 pmol/L | [84] |
| Graphene electrical conductance | Buffer solution | 35 pmol/L | 100 pmol/L–1 μmol/L | [85] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Psoma, S.D.; Kanthou, C. Wearable Insulin Biosensors for Diabetes Management: Advances and Challenges. Biosensors 2023, 13, 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13070719
Psoma SD, Kanthou C. Wearable Insulin Biosensors for Diabetes Management: Advances and Challenges. Biosensors. 2023; 13(7):719. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13070719
Chicago/Turabian StylePsoma, Sotiria D., and Chryso Kanthou. 2023. "Wearable Insulin Biosensors for Diabetes Management: Advances and Challenges" Biosensors 13, no. 7: 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13070719
APA StylePsoma, S. D., & Kanthou, C. (2023). Wearable Insulin Biosensors for Diabetes Management: Advances and Challenges. Biosensors, 13(7), 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13070719





