A Prototype Assay Multiplexing SARS-CoV-2 3CL-Protease and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 for Saliva-Based Diagnostics in COVID-19
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Assay Buffers I and II
2.3. Preparation of Protease Standards
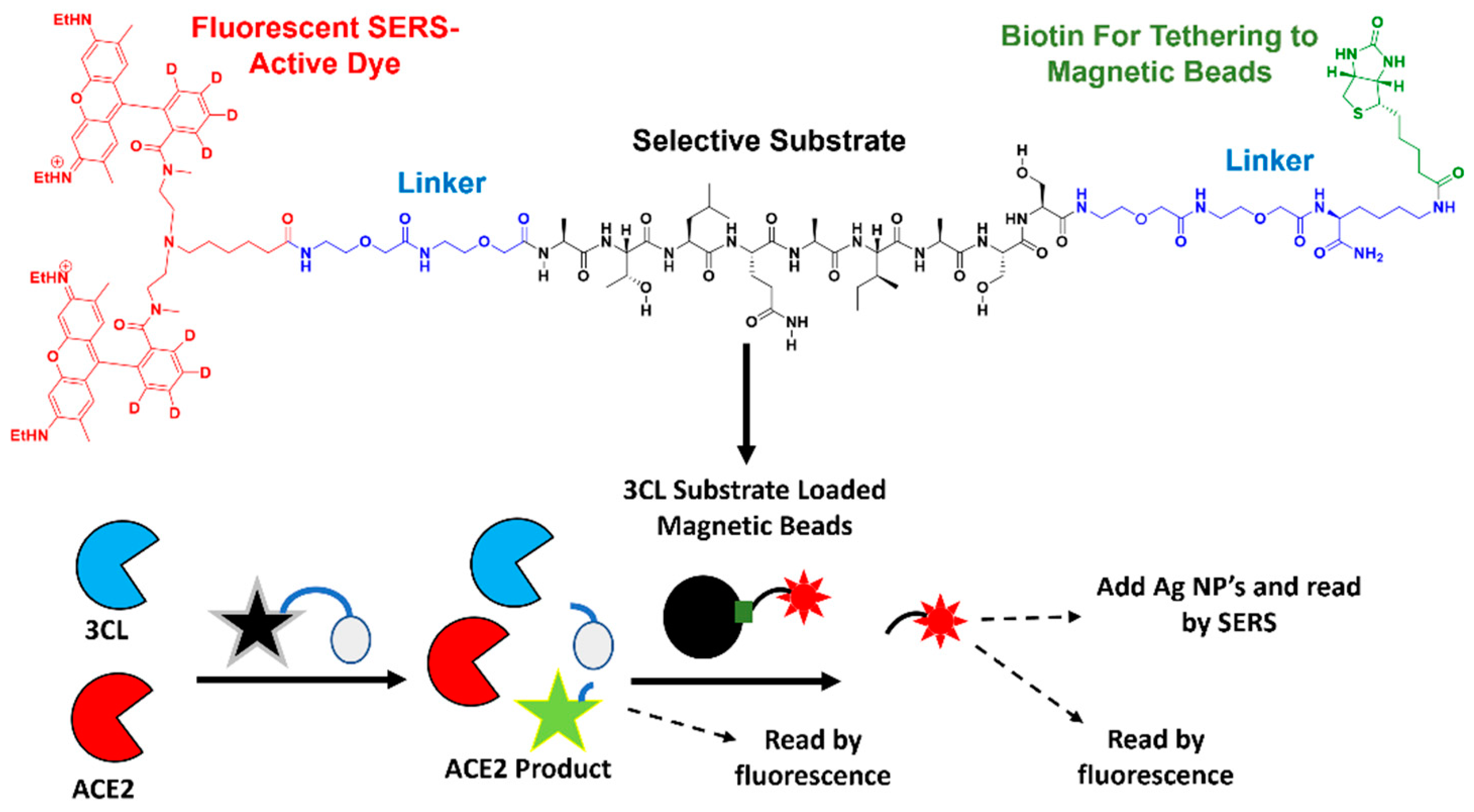
2.4. Preparation of Magnetic Beads
2.5. Preparation of ACE2 Fluorescent Substrate
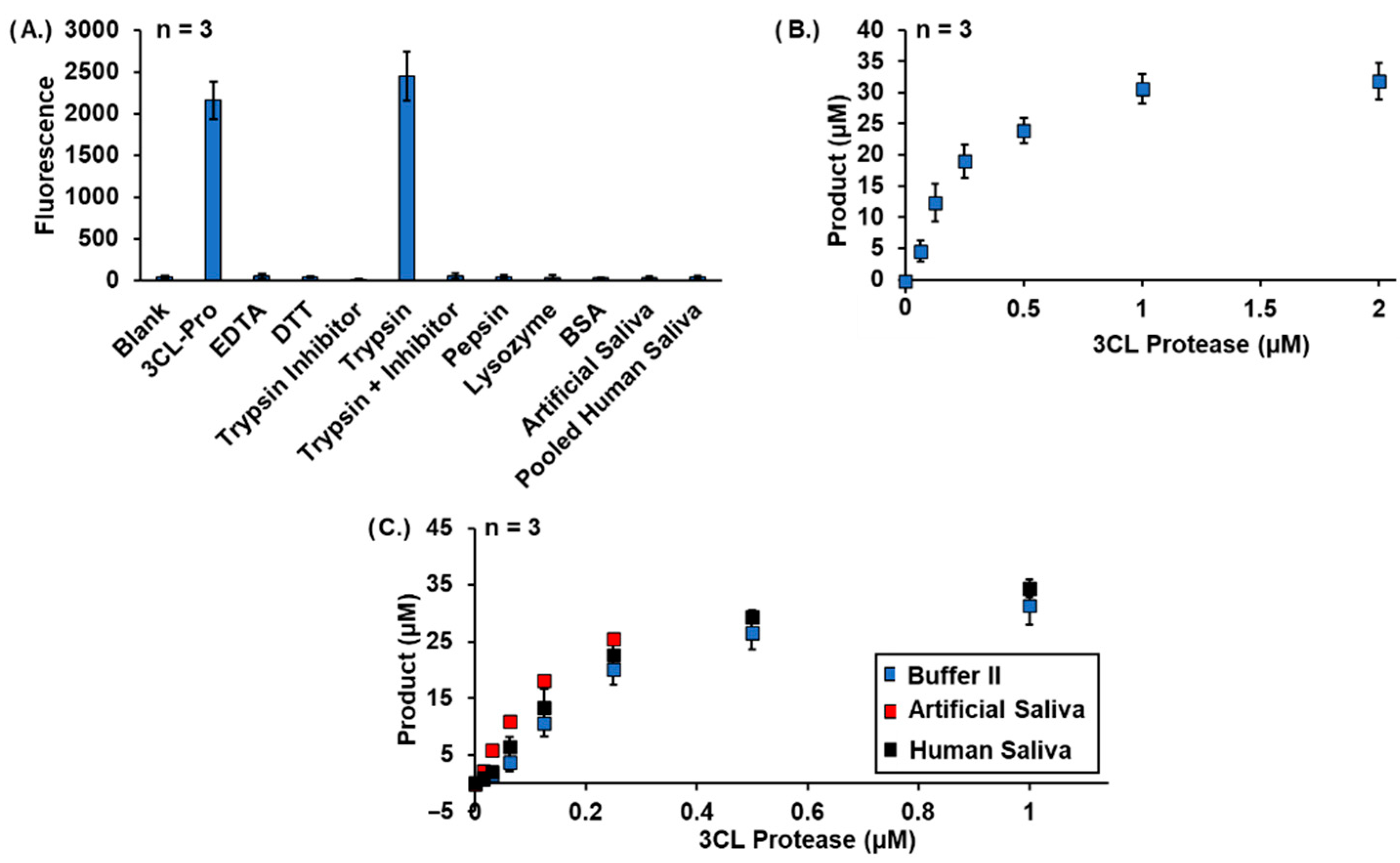
2.6. 3CL Protease Assay
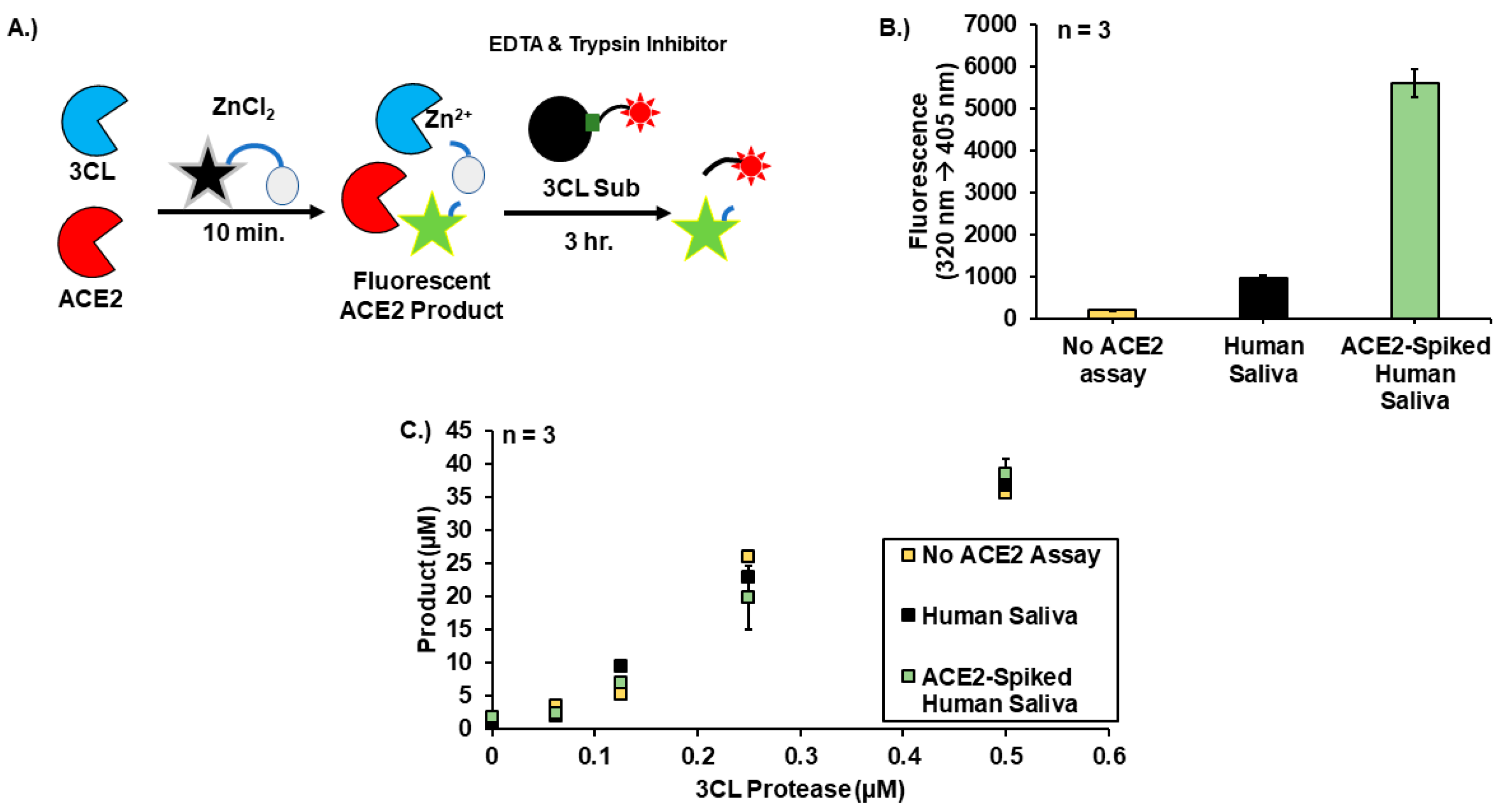
2.7. ACE2 Assay
2.8. 30-Minute Sequential ACE2-3CL Assay
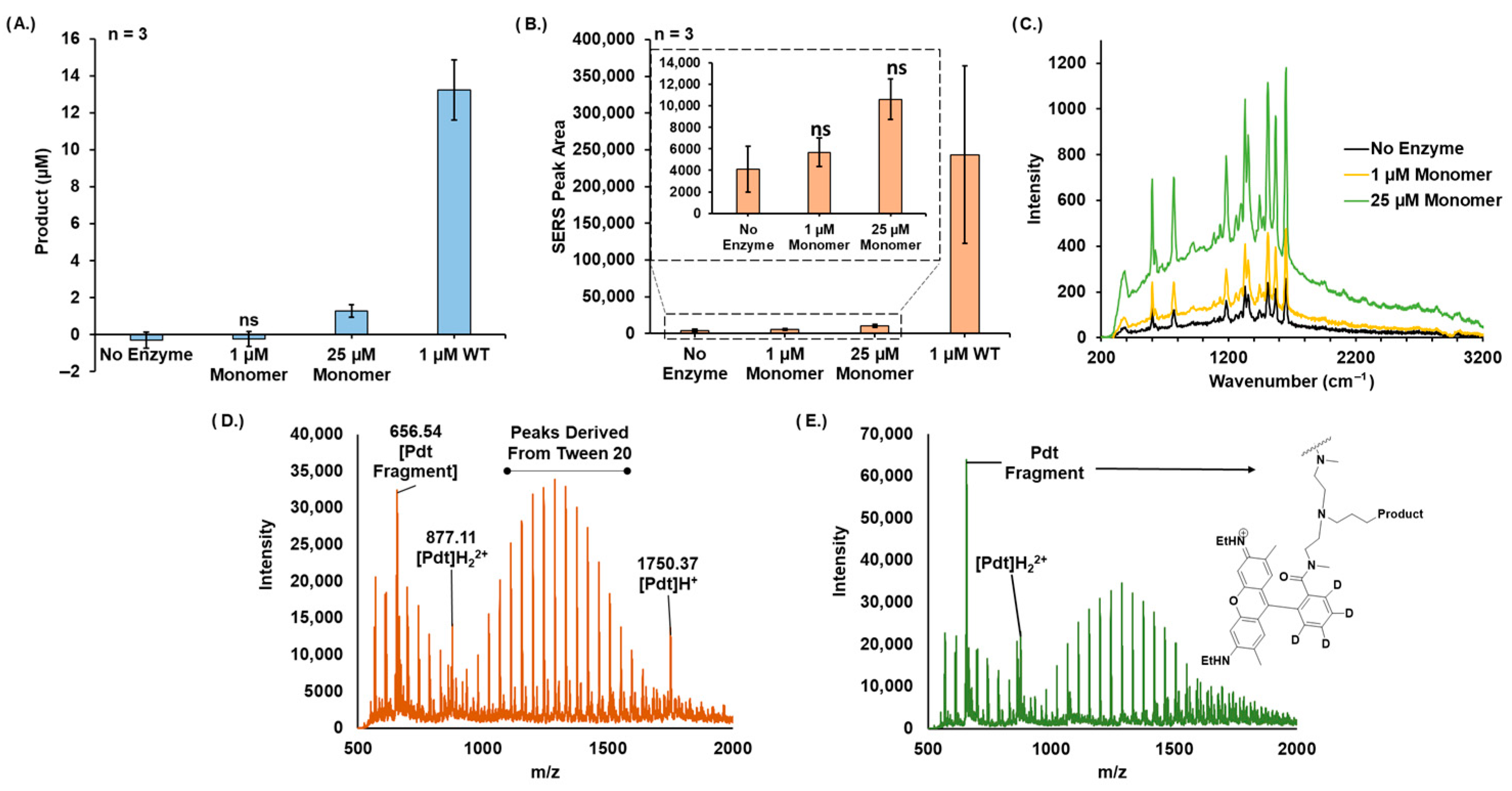
2.9. Raman Spectroscopy
2.10. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS)
2.11. Collection of Clinical Samples (IRB, etc.)
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int (accessed on 16 November 2022).
- Wang, H.; Paulson, K.R.; Pease, S.A.; Watson, S.; Comfort, H.; Zheng, P.; Aravkin, A.Y.; Bisignano, C.; Barber, R.M.; Alam, T.; et al. Estimating Excess Mortality Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Analysis of COVID-19-Related Mortality, 2020–2021. Lancet 2022, 399, 1513–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Lancet Infectious Diseases. Transitioning to Endemicity with COVID-19 Research. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissleder, R.; Lee, H.; Ko, J.; Pittet, M.J. COVID-19 Diagnostics in Context. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eabc1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, W.Y.; Cheung, P.P.H. Diagnostic Performances of Common Nucleic Acid Tests for SARS-CoV-2 in Hospitals and Clinics: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e704–e714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunstein, G.D.; Schwartz, L.; Hymel, P.; Fielding, J. False Positive Results With SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR Tests and How to Evaluate a RT-PCR-Positive Test for the Possibility of a False Positive Result. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2021, 63, e159–e162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, B.; Khan, A.; Metezai, H.; Blyth, I.; Asad, H. The Impact of False Positive COVID-19 Results in an Area of Low Prevalence. Clin. Med. 2021, 21, e54–e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Wu, W.; Xiang, C.; Wu, L.; Li, J.; Hou, W.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Nie, Z.; et al. Laboratory Testing Implications of Risk-Stratification and Management of COVID-19 Patients. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 699706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Ren, L.; Yang, S.; Xiao, M.; Chang, D.; Yang, F.; Dela Cruz, C.S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Profiling Early Humoral Response to Diagnose Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ast, V.; Costina, V.; Eichner, R.; Bode, A.; Aida, S.; Gerhards, C.; Thiaucourt, M.; Dobler, G.; Geilenkeuser, W.-J.; Wölfel, R.; et al. Assessing the Quality of Serological Testing in the COVID-19 Pandemic: Results of a European External Quality Assessment (EQA) Scheme for Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Detection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e00559-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Ma, P.; Wang, M.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, M.; Ye, L.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, C. Efficacy and Safety of Paxlovid for COVID-19:A Meta-Analysis. J. Infect. 2022, 86, 66–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vito, A.; Colpani, A.; Bitti, A.; Zauli, B.; Meloni, M.C.; Fois, M.; Denti, L.; Bacciu, S.; Marcia, C.; Maida, I.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Molnupiravir in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Patients: A Real-Life Experience. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 5582–5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC Labs. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/serology-testing.html (accessed on 16 November 2022).
- Peroni, L.A.; Toscaro, J.M.; Canateli, C.; Tonoli, C.C.C.; de Olivera, R.R.; Benedetti, C.E.; Coimbra, L.D.; Pereira, A.B.; Marques, R.E.; Proença-Modena, J.L.; et al. Serological Testing for COVID-19, Immunological Surveillance, and Exploration of Protective Antibodies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 635701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwong, G.A.; Ghosh, S.; Gamboa, L.; Patriotis, C.; Srivastava, S.; Bhatia, S.N. Synthetic Biomarkers: A Twenty-First Century Path to Early Cancer Detection. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Silva, R.; Sousa-Jerónimo, M.; Botequim, D.; Silva, N.J.O.; Paulo, P.M.R.; Prazeres, D.M.F. Monitoring Proteolytic Activity in Real Time: A New World of Opportunities for Biosensors. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2020, 45, 604–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, D.; Martínez-Sanz, J.; Sainz, T.; Calvo, C.; Méndez-Echevarría, A.; Moreno, E.; Blázquez-Gamero, D.; Vizcarra, P.; Rodríguez, M.; Jenkins, R.; et al. Differences in Saliva ACE2 Activity among Infected and Non-Infected Adult and Pediatric Population Exposed to SARS-CoV-2. J. Infect. 2022, 85, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniell, H.; Nair, S.K.; Esmaeili, N.; Wakade, G.; Shahid, N.; Ganesan, P.K.; Islam, M.R.; Shepley-McTaggart, A.; Feng, S.; Gary, E.N.; et al. Debulking SARS-CoV-2 in Saliva Using Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 in Chewing Gum to Decrease Oral Virus Transmission and Infection. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 1966–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersh, E.V.; Wolff, M.; Moore, P.A.; Theken, K.N.; Daniell, H. A Pair of “ACEs”. J. Dent. Res. 2022, 101, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malard, L.; Kakinami, L.; O’Loughlin, J.; Roy-Gagnon, M.-H.; Labbe, A.; Pilote, L.; Hamet, P.; Tremblay, J.; Paradis, G. The Association between the Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-2 Gene and Blood Pressure in a Cohort Study of Adolescents. BMC Med. Genet. 2013, 14, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Cheng, T.; Koohi-Moghadam, M.; Wu, M.-Z.; Yu, S.Y.; Ding, X.; Pelekos, G.; Yiu, K.H.; Jin, L. Salivary ACE2 and TMPRSS2 Link to Periodontal Status and Metabolic Parameters. Clin. Transl. Discov. 2022, 2, e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trougakos, I.P.; Stamatelopoulos, K.; Terpos, E.; Tsitsilonis, O.E.; Aivalioti, E.; Paraskevis, D.; Kastritis, E.; Pavlakis, G.N.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Insights to SARS-CoV-2 Life Cycle, Pathophysiology, and Rationalized Treatments That Target COVID-19 Clinical Complications. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 28, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Mantri, Y.; Retout, M.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, J.; Jorns, A.; Fajtova, P.; Yim, W.; Moore, C.; Xu, M.; et al. A Charge-Switchable Zwitterionic Peptide for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202112995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Liu, G.; La, M.; Liu, L. Colorimetric and Electrochemical Methods for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease by Peptide-Triggered Assembly of Gold Nanoparticles. Molecules 2022, 27, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garland, G.D.; Harvey, R.F.; Mulroney, T.E.; Monti, M.; Fuller, S.; Haigh, R.; Gerber, P.P.; Barer, M.R.; Matheson, N.J.; Willis, A.E. Development of a Colorimetric Assay for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Activity. Biochem. J. 2022, 479, 901–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borberg, E.; Granot, E.; Patolsky, F. Ultrafast One-Minute Electronic Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Infection by 3CLpro Enzymatic Activity in Untreated Saliva Samples. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, G.; Li, D.; Lin, Y.; Fu, Z.; Qi, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Si, S.; Chen, Y. Development of a Simple and Miniaturized Sandwich-like Fluorescence Polarization Assay for Rapid Screening of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dražić, T.; Kühl, N.; Leuthold, M.M.; Behnam, M.A.M.; Klein, C.D. Efficiency Improvements and Discovery of New Substrates for a SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease FRET Assay. SLAS DISCOVERY Adv. Sci. Drug Discov. 2021, 26, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, C.; Gallo, G.; Campos, C.B.; Hardy, L.; Würtele, M. Biochemical Screening for SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Cho, C.-C.D.; Geng, Z.Z.; Shaabani, N.; Ma, X.R.; Vatansever, E.C.; Alugubelli, Y.R.; Ma, Y.; Chaki, S.P.; Ellenburg, W.H.; et al. Evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors Using a Novel Cell-Based Assay. ACS Cent. Sci. 2022, 8, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legare, S.; Heide, F.; Bailey-Elkin, B.A.; Stetefeld, J. Improved SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease High-Throughput Screening Assay Using a 5-Carboxyfluorescein Substrate. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijuan-Galito, S.; Tarantini, F.S.; Tomlin, H.; Jenkins, H.; Thompson, J.L.; Scales, D.; Stroud, A.; Tellechea Lopez, A.; Hassall, J.; McTernan, P.G.; et al. Saliva for COVID-19 Testing: Simple but Useless or an Undervalued Resource? Front. Virol. 2021, 1, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.H.; Kronenberger, T.; Almeida, R.G.; Silva, E.B.; Rocha, R.E.O.; Oliveira, J.C.; Barreto, L.V.; Skinner, D.; Fajtová, P.; Giardini, M.A.; et al. Structure-Based Identification of Naphthoquinones and Derivatives as Novel Inhibitors of Main Protease Mpro and Papain-like Protease PLpro of SARS-CoV-2. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2022, 62, 6553–6573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolowits, M.D.; Xin, M.; Petrov, D.P.; Tague, T.J.; Davisson, V.J. Multimeric Rhodamine Dye-Induced Aggregation of Silver Nanoparticles for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, V.; Byers, K.; Rajesh, U.C.; Caiazza, F.; Zhu, G.; Craik, C.S.; Kirkwood, K.; Davisson, V.J.; Sheik, D.A. Translation of a Protease Turnover Assay for Clinical Discrimination of Mucinous Pancreatic Cysts. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, E.A.; Bardine, C.; Gahbauer, S.; Singh, I.; White, K.; Gu, S.; Wan, X.; Ary, B.; Glenn, I.; O’Connell, J.; et al. Large Library Docking for Novel SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Non-Covalent and Covalent Inhibitors. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tropea, J.E.; Cherry, S.; Waugh, D.S. Expression and Purification of Soluble His(6)-Tagged TEV Protease. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 498, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamplecoskie, K.G.; Scaiano, J.C.; Tiwari, V.S.; Anis, H. Optimal Size of Silver Nanoparticles for Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, B.O.; Li, L. Three-Layer Matrix/Sample Preparation Method for MALDI MS Analysis of Low Nanomolar Protein Samples. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 17, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlak, S.M.; Schendel, L.C.; Gaub, H.E.; Bernardi, R.C. Streptavidin/Biotin: Tethering Geometry Defines Unbinding Mechanics. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söder, P.-Ö.; Modéer, T. Characterization of Trypsin-like Enzymes from Human Saliva Isolated by Use of Affinity Chromatography. Acta Odontol. Scand. 1977, 35, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, G.J.S.; Nadler, H.L. Deficiency of Trypsin-like Activity in Saliva of Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. J. Pediatr. 1972, 80, 573–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.T.-A.; Kuo, C.-J.; Hsieh, H.-P.; Wang, Y.-C.; Huang, K.-K.; Lin, C.P.-C.; Huang, P.-F.; Chen, X.; Liang, P.-H. Evaluation of Metal-Conjugated Compounds as Inhibitors of 3CL Protease of SARS-CoV. FEBS Lett. 2004, 574, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-C.; Kuo, C.-J.; Hsu, M.-F.; Liang, P.-H.; Fang, J.-M.; Shie, J.-J.; Wang, A.H.-J. Structural Basis of Mercury- and Zinc-Conjugated Complexes as SARS-CoV 3C-like Protease Inhibitors. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 5454–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestrini, L.; Belhaj, N.; Comez, L.; Gerelli, Y.; Lauria, A.; Libera, V.; Mariani, P.; Marzullo, P.; Ortore, M.G.; Palumbo Piccionello, A.; et al. The Dimer-Monomer Equilibrium of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Is Affected by Small Molecule Inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nashed, N.T.; Aniana, A.; Ghirlando, R.; Chiliveri, S.C.; Louis, J.M. Modulation of the Monomer-Dimer Equilibrium and Catalytic Activity of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease by a Transition-State Analog Inhibitor. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, D.; Sun, X.; Curth, U.; Drosten, C.; Sauerhering, L.; Becker, S.; Rox, K.; Hilgenfeld, R. Crystal Structure of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Provides a Basis for Design of Improved α-Ketoamide Inhibitors. Science 2020, 368, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suresh, V.; Sheik, D.A.; Detomasi, T.C.; Zhao, T.; Zepeda, T.; Saladi, S.; Rajesh, U.C.; Byers, K.; Craik, C.S.; Davisson, V.J. A Prototype Assay Multiplexing SARS-CoV-2 3CL-Protease and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 for Saliva-Based Diagnostics in COVID-19. Biosensors 2023, 13, 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13070682
Suresh V, Sheik DA, Detomasi TC, Zhao T, Zepeda T, Saladi S, Rajesh UC, Byers K, Craik CS, Davisson VJ. A Prototype Assay Multiplexing SARS-CoV-2 3CL-Protease and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 for Saliva-Based Diagnostics in COVID-19. Biosensors. 2023; 13(7):682. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13070682
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuresh, Vallabh, Daniel A. Sheik, Tyler C. Detomasi, Tianqi Zhao, Theresa Zepeda, Shyam Saladi, Ummadisetti Chinna Rajesh, Kaleb Byers, Charles S. Craik, and Vincent Jo Davisson. 2023. "A Prototype Assay Multiplexing SARS-CoV-2 3CL-Protease and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 for Saliva-Based Diagnostics in COVID-19" Biosensors 13, no. 7: 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13070682
APA StyleSuresh, V., Sheik, D. A., Detomasi, T. C., Zhao, T., Zepeda, T., Saladi, S., Rajesh, U. C., Byers, K., Craik, C. S., & Davisson, V. J. (2023). A Prototype Assay Multiplexing SARS-CoV-2 3CL-Protease and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 for Saliva-Based Diagnostics in COVID-19. Biosensors, 13(7), 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13070682






