Simple, Fast and Convenient Magnetic Bead-Based Sample Preparation for Detecting Viruses via Raman-Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
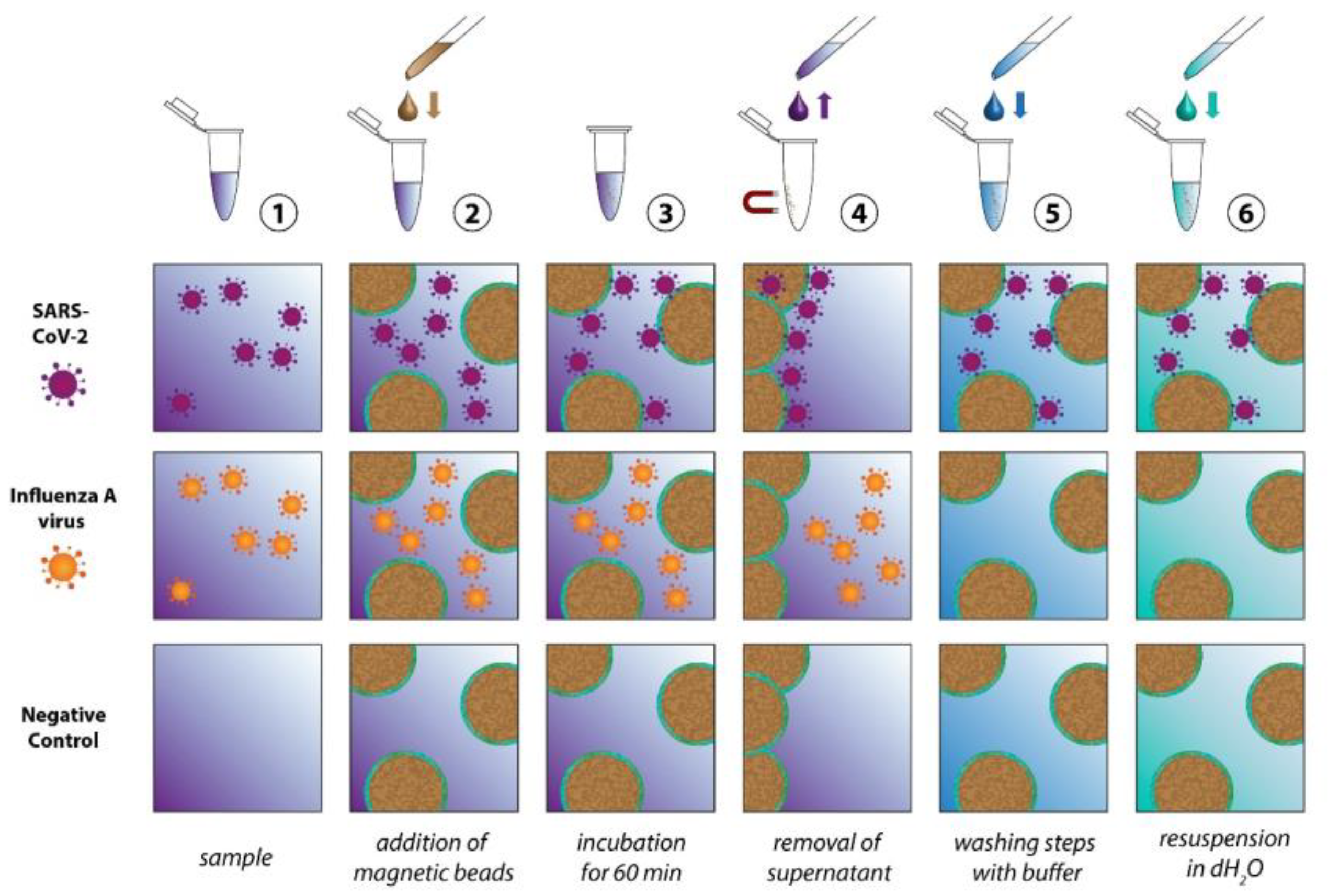
2. Methods
2.1. Preparation of ACE2 Beads
2.2. Virus Isolation
2.3. Raman Measurements
2.4. Data Processing
2.5. Cell Culture and Viral Propagation
2.6. Virus Lysis and qRT-PCR
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalvatchev, N.; Sirakov, I. Respiratory viruses crossing the species barrier and emergence of new human coronavirus infectious disease. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2021, 35, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menachery, V.D.; Graham, R.L.; Baric, R.S. Jumping species—A mechanism for coronavirus persistence and survival. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 23, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjuán, R.; Domingo-Calap, P. Mechanisms of viral mutation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 4433–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhama, K.; Patel, S.K.; Sharun, K.; Pathak, M.; Tiwari, R.; Yatoo, M.I.; Malik, Y.S.; Sah, R.; Rabaan, A.A.; Panwar, P.K. SARS-CoV-2 jumping the species barrier: Zoonotic lessons from SARS, MERS and recent advances to combat this pandemic virus. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 37, 101830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, R.A.; McMichael, A.J. Social and environmental risk factors in the emergence of infectious diseases. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S70–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Li, X.; Ge, C.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, T.; Cao, S.; Meng, L.; Lu, S. Molecular detection of SARS-CoV-2 being challenged by virus variation and asymptomatic infection. J. Pharm. Anal. 2021, 11, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassedy, A.; Parle-McDermott, A.; O’Kennedy, R. Virus Detection: A Review of the Current and Emerging Molecular and Immunological Methods. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 637559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, B.A.S.; Hodel, K.V.S.; Barbosa-Júnior, V.G.; Soares, M.B.P.; Badaró, R. The Main Molecular and Serological Methods for Diagnosing COVID-19: An Overview Based on the Literature. Viruses 2020, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlow, S.; Meisel, S.; Cialla-May, D.; Weber, K.; Rösch, P.; Popp, J. Isolation and identification of bacteria by means of Raman spectroscopy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 89, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, B.; Wichmann, C.; Stöckel, S.; Rösch, P.; Popp, J. Cultivation-free Raman spectroscopic investigations of bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan Jr, C.; Kettleson, E.; Lee, M.H.; Ramaswami, B.; Angenent, L.; Biswas, P. Sampling methodologies and dosage assessment techniques for submicrometre and ultrafine virus aerosol particles. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 99, 1422–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, A.C.; Louis, V.; Dilip, D.; Cherian, K.A. Purification of recombinant Cucumber mosaic virus (banana isolate) coat protein by sucrose density gradient ultra-centrifugation. J. Trop. Agric. 2021, 58, 280–284. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.; Zhang, C.; Piatkovsky, M.; Ulbricht, M.; Herzberg, M.; Nguyen, T.H. Improvement of virus removal using ultrafiltration membranes modified with grafted zwitterionic polymer hydrogels. Water Res. 2017, 116, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, L.M.; Wolff, M.W.; Reichl, U. Purification of cell culture-derived influenza A virus via continuous anion exchange chromatography on monoliths. Vaccine 2018, 36, 3153–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Lv, G.; Li, H.; Tong, D.; Lv, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Wu, G. Quantitative analysis of hepatitis B virus DNA based on raman spectroscopy combined with multivariate statistical methods. Laser Phys. Lett. 2020, 17, 025001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.; Chen, C.; Zhang, J.; Lv, G.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, X. Application of Raman spectroscopy in the detection of hepatitis B virus infection. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2019, 28, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlomagno, C.; Bertazioli, D.; Gualerzi, A.; Picciolini, S.; Banfi, P.I.; Lax, A.; Messina, E.; Navarro, J.; Bianchi, L.; Caronni, A.; et al. COVID-19 salivary Raman fingerprint: Innovative approach for the detection of current and past SARS-CoV-2 infections. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saviñon-Flores, F.; Méndez, E.; López-Castaños, M.; Carabarin-Lima, A.; López-Castaños, K.A.; González-Fuentes, M.A.; Méndez-Albores, A. A Review on SERS-Based Detection of Human Virus Infections: Influenza and Coronavirus. Biosensors 2021, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Hu, Z.; Riley, L.K.; Purdy, G.A.; Mustapha, A.; Lin, M. Detecting Food-and Waterborne Viruses by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, M302–M307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitjar, J.; Der-Liao, J.; Lee, H.; Tsai, H.-P.; Wang, J.-R.; Liu, P.-Y. Challenges of SERS technology as a non-nucleic acid or-antigen detection method for SARS-CoV-2 virus and its variants. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 181, 113153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.-T.; Gulino, K.; Zhang, Y.; Sabestien, A.; Chou, T.-W.; Zhou, B.; Lin, Z.; Albert, I.; Lu, H.; Swaminathan, V.; et al. A rapid and label-free platform for virus capture and identification from clinical samples. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lin, C.; Peng, Y.; He, J.; Yang, Y. High-sensitivity and point-of-care detection of SARS-CoV-2 from nasal and throat swabs by magnetic SERS biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 365, 131974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, J.E.; Jaramillo, S.A.; Settles, E.; Salazar, J.J.V.; Lehr, A.; Gonzalez, J.; Aranda, C.R.; Navarro-Contreras, H.R.; Raniere, M.O.; Harvey, M. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 and its S and N proteins using surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 25788–25794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skvortsova, Y.; Wang, G.; Geng, M.L. Statistical two-dimensional correlation coefficient mapping of simulated tissue phantom data: Boundary determination in tissue classification for cancer diagnosis. J. Mol. Struct. 2006, 799, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.; Crowley, J. Comparison of Correlation Techniques. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Autonomous System, Karlsruhe, Germany, 27–30 March 1995; IOS Press: Karlsruhe, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Hisham, M.B.; Yaakob, S.N.; Raof, R.A.A.; Nazren, A.B.A.; Wafi, N.M. Template Matching using Sum of Squared Difference and Normalized Cross Correlation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Student Conference on Research and Development (SCOReD), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 13–14 December 2015; pp. 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Pahlow, S.; Kloß, S.; Blättel, V.; Kirsch, K.; Hübner, U.; Cialla, D.; Rösch, P.; Weber, K.; Popp, J. Isolation and enrichment of pathogens with a surface-modified aluminium chip for Raman spectroscopic applications. ChemPhysChem 2013, 14, 3600–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storozhuk, D.; Ryabchykov, O.; Popp, J.; Bocklitz, T. RAMANMETRIX: A delightful way to analyze Raman spectra. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.07586. [Google Scholar]
- R Development Core Team; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2011.
- Deinhardt-Emmer, S.; Böttcher, S.; Häring, C.; Giebeler, L.; Henke, A.; Zell, R.; Jungwirth, J.; Jordan, P.M.; Werz, O.; Hornung, F.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Causes Severe Epithelial Inflammation and Barrier Dysfunction. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e00110-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Ye, G.; Shi, K.; Wan, Y.; Luo, C.; Aihara, H.; Geng, Q.; Auerbach, A.; Li, F. Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 581, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Wan, Y.; Luo, C.; Ye, G.; Geng, Q.; Auerbach, A.; Li, F. Cell entry mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 11727–11734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, W.; Farzan, M.; Harrison, S.C. Structure of SARS coronavirus spike receptor-binding domain complexed with receptor. Science 2005, 309, 1864–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.-J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292.e286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bestle, D.; Heindl, M.R.; Limburg, H.; Van Lam Van, T.; Pilgram, O.; Moulton, H.; Stein, D.A.; Hardes, K.; Eickmann, M.; Dolnik, O.; et al. TMPRSS2 and furin are both essential for proteolytic activation of SARS-CoV-2 in human airway cells. Life Sci. Alliance 2020, 3, e202000786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, M.; Ferguson, I.D.; Miao, W.; Khavari, P.A. SARS-CoV-2 B. 1.1. 7 and B. 1.351 Spike variants bind human ACE2 with increased affinity. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, N.M. Avidin. 3. The Nature of the Biotin-Binding Site. Biochem. J. 1963, 89, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.D.; Wright, L.D. Heat Stability of Avidin and Avidin-Biotin Complex and Influence of Ionic Strength on Affinity of Avidin for Biotin. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1964, 117, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lan, W.; Zhao, S.; Wu, J.; Seto, D.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Q. RBD mutations from circulating SARS-CoV-2 strains enhance the structural stability and human ACE2 affinity of the spike protein. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrapp, D.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Abiona, O.; Graham, B.S.; McLellan, J.S. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science 2020, 367, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, T.; Blarer, P.; Storck, F.R.; Pittroff, M.; Wernicke, T.; Burkhardt-Holm, P. Repeated detection of polystyrene microbeads in the lower Rhine River. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugelstad, J.; Stenstad, P.; Kilaas, L.; Prestvik, W.; Herje, R.; Berge, A.; Hornes, E. Monodisperse magnetic polymer particles. Blood Purif. 1993, 11, 349–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzotti, G.; Boschetto, F.; Ohgitani, E.; Fujita, Y.; Shin-Ya, M.; Adachi, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Kanamura, N.; Marin, E.; Zhu, W. Raman molecular fingerprints of SARS-CoV-2 British variant and the concept of Raman barcode. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2103287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Chemometrics: Statistics and Computer Application in Analytical Chemistry; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brereton, R.G. Chemometrics: Data Driven Extraction for Science; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Conover, W.J. Practical Nonparametric Statistics; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 428–432. [Google Scholar]
- Marsaglia, G.; Tsang, W.W.; Wang, J. Evaluating Kolmogorov's distribution. J. Stat. Softw. 2003, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


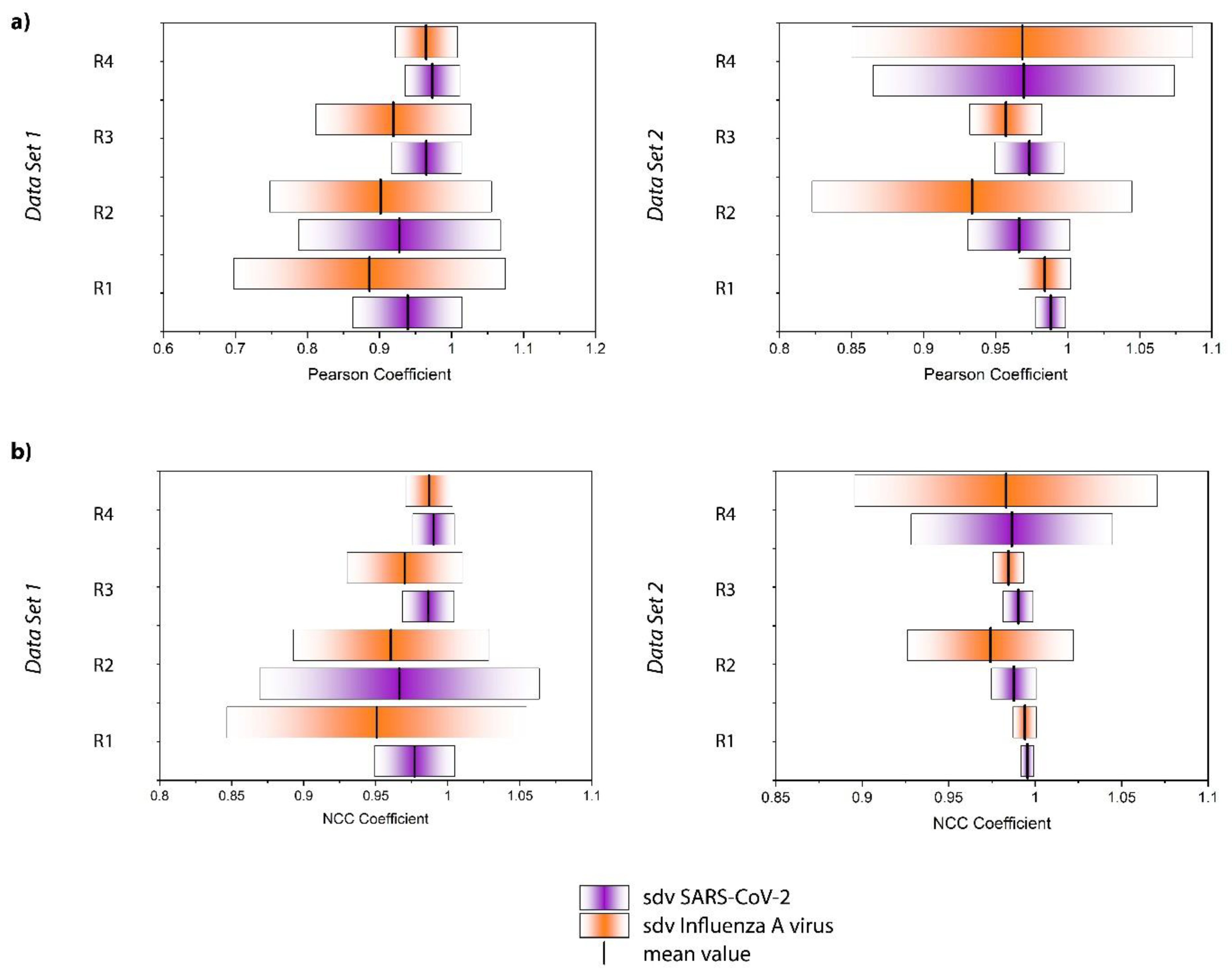
| (a) NCC Coefficient | ||||
| SARS-CoV-2 Mean ± Sd | Influenza A Virus Mean ± Sd | Mean Value | p-Value Bold: Significant at α = 0.05 | |
| Data Set 1 | ||||
| Replicate 1 | 0.977 ± 0.028 | 0.951 ± 0.104 |  | 0.0261 |
| Replicate 2 | 0.966 ± 0.097 | 0.960 ± 0.068 |  | 0.0889 |
| Replicate 3 | 0.986 ± 0.018 | 0.970 ± 0.040 |  | 0.0340 |
| Replicate 4 | 0.990 ± 0.015 | 0.987 ± 0.016 |  | 0.0154 |
| Data Set 2 | ||||
| Replicate 1 | 0.996 ± 0.004 | 0.994 ± 0.007 |  | 0.0258 |
| Replicate 2 | 0.988 ± 0.013 | 0.974 ± 0.048 |  | 2.93 × 10−8 |
| Replicate 3 | 0.990 ± 0.009 | 0.985 ± 0.009 |  | 3.08 × 10−7 |
| Replicate 4 | 0.987 ± 0.058 | 0.983 ± 0.088 |  | 0.944 |
| (b) Pearson coefficient | ||||
| Data Set 1 | ||||
| Replicate 1 | 0.939 ± 0.076 | 0.886 ± 0.188 |  | 0.0682 |
| Replicate 2 | 0.928 ± 0.140 | 0.902 ± 0.154 |  | 0.0889 |
| Replicate 3 | 0.965 ± 0.049 | 0.919 ± 0.108 |  | 0.0198 |
| Replicate 4 | 0.973 ± 0.038 | 0.965 ± 0.043 |  | 0.0154 |
| Data Set 2 | ||||
| Replicate 1 | 0.988 ± 0.010 | 0.984 ± 0.018 |  | 0.0258 |
| Replicate 2 | 0.966 ± 0.035 | 0.934 ± 0.111 |  | 4.60 × 10−5 |
| Replicate 3 | 0.973 ± 0.038 | 0.957 ± 0.025 |  | 1.22 × 10−7 |
| Replicate 4 | 0.970 ± 0.105 | 0.969 ± 0.118 |  | 0.944 |
 SARS-CoV-2 SARS-CoV-2  Influenza A virus Influenza A virus | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pahlow, S.; Richard-Lacroix, M.; Hornung, F.; Köse-Vogel, N.; Mayerhöfer, T.G.; Hniopek, J.; Ryabchykov, O.; Bocklitz, T.; Weber, K.; Ehricht, R.; et al. Simple, Fast and Convenient Magnetic Bead-Based Sample Preparation for Detecting Viruses via Raman-Spectroscopy. Biosensors 2023, 13, 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13060594
Pahlow S, Richard-Lacroix M, Hornung F, Köse-Vogel N, Mayerhöfer TG, Hniopek J, Ryabchykov O, Bocklitz T, Weber K, Ehricht R, et al. Simple, Fast and Convenient Magnetic Bead-Based Sample Preparation for Detecting Viruses via Raman-Spectroscopy. Biosensors. 2023; 13(6):594. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13060594
Chicago/Turabian StylePahlow, Susanne, Marie Richard-Lacroix, Franziska Hornung, Nilay Köse-Vogel, Thomas G. Mayerhöfer, Julian Hniopek, Oleg Ryabchykov, Thomas Bocklitz, Karina Weber, Ralf Ehricht, and et al. 2023. "Simple, Fast and Convenient Magnetic Bead-Based Sample Preparation for Detecting Viruses via Raman-Spectroscopy" Biosensors 13, no. 6: 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13060594
APA StylePahlow, S., Richard-Lacroix, M., Hornung, F., Köse-Vogel, N., Mayerhöfer, T. G., Hniopek, J., Ryabchykov, O., Bocklitz, T., Weber, K., Ehricht, R., Löffler, B., Deinhardt-Emmer, S., & Popp, J. (2023). Simple, Fast and Convenient Magnetic Bead-Based Sample Preparation for Detecting Viruses via Raman-Spectroscopy. Biosensors, 13(6), 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13060594








