A Magnetic-Bead-Based Immunoassay with a Newly Developed Monoclonal Antibody for Rapid and Highly Sensitive Detection of Forchlorfenuron
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Production of Monoclonal Antibody aganist CPPU
2.3. Development of Conventional icELISA
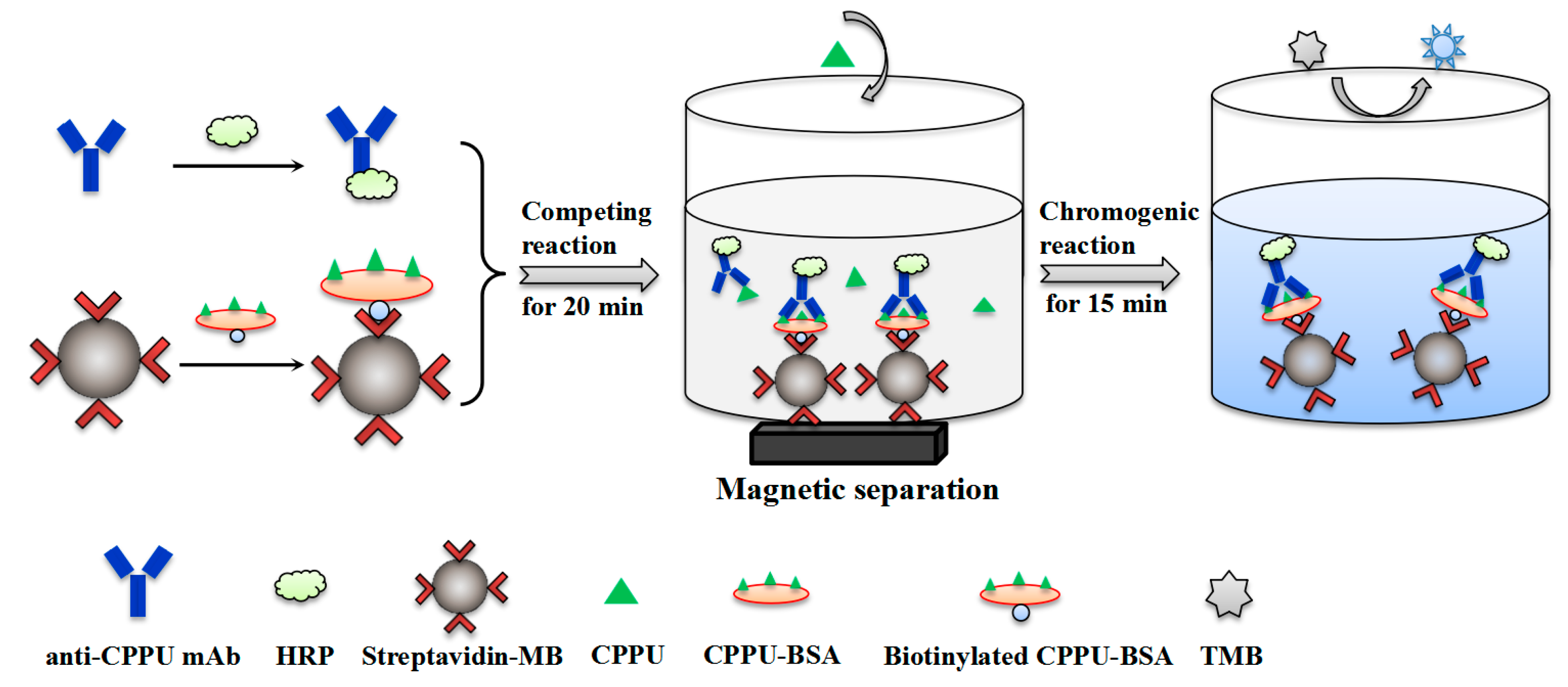
2.4. Development of MB-Based Assay
2.4.1. Immobilization of Biotinylated CPPU–BSA on Streptavidin Magnetic Beads
2.4.2. Preparation of HRP-Labeled mAb
2.4.3. MB-Based Assay Procedure
2.4.4. Optimization of MB-Based Assay
2.5. Selectivity Determination
2.6. Sample Preparation
3. Results and Discussion
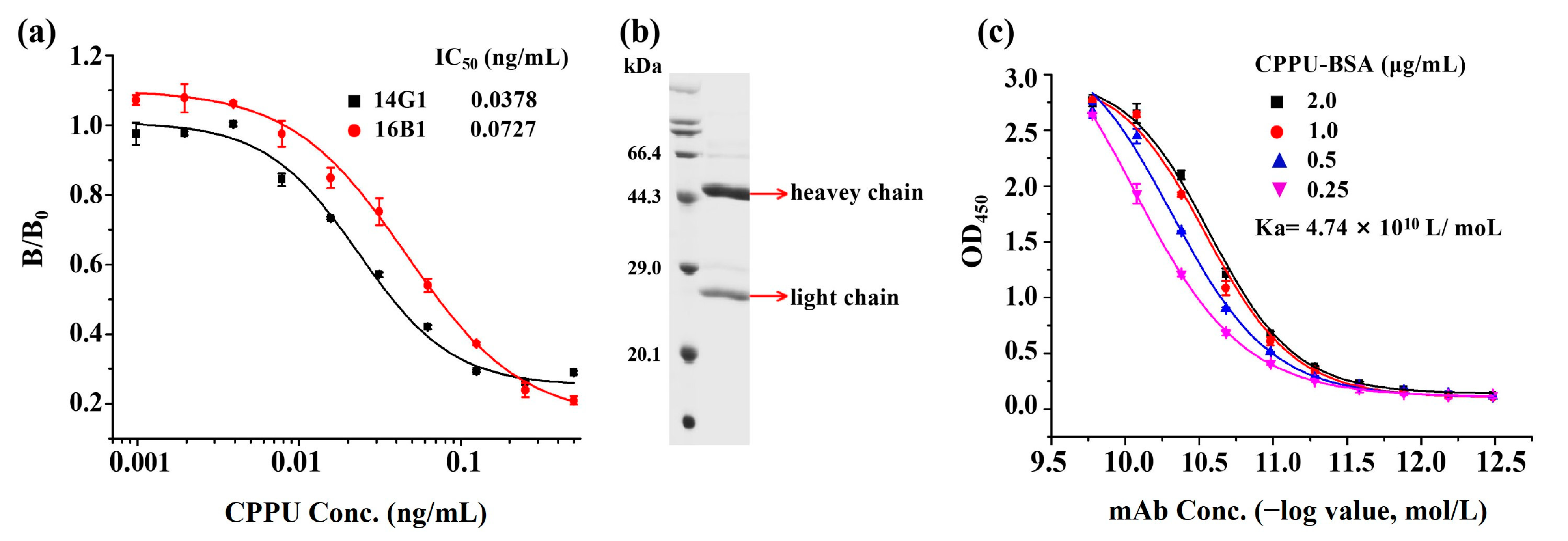
3.1. Production and Characterization of Anti-CPPU mAb
3.2. Optimization of an Indirect Competitive ELISA
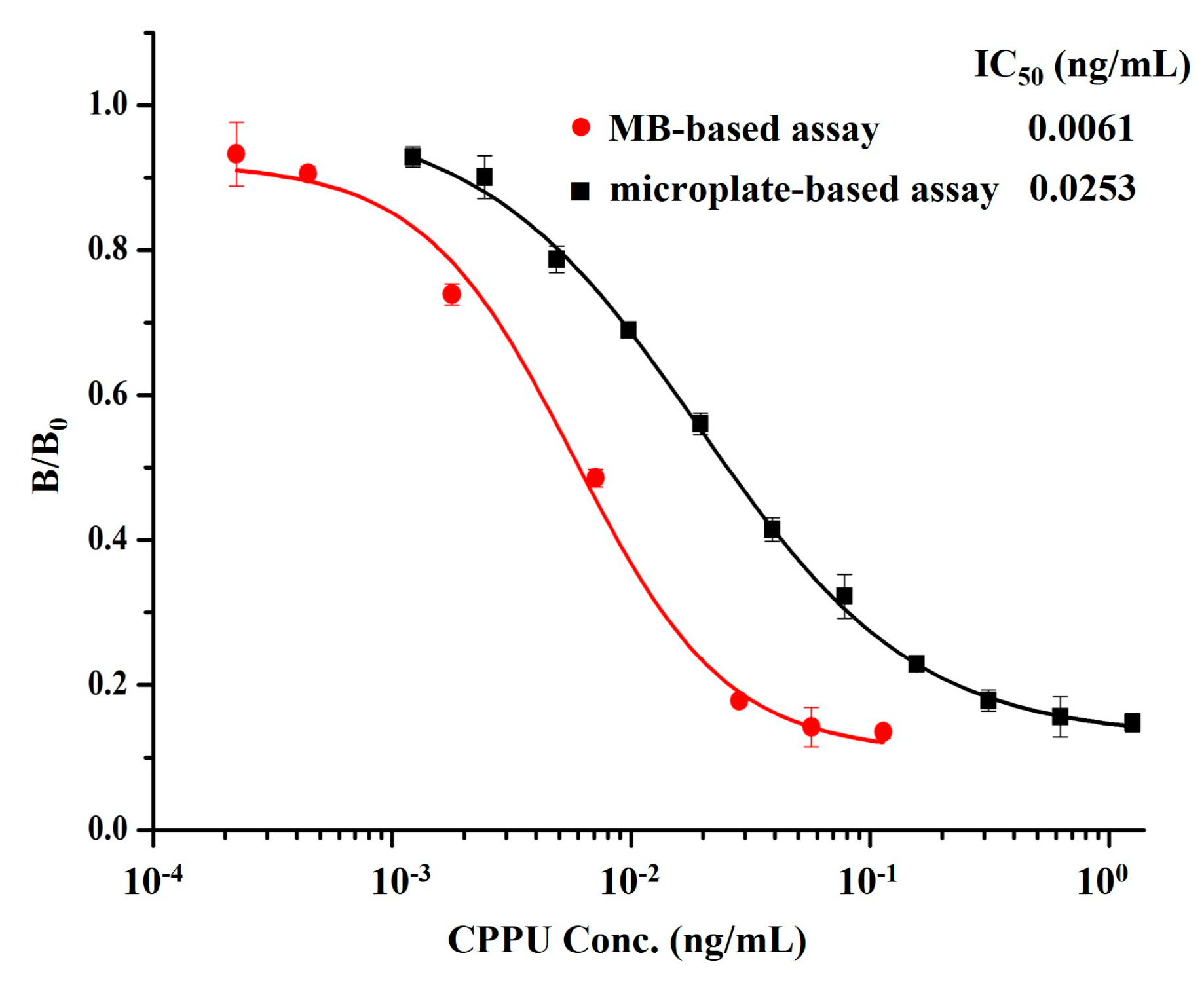
3.3. Development and Optimization of MB-Based Assay
3.4. Selectivity of MB-Based Assay and icELISA
3.5. Sample Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, W.J.; Jiao, B.N.; Su, X.S.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Qin, D.M.; Wang, C.Q. Dissipation and residue of forchlorfenuron in citrus fruits. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 90, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.G.; Takami, Y.; Mizugami, T.; Beppu, K.; Fukuda, T.; Kataoka, I. CPPU application on size and quality of hardy kiwifruit. Sci. Hortic. 2006, 110, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.S.; Luo, Y.C.; Wang, S.W.; Wang, H.C.; Harpaz-Saad, S.; Huang, X.M. Residue analysis and the effect of preharvest forchlorfenuron (CPPU) application on on-tree quality maintenance of ripe fruit in “Feizixiao” Litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 829635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 2763-2021; National Food Safety Standards-Maximum Residue Limits for Pesticides in Food. China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- The Commission of the European Communities. Commission Regulation (EU) No 398/2014 of 22 April 2014 amending Annexes II and III to Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards maximum residue levels for benthiavalicarb, cyazofamid, cyhalofop-butyl, forchlorfenuron, pymetrozine and silthiofam in or on certain products. Off. J. Eur. Union 2014, L119/3–L119/39.
- Bu, Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Xie, H.C.; Zhong, K.; Wu, Y.P.; Zhang, J.Q.; Wang, Z.S.; Gao, H.; Huang, Y.N. 180 day repeated-dose toxicity study on forchlorfenuron in Sprague Dawley rats and its effects on the production of steroid hormones. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 10207–10213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Kam, H.; Tse, Y.; Lee, S.M. Cardiotoxicity of forchlorfenuron (CPPU) in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Kam, H.; Tse, Y.; Giesy, J.P.; Seto, S.W.; Lee, S.M. Forchlorfenuron (CPPU) causes disorganization of the cytoskeleton and dysfunction of human umbilical vein endothelial cells, and abnormal vascular development in zebrafifish embryos. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 115791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.M.; Xiang, P.; Xie, Q.L.; Yang, H.X.; Liu, S.H. Rapid analysis of forchlorfenuron in fruits using molecular complex-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. Food Addit. Contam. Part A-Chem. 2021, 38, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.M.; Jin, F.; Huang, Y.T.; Du, X.W.; Li, C.M.; Wang, M.; Shao, H.; Jin, M.J.; Wang, J. Determination of five plant growth regulators in fruits by modified quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged, and safe (QuEChERS) extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campillo, N.; Vinas, P.; Ferez-Melgarejo, G.; Hernandez-Cordoba, M. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of three cytokinin compounds in fruits and vegetables by liquid chromatography with time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Talanta 2013, 116, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.Y.; Hu, S.; Lai, X.C.; Peng, J.; Lai, W.H. Developmental trend of immunoassays for monitoring hazards in food samples: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 68–88. [Google Scholar]
- Suarez-Pantaleon, C.; Mercader, J.V.; Agullo, C.; Abad-Somovilla, A.; Abad-Fuentes, A. Hapten synthesis and polyclonal antibody-based immunoassay development for the analysis of forchlorfenuron in kiwifruit. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 8502–8511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez-Pantaleon, C.; Esteve-Turrillas, F.A.; Mercader, J.V.; Agullo, C.; Abad-Somovilla, A.; Abad-Fuentes, A. Development and validation of a direct competitive monoclonal antibody-based immunoassay for the sensitive and selective analysis of the phytoregulator forchlorfenuron. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Pantaleon, C.; Wichers, J.; Abad-Somovilla, A.; van Amerongen, A.; Abad-Fuentes, A. Development of an immunochromatographic assay based on carbon nanoparticles for the determination of the phytoregulator forchlorfenuron. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.M.; Xie, B.; Cheng, Y.J.; Luo, L.; Liang, Y.F.; Xiao, Z.L. A sensitive monoclonal-antibody-based ELISA for forchlorfenuron residue analysis in food samples. Biosensors 2022, 12, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez-Pantaleon, C.; Mercader, J.V.; Agullo, C.; Abad-Somovilla, A.; Abad-Fuentes, A. Production and characterization of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies to forchlorfenuron. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 11122–11131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Pantaleon, C.; Mercader, J.V.; Agullo, C.; Abad-Somovilla, A.; Abad-Fuentes, A. Forchlorfenuron-mimicking haptens: From immunogen design to antibody characterization by hierarchical clustering analysis. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 4863–4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, T.T.; Zhang, X.; Guo, C.F.; Guo, S.H.; Zhao, X.B.; Yuan, Y.H.; Yue, T.L. Identity, synthesis, and cytotoxicity of forchlorfenuron metabolites in kiwifruit. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 9529–9535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lin, J.H. Recent advances on magnetic nanobead based biosensors: From separation to detection. Trac. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 128, 115915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Li, X.; Ma, X. Magnetic beads-based multicolor colorimetric immunoassay for ultrasensitive detection of aflatoxin B1. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 1462–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, P.; Zhou, Y. Antibody-biotin-streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase (HRP) sensor for rapid and ultra-sensitive detection of fumonisins. Food Chem. 2020, 316, 126356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaiani, G.; Leonardo, S.; Tudo, A.; Toldra, A.; Rey, M.; Andree, K.B.; Tsumuraya, T.; Hirama, M.; Diogene, J.; O’Sullivan, C.K.; et al. Rapid detection of ciguatoxins in Gambierdiscus and Fukuyoa with immunosensing tools. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2020, 204, 111004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyos-Rodriguez, C.; Llamedo-Gonzalez, A.; Pando, D.; Garcia, S.; Garcia, J.A.; Garcia-Alonso, F.J.; De la Escosura-Muniz, A. Novel magnetic beads with improved performance for Alzheimer’s disease biomarker detection. Microchem. J. 2022, 175, 107211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manclus, J.J.; Primo, J.; Montoya, A. Development of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for the insecticide chlorpyrifos. 1. Monoclonal antibody production and immunoassay design. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 4052–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.H.; Li, P.W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Y.L.; Ding, X.X.; Jiang, J. Production of ultrasensitive generic monoclonal antibodies against major aflatoxins using a modified two-step screening procedure. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 636, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beatty, J.D.; Barbara, B.G.; Vlahos, W.G. Measurement of monoclonal antibody affinity by non-competitive enzyme immunoassay. J. Immunol. Methods 1987, 100, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 23200.110-2018; Determination of Forchlorfenuron in Foods of Plant Origin-Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Anfossi, L.; Calderara, M.; Baggiani, C.; Giovannoli, C.; Arletti, E.; Giraudi, G. Development and application of solvent-free extraction for the detection of aflatoxin M1 in dairy products by enzyme immunoassay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1852–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Huang, Z.; Wang, C.; Peng, J.; Lai, W.H. Using hapten cross-reactivity to screen heterologous competitive antigens for improving the sensitivity of ELISA. Food Chem. 2020, 303, 125379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.K.; Wang, Y.C.; Wang, H.A.; Ji, W.H.; Sun, J.H.; Yan, Y.X. An immunomagnetic-bead-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for sensitive quantification of fumonisin B1. Food Control 2014, 40, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, G.S.; Toscano, I.A.; Barcelo, D. Analysis of pesticides in food and environmental samples by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. Trac. Trends Anal. Chem. 1998, 17, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Analytes | Structure | MB-Based Assay | icELISA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (ng/mL) | CR (%) | IC50 (ng/mL) | CR (%) | ||
| Forchlorfenuron (CPPU) | 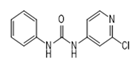 | 0.0061 | 100 | 0.0253 | 100 |
| Diuron | 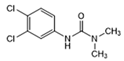 | >1.0 | <0.6 | >2.5 | <1.0 |
| Chlorotoluron | 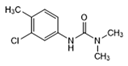 | >1.0 | <0.6 | >2.5 | <1.0 |
| Thidiazuron | 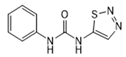 | >1.0 | <0.6 | >2.5 | <1.0 |
| Linuron |  | >1.0 | <0.6 | >2.5 | <1.0 |
| Clofentezine | 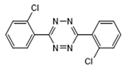 | >1.0 | <0.6 | >2.5 | <1.0 |
| Samples | Spiked Level (μg/kg) | MB-Based Assay | HPLC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD (μg/kg) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Mean ± SD (μg/kg) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | ||
| Kiwifruit | 10 | 8.6 ± 0.6 | 86.0 | 7.0 | 8.9 ± 0.5 | 89.0 | 5.6 |
| 20 | 19.3 ± 0.5 | 96.5 | 2.6 | 23.3 ± 3.0 | 116.5 | 12.9 | |
| 50 | 45.1 ± 4.5 | 90.2 | 10.0 | 52.3 ± 1.3 | 104.6 | 2.5 | |
| Grape | 10 | 12.0 ± 0.2 | 120.0 | 1.7 | 8.7 ± 1.2 | 87.0 | 13.8 |
| 20 | 20.3 ± 1.2 | 101.5 | 5.9 | 16.4 ± 0.5 | 82.0 | 3.0 | |
| 50 | 46.5 ± 1.3 | 93.0 | 2.8 | 48.4 ± 3.6 | 96.8 | 7.4 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shan, Y.; He, T.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yue, X.; Yang, Y. A Magnetic-Bead-Based Immunoassay with a Newly Developed Monoclonal Antibody for Rapid and Highly Sensitive Detection of Forchlorfenuron. Biosensors 2023, 13, 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13060593
Shan Y, He T, Li Y, Zhu J, Yue X, Yang Y. A Magnetic-Bead-Based Immunoassay with a Newly Developed Monoclonal Antibody for Rapid and Highly Sensitive Detection of Forchlorfenuron. Biosensors. 2023; 13(6):593. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13060593
Chicago/Turabian StyleShan, Yubao, Ting He, Ying Li, Jiang Zhu, Xiali Yue, and Yunhuang Yang. 2023. "A Magnetic-Bead-Based Immunoassay with a Newly Developed Monoclonal Antibody for Rapid and Highly Sensitive Detection of Forchlorfenuron" Biosensors 13, no. 6: 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13060593
APA StyleShan, Y., He, T., Li, Y., Zhu, J., Yue, X., & Yang, Y. (2023). A Magnetic-Bead-Based Immunoassay with a Newly Developed Monoclonal Antibody for Rapid and Highly Sensitive Detection of Forchlorfenuron. Biosensors, 13(6), 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13060593





